Anticancer Activity of Vitex agnus-castus Seed Extract on Gastric Cancer Cells
Highlights
- Vitex agnus-castus seed extract shows strong antioxidant and anticancer effects against gastric cancer cells with minimal toxicity to heathy fibroblasts.
- Induces apoptosis, cell cycle arrest, and disrupts mitochondrial membrane potential.
- Inhibits migration, spheroid formation, and EMT, indicating therapeutic potential.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Extraction of Vitex agnus-castus Seeds
2.2. Antioxidant Activity of Vitex agnus-castus Seeds’ Extract
2.2.1. DPPH Assay
2.2.2. ABTS Assay
2.3. Total Phenolic Content of Vitex agnus-castus Seeds’ Extract
2.4. Total Flavonoid Content of Vitex agnus-castus Seeds’ Extract
2.5. Cell Culture and MTT Cytotoxicity Assay
2.6. Spheroid Formation Assay
2.7. RNA Extraction and Real-Time Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-qPCR) and Gene Enrichment Analysis
2.8. Apoptosis Assay
2.9. Wound Healing Assay
2.10. Analysis of Mitochondrial Membrane Potential by Rhodamine 123 Staining
2.11. Cell Cycle Analysis
2.12. Determination of Apoptotic Protein Levels by ELISA
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Phytochemical Composition and Antioxidant Properties of Vitex Agnus-Castus Extract
