Matcha Green Tea Improves Cafeteria-Diet-Induced NAFLD by Modulating the Gut Microbiota in Rats
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Matcha Powder
2.2. Animals and Diets
Study Design
2.3. Blood Biochemical Analyses
2.4. Liver TC and TG Concentrations
2.5. Liver Histopathological Analysis
2.6. Insulin Resistance (IR)
2.7. Liver Cytokine Levels
2.8. Plasma Adipokine Concentrations
2.9. Epididymal White Adipose Tissue (eWAT) Histopathological Analysis
2.10. Assessment of the Fecal Microbiotic Composition
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
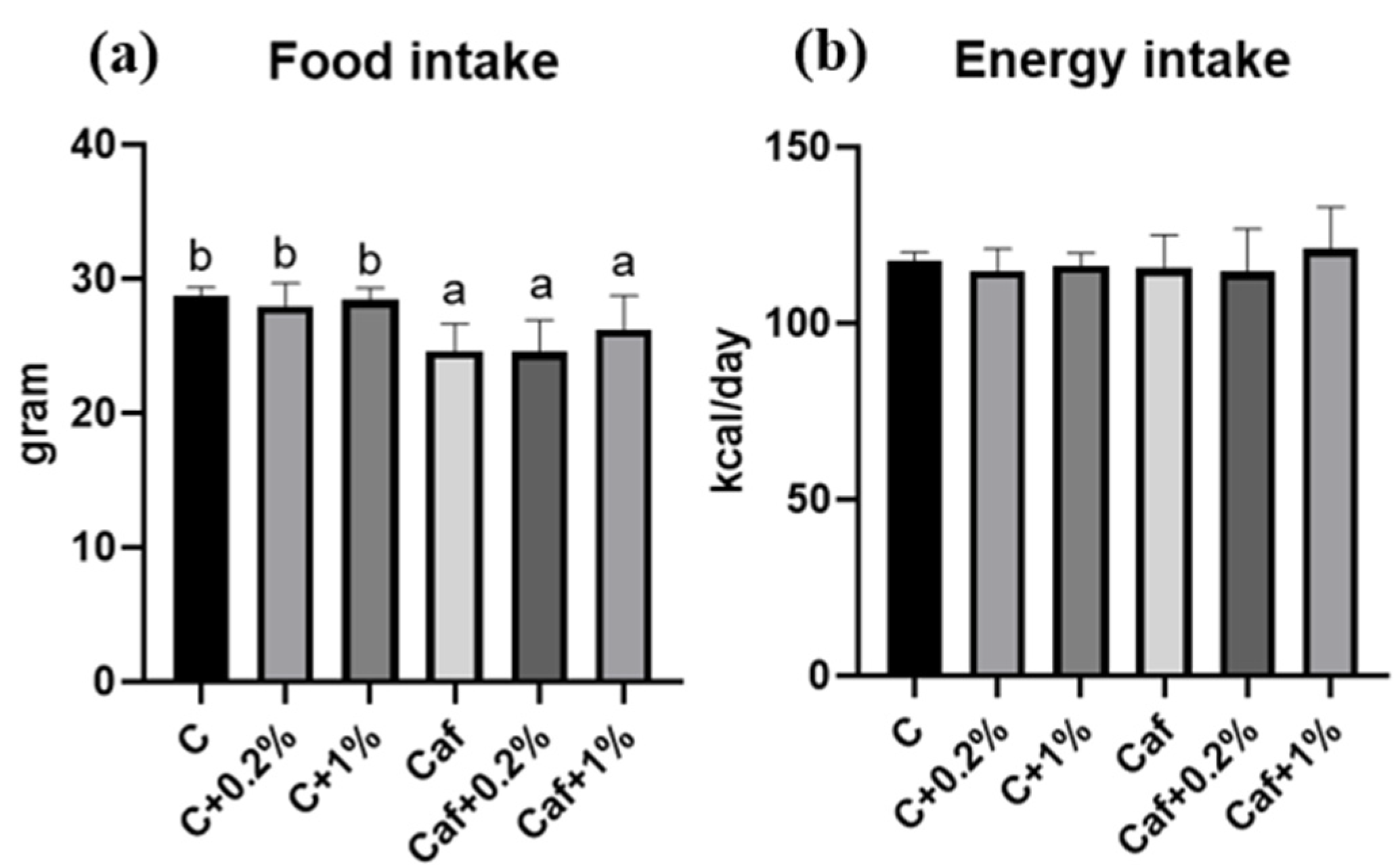
3.1. Effect of Matcha on Food Intake, Energy Intake, and BWs
3.2. Effects of Matcha on Liver, eWAT, and Perirenal (p)WAT Weights
3.3. Effect of Matcha on Liver Function and the Lipid Profile
3.4. Effect of Matcha on Liver TC and TGs
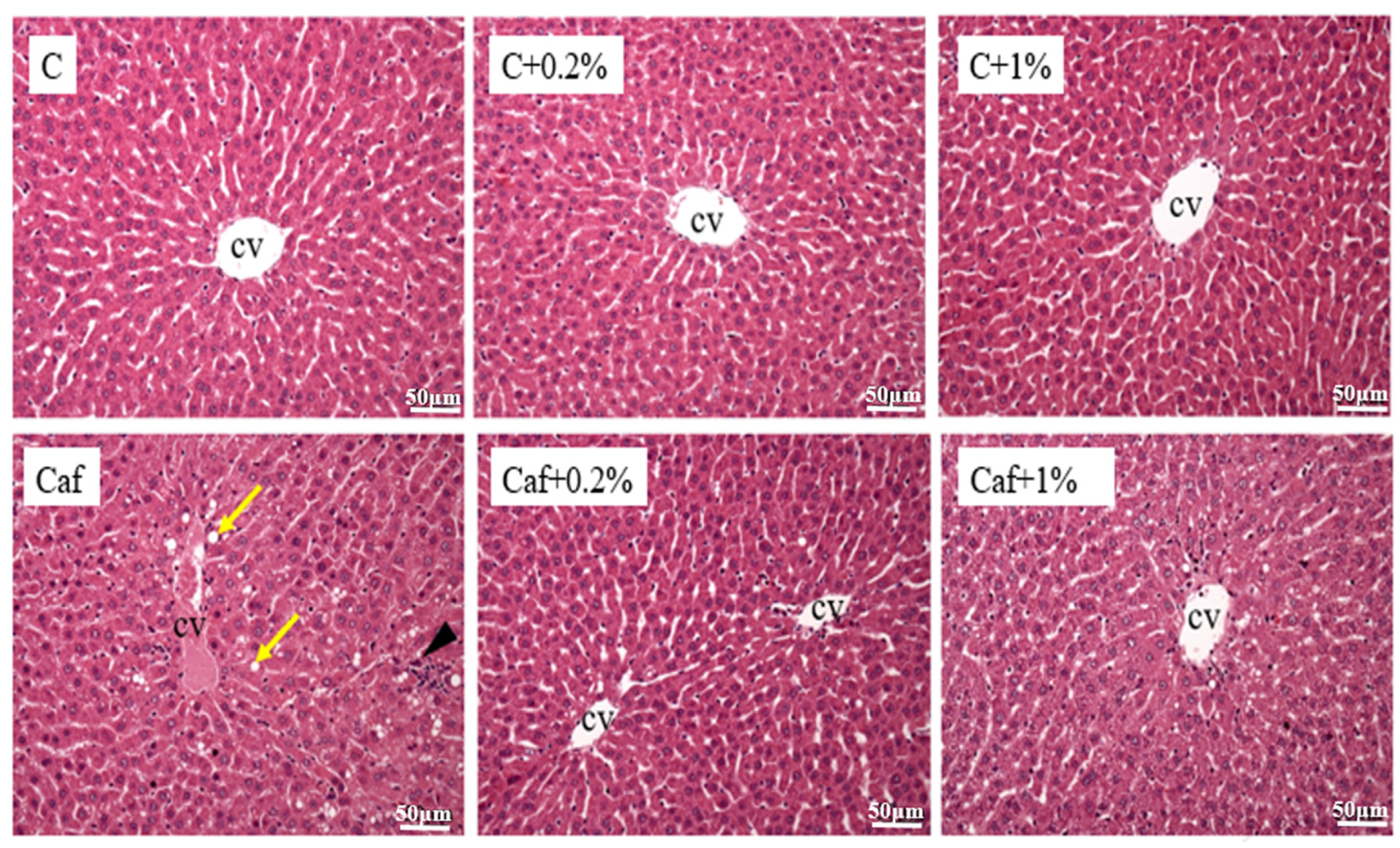
3.5. Effect of Matcha on Liver Histopathological Changes
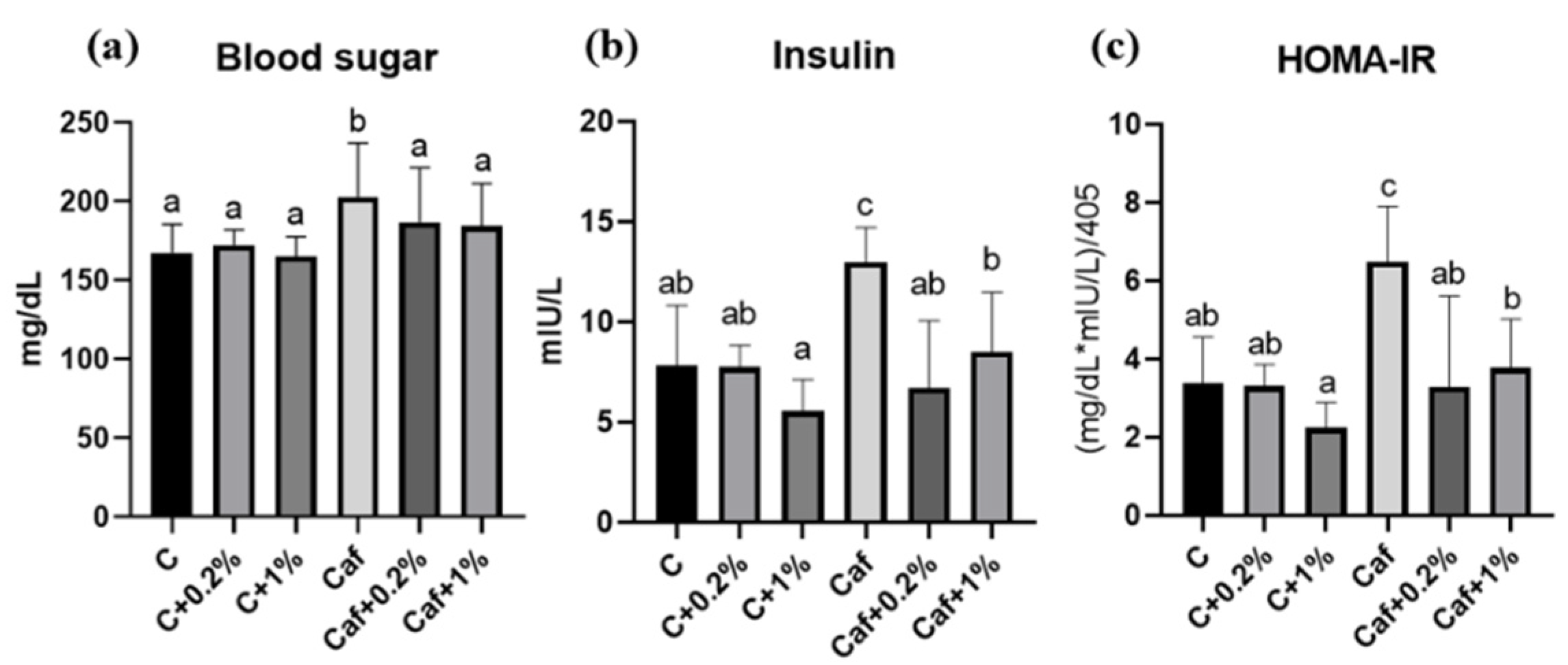
3.6. Effect of Matcha on IR
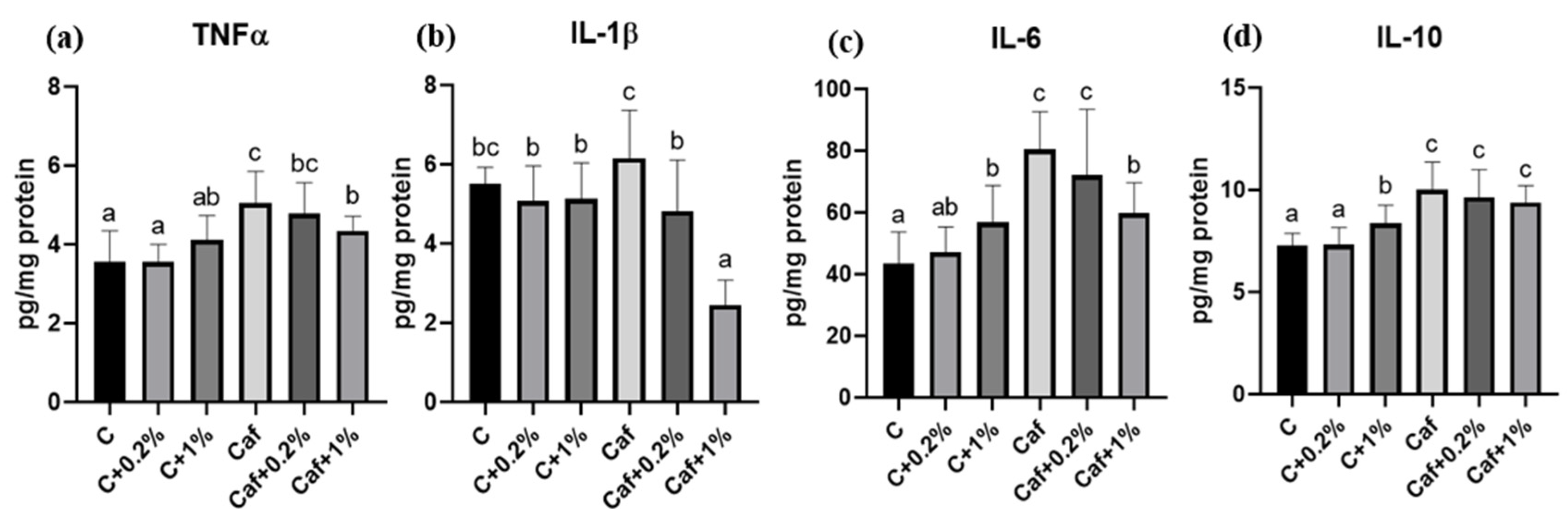
3.7. Effect of Matcha on Liver Cytokines Levels
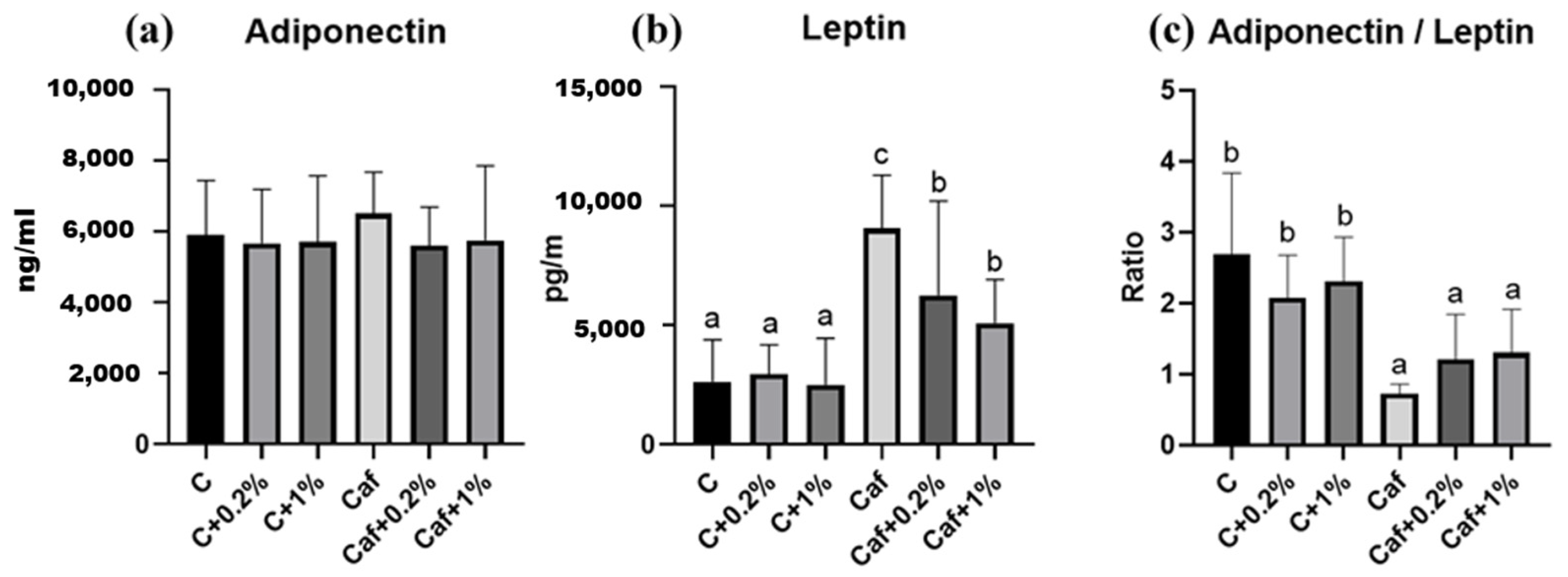
3.8. Effect of Matcha on Plasma Adipokine Concentrations
3.9. Effect of Matcha on eWAT Histopathological Staining
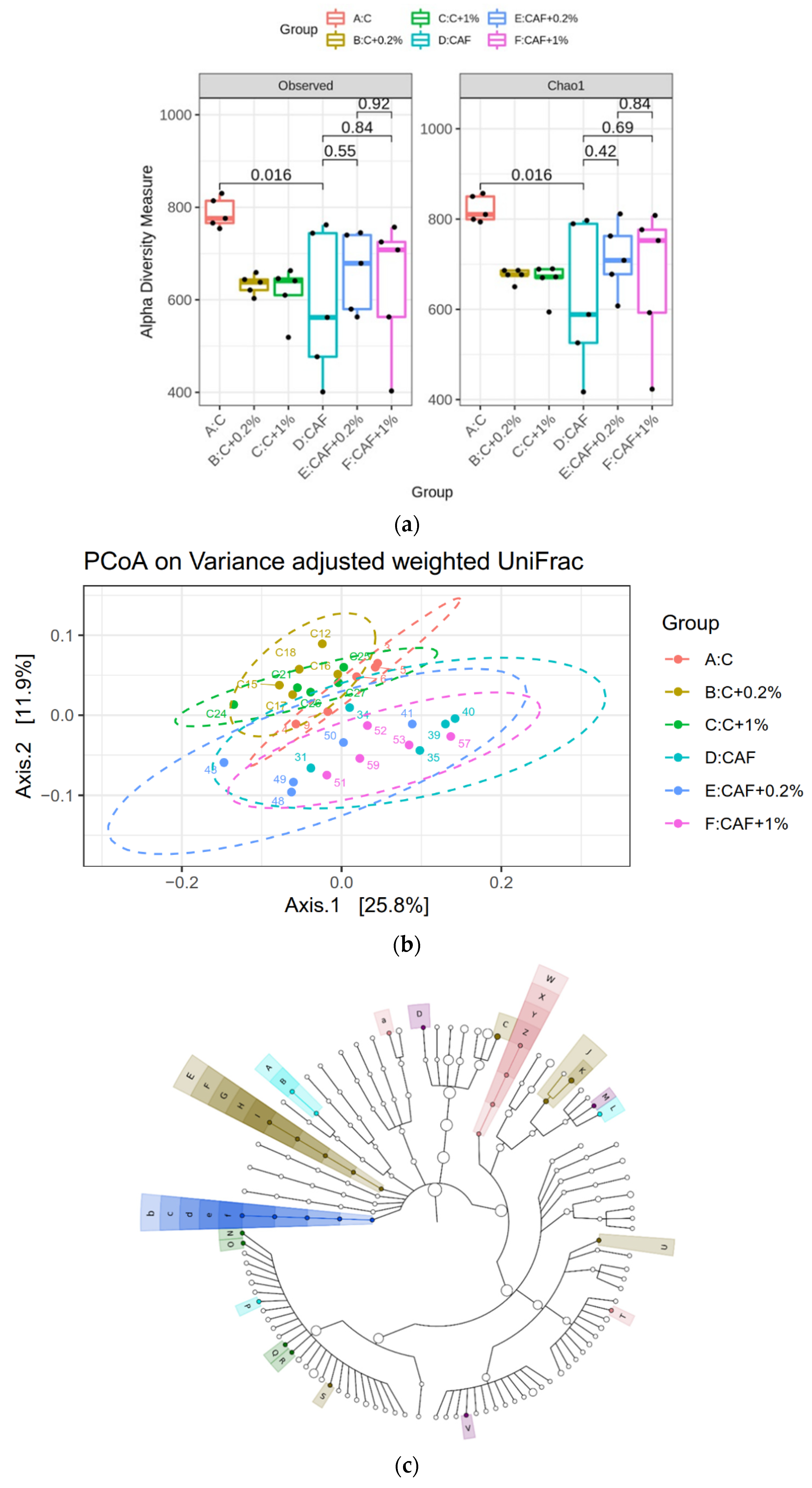
3.10. Effect of Matcha on the Gut Microbiotic Composition
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Teng, M.L.; Ng, C.H.; Huang, D.Q.; Chan, K.E.; Tan, D.J.; Lim, W.H.; Yang, J.D.; Tan, E.; Muthiah, M.D. Global incidence and prevalence of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2023, 29, S32–S42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pouwels, S.; Sakran, N.; Graham, Y.; Leal, A.; Pintar, T.; Yang, W.; Kassir, R.; Singhal, R.; Mahawar, K.; Ramnarain, D. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): A review of pathophysiology, clinical management and effects of weight loss. BMC Endocr. 2022, 22, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godoy-Matos, A.F.; Silva Júnior, W.S.; Valerio, C.M. NAFLD as a continuum: From obesity to metabolic syndrome and diabetes. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2020, 12, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalasani, N.; Younossi, Z.; Lavine, J.E.; Diehl, A.M.; Brunt, E.M.; Cusi, K.; Charlton, M.; Sanyal, A.J. The diagnosis and management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Practice Guideline by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases, American College of Gastroenterology, and the American Gastroenterological Association. Hepatology 2012, 55, 2005–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-H.; Wu, W.-K.; Wu, M.-S. Microbiota-associated therapy for non-alcoholic steatohepatitis-induced liver cancer: A review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bessone, F.; Razori, M.V.; Roma, M.G. Molecular pathways of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease development and progression. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2019, 76, 99–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takaki, A.; Kawai, D.; Yamamoto, K. Multiple hits, including oxidative stress, as pathogenesis and treatment target in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 20704–20728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masarone, M.; Rosato, V.; Dallio, M.; Gravina, A.G.; Aglitti, A.; Loguercio, C.; Federico, A.; Persico, M. Role of oxidative stress in pathophysiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adolph, T.E.; Grander, C.; Grabherr, F.; Tilg, H. Adipokines and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Multiple