Alfalfa Polysaccharide Alleviates Colitis by Regulating Intestinal Microbiota and the Intestinal Barrier Against the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB Pathway
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Disease Activity Index (DAI) Evaluation
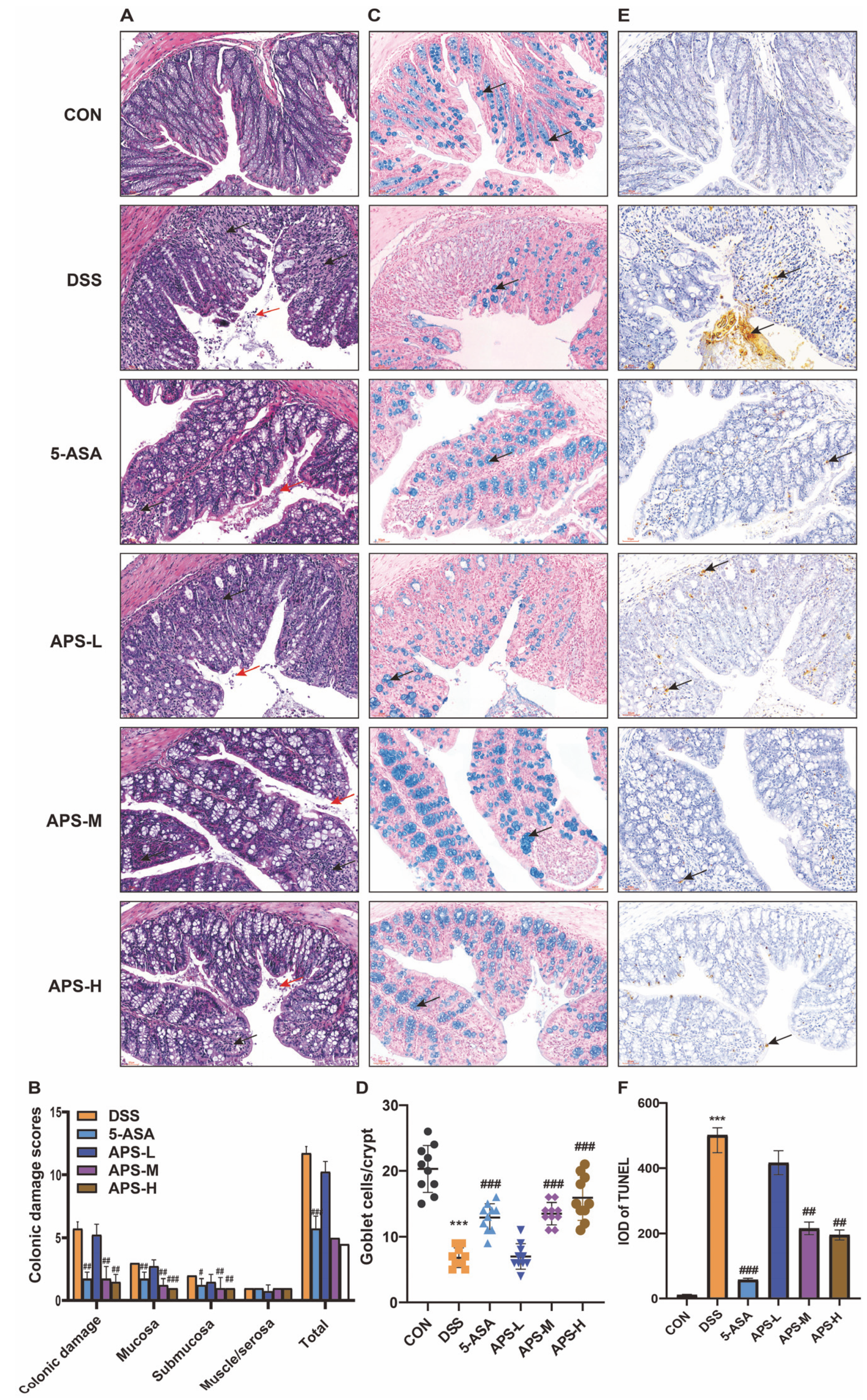
2.4. Histological Examination
2.5. Alcian Blue Staining
2.6. Apoptosis Detection Test
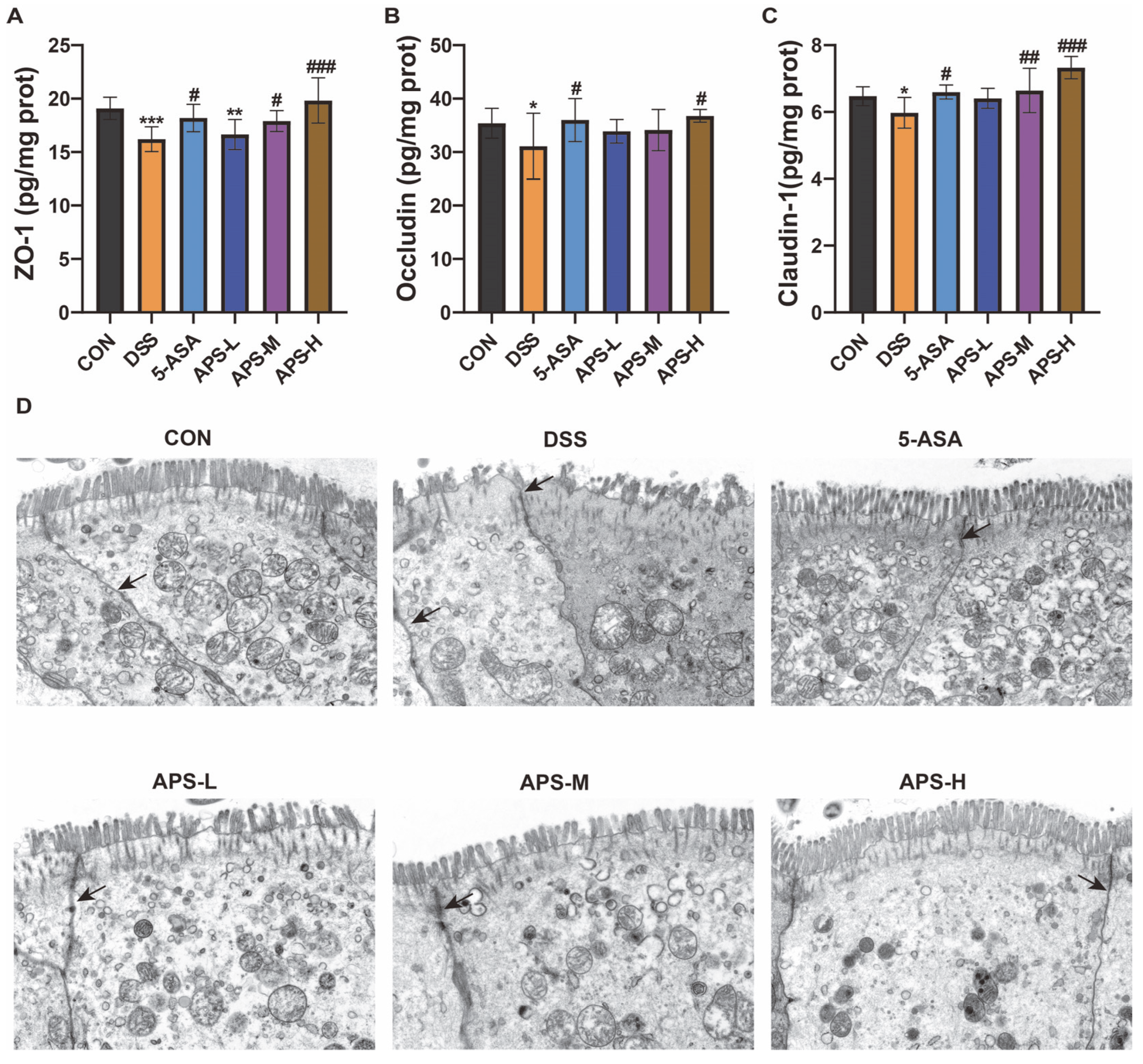
2.7. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) Analysis
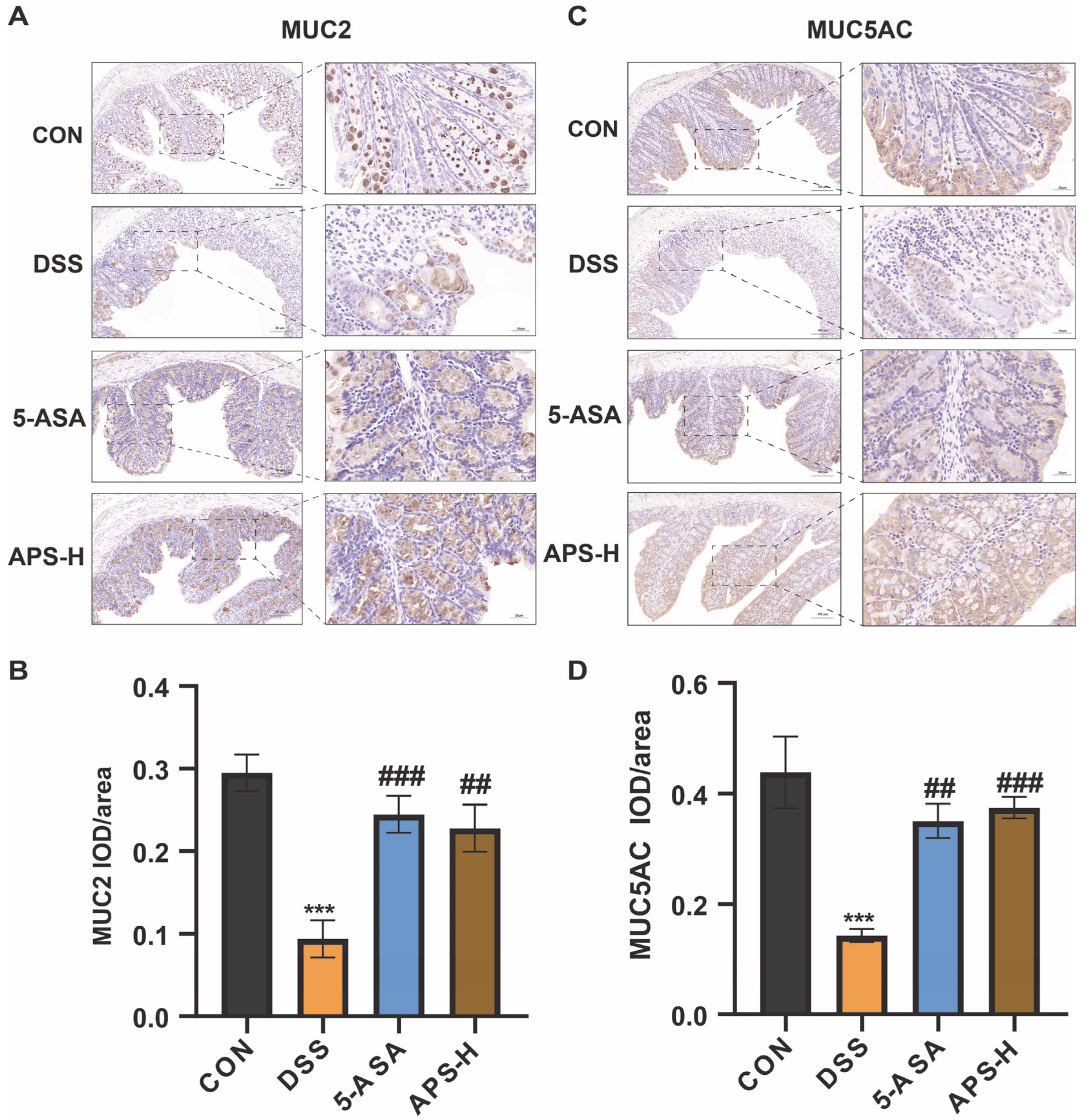
2.8. Immuno-Histochemical Assay
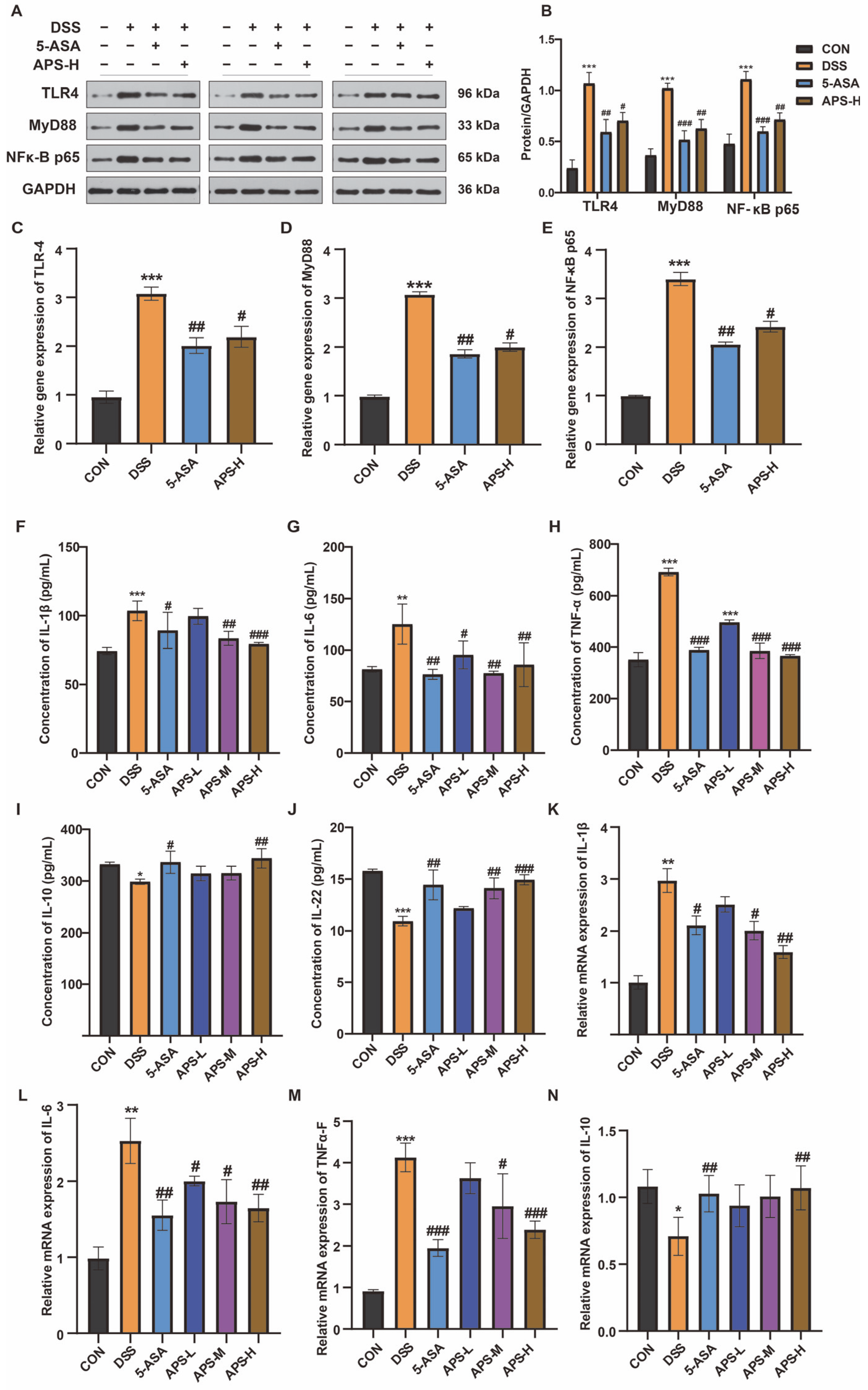
2.9. RNA Extraction and q-PCR
2.10. Western Blot Assay
2.11. Biochemical Indices in Serum and Colon Analysis
2.12. DNA Extraction and Metagenome Sequencing
2.13. Microbiome Analysis
2.14. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. APS Mitigated the Symptoms of Colitis
3.2. APS Maintains Gut Integrity
3.3. APS Restores the Tight Junctions and Enhances Protein Production
3.4. APS Restores MUC2 and MUC5AC Secretions
3.5. Protective Effect of APS-H Against Inflammation Through TLR4, MyD88, and the NF-κB Pathway
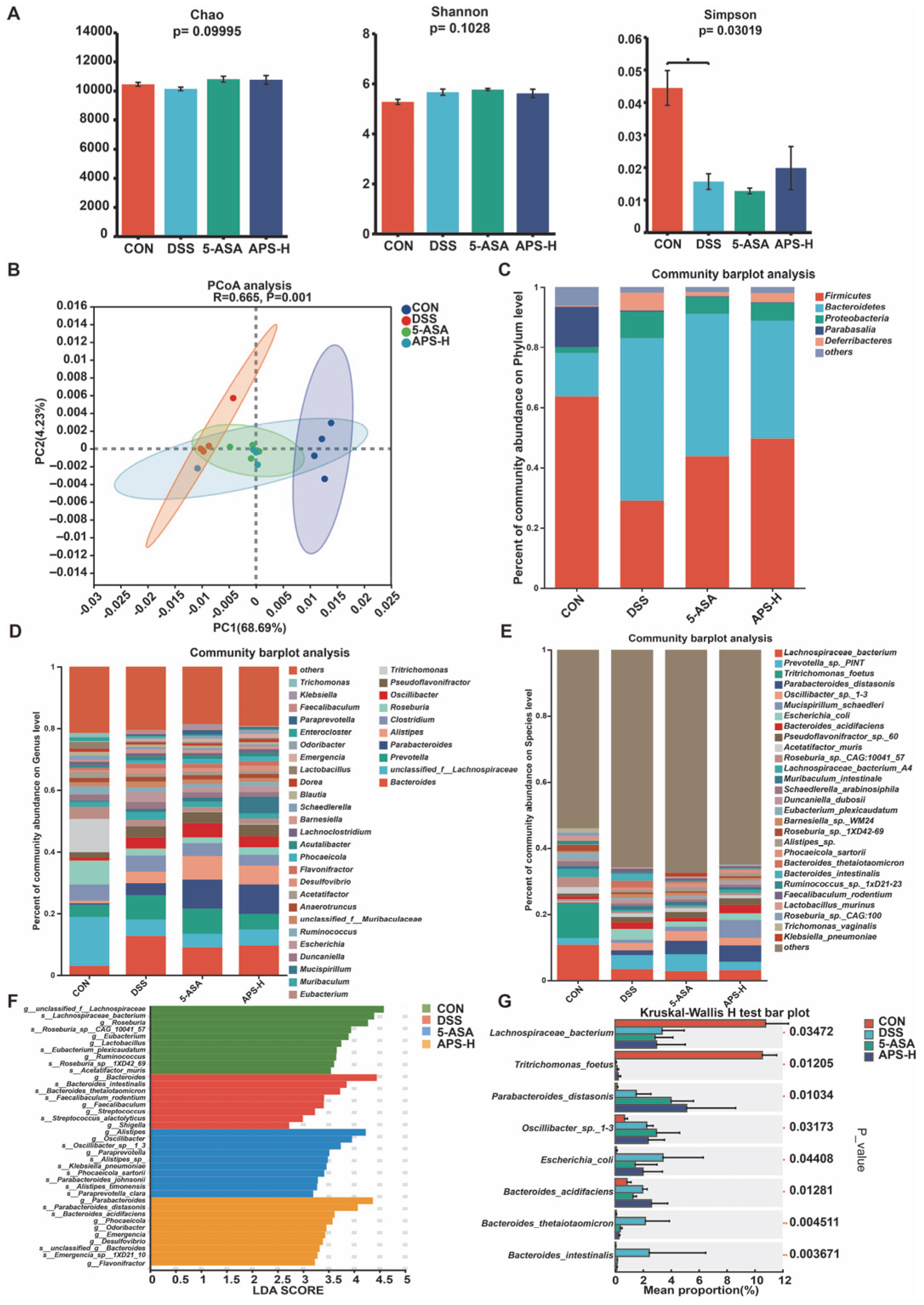
3.6. Alfalfa Polysaccharide Improves Intestinal Flora Imbalance
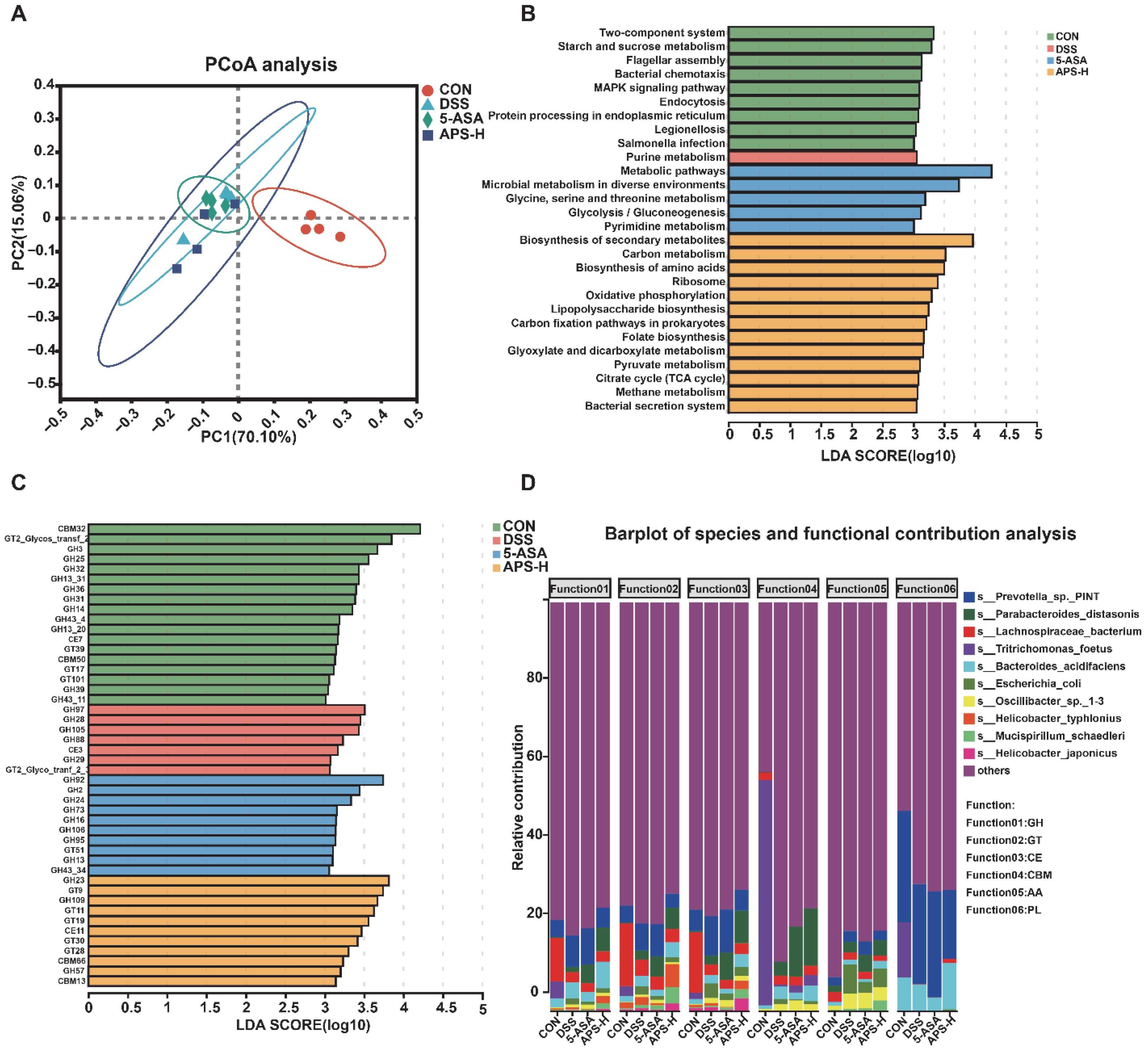
3.7. Functional Transformation of APS on Intestinal Microorganisms in DSS-Induced Colitis Mice
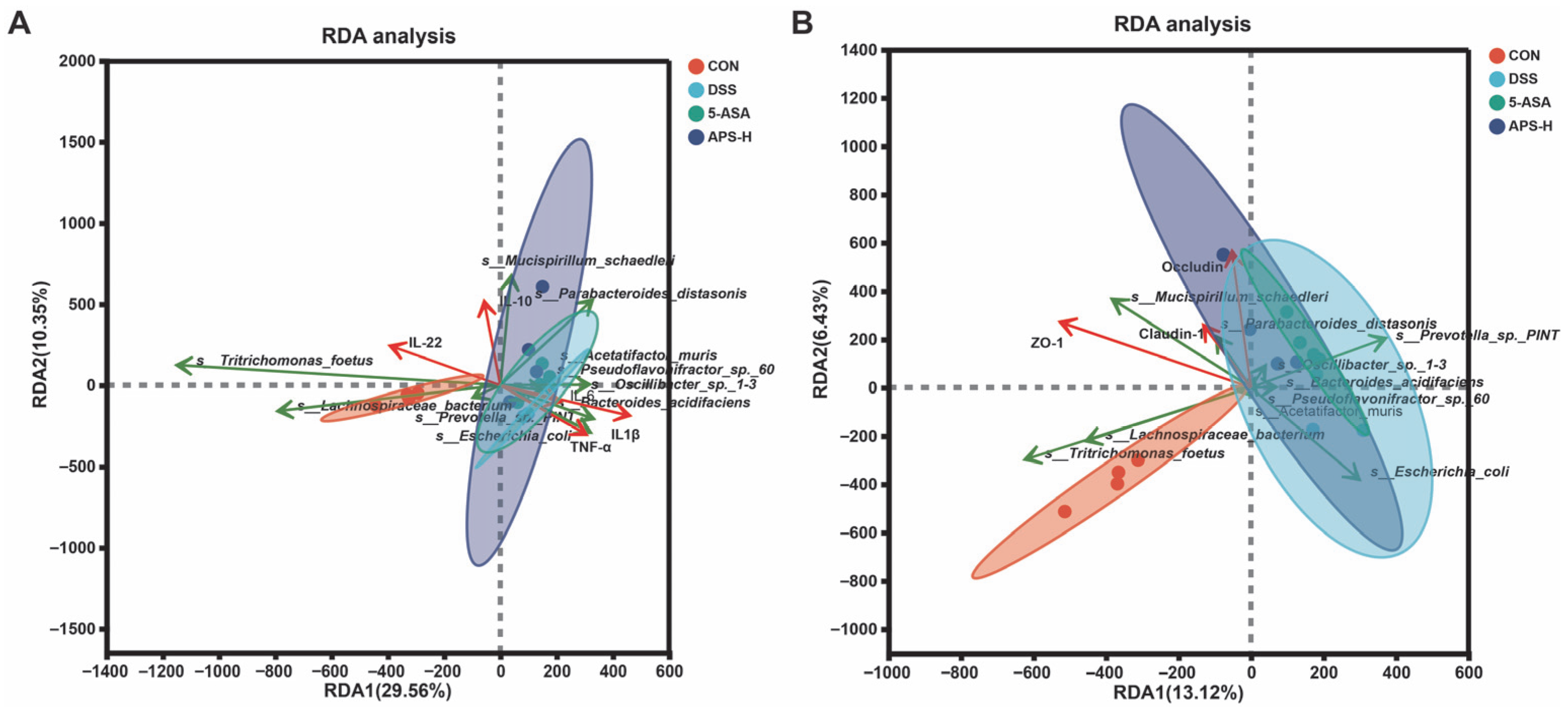
3.8. Correlation Analysis of Microflora with Inflammatory Cytokines and Tight Junction Protein
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AB | Alcian blue |
| APS | Alfalfa polysaccharide |
| CAZyme | Carbohydrate-active enzyme |
| DAI | Disease activity index |
| DSS | Dextran sulfate sodium |
| GAPDH | Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase |
| H&E | hematoxylin and eosin |
| IBD | Inflammatory bowel diseases |
| IOD | Integrated optical density |
| KEGG | Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes |
| LDA | Linear discriminant analysis |
| LEfSe | Linear discriminant analysis effect size |
| NR database | Non-Redundant Protein Sequence Database |
| PCoA | Principal Co-ordinates Analysis |
| RDA | Redundancy analysis |
| TEM | Transmission electron microscopy |
| UC | Ulcerative colitis |
| 5-ASA | 5-Aminosalicylic Acid |
References
