Anti-Obesity Potential of Modified Pomelo-Peel Dietary Fiber-Based Pickering Emulsion
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Emulsion Preparation
2.3. Material Characterization
2.4. Animals and Experimental Design
2.5. Blood Glucose Index Analysis
2.6. Detection of Biochemical Indexes
2.7. Histological Analysis
2.8. Determination of SCFAs
2.9. Gut Microbiota Analysis
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Physicochemical Properties and Stability Mechanism Basis of EPI and OSA-EPI
3.2. Effect of EPI and OSA-EPI on Body Weight of HFD Mice
3.3. Effects of EPI and OSA-EPI on FBG and Insulin Resistance Indices in HFD Mice
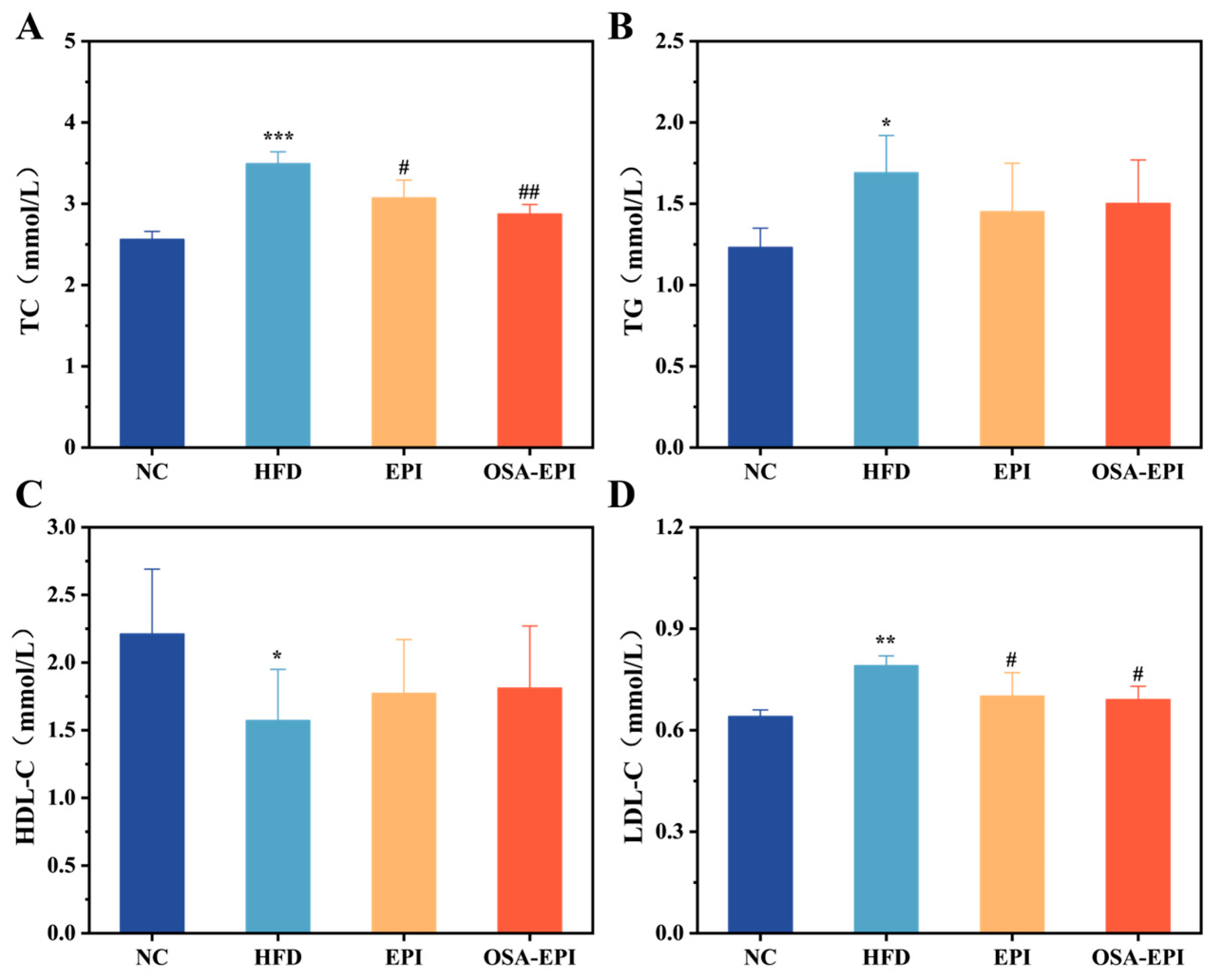
3.4. Effects of EPI and OSA-EPI on Lipid Profiles in HFD Mice
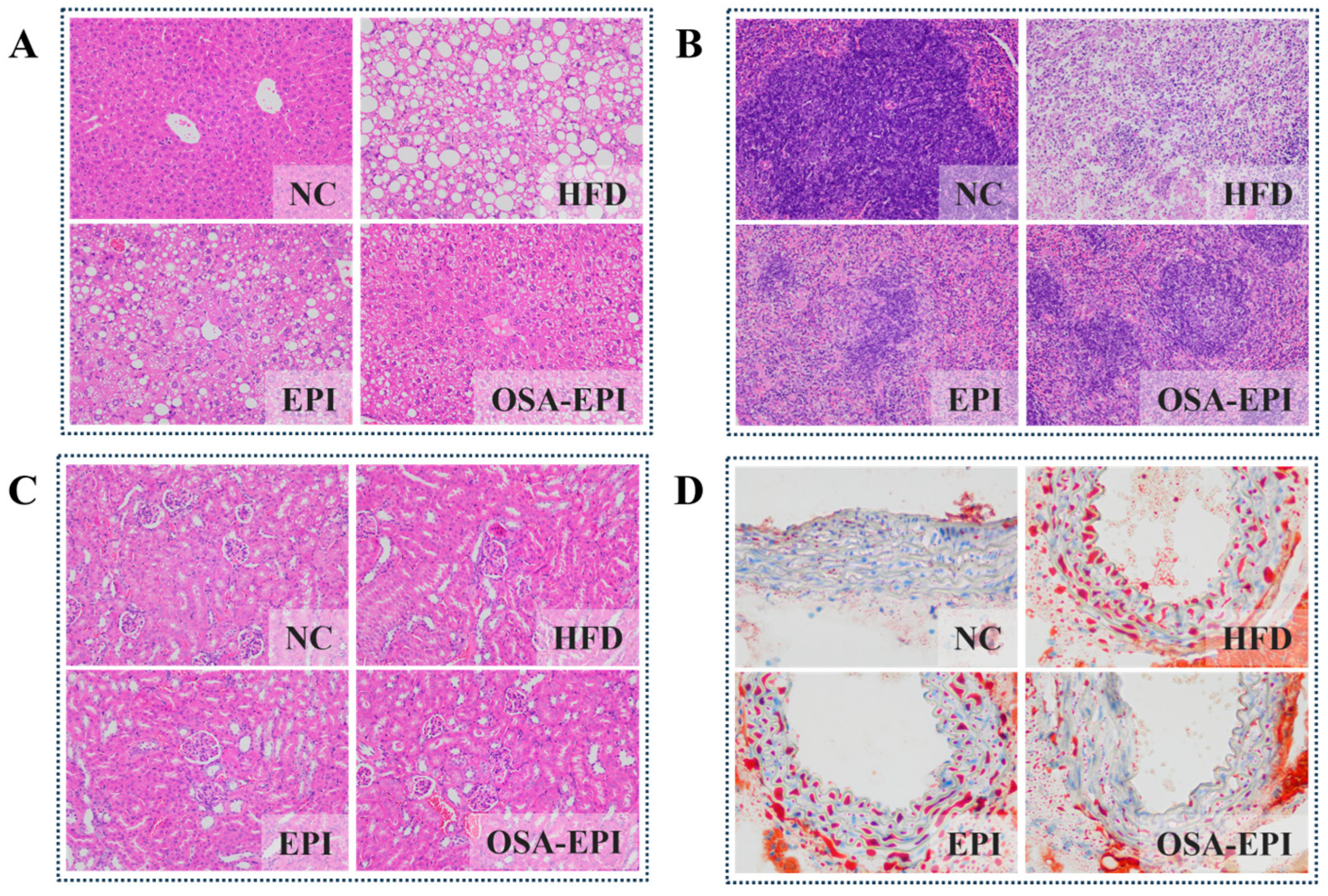
3.5. Effects of EPI and OSA-EPI on the Morphology of HFD Mice Organs
3.6. Effects of EPI and OSA-EPI on Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in HFD Mice
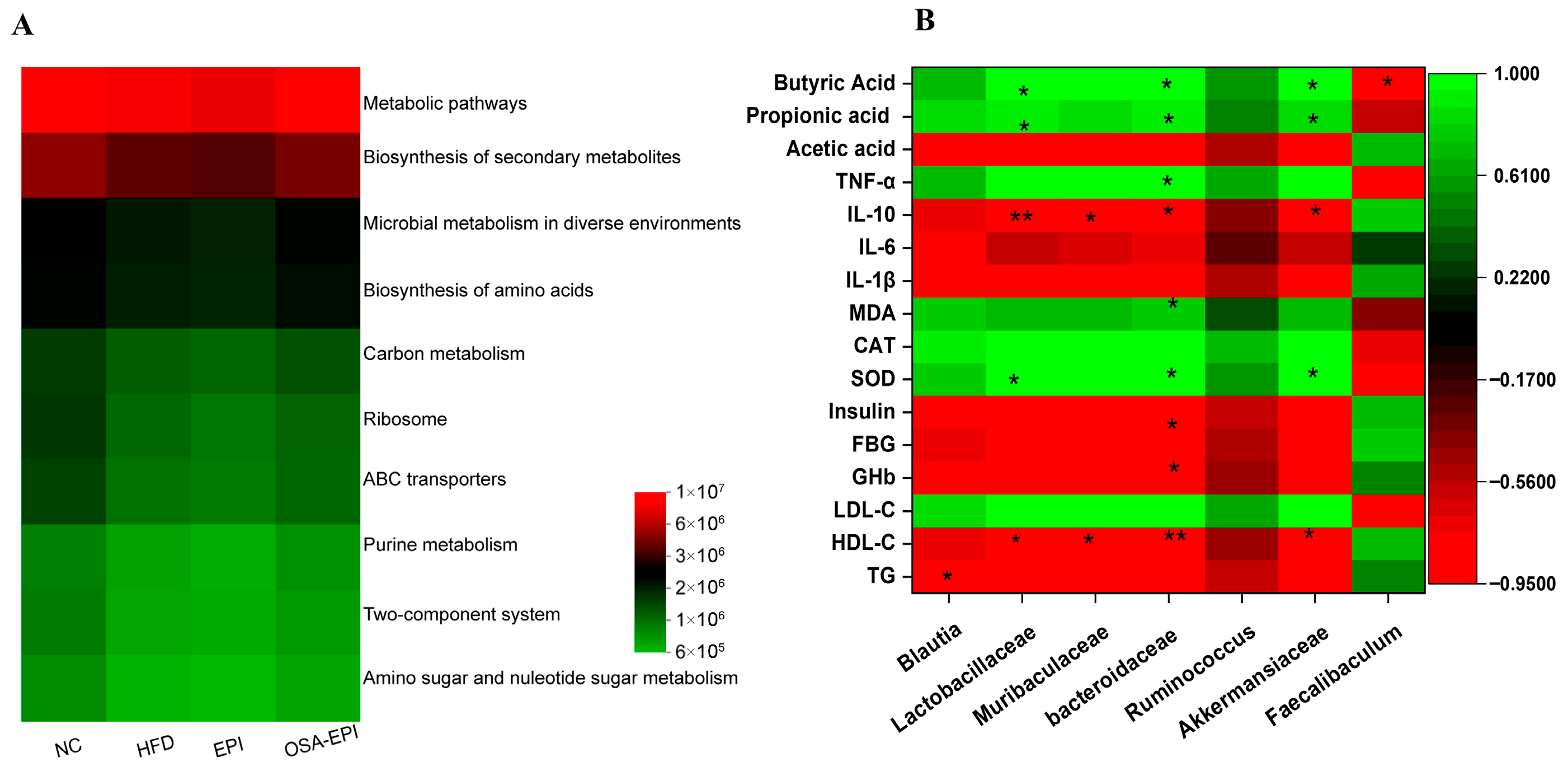
3.7. Effects of Insoluble Dietary Fiber Emulsion on Intestinal SCFAs in HFD Mice
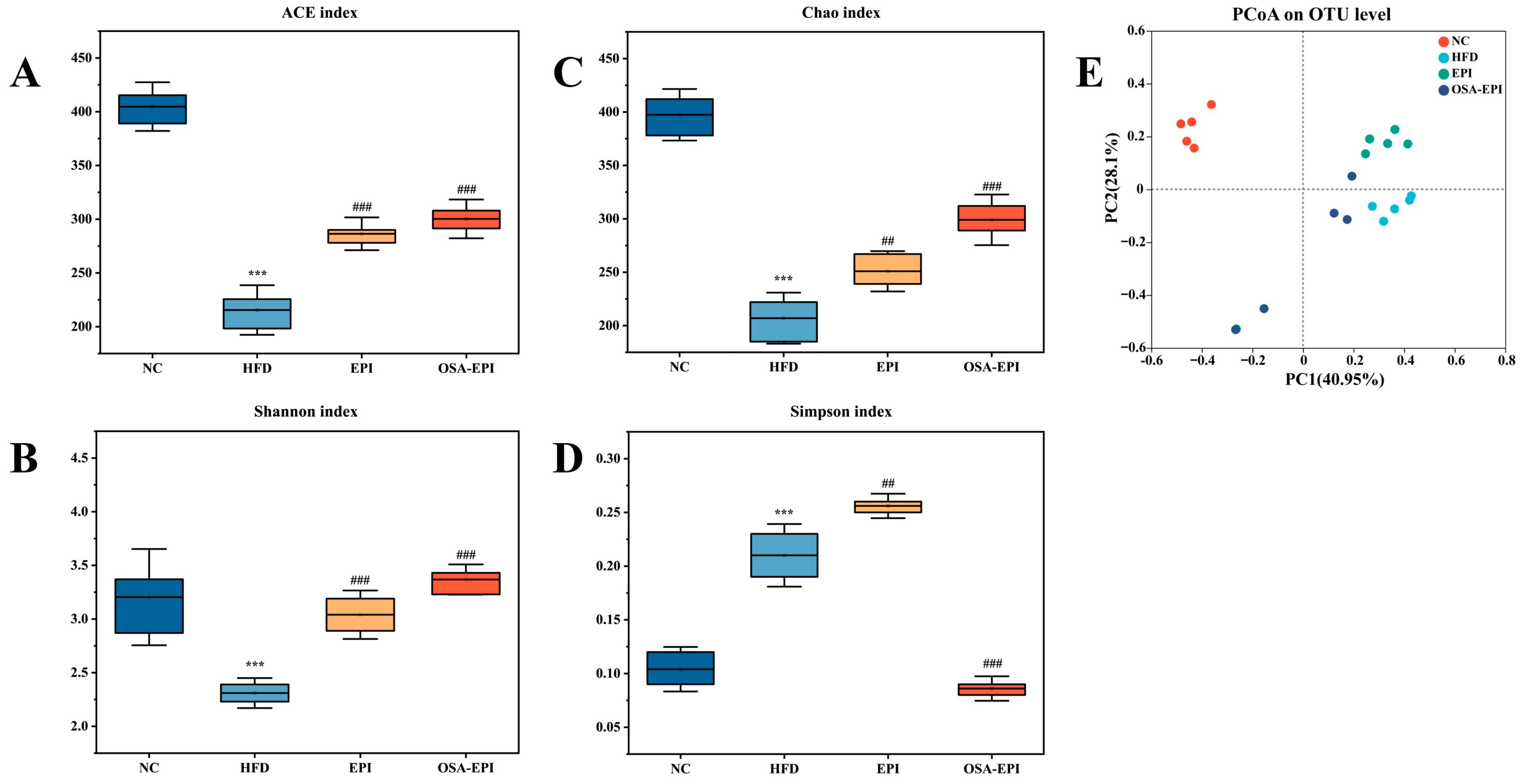
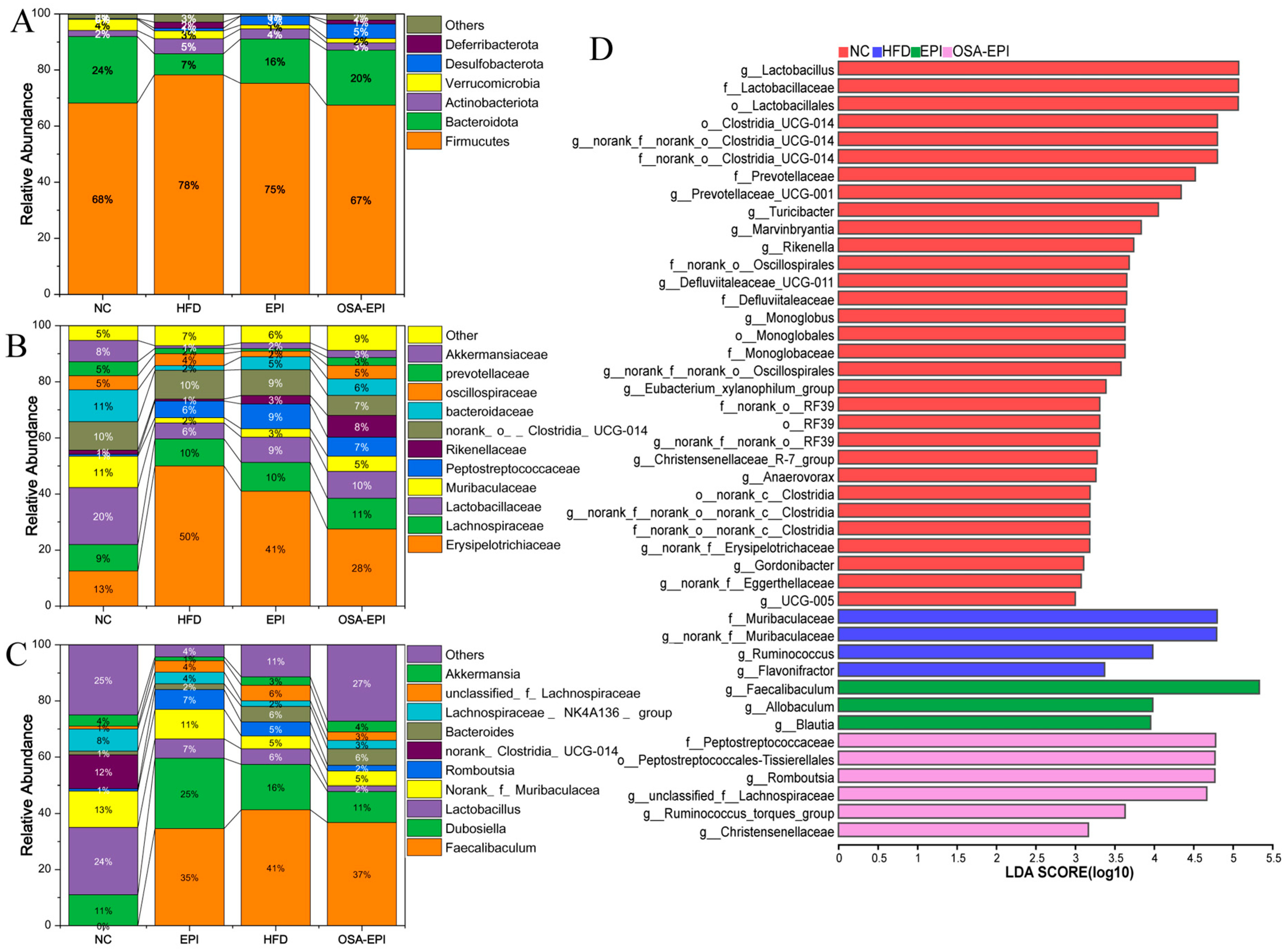
3.8. Effects of Insoluble Dietary Fiber Emulsion on Intestinal Flora in HFD Mice
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tang, C.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Chen, D.; Xu, J.; Yang, D.; Zhang, L.; Liu, J.; Kan, J. The Relationships between High-Fat Diet and Metabolic Syndrome: Potential Mechanisms. Food Biosci. 2024, 59, 104261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, S.; Gastaldelli, A.; Yki-Järvinen, H.; Scherer, P.E. Why Does Obesity Cause Diabetes? Cell Metab. 2022, 34, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruperez, C.; Madeo, F.; de Cabo, R.; Kroemer, G.; Abdellatif, M. Obesity Accelerates Cardiovascular Ageing. Eur. Heart J. 2025, 46, 2161–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scully, T.; Ettela, A.; LeRoith, D.; Gallagher, E.J. Obesity, Type 2 Diabetes, and Cancer Risk. Front. Oncol. 2021, 10, 615375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuevas-Sierra, A.; Ramos-Lopez, O.; Riezu-Boj, J.I.; Milagro, F.I.; Martinez, J.A. Diet, Gut Microbiota, and Obesity: Links with Host Genetics and Epigenetics and Potential Applications. Adv. Nutr. 2019, 10, S17–S30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P. Influence of Foods and Nutrition on the Gut Microbiome and Implications for Intestinal Health. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, S.K.; Rossi, M.; Bajka, B.; Whelan, K. Dietary Fibre in Gastrointestinal Health and Disease. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 18, 101–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baky, M.H.; Salah, M.; Ezzelarab, N.; Shao, P.; Elshahed, M.S.; Farag, M.A. Insoluble Dietary Fibers: Structure, Metabolism, Interactions with Human Microbiome, and Role in Gut Homeostasis. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 64, 1954–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhao, Y.; Li, J.; Ban, L.; Yang, L.; Wang, S.; Zhu, L.; Song, H.; Liu, H. The Adhesion of the Gut Microbiota to Insoluble Dietary Fiber from Soy Hulls Promoted the Proliferation of Probiotics in Vitro. LWT 2022, 153, 112560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Q.; Li, H.; Zheng, Z.; Yang, K.; Li, P.; Xiao, Z.; Xiao, G.; Mao, J. In Vitro Fecal Fermentation Characteristics of Bamboo Insoluble Dietary Fiber and Its Impacts on Human Gut Microbiota. Food Res. Int. 2022, 156, 111173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, J.; Shangguan, Y.; Jiang, L.; He, C.; Ma, Y.; Xiong, H. Pomelo Peel Dietary Fiber Ameliorates Alterations in Obesity-Related Features and Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis in Mice Fed on a High-Fat Diet. Food Chem. X 2023, 20, 100993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Yu, H.; He, Y.; Wen, L.; Gu, J.; Wang, X.; Miao, X.; Qiu, G.; Wang, H. Effect of Soybean Insoluble Dietary Fiber on Prevention of Obesity in High-Fat Diet Fed Mice via Regulation of the Gut Microbiota. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 7923–7937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.; Ao, T.; Zhao, X.; Chen, Y.; Xie, J.; Gao, X.; Liu, L.; Hu, X.; Yu, Q. Comprehensive Assessment of the Anti-Obesity Effects of Highland Barley Total, Insoluble, and Soluble Dietary Fiber through Multi-Omics Analysis. Food Res. Int. 2024, 189, 114535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, K.; Liu, T.