Prevalence and Predictors of Self-Prescribed Vitamin D Supplementation Among University Students in the UAE
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Data Collection Procedure
2.3. Survey Instrument and Content
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographic Factors and Vitamin D Prescription Type
3.2. Usage Patterns and Motivations for Vitamin D Supplementation
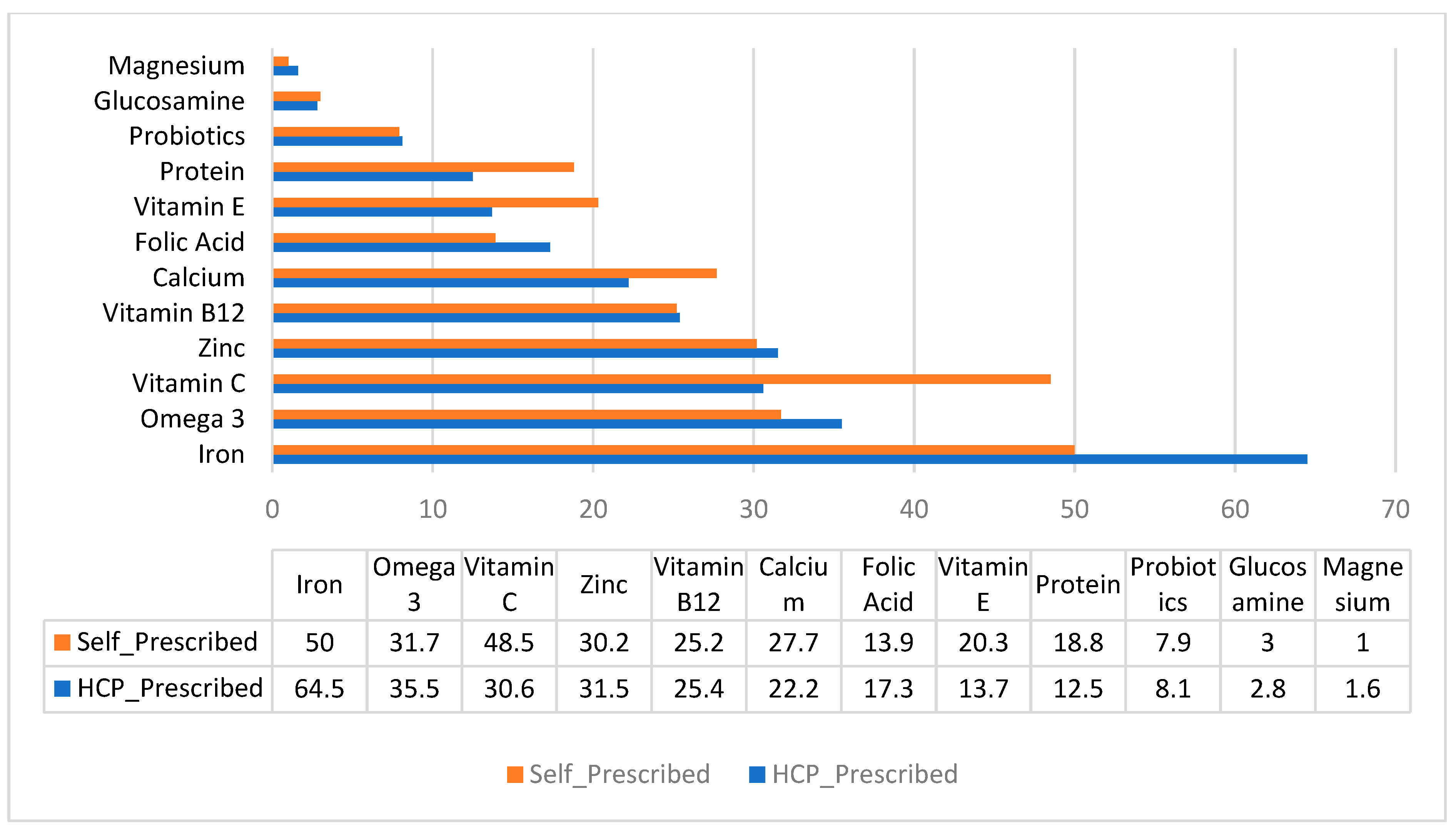
3.3. Co-Use of Other Dietary Supplements
3.4. Predictors of Self-Prescribed Vitamin D Use
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Izzo, M.; Carrizzo, A.; Izzo, C.; Cappello, E.; Cecere, D.; Ciccarelli, M.; Iannece, P.; Damato, A.; Vecchione, C.; Pompeo, F. Vitamin D: Not just bone metabolism but a key player in cardiovascular diseases. Life 2021, 11, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salmanpour, V.A.; Ibrahim, H.S.; Salameh, A.G.; Yahya, A.M.; Debal, B.K. Vitamin D deficiency: Knowledge and practices among the adult population in Sharjah, United Arab Emirates. Arch. Osteoporos. 2016, 11, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muneer, S.; Siddiqui, I.; Majid, H.; Zehra, N.; Jafri, L.; Khan, A.H. Practices of vitamin D supplementation leading to vitamin D toxicity: Experience from a low-middle income country. Ann. Med. Surg. 2022, 73, 103227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haq, A.; Wimalawansa, S.J.; Pludowski, P.; Al Anouti, F. Clinical practice guidelines for vitamin D in the United Arab Emirates. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2018, 175, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shea, R.L.; Berg, J.D. Self-administration of vitamin D supplements in the general public may be associated with high 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentrations. Ann. Clin. Biochem. 