- Pierre, J.F.; Hinterleitner, R.; Bouziat, R.; Hubert, N.A.; Leone, V.; Miyoshi, J.; Jabri, B.; Chang, E.B. Dietary antioxidant micronutrients alter mucosal inflammatory risk in a murine model of genetic and microbial susceptibility. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2018, 54, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halfvarson, J.; Brislawn, C.J.; Lamendella, R.; Vazquez-Baeza, Y.; Walters, W.A.; Bramer, L.M.; D’Amato, M.; Bonfiglio, F.; McDonald, D.; Gonzalez, A.; et al. Dynamics of the human gut microbiome in inflammatory bowel disease. Nat. Microbiol. 2017, 2, 17004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Guan, B.; Lin, L.; Wang, Y. Improvement of intestinal barrier function, gut microbiota, and metabolic endotoxemia in type 2 diabetes rats by curcumin. Bioengineered 2021, 12, 11947–11958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajilic-Stojanovic, M.; Shanahan, F.; Guarner, F.; de Vos, W.M. Phylogenetic analysis of dysbiosis in ulcerative colitis during remission. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2013, 19, 481–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Ren, Z.; Huo, Y.; Yang, W.; Peng, L.; Lv, H.; Nie, L.; Wei, H.; Wan, C. Targeting the gut microbiota to investigate the mechanism of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum 1201 in negating colitis aggravated by a high-salt diet. Food Res. Int. 2022, 162, 112010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, R.; Cope, J.L.; Nagy-Szakal, D.; Dowd, S.; Versalovic, J.; Hollister, E.B.; Kellermayer, R. Composition and function of the pediatric colonic mucosal microbiome in untreated patients with ulcerative colitis. Gut Microbes 2016, 7, 384–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelakkot, C.; Ghim, J.; Ryu, S.H. Mechanisms regulating intestinal barrier integrity and its pathological implications. Exp. Mol. Med. 2018, 50, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terciolo, C.; Dapoigny, M.; Andre, F. Beneficial effects of Saccharomyces boulardii CNCM I-745 on clinical disorders associated with intestinal barrier disruption. Clin. Exp. Gastroenter 2019, 12, 67–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Yang, B.; Ross, R.P.; Jin, Y.; Stanton, C.