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Song, X.; Luo, X.; Ruan, R.; Deng, L.; Cui, X.; Liu, Y. Stabilization of Emulsions Prepared by Ball Milling and Cellulase Treated Pomelo Peel Insoluble Dietary Fiber: Integrity of Porous Fiber Structure Dominates the Stability. Food Chem. 2024, 440, 138189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, K.; Liu, Y.; Liu, T.; Song, X.; Ruan, R.; Feng, S.; Wang, X.; Cui, X. OSA Improved the Stability and Applicability of Emulsions Prepared with Enzymatically Hydrolyzed Pomelo Peel Insoluble Fiber. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 132, 107806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, W.; Song, X.; Wang, R.; He, W.; Yin, J.; Nie, S. Mechanism Exploration of Intestinal Mucus Penetration of Nano-Se: Regulated by Polysaccharides with Different Functional Groups and Molecular Weights. J. Control. Release 2025, 379, 524–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Dong, X.; Zhou, M.; Xu, Z.; Xiang, X. Modulation of Lipid Metabolism by Oyster Peptides in Mice with High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity. Food Biosci. 2024, 58, 103529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, D.; Wang, D.; Ma, G.; Ji, Y.; Zheng, H.; Chen, H.; Zhao, M.; Hu, Q.; Zhao, L. Auricularia Polytricha Noodles Prevent Hyperlipemia and Modulate Gut Microbiota in High-Fat Diet Fed Mice. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2021, 10, 431–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Yang, H.; Lu, Y. Capsaicin Alleviates Lipid Metabolism Disorder in High Beef Fat-Fed Mice. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 60, 103444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Q.; Sun, Y.; Hu, W.; Chen, C.; Lin, Q.; Nie, S. Glucomannan Promotes Bacteroides Ovatus to Improve Intestinal Barrier Function and Ameliorate Insulin Resistance. iMeta 2024, 3, e163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Tang, L.; Qu, Z.; Lei, S.-H.; Li, W.; Wang, Y.-H. Hippocampal Insulin Resistance and the Sirtuin 1 Signaling Pathway in Diabetes-Induced Cognitive Dysfunction. Neural Regen. Res. 2021, 16, 2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.-L.; Chen, M.; Pan, W.-L.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, J.-X.; Lin, Y.-C.; Li, L.; Liu, B.; Bai, W.-D.; Zhang, Y.