Gentianaceae Family—Derived Bioactive Compounds—Therapeutic Values and Supporting Role in Inflammation and Detoxification
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology for Search Strategy and Inclusion Criteria
3. Development of Gentiana-Based Supplements and Herbal Remedies
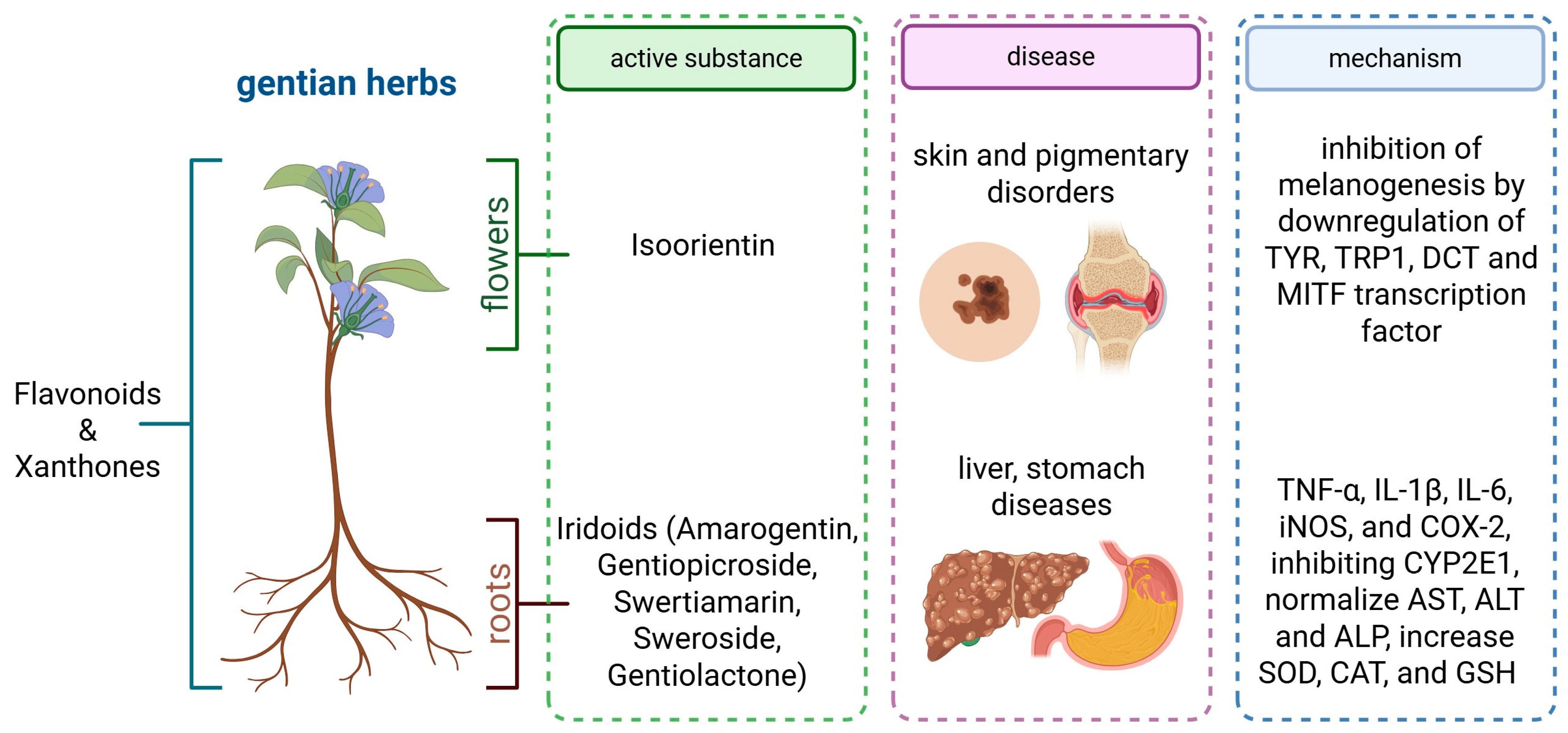
4. Overview of Gentian Herbs
4.1. Phytochemistry of Gentian Herbs
4.1.1. Amarogentin—Anti-Fibrotic and Antithrombotic Activity
4.1.2. Gentiopicroside and Inflammatory Properties
4.1.3. Swertiamarin—Neuro- and Hepatoprotection
4.1.4. Luteoloside—Autophagy-Mediated Anticancer Effects
4.1.5. Isovitexin—Anti-Atherosclerotic Potential
4.1.6. Isoorientin—Anti-Melanogenic Activity
4.1.7. Gentiolactone—Targeted Anti-Inflammation
4.1.8. Bellidifolin—Neuroprotection in Ischemia
4.2. Chemical Composition and Pharmacological Significance
5. Therapeutic Properties of Gentian Herbs
6. Digestive Health Benefits—Potential Role in Liver Protection and Detoxification
7. Other Applications for Gentian Extracts in Medicine
7.1. Anti-Bacterial and Anti-Inflammatory Effects
7.2. Appetite Stimulation
8. Discussion
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barone, R.P.; Knittel, D.K.; Ooka, J.K.; Porter, L.N.; Smith, N.T.; Owens, D.K. The Production of Plant Natural Products Beneficial to Humanity by Metabolic Engineering. Curr. Plant Biol. 2020, 24, 100121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaee, F.; Hosseini, A.; Jouybari, H.B.; Davoodi, A.; Azadbakht, M. Medicinal, Biological and Phytochemical Properties of Gentiana Species. J. Tradit. Complement. Med. 2017, 7, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Cui, B.W.; Wu, Y.L.; Nan, J.X.; Lian, L.H. Genus Gentiana: A Review on Phytochemistry, Pharmacology and Molecular Mechanism. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 264, 113391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirintsos, S.; Panagiotopoulos, A.; Bariotakis, M.; Daskalakis, V.; Lionis, C.; Sourvinos, G.; Karakasiliotis, I.; Kampa, M.; Castanas, E. From Traditional Ethnopharmacology to Modern Natural Drug Discovery: A Methodology Discussion and Specific Examples. Molecules 2022, 27, 4060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maley, A.M.; Arbiser, J.L. Gentian Violet: A 19th Century Drug Re-emerges in the 21st Century. Exp. Dermatol. 2013, 22, 775–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasdaran, A.; Naychov, Z.; Batovska, D.; Kerr, P.; Favre, A.; Dimitrov, V.; Aneva, I.; Hamedi, A.; Kozuharova, E. Some European Gentiana Species Are Used Traditionally to Cure Wounds: Bioactivity and Conservation Issues. Diversity 2023, 15, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Gong, X.; Bo, A.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, M.; Zang, E.; Zhang, C.; Li, M. Iridoids: Research Advances in Their Phytochemistry, Biological Activities, and Pharmacokinetics. Molecules 2020, 25, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, A.; Khan, A.; Ahmad, I.; Alghamdi, S.; Rajab, B.S.; Babalghith, A.O.; Alshahrani, M.Y.; Islam, S.; Islam, M.R. Flavonoids a Bioactive Compound from Medicinal Plants and Its Therapeutic Applications. BioMed Res. Int. 2022, 2022, 5445291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panche, A.N.; Diwan, A.D.; Chandra, S.R. Flavonoids: An Overview. J. Nutr. Sci. 2016, 5, e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hostettmann-Kaldas, M.; Hostettmann, K.; Sticher, O. Xanthones, Flavones and Secoiridoids of American Gentiana Species. Phytochemistry 1981, 20, 443–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amarogentin|C29H30O13|CID 115149—PubChem. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Amarogentin (accessed on 4 August 2025).
- Gentiopicroside|C16H20O9|CID 88708—PubChem. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Gentiopicroside (accessed on 4 August 2025).
- Swertiamarin|C16H22O10|CID 442435—PubChem. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Swertiamarin (accessed on 4 August 2025).
- Luteolin 7-O-Glucoside|C21H20O11|CID 5280637—PubChem. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Luteolin-7-O-glucoside (accessed on 4 August 2025).
- Isovitexin|C21H20O10|CID 162350—PubChem. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Isovitexin (accessed on 4 August 2025).
- Isoorientin|C21H20O11|CID 114776—PubChem. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Isoorientin (accessed on 4 August 2025).
- SID 241116665—PubChem. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/241116665 (accessed on 4 August 2025).