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W. Orally Administered CLA Ameliorates DSS-Induced Colitis in Mice via Intestinal Barrier Improvement, Oxidative Stress Reduction, and Inflammatory Cytokine and Gut Microbiota Modulation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 13282–13298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, H.; Li, H.; Wen, Y.; Jiang, D.; Zhu, S.; He, X.; Xiong, Q.; Gao, J.; Hou, S.; Huang, S.; et al. Tremella fuciformis polysaccharides ameliorated ulcerative colitis via inhibiting inflammation and enhancing intestinal epithelial barrier function. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 180, 633–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, S.; Liu, W.; Zhao, Q.; Li, K.; Zhu, J.; Yao, W.; Gao, X. Combination of polysaccharides from Astragalus membranaceus and Codonopsis pilosula ameliorated mice colitis and underlying mechanisms. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 264, 113280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.Y.; Lin, L.H.; Liang, H.J.; Li, Y.Q.; Zhao, F.Q.; Sun, T.Y.; Liu, Z.Y.; Zhu, J.Y.; Gu, F.; Xu, J.N.; et al. Lycium barbarum polysaccharide alleviates DSS-induced chronic ulcerative colitis by restoring intestinal barrier function and modulating gut microbiota. Ann. Med. 2023, 55, 2290213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Tang, Y.; Meng, X.; Guan, N.; Yu, Y. The proliferative effects of alfalfa polysaccharides on the mouse immune cells. Life Sci. J. 2013, 10, 868–873. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Y.H.; Wang, L.X.; Sun, H.; Wang, Y.X.; Yang, Z.B.; Zhang, G.G.; Jiang, S.Z.; Yang, W.R. Polysaccharide from alfalfa activates RAW 264.7 macrophages through MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathways. Int. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 126, 960–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, P.; Bian, J.; Xu, S.; Liu, C.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, G.; Li, D.; Liu, X. Structural features, selenization modification, antioxidant and anti-tumor effects of polysaccharides from alfalfa roots. Int. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 149, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Sang, R.; Feng, G.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, R.; Yan, X. Microbiological and metabolic pathways analysing the mechanisms of alfalfa polysaccharide and sulfated alfalfa polysaccharide in alleviating obesity. Int. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 263, 130334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Wang, L.; Sun, H.