Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus Probio-M9 Alters the Gut Microbiota and Mitigates Pulmonary Hypertension in a Rat Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Monocrotaline (MCT)-Induced PH Model Rats
2.2. Echocardiography in Rats
2.3. Immunofluorescence Staining of the Lung
2.4. Clinical Samples for Histological Evaluations
2.5. Extraction of Fecal DNA and Metagenomic Sequencing
2.6. Quality Control of Metagenomic Data
2.7. Metagenomic Assembly, Contig Binning, Genome Dereplication
2.8. Taxonomic Annotation, Abundance, Prediction of Gut Metabolic Modules of SGBs
2.9. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
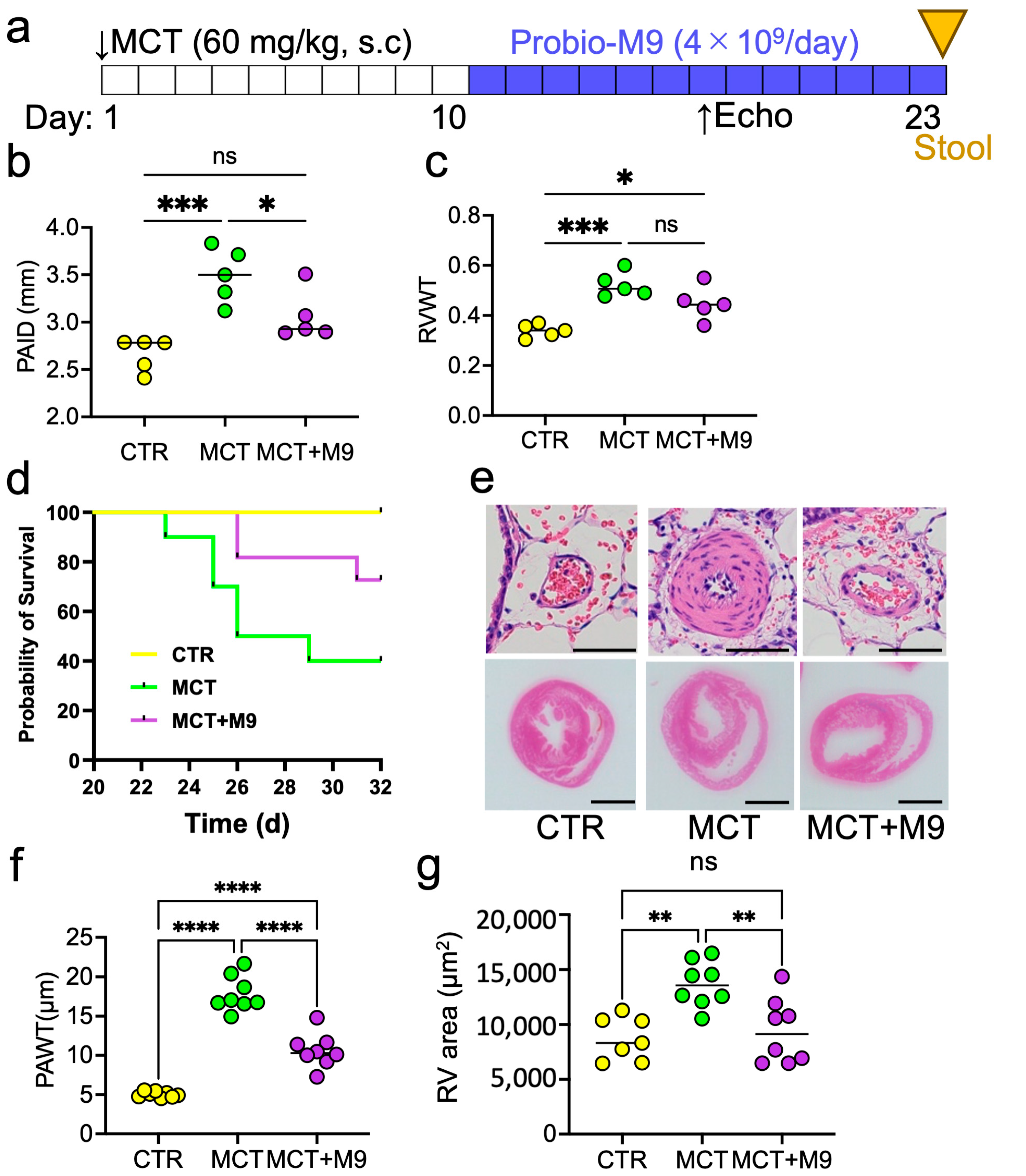
3.1. Probio-M9 Prolonged Survival and Mitigated the Pathology in MCT Rats
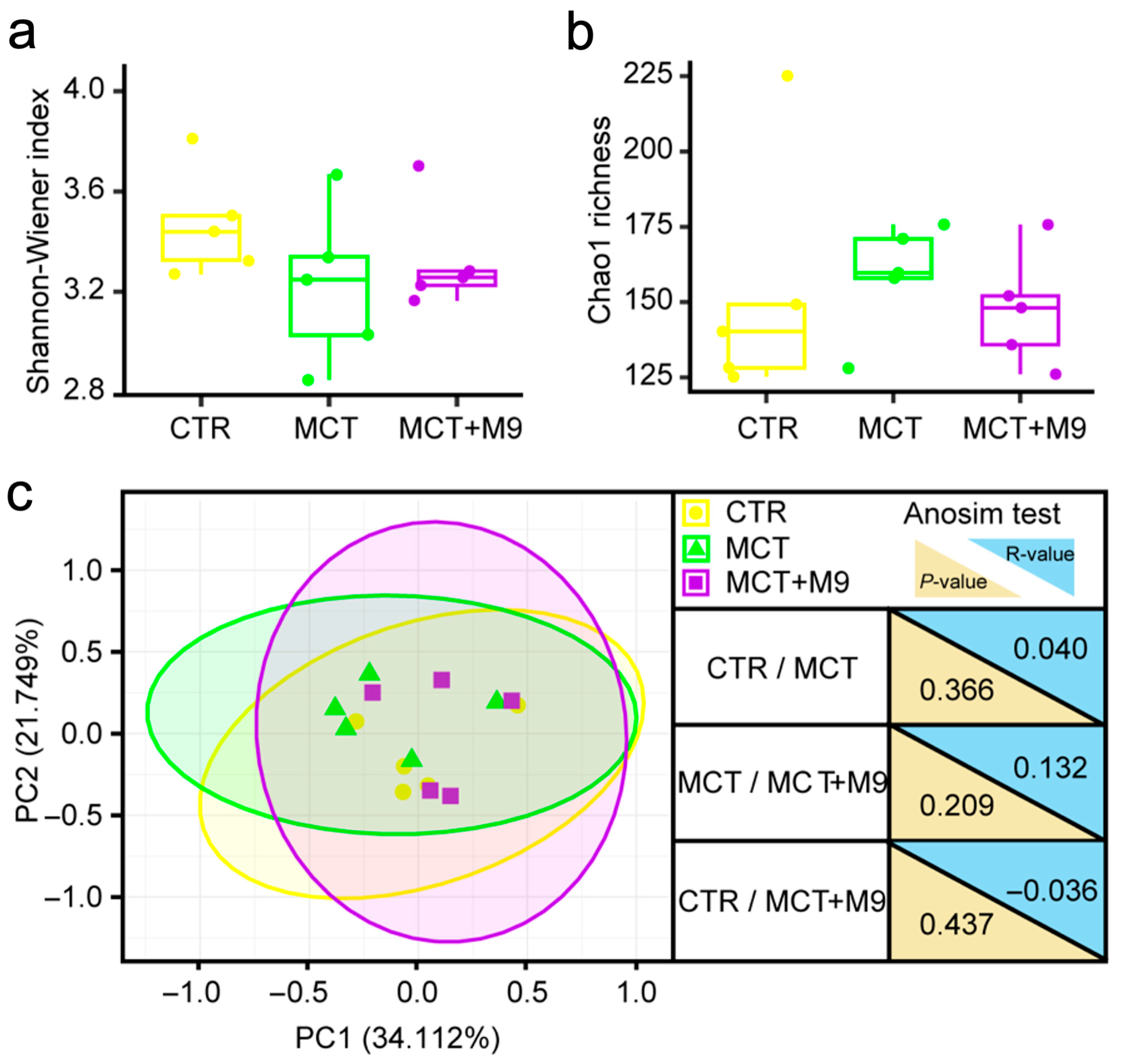
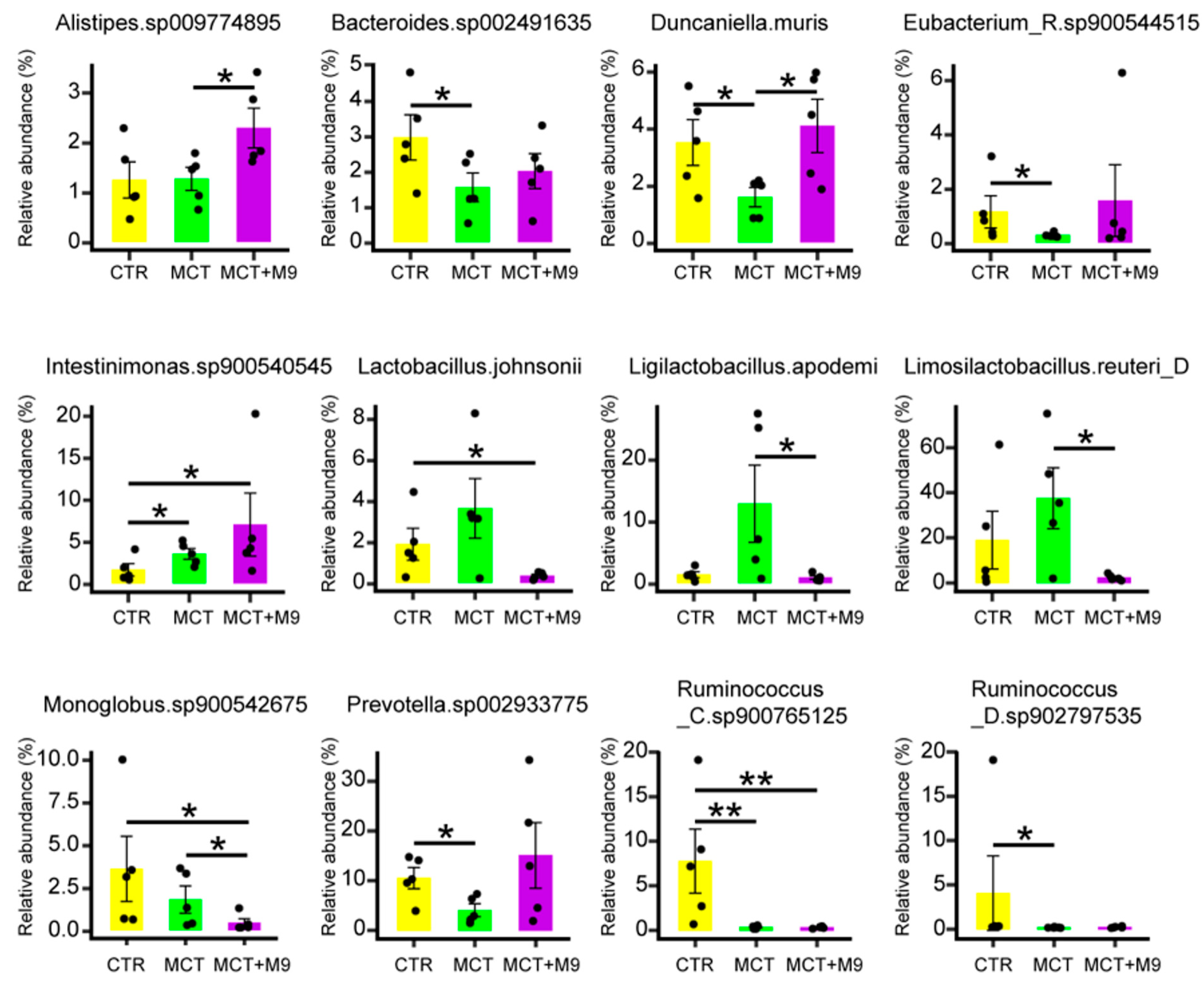
3.2. Probio-M9 Supplementation Significantly Modulated Gut Microbiota of MCT Model Rat
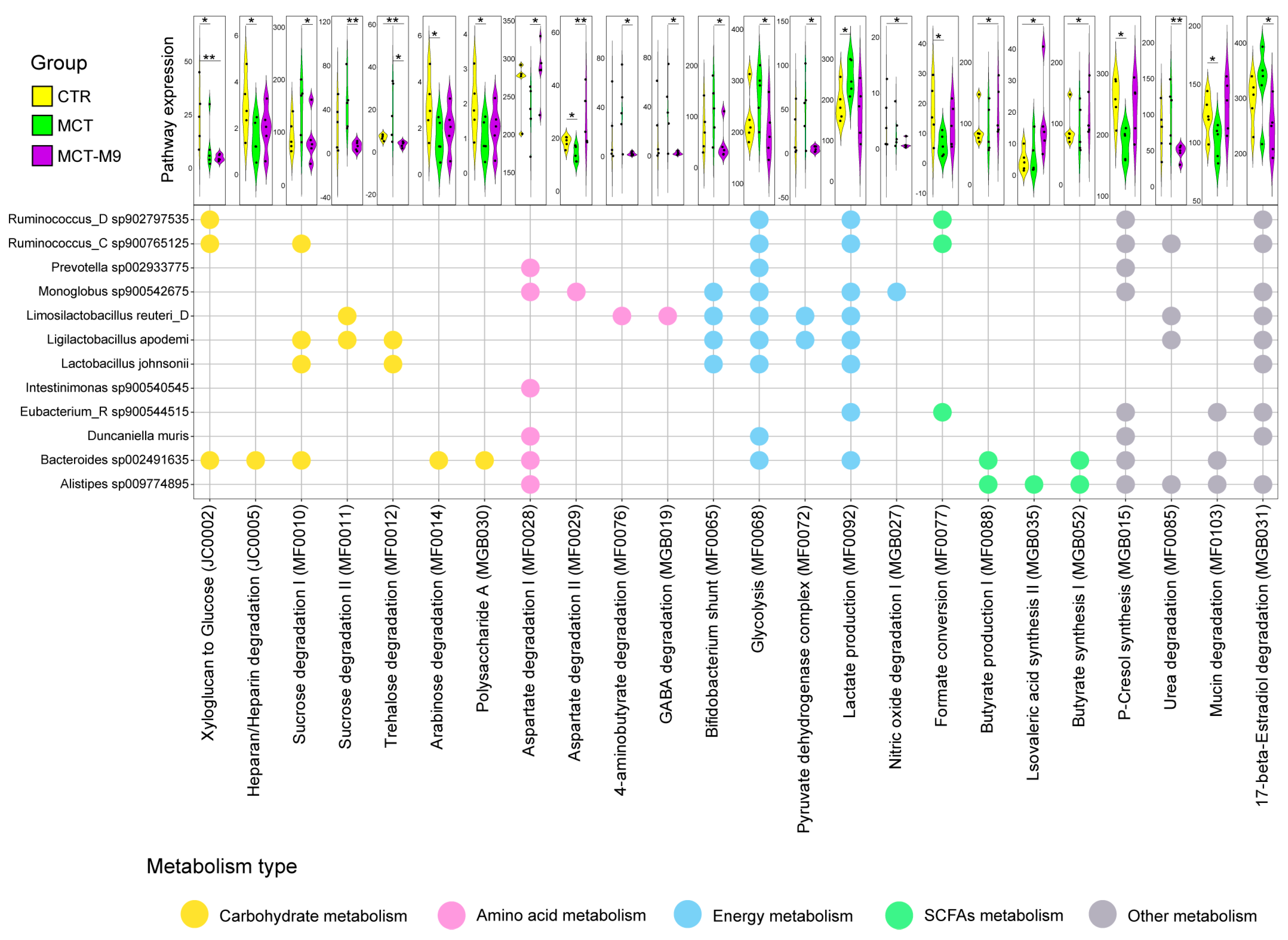
3.3. Probio-M9 Supplementation Significantly Modulated the Metabolic Processes of Predicted Gut Bioactive Metabolites of MCT Model Rats
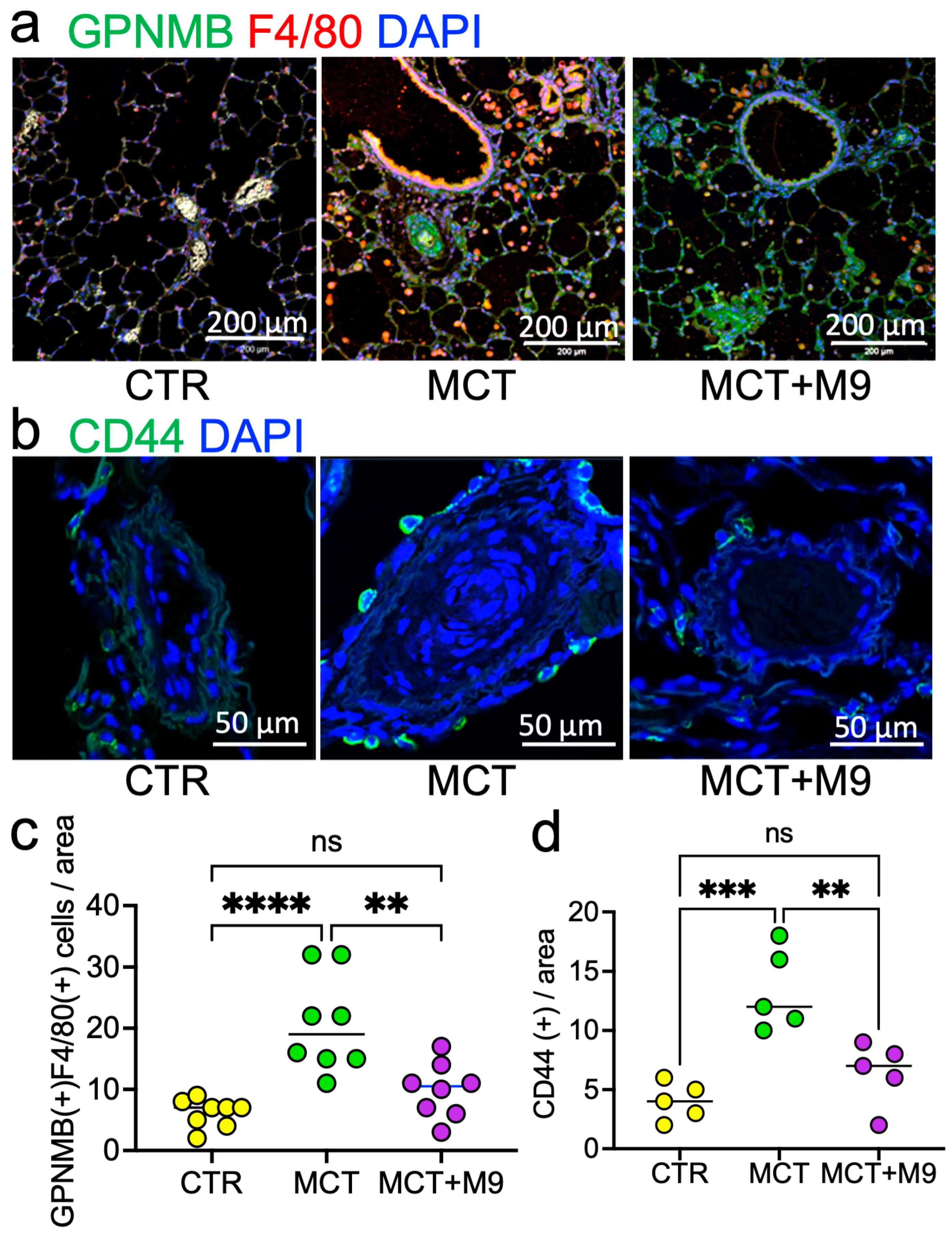
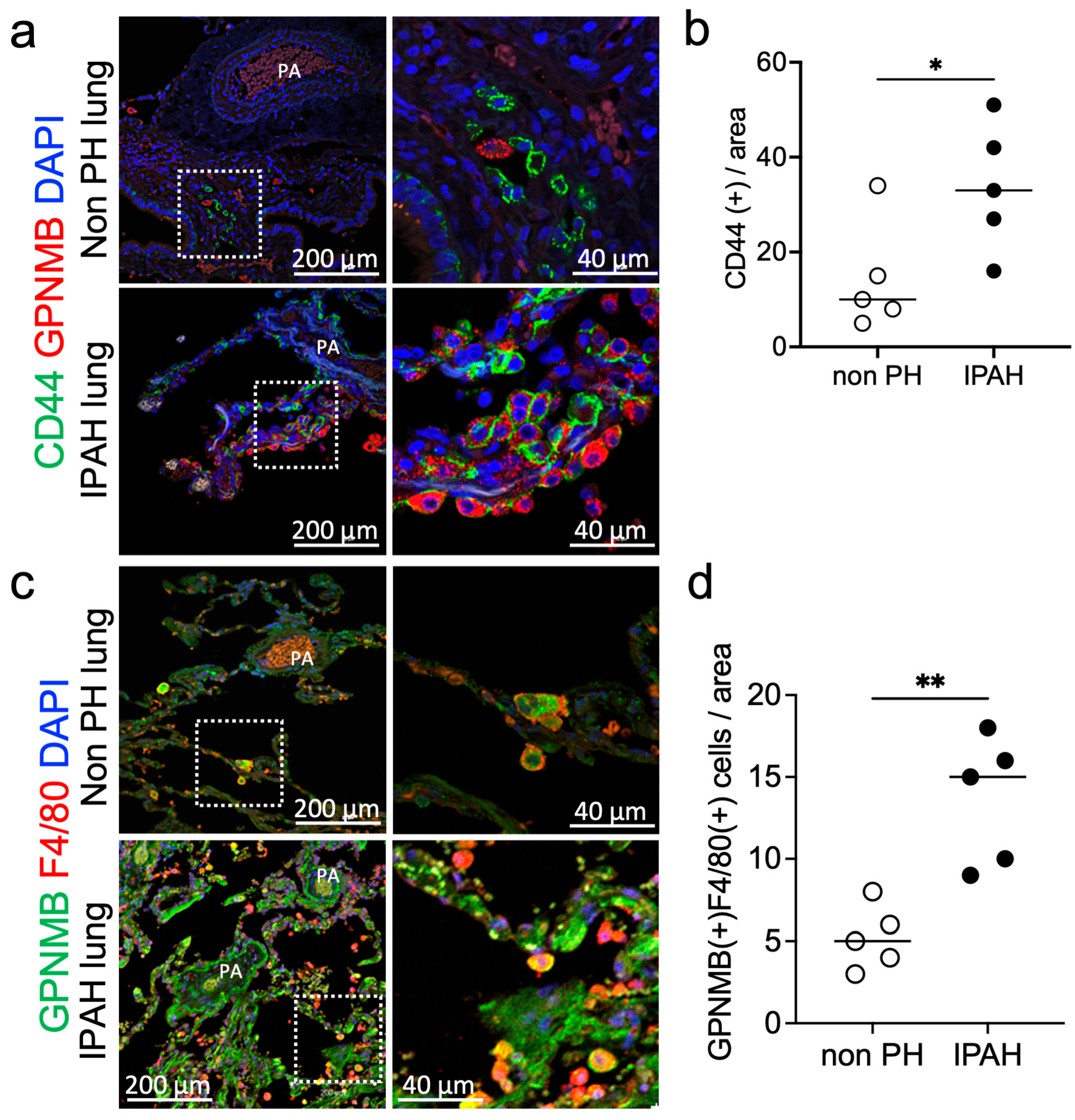
3.4. Probio-M9 Downregulated Upregulated CD44 and GPNMB Expressing PA in MCT Rats
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| α-SMA | α-smooth muscle actin |
| IPAH | Idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension |
| MCT | Monocrotaline |
| PA | Pulmonary artery |
| PH | Pulmonary hypertension |
| PASMC | Pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells |
| RVID | Right ventricular internal diameter |
| RVWT | Right ventricular wall thickness |
References