interactions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanai, H.; Yoshida, H. Beneficial effects of adiponectin on glucose and lipid metabolism and atherosclerotic progression: Mechanisms and perspectives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Ding, Z.; Ishaq, M.; Bacha, A.S.; Khan, I.; Hanif, A.; Li, W.; Guo, X. Understanding the effects of gut microbiota dysbiosis on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and the possible probiotics role: Recent updates. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 17, 818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boursier, J.; Mueller, O.; Barret, M.; Machado, M.; Fizanne, L.; Araujo-Perez, F.; Guy, C.D.; Seed, P.C.; Rawls, J.F.; David, L.A. The severity of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease is associated with gut dysbiosis and shift in the metabolic function of the gut microbiota. Hepatology 2016, 63, 764–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalanza, J.F.; Snoeren, E.M. The cafeteria diet: A standardized protocol and its effects on behavior. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2021, 122, 92–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Correa, E.; González-Pérez, I.; Clavel-Pérez, P.I.; Contreras-Vargas, Y.; Carvajal, K. Biochemical and nutritional overview of diet-induced metabolic syndrome models in rats: What is the best choice? Nutr. Diabetes 2020, 10, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leigh, S.-J.; Kendig, M.D.; Morris, M.J. Palatable western-style cafeteria diet as a reliable method for modeling diet-induced obesity in rodents. J. Vis. Exp. 2019, 153, e60262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koláčková, T.; Kolofiková, K.; Sytařová, I.; Snopek, L.; Sumczynski, D.; Orsavová, J. Matcha tea: Analysis of nutritional composition, phenolics and antioxidant activity. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2020, 75, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kochman, J.; Jakubczyk, K.; Antoniewicz, J.; Mruk, H.; Janda, K. Health benefits and chemical composition of matcha green tea: A review. Molecules 2020, 26, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sokary, S.; Al-Asmakh, M.; Zakaria, Z.; Bawadi, H. The therapeutic potential of matcha tea: A critical review on human and animal studies. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2022, 23, 100396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, Y.C.; Fu, L.C.; Chong, H.C.; Tang, S.T.; Yang, S.C.; Huang, W.C.; Yang, Y.S.; Chen, Y.L. Consumption of a Taiwanese cafeteria diet induces metabolic disorders and fecal flora changes in obese rats. Nutrition 2024, 117, 112230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Menke, A.L.; Driessen, A.; Koek, G.H.; Lindeman, J.H.; Stoop, R.; Havekes, L.M.; Kleemann, R.; van den Hoek, A.M. Establishment of a general NAFLD scoring system for rodent models and comparison to human liver pathology. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e115922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-L.; Shirakawa, H.; Lu, N.-S.; Peng, H.-C.; Xiao, Q.; Yang, S.-C. Impacts of fish oil on the gut microbiota of rats with alcoholic liver damage. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2020, 86, 108491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.-C.S.; Chang, H.-W.; Lin, I.-H.; Chien, L.-N.; Wu, M.-J.; Liu, Y.-R.; Chu, P.G.; Xie, G.; Dong, F.; Jia, W. Long-term proton pump inhibitor administration caused physiological and microbiota changes in rats. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sclafani, A.; Springer, D. Dietary obesity in adult rats: Similarities to hypothalamic and human obesity syndromes. Physiol. Behav. 