Integrating Precision Medicine and Digital Health in Personalized Weight Management: The Central Role of Nutrition
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
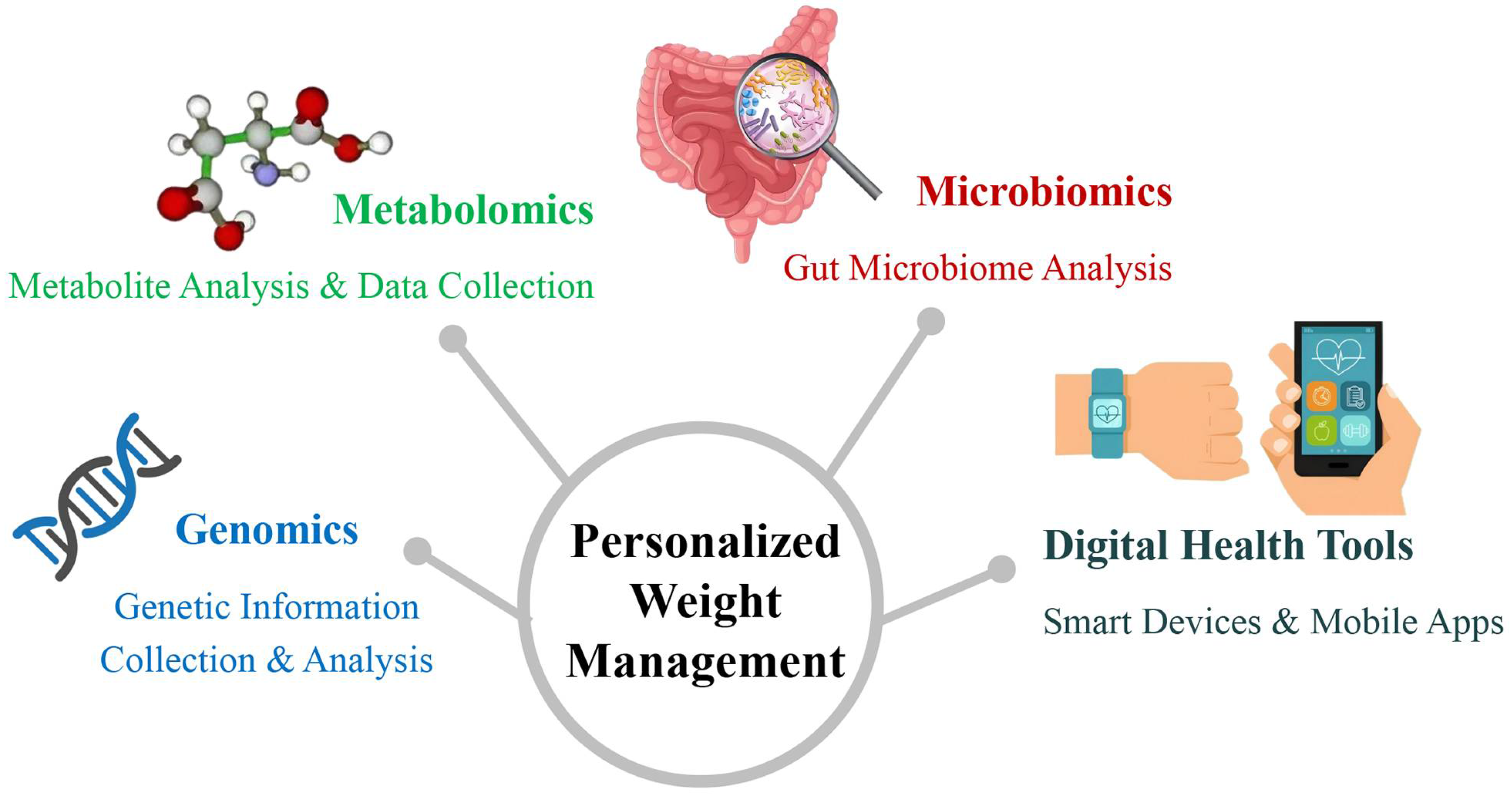
3. Biological Basis of Precision Medicine in Weight Management
3.1. Genetics and Obesity
3.2. Metabolomics: A New Perspective on Weight Management
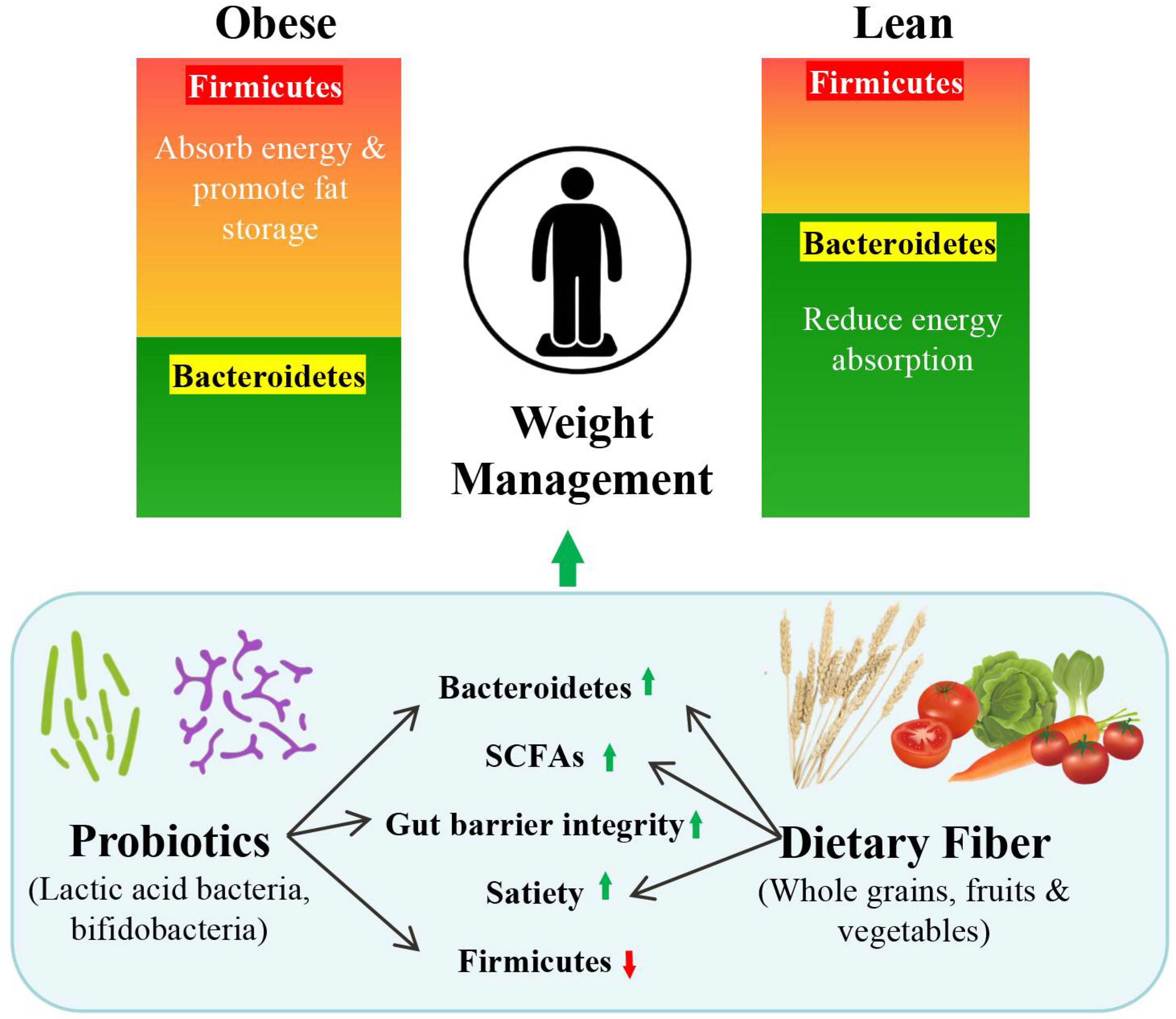
3.3. The Role of the Microbiome in Obesity
3.4. Summary of Biological Foundations in Precision Weight Management
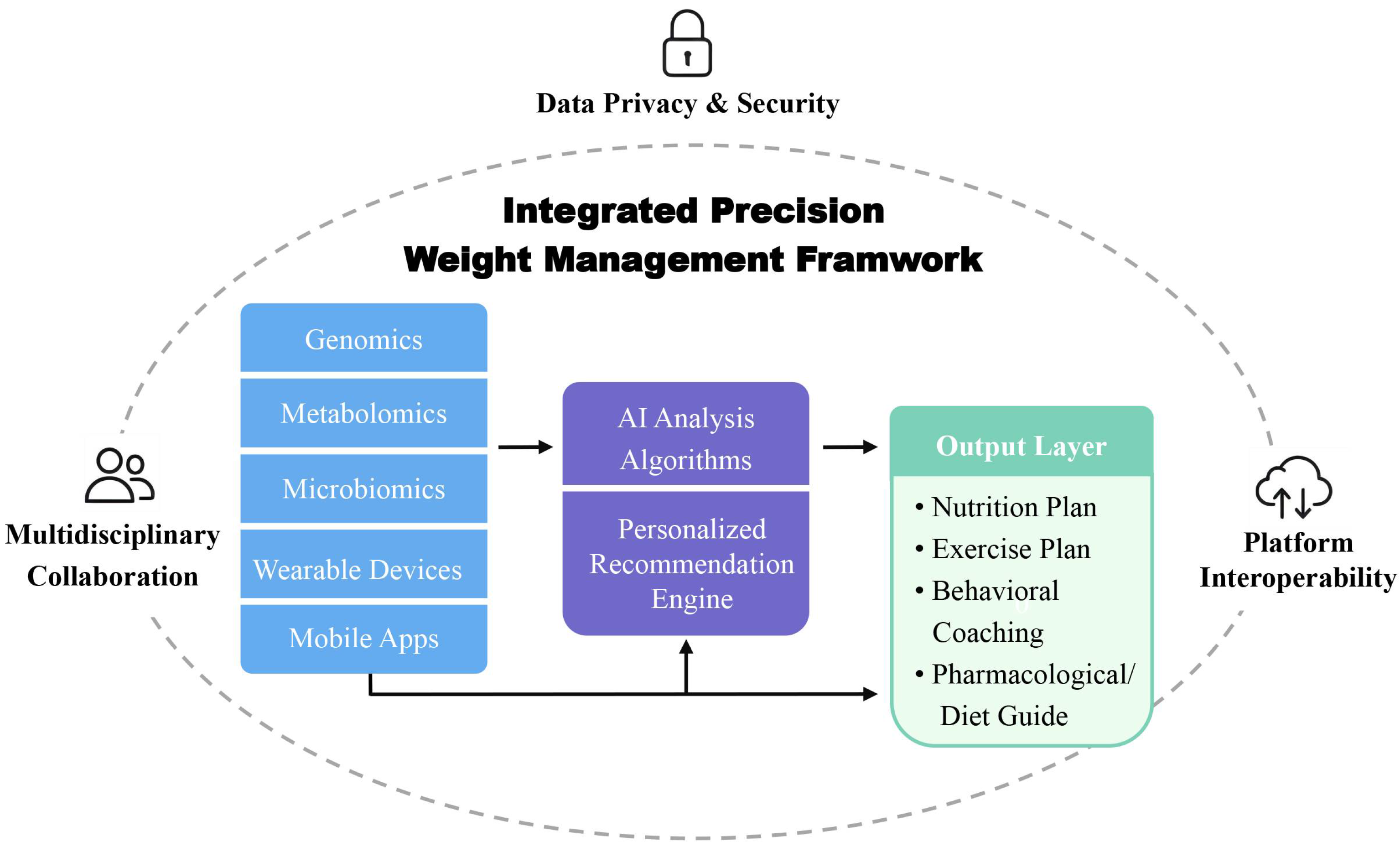
4. Digital Health Tools for Precision Weight Management
4.1. Smart Health Devices and Personalized Monitoring
| Technology Type | Representative Tools | Intervention Form | Advantages | Limitations | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genomics | 23andMe, DNAfit (√) | Personalized diet and exercise plans | Individualized guidance | High cost; limited generalizability across populations | [83] |
| Metabolomics | Serum profiling (△) | Nutrition adjustment | Real-time feedback | Laboratory-dependent; low accessibility in remote areas | [84] |
| Microbiomics | Viome, 16S rRNA (△) | Probiotic/dietary adjustment | Improves gut health | Expensive; complex interpretation; limited standardization | [85] |
| Digital Tools | MyFitnessPal, wearables (√) | Self-tracking, coaching | Boosts adherence | Digital divide; limited access in low-income populations | [79] |
4.2. BCAAs and Muscle Damage
| Design & Sample | Intervention | Duration | Main Findings | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RCT; N = 150 adults with obesity (BMI ≥ 30) | Multimodal app (“zanadio”) (√) | 12 months | Mean weight loss 7.75% (95% CI –9.66 to –5.84); improvements in waist-to-height ratio and QoL. | [95] |
| RCT; N = 168 adults with BMI 30–40 | Multimodal app (ADHOC) vs. delayed access (√) | 12 weeks + 12-week follow-up | Greater short-term weight reduction and improved dietary intake and QoL. | [96] |
| Systematic review and component network meta-analysis; includes 68 RCTs | Digital support features across weight-loss apps (√) | Up to 12 months | Identified key components (education; specialist contact) associated with weight loss (–2.52 kg at 6 months; –2.11 kg at 12 months). | [80] |
| Umbrella review; 507 RCTs (N ≈ 206,873) | Digital health (apps, wearables, and SMS) (√) | Mostly 3–6 months | Modest but significant improvements: weight (–1.89 kg), steps/day (+1329), sedentary behavior, and energy intake (–103 kcal/day). | [97] |
| Cohort study; N = 46,579 adults | Wearables vs. pedometer apps (√) | 12–24 weeks | Wearable users showed higher physical activity, improved diet, and reduced metabolic syndrome risk. | [81] |
| Observational real-world study; N = 2217 CGM users | CGM + wearables + app-based coaching (√) | 28 days | Reduced caloric intake, increased activity, and improved glycemic and metabolic outcomes. | [82] |
4.3. Data Sharing and Cross-Platform Collaboration
4.4. Personalized Dietary Interventions in Precision Weight Management
4.4.1. Dietary Strategies Based on Individual Phenotypes
4.4.2. Macronutrient-Specific Precision Interventions
4.4.3. Gene–Diet Interactions and Nutrigenomics
| Intervention Type | Target Population | Mechanistic Rationale | Digital/Omics Tools | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low-Carbohydrate/Ketogenic Diet | Insulin-resistant individuals, prediabetes, and type 2 diabetes | Reduces insulin secretion and enhances fat oxidation | Continuous glucose monitor; activity tracker (√) | [120] |
| Green-Mediterranean Diet | Individuals with visceral obesity and chronic inflammation | Activates AMPK and short-chain fatty acid production; improves body composition | 16S rRNA sequencing; MRI (△) | [121] |
| Resistant Starch Supplementation | Individuals with low gut microbiota diversity | Increases SCFA production; supports satiety hormone signaling | Metagenomics; targeted metabolomics (△) | [65] |
| Digital Nutrition Feedback System | Individuals with poor dietary adherence or metabolic risk | Improves self-regulation via real-time glucose and activity feedback | App-based monitoring system; wearable sensors (√) | [82] |
| Genotype-Based Dietary Advice | Carriers of FTO- or polygenic-risk alleles | Aligns macronutrient ratios with genetic response patterns | Genetic risk profiling; nutrigenomics (△) | [102] |
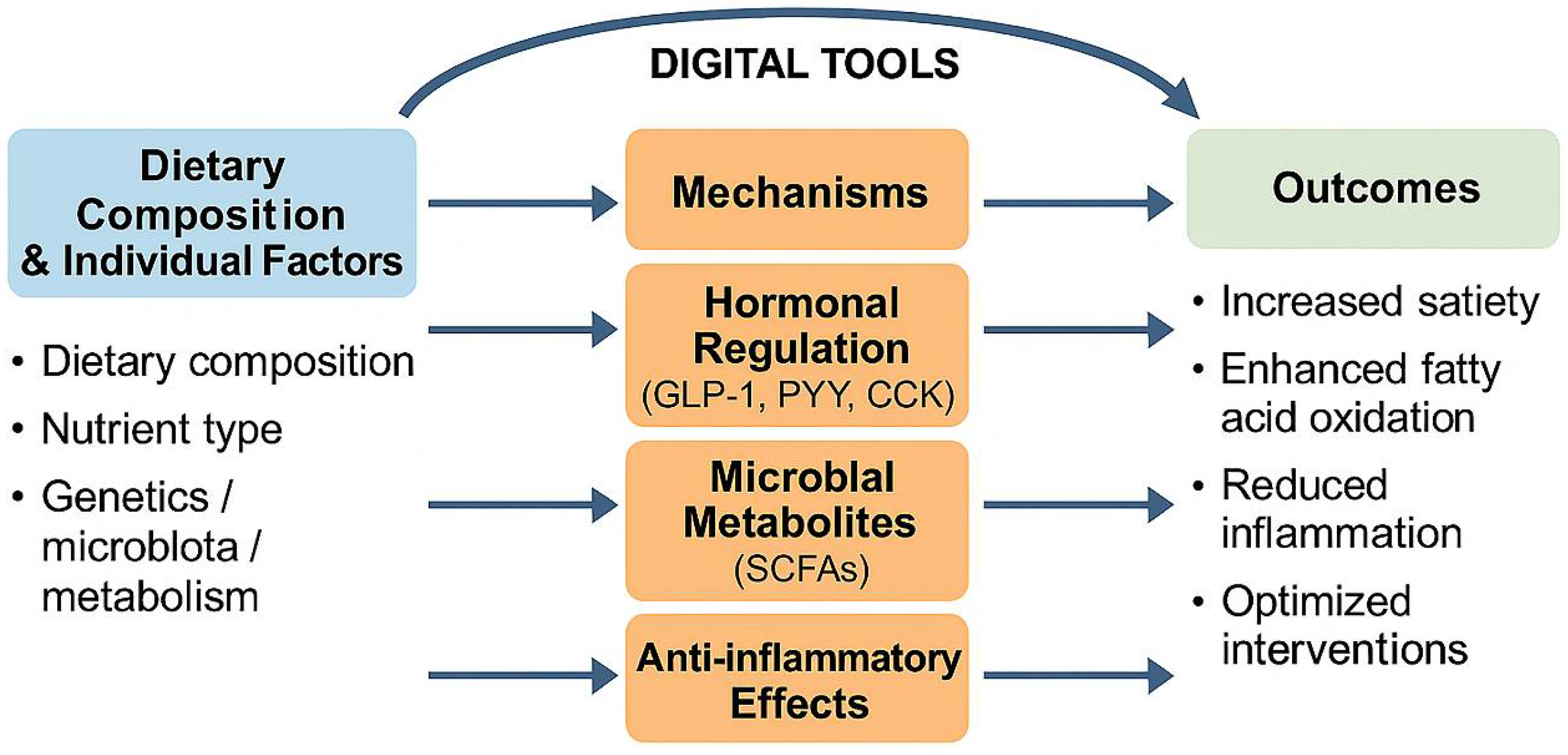
4.5. Mechanistic Foundations of Nutritional Interventions in Personalized Weight Managementt
4.5.1. Gut–Brain Axis and Hormonal Satiety Signaling
4.5.2. Microbiota-Driven Fermentation and Energy Balance
4.5.3. Molecular and Genomic Modulation of Metabolism
4.5.4. Anti-Inflammatory Pathways and Adipokine Regulation
4.5.5. System-Level Integration with Digital Platforms
| Pathway | Key Mechanisms | Target Biomarkers | Representative Interventions | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gut–Brain Axis | Secretion of satiety hormones (GLP-1, PYY, and CCK) that modulate hypothalamic appetite control | Post-prandial GLP-1/PYY, fasting insulin, and ghrelin | High-protein/low-GI snacks (e.g., tree-nut inclusion) | [136] |
| Microbiota–SCFA | Fermentation of prebiotic fibers into SCFAs which activate GPR43/41, enhance gut barrier, and raise energy expenditure | Fecal/plasma SCFAs, α-diversity, and A. muciniphila abundance | Inulin or resistant starch supplementation | [12] |
| Nutrigenomics | Diet-driven modulation of gene expression (AMPK; PPAR-γ) and epigenetic marks according to omic phenotype | FTO, MC4R variants; DNA-methylation profiles | Polyphenol-rich or genotype-matched meal plans | [4] |
| Inflammatory Modulation | Anti-inflammatory nutrients rebalance adipokines and lower CRP/IL-6/TNF-α | CRP, IL-6, TNF-α, and adiponectin | Curcumin (with piperine) 1 g·d−1 | [137] |
| Digital Feedback Loop | Real-time data (CGM; wearables) drive AI-guided adjustment of diet and activity prescriptions | CGM metrics, step count, and adaptive macronutrient targets | mHealth app + self-experimentation protocol | [138] |
5. Challenges and Future Prospects
5.1. Technical Challenges
5.2. Data Challenges
5.3. Ethical and Policy Challenges