- Dai, J.; Chen, H.; Fang, J.; Wu, S.; Jia, Z. Vascular Remodeling: The Multicellular Mechanisms of Pulmonary Hypertension. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, Z.; Liang, L.; Li, J.; Meng, L.; Yuan, W.; Xie, B.; Zhang, X.; Feng, L.; Jia, Y.; et al. Multi-kingdom gut microbiota dysbiosis is associated with the development of pulmonary arterial hypertension. eBioMedicine 2025, 115, 105686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Chai, S.; Ding, Y.; Pang, K.; Dong, T.; Dai, D.; Wang, J.; Wang, S.; Liu, S. Gut microbiota modulates lung gene expression and metabolism to aid SD rats in adapting to low-pressure hypoxia. Microbiol. Spectr. 2025, 13, e0004525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Chen, M.; Duo, L.; Wang, J.; Guo, S.; Sun, H.; Menghe, B.; Zhang, H. Characterization of potentially probiotic lactic acid bacteria and bifidobacteria isolated from human colostrum. J. Dairy Sci. 2020, 103, 4013–4025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Hiraishi, K.; Kurahara, L.H.; Nakano-Narusawa, Y.; Li, X.; Hu, Y.; Matsuda, Y.; Zhang, H.; Hirano, K. Inhibitory Effects of Breast Milk-Derived Lactobacillus rhamnosus Probio-M9 on Colitis-Associated Carcinogenesis by Restoration of the Gut Microbiota in a Mouse Model. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, H.; Yamamoto, N.; Kurahara, L.H.; Izumori, K.; Yoshihara, A. X-ray structure and characterization of a probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus Probio-M9 L-rhamnose isomerase. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2024, 108, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, F.; Hiraishi, K.; Li, X.; Hu, Y.; Kojima, D.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, H.; Kurahara, L.H. Long-Term Tracking of the Effects of Colostrum-Derived Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus Probio-M9 on Gut Microbiota in Mice with Colitis-Associated Tumorigenesis. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.; Huang, H.; Xie, M.; Liu, Z.; Jiang, L.; Shi, H.; Wu, X.; Hao, S.; Li, S. Single-cell characterization of the immune heterogeneity of pulmonary hypertension identifies novel targets for immunotherapy. BMC Immunol. 