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, G.; Yang, W. Immunomodulatory, antioxidant and intestinal morphology-regulating activities of alfalfa polysaccharides in mice. Int. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 133, 1107–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seril, D.N.; Liao, J.; Ho, K.-L.K.; Yang, C.S.; Yang, G.-Y. Inhibition of chronic ulcerative colitis-associated colorectal adenocarcinoma development in a murine model by N-acetylcysteine. Carcinogenesis 2002, 23, 993–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clapper, M.L.; Gary, M.A.; Coudry, R.A.; Litwin, S.; Chang, W.-C.L.; Devarajan, K.; Lubet, R.A.; Cooper, H.S. 5-aminosalicylic acid inhibits colitis-associated colorectal dysplasias in the mouse model of azoxymethane/dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2008, 14, 1341–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salim, S.Y.; Soderholm, J.D. Importance of disrupted intestinal barrier in inflammatory bowel diseases. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2011, 17, 362–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.Y.; Chen, S.Y.; Wu, Y.H.; Liao, Y.L.; Yen, G.C. Ameliorative effect of buckwheat polysaccharides on colitis via regulation of the gut microbiota. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 227, 872–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.F.; Li, C.Y.; Fu, Y.P.; JiZe, X.P.; Zhao, Y.Z.; Peng, X.; Wang, J.Y.; Yin, Z.Q.; Li, Y.P.; Song, X.; et al. Angelica sinensis aboveground part polysaccharide and its metabolite 5-MT ameliorate colitis via modulating gut microbiota and TLR4/MyD88/NF-kappaB pathway. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 242, 124689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.Y.; Gan, L.P.; Du, M.Y.; Shang, Q.H.; Xie, Y.H.; Zhang, G.G. Effects of dietary supplementation of alfalfa polysaccharides on growth performance, small intestinal enzyme activities, morphology, and large intestinal selected microbiota of piglets. Livest. Sci. 2019, 223, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlowska, B.; Sobieszczanska, B.M. Intestinal epithelial barrier: The target for pathogenic Escherichia coli. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2017, 26, 1437–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Zhao, J.; Xie, H.; Cai, M.; Yao, L.; Li, J.; Han, L.; Chen, W.; Yu, N.; Peng, D. Dendrobium huoshanense polysaccharides ameliorate ulcerative colitis by improving intestinal mucosal barrier and regulating gut microbiota. J. Funct. Foods 2022, 96, 105231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Shen, M.; Chen, Y.; Yu, Q.; Chen, T.; Xie, J. Alleviative effects of natural plant polysaccharides against DSS-induced ulcerative colitis via inhibiting inflammation and modulating gut microbiota. Food Res. Int. 2023, 167, 112630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Zhang, F.; Li, X.; Luo, J.; Sun, Y.; Wu, J.; Li, M.; Wen, Y.; Liang, H.; Wang, K.; et al. Heat shock transcription factor 2 inhibits intestinal epithelial cell apoptosis through the mitochondrial pathway in ulcerative colitis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 527, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.; Ying, M.; Xie, J.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ding, X.; Hong, J.; Liao, W.; Yu, Q. A Ganoderma atrum polysaccharide alleviated DSS-induced ulcerative colitis by protecting the apoptosis/autophagy-regulated physical barrier and the DC-related immune barrier. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 10690–10699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Wang, H.; Wang, Z.; Geng, Y. Pine Pollen Polysaccharides’ and Sulfated Polysaccharides’ Effects on UC Mice through Modulation of Cell Tight Junctions and RIPK3-Dependent Necroptosis Pathways. Molecules 2022, 27, 7682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurashima, Y.; Kigoshi, T.; Murasaki, S.; Arai, F.; Shimada, K.; Seki, N.; Kim, Y.G.; Hase, K.; Ohno, H.; Kawano, K.; et al. Pancreatic glycoprotein 2 is a first line of defense for mucosal protection in intestinal inflammation. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, G.; Jiang, H.; Feng, J.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, D.; Jiang, C.; Zhang, J. Aloe vera mitigates dextran sulfate sodium-induced rat ulcerative colitis by potentiating colon mucus barrier. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 279, 114108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dejban, P.; Nikravangolsefid, N.; Chamanara, M.; Dehpour, A.; Rashidian, A. The role of medicinal products in the treatment of inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) through inhibition of TLR4/NF-kappaB pathway. Phytother. Res. 2021, 35, 835–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Bai, J.Y.; Wang, B.T.; Yu, L.L.; Tian, F.W.; Zhao, J.X.; Zhang, H.; Suo, H.Y.; Chen, W.; Zhai, Q.X. Stachyose modulates gut microbiota and alleviates DSS-induced ulcerative colitis in mice. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2023, 12, 2211–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, A.W.; Sanderson, J.D.; Churcher, C.; Parkes, G.C.; Hudspith, B.N.; Rayment, N.; Brostoff, J.; Parkhill, J.; Dougan, G.; Petrovska, L. High-throughput clone library analysis of the mucosa-associated microbiota reveals dysbiosis and differences between inflamed and non-inflamed regions of the intestine in inflammatory bowel disease. BMC Microbiol. 2011, 11, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lepage, P.; Häsler, R.; Spehlmann, M.E.; Rehman, A.; Zvirbliene, A.; Begun, A.; Ott, S.; Kupcinskas, L.; Doré, J.; Raedler, A.; et al. Twin Study Indicates Loss of Interaction Between Microbiota and Mucosa of Patients with Ulcerative Colitis. Gastroenterology 2011, 141, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Li, P.; An, Y.; Ren, J.; Yan, D.; Cui, J.; Li, D.; Li, M.; Wang, M.; Zhong, G. Phloretin ameliorates dextran sulfate sodium-induced ulcerative colitis in mice by regulating the gut microbiota. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 150, 104489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abaidullah, M.; La, S.; Liu, M.Q.; Liu, B.S.; Cui, Y.L.; Wang, Z.C.; Sun, H.; Ma, S.; Shi, Y.H. Polysaccharide from Roxb Mitigates Intestinal Mucosal Damage by Therapeutically Restoring the Interactions between Gut Microbiota and Innate Immune Functions. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, R.H.; Dulai, P.S.; Vazquez-Baeza, Y.; Sauceda, C.; Daniel, N.; Gerner, R.R.; Batachari, L.E.; Malfavon, M.; Zhu, Q.; Weldon, K.; et al. Multi-omics analyses of the ulcerative colitis gut microbiome link Bacteroides vulgatus proteases with disease severity. Nat. Microbiol. 