5.4. Future Prospects
5.5. Equity and Accessibility Considerations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Janić, M.; Janež, A.; El-Tanani, M.; Rizzo, M. Obesity: Recent Advances and Future Perspectives. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, M.; Gakidou, E.; Lo, J.; Abate, Y.H.; Abbafati, C.; Abbas, N.; Abbasian, M.; ElHafeez, S.A.; Abdel-Rahman, W.M.; Abd-Elsalam, S.; et al. Global, Regional, and National Prevalence of Adult Overweight and Obesity, 1990–2021, with Forecasts to 2050: A Forecasting Study for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet 2025, 405, 813–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khattab, R. Weight Loss Programs: Why Do They Fail? A Multidimensional Approach for Obesity Management. Curr. Nutr. Rep. 2024, 13, 478–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermingham, K.M.; Linenberg, I.; Polidori, L.; Asnicar, F.; Arrè, A.; Wolf, J.; Badri, F.; Bernard, H.; Capdevila, J.; Bulsiewicz, W.J.; et al. Effects of a Personalized Nutrition Program on Cardiometabolic Health: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Nat. Med. 2024, 30, 1888–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kheniser, K.; Saxon, D.R.; Kashyap, S.R. Long-Term Weight Loss Strategies for Obesity. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 106, 1854–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Chen, S.; Ding, X. The Effectiveness of Digital Twins in Promoting Precision Health across the Entire Population: A Systematic Review. Npj Digit. Med. 2024, 7, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molla, G.; Bitew, M. Revolutionizing Personalized Medicine: Synergy with Multi-Omics Data Generation, Main Hurdles, and Future Perspectives. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 2750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irvin, L.; Madden, L.A.; Marshall, P.; Vince, R.V. Digital Health Solutions for Weight Loss and Obesity: A Narrative Review. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Gao, Z.-J.; Yu, X.; Wang, P. Dietary Regulation in Health and Disease. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinelli, V.; Biscotti, P.; Martini, D.; Del Bo’, C.; Marino, M.; Meroño, T.; Nikoloudaki, O.; Calabrese, F.M.; Turroni, S.; Taverniti, V.; et al. Effects of Dietary Fibers on Short-Chain Fatty Acids and Gut Microbiota Composition in Healthy Adults: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, R.; Yu, L.; Tian, F.; Zhao, J.; Chen, W.; Zhai, Q. Effect of Inulin, Galacto-Oligosaccharides, and Polyphenols on the Gut Microbiota, with a Focus on Akkermansia Muciniphila. Food Funct. 2024, 15, 4763–4772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirschner, S.K.; Engelen, M.P.; Haas, P.; Bischoff, S.C.; Deutz, N.E. Short-Chain Fatty Acid Kinetics and Concentrations Are Higher after Inulin Supplementation in Young and Older Adults: A Randomized Trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2025, 121, 1224–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Hu, D.; Liu, X.; Li, Z.; Lu, L. Branched-Chain Amino Acids and Inflammation Management in Endurance Sports: Molecular Mechanisms and Practical Implications. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penggalih, M.H.S.T.; Sutanto, Y.S.; Taslim, N.A.; Syahputra, R.A.; Hardinsyah, H.; Tjandrawinata, R.R.; Nurkolis, F. Precision Nutrition in Sports Science: An Opinion on Omics-Based Personalization and Athletic Outcomes. Front. Nutr. 2025, 12, 1611440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aronica, L.; Landry, M.J.; Rigdon, J.; Gardner, C.D. Weight, Insulin Resistance, Blood Lipids, and Diet Quality Changes Associated with Ketogenic and Ultra Low-Fat Dietary Patterns: A Secondary Analysis of the DIETFITS Randomized Clinical Trial. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1220020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelicha, H.; Kloting, N.; Kaplan, A.; Yaskolka Meir, A.; Rinott, E.; Tsaban, G.; Chassidim, Y.; Bluher, M.; Ceglarek, U.; Isermann, B.; et al. The Effect of High-Polyphenol Mediterranean Diet on Visceral Adiposity: The DIRECT PLUS Randomized Controlled Trial. Bmc Med. 2022, 20, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Żarnowski, A.; Jankowski, M.; Gujski, M. Use of Mobile Apps and Wearables to Monitor Diet, Weight, and Physical Activity: A Cross-Sectional Survey of Adults in Poland. Med. Sci. Monit. 2022, 28, e937948-1–e937948-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Sun, Z.; Xue, H.; An, R. Artificial Intelligence Applications to Personalized Dietary Recommendations: A Systematic Review. Healthcare 2025, 13, 1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papastratis, I.; Konstantinidis, D.; Daras, P.; Dimitropoulos, K. AI Nutrition Recommendation Using a Deep Generative Model and ChatGPT. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 14620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abeltino, A.; Riente, A.; Bianchetti, G.; Serantoni, C.; De Spirito, M.; Capezzone, S.; Esposito, R.; Maulucci, G. Digital Applications for Diet Monitoring, Planning, and Precision Nutrition for Citizens and Professionals: A State of the Art. Nutr. Rev. 2025, 83, e574–e601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsolakidis, D.; Gymnopoulos, L.P.; Dimitropoulos, K. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Technologies for Personalized Nutrition: A Review. Informatics 2024, 11, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, Y.; Wong, S.H.; Chee, D.G.H.; Ng, B.S.P.; Ang, W.W.; Han, C.Y.; Cheng, L.J. Technology-Delivered Personalized Nutrition Intervention on Dietary Outcomes among Adults with Overweight and Obesity: A Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis, and Meta-Regression. Obes. Rev. 2024, 25, e13699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, R.; Kimonis, V.; Butler, M.G. Genetics of Obesity in Humans: A Clinical Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loos, R.J.F.; Yeo, G.S.H. The Genetics of Obesity: From Discovery to Biology. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2022, 23, 120–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maculewicz, E.; Leońska-Duniec, A.; Mastalerz, A.; Szarska, E.; Garbacz, A.; Lepionka, T.; Łakomy, R.; Anyżewska, A.; Bertrandt, J. The Influence of FTO, FABP2, LEP, LEPR, and MC4R Genes on Obesity Parameters in Physically Active Caucasian Men. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 6030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Górczyńska-Kosiorz, S.; Kosiorz, M.; Dzięgielewska-Gęsiak, S. Exploring the Interplay of Genetics and Nutrition in the Rising Epidemic of Obesity and Metabolic Diseases. Nutrients 2024, 16, 3562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajcsanyi, L.S.; Zheng, Y.; Herpertz-Dahlmann, B.; Seitz, J.; de Zwaan, M.; Herzog, W.; Ehrlich, S.; Zipfel, S.; Giel, K.; Egberts, K.; et al. Unexpected Identification of Obesity-Associated Mutations in LEP and MC4R Genes in Patients with Anorexia Nervosa. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 7067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vranceanu, M.; Filip, L.; Hegheș, S.-C.; de Lorenzo, D.; Cozma-Petruț, A.; Ghitea, T.C.; Stroia, C.M.; Banc, R.; Mîrza, O.M.; Miere, D.; et al. Genes Involved in Susceptibility to Obesity and Emotional Eating Behavior in a Romanian Population. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivera-Iñiguez, I.; Hunot-Alexander, C.; Sepúlveda-Villegas, M.; Campos-Medina, L.; Roman, S. Relationship between Energy Balance and Reward System Gene Polymorphisms and Appetitive Traits in Young Mexican Subjects. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1373578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eghbali, M.; Mottaghi, A.; Taghizadeh, S.; Cheraghi, S. Genetic Variants in the Fat Mass and Obesity-Associated Gene and Risk of Obesity/Overweight in Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Endocrinol. Diabetes Metab. 2024, 7, e00510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.; Waheed, A.; Elahi, A.; Mustafa, G. Fat Mass and Obesity-Related (FTO) Gene Variant Is a Predictor of CVD in T2DM Patients. J. Diabetes Res. 2024, 2024, 5914316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponce-Gonzalez, J.G.; Martínez-Ávila, Á.; Velázquez-Díaz, D.; Perez-Bey, A.; Gómez-Gallego, F.; Marín-Galindo, A.; Corral-Pérez, J.; Casals, C. Impact of the FTO Gene Variation on Appetite and Fat Oxidation in Young Adults. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzago, M.; Di Nicola, M.; Fraticelli, F.; Marchioni, M.; Stuppia, L.; Vitacolonna, E. Nutrigenetic Variants and Response to Diet/Lifestyle Intervention in Obese Subjects: A Pilot Study. Acta Diabetol. 2022, 59, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poosri, S.; Boonyuen, U.; Chupeerach, C.; Soonthornworasiri, N.; Kwanbunjan, K.; Prangthip, P. Association of FTO Variants Rs9939609 and Rs1421085 with Elevated Sugar and Fat Consumption in Adult Obesity. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 25618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anazco, D.; Acosta, A. Precision Medicine for Obesity: Current Evidence and Insights for Personalization of Obesity Pharmacotherapy. Int. J. Obes. 2025, 49, 452–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunnathodi, F.; Arafat, A.A.; Alhazzani, W.; Mustafa, M.; Azmi, S.; Ahmad, I.; Selan, J.S.; Anvarbatcha, R.; Alotaibi, H.F. Unraveling the Genetic Architecture of Obesity: A Path to Personalized Medicine. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, P.R.; Vos, N.; van Uhm, J.; Dekkers, I.A.; van der Meer, R.; Mannens, M.M.A.M.; van Haelst, M.M. The Utility of Obesity Polygenic Risk Scores from Research to Clinical Practice: A Review. Obes. Rev. 2024, 25, e13810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi, M.R.; Symonds, M.E. Effect of FTO Genotype on Exercise Training and Diet-Indued Weight Loss in Overweight and Obese Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. 2024, 65, 4080–4096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woldemariam, S.; Dorner, T.E.; Wiesinger, T.; Stein, K.V. Multi-Omics Approaches for Precision Obesity Management. Wien. Klin. Wochenschr. 2023, 135, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathmasiri, W.; Rushing, B.R.; McRitchie, S.; Choudhari, M.; Du, X.; Smirnov, A.; Pelleigrini, M.; Thompson, M.J.; Sakaguchi, C.A.; Nieman, D.C.; et al. Untargeted Metabolomics Reveal Signatures of a Healthy Lifestyle. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 13630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kortesniemi, M.; Noerman, S.; Kårlund, A.; Raita, J.; Meuronen, T.; Koistinen, V.; Landberg, R.; Hanhineva, K. Nutritional Metabolomics: Recent Developments and Future Needs. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2023, 77, 102400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bihlmeyer, N.A.; Kwee, L.C.; Clish, C.B.; Deik, A.A.; Gerszten, R.E.; Pagidipati, N.J.; Laferrère, B.; Svetkey, L.P.; Newgard, C.B.; Kraus, W.E.; et al. Metabolomic Profiling Identifies Complex Lipid Species and Amino Acid Analogues Associated with Response to Weight Loss Interventions. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0240764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Näätänen, M.; Kårlund, A.; Mikkonen, S.; Klåvus, A.; Savolainen, O.; Lehtonen, M.; Karhunen, L.; Hanhineva, K.; Kolehmainen, M. Metabolic Profiles Reflect Weight Loss Maintenance and the Composition of Diet after Very-Low-Energy Diet. Clin. Nutr. 2023, 42, 1126–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, S.; Wu, Y.; Guo, Y.; Wang, X. Baseline Serum BCAAs Are Related to the Improvement in Insulin Resistance in Obese People after a Weight Loss Intervention. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2023, 16, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, L.; Granet, J.; Marcangeli, V.; Dulac, M.; Hajj-Boutros, G.; Reynaud, O.; Buckinx, F.; Gaudreau, P.; Morais, J.A.; Mauriège, P.; et al. Clinical and Biological Adaptations in Obese Older Adults Following 12-Weeks of High-Intensity Interval Training or Moderate-Intensity Continuous Training. Healthcare 2022, 10, 1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theodorakis, N.; Kreouzi, M.; Pappas, A.; Nikolaou, M. Beyond Calories: Individual Metabolic and Hormonal Adaptations Driving Variability in Weight Management—A State-of-the-Art Narrative Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 13438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, E.D.; Ferguson, J.J.; Stanford, J.; Collins, C.E. Dietary Assessment and Metabolomic Methodologies in Human Feeding Studies: A Scoping Review. Adv. Nutr. 2023, 14, 1453–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankararaman, S.; Noriega, K.; Velayuthan, S.; Sferra, T.; Martindale, R. Gut Microbiome and Its Impact on Obesity and Obesity-Related Disorders. Curr. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2023, 25, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hul, M.; Cani, P.D. The Gut Microbiota in Obesity and Weight Management: Microbes as Friends or Foe? Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2023, 19, 258–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarahmadi, A.; Afkhami, H.; Javadi, A.; Kashfi, M. Understanding the Complex Function of Gut Microbiota: Its Impact on the Pathogenesis of Obesity and beyond: A Comprehensive Review. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2024, 16, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, W.-K. Comparison between Obese and Non-Obese Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2023, 29, S58–S67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Yu, C.; He, Y.; Zhu, S.; Wang, S.; Xu, Z.; You, S.; Jiao, Y.; Liu, S.-L.; Bao, H. Integrative Metagenomic Analysis Reveals Distinct Gut Microbial Signatures Related to Obesity. Bmc Microbiol. 2024, 24, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.A.; Karavetian, M.; Moubareck, C.A.; Wazz, G.; Mahdy, T.; Venema, K. Association of the Gut Microbiota with Clinical Variables in Obese and Lean Emirati Subjects. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1182460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patloka, O.; Komprda, T.; Franke, G. Review of the Relationships between Human Gut Microbiome, Diet, and Obesity. Nutrients 2024, 16, 3996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarmiento-Andrade, Y.; Suárez, R.; Quintero, B.; Garrochamba, K.; Chapela, S.P. Gut Microbiota and Obesity: New Insights. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 1018212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Dang, Y. Roles of Gut Microbiota and Metabolites in Overweight and Obesity of Children. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 994930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Zhang, L.; Yang, L.; Chu, H. The Critical Role of Gut Microbiota in Obesity. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 1025706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamun, M.A.A.; Rakib, A.; Mandal, M.; Singh, U.P. Impact of a High-Fat Diet on the Gut Microbiome: A Comprehensive Study of Microbial and Metabolite Shifts during Obesity. Cells 2025, 14, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogal, B.; Blumberg, J.B.; Blander, G.; Jorge, M. Gut Microbiota–Informed Precision Nutrition in the Generally Healthy Individual: Are We There Yet? Curr. Dev. Nutr. 2021, 5, nzab107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Daza, M.C.; de Vos, W.M. Polyphenols as Drivers of a Homeostatic Gut Microecology and Immuno-Metabolic Traits of Akkermansia Muciniphila: From Mouse to Man. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 24, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Yue, C.; Tian, R.; Yu, L.; Tian, F.; Zhao, J.; Chen, W.; Zhai, Q. Akkermansia Muciniphila-Directed Polyphenol Chlorogenic Acid Intervention for Obesity in Mice. Food Sci. Hum. Well 2024, 13, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusco, W.; Lorenzo, M.B.; Cintoni, M.; Porcari, S.; Rinninella, E.; Kaitsas, F.; Lener, E.; Mele, M.C.; Gasbarrini, A.; Collado, M.C.; et al. Short-Chain Fatty-Acid-Producing Bacteria: Key Components of the Human Gut Microbiota. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, Y.P.; Bernardi, A.; Frozza, R.L. The Role of Short-Chain Fatty Acids from Gut Microbiota in Gut-Brain Communication. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 508738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Zheng, Y.; Gao, Y.; Xu, W. Dietary Fiber Intake and Gut Microbiota in Human Health. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 2507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, L.; Li, J.; Wu, Q.; Qian, L.; He, J.; Ni, Y.; Kovatcheva-Datchary, P.; Yuan, R.; Liu, S.; et al. Resistant Starch Intake Facilitates Weight Loss in Humans by Reshaping the Gut Microbiota. Nat. Metab. 2024, 6, 578–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbons, S.M.; Gurry, T.; Lampe, J.W.; Chakrabarti, A.; Dam, V.; Everard, A.; Goas, A.; Gross, G.; Kleerebezem, M.; Lane, J.; et al. Perspective: Leveraging the Gut Microbiota to Predict Personalized Responses to Dietary, Prebiotic, and Probiotic Interventions. Adv. Nutr. 2022, 13, 1450–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouskas, K.; Guela, M.; Pantoura, M.; Pagkalos, I.; Hassapidou, M.; Lalama, E.; Pfeiffer, A.F.H.; Decorte, E.; Cornelissen, V.; Wilson-Barnes, S.; et al. The Influence of an AI-Driven Personalized Nutrition Program on the Human Gut Microbiome and Its Health Implications. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Calderón, P.; Wiedemann, L.; Benítez-Páez, A. The Microbiota Composition Drives Personalized Nutrition: Gut Microbes as Predictive Biomarkers for the Success of Weight Loss Diets. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 1006747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chimatapu, S.N.; Mittelman, S.D.; Habib, M.; Osuna-Garcia, A.; Vidmar, A.P. Wearable Devices beyond Activity Trackers in Youth with Obesity: Summary of Options. Child. Obes. 2024, 20, 208–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del-Valle-Soto, C.; López-Pimentel, J.C.; Vázquez-Castillo, J.; Nolazco-Flores, J.A.; Velázquez, R.; Varela-Aldás, J.; Visconti, P. A Comprehensive Review of Behavior Change Techniques in Wearables and IoT: Implications for Health and Well-Being. Sensors 2024, 24, 2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, T.; Olds, T.; Curtis, R.; Blake, H.; Crozier, A.J.; Dankiw, K.; Dumuid, D.; Kasai, D.; O’Connor, E.; Virgara, R.; et al. Effectiveness of Wearable Activity Trackers to Increase Physical Activity and Improve Health: A Systematic Review of Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses. Lancet Digit. Health 2022, 4, e615–e626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mun, S.; Park, K.; Kim, J.