2025, 26, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Sun, Y.; Ma, L.; Hou, J.; Wang, L.; Gong, Y.; Sun, X.; Wu, S.; Wang, J.; Ji, Z.; et al. A novel molecular mechanism of vascular fibrosis in Takayasu arteritis: Macrophage-derived GPNMB promoting adventitial fibroblast extracellular matrix production in the aorta. Transl. Res. 2023, 255, 128–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Long, M.; Yuan, M.; Yin, J.; Luo, W.; Wang, S.; Cai, Y.; Jiang, W.; Chao, J. Macrophage-derived GPNMB trapped by fibrotic extracellular matrix promotes pulmonary fibrosis. Commun. Biol. 2023, 6, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liguori, M.; Digifico, E.; Vacchini, A.; Avigni, R.; Colombo, F.S.; Borroni, E.M.; Farina, F.M.; Milanesi, S.; Castagna, A.; Mannarino, L.; et al. The soluble glycoprotein NMB (GPNMB) produced by macrophages induces cancer stemness and metastasis via CD44 and IL-33. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2021, 18, 711–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Liu, P.; Zhu, H.; Yang, H.; Zha, J.; Yao, H.; Zhang, S.; Huang, J.; Li, G.; Jiang, G.; et al. T follicular helper cell is essential for M2 macrophage polarization and pulmonary vascular remodeling in hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension. Respir. Res. 2024, 25, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, F.; Miao, H.R.; Hui, H.L.; Qiu, L.J.; Chen, Y.; Luo, M.; Zhang, J.C.; Lin, Y.G.; Li, D.; Ong, S.B.; et al. MHCIIhiLYVE1loCCR2hi Interstitial Macrophages Promote Medial Fibrosis in Pulmonary Arterioles and Contribute to Pulmonary Hypertension. Circ. Res. 2025, 137, 46–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Shao, F.; Yu, D.