Shiitake Mushroom-Derived Vesicle-like Nanoparticles Improve Cognitive Function and Reshape Gut Microbiota and Fecal Metabolome in Aged Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Extraction and Characterization of S-VLNs
2.2. Mice
2.3. Tissue Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) Staining
2.4. Biodistrubtion of S-VLNs In Vivo
2.5. 16S Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) Analyses of Mouse Fecal Samples
2.6. Untargeted Metabolomics Analyses of Mouse Fecal Samples
2.7. Integrative Analyses of 16S rRNA Sequencing Data and Untargeted Metabolomics Data
3. Results
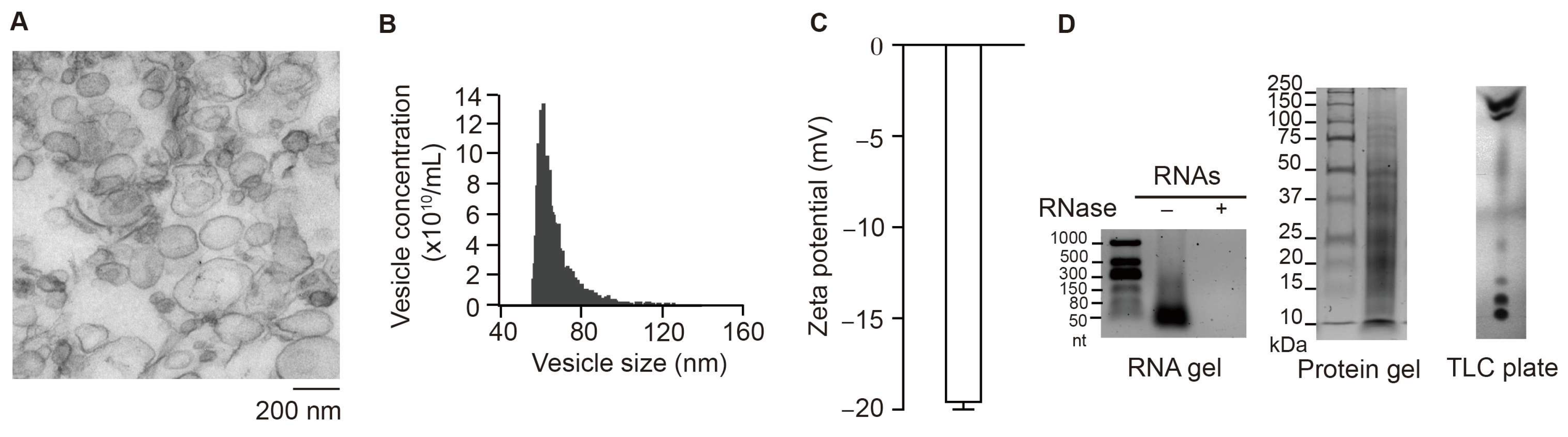
3.1. Characterization of S-VLNs
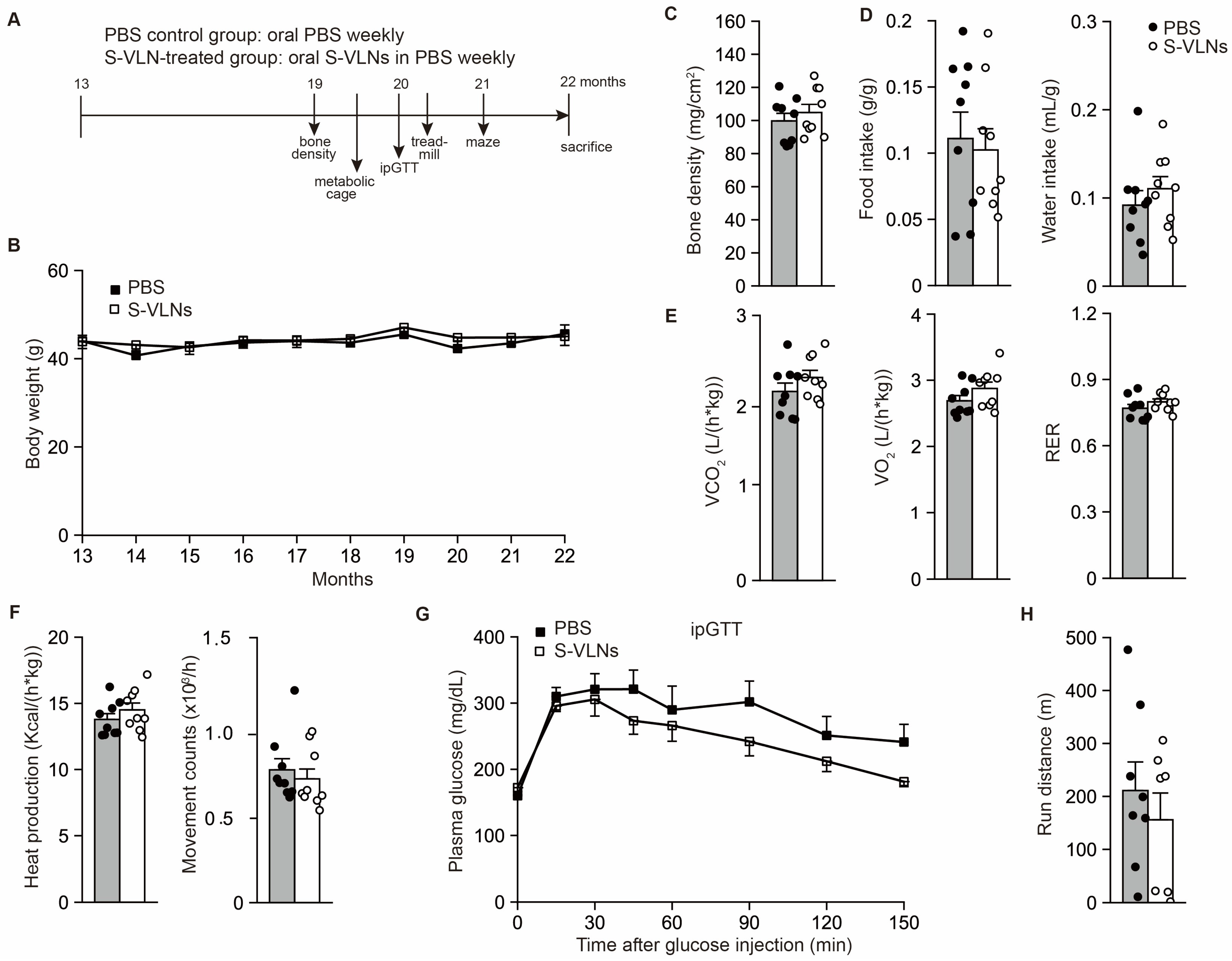
3.2. Oral Administration of S-VLNs Improved the Cognitive Function of Aged Mice
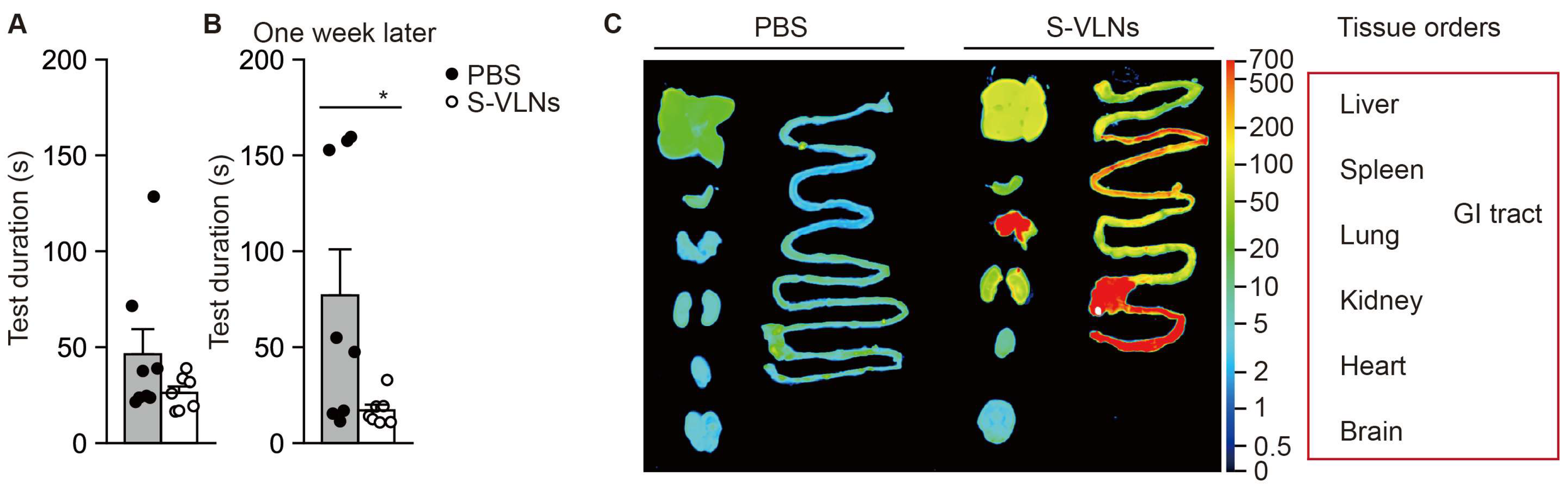
3.3. Orally Administered S-VLNs Did Not Reach the Brain
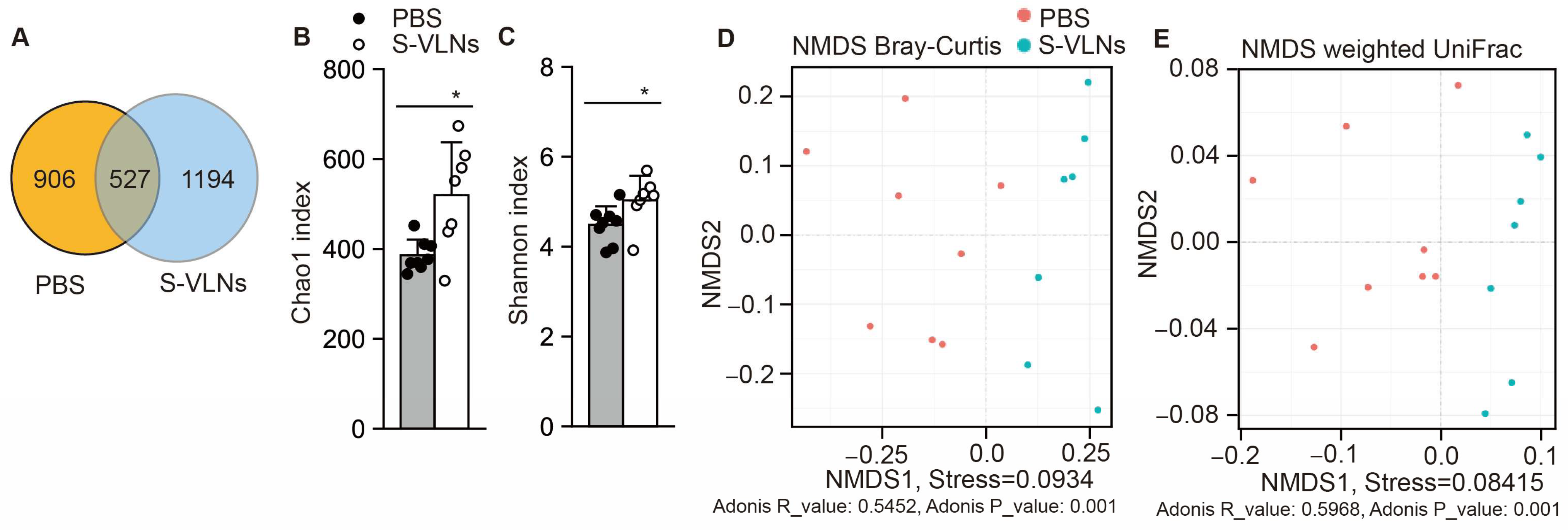
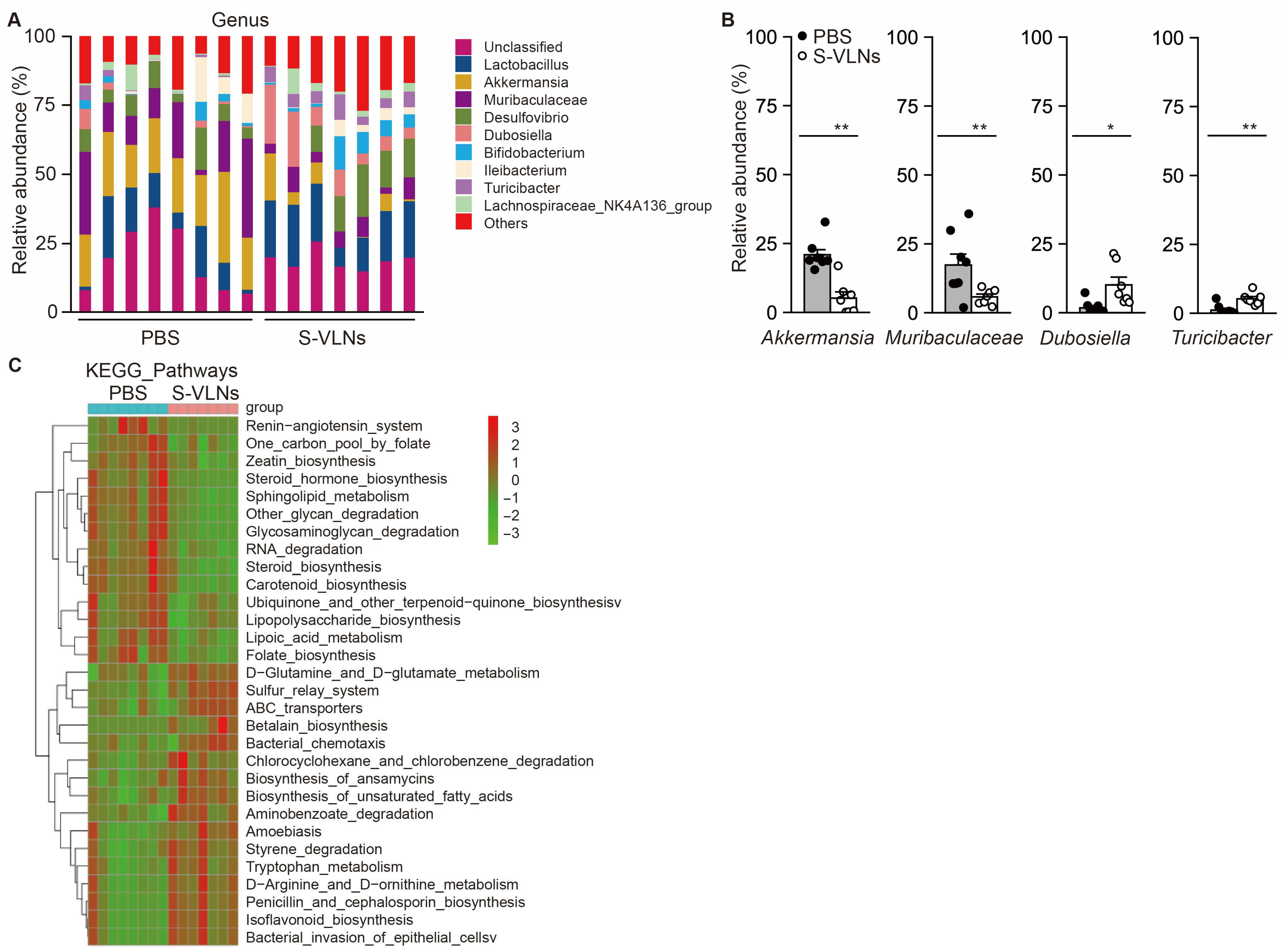
3.4. S-VLN Intake Significantly Reshaped Gut Microbiota
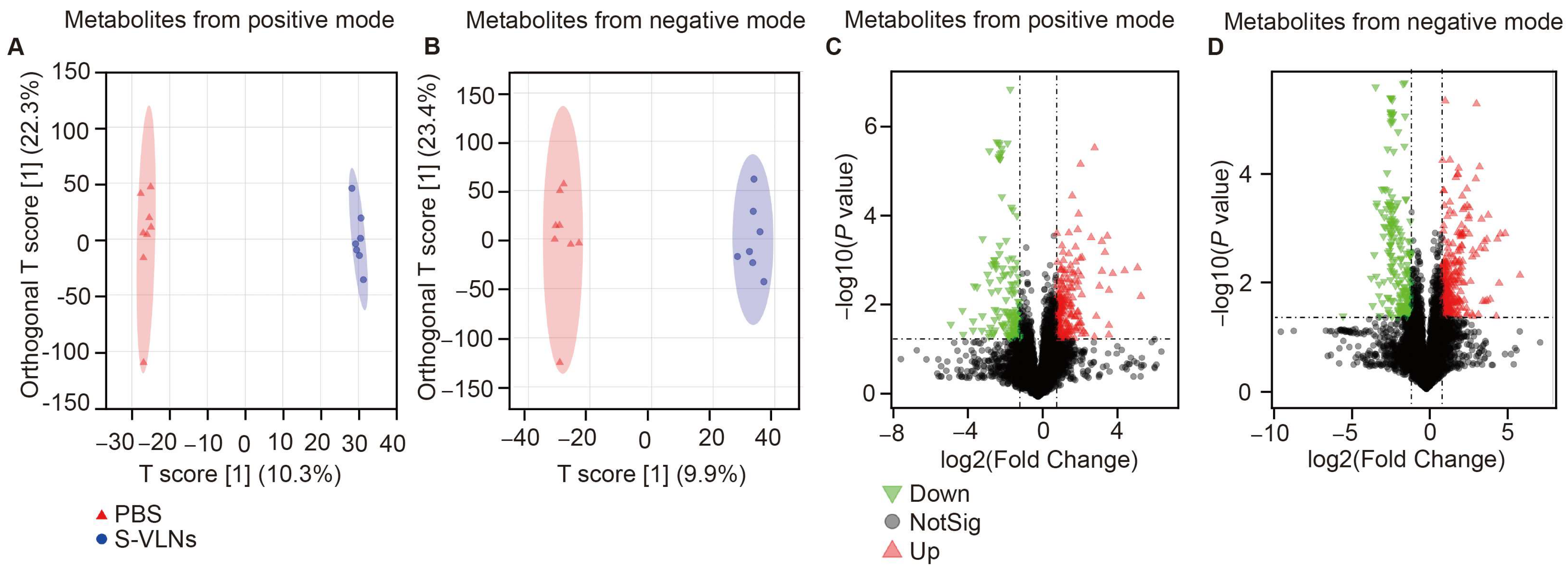
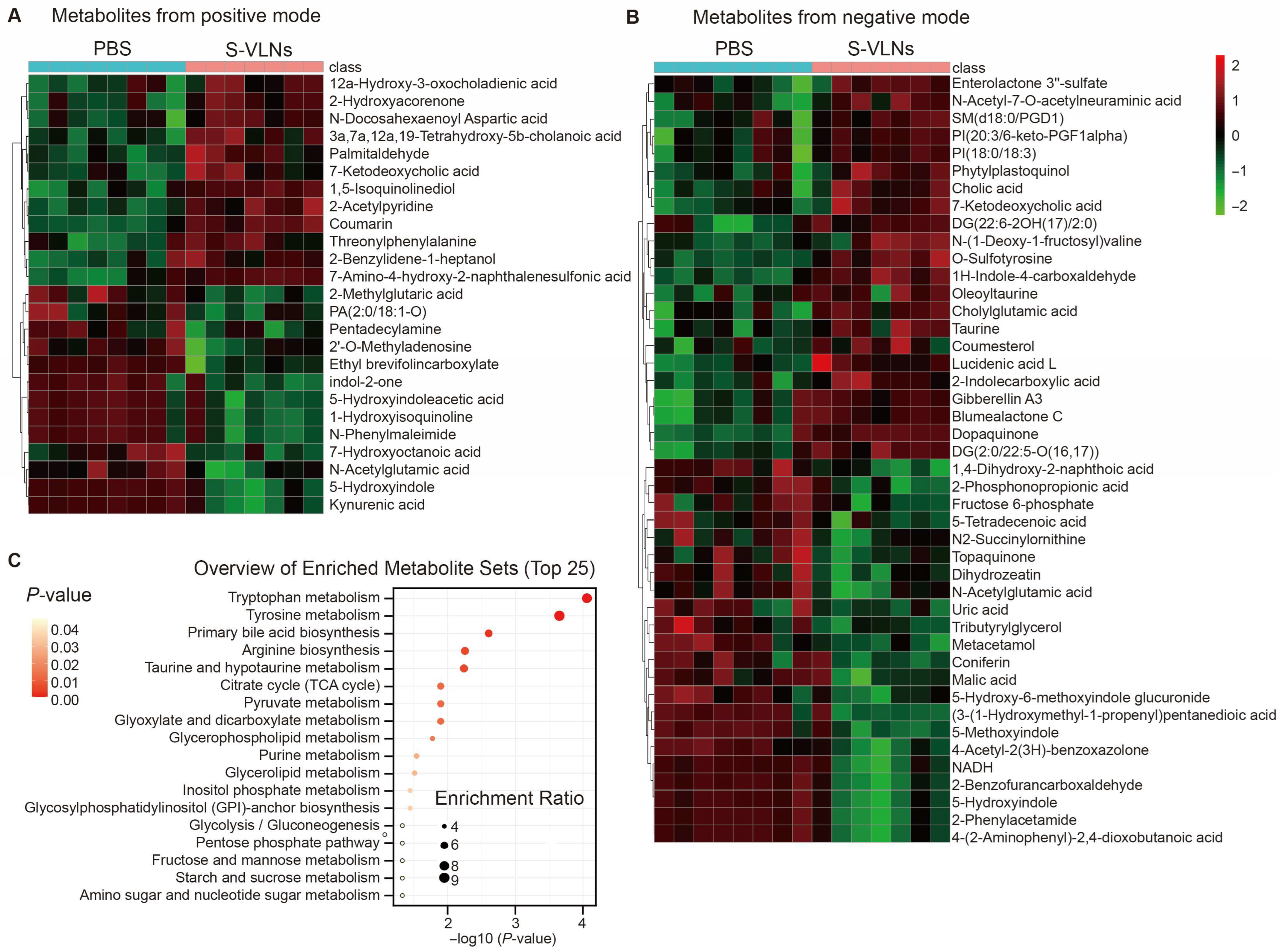