- Bellidifolin|C14H10O6|CID 5281623—PubChem. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Bellidifolin (accessed on 4 August 2025).
- Azman, N.A.M.; Segovia, F.; Martínez-Farré, X.; Gil, E.; Almajano, M.P. Screening of Antioxidant Activity of Gentian Lutea Root and Its Application in Oil-in-Water Emulsions. Antioxidants 2014, 3, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibitz-Eisath, N.; Seger, C.; Schwaiger, S.; Sturm, S.; Stuppner, H. Simultaneous Quantitative Analysis of the Major Bioactive Compounds in Gentianae Radix and Its Beverages by UHPSFC-DAD. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 7586–7593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.Y.; Wong, Z.C.F.; Wang, C.; Fung, A.H.Y.; Wong, E.O.Y.; Chan, G.K.L.; Dong, T.T.X.; Chen, Y.; Tsim, K.W.K. Isoorientin Derived from Gentiana veitchiorum Hemsl. Flowers Inhibits Melanogenesis by down-Regulating MITF-Induced Tyrosinase Expression. Phytomedicine 2019, 57, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cafaro, T.; Carnicelli, V.; Caprioli, G.; Maggi, F.; Celenza, G.; Perilli, M.; Bozzi, A.; Amicosante, G.; Brisdelli, F. Anti-Apoptotic and Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Gentiana lutea Root Extract. Adv. Tradit. Med. 2020, 20, 619–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tovilovic-Kovacevic, G.; Zogovic, N.; Krstic-Milosevic, D. Secondary Metabolites from Endangered Gentiana, Gentianella, Centaurium, and Swertia Species (Gentianaceae): Promising Natural Biotherapeutics. In Biodiversity and Biomedicine: Our Future; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 335–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-Z.; Maier, U.H.; Eisenreich, W.; Adam, P.; Obersteiner, I.; Keil, M.; Bacher, A.; Zenk, M.H. Unexpected Biosynthetic Precursors of Amarogentin—A Retrobiosynthetic 13C NMR Study. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2001, 2001, 1459–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, H.; Li, H.; Cao, W.; Wang, F.; Zhang, T.; Wang, S.-W. Protective Effects of Amarogentin against Carbon Tetrachloride-Induced Liver Fibrosis in Mice. Molecules 2017, 22, 754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, S. Cytokines and Fibrogenesis. Semin. Liver Dis. 1999, 19, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, T.-L.; Lu, W.-J.; Lien, L.-M.; Thomas, P.A.; Lee, T.-Y.; Chiu, H.-C.; Sheu, J.-R.; Lin, K.-H. Amarogentin, a Secoiridoid Glycoside, Abrogates Platelet Activation through PLC γ 2-PKC and MAPK Pathways. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 728019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, K.; Yi, X.-J.; Huang, X.-J.; Muhammad, A.; Li, M.; Li, J.; Yang, G.-Z.; Gao, Y. Hepatoprotective Activity of Iridoids, Seco-Iridoids and Analog Glycosides from Gentianaceae on HepG2 Cells via CYP3A4 Induction and Mitochondrial Pathway. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 2673–2683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.-T.; Zhao, Y.-P.; Jiao, Y.-F.; Zheng, J.; Yang, W.-L.; Zhou, R.; Niu, Y.; Sun, T.; Li, Y.-X.; Yu, J.-Q. Protective Effect of Gentiopicroside against Dextran Sodium Sulfate Induced Colitis in Mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2016, 39, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Yu, F.; Li, R.; Wang, R. Inhibitory Effects of the Gentiana macrophylla (Gentianaceae) Extract on Rheumatoid Arthritis of Rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2004, 95, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, R.X.; Wolfender, J.L.; Zhang, L.X.; Ma, W.G.; Fuzzati, N.; Marston, A.; Hostettmann, K. Acyl Secoiridoids and Antifungal Constituents from Gentiana macrophylla. Phytochemistry 1996, 42, 1305–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, L.-H.; Wu, Y.-L.; Song, S.-Z.; Wan, Y.; Xie, W.-X.; Li, X.; Bai, T.; Ouyang, B.-Q.; Nan, J.-X. Gentiana manshurica Kitagawa Reverses Acute Alcohol-Induced Liver Steatosis through Blocking Sterol Regulatory Element-Binding Protein-1 Maturation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 13013–13019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, Q.; Xia, K.; Jiang, M.; Cui, B.; Wu, Y.; Song, S.; Lian, L.; Nan, J. Liver Kinase B1/AMP-activated Protein Kinase-mediated Regulation by Gentiopicroside Ameliorates P2X7 Receptor-dependent Alcoholic Hepatosteatosis. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 175, 1451–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lian, L.-H.; Wu, Y.-L.; Wan, Y.; Li, X.; Xie, W.-X.; Nan, J.-X. Anti-Apoptotic Activity of Gentiopicroside in d-Galactosamine/Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Murine Fulminant Hepatic Failure. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2010, 188, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Yang, Q.; Yang, F.; Gong, J.; Han, H.; Yang, L.; Wang, Z. Target Profiling Analyses of Bile Acids in the Evaluation of Hepatoprotective Effect of Gentiopicroside on ANIT-Induced Cholestatic Liver Injury in Mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 194, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, M.; Yin, J.; Zhang, X.; Hong, Z. Gentiopicroside Ameliorates Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis in Mice via Inhibiting Inflammatory and Fibrotic Process. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 495, 2396–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Xie, L.; Kang, R.; Deng, R.; Xi, Z.; Sun, D.; Zhu, J.; Wang, L. Gentiopicroside Inhibits RANKL-Induced Osteoclastogenesis by Regulating NF-ΚB and JNK Signaling Pathways. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 100, 142–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.-T.; Wang, X.-S.; Zhao, M.-G.; Huang, X.-X.; Xu, X.-L. Gentiopicroside Protects Neurons from Astrocyte-Mediated Inflammatory Injuries by Inhibition of Nuclear Factor-ΚB and Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Signaling Pathways. Neuroreport 2018, 29, 1114–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konya, R.; Reis, R.; Sipahi, H.; Barta, A.; Hohmann, J.; Kırmızıbekmez, H. Secondary Metabolites from Gentiana cruciata L. and Their Anti-Inflammatory and Analgesic Activities. Nat. Prod. Res. 2023, 37, 3025–3032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Wei, W.; Lan, X.; Liu, N.; Li, Y.; Ma, H.; Sun, T.; Peng, X.; Zhuang, C.; Yu, J. Neuroprotective Effect of Swertiamain on Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury by Inducing the Nrf2 Protective Pathway. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2019, 10, 2276–2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.M.U.; Luo, L.; Namani, A.; Wang, X.J.; Tang, X. Nrf2 Signaling Pathway: Pivotal Roles in Inflammation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Basis Dis. 2017, 1863, 585–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wang, Q.; Tao, Y.; Liu, C. Swertiamarin Attenuates Experimental Rat Hepatic Fibrosis by Suppressing Angiotensin II-Angiotensin Type 1 Receptor-Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase Signaling. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2016, 359, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Song, H. Antioxidant and Hepatoprotective Effect of Swertiamarin on Carbon Tetrachloride-Induced Hepatotoxicity via the Nrf2/HO-1 Pathway. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 41, 2242–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaishree, V.; Badami, S. Antioxidant and Hepatoprotective Effect of Swertiamarin from Enicostemma Axillare against D-Galactosamine Induced Acute Liver Damage in Rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2010, 130, 103–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Shen, S.; Zhao, X.; Gong, X. Luteoloside Induces G0/G1 Arrest and pro-Death Autophagy through the ROS-Mediated AKT/MTOR/P70S6K Signalling Pathway in Human Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cell Lines. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 494, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.; Wang, Y.; Lu, J.; Zheng, Y.; Wu, D.; Li, M.; Hu, B.; Zhang, Z.; Cheng, W.; Shan, Q. Luteoloside Suppresses Proliferation and Metastasis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells by Inhibition of NLRP3 Inflammasome. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e89961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olennikov, D.; Kashchenko, N.; Chirikova, N.; Tankhaeva, L. Iridoids and Flavonoids of Four Siberian Gentians: Chemical Profile and Gastric Stimulatory Effect. Molecules 2015, 20, 19172–19188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kesavan, R.; Potunuru, U.R.; Nastasijević, B.; T, A.; Joksić, G.; Dixit, M. Inhibition of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Proliferation by Gentiana lutea Root Extracts. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesavan, R.; Chandel, S.; Upadhyay, S.; Bendre, R.; Ganugula, R.; Potunuru, U.R.; Giri, H.; Sahu, G.; Kumar, P.U.; Reddy, G.B.; et al. Gentiana lutea Exerts Anti-Atherosclerotic Effects by Preventing Endothelial Inflammation and Smooth Muscle Cell Migration. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2016, 26, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, H.; Kikuchi, S.; Inui, T.; Takahashi, H.; Kimura, K. Gentiolactone, a Secoiridoid Dilactone from Gentiana triflora, Inhibits TNF-α, INOS and Cox-2 MRNA Expression and Blocks NF-ΚB Promoter Activity in Murine Macrophages. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e113834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Gao, Y.; Gao, L.; Zhang, M.; Wang, H.; Zhang, C. Protective Effects of Bellidifolin in Hypoxia-Induced in Pheochromocytoma Cells (PC12) and Underlying Mechanisms. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A 2017, 80, 1187–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihailović, V.; Katanić, J.; Mišić, D.; Stanković, V.; Mihailović, M.; Uskoković, A.; Arambašić, J.; Solujić, S.; Mladenović, M.; Stanković, N. Hepatoprotective Effects of Secoiridoid-Rich Extracts from Gentiana cruciata L. against Carbon Tetrachloride Induced Liver Damage in Rats. Food Funct. 2014, 5, 1795–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.-H.; Liu, C.-T.; Raghu, R.; Sheen, L.-Y. Therapeutic Potential of Chinese Herbal Medicines in Alcoholic Liver Disease. J. Tradit. Complement. Med. 2012, 2, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.-H.; Liu, X.-Q.; Zhang, C.; He, W.; Wang, H.; Chen, Y.-H.; Liu, X.-J.; Chen, X.; Xu, D.-X. Tlr4-Mutant Mice Are Resistant to Acute Alcohol-Induced Sterol-Regulatory Element Binding Protein Activation and Hepatic Lipid Accumulation. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, M.; Yu, B.; Xu, L.; Zhang, L.; Long, J.; Shen, X. Attenuation of Stress-Induced Gastrointestinal Motility Disorder by Gentiopicroside, from Gentiana macrophylla Pall. Fitoterapia 2015, 103, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayebi, E.; Azadbakht, M.; Zamanfar, D.; Karami, H.; Fard, R.E.; Kokhdan, A.J.; Cherati, J.Y. Appetizing Effect of Gentiana olivieri Extract in Children with Anorexia. J. Mazandaran Univ. Med. Sci. 2016, 26, 58–66. [Google Scholar]
- Niiho, Y.; Yamazaki, T.; Nakajima, Y.; Yamamoto, T.; Ando, H.; Hirai, Y.; Toriizuka, K.; Ida, Y. Gastroprotective Effects of Bitter Principles Isolated from Gentian Root and Swertia Herb on Experimentally-Induced Gastric Lesions in Rats. J. Nat. Med. 2006, 60, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joksic, G.; Radak, D.; Sudar-Milovanovic, E.; Obradovic, M.; Radovanovic, J.; Isenovic, E.R. Effects of Gentiana lutea Root on Vascular Diseases. Curr. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2021, 19, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wölfle, U.; Haarhaus, B.; Seiwerth, J.; Cawelius, A.; Schwabe, K.; Quirin, K.-W.; Schempp, C. The Herbal Bitter Drug Gentiana lutea Modulates Lipid Synthesis in Human Keratinocytes In Vitro and In Vivo. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmieder, A.; Schwaiger, S.; Csordas, A.; Backovic, A.; Messner, B.; Wick, G.; Stuppner, H.; Bernhard, D. Isogentisin—A Novel Compound for the Prevention of Smoking-Caused Endothelial Injury. Atherosclerosis 2007, 194, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Ye, J.; Wu, G.; Peng, X.; Xia, P.; Ren, Y. Gentiopicroside Prevents Interleukin-1 Beta Induced Inflammation Response in Rat Articular Chondrocyte. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 172, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, A. Ketoconazole-Induced Testicular Damage in Rats Reduced by Gentiana Extract. Exp. Toxicol. Pathol. 2008, 59, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Xi, S.; He, W.; Ma, X.; Liu, L.; Xu, J.; Zhang, K.; Li, Y.; Jin, L. The Effects of Gentiana dahurica Fisch on Alcoholic Liver Disease Revealed by RNA Sequencing. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 279, 113422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Song, X.; Sun, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, D. A Comprehensive Review of Phytochemistry, Pharmacology and Clinical Application of Gentianae macrophyllae Radix. Nat. Prod. Res. 2024, 38, 4446–4467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viljoen, A.; Mncwangi, N.; Vermaak, I. Anti-Inflammatory Iridoids of Botanical Origin. Curr. Med. Chem. 2012, 19, 2104–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, N.; Ma, H.; Zhang, T.; Wang, L.; Cui, J.; Zha, Y.; Ding, Y.; Wang, J. Gentiopicroside Attenuates Collagen-Induced Arthritis in Mice via Modulating the CD147/P38/NF-ΚB Pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2022, 108, 108854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.-Q.; Luo, Y.-X.; Zhang, Y.-J.; Li, Z.-X.; Wen, Y.; Zhang, K.; Li, D.-L.; Jin, J.-W.; Wu, R.-H.; Gan, L.