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Z.; Ma, J.; Xia, P.; Wang, S. Maturation and specialization of group 2 innate lymphoid cells through the lung-gut axis. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 7600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, M.; Zhang, X.; Cai, J. Microbiota-gut-brain axis: Interplay between microbiota, barrier function and lymphatic system. Gut Microbes 2024, 16, 2387800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Pelgrim, C.E.; Peralta Marzal, L.N.; Korver, S.; van Ark, I.; Leusink-Muis, T.; van Helvoort, A.; Keshavarzian, A.; Kraneveld, A.D.; Garssen, J.; et al. Changes in intestinal homeostasis and immunity in a cigarette smoke- and LPS-induced murine model for COPD: The lung-gut axis. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2022, 323, L266–L280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Qin, P.; Huang, J.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, C.; Chen, Y.; Liu, L.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Stroke-Associated Pneumonia and the Brain-Gut-Lung Axis: A Systematic Literature Review. Neurologist 2025, 30, 237–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohn, K.H.; Baek, M.G.; Choi, S.M.; Bae, B.; Kim, R.Y.; Kim, Y.C.; Kim, H.Y.; Yi, H.; Kang, H.R. Alteration of Lung and Gut Microbiota in IL-13-Transgenic Mice Simulating Chronic Asthma. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 30, 1819–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, Z.Y.; Li, H.M.; Zhang, S.B.; Fei, Y.Q.; Yao, M.F.; Li, L.J. Administration of A. muciniphila ameliorates pulmonary arterial hypertension by targeting miR-208a-3p/NOVA1 axis. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2023, 44, 2201–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gheblawi, M.; Wang, K.; Oudit, G.Y. ACE2 (Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2)-Mediated Protection from Pulmonary Hypertension: Lung-Gut Axis at Center Stage. Hypertension 2020, 76, 28–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, T.; Xing, Y.; Lu, W.; Chen, J.; Luo, X.; Wu, X.; Liu, S.