-Y.; et al. Hypoglycemic and Hypolipidemic Mechanism of Organic Chromium Derived from Chelation of Grifola Frondosa Polysaccharide-Chromium (III) and Its Modulation of Intestinal Microflora in High Fat-Diet and STZ-Induced Diabetic Mice. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 145, 1208–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; You, L.-J.; Huang, Q.; Fu, X.; Zhang, B.; Liu, R.-H.; Li, C. Modulation of Gut Microbiota by Mulberry Fruit Polysaccharide Treatment of Obese Diabetic Db/Db Mice. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 3732–3742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamabadusuriya, D.A.; Jayasena, H.; Bopitiya, A.K.; De Silva, A.D.; Jayasekera, P. Obesity-Driven Inflammation and Cancer Risk: A Comprehensive Review. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2025, 114, 256–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Zhou, W.; Yue, H.; Zhang, C.; Ou, Y.; Yang, Z.; Hu, W. Compound AD110 Acts as Therapeutic Management for Alzheimer’s Disease and Stroke in Mouse and Rat Models. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2020, 11, 929–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glorieux, C.; Buc Calderon, P. Targeting Catalase in Cancer. Redox Biol. 2024, 77, 103404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza, S.; Rosario Claudio, J.; Sim, J.; Inyang, K.E.; Dagenais, A.; Monahan, K.; Lee, B.; Ramakrishnan, H.; Parmar, V.; Geron, M.; et al. Interleukin-10 Signaling in Somatosensory Neurons Controls CCL2 Release and Inflammatory Response. Brain Behav. Immun. 2024, 116, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, R.-G.; Zhou, D.-D.; Wu, S.-X.; Huang, S.-Y.; Saimaiti, A.; Yang, Z.-J.; Shang, A.; Zhao, C.-N.; Gan, R.-Y.; Li, H.-B. Health Benefits and Side Effects of Short-Chain Fatty Acids. Foods 2022, 11, 2863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, G.; Chen, T.; Huang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, Y.; Qu, S.; Yin, X.; Liang, L.; Yan, J.; Liu, W. Tremella fuciformis Polysaccharide Reduces Obesity in High-Fat Diet-Fed Mice by Modulation of Gut Microbiota. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1073350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, H.; Cao, M.; Guo, M.; He, J.; Zhang, B.; Xiao, C. Gut Microbiota Characteristics of People with Obesity by Meta-Analysis of Existing Datasets. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, G.H.; Yoo, K.M.; Kim, S.-Y.; Lee, D.H.; Chung, H.; Jung, S.-C.; Park, S.-K.; Kim, J.-S. Collagen Peptide Exerts an Anti-Obesity Effect by Influencing the Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes Ratio in the Gut. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Zhan, L.; Zhou, W.; Chen, W.; Luo, J.; Zhang, L.; Weng, Z.; Zhao, C.; Liu, S. The Effects of Erchen Decoction on Gut Microbiota and Lipid Metabolism Disorders in Zucker Diabetic Fatty Rats. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 647529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, H.; Larson, K.J.; Cheng, W.-H.; Bukowski, M.R.; Safratowich, B.D.; Liu, Z.; Hakkak, R. Advanced Liver Steatosis Accompanies an Increase in Hepatic Inflammation, Colonic, Secondary Bile Acids and Lactobacillaceae/Lachnospiraceae Bacteria in C57BL/6 Mice Fed a High-Fat Diet. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2020, 78, 108336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, M.; Wang, Q.; Wang, X.; Fan, C.; Luan, T.; Yan, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, X.; Dai, Y.; Li, P. The Protective Effects of Inulin-Type Fructans against High-Fat/Sucrose Diet-Induced Gestational Diabetes Mice in Association with Gut Microbiota Regulation. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 832151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, T.; Liu, Y.; Yang, C.; Liu, L.; Zhang, X.; Yang, X. Heimao Tea Polysaccharides Ameliorate Obesity by Enhancing Gut Microbiota-Dependent Adipocytes Thermogenesis in Mice Fed with High Fat Diet. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 13014–13027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michels, N.; Zouiouich, S.; Vanderbauwhede, B.; Vanacker, J.; Indave Ruiz, B.I.; Huybrechts, I. Human Microbiome and Metabolic Health: An Overview of Systematic Reviews. Obes. Rev. 2022, 23, e13409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, N.; Yang, L.; Hong, Z.; Cai, B.; Le, Q.; Yang, T.; Shi, L.; He, J.; Cui, C.-B. Insoluble Dietary Fiber Derived from Brown Seaweed Laminaria Japonica Ameliorate Obesity-Related Features via Modulating Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis in High-Fat Diet–Fed Mice. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 587–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henke, M.T.; Kenny, D.J.; Cassilly, C.D.; Vlamakis, H.; Xavier, R.J.; Clardy, J. Ruminococcus gnavus, a Member of the Human Gut Microbiome Associated with Crohn’s Disease, Produces an Inflammatory Polysaccharide. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 12672–12677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cani, P.D.; Jordan, B.F. Gut Microbiota-Mediated Inflammation in Obesity: A Link with Gastrointestinal Cancer. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 15, 671–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, J.; Zhao, D.-G.; Ma, Y.-Y.; Li, D.; Ho, C.-T.; Huang, Q. Bidirectional Interaction of Nobiletin and Gut Microbiota in Mice Fed with a High-Fat Diet. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 3516–3526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Zhu, Y.; Dong, Y. Modulation of Gut Microbiota and Gut-Generated Metabolites by Bitter Melon Results in Improvement in the Metabolic Status in High Fat Diet-Induced Obese Rats. J. Funct. Foods 2018, 41, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, J.; Xue, Z.; Zhang, M.; Pang, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, L. Modulation of Gut Microbiota by Berberine and Metformin during the Treatment of High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity in Rats. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waters, J.L.; Ley, R.E. The Human Gut Bacteria Christensenellaceae Are Widespread, Heritable, and Associated with Health. BMC Biol. 2019, 17, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chew, K.Y.; Brownlee, I.A. The Impact of Supplementation with Dietary Fibers on Weight Loss: A Systematic Review of Randomised Controlled Trials. Bioact. Carbohydr. Diet. Fibre 2018, 14, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Wang, D.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, J.; Ding, Y.; Lyu, F. Effect and Mechanism of Insoluble Dietary Fiber on Postprandial Blood Sugar Regulation. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 146, 104354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Wang, Y.; Chen, S.; Gu, J.; Ni, Y. Insoluble and Soluble Dietary Fibers from Kiwifruit (Actinidia Deliciosa) Modify Gut Microbiota to Alleviate High-Fat Diet and Streptozotocin-Induced TYPE 2 Diabetes in Rats. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, F.; Wang, X.; Du, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Shi, L.; Cao, T.; Shen, Y.; Sun, L.; Liu, X. Pumpkin Soluble Dietary Fiber Instead of Insoluble One Ameliorates Hyperglycemia via the Gut Microbiota–Gut–Liver Axis in Db/Db Mice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2025, 73, 1293–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Y.; Luo, F. Dietary Fiber: An Opportunity for a Global Control of Hyperlipidemia. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 5542342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Gutiérrez, G.; Rubio-Senent, F.; Lama-Muñoz, A.; García, A.; Fernández-Bolaños, J. Properties of Lignin, Cellulose, and Hemicelluloses Isolated from Olive Cake and Olive Stones: Binding of Water, Oil, Bile Acids, and Glucose. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 8973–8981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Chen, L.; Luo, D.; Wang, Y.; Liang, F. Unlocking the Potential: How Acupuncture Reshapes the Liver-Centered Lipid Metabolism Pattern to Fight Obesity. J. Integr. Med. 2024, 22, 523–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, M.; Matsuoka, R.; Xi, Y.; Wang, X. Comparison of Egg Yolk and Soybean Phospholipids on Hepatic Fatty Acid Profile and Liver Protection in Rats Fed a High-Fructose Diet. Foods 2021, 10, 1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, B.; Tan, X.; Luo, P.; Huang, Q.; Shi, L.; Li, X. Hericium Erinaceus Insoluble Dietary Fiber Alleviates Obesity Induced by High-Fat Diet through Regulating the Metabolic Pathway Influenced by Gut Microbiota. J. Agric. Food Res. 2025, 19, 101560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiantera, V.; Laganà, A.S.; Basciani, S.; Nordio, M.; Bizzarri, M. A Critical Perspective on the Supplementation of Akkermansia Muciniphila: Benefits and Harms. Life 2023, 13, 1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.; Wei, J.; Li, A.; Liu, Z.; Yang, P.; Jing, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhao, T.; Bai, Y.; Zha, L.; et al. Lactobacillus Plantarum Strains Attenuated DSS-Induced Colitis in Mice by Modulating the Gut Microbiota and Immune Response. Int. Microbiol. 2022, 25, 587–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.-G.; Zhang, M.