1976, 17, 461–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Yu, Y.; Ding, L.; Xu, P.; Wang, Y. Matcha green tea alleviates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in high-fat diet-induced obese mice by regulating lipid metabolism and inflammatory responses. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Ying, L.; Hong, G.; Wang, Y. The effects of the aqueous extract and residue of Matcha on the antioxidant status and lipid and glucose levels in mice fed a high-fat diet. Food Funct. 2016, 7, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mašek, T.; Barišić, J.; Micek, V.; Starčević, K. Cafeteria diet and high-fructose rodent models of NAFLD differ in the metabolism of important PUFA and palmitoleic acid without additional influence of sex. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Paglicawan, L.; Soomro, S.; Abunofal, O.; Baig, S.; Vanarsa, K.; Hicks, J.; Mohan, C. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate dampens non-alcoholic fatty liver by modulating liver function, lipid profile, and macrophage polarization. Nutrients 2021, 13, 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakurai, Y.; Kubota, N.; Yamauchi, T.; Kadowaki, T. Role of insulin resistance in MAFLD. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Nagata, N.; Ota, T. Impact of glucoraphanin-mediated activation of Nrf2 on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease with a focus on mitochondrial dysfunction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Song, P.; Perry, R.; Penfold, C.; Cooper, A.R. The effectiveness of green tea or green tea extract on insulin resistance and glycemic control in type 2 diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis. Diabetes