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Airway delivery of Streptococcus salivarius is sufficient to induce experimental pulmonary hypertension in rats. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2023, 180, 2102–2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prisco, S.Z.; Blake, M.; Kazmirczak, F.; Moon, R.; Kremer, B.P.; Hartweck, L.M.; Kim, M.; Vogel, N.; Mendelson, J.B.; Moutsoglou, D.; et al. Lactobacillus Restructures the Micro/Mycobiome to Combat Inflammation-Mediated Right Ventricular Dysfunction in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. Circ. Heart Fail. 2025, 18, e012524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mocumbi, A.; Humbert, M.; Saxena, A.; Jing, Z.-C.; Sliwa, K.; Thienemann, F.; Archer, S.L.; Stewart, S. Pulmonary hypertension. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2024, 10, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suswał, K.; Tomaszewski, M.; Romaniuk, A.; Świechowska-Starek, P.; Zygmunt, W.; Styczeń, A.; Romaniuk-Suswał, M. Gut–Lung Axis in Focus: Deciphering the Impact of Gut Microbiota on Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 14, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callejo, M.; Mondejar-Parreño, G.; Barreira, B.; Izquierdo-Garcia, J.L.; Morales-Cano, D.; Esquivel-Ruiz, S.; Moreno, L.; Cogolludo, Á.; Duarte, J.; Perez-Vizcaino, F. Pulmonary arterial hypertension affects the rat gut microbiome. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 9681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, W.; Mo, Q.; Wang, L. Changes in the gut microbiome and metabolome in a rat model of pulmonary arterial hypertension. Bioengineered 2021, 12, 5173–5183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, G.; Shen, S.