-S. Terpenoid Glucosides from Gentiana macrophylla That Attenuate TNF-α Induced Pulmonary Inflammation in A549 Cells. Molecules 2023, 28, 6613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konya, R.; Reis, R.; Sipahi, H.; Barta, A.; Hohmann, J.; Kirmizibekmez, H. Iridoids and Flavonoids from the Aerial Parts of Gentiana asclepiadea L. with Anti-Inflammatory and Analgesic Activities. J. Res. Pharm. 2023, 27, 1202–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Mao, J.; Liang, Y.; Gao, T.; Wang, S.; Zhang, D. Comparative Analysis of Four Iridoids between Gentiana rigescens and G. cephalantha from the Sympatric and Allopatric Distributions. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2024, 114, 104817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olennikov, D.N.; Gadimli, A.I.; Isaev, J.I.; Kashchenko, N.I.; Prokopyev, A.S.; Kataeva, T.N.; Chirikova, N.K.; Vennos, C. Caucasian Gentiana Species: Untargeted LC-MS Metabolic Profiling, Antioxidant and Digestive Enzyme Inhibiting Activity of Six Plants. Metabolites 2019, 9, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, W.; Zheng, P.; He, Y.; Cui, L.; Kong, W.; Wang, Z. An Insight into the Genes Involved in Secoiridoid Biosynthesis in Gentiana macrophylla by RNA-Seq. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2014, 41, 4817–4825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Wang, M.; Li, Z.; Wu, X.; Liu, X. Transcriptome Analysis and Exploration of Genes Involved in the Biosynthesis of Secoiridoids in Gentiana rhodantha. PeerJ 2023, 11, e14968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maituoheti, R.; Rouzimaimaiti, R.; Tang, D.; Zhao, J.; Aisa, H.A. Seco-Iridoid Glycosides from the Gentiana olivieri Griseb and Their Bioactivities. Phytochemistry 2023, 215, 113839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karalija, E.; Ćavar Zeljković, S.; Dahija, S.; Bešta-Gajević, R.; Parić, A. Phenolics of Aerial Parts of Gentiana lutea L. and Their Biological Activity. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olennikov, D.N.; Chirikova, N.K. New Compounds from Siberian Gentiana Species. I. Iridoid Glycosides. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2021, 57, 673–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaska, A.; Seçme, M. The Antioxidant Potential, Phenolic Compounds, Cytotoxic Activity and Mineral Element Analysis of Gentiana septemfida Pallas and Its Antiproliferative Effect on HT-29 Cell Line. Eur. J. Integr. Med. 2023, 59, 102240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, C.; Xie, L.; Guo, Y. Phytochemical Analysis and Antibacterial Activity of Gentiana macrophylla Extract against Bacteria Isolated from Burn Wound Infections. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 114, 25–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asnaashari, S.; Dastmalchi, S.; Javadzadeh, Y. Gastroprotective Effects of Herbal Medicines (Roots). Int. J. Food Prop. 2018, 21, 902–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudrić, J.; Šavikin, K.; Đekić, L.; Pavlović, S.; Kurćubić, I.; Ibrić, S.; Đuriš, J. Development of Lipid-Based Gastroretentive Delivery System for Gentian Extract by Double Emulsion–Melt Dispersion Technique. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudrić, J.; Pajić, M.; Bigović, D.; Ðuriš, J. Development of Gastroretentive Floating Granules with Gentian Root Extract by Hot-Melt Granulation. Lek. Sirovine 2020, 40, 40–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Huang, B.; He, J.; Han, L.; Zhan, Y.; Wang, Y. In Vitro and in Vivo Antioxidant Effects of the Ethanolic Extract of Swertia chirayita. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 136, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swati, K.; Bhatt, V.; Sendri, N.; Bhatt, P.; Bhandari, P. Swertia chirayita: A Comprehensive Review on Traditional Uses, Phytochemistry, Quality Assessment and Pharmacology. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023, 300, 115714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagalekshmi, R.; Menon, A.; Chandrasekharan, D.K.; Nair, C.K.K. Hepatoprotective Activity of Andrographis Paniculata and Swertia chirayita. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2011, 49, 3367–3373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, N.-J.; Geng, C.-A.; Huang, X.-Y.; Ma, Y.-B.; Zhang, X.-M.; Wang, J.-L.; Chen, J.-J. Anti-Hepatitis B Virus Active Constituents from Swertia chirayita. Fitoterapia 2015, 100, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.L.; Dorje, G.; Wang, Z.T. Identification of Medicinal Plants Used as Tibetan Traditional Medicine Jie-Ji. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2010, 132, 122–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, L.P. Acetaminophen. In Drug-Induced Liver Disease; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 331–341. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, A.-Y.; Lian, L.-H.; Jiang, Y.-Z.; Wu, Y.-L.; Nan, J.-X. Gentiana manshurica Kitagawa Prevents Acetaminophen-Induced Acute Hepatic Injury in Mice via Inhibiting JNK/ERK MAPK Pathway. World J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 16, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Ge, Y.-B.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, X.-J.; Chen, G.-X. The Distribution, Uses, and Characteristic Components of Gentianaceae Plants in China. World J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2021, 7, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J. Bioactive Glycosides from Chinese Medicines. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 1991, 86, 231–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, X.; Zhang, F.; Gao, Q.; Xing, R.; Chen, S. A Review on the Ethnomedicinal Usage, Phytochemistry, and Pharmacological Properties of Gentianeae (Gentianaceae) in Tibetan Medicine. Plants 2021, 10, 2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Q.-E.; A, Y.-S.; Bai, Y.-Q.; Sa, C.-L. Gentiana macrophylla Pall.: A Review of the Basic Source, Traditional Use, Chemical Components, Pharmacological Activities and Quality Control. Tradit. Med. Res. 2024, 9, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Jiang, L.; Shao, Y.; Mei, L.; Tao, Y. Anti-Alcohol Liver Disease Effect of Gentianae macrophyllae Extract through MAPK/JNK/P38 Pathway. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2019, 71, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheu, M.-J.; Chiu, C.-C.; Yang, D.-J.; Hsu, T.-C.; Tzang, B.-S. The Root Extract of Gentiana macrophylla Pall. Alleviates B19-NS1-Exacerbated Liver Injuries in NZB/W F1 Mice. J. Med. Food 2017, 20, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitić, N.; Živković, J.; Šavikin, K.; Randjelović, M.; Jovanović, M.; Kitić, D.; Miladinović, B.; Milutinović, M.; Stojiljković, N.; Branković, S. Spasmolytic Activity of Gentiana lutea L. Root Extracts on the Rat Ileum: Underlying Mechanisms of Action. Plants 2024, 13, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, O.; Singh, R.; Kumar, S.; Srivastava, S.; Ved, A. Gentiana lutea Linn. (Yellow Gentian): A Comprehensive Review. J. Ayurvedic Herb. Med. 2017, 3, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marković, M.; Pljevljakušić, D.; Menković, N.; Matejić, J.; Papović, O.; Stankov-Jovanović, V. Traditional Knowledge on the Medicinal Use of Plants from Genus Gentiana in the Pirot County (Serbia). Lek. Sirovine 2021, 41, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Xu, Y.; Jiang, W.; Zhang, Y. Isolation and Identification of Constituents with Activity of Inhibiting Nitric Oxide Production in Raw 264.7 Macrophages from Gentiana triflora. Planta Med. 2013, 79, 680–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šavikin, K.; Menković, N.; Zdunić, G.; Stević, T.; Radanović, D.; Janković, T. Antimicrobial Activity of Gentiana lutea L. Extracts. Z. Naturforschung C 2009, 64, 339–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Yin, B.; Lv, L.; He, J.; Chen, Z.; Wen, X.; Qiao, B.; Sun, W.; et al. Protective Effect of Gentiopicroside from Gentiana macrophylla Pall. in Ethanol-induced Gastric Mucosal Injury in Mice. Phytother. Res. 2018, 32, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, S.; Laermans, J.; Verhulst, P.-J.; Thijs, T.; Tack, J.; Depoortere, I. Bitter Taste Receptors and α-Gustducin Regulate the Secretion of Ghrelin with Functional Effects on Food Intake and Gastric Emptying. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 2094–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, M.; Tang, J.; Zhang, T.; Han, H. Swertiamarin, an Active Iridoid Glycoside from Swertia pseudochinensis H. Hara, Protects against Alpha-Naphthylisothiocyanate-Induced Cholestasis by Activating the Farnesoid X Receptor and Bile Acid Excretion Pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 291, 115164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akileshwari, C.; Muthenna, P.; Nastasijević, B.; Joksić, G.; Petrash, J.M.; Reddy, G.B. Inhibition of Aldose Reductase by Gentiana lutea Extracts. Exp. Diabetes Res. 2012, 2012, 147965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öztürk, N.; Herekman-Demir, T.; Öztürk, Y.; Bozan, B.; Başer, K.H.C. Choleretic Activity of Gentiana lutea Ssp. Symphyandra in Rats. Phytomedicine 1998, 5, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, E.; Lee, C.G.; Kim, J.; Yeo, S.; Kim, J.A.; Choi, C.W.; Jeong, S.