Metab. J. 2017, 41, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Tian, J.; Jiang, J.; Li, L.; Ying, X.; Tian, H.; Nie, M. Effects of green tea or green tea extract on insulin sensitivity and glycaemic control in populations at risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 2014, 27, 501–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, V.W.-S.; Wong, G.L.-H.; Choi, P.C.-L.; Chan, A.W.-H.; Li, M.K.-P.; Chan, H.-Y.; Chim, A.M.-L.; Yu, J.; Sung, J.J.-Y.; Chan, H.L.-Y. Disease progression of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A prospective study with paired liver biopsies at 3 years. Gut 2010, 59, 969–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, H.; Abe, I.; Gotoh, K.; Fukui, A.; Takanari, H.; Ishii, Y.; Ikebe, Y.; Kira, S.; Oniki, T.; Saito, S. Interleukin 10 treatment ameliorates high-fat diet–induced inflammatory atrial remodeling and fibrillation. Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 2018, 11, e006040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilg, H.; Hotamisligil, G.S. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Cytokine-adipokine interplay and regulation of insulin resistance. Gastroenterology 2006, 131, 934–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hui, J.M.; Hodge, A.; Farrell, G.C.; Kench, J.G.; Kriketos, A.; George, J. Beyond insulin resistance in NASH: TNF-α or adiponectin? Hepatology 2004, 40, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frühbeck, G.; Catalán, V.; Rodríguez, A.; Ramírez, B.; Becerril, S.; Salvador, J.; Colina, I.; Gómez-Ambrosi, J. Adiponectin-leptin Ratio is a Functional Biomarker of Adipose Tissue Inflammation. Nutrients 2019, 11, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astbury, S.; Atallah, E.; Vijay, A.; Aithal, G.P.; Grove, J.I.; Valdes, A.M. Lower gut microbiome