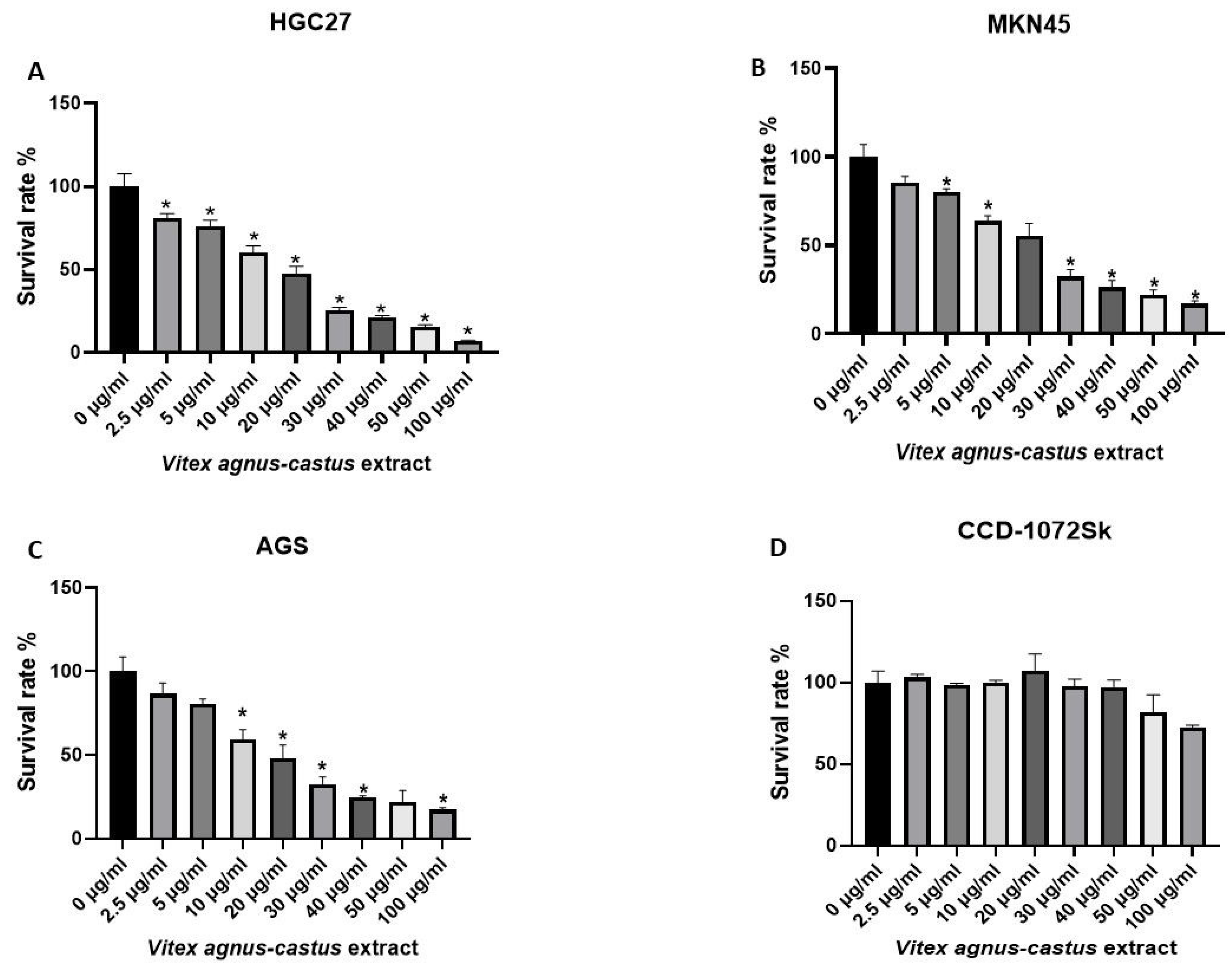
3.2. Cytotoxic Activity of the Vitex Agnus-Castus Extracts on HGC27, MKN45, AGS, and CCD-1072Sk Cells
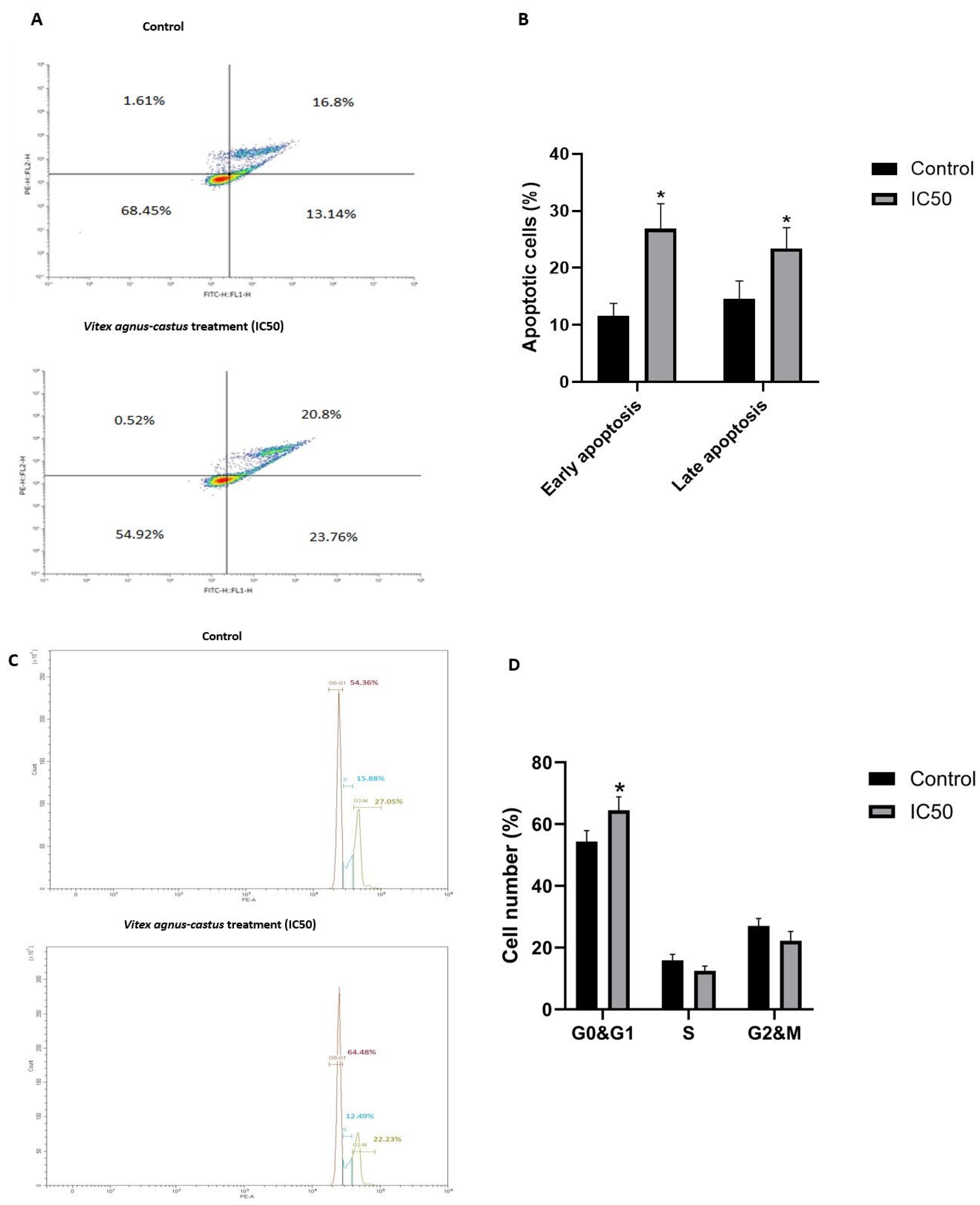
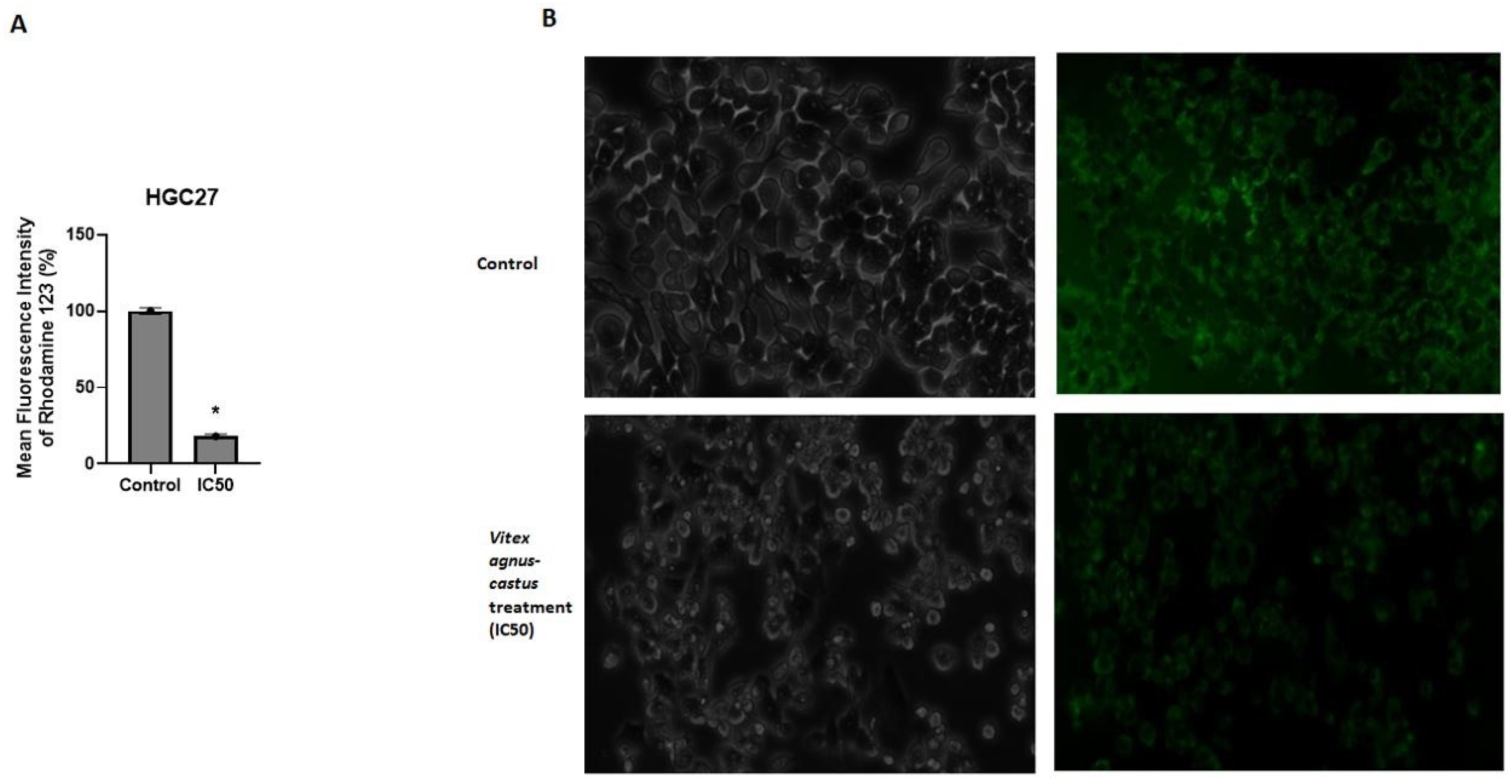
3.3. The Effect of the Vitex Agnus-Castus Extract on Apoptosis and Cell Cycle Regulation of HGC27 Cells
3.4. The Extract Treatment Decreased the Spheroid Formation and Migration Capacity of HGC27 Cells
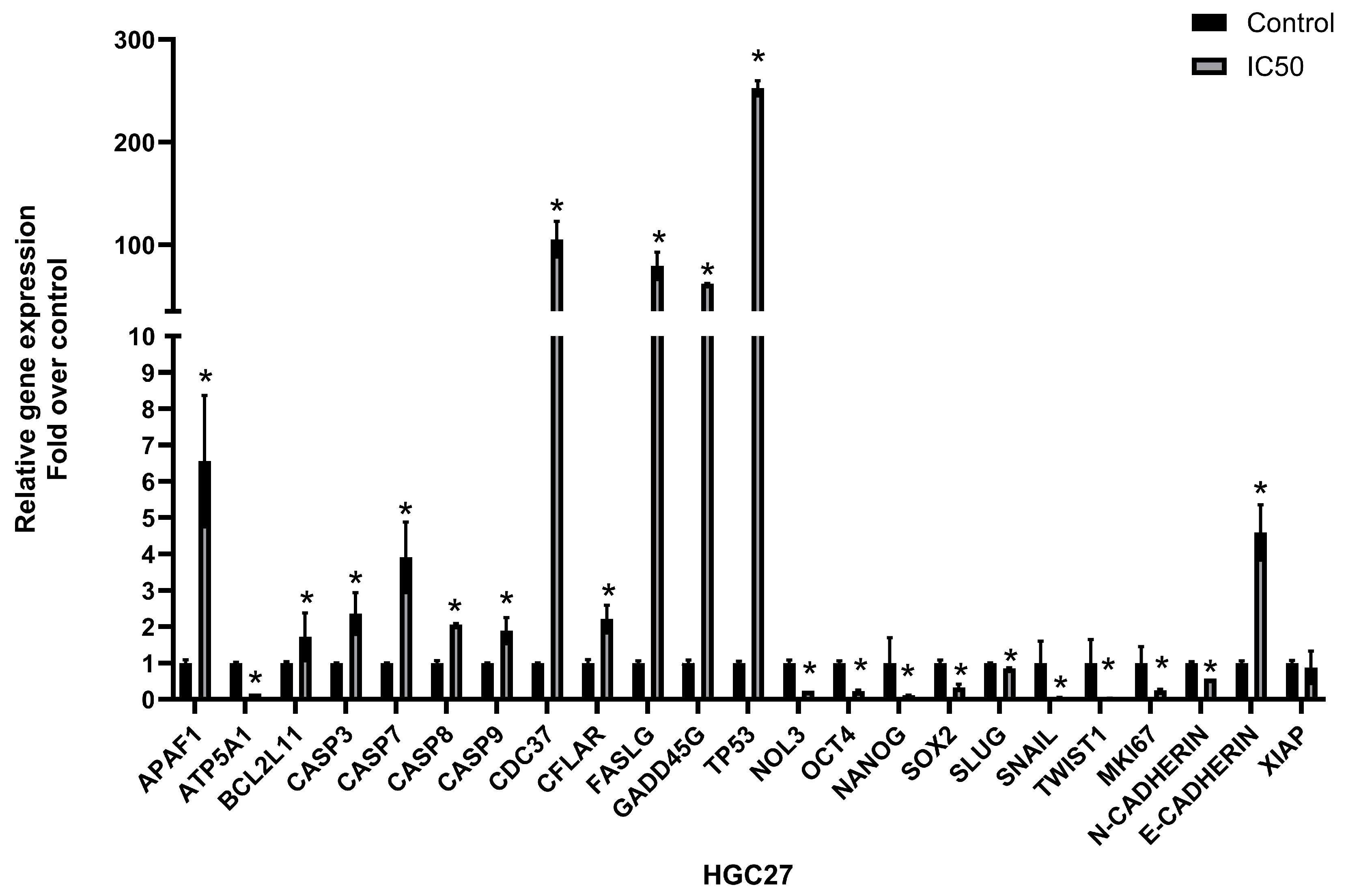
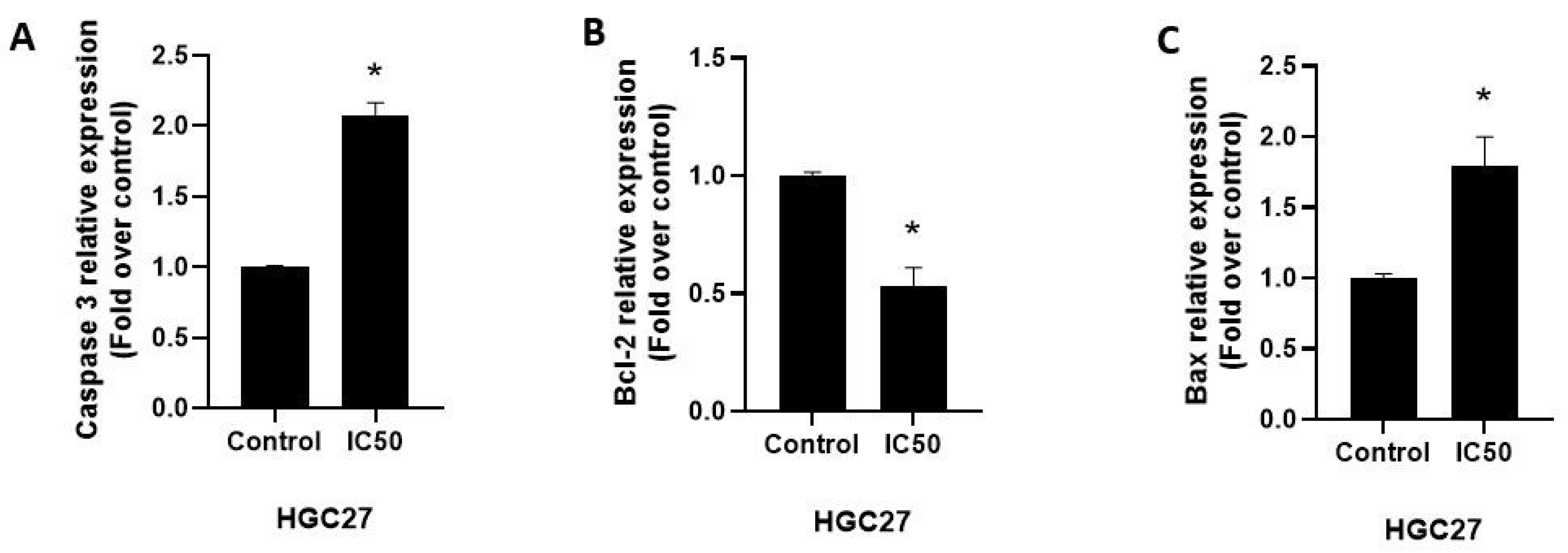
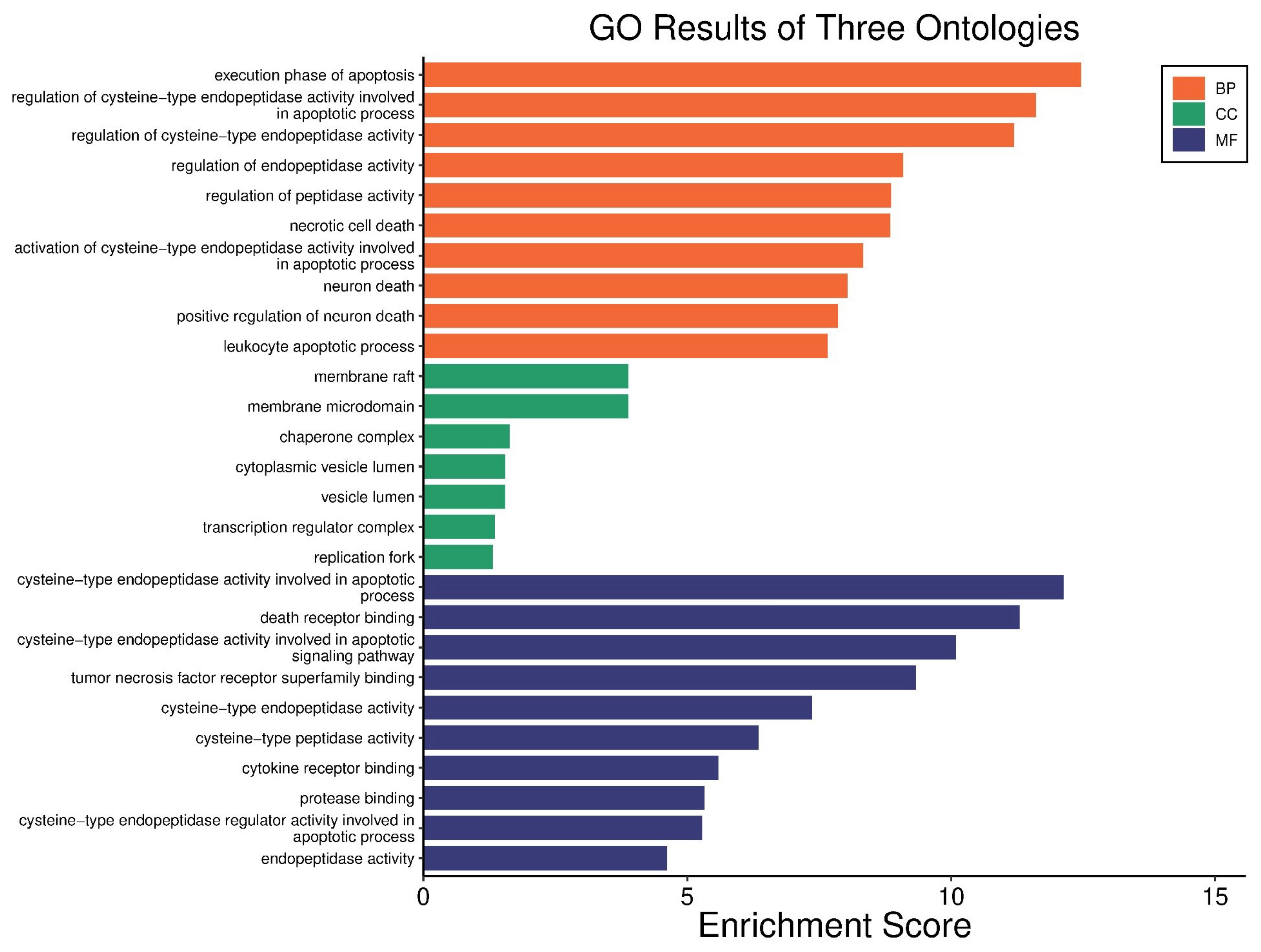
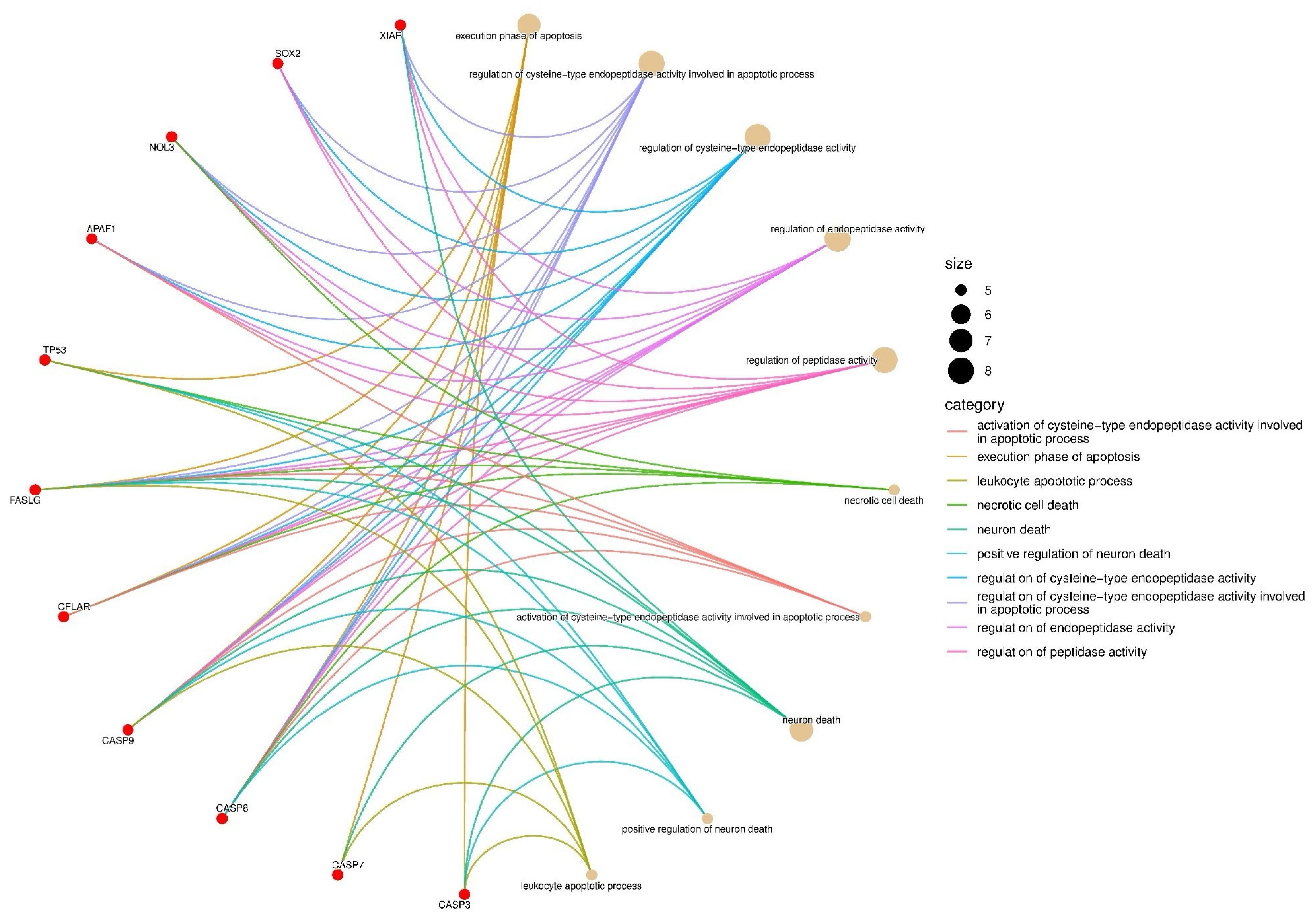
3.5. The Extract Treatment-Altered Gene and Protein Expression in HGC27 Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ADM | Adrenomedullin |
| APAF1 | Apoptotic Protease Activating Factor 1 |
| ATP5A1 | ATP Synthase F1 Subunit Alpha 1 |
| BCL2L11 | BCL2 Like 11 |
| BIRC3 | Baculoviral IAP Repeat Containing 3 |
| CASP | Caspase |
| CDH2 | Cadherin 2 |
| CDC37 | Cell Division Cycle 37 |
| CFLAR | CASP8 and FADD Like Apoptosis Regulator |
| ELISA | Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay |
| FASLG | Fas Ligand |
| FBS | Fetal Bovine Serum |
| GADD45G | Growth Arrest and DNA Damage-Inducible Gamma |