-Y. Antiobesity Effects of Gentiana lutea Extract on 3T3-L1 Preadipocytes and a High-Fat Diet-Induced Mouse Model. Molecules 2020, 25, 2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mennella, I.; Fogliano, V.; Ferracane, R.; Arlorio, M.; Pattarino, F.; Vitaglione, P. Microencapsulated Bitter Compounds (from Gentiana lutea) Reduce Daily Energy Intakes in Humans. Br. J. Nutr. 2016, 116, 1841–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cvetković, S.; Vuletić, S.; Vunduk, J.; Klaus, A.; Mitić-Ćulafić, D.; Nikolić, B. The Role of Gentiana lutea Extracts in Reducing UV-Induced DNA Damage. Mutagenesis 2023, 38, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Deng, K.; Qiu, S.; Wang, M.; Avula, B.; Tripathi, S.K.; Jacob, M.R.; Gong, L.; Wang, W.; Khan, I.A.; et al. Identification of Antifungal Bisphosphocholines from Medicinal Gentiana Species. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 3207–3211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azadbakht, M.; Nayebi, E.; Enayati Fard, R.; Khaleghi, F. Standardization and Formulation of an Herbal Appetite-Stimulating Drug from Gentiana olivieri. J. Herb. Med. 2020, 19, 100306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Fan, J.Y.; Zhong, S.H.; Gu, R. Tibetan Medicine Bang Jian: A Comprehensive Review on Botanical Characterization, Traditional Use, Phytochemistry, and Pharmacology. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1295789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jovanović, J.A.; Krstić-Milošević, D.; Vinterhalter, B.; Dinić, S.; Grdović, N.; Uskoković, A.; Rajić, J.; Đorđević, M.; Sarić, A.; Vidaković, M.; et al. Evaluation of the Antidiabetic Potential of Xanthone-Rich Extracts from Gentiana dinarica and Gentiana utriculosa. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 9066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.-Y.; Hsu, T.-C.; Kuo, W.-W.; Liou, Y.-F.; Lee, S.-D.; Ju, D.-T.; Kuo, C.-H.; Tzang, B.-S. The Root Extract of Gentiana macrophylla Pall. Alleviates Cardiac Apoptosis in Lupus Prone Mice. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0127440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, H.W.; Lee, K.B.; Kim, K.S.; Yang, H.J.; Choi, E.K.; Shin, M.H.; Park, Y.S.; Na, Y.C.; Ahn, K.S.; Jang, Y.P.; et al. A Bitter Herbal Medicine Gentiana scabra Root Extract Stimulates Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Secretion and Regulates Blood Glucose in Db/Db Mouse. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 172, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Jiang, Y.; Yu, Q.; Xiao, C.; Sun, J.; Weng, L.; Qiu, Y. Gentiopicroside Improves High-Fat Diet-Induced NAFLD in Association with Modulation of Host Serum Metabolome and Gut Microbiome in Mice. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1145430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.Y.; Ju, J.M.; Mo, L.H.; Ma, L.; Hu, W.H.; You, R.R.; Chen, X.Q.; Chen, Y.Y.; Liu, Z.Q.; Qiu, S.Q.; et al. Anti-Inflammation Action of Xanthones from Swertia chirayita by Regulating COX-2/NF-ΚB/MAPKs/Akt Signaling Pathways in RAW 264.7 Macrophage Cells. Phytomedicine 2019, 55, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, W.; Wang, Y. Phytochemistry and Pharmacological Activities of the Genus Gentiana (Gentianaceae). Chem. Biodivers. 2016, 13, 107–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antoniadi, L.; Bartnik, M.; Angelis, A.; Wawruszak, A.; Halabalaki, M.; Kukula-Koch, W.; Skaltsounis, L.A. Gentiopicroside-An Insight into Its Pharmacological Significance and Future Perspectives. Cells 2023, 13, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Compound | Structure |
|---|---|
| Amarogentin [11] | 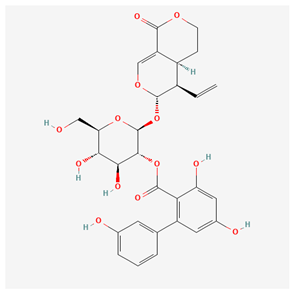 |
| Gentiopicroside [12] | 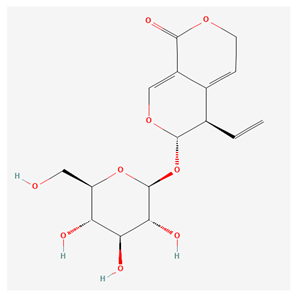 |
| Swertiamarin [13] | 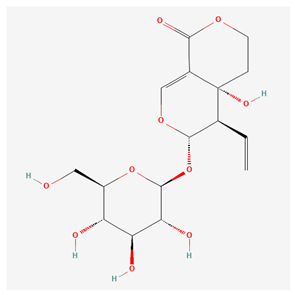 |
| Luteoloside [14] | 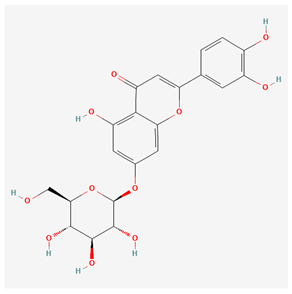 |
| Isovitexin [15] | 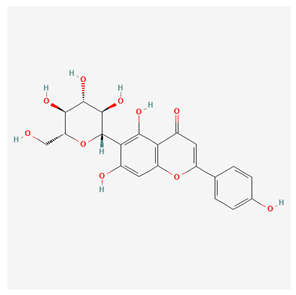 |
| Isoorientin [16] |  |
| Gentiolactone [17] | 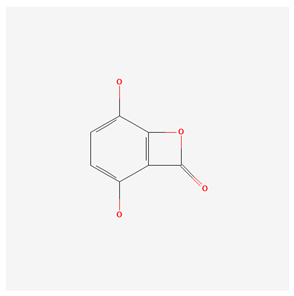 |
| Bellidifolin [18] | 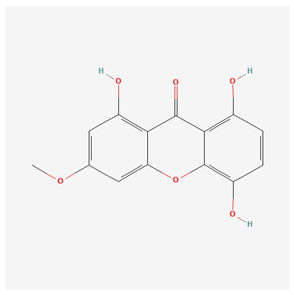 |
| Gentiana Species | Properties | References |
|---|---|---|
| Gentiana macrophylla | hepatoprotective activity | [88,91,92,93] |
| anti-inflammatory function | [28,29,42,64,73,91] | |
| blood sugar rises | [93] | |
| gastrointestinal tract protection | [44,52,99] | |
| allergic shock prevention | [96,97] | |
| anti-histamine effect | [68] | |
| appetite stimulation | [66,67,100] | |
| Gentiana lutea | spasmolytic effect on the gastrointestinal system | [94] |
| appetite stimulation | [56,101] | |