-N.; Wen, X.; He, L.; Zhang, M.-H.; Zhang, J.-L.; Yang, X.-Z. Cepharanthine Ameliorates Dextran Sulphate Sodium-Induced Colitis through Modulating Gut Microbiota. Microb. Biotechnol. 2022, 15, 2208–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, T.; Chatterjee, N.; Capanoglu, E.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Das, A.K.; Dhar, P. The Synergistic Ramification of Insoluble Dietary Fiber and Associated Non-Extractable Polyphenols on Gut Microbial Population Escorting Alleviation of Lifestyle Diseases. Food Chem. X 2023, 18, 100697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| NC | HFD | EPI | OSA-EPI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SOD (U/mL) | 146.78 ± 8.98 | 97.21 ± 6.5 *** | 112.34 ± 6.40 # | 119.6 ± 9.76 ## |
| CAT (U/mL) | 18.89 ± 2.47 | 10.35 ± 1.53 ** | 16.64 ± 2.09 ## | 17.03 ± 2.28 ## |
| MDA (nmol/mL) | 4.63 ± 0.34 | 7.99 ± 0.57 *** | 6.38 ± 0.62 ## | 6.29 ± 0.59 ## |
| IL-1β (pg/mL) | 127.54 ± 15.25 | 156.23 ± 9.78 * | 132.77 ± 11.88 # | 129.12 ± 12.34 # |
| IL-6 (pg/mL) | 10.09 ± 2.12 | 16.23 ± 3.48 * | 12.89 ± 2.34 | 13.78 ± 1.98 |
| IL-10 (pg/mL) | 7.67 ± 1.19 | 5.98 ± 0.98 * | 6.37 ± 1.02 | 6.26 ± 1.21 |
| TNF-α (pg/mL) | 280.57 ± 19.34 | 390.98 ± 20.88 *** | 338.76 ± 16.37 ## | 340.12 ± 13.28 ## |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peng, K.; Tian, S.; Bi, S.; Cui, X.; Gao, K.; Liu, Y. Anti-Obesity Potential of Modified Pomelo-Peel Dietary Fiber-Based Pickering Emulsion. Nutrients 2025, 17, 3036. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17193036
Peng K, Tian S, Bi S, Cui X, Gao K, Liu Y. Anti-Obesity Potential of Modified Pomelo-Peel Dietary Fiber-Based Pickering Emulsion. Nutrients. 2025; 17(19):3036. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17193036
Chicago/Turabian StylePeng, Kaitao, Shiyi Tian, Shuang Bi, Xian Cui, Kaili Gao, and Yuhuan Liu. 2025. "Anti-Obesity Potential of Modified Pomelo-Peel Dietary Fiber-Based Pickering Emulsion" Nutrients 17, no. 19: 3036. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17193036
APA StylePeng, K., Tian, S., Bi, S., Cui, X., Gao, K., & Liu, Y. (2025). Anti-Obesity Potential of Modified Pomelo-Peel Dietary Fiber-Based Pickering Emulsion. Nutrients, 17(19), 3036. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17193036