| MMP | Mitochondrial Membrane Potential |
| NANOG | Homeobox Transcription Factor Nanog |
| NOL3 | Nucleolar Protein 3 |
| PBS | Phosphate-Buffered Saline |
| POU5F1 | POU Class 5 Homeobox 1 |
| SLUG | Snail Family Transcriptional Repressor 2 |
| SNAIL | Snail Family Transcriptional Repressor 1 |
| TWIST1 | Twist Family BHLH Transcription Factor 1 |
| XIAP | X-Linked Inhibitor of Apoptosis Protein |
References
- Ibrahim, F.M.; Ibrahim, A.Y.; El-Newary, S.A.; Hendawy, S.F.; Mahomoodally, M.F. Vitex agnus-castus L. (Chasteberry) extracts shows in vitro and in vivo anti-inflammatory and anti-tumor propensities via reduction of cyclooxygenase-2 activity and oxidative stress complications. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2021, 143, 363–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boujbiha, M.A.; Chahdoura, H.; Adouni, K.; Ziani, B.E.C.; Snoussi, M.; Chakroun, Y.; Ciudad-Mulero, M.; Fernández-Ruiz, V.; Achour, L.; Selmi, B.; et al. Wild Vitex agnus-castus L.: Phytochemical Characterization, Acute Toxicity, and Bioactive Properties. Molecules 2023, 28, 5096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niroumand, M.C.; Heydarpour, F.; Farzaei, M.H. Pharmacological and therapeutic effects of Vitex agnus-castus L.: A review. Phcog. Rev. 2018, 12, 103. [Google Scholar]