| mild dyspepsia | [30,101] | |
| duodenal ulcer protection | [102] | |
| antipyretic effect | [57,103] | |
| wound healing | [2,71] | |
| hypoglycemic effect | [77] | |
| anti-anemic effect | [95,104] | |
| hepatoprotective effect | [55,105] | |
| skin disorders | [21] | |
| immune stimulant | [56] | |
| astringent activity | [94] | |
| antibacterial effect | [95,98,106,107] | |
| Gentiana scabrae | stomach muscle strengthening | [66] |
| liver protection | [66] | |
| cholagogic effect | [54] | |
| anti-inflammatory effect | [2] | |
| anti-bacterial effect | [91] | |
| Gentiana dinarica | blood sugar level regulation | [93] |
| Gentiana utriculosa | blood sugar level regulation | [93] |
| Gentiana cruciata | appetite stimulation | [75] |
| duodenal ulcer protection | [75] | |
| wound healing | [64] | |
| hepatoprotective effect | [13,37] | |
| Gentiana rigescens | strengthening the stomach muscle | [66] |
| liver protection | [66] | |
| cholagogue effect | [68] | |
| anti-inflammatory effect | [68] | |
| anti-bacterial effect | [68] | |
| Gentiana triflora | chronic stomach disease treatment | [97] |
| appetite stimulation | [44] | |
| jaundice treatment | [48] | |
| hepatitis treatment | [48] | |
| Gentiana punctata | wound healing | [64] |
| Gentiana asclepiadea | wound healing | [64] |
| appetite stimulation | [67] | |
| anti-anemic effect | [64] | |
| gall and liver disease treatment | [65] | |
| Gentiana septemfida | hemorrhoids protection | [76] |
| anti-inflammatory function | [60] | |
| wound healing | [64] | |
| Gentiana olivieri | appetite stimulation | [53,70,108] |
| wound healing | [64] |
| Plant Parts | Compound | Functional Activity | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| root | amarogentin | anti-inflammatory, anti-bacterial, hepatoprotective, gastroprotective | [9,10,11,12,13,54] |
| root, aerial part | bellidifolin | neuroprotective properties against ischemia and sciatic nerve injury | [48] |
| root | bisphosphocholines | antifungal properties | [107] |
| root | carboxygentisic acid | hepatoprotective activity | [3] |
| root, aerial part | gentian violet | anti-bacterial, sepsis, meningitis | [111] |
| root | gentiolactone | anti-inflammatory | [49] |
| root | gentiopicroside | anti-inflammatory, anti-rheumatic, hepatoprotective, and preventing osteoclastogenesis | [14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22] |
| root, aerial part | isogentisin | cellular repair mechanisms, anti-bacterial | [2,78] |
| flowers | isoorientin | pigmentary skin disorders | [47] |
| leaves | isosreintin | chronic stomach diseases, appetite stimulation | [45] |
| root | isovitexin | atherosclerosis prevention, reduction in total cholesterol levels | [44,45,46] |
| root, aerial part | luteoloside | anti-cancer effect, antioxidative | [43,44] |
| root, aerial part | sweroside | hepatoprotective, antioxidative | [13] |
| root, aerial part | swertiamarin | hepatoprotective, reduction in cerebral ischemia, gastroprotective | [37,38,39,40,41,54] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Andryszkiewicz, W.; Chmielewska, M.; Ciecierska, J.; Lenkiewicz, P.; Marciniak, W.; Raczycka, W.; Wojno, A.; Kulbacka, J.; Niewiński, P.; Bieżuńska-Kusiak, K. Gentianaceae Family—Derived Bioactive Compounds—Therapeutic Values and Supporting Role in Inflammation and Detoxification. Nutrients 2025, 17, 2619. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17162619
Andryszkiewicz W, Chmielewska M, Ciecierska J, Lenkiewicz P, Marciniak W, Raczycka W, Wojno A, Kulbacka J, Niewiński P, Bieżuńska-Kusiak K. Gentianaceae Family—Derived Bioactive Compounds—Therapeutic Values and Supporting Role in Inflammation and Detoxification. Nutrients. 2025; 17(16):2619. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17162619
Chicago/Turabian StyleAndryszkiewicz, Wiktoria, Milena Chmielewska, Julia Ciecierska, Paulina Lenkiewicz, Wiktoria Marciniak, Wiktoria Raczycka, Agata Wojno, Julita Kulbacka, Przemysław Niewiński, and Katarzyna Bieżuńska-Kusiak. 2025. "Gentianaceae Family—Derived Bioactive Compounds—Therapeutic Values and Supporting Role in Inflammation and Detoxification" Nutrients 17, no. 16: 2619. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17162619
APA StyleAndryszkiewicz, W., Chmielewska, M., Ciecierska, J., Lenkiewicz, P., Marciniak, W., Raczycka, W., Wojno, A., Kulbacka, J., Niewiński, P., & Bieżuńska-Kusiak, K. (2025). Gentianaceae Family—Derived Bioactive Compounds—Therapeutic Values and Supporting Role in Inflammation and Detoxification. Nutrients, 17(16), 2619. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17162619