2017, 54, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, P.N.; Davies, J.S. A review of the growing risk of vitamin D toxicity from inappropriate practice. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2018, 84, 1121–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fedorov, Y.; Kovpak, A. Vitamin D Toxicity and Clinical Consequences of Hypervitaminosis. SSP Mod. Pharm. Med. 2025, 5, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Paula, A.L.T.; Gonzaga, W.P.F.; Oliveira, L.M.; Feibelmann, T.C.M.; Markus, J. Exogenous intoxication by non-prescribed use of vitamin D, a case report. BMC Geriatr. 2020, 20, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilgin, D.D.; Karabayir, N.; Çetinkaya, H.B.; Kacir, A.; Öçal, Ö.; Başibüyük, M.; Büke, Ö. Reasons, associated factors, and attitudes toward breastfeeding mothers’ use of complementary medicine products: A study from Türkiye. Int. Breastfeed. J. 2025, 20, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-H.; Chao, S.-L.; Chu, Y.-W. Effects of perceived benefit on vitamin D supplementation intention: A theory of planned behaviour perspective. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazhar, I.; Rai, M.M.; Khan, Q.U.; Pramaningtyas, M.D.; Aaien, K.U.; Zia, R. Determining Awareness of Vitamin D Necessity, Deficiency and its Appropriate Attainment among Medical undergraduate students of a private medical college: A Descriptive cross-sectional study. Pak. J. Med. Health Sci. 2023, 17, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Hadhrami, R.S.; Al Kaabi, R.; Al Shuaibi, H.J.; Al Abdulsalam, R.S. Assessment of vitamin D-related knowledge, attitudes and practices among Sultan Qaboos University students in Oman: A cross-sectional study. BMJ Public Health 2024, 2, e000539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raosoft Inc. Sample Size Calculator. Available online: http://www.raosoft.com/samplesize.html (accessed on 1 September 2025).
- Laleye, L.C.; Kerkadi, A.H.; Wasesa, A.A.; Rao, M.V.; Aboubacar, A. Assessment of vitamin D and vitamin A intake by female students at the United Arab Emirates University based on self-reported dietary and selected fortified food consumption. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2011, 62, 370–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qatatsheh, A.; Tayyem, R.; Al-Shami, I.; Al-Holy, M.A.; Al-Rethaia, A.S. Vitamin D deficiency among Jordanian university students and employees. Nutr. Food Sci. 2015, 45, 68–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steele, M.; Senekal, M. Dietary supplement use and associated factors among university students. S. Afr. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 18, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noaman, A.M. Study the Prevalence of Dietary Supplements Use Among Students in Tikrit University. Coll. Lit. 2024, 5, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Tariq, A.; Khan, S.R.; Basharat, A. Assessment of knowledge, attitudes and practice towards Vitamin D among university students in Pakistan. BMC Public Health 2020, 20, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharbi, A.A.; Alharbi, M.A.; Aljafen, A.S.; Aljuhani, A.M.; Almarshad, A.I.; Alomair, I.A.; Alfalah, M.A. Gender-specific differences in the awareness and intake of Vitamin D among adult population in Qassim Region. J. Fam. Community Med. 2018, 25, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ficarra, G.; Rottura, M.; Irrera, P.; Bitto, A.; Trimarchi, F.; Di Mauro, D. Use of drugs and dietary supplements in university students of sports science: Results of a survey-based cross-sectional study. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, J.; Zakar, R.; Butt, M.S.; Kaleem, R.; Chaudhary, A.; Chandna, J.; Jolliffe, D.A.; Piper, J.; Abbas, Z.; Tang, J.C. High-dose vitamin D3 to improve outcomes in the convalescent phase of complicated severe acute malnutrition in Pakistan: A double-blind randomised controlled trial (ViDiSAM). Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 2554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giustina, A.; Bilezikian, J.P.; Adler, R.A.; Banfi, G.; Bikle, D.D.; Binkley, N.C.; Bollerslev, J.; Bouillon, R.; Brandi, M.L.; Casanueva, F.F. Consensus statement on vitamin D status assessment and supplementation: Whys, whens, and hows. Endocr. Rev. 2024, 45, 625–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogorek, A.N.; Samara, V.A. New Clinical Practice Guidelines for Vitamin D Supplementation and Testing. Clin. Chem. 2025, 71, 526–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aversa, R.; Petrescu, R.V.; Apicella, A.; Petrescu, F.I. We are addicted to vitamins C and EA review. Am. J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2016, 9, 1003–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virú-Loza, M.A.; Alvarado-Gamarra, G.; Zapata-Sequeiros, R.I.; Flores-Nakandakare, H.F. Life-threatening hypercalcemia in a child with vitamin D intoxication due to parental self-medication: A case report. SAGE Open Med. Case Rep. 2024, 12, 2050313X241269560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggini, V.; Crescioli, G.; Ippoliti, I.; Gallo, E.; Menniti-Ippolito, F.; Chiaravalloti, A.; Mascherini, V.; Da Cas, R.; Potenza, S.; Gritti, G. Safety profile of vitamin D in Italy: An analysis of spontaneous reports of adverse reactions related to drugs and food supplements. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 4726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsahoryi, N.A.; Odeh, M.M.; Jadayil, S.A.; McGrattan, A.M.; Hammad, F.J.; Al-Maseimi, O.D.; Alzoubi, K.H. Prevalence of dietary supplement use and knowledge, attitudes, practice (KAP) and associated factors in student population: A cross-sectional study. Heliyon 2023, 9, e14736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominguez, L.J.; Farruggia, M.; Veronese, N.; Barbagallo, M. Vitamin D sources, metabolism, and deficiency: Available compounds and guidelines for its treatment. Metabolites 2021, 11, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadka, K.; Pałkowska-Goździk, E.; Rosołowska-Huszcz, D. The state of knowledge about nutrition sources of vitamin D, its role in the human body, and necessity of supplementation among parents in central Poland. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable | Value |
|---|---|
| Sex, n (%) | |
| Female | 398 (88.4) |
| Male | 52 (11.6) |
| Age (years), mean (SD) | 22.1 (4.8) |
| Age, n (%) | |
| <21 | 215 (47.8) |
| ≥21 | 235 (52.2) |
| Weight (kg), mean (SD) | 61.9 (15.6) |
| Height (cm), mean (SD) | 161.0 (10.0) |
| BMI (kg/m2), mean (SD) | 23.8 (5.2) |
| BMI, n (%) | |
| Underweight | 69 (15.33) |
| Normal | 226 (50.22) |
| Overweight | 95 (21.11) |
| Obesity | 60 (13.33) |
| Education, n (%) | |
| Bachelor | 377 (83.8) |
| Master/Doctorate | 73 (16.2) |
| Academic major, n (%) | |
| Engineering/Science | 203 (45.11) |
| Humanities/Social Sciences | 137 (30.44) |
| Medicine/Agriculture | 110 (24.44) |
| Self-perceived health, n (%) | |
| Poor/fair | 48 (10.7) |
| Good | 126 (28.0) |
| Very good/excellent | 276 (61.3) |
| Vitamin D prescription type, n (%) | |
| Self-prescribed | 202 (44.9) |
| HCP-prescribed | 248 (55.1) |
| Variable | Prescription Type | χ2 | p-Value * | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HCP 248 (55.1%) | Self 202 (44.9%) | |||
| Sex, n (%) | 6.588 | 0.010 | ||
| Female | 228 (91.9) | 170 (84.2) | ||
| Male | 20 (8.1) | 32 (15.8) | ||
| Age, n (%) | 0.227 | 0.634 | ||
| <21 | 121 (48.8) | 94 (46.5) | ||
| ≥21 | 127 (51.2) | 108 (53.5) | ||
| BMI, n (%) | 4.608 | 0.203 | ||
| Underweight | 46 (18.5) | 23 (11.4) | ||
| Normal | 122 (49.2) | 104 (51.5) | ||
| Overweight | 49 (19.8) | 46 (22.8) | ||
| Obesity | 31 (12.5) | 29 (14.4) | ||
| Self-perceived health, n (%) | 1.994 | 0.369 | ||
| Poor/fair | 31 (12.5) | 17 (8.4) | ||
| Good | 69 (27.8) | 57 (28.2) | ||
| Very good/excellent | 148 (59.7) | 128 (63.4) | ||
| Education, n (%) | 0.004 | 0.953 | ||
| Bachelor | 208 (83.9) | 169 (83.7) | ||
| Master/Doctorate | 40 (16.1) | 33 (16.3) | ||
| Academic major, n (%) | 3.390 | 0.184 | ||
| Engineering/Science | 115 (46.4) | 88 (43.5) | ||
| Humanities/Social Sciences | 67 (27.0) | 70 (34.7) | ||
| Medicine/Agriculture | 66 (26.6) | 44 (21.8) | ||
| Variable | Prescription Type | χ2 | p-Value * | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HCP 248 (55.1%) | Self 202 (44.9%) | |||
| Duration of use, n (%) | 26.118 | <0.001 | ||
| 1 month | 40 (16.1) | 64 (37.1) | ||
| 2 months | 67 (27.0) | 69 (34.2) | ||
| 3–5 months | 59 (23.8) | 26 (12.9) | ||
| 6 months or more | 82 (33.1) | 43 (21.3) | ||
| Daily supplement use, n (%) | 82 (33.1) | 28 (13.9) | 22.227 | <0.001 |
| Source of used supplement, n (%) | 8.763 | 0.067 | ||
| Pharmacy/over the counter | 77 (31.0) | 78 (38.6) | ||
| Healthy food store | 76 (30.6) | 55 (27.2) | ||
| Foreign country | 15 (6.0) | 11 (5.4) | ||
| Other | 50 (20.2) | 24 (11.9) | ||
| Do not know | 30 (12.1) | 34 (16.8) | ||
| Reason/s for supplement use, n (%) | ||||
| Disease/deficiency | 141 (56.9) | 80 (39.6) | 13.256 | <0.001 |
| Pregnancy/lactation | 18 (7.3) | 22 (10.9) | 1.814 | 0.178 |
| Beauty | 77 (31.0) | 69 (34.2) | 0.491 | 0.483 |
| Improve health | 192 (77.4) | 170 (84.2) | 3.214 | 0.073 |
| Improve physical performance | 21 (8.5) | 35 (17.3) | 8.019 | 0.005 |
| Always read instructions, n (%) | 128 (51.6) | 100 (49.5) | 0.198 | 0.656 |
| Variable | Odds Ratio | 95% CI | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | |||
| Sex | 0.220 | |||
| Female | 1 | |||
| Male | 1.556 | 0.767 | 3.155 | |
| Academic major | 0.176 | |||
| Engineering/Science | 1 | |||
| Humanities/Social Sciences | 1.608 | 0.976 | 2.649 | |
| Medicine/Agriculture | 1.224 | 0.712 | 2.105 | |
| Duration of use | 0.001 | |||
| 1 month | 1 | |||
| 2 months | 0.512 | 0.284 | 0.922 | |
| 3–5 months | 0.280 | 0.139 | 0.567 | |
| 6 months or more | 0.318 | 0.166 | 0.611 | |
| Daily supplement use | <0.001 | |||
| No | 1 | |||
| Yes | 0.287 | 0.156 | 0.526 | |
| Source of used supplement | 0.155 | |||
| Pharmacy/over the counter | 1 | |||
| Healthy food store | 1.710 | 0.991 | 2.950 | |
| Foreign country | 1.323 | 0.494 | 3.544 | |
| Other | 0.799 | 0.405 | 1.576 | |
| Do not know | 1.393 | 0.696 | 2.784 | |
| Diseases/deficiency | 0.080 | |||
| No | 1 | |||
| Yes | 0.673 | 0.432 | 1.049 | |
| Pregnancy/lactation | 0.860 | |||
| No | 1 | |||
| Yes | 0.929 | 0.412 | 2.095 | |
| Improve health | 0.388 | |||
| No | 1 | |||
| Yes | 1.287 | 0.726 | 2.281 | |
| Improve physical performance | 0.010 | |||
| No | 1 | |||
| Yes | 2.724 | 1.276 | 5.818 | |
| Vitamin C | 0.014 | |||
| No | 1 | |||
| Yes | 1.850 | 1.134 | 3.019 | |
| Vitamin E | 0.412 | |||
| No | 1 | |||
| Yes | 1.305 | 0.691 | 2.467 | |
| Calcium | 0.276 | |||
| No | 1 | |||
| Yes | 1.369 | 0.778 | 2.410 | |
| Iron | 0.061 | |||
| No | 1 | |||
| Yes | 0.656 | 0.422 | 1.020 | |
| Protein | 0.825 | |||
| No | 1 | |||
| Yes | 1.081 | 0.542 | 2.156 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alnaqbi, A.H.; Sabir, R.; Shahbaz, H.M.; Khan, Z.; Bataineh, M.F. Prevalence and Predictors of Self-Prescribed Vitamin D Supplementation Among University Students in the UAE. Nutrients 2025, 17, 2915. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17182915
Alnaqbi AH, Sabir R, Shahbaz HM, Khan Z, Bataineh MF. Prevalence and Predictors of Self-Prescribed Vitamin D Supplementation Among University Students in the UAE. Nutrients. 2025; 17(18):2915. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17182915
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlnaqbi, Aaesha H., Rubina Sabir, Hafiz M. Shahbaz, Zahra Khan, and Mo’ath F. Bataineh. 2025. "Prevalence and Predictors of Self-Prescribed Vitamin D Supplementation Among University Students in the UAE" Nutrients 17, no. 18: 2915. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17182915
APA StyleAlnaqbi, A. H., Sabir, R., Shahbaz, H. M., Khan, Z., & Bataineh, M. F. (2025). Prevalence and Predictors of Self-Prescribed Vitamin D Supplementation Among University Students in the UAE. Nutrients, 17(18), 2915. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17182915