- Ohyama, K.; Akaike, T.; Hirobe, C.; Yamakawa, T. Cytotoxicity and apoptotic inducibility of Vitex agnus-castus fruit extract in cultured human normal and cancer cells and effect on growth. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2003, 26, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kour, M.; Anantharaya, M.V.N.; Bhat, K.M.R.; Chakraborti, S.; Kodavanji, B. Effect of Vitex agnus extract on MNU induced mammary tumor of Sprague Dawley rats. J. Young Pharm. 2017, 9, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavaz, A.; Işık, M.; Dikici, E.; Yüksel, M. Anticholinergic, antioxidant, and antibacterial properties of Vitex agnus-castus L. seed extract: Assessment of its phenolic content by LC/MS/MS. Chem. Biodivers. 2022, 19, e202200143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, E.W.C.; Wong, S.K.; Chan, H.T. Casticin from Vitex species: A short review on its anticancer and anti-inflammatory properties. J. Integr. Med. 2018, 16, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultan Aslantürk, Ö.; Çelik, A.T. Antioxidant activity and anticancer effect of Vitex agnus-castus L.(Verbenaceae) seed extracts on MCF–7 breast cancer cells. Caryologia 2013, 66, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisskopf, M.; Schaffner, W.; Jundt, G.; Sulser, T.; Wyler, S.; Tullberg-Reinert, H. A Vitex agnus-castus extract inhibits cell growth and induces apoptosis in prostate epithelial cell lines. Planta Med. 2005, 71, 910–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekici, S.; Bozkaya, E.; Bozkaya, O.; Cerci, N.A.; Aluc, Y.; Ekici, H. Vitex Agnus-Castus L. Nanoparticles: Preparation, Characterization and Assessment of Antimicrobial and Anticancer Activity. ChemistrySelect 2023, 8, e202302102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohyama, K.; Akaike, T.; Imai, M.; Toyoda, H.; Hirobe, C.; Bessho, T. Human gastric signet ring carcinoma (KATO-III) cell apoptosis induced by Vitex agnus-castus fruit extract through intracellular oxidative stress. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2005, 37, 1496–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uslu, B.; Yaman, M.; Sanci, T.Ö.; Güngörmüş, M.; Köprü, Ç.Z.; Güneş, F.E. Acetone extracts of Berberis vulgaris and Cornus mas L. induce apoptosis in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Turk. J. Med. Sci. 2023, 53, 1476–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand-Williams, W.; Cuvelier, M.E.; Berset, C. Use of a free radical method to evaluate antioxidant activity. Lwt-Food Sci. Technol. 