3.5. S-VLN Intake Had a Significant Impact on the Fecal Metabolome
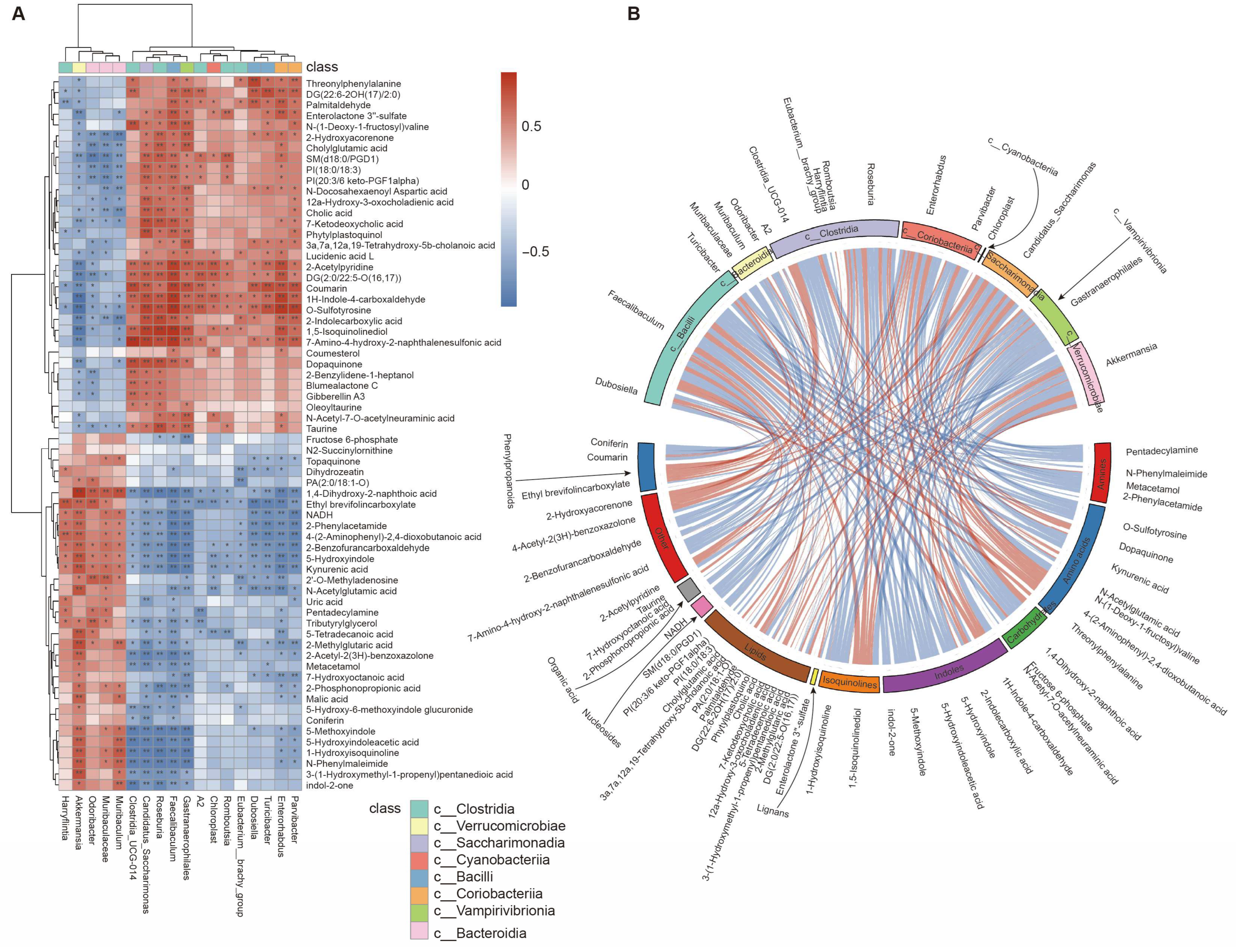
3.6. Integrative Analyses of Gut Microbiota and Fecal Metabolome
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AD | Alzheimer’s Disease |
| ASVs | Amplicon Sequence Variants |
| dd-MS2 | data dependent- Mass Spectrometry2 |
| ESI | ElectroSpray Ionization |
| FMT | Fecal microbiota transplantation |
| GI | Gastrointestinal |
| HCA | Hierarchical Cluster Analysis |
| H&E | Hematoxylin and Eosin |
| ipGTT | intraperitoneal Glucose Tolerance Test |
| KEGG | Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes |
| KYNA | Kynurenic Acid |
| MCI | Mild Cognitive Impairment |
| MIND | Mediterranean-dash intervention for neurodegenerative delay |
| MS | Mass Spectrometry |
| NMDS | Non-MetricMulti-Dimensional Scaling |
| OPLS-DA | Orthogonal Partial Least Squares-Discriminant Analysis |
| PBS | Phosphate-Buffered Saline |
| PICRUSt | Phylogenetic Investigation of Communities by Reconstruction of Unobserved States |
| RDA | Redundancy Analysis |
| RER | Respiratory Exchange Ratio |
| rRNA | ribosomal RNA |
| S-VLNs | Shiitake Mushroom-Derived Vesicle-Like Nanoparticles |
| TEM | Transmission Electron Microscopy |
| TLC | Thin-Layer Chromatography |
| UPLC | Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography |
| VLNs | Vesicle-Like Nanoparticles |
| VIP | Variable Importance in Projection |
References
- U.S. Census Bureau. 2023 National Population Projections Tables: Main Series. 2023. Available online: https://www2.census.gov/programs-surveys/popproj/technical-documentation/methodology/methodstatement23.pdf (accessed on 24 April 2025).