-K.; Kim, J.; Lee, S. Assessment of Heart Rate Measurements by Commercial Wearable Fitness Trackers for Early Identification of Metabolic Syndrome Risk. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 23865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Naabi, Y.; Ibrahim, N.; Dhillon, J.S. Designing Sustainable Mobile Weight Management Applications: Information Technology (IT) Experts Perspectives. Mhealth 2024, 10, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coman, L.-I.; Ianculescu, M.; Paraschiv, E.-A.; Alexandru, A.; Bădărău, I.-A. Smart Solutions for Diet-Related Disease Management: Connected Care, Remote Health Monitoring Systems, and Integrated Insights for Advanced Evaluation. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, S.; Zhang, M.; Harris, K.; Fletcher, L.M.; Reneker, J.C. The Impact of Consumer Wearable Devices on Physical Activity and Adherence to Physical Activity in Patients with Cardiovascular Disease: A Systematic Review of Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses. Telemed. e-Health 2023, 29, 986–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Fan, C.; Cheng, L.; Wang, Y.; Peng, D.; Li, F.; Han, Y.; Wang, H. A Comparative Analysis of Energy Expenditure and Substrate Metabolism in Male University Students with Overweight/Obesity: Tabata vs HIIT and MICT. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1323093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, W.W.; Su, H.; Lan, X.Y.; Ni, Q.Y.; Wang, X.Y.; Cui, K.Y.; Zhang, L. Effects of High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) and Maximum Fat Oxidation Intensity Training (MFOIT) on Body Composition, Inflammation in Overweight and Obese Adults. Sci. Sport 2024, 39, 348–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Du, Y.; Liu, Y.; Hong, J.; Yin, X.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Chen, J.; Zhang, B.; et al. Development and Validation of a Smartwatch Algorithm for Differentiating Physical Activity Intensity in Health Monitoring. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 9530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, D.A.; Naoimh, M.M.; Josephine, G.; Weldon, J.C.; Farkowski, M.M.; Radoslaw, L.; Watkins, C.L.; Polychronis, D.; Caiani, E.G.; Potpara, T.S. Mobile Health Applications for Managing Atrial Fibrillation for Healthcare Professionals and Patients: A Systematic Review. EP Eur. 2020, 10, 1567–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunns, M.; Febrey, S.; Abbott, R.; Buckland, J.; Whear, R.; Shaw, L.; Bethel, A.; Boddy, K.; Coon, J.T.; Melendez-Torres, G.J. Evaluation of the Aspects of Digital Interventions That Successfully Support Weight Loss: Systematic Review with Component Network Meta-Analysis. J. Med. Internet Res. 2025, 27, e65443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joung, K.-I.; An, S.H.; Bang, J.S.; Kim, K.J. Comparative Effectiveness of Wearable Devices and Built-in Step Counters in Reducing Metabolic Syndrome Risk in South Korea: Population-Based Cohort Study. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth 2025, 13, e64527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahedani, A.D.; McLaughlin, T.; Veluvali, A.; Aghaeepour, N.; Hosseinian, A.; Agarwal, S.; Ruan, J.; Tripathi, S.; Woodward, M.; Hashemi, N.; et al. Digital Health Application Integrating Wearable Data and Behavioral Patterns Improves Metabolic Health. Npj Digit. Med. 2023, 6, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oster, H.S.; Gvili Perelman, M.; Kolomansky, A.; Neumann, D.; Mittelman, M. Erythropoietin Treatment Is Associated with Decreased Blood Glucose Levels in Hematologic Patients. Acta Haematol. 2020, 144, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.-C.; Hsieh, C.-Y.; Lu, K.-Y.; Sung, C.-H.; Ho, H.-Y.; Cheng, M.-L.; Chen, A.P.; Ng, S.-H.; Chen, F.-H.; Lin, G. Monitoring Early Glycolytic Flux Alterations Following Radiotherapy in Cancer and Immune Cells: Hyperpolarized Carbon-13 Magnetic Resonance Imaging Study. Metabolites 2021, 11, 518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pongutta, S.; Ajetunmobi, O.; Davey, C.; Ferguson, E.; Lin, L. Impacts of School Nutrition Interventions on the Nutritional Status of School-Aged Children in Asia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2022, 14, 589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albarrak, M.M.; Zakaria, N.; Meo, S.A. The Role of Mobile Health Applications (mHealth Apps) in Reshaping the Body Weight for Better Healthcare: A Cross-Sectional Study. Pak. J. Med. Sci. 2024, 40, 1930–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, M.W.; Rahman, R.; Nilima, S.I.; Tasnim, A.F.; Aziz, M.B. Health Behaviors and Outcomes of Mobile Health Apps and Patient Engagement in the USA. J. Comput. Commun. 2024, 12, 78–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoun, J.; Itani, H.; Alarab, N.; Elsehmawy, A. The Effectiveness of Combining Nonmobile Interventions with the Use of Smartphone Apps with Various Features for Weight Loss: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth 2022, 10, e35479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, C.E.; Zheng, K.; Chua, W.Y.; Nguyen, T.; Liu, C.; Koh, C.K.; Lee, G.K.Y.; Tay, C.M.; Ooi, B.C.; Wong, M.L. Development of a Dental Diet-Tracking Mobile App for Improved Caries-Related Dietary Behaviours: Key Features and Pilot Evaluation of Quality. Digit. Health 2024, 10, 20552076241228433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theodore Armand, T.P.; Kim, H.-C.; Kim, J.-I. Digital Anti-Aging Healthcare: An Overview of the Applications of Digital Technologies in Diet Management. J. Pers. Med. 2024, 14, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaiprasert, C.; Hidayanto, A.N. AI-Powered in the Digital Age: Ensemble Innovation Personalizes the Food Recommendations. J. Open Innov. Technol. Mark. Complex. 2024, 10, 100261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, W.; Kleter, G.A.; Bouzembrak, Y.; Dupouy, E.; Frewer, L.J.; Radwan Al Natour, F.N.; Marvin, H.J.P. Making Food Systems More Resilient to Food Safety Risks by Including Artificial Intelligence, Big Data, and Internet of Things into Food Safety Early Warning and Emerging Risk Identification Tools. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2024, 23, e13296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolivas, D.; Fraser, L.; Schweitzer, R.; Brukner, P.; Moschonis, G. A 6-Month mHealth Low-Carbohydrate Dietary Intervention Ameliorates Glycaemic and Cardiometabolic Risk Profile in People with Type 2 Diabetes. Nutrients 2025, 17, 937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarry, A.; Rice, J.; O’Connor, E.M.; Tierney, A.C. Usage of Mobile Applications or Mobile Health Technology to Improve Diet Quality in Adults. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, L.; Ordnung, M.; Forkmann, K.; Mehl, N.; Horstmann, A. A Randomized-Controlled Trial to Evaluate the App-Based Multimodal Weight Loss Program Zanadio for Patients with Obesity. Obesity 2023, 31, 1300–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gemesi, K.; Winkler, S.; Schmidt-Tesch, S.; Schederecker, F.; Hauner, H.; Holzapfel, C. Efficacy of an App-Based Multimodal Lifestyle Intervention on Body Weight in Persons with Obesity: Results from a Randomized Controlled Trial. Int. J. Obes. 2024, 48, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwakura, M.; Ozeki, C.; Jung, S.; Yamazaki, T.; Miki, T.; Nohara, M.; Nomura, K. An Umbrella Review of Efficacy of Digital Health Interventions for Workers. Npj Digit. Med. 2025, 8, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Yang, K. A Study of Massive Multidimensional Data Sharing and Interaction Algorithms Based on Cloud-Edge Collaboration. Discov. Appl. Sci. 2025, 7, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, D.; Lewerenz, S.; Carmo, A.; Martins, H. Interoperability of Telemonitoring Data in Digital Health Solutions: A Scoping Review. Front. Digit. Health 2025, 7, 1502260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christenson, A.; Hemmingsson, J.U.; Lagerros, Y.T. A National Data Sharing Solution for the Prevention and Treatment of Obesity—A Qualitative Study of Stakeholders’ Needs. Digit. Health 2024, 10, 20552076241297740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, I.; Lages, M.; Grilo, C.; Barros, R.; Guarino, M.P. mHealth Applications to Monitor Lifestyle Behaviors and Circadian Rhythm in Clinical Settings: Current Perspective and Future Directions. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 862065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höchsmann, C.; Yang, S.; Ordovás, J.M.; Dorling, J.L.; Champagne, C.M.; Apolzan, J.W.; Greenway, F.L.; Cardel, M.I.; Foster, G.D.; Martin, C.K. The Personalized Nutrition Study (POINTS): Evaluation of a Genetically Informed Weight Loss Approach, a Randomized Clinical Trial. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 6321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baines, R.; Stevens, S.; Austin, D.; Anil, K.; Bradwell, H.; Cooper, L.; Maramba, I.D.; Chatterjee, A.; Leigh, S. Patient and Public Willingness to Share Personal Health Data for Third-Party or Secondary Uses: Systematic Review. J. Med. Internet Res. 2024, 26, e50421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Mejías, S.; Degli-Esposti, S.; González-García, S.; Parra-Calderón, C.L. Toward the European Health Data Space: The IMPaCT-Data Secure Infrastructure for EHR-Based Precision Medicine Research. J. Biomed. Inform. 2024, 156, 104670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Drumpt, S.; Chawla, K.; Barbereau, T.; Spagnuelo, D.; van de Burgwal, L. Secondary Use under the European Health Data Space: Setting the Scene and towards a Research Agenda on Privacy-Enhancing Technologies. Front. Digit. Health 2025, 7, 1602101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Back, E.; Lee, S.; Shipley, R.; Mapitse, N.; Elbe, S.; Smallman, M.; Wilson, J.; Yasin, I.; Rees, G.; et al. Balancing Risks and Opportunities: Data-Empowered-Health Ecosystems. J. Med. Internet Res. 2025, 27, e57237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, K.; Wilmanski, T.; Diener, C.; Earls, J.C.; Zimmer, A.; Lincoln, B.; Hadlock, J.J.; Lovejoy, J.C.; Gibbons, S.M.; Magis, A.T.; et al. Multiomic Signatures of Body Mass Index Identify Heterogeneous Health Phenotypes and Responses to a Lifestyle Intervention. Nat. Med. 2023, 29, 996–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Kellogg, R.; Panyard, D.J.; Bararpour, N.; Castillo, K.E.; Lee-McMullen, B.; Delfarah, A.; Ubellacker, J.; Ahadi, S.; Rosenberg-Hasson, Y.; et al. Multi-Omics Microsampling for the Profiling of Lifestyle-Associated Changes in Health. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2024, 8, 11–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavai, A.K.; Hillegersberg, J. van AI-Driven Personalized Nutrition: RAG-Based Digital Health Solution for Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes. PLoS Digit. Health 2025, 4, e0000758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyene, H.B.; Giles, C.; Huynh, K.; Wang, T.; Cinel, M.; Mellett, N.A.; Olshansky, G.; Meikle, T.G.; Watts, G.F.; Hung, J.; et al. Metabolic Phenotyping of BMI to Characterize Cardiometabolic Risk: Evidence from Large Population-Based Cohorts. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 6280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trouwborst, I.; Gijbels, A.; Jardon, K.M.; Siebelink, E.; Hul, G.B.; Wanders, L.; Erdos, B.; Péter, S.; Singh-Povel, C.M.; de Bosch, J.V.; et al. Cardiometabolic Health Improvements upon Dietary Intervention Are Driven by Tissue-Specific Insulin Resistance Phenotype: A Precision Nutrition Trial. Cell Metab. 2023, 35, 71–83.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pescari, D.; Mihuta, M.S.; Bena, A.; Stoian, D. Quantitative Analysis of the Caloric Restriction versus Isocaloric Diets Models Based on Macronutrients Composition: Impacts on Body Weight Regulation, Anthropometric, and Bioimpedance Parameters in Women with Obesity. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1493954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekar, P.; Ventura, E.F.; Dhanapal, A.C.T.A.; Cheah, E.S.G.; Loganathan, A.; Quen, P.L.; Appukutty, M.; Taslim, N.A.; Hardinsyah, H.; Md Noh, M.F.; et al. Gene–Diet Interactions on Metabolic Disease-Related Outcomes in Southeast Asian Populations: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nacis, J.S.; Labrador, J.P.H.; Ronquillo, D.G.D.; Rodriguez, M.P.; Dablo, A.M.F.D.; Frane, R.D.; Madrid, M.L.; Santos, N.L.C.; Carrillo, J.J.V.; Fernandez, M.G.; et al. A Study Protocol for a Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial to Evaluate the Effectiveness of a Gene-Based Nutrition and Lifestyle Recommendation for Weight Management among Adults: The MyGeneMyDiet® Study. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1238234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, A.-R.; Hong, K.-W.; Kwon, Y.-J.; Choi, J.-E.; Lee, H.-S.; Kim, H.-M.; Bae, S.J.; Ahn, S.G.; Jeong, J.; Lee, J.-W. Effects of Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms and Mediterranean Diet in Overweight or Obese Postmenopausal Women with Breast Cancer Receiving Adjuvant Hormone Therapy: A Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 882717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasaei, N.; Fallah, M.; Nemati, M.; Gholami, F.; Ghaffarian-Ensaf, R.; Mirzaei, K. Investigation the Interaction of Dietary Fat Quality Indices and the MC4R Gene in Metabolically Healthy and Unhealthy Overweight and Obese Women. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 12183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imangaliyeva, A.; Sikhayeva, N.; Bolatov, A.; Utupov, T.; Romanova, A.; Akhmetollayev, I.; Zholdybayeva, E. Genetic Insights into Severe Obesity: A Case Study of MC4R Variant Identification and Clinical Implications. Genes 2025, 16, 508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohlmeier, M.; Baah, E.; Washko, M.; Adams, K. Genotype-Informed Nutrition Counselling in Clinical Practice. BMJ Nutr. Prev. Health 2023, 6, 407–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.-H.; Choi, H.-K.; Park, J.H.; Hwang, J.-T. Current Insights into Genome-Based Personalized Nutrition Technology: A Patent Review. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1346144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merovci, A.; Finley, B.; Hansis-Diarte, A.; Neppala, S.; Abdul-Ghani, M.A.; Cersosimo, E.; Triplitt, C.; DeFronzo, R.A. Effect of Weight-Maintaining Ketogenic Diet on Glycemic Control and Insulin Sensitivity in Obese T2D Subjects. BMJ Open Diabetes Res. Care 2024, 12, e004199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinott, E.; Meir, A.Y.; Tsaban, G.; Zelicha, H.; Kaplan, A.; Knights, D.; Tuohy, K.; Scholz, M.U.; Koren, O.; Stampfer, M.J.; et al. The Effects of the Green-Mediterranean Diet on Cardiometabolic Health Are Linked to Gut Microbiome Modifications: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Genome Med. 2022, 14, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duca, F.A.; Waise, T.M.Z.; Peppler, W.T.; Lam, T.K.T. The Metabolic Impact of Small Intestinal Nutrient Sensing. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Liu, M.; Cao, S.; Liu, B.; Li, D.; Wang, Z.; Sun, H.; Cui, Y.; Shi, Y. The Mechanism of the Gut-Brain Axis in Regulating Food Intake. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, R.; Fogelholm, M.; Larsen, T.M.; Poppitt, S.D.; Silvestre, M.P.; Vestentoft, P.S.; Jalo, E.; Navas-Carretero, S.; Huttunen-Lenz, M.; Taylor, M.A.; et al. A High-Protein, Low Glycemic Index Diet Suppresses Hunger but Not Weight Regain after Weight Loss: Results from a Large, 3-Years Randomized Trial (PREVIEW). Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 685648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van-Wehle, T.; Vital, M. Investigating the Response of the Butyrate Production Potential to Major Fibers in Dietary Intervention Studies. Npj Biofilms Microbiomes 2024, 10, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, H.; Tan, Y.; Yu, D.; Qiu, S.; Bai, Y.; He, J.; Cao, H.; Che, Q.; Guo, J.; Su, Z. The Therapeutic Effect of SCFA-Mediated Regulation of the Intestinal Environment on Obesity. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 886902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, R.; Chen, Y.; Cao, Z.; Liu, C.; Bao, R.; Wang, Y.; Huang, S.; Pan, S.; Qin, L.; et al. Akkermansia Muciniphila Supplementation in Patients with Overweight/Obese Type 2 Diabetes: Efficacy Depends on Its Baseline Levels in the Gut. Cell Metab. 2025, 37, 592–605.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoer, S.; Shilo, S.; Godneva, A.; Ben-Yacov, O.; Rein, M.; Wolf, B.C.; Lotan-Pompan, M.; Bar, N.; Weiss, E.I.; Houri-Haddad, Y.; et al. Impact of Dietary Interventions on Pre-Diabetic Oral and Gut Microbiome, Metabolites and Cytokines. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 5384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monnard, C.R.; Dulloo, A.G. Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids as Modulators of Fat Mass and Lean Mass in Human Body Composition Regulation and Cardiometabolic Health. Obes. Rev. 2021, 22, e13197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Chen, Z. Effect of Dietary Polyphenols along with Exercise on Hepatic Transcriptional Regulators of Lipid Metabolism. Front. Nutr. 2025, 12, 1531327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, A.; Meir, A.Y.; Hagemann, T.; Czechowski, P.; Müller, L.; Engelmann, B.; Haange, S.-B.; Rolle-Kampczyk, U.; Tsaban, G.; Zelicha, H.; et al. A Polyphenol-Rich Green Mediterranean Diet Enhances Epigenetic Regulatory Potential: The DIRECT PLUS Randomized Controlled Trial. Metabolism 2023, 145, 155594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rondanelli, M.; Gasparri, C.; Pirola, M.; Barrile, G.C.; Moroni, A.; Sajoux, I.; Perna, S. Does the Ketogenic Diet Mediate Inflammation Markers in Obese and Overweight Adults? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials. Nutrients 2024, 16, 4002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.-M.; Kim, Y. Is Curcumin Intake Really Effective for Chronic Inflammatory Metabolic Disease? A Review of Meta-Analyses of Randomized Controlled Trials. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhry, M.; Kumar, M.; Singhal, V.; Srinivasan, B. Metabolic Health Tracking Using Ultrahuman M1 Continuous Glucose Monitoring Platform in Non- and Pre-Diabetic Indians: A Multi-Armed Observational Study. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 6490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corfmat, M.; Martineau, J.T.; Régis, C. High-Reward, High-Risk Technologies? An Ethical and Legal Account of AI Development in Healthcare. Bmc Med. Ethics 2025, 26, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, J.C.; Breen, J.A.; Pan, Z.; Nicklas, J.; Cornier, M.-A. A Randomized, Crossover Trial Assessing Appetite, Energy Metabolism, Blood Biomarkers, and Ad Libitum Food Intake Responses to a Mid-Morning Pecan Snack vs. an Equicaloric High-Carbohydrate Snack in Healthy Volunteers with Overweight/Obesity. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, H.; Bagherniya, M.; Sahebkar, A.; Iraj, B.; Majeed, M.; Askari, G. The Effect of Curcumin-Piperine Supplementation on Lipid Profile, Glycemic Index, Inflammation, and Blood Pressure in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Hypertriglyceridemia. Phytother. Res. 2024, 38, 5150–5161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, C.E.; Hatley, K.E.; Polzien, K.; Diamond, M.; Tate, D.F. Testing a Personalized Behavioral Weight Loss Approach Using Multifactor Prescriptions and Self-experimentation: 12-week mHealth Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial Results. Obes. Sci. Pract. 2025, 11, e70051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Huang, K.; Yang, D.; Zhao, W.; Zhou, X. Biomedical Big Data Technologies, Applications, and Challenges for Precision Medicine: A Review. Glob. Chall. 2024, 8, 2300163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alarcón Garavito, G.A.; Moniz, T.; Déom, N.; Redin, F.; Pichini, A.; Vindrola-Padros, C. The Implementation of Large-Scale Genomic Screening or Diagnostic Programmes: A Rapid Evidence Review. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2023, 31, 282–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Singh, R.P.; Yadav, P.; Kumar, I.; Kaushik, A.; Roychowdhury, R.; Mubeen, M.; Singh, S.K.; Kumar, A.; Wang, J. Recent Advances in Biotechnology and Bioengineering for Efficient Microalgal Biofuel Production. Fuel Process Technol. 2025, 270, 108199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambalavanan, R.; Snead, R.S.; Marczika, J.; Towett, G.; Malioukis, A.; Mbogori-Kairichi, M. Challenges and Strategies in Building a Foundational Digital Health Data Integration Ecosystem: A Systematic Review and Thematic Synthesis. Front. Health Serv. 2025, 5, 1600689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatiwada, P.; Yang, B.; Lin, J.-C.; Blobel, B. Patient-Generated Health Data (PGHD): Understanding, Requirements, Challenges, and Existing Techniques for Data Security and Privacy. J. Pers. Med. 2024, 14, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripura, U.; Nagrale, N.V.; Singh, O.G.; Dey, A.; Venkatesh, J. Ethical, social, and legal issues related to precision medicine in India: Challenges and solutions. Ann. Afr. Med. 2025, 10, 4103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azmi, S.; Kunnathodi, F.; Alotaibi, H.F.; Alhazzani, W.; Mustafa, M.; Ahmad, I.; Anvarbatcha, R.; Lytras, M.D.; Arafat, A.A. Harnessing Artificial Intelligence in Obesity Research and Management: A Comprehensive Review. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta, J.N.; Falcone, G.J.; Rajpurkar, P.; Topol, E.J. Multimodal Biomedical AI. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 1773–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charfare, R.H.; Desai, A.U.; Keni, N.N.; Nambiar, A.S.; Cherian, M.M. Smart Healthcare Framework: Real-Time Vital Monitoring and Personalized Diet and Fitness Recommendations Using IoT and Machine Learning. Int. J. Robot. Control Syst. 2025, 5, 1254–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spring, B.; Pfammatter, A.F.; Scanlan, L.; Daly, E.; Reading, J.; Battalio, S.; McFadden, H.G.; Hedeker, D.; Siddique, J.; Nahum-Shani, I. An Adaptive Behavioral Intervention for Weight Loss Management: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2024, 332, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luca, V.; Virgolesi, M.; Vetrani, C.; Aprano, S.; Cantelli, F.; Di Martino, A.; Mercurio, L.; Iaccarino, G.; Isgrò, F.; Arpaia, P.; et al. Digital Interventions for Weight Control to Prevent Obesity in Adolescents: A Systematic Review. Front. Public Health 2025, 13, 1584595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, X.; Xu, M.; Wang, H.; Zhu, L. Integrating Precision Medicine and Digital Health in Personalized Weight Management: The Central Role of Nutrition. Nutrients 2025, 17, 2695. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17162695
Liu X, Xu M, Wang H, Zhu L. Integrating Precision Medicine and Digital Health in Personalized Weight Management: The Central Role of Nutrition. Nutrients. 2025; 17(16):2695. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17162695
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Xiaoguang, Miaomiao Xu, Huiguo Wang, and Lin Zhu. 2025. "Integrating Precision Medicine and Digital Health in Personalized Weight Management: The Central Role of Nutrition" Nutrients 17, no. 16: 2695. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17162695
APA StyleLiu, X., Xu, M., Wang, H., & Zhu, L. (2025). Integrating Precision Medicine and Digital Health in Personalized Weight Management: The Central Role of Nutrition. Nutrients, 17(16), 2695. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17162695