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, J.; Huang, S.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, H. Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus Probio-M9 enhanced the antitumor response to anti-PD-1 therapy by modulating intestinal metabolites. eBioMedicine 2023, 91, 104533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, G.; Ma, T.; Zhang, T.; Jin, H.; Li, Y.; Kwok, L.-Y.; Zhang, H.; Sun, Z. Adjunctive probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus probio-M9 administration enhances the effect of anti-PD-1 antitumor therapy via restoring antibiotic-disrupted gut microbiota. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 772532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, B.J.; Wearsch, P.A.; Veloo, A.C.; Rodriguez-Palacios, A. The genus Alistipes: Gut bacteria with emerging implications to inflammation, cancer, and mental health. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rau, M.; Rehman, A.; Dittrich, M.; Groen, A.K.; Hermanns, H.M.; Seyfried, F.; Beyersdorf, N.; Dandekar, T.; Rosenstiel, P.; Geier, A. Fecal SCFAs and SCFA-producing bacteria in gut microbiome of human NAFLD as a putative link to systemic T-cell activation and advanced disease. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2018, 6, 1496–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Zhuo, H.; Ouyang, H.; Liu, Y.; Yuan, F.; Sun, L.; Liu, F.; Liu, H. Glycoprotein non-metastatic melanoma protein b (Gpnmb) is highly expressed in macrophages of acute injured kidney and promotes M2 macrophages polarization. Cell. Immunol. 