1995, 28, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Re, R.; Pellegrini, N.; Proteggente, A.; Pannala, A.; Yang, M.; Rice-Evans, C. Antioxidant activity applying an improved ABTS radical cation decolorization assay. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1999, 26, 1231–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singleton, V.L.; Rossi, J.A. Colorimetry of total phenolics with phosphomolybdic-phosphotungstic acid reagents. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 1965, 16, 144–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorim, E.; Castro, V.T.N.A.; Melo, J.; Corrêa, A.; Peixoto Sobrinho, T.J.S. Standard operating procedures (SOP) for the spectrophotometric determination of phenolic compounds contained in plant samples. In Latest Research into Quality Control; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2012; pp. 47–66. [Google Scholar]
- Chiamenti, L.; Silva, F.P.D.; Schallemberger, K.; Demoliner, M.; Rigotto, C.; Fleck, J.D. Cytotoxicity and antiviral activity evaluation of Cymbopogon spp hydroethanolic extracts. Braz. J. Pharm. 2019, 55, e18063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Türksoy, Ö.; Terzioğlu, G. Effects of growth factor deprivation on MKN-45 spheroid cells. Turk. J. Biol. 2023, 47, 94–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, D.; Chen, M.; Huang, X.; Zhang, G.; Zeng, L.; Zhang, G.; Wu, S.; Wang, Y. SRplot: A free online platform for data visualization and graphing. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0294236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grada, A.; Otero-Vinas, M.; Prieto-Castrillo, F.; Obagi, Z.; Falanga, V. Research techniques made simple: Analysis of collective cell migration using the wound healing assay. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2017, 137, e11–e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Türksoy Terzioğlu, Ö.; Terzioğlu, G.; Bayrak, Ö.F. Mitochondrial DNA depletion promotes vasculogenic properties through mesenchymal alteration in glioblastoma. J. Taibah Univ. Sci. 2025, 19, 2479983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Türksoy Terzioğlu, Ö.; Terzioğlu, G.; Bayrak, Ö.F. Identification of an mtDNA setpoint associated with highest levels of CD44 positivity and chemoresistance in HGC-27 and MKN-45 gastric cancer cell lines. Cell J. 2018, 20, 312. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Y.; Vignali, P.; Ruoning, W. Rapid profiling cell cycle by flow cytometry using concurrent staining of DNA and mitotic markers. Bio-Protocol 2017, 7, e2517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahim, C.; Abdollah, M.R.; Labib, R.M.; Ibrahim, N.; Swilam, N. Phytochemical Analysis and In Vivo Anticancer Effect of Becium grandiflorum: Isolation and Characterization of a Promising Cytotoxic Diterpene. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tronina, T.; Bartmańska, A.; Popłoński, J.; Rychlicka, M.; Sordon, S.; Filip-Psurska, B.; Milczarek, M.; Wietrzyk, J.; Huszcza, E. Prenylated Flavonoids with Selective Toxicity against Human Cancers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matter, M.L.; Gkretsi, V. Molecular Regulation of Tumor Cells Migration and Metastatic Growth. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1329053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, A.Y.; El-Newary, S.A.; Youness, E.R.; Ibrahim, A.M.; El Kashak, W.A. Protective and therapeutic effect of Vitex agnus-castus against prostate cancer in rat. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 7, 133–143. [Google Scholar]
- Marvibaigi, M.; Amini, N.; Supriