Protective Role of Multiple Essential Minerals Against Cadmium-Related Cognitive Decline in Middle-Aged and Older Adults: A Prospective Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
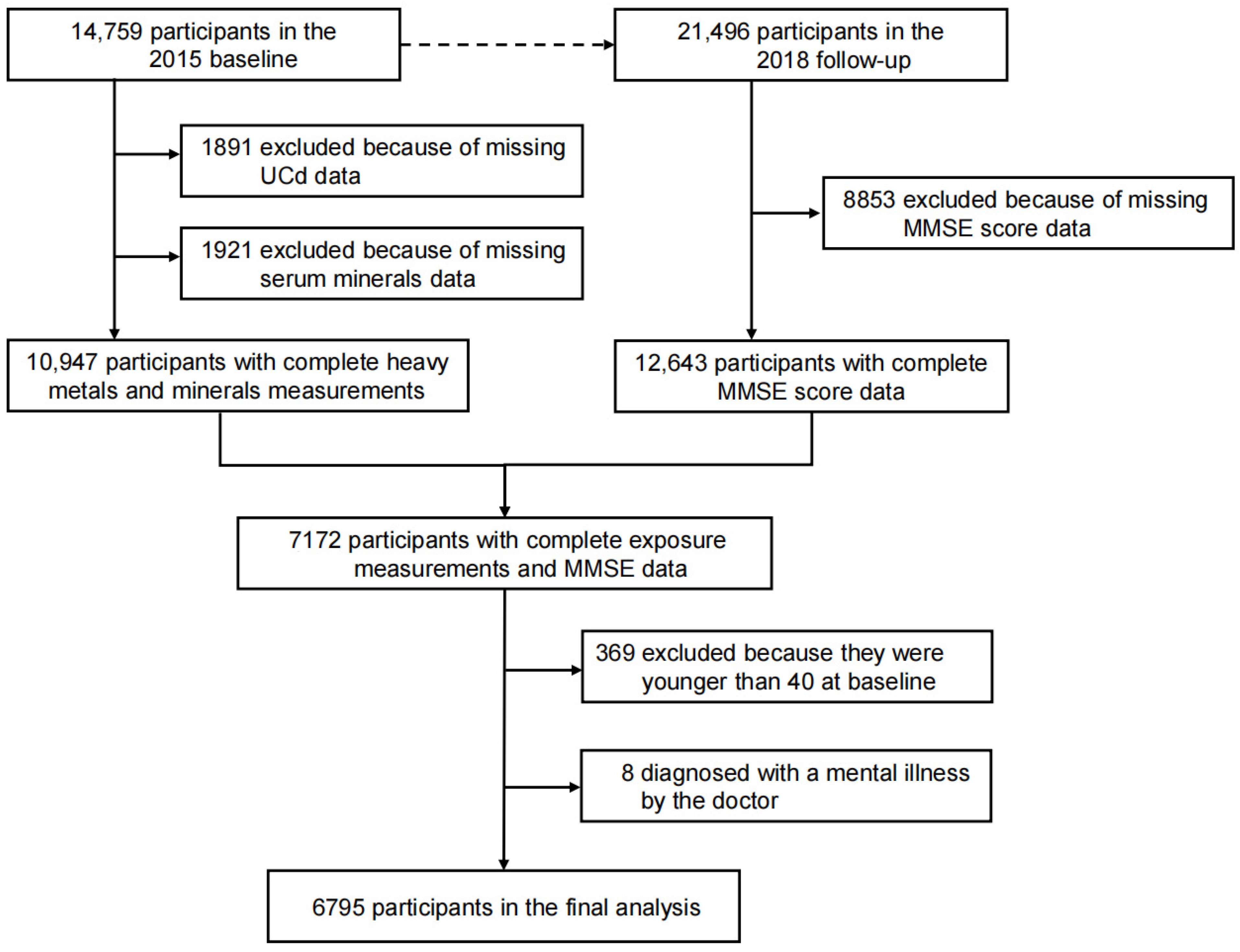
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Laboratory Quantification of UCd and Serum Minerals
2.3. Cognitive Function Assessment
2.4. Anthropometric and Laboratory Measurements
2.5. Covariates
2.6. Statistical Analysis
2.6.1. Single-Exposure Association Analysis
2.6.2. Effect Modification Analysis
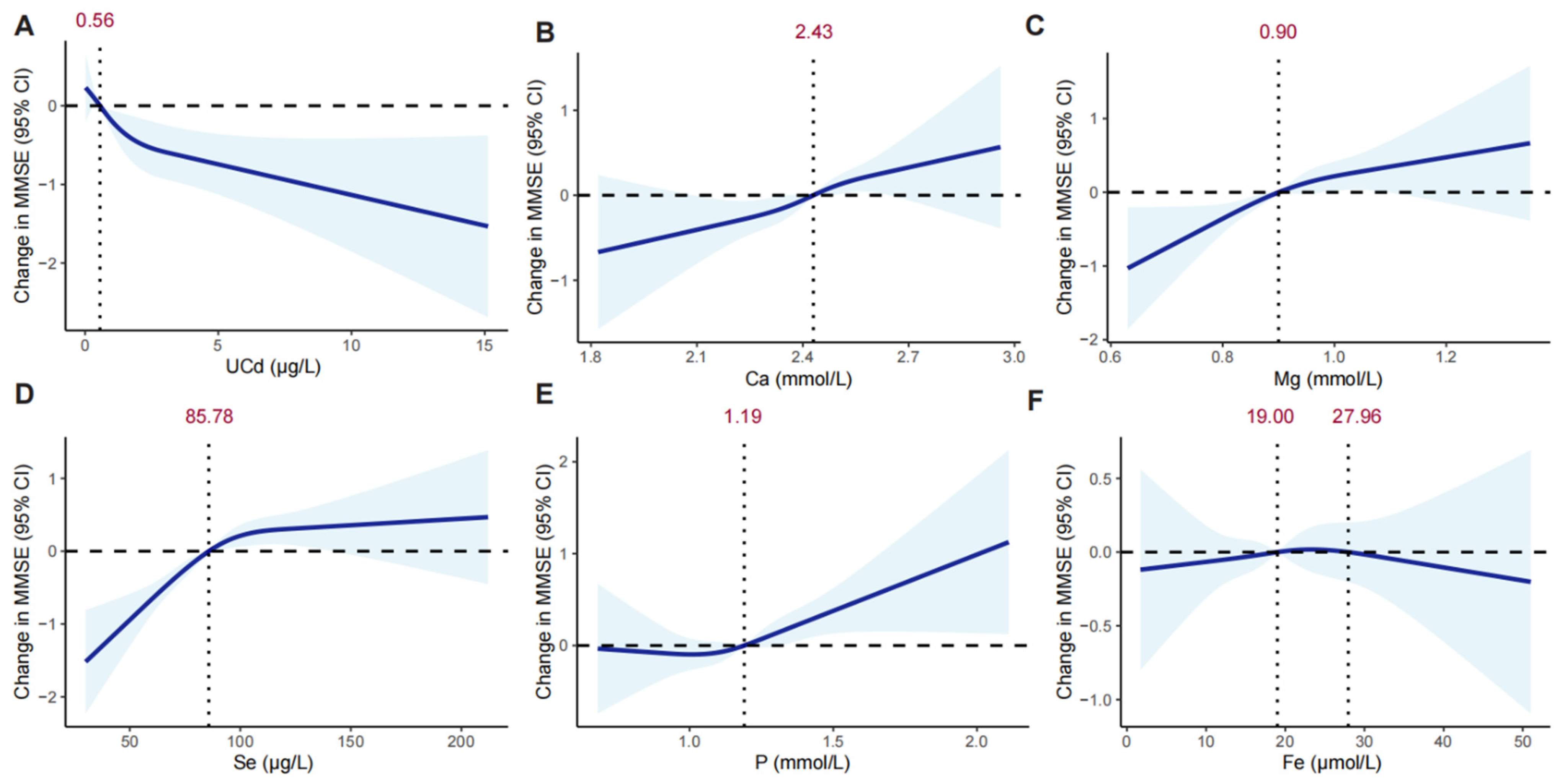
2.6.3. Exposure-Response Analysis
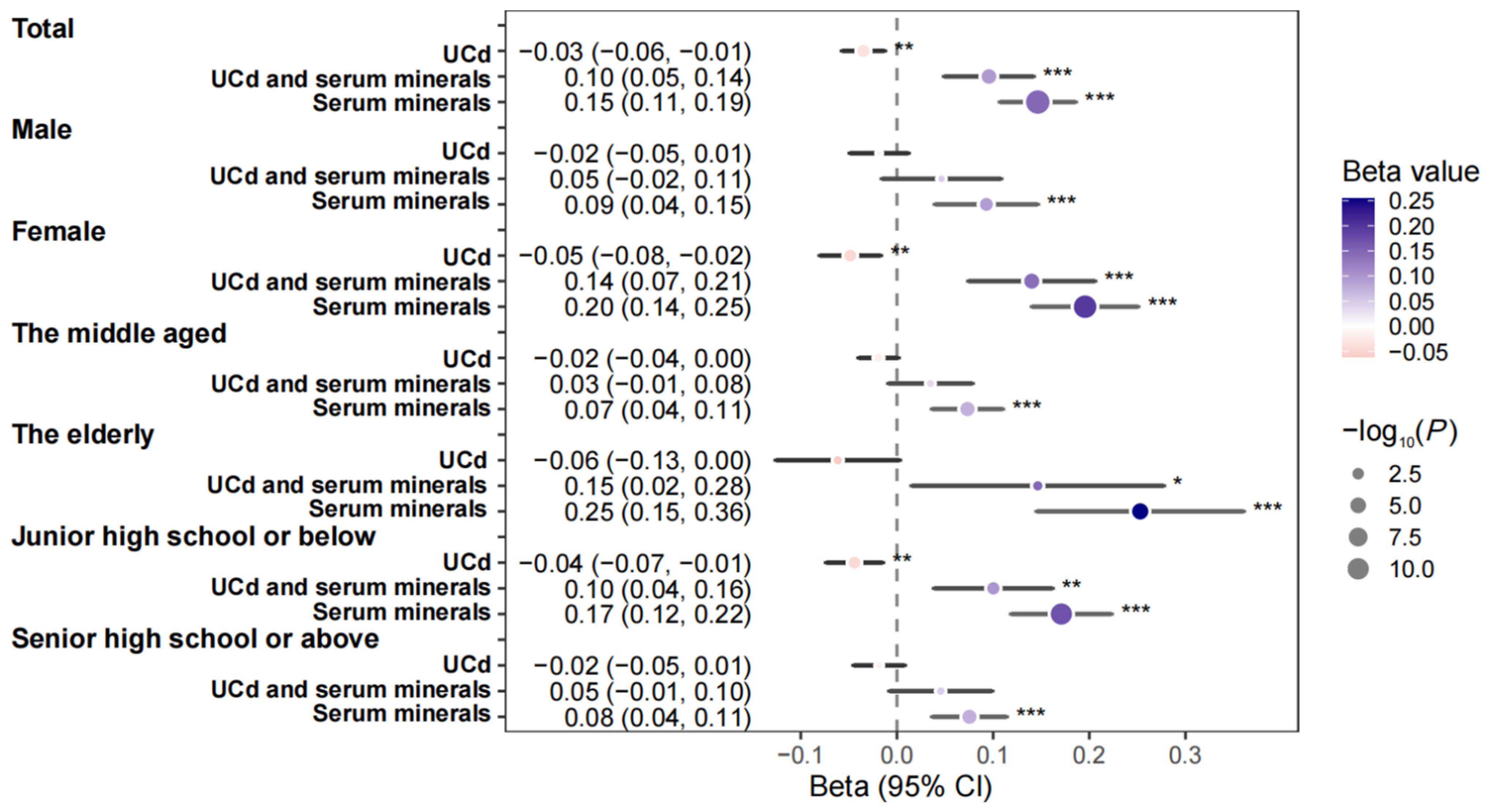
2.6.4. Stratified Analysis
2.6.5. Mixed-Exposure Association Analysis
2.6.6. Sensitivity Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Participant Characteristics
3.2. Associations of UCd Exposure and Minerals with MMSE
3.3. Modifying Effects of Minerals on Cadmium-Related Cognitive Decline
3.4. Stratified Analysis
3.5. Joint Associations of UCd and Minerals with MMSE
3.6. Sensitivity Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Gray, M.; Gills, J.L.; Glenn, J.M.; Vincenzo, J.L.; Walter, C.S.; Madero, E.N.; Hall, A.; Fuseya, N.; Bott, N.T. Cognitive Decline Negatively Impacts Physical Function. Exp. Gerontol. 2021, 143, 111164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Hotterbeex, P.; Marent, P.-J.; Cerin, E.; Thomis, M.; van Uffelen, J. Physical Activity, Sedentary Behaviour, and Cognitive Function among Older Adults: A Bibliometric Analysis from 2004 to 2024. Ageing Res. Rev. 2024, 97, 102283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Giles, J.; Yao, Y.; Yip, W.; Meng, Q.; Berkman, L.; Chen, H.; Chen, X.; Feng, J.; Feng, Z.; et al. The Path to Healthy Ageing in China: A Peking University-Lancet Commission. Lancet 2022, 400, 1967–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Du, Y.; Chu, L.; Zhang, Z.; Li, F.; Lyu, D.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhu, M.; Jiao, H.; et al. Prevalence, Risk Factors, and Management of Dementia and Mild Cognitive Impairment in Adults Aged 60 Years or Older in China: A Cross-Sectional Study. Lancet Public Health 2020, 5, e661–e671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Qi, J.L.; Liu, X.Y.; Ren, R.J.; Lin, Z.H.; Hu, Y.S.; Li, H.X.; Xie, X.Y.; Wang, J.T.; Li, J.P.; et al. China Alzheimer Report 2024. J. Diagn. Concepts Pract. 2024, 23, 219–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, R.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, H.; Chang, J. Association of Long-Term Exposure to Various Ambient Air Pollutants, Lifestyle, and Genetic Predisposition with Incident Cognitive Impairment and Dementia. BMC Public Health 2024, 24, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, J.-Y.; Min, K.-B. Blood Cadmium Levels and Alzheimer’s Disease Mortality Risk in Older US Adults. Environ. Health 2016, 15, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Q.; Bakulski, K.M.; Nan, B.; Park, S.K. Cadmium and Alzheimer’s Disease Mortality in U.S. Adults: Up-dated Evidence with a Urinary Biomarker and Extended Follow-up Time. Environ. Res. 2017, 157, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, G.; Rahaman, M.S.; Perez, E.; Khan, K.M. Associations of Environmental Exposure to Arsenic, Man-ganese, Lead, and Cadmium with Alzheimer’s Disease: A Review of Recent Evidence from Mechanistic Studies. J. Xenobiotics 2025, 15, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peana, M.; Pelucelli, A.; Chasapis, C.T.; Perlepes, S.P.; Bekiari, V.; Medici, S.; Zoroddu, M.A. Biological Effects of Human Exposure to Environmental Cadmium. Biomolecules 2022, 13, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branca, J.J.V.; Morucci, G.; Pacini, A. Cadmium-Induced Neurotoxicity: Still Much Ado. Neural Regen. Res. 2018, 13, 1879–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Zan, G.; Qin, J.; Wei, X.; Lu, G.; Li, X.; Zhang, H.; Zou, Y.; Yang, L.; He, M.; et al. Combined Exposure to Multiple Metals and Cognitive Function in Older Adults. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 222, 112465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qing, Y.; Zheng, J.; Luo, Y.; Li, S.; Liu, X.; Yang, S.; Du, J.; Li, Y. The Impact of Metals on Cognitive Impairment in the Elderly and the Mediating Role of Oxidative Stress: A Cross-Sectional Study in Shanghai, China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 286, 117152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Angley, M.; Bejerano, S.; Brockman, J.D.; McClure, L.A.; Unverzagt, F.W.; Fly, A.D.; Kahe, K. Association of Urinary Cadmium Concentration with Cognitive Impairment in US Adults: A Longitudinal Cohort Study. Neurology 2024, 103, e209808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Li, A.; Mei, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zhou, Q.; Li, Y.; Yang, M.; Xu, Q. Trace Elements and Alzheimer Dementia in Population-Based Studies: A Bibliometric and Meta-Analysis. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 318, 120782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo, C.; Núñez, M.T. Calcium, Iron and Neuronal Function. IUBMB Life 2007, 59, 280–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkland, A.E.; Sarlo, G.L.; Holton, K.F. The Role of Magnesium in Neurological Disorders. Nutrients 2018, 10, 730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Wang, J.; Cheng, Y.; Li, R.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Scott, T.; Tucker, K.L. Magnesium and Cognitive Health in Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Adv. Nutr. 2024, 15, 100272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rroji, M.; Figurek, A.; Viggiano, D.; Capasso, G.; Spasovski, G. Phosphate in the Context of Cognitive Impairment and Other Neurological Disorders Occurrence in Chronic Kidney Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, S.-F.; Long, C.-H.; Zhang, X.; Yuan, M.; Li, J.; Wu, H.-G. Causal Effects of Circulating Micronutrients on Cognitive Function: Evidence from a Mendelian Randomization Study. Brain Behav. 2025, 15, e70488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-C.; Han, S.-H.; Byun, M.S.; Yi, D.; Lee, J.H.; Park, K.; Lee, D.Y.; Mook-Jung, I. Low Serum Phosphorus Correlates with Cerebral Aβ Deposition in Cognitively Impaired Subjects: Results from the KBASE Study. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2017, 9, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Gao, G.; Zhang, S.; Wang, H.; Ke, L.; Zhou, J.; Rao, P.; Wang, Q.; Li, J. Influences of Calcium and Magnesium Ions on Cellular Antioxidant Activity (CAA) Determination. Food Chem. 2020, 320, 126625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genchi, G.; Lauria, G.; Catalano, A.; Sinicropi, M.S.; Carocci, A. Biological Activity of Selenium and Its Impact on Human Health. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, S. Protective Role of the Essential Trace Elements in the Obviation of Cadmium Toxicity: Glimpses of Mechanisms. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2022, 200, 2239–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Liu, N.; Wang, G.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, X.; Chang, H.; Yu, Z.; Liu, X. Sex Specificity in the Mixed Effects of Blood Heavy Metals and Cognitive Function on Elderly: Evidence from NHANES. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grundeken, M.; Gustin, K.; Vahter, M.; Delaval, M.; Barman, M.; Sandin, A.; Sandberg, A.-S.; Wold, A.E.; Brob-erg, K.; Kippler, M. Toxic Metals and Essential Trace Elements in Placenta and Their Relation to Placental Function. Environ. Res. 2024, 248, 118355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Zhai, F.Y.; Du, S.F.; Popkin, B.M. The China Health and Nutrition Survey, 1989–2011. Obes. Rev. 2014, 15 (Suppl. 1), 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, L.; Kou, J.; Wang, M.; Ji, G.; Li, X.; Su, C.; Zheng, F.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Y.; Chen, T.; et al. An Exposome Atlas of Serum Reveals the Risk of Chronic Diseases in the Chinese Population. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katzman, R.; Zhang, M.Y.; Ouang-Ya-Qu Wang, Z.Y.; Liu, W.T.; Yu, E.; Wong, S.C.; Salmon, D.P.; Grant, I. A Chinese Version of the Mini-Mental State Examination; Impact of Illiteracy in a Shanghai Dementia Survey. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 1988, 41, 971–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, C.T.; Seward, K.; Patterson, A.; Melton, A.; MacDonald-Wicks, L. Evaluation of Available Cognitive Tools Used to Measure Mild Cognitive Decline: A Scoping Review. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Jiao, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, S.; Hao, L.; Wang, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhang, B.; Ding, G.; Jiang, H. Association of Serum Magnesium with Insulin Resistance and Type 2 Diabetes among Adults in China. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keil, A.P.; Buckley, J.P.; O’Brien, K.M.; Ferguson, K.K.; Zhao, S.; White, A.J. A Quantile-Based g-Computation Approach to Addressing the Effects of Exposure Mixtures. Environ. Health Perspect. 2020, 128, 47004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, S.V.; Newcomb, P.A. Cadmium Blood and Urine Concentrations as Measures of Exposure: NHANES 1999–2010. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2014, 24, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naderi, M.; Puar, P.; Zonouzi-Marand, M.; Chivers, D.P.; Niyogi, S.; Kwong, R.W.M. A Comprehensive Review on the Neuropathophysiology of Selenium. Sci. Total. Environ. 2021, 767, 144329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Xu, X.; Cao, L.; Xiang, Q.; Gao, Q.; Duan, H.; Wang, S.; Zhou, L.; Yang, X. Single and Joint Exposure of Pb, Cd, Hg, Se, Cu, and Zn Were Associated with Cognitive Function of Older Adults. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 28567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, R.; Gamble, M.; Wasserman, G.A.; Liu, X.; Parvez, F.; Navas-Acien, A.; Islam, T.; Factor-Litvak, P.; Uddin, M.N.; Kioumourtzoglou, M.-A.; et al. Mixed Metals Exposure and Cognitive Function in Bangladeshi Adolescents. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 232, 113229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, N.; Carpenter, D.O. Associations between Metal Exposures and Cognitive Function in American Older Adults. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Ahmad, M.A.; Abbas, G.; Ahmed, U.; Javed, R.; Ali, I.; Ao, Q.; Deng, X. From Particulates to Pathways: Environmental Exposures and Their Impact on Alzheimer’s Disease. Brain Res. 2025, 1865, 149880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doroszkiewicz, J.; Farhan, J.A.; Mroczko, J.; Winkel, I.; Perkowski, M.; Mroczko, B. Common and Trace Metals in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Gu, Q.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Han, Y.; Feng, L.; Qin, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, Z.; Chang, X. Restoration of Mitochondrial Homeostasis by Wnt3a/β-Catenin/c-Myc Alleviates Cadmium-Induced Neural Stem Cell Senescence and Cognitive Impairment in Mouse Hippocampus. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 495, 138972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwolak, I. Disentangling the Role of Selenium in Antagonizing the Toxicity of Arsenic and Cadmium. Arch. Toxicol. 2025, 99, 513–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stachowicz, K. Regulation of COX-2 Expression by Selected Trace Elements and Heavy Metals: Health Implications, and Changes in Neuronal Plasticity. A Review. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2023, 79, 127226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pochwat, B.; Sowa-Kucma, M.; Kotarska, K.; Misztak, P.; Nowak, G.; Szewczyk, B. Antidepressant-like Activity of Magnesium in the Olfactory Bulbectomy Model Is Associated with the AMPA/BDNF Pathway. Psychopharmacology 2015, 232, 355–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Shi, Z.; Liu, J. Nutrient-Heavy Metal Interaction and Mixed Heavy Metal Exposure in Relation to Cognition across Lifespan: Review Evidence, Potential Mechanisms, and Implications. Nutr. Neurosci. 2025, 28, 928–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.-T.; Zhen, J.; Leng, J.-Y.; Cai, L.; Ji, H.-L.; Keller, B.B. Zinc as a Countermeasure for Cadmium Toxicity. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2021, 42, 340–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Sun, C.; Zhu, L.; Zeng, Y.; Li, J.; Mei, Y. High Cadmium Exposure Impairs Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis via Disruption of Store-Operated Calcium Entry. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 286, 117162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obeid, O.A. Low Phosphorus Status Might Contribute to the Onset of Obesity. Obes. Rev. 2013, 14, 659–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, R.J.; Zucca, F.A.; Duyn, J.H.; Crichton, R.R.; Zecca, L. The Role of Iron in Brain Ageing and Neurodegenerative Disorders. Lancet Neurol. 2014, 13, 1045–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toro-Román, V.; Robles-Gil, M.C.; Muñoz, D.; Bartolomé, I.; Grijota, F.J.; Maynar-Mariño, M. Sex Differences in Cadmium and Lead Concentrations in Different Biological Matrices in Athletes. Relationship with Iron Status. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2023, 99, 104107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoji, T.; Mori, K.; Nagakura, Y.; Kabata, D.; Kuriu, K.; Nakatani, S.; Uedono, H.; Nagata, Y.; Fujii, H.; Imanishi, Y.; et al. Associations of Cognitive Function with Serum Magnesium and Phosphate in Hemodialysis Patients: A Cross-Sectional Analysis of the Osaka Dialysis Complication Study (ODCS). Nutrients 2024, 16, 3776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kravchenko, G.; Stephenson, S.S.; Gutowska, A.; Klimek, K.; Chrząstek, Z.; Pigłowska, M.; Kostka, T.; Sołtysik, B.K. The Concurrent Association of Magnesium and Calcium Deficiencies with Cognitive Function in Older Hospitalized Adults. Nutrients 2024, 16, 3756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matović, V.; Buha, A.; Bulat, Z.; Ðukić-Ćosić, D.; Miljković, M.; Ivanišević, J.; Kotur-Stevuljević, J. Route-Dependent Effects of Cadmium/Cadmium and Magnesium Acute Treatment on Parameters of Oxidative Stress in Rat Liver. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2012, 50, 552–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vahter, M.; Akesson, A.; Lidén, C.; Ceccatelli, S.; Berglund, M. Gender Differences in the Disposition and Toxicity of Metals. Environ. Res. 2007, 104, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Cardoso, B.; Hare, D.J.; Macpherson, H. Sex-Dependent Association between Selenium Status and Cognitive Performance in Older Adults. Eur. J. Nutr. 2021, 60, 1153–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- North American Menopause Society. The Role of Calcium in Peri- and Postmenopausal Women: 2006 Position Statement of the North American Menopause Society. Menopause 2006, 13, 862–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auerbach, M.; DeLoughery, T.G.; Tirnauer, J.S. Iron Deficiency in Adults: A Review. JAMA 2025, 333, 1813–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, A.D.; Paglia, A.; Bellanti, F.; Villani, R.; Sangineto, M.; Vendemiale, G.; Serviddio, G. Molecular Aspects and Treatment of Iron Deficiency in the Elderly. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Total (n = 6795) | Male (n = 3090) | Female (n = 3705) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, year | 57.96 (10.46) | 58.26 (10.50) | 57.71 (10.43) | 0.033 |
| Rural, n (%) | 2512 (37.0) | 1117 (36.1) | 1395 (37.7) | 0.210 |
| Education, n (%) | <0.001 | |||
| Primary school or below | 4761 (70.1) | 2017 (65.3) | 2744 (74.1) | |
| Junior high school | 1431 (21.1) | 737 (23.9) | 694 (18.7) | |
| Senior high school or above | 603 (8.9) | 336 (10.9) | 267 (7.2) | |
| Annual household income, yuan (%) | 0.310 | |||
| Low | 2803 (41.3) | 1237 (40.0) | 1566 (42.3) | |
| Medium | 2378 (35.0) | 1099 (35.6) | 1279 (34.5) | |
| High | 976 (14.4) | 457 (14.8) | 519 (14.0) | |
| Very high | 638 (9.4) | 297 (9.6) | 341 (9.2) | |
| T2DM, n (%) | 829 (12.2) | 395 (12.8) | 434 (11.7) | 0.192 |
| Hypertension, n (%) | 2943 (43.3) | 1412 (45.7) | 1531 (41.3) | <0.001 |
| Smoker, n (%) | 1815 (26.7) | 1737 (56.2) | 78 (2.1) | <0.001 |
| Alcohol user, n (%) | 1893 (27.9) | 1672 (54.1) | 221 (6.0) | <0.001 |
| Physical activity, MET h/week | 103.75 [47.43, 209.60] | 112.30 [43.52, 226.50] | 98.00 [48.71, 196.93] | 0.129 |
| Total energy intake, kcal | 1912.59 [1514.39, 2422.72] | 2092.07 [1668.00, 2661.64] | 1761.91 [1407.69, 2212.75] | <0.001 |
| Total fat intake, g | 71.91 [51.06, 100.99] | 79.21 [55.84, 109.92] | 65.90 [47.65, 92.73] | <0.001 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 24.27 [22.07, 26.61] | 24.20 [21.94, 26.58] | 24.32 [22.17, 26.70] | 0.058 |
| Urinary creatinine, μmol/L/24 h | 5676.00 [3249.00, 9123.50] | 6643.50 [3906.00, 10,439.00] | 4973.00 [2808.00, 8003.00] | <0.001 |
| MMSE score | 27.12 (4.78) | 27.62 (4.26) | 26.71 (5.14) | <0.001 |
| Ca, mmol/L | 2.42 (0.14) | 2.42 (0.14) | 2.42 (0.14) | 0.060 |
| Mg, mmol/L | 0.91 (0.09) | 0.91 (0.09) | 0.90 (0.08) | <0.001 |
| Fe, μmol/L | 19.00 [14.90, 23.80] | 21.30 [16.80, 26.60] | 17.40 [13.70, 21.40] | <0.001 |
| P, mmol/L | 1.19 [1.07, 1.30] | 1.12 [1.01, 1.23] | 1.24 [1.13, 1.35] | <0.001 |
| Se, μg/L | 85.78 [72.70, 98.62] | 85.82 [73.09, 98.90] | 85.76 [72.26, 98.32] | 0.413 |
| UCd, μg/L | 0.56 [0.27, 1.22] | 0.60 [0.28, 1.27] | 0.54 [0.26, 1.18] | 0.010 |
| Exposure | Beta (95% CI) | Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 | P-trend |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UCd | −0.035 (−0.057, −0.013) | Ref. | 0.00 (−0.06, 0.06) | −0.05 (−0.11, 0.01) | −0.09 (−0.15, −0.02) | 0.003 |