2017, 316, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Xu, J.; Shu, S.; Wang, P.; Ding, S.; Huang, Y.; Zheng, L.; Yang, Y. Promising dawn in the management of pulmonary hypertension: The mystery veil of gut microbiota. iMeta 2024, 3, e159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deliu, N.; Das, R.; May, A.; Newman, J.; Steele, J.; Duckworth, M.; Jones, R.J.; Wilkins, M.R.; Toshner, M.R.; Villar, S.S. StratosPHere 2: Study protocol for a response-adaptive randomised placebo-controlled phase II trial to evaluate hydroxychloroquine and phenylbutyrate in pulmonary arterial hypertension caused by mutations in BMPR2. Trials 2024, 25, 680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karoor, V.; Strassheim, D.; Sullivan, T.; Verin, A.; Umapathy, N.S.; Dempsey, E.C.; Frank, D.N.; Stenmark, K.R.; Gerasimovskaya, E. The short-chain fatty acid butyrate attenuates pulmonary vascular remodeling and inflammation in hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, N.T.; Li, F.; Lee-Sarwar, K.A.; Tun, H.M.; Brown, B.P.; Pannaraj, P.S.; Bender, J.M.; Azad, M.B.; Thompson, A.L.; Weiss, S.T.; et al. Meta-analysis of effects of exclusive breastfeeding on infant gut microbiota across populations. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bucca, C.; Magnino, C.; Marra, W.G.; Vaudano, A.; Parisi, I.; Masoero, M.; Brussino, L.; Milan, A. Pulmonary Artery Pressure and Bronchial Nitric Oxide Flux. Chest 2012, 142, 838A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Antibody | Host Species | Dilution | Purpose | Product Information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CD44 | Rabbit | 1/1000 | IH (rat, human) | (Abcam Cat# ab157107, Cambridge, UK) |
| F4/80 | Rabbit | 1/1000 | IH (rat) | (Cell Signaling Cat# 70076, Danvers, MA, USA) |
| F4/80 | Rabbit | 1/1000 | IH (human) | (DLdevelop Cat# DL98552A, Kelowna, BC, Canada) |
| GPMNB | Mouse | 1/1000 | IH (rat, human) | (Proteintech Cat# 66926-1, Rosemont, IL, USA) |
| Sample Number | Age | Sex | Disease | Sampling Methods | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lung tissue | PH1 | 11 | F | HPAH | biopsies |
| PH2 | 23 | F | IPAH | biopsies | |