diversity and higher abundance of proinflammatory genus Collinsella are associated with biopsy-proven nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Gut Microbes 2020, 11, 569–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Sun, H.; Yang, Y.; Yan, Y. Sesamolin alleviates nonalcoholic fatty liver disease through modulating gut microbiota and metabolites in high-fat and high-fructose diet-fed mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 13853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, J.-J.; Li, M.-Z.; Chen, C.-H.; Hong, T.; Yang, J.-R.; Huang, X.-J.; Geng, F.; Hu, J.-L.; Nie, S.-P. Tea polyphenol and epigallocatechin gallate ameliorate hyperlipidemia via regulating liver metabolism and remodeling gut microbiota. Food Chem. 2023, 404, 134591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Gao, W.; Liu, Z.; Fang, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Lu, W.; Chen, W. Specific strains of Faecalibacterium prausnitzii ameliorate nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in mice in association with gut microbiota regulation. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Active Compound | Content |
|---|---|
| Total polyphenols (mg GAE/g) | 81.0 |
| Caffeine (mg/g) | 24.9 |
| GC (mg/g) | 1.4 |
| EC (mg/g) | 6.4 |
| ECG (mg/g) | 11.3 |
| EGC (mg/g) | 36.5 |
| EGCG (mg/g) | 50.4 |
| Body Weight (g) | C | C + 0.2% | C + 1% | Caf | Caf + 0.2% | Caf + 1% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0th week | 293.4 ± 17.2 | 293.4 ± 13.0 | 286.1 ± 12.8 | 289.4 ± 11.4 | 289.3 ± 15.8 | 284.3 ± 13.8 |
| 4th week | 407.4 ± 15.9 a | 408.8 ± 13.7 a | 392.8 ± 18.3 a | 450.6 ± 26.8 b | 434.8 ± 22.3 b | 445.6 ± 23.6 b |
| 8th week | 481.0 ± 20.4 a | 482.4 ± 10.6 a | 455.1 ± 18.2 a | 538.5 ± 45.9 b | 518.9 ± 44.1 b | 543.1 ± 48.5 b |