| Ca | 0.042 (0.020, 0.064) | Ref. | 0.06 (0.00, 0.12) | 0.10 (0.04, 0.16) | 0.10 (0.04, 0.16) | <0.001 |
| Fe | 0.014 (−0.008, 0.036) | Ref. | 0.06 (0.00, 0.12) | 0.05 (−0.01, 0.11) | 0.05 (−0.02, 0.11) | 0.199 |
| Mg | 0.053 (0.031, 0.074) | Ref. | 0.11 (0.05, 0.17) | 0.13 (0.07, 0.19) | 0.15 (0.09, 0.21) | <0.001 |
| P | 0.041 (0.019, 0.064) | Ref. | 0.01 (−0.05, 0.07) | 0.06 (0.00, 0.12) | 0.12 (0.05, 0.18) | <0.001 |
| Se | 0.080 (0.058, 0.102) | Ref. | 0.14 (0.07, 0.20) | 0.22 (0.15, 0.28) | 0.20 (0.14, 0.26) | <0.001 |
| Minerals | Exposure | Beta (95% CI) | P-interaction | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| High UCd and Low Minerals | Low UCd and Low Minerals | High UCd and High Minerals | Low UCd and High Minerals | |||
| Ca | UCd | Reference | 0.08 (0.02, 0.15) | 0.06 (0.00, 0.12) | 0.16 (0.09, 0.22) | 0.749 |
| Fe | UCd | Reference | 0.10 (0.03, 0.16) | 0.02 (−0.04, 0.08) | 0.11 (0.05, 0.18) | 0.853 |
| Mg | UCd | Reference | 0.08 (0.01, 0.14) | 0.07 (0.01, 0.13) | 0.18 (0.11, 0.24) | 0.749 |
| P | UCd | Reference | 0.10 (0.04, 0.17) | 0.09 (0.03, 0.16) | 0.17 (0.10, 0.23) | 0.749 |
| Se | UCd | Reference | 0.11 (0.05, 0.18) | 0.15 (0.09, 0.21) | 0.25 (0.18, 0.32) | 0.749 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, J.; Li, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Hu, Y.; Guo, X.; Kang, X.; Wu, Z.; Su, C.; Zhang, T. Protective Role of Multiple Essential Minerals Against Cadmium-Related Cognitive Decline in Middle-Aged and Older Adults: A Prospective Study. Nutrients 2025, 17, 2910. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17182910
Yang J, Li Z, Zhao Y, Hu Y, Guo X, Kang X, Wu Z, Su C, Zhang T. Protective Role of Multiple Essential Minerals Against Cadmium-Related Cognitive Decline in Middle-Aged and Older Adults: A Prospective Study. Nutrients. 2025; 17(18):2910. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17182910
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Jing, Zongyao Li, Yongbin Zhao, Yanzhen Hu, Xinyang Guo, Xi Kang, Zhenyu Wu, Chang Su, and Tao Zhang. 2025. "Protective Role of Multiple Essential Minerals Against Cadmium-Related Cognitive Decline in Middle-Aged and Older Adults: A Prospective Study" Nutrients 17, no. 18: 2910. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17182910
APA StyleYang, J., Li, Z., Zhao, Y., Hu, Y., Guo, X., Kang, X., Wu, Z., Su, C., & Zhang, T. (2025). Protective Role of Multiple Essential Minerals Against Cadmium-Related Cognitive Decline in Middle-Aged and Older Adults: A Prospective Study. Nutrients, 17(18), 2910. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17182910