- United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs Population Division. World Population Prospects 2022: Summary of Results. UN DESA/POP/2022/TR/NO. 3. 2022. Available online: https://www.un.org/development/desa/pd/sites/www.un.org.development.desa.pd/files/wpp2022_summary_of_results.pdf (accessed on 24 April 2025).
- Abdolmaleky, H.M.; Zhou, J.R. Underlying Mechanisms of Brain Aging and Neurodegenerative Diseases as Potential Targets for Preventive or Therapeutic Strategies Using Phytochemicals. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franceschi, C.; Garagnani, P.; Morsiani, C.; Conte, M.; Santoro, A.; Grignolio, A.; Monti, D.; Capri, M.; Salvioli, S. The Continuum of Aging and Age-Related Diseases: Common Mechanisms but Different Rates. Front. Med. 2018, 5, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arosio, B.; Calvani, R.; Ferri, E.; Coelho-Junior, H.J.; Carandina, A.; Campanelli, F.; Ghiglieri, V.; Marzetti, E.; Picca, A. Sarcopenia and Cognitive Decline in Older Adults: Targeting the Muscle-Brain Axis. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brito, D.V.C.; Esteves, F.; Rajado, A.T.; Silva, N.; Consortium, A.s.; Araujo, I.; Braganca, J.; Castelo-Branco, P.; Nobrega, C. Assessing cognitive decline in the aging brain: Lessons from rodent and human studies. NPJ Aging 2023, 9, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, C.N.; Natelson Love, M.C.; Triebel, K.L. Normal cognitive aging. Clin. Geriatr. Med. 2013, 29, 737–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 2022 Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimers Dement. 2022, 18, 700–789. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.X.; Liang, N.; Li, X.L.; Yang, S.H.; Wang, Y.P.; Shi, N.N. Diagnosis and Treatment for Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Systematic Review of Clinical Practice Guidelines and Consensus Statements. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 719849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Z.; Dieciuc, M.; Carr, D.; Chakraborty, S.; Singh, A.; Fowe, I.E.; Zhang, S.; Lustria, M.L.A.; Terracciano, A.; Charness, N.; et al. New Opportunities for the Early Detection and Treatment of Cognitive Decline: Adherence Challenges and the Promise of Smart and Person-Centered Technologies. BMC Digit. Health 2023, 1, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loh, J.S.; Mak, W.Q.; Tan, L.K.S.; Ng, C.X.; Chan, H.H.; Yeow, S.H.; Foo, J.B.; Ong, Y.S.; How, C.W.; Khaw, K.Y. Microbiota-gut-brain axis and its therapeutic applications in neurodegenerative diseases. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallo, A.; Martone, A.M.; Liperoti, R.; Cipriani, M.C.; Ibba, F.; Camilli, S.; Rognoni, F.M.; Landi, F.; Montalto, M. Mild cognitive impairment and microbiota: What is known and future perspectives. Front. Med. 2024, 11, 1410246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charbit, J.; Vidal, J.S.; Hanon, O. Effects of Dietary Interventions on Cognitive Outcomes. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, M.; Tan, S.; Li, S.; Gao, L.; Huang, L.; Zhang, H.G.; Qiao, H. Technology insight: Plant-derived vesicles-How far from the clinical biotherapeutics and therapeutic drug carriers? Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2022, 182, 114108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, N.; Li, J.; Zeng, L.; You, J.; Li, R.; Qin, A.; Liu, X.; Yan, F.; Zhou, Z. Plant-Derived Exosome-Like Nanovesicles: Current Progress and Prospects. Int. J. Nanomed. 2023, 18, 4987–5009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivero-Pino, F.; Marquez-Paradas, E.; Montserrat-de la Paz, S. Food-derived vesicles as immunomodulatory drivers: Current knowledge, gaps, and perspectives. Food Chem. 2024, 457, 140168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Li, Q.; Liang, Y.; Zu, M.; Chen, N.; Canup, B.S.B.; Luo, L.; Wang, C.; Zeng, L.; Xiao, B. Natural exosome-like nanovesicles from edible tea flowers suppress metastatic breast cancer via ROS generation and microbiota modulation. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2022, 12, 907–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Nguyen, P.L.; Yu, H.; Li, X.; Wang, H.; Nguyen, T.G.B.; Sahoo, P.K.; Sur, M.; Reddy, J.; Sillman, S.; et al. Honey vesicle-like nanoparticles protect aged liver from non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2024, 14, 3661–3679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, F.; Ebea, P.; Mutai, E.; Wang, H.; Sukreet, S.; Navazesh, S.; Dogan, H.; Li, W.; Cui, J.; Ji, P.; et al. Small Extracellular Vesicles in Milk Cross the Blood-Brain Barrier in Murine Cerebral Cortex Endothelial Cells and Promote Dendritic Complexity in the Hippocampus and Brain Function in C57BL/6J Mice. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 838543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Lu, Y.; Chen, X.; Muthuraj, P.G.; Li, X.; Pattabiraman, M.; Zempleni, J.; Kachman, S.D.; Natarajan, S.K.; Yu, J. Protective Role of Shiitake Mushroom-Derived Exosome-Like Nanoparticles in D-Galactosamine and Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Liver Injury in Mice. Nutrients 2020, 12, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Liu, B.; Li, X.; An, T.T.; Zhou, Y.; Li, G.; Wu-Smart, J.; Alvarez, S.; Naldrett, M.J.; Eudy, J.; et al. Identification of anti-inflammatory vesicle-like nanoparticles in honey. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2021, 10, e12069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Li, X.; Yu, H.; Shi, X.; Zhou, Y.; Alvarez, S.; Naldrett, M.J.; Kachman, S.D.; Ro, S.H.; Sun, X.; et al. Therapeutic potential of garlic chive-derived vesicle-like nanoparticles in NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated inflammatory diseases. Theranostics 2021, 11, 9311–9330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Hoon, M.J.; Imoto, S.; Nolan, J.; Miyano, S. Open source clustering software. Bioinformatics 2004, 20, 1453–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kearns, R. The Kynurenine Pathway in Gut Permeability and Inflammation. Inflammation 2025, 48, 1063–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiedlocha, M.; Marcinowicz, P.; Janoska-Jazdzik, M.; Szulc, A. Gut microbiota, kynurenine pathway and mental disorders—Review. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2021, 106, 110145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badawy, A.A. Kynurenine Pathway of Tryptophan Metabolism: Regulatory and Functional Aspects. Int. J. Tryptophan Res. 2017, 10, 1178646917691938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toubiana, D.; Maruenda, H. Guidelines for correlation coefficient threshold settings in metabolite correlation networks exemplified on a potato association panel. BMC Bioinform. 2021, 22, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, F.; Mu, J.; Teng, Y.; Zhang, X.; Sundaram, K.; Sriwastva, M.K.; Kumar, A.; Lei, C.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Q.M.; et al. Restoring Oat Nanoparticles Mediated Brain Memory Function of Mice Fed Alcohol by Sorting Inflammatory Dectin-1 Complex Into Microglial Exosomes. Small 2022, 18, e2105385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, S.; Wang, D.; Zhang, S.; Xia, J.; Li, S.; Qiu, Q.; Lee, H.; Wang, J. Anti-glioma effect of ginseng-derived exosomes-like nanoparticles by active blood-brain-barrier penetration and tumor microenvironment modulation. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2023, 21, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhang, R.; Wang, A.; Li, Y.; Zhang, M.; Kim, J.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, Y.; et al. Panax notoginseng: Derived exosome-like nanoparticles attenuate ischemia reperfusion injury via altering microglia polarization. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2023, 21, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odamaki, T.; Kato, K.; Sugahara, H.; Hashikura, N.; Takahashi, S.; Xiao, J.Z.; Abe, F.; Osawa, R. Age-related changes in gut microbiota composition from newborn to centenarian: A cross-sectional study. BMC Microbiol. 2016, 16, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogt, N.M.; Kerby, R.L.; Dill-McFarland, K.A.; Harding, S.J.; Merluzzi, A.P.; Johnson, S.C.; Carlsson, C.M.; Asthana, S.; Zetterberg, H.; Blennow, K.; et al. Gut microbiome alterations in Alzheimer’s disease. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badal, V.D.; Vaccariello, E.D.; Murray, E.R.; Yu, K.E.; Knight, R.; Jeste, D.V.; Nguyen, T.T. The Gut Microbiome, Aging, and Longevity: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, Z.; Deng, L.; Lu, Z.; Wu, F.; Liu, W.; Huang, D.; Peng, Y. Protective effects of Akkermansia muciniphila on cognitive deficits and amyloid pathology in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Nutr. Diabetes 2020, 10, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Yan, C.; Zhao, S.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, R.; Li, Y. The preventive effects of probiotic Akkermansia muciniphila on D-galactose/AlCl3 mediated Alzheimer’s disease-like rats. Exp. Gerontol. 2022, 170, 111959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, J.S.; Kim, S.; Han, E.J.; Hong, S.T.; Chung, H.J. Increasing spatial working memory in mice with Akkermansia muciniphila. Commun. Biol. 2025, 8, 546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzini, L.; Zanella, L.; Sannia, M.; Baldassarro, V.A.; Moretti, M.; Cescatti, M.; Quadalti, C.; Baldi, S.; Bartolucci, G.; Di Gloria, L.; et al. Experimental colitis in young Tg2576 mice accelerates the onset of an Alzheimer’s-like clinical phenotype. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 2024, 16, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, P.; Zhu, H.; Li, X.; Shi, W.; Guo, Y.; Du, X.; Zhang, L.; Su, L.; Qin, C. Comparative Metagenomics and Metabolomes Reveals Abnormal Metabolism Activity Is Associated with Gut Microbiota in Alzheimer’s Disease Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escobar, Y.H.; O’Piela, D.; Wold, L.E.; Mackos, A.R. Influence of the Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis on Cognition in Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2022, 87, 17–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Gao, M.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Tu, H.; Lei, L.; Wu, P.; Zhang, A.; Yang, C.; Li, G.; et al. Gut Microbiome Composition Linked to Inflammatory Factors and Cognitive Functions in First-Episode, Drug-Naive Major Depressive Disorder Patients. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 800764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Fan, Y.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Y. Dynamic network modeling of gut microbiota during Alzheimer’s disease progression in mice. Gut Microbes 2023, 15, 2172672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadovnikova, I.S.; Gureev, A.P.; Ignatyeva, D.A.; Gryaznova, M.V.; Chernyshova, E.V.; Krutskikh, E.P.; Novikova, A.G.; Popov, V.N. Nrf2/ARE Activators Improve Memory in Aged Mice via Maintaining of Mitochondrial Quality Control of Brain and the Modulation of Gut Microbiome. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Amato, A.; Di Cesare Mannelli, L.; Lucarini, E.; Man, A.L.; Le Gall, G.; Branca, J.J.V.; Ghelardini, C.; Amedei, A.; Bertelli, E.; Regoli, M.; et al. Faecal microbiota transplant from aged donor mice affects spatial learning and memory via modulating hippocampal synaptic plasticity- and neurotransmission-related proteins in young recipients. Microbiome 2020, 8, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, C.; Zhou, W.; Wang, W.; Xiang, H.; Xu, H.; Liang, L.; Sui, H.; Zhan, L.; Lu, X. ZiBuPiYin recipe improves cognitive decline by regulating gut microbiota in Zucker diabetic fatty rats. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 27693–27703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savonije, K.; Weaver, D.F. The Role of Tryptophan Metabolism in Alzheimer’s Disease. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, P.J.; Cryan, J.F.; Dinan, T.G.; Clarke, G. Kynurenine pathway metabolism and the microbiota-gut-brain axis. Neuropharmacology 2017, 112, 399–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kepplinger, B.; Baran, H.; Kainz, A.; Ferraz-Leite, H.; Newcombe, J.; Kalina, P. Age-related increase of kynurenic acid in human cerebrospinal fluid—IgG and beta2-microglobulin changes. Neurosignals 2005, 14, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baran, H.; Jan Pietryja, M.; Kepplinger, B. Importance of Modulating Kynurenic Acid Metabolism-Approaches for the Treatment of Dementia. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, B.; Zhang, X.; Song, Z.; Dai, Z.; Luo, K.; Chen, B.; Zhou, Z.; Cui, Y.; Feng, B.; Zhu, Z.; et al. Targeting gut microbiota-derived kynurenine to predict and protect the remodeling of the pressure-overloaded young heart. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eadg7417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Fan, Y.; Xu, L.; Yu, Z.; Wang, S.; Xu, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, L.; Liu, W.; Wu, L.; et al. Microbiome and tryptophan metabolomics analysis in adolescent depression: Roles of the gut microbiota in the regulation of tryptophan-derived neurotransmitters and behaviors in human and mice. Microbiome 2023, 11, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugita, S.; Tahir, P.; Kinjo, S. The effects of microbiome-targeted therapy on cognitive impairment and postoperative cognitive dysfunction-A systematic review. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0281049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, J.; Katsumata, N.; Bernier, F.; Ohno, K.; Yamauchi, Y.; Odamaki, T.; Yoshikawa, K.; Ito, K.; Kaneko, T. Probiotic Bifidobacterium breve in Improving Cognitive Functions of Older Adults with Suspected Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2020, 77, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.S.; Kim, Y.; Choi, H.; Kim, W.; Park, S.; Lee, D.; Kim, D.K.; Kim, H.J.; Choi, H.; Hyun, D.W.; et al. Transfer of a healthy microbiota reduces amyloid and tau pathology in an Alzheimer’s disease animal model. Gut 2020, 69, 283–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, K.R.; Naik, S.R.; Vakil, B.V. Probiotics, prebiotics and synbiotics—A review. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 52, 7577–7587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahle, Z.; Engidaye, G.; Shenkute Gebreyes, D.; Adenew, B.; Abebe, T.A. Fecal microbiota transplantation and next-generation therapies: A review on targeting dysbiosis in metabolic disorders and beyond. SAGE Open Med. 2024, 12, 20503121241257486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavrinou, P.S.; Andreou, E.; Aphamis, G.; Pantzaris, M.; Ioannou, M.; Patrikios, I.S.; Giannaki, C.D. The Effects of a 6-Month High Dose Omega-3 and Omega-6 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids and Antioxidant Vitamins Supplementation on Cognitive Function and Functional Capacity in Older Adults with Mild Cognitive Impairment. Nutrients 2020, 12, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortier, M.; Castellano, C.A.; Croteau, E.; Langlois, F.; Bocti, C.; St-Pierre, V.; Vandenberghe, C.; Bernier, M.; Roy, M.; Descoteaux, M.; et al. A ketogenic drink improves brain energy and some measures of cognition in mild cognitive impairment. Alzheimers Dement. 2019, 15, 625–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Liu, B.; Sekar, D.; Sur, M.; Reddy, J.; Natarajan, S.K.; Lund, P.J.; Yu, J. Shiitake Mushroom-Derived Vesicle-like Nanoparticles Improve Cognitive Function and Reshape Gut Microbiota and Fecal Metabolome in Aged Mice. Nutrients 2025, 17, 2902. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17172902
Li X, Liu B, Sekar D, Sur M, Reddy J, Natarajan SK, Lund PJ, Yu J. Shiitake Mushroom-Derived Vesicle-like Nanoparticles Improve Cognitive Function and Reshape Gut Microbiota and Fecal Metabolome in Aged Mice. Nutrients. 2025; 17(17):2902. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17172902
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xingzhi, Baolong Liu, Deekshika Sekar, Meghna Sur, Jay Reddy, Sathish Kumar Natarajan, Peder J. Lund, and Jiujiu Yu. 2025. "Shiitake Mushroom-Derived Vesicle-like Nanoparticles Improve Cognitive Function and Reshape Gut Microbiota and Fecal Metabolome in Aged Mice" Nutrients 17, no. 17: 2902. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17172902
APA StyleLi, X., Liu, B., Sekar, D., Sur, M., Reddy, J., Natarajan, S. K., Lund, P. J., & Yu, J. (2025). Shiitake Mushroom-Derived Vesicle-like Nanoparticles Improve Cognitive Function and Reshape Gut Microbiota and Fecal Metabolome in Aged Mice. Nutrients, 17(17), 2902. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17172902