2022, 7, 262–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, X.; Liu, C.; Ding, Y.; Ni, Y.; Ji, F.; Lau, H.C.H.; Jiang, L.; Sung, J.J.; Wong, S.H.; Yu, J. Roseburia intestinalis generated butyrate boosts anti-PD-1 efficacy in colorectal cancer by activating cytotoxic CD8(+) T cells. Gut 2023, 72, 2112–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.K.K. Parabacteroides distasonis: An emerging probiotic? Gut 2023, 72, 1635–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.L.; Guo, D.D.; Fang, L.; Sang, T.T.; Wu, J.J.; Guo, C.J.; Wang, Y.J.; Wang, Y.; Chen, C.J.; Chen, J.J.; et al. Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharide modulates gut microbiota and immune cell function to inhibit inflammation and tumorigenesis in colon. Carbohyd. Polym. 2021, 267, 118231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Fu, T.Y.; Cheng, H.; Mi, J.C.; Shang, Q.S.; Yu, G.L. Polysaccharide from edible alga Gloiopeltis furcata attenuates intestinal mucosal damage by therapeutically remodeling the interactions between gut microbiota and mucin O-glycans. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 278, 118921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duboc, H.; Rajca, S.; Rainteau, D.; Benarous, D.; Maubert, M.A.; Quervain, E.; Thomas, G.; Barbu, V.; Humbert, L.; Despras, G.; et al. Connecting dysbiosis, bile-acid dysmetabolism and gut inflammation in inflammatory bowel diseases. Gut 2013, 62, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, D.N.; Amand, A.L.S.; Feldman, R.A.; Boedeker, E.C.; Harpaz, N.; Pace, N.R. Molecular-phylogenetic characterization of microbial community imbalances in human inflammatory bowel diseases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 13780–13785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Chen, H.; Kan, J.; Gou, Y.R.; Liu, J.; Zhang, X.; Wu, X.N.; Tang, S.X.; Sun, R.; Qian, C.L.; et al. Anti-inflammatory properties and gut microbiota modulation of an alkali-soluble polysaccharide from purple sweet potato in DSS-induced colitis mice. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 153, 708–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Ishima, T.; Qu, Y.; Shan, J.; Chang, L.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, J.; Pu, Y.; Fujita, Y.; Tan, Y.; et al. Ingestion of Faecalibaculum rodentium causes depression-like phenotypes in resilient Ephx2 knock-out mice: A role of brain-gut-microbiota axis via the subdiaphragmatic vagus nerve. J. Affect. Disord. 