| PH3 | 10 | M | IPAH | biopsies | |
| PH4 | 25 | M | IPAH | biopsies | |
| PH5 | 27 | F | IPAH | biopsies | |
| NonPH1 | 14 | M | Pneumothorax | biopsies | |
| NonPH2 | 22 | M | Pneumothorax | biopsies | |
| NonPH3 | 27 | M | Pneumothorax | biopsies | |
| NonPH4 | 16 | M | Pneumothorax | biopsies | |
| NonPH5 | 22 | M | Pneumothorax | biopsies |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, Z.; Li, G.; Ohmichi, K.; Li, X.; Zhao, F.; Ishikawa, K.; Ishikawa, R.; Nakamura, K.; Yokota, N.; Sun, Z.; et al. Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus Probio-M9 Alters the Gut Microbiota and Mitigates Pulmonary Hypertension in a Rat Model. Nutrients 2025, 17, 2927. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17182927
Zhao Z, Li G, Ohmichi K, Li X, Zhao F, Ishikawa K, Ishikawa R, Nakamura K, Yokota N, Sun Z, et al. Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus Probio-M9 Alters the Gut Microbiota and Mitigates Pulmonary Hypertension in a Rat Model. Nutrients. 2025; 17(18):2927. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17182927
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Zhixin, Gaopeng Li, Kiyomi Ohmichi, Xiaodong Li, Feiyan Zhao, Kaori Ishikawa, Ryou Ishikawa, Kazufumi Nakamura, Naoya Yokota, Zhihong Sun, and et al. 2025. "Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus Probio-M9 Alters the Gut Microbiota and Mitigates Pulmonary Hypertension in a Rat Model" Nutrients 17, no. 18: 2927. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17182927
APA StyleZhao, Z., Li, G., Ohmichi, K., Li, X., Zhao, F., Ishikawa, K., Ishikawa, R., Nakamura, K., Yokota, N., Sun, Z., & Kurahara, L. H. (2025). Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus Probio-M9 Alters the Gut Microbiota and Mitigates Pulmonary Hypertension in a Rat Model. Nutrients, 17(18), 2927. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17182927