| 12th week | 540.3 ± 30.6 ab | 552.3 ± 24.9 ab | 521.2 ± 18.1 a | 610.8 ± 55.0 c | 584.0 ± 58.1 bc | 616.6 ± 59.2 c |
| Item | C | C + 0.2% | C + 1% | Caf | Caf + 0.2% | Caf + 1% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steatosis score | 0.0 ± 0.0 a | 0.0 ± 0.0 a | 0.0 ± 0.0 a | 0.8 ± 0.3 c | 0.3 ± 0.4 ab | 0.2 ± 0.4 ab |
| Inflammation score | 0.2 ± 0.4 a | 0.2 ± 0.4 a | 0.8 ± 0.4 ab | 1.4 ± 0.9 b | 1.6 ± 0.5 b | 1.6 ± 1.1 b |
| NAFLD activity score | 0.2 ± 0.4 a | 0.2 ± 0.4 a | 0.8 ± 0.4 a | 2.2 ± 1.0 b | 1.9 ± 0.2 b | 1.8 ± 1.3 b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chong, H.-C.; Tang, S.-T.; Tseng, Y.-C.; Yang, S.-C.; Watanabe, Y.; Yamada, S.; Yang, Y.-C.S.H.; Chen, Y.-L. Matcha Green Tea Improves Cafeteria-Diet-Induced NAFLD by Modulating the Gut Microbiota in Rats. Nutrients 2025, 17, 3051. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17193051
Chong H-C, Tang S-T, Tseng Y-C, Yang S-C, Watanabe Y, Yamada S, Yang Y-CSH, Chen Y-L. Matcha Green Tea Improves Cafeteria-Diet-Induced NAFLD by Modulating the Gut Microbiota in Rats. Nutrients. 2025; 17(19):3051. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17193051
Chicago/Turabian StyleChong, Ho-Ching, Shu-Ting Tang, Yu-Chieh Tseng, Suh-Ching Yang, Yasuo Watanabe, Shizuo Yamada, Yu-Chen S. H. Yang, and Ya-Ling Chen. 2025. "Matcha Green Tea Improves Cafeteria-Diet-Induced NAFLD by Modulating the Gut Microbiota in Rats" Nutrients 17, no. 19: 3051. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17193051
APA StyleChong, H.-C., Tang, S.-T., Tseng, Y.-C., Yang, S.-C., Watanabe, Y., Yamada, S., Yang, Y.-C. S. H., & Chen, Y.-L. (2025). Matcha Green Tea Improves Cafeteria-Diet-Induced NAFLD by Modulating the Gut Microbiota in Rats. Nutrients, 17(19), 3051. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17193051