2021, 292, 565–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flynn, K.J.; Baxter, N.T.; Schloss, P.D. Metabolic and Community Synergy of Oral Bacteria in Colorectal Cancer. Msphere 2016, 1, e00102-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metwaly, A.; Dunkel, A.; Waldschmitt, N.; Raj, A.C.D.; Lagkouvardos, I.; Corraliza, A.M.; Mayorgas, A.; Martinez-Medina, M.; Reiter, S.; Schloter, M.; et al. Integrated microbiota and metabolite profiles link Crohn’s disease to sulfur metabolism. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, G.Y.; Kane, A.; Lee, K.; Xu, Q.; Wu, X.; Roper, J.; Mason, J.B.; Crott, J.W. Parabacteroides distasonis attenuates toll-like receptor 4 signaling and Akt activation and blocks colon tumor formation in high-fat diet-fed azoxymethane-treated mice. Int. J. Cancer 2018, 143, 1797–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Berre, C.; Roda, G.; Protic, M.N.; Danese, S.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L. Modern use of 5-aminosalicylic acid compounds for ulcerative colitis. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2020, 20, 363–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
La, S.; Abaidullah, M.; Li, H.; Cui, Y.; Liu, B.; Shi, Y. Alfalfa Polysaccharide Alleviates Colitis by Regulating Intestinal Microbiota and the Intestinal Barrier Against the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB Pathway. Nutrients 2025, 17, 3001. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17183001
La S, Abaidullah M, Li H, Cui Y, Liu B, Shi Y. Alfalfa Polysaccharide Alleviates Colitis by Regulating Intestinal Microbiota and the Intestinal Barrier Against the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB Pathway. Nutrients. 2025; 17(18):3001. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17183001
Chicago/Turabian StyleLa, Shaokai, Muhammad Abaidullah, Hao Li, Yalei Cui, Boshuai Liu, and Yinghua Shi. 2025. "Alfalfa Polysaccharide Alleviates Colitis by Regulating Intestinal Microbiota and the Intestinal Barrier Against the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB Pathway" Nutrients 17, no. 18: 3001. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17183001
APA StyleLa, S., Abaidullah, M., Li, H., Cui, Y., Liu, B., & Shi, Y. (2025). Alfalfa Polysaccharide Alleviates Colitis by Regulating Intestinal Microbiota and the Intestinal Barrier Against the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB Pathway. Nutrients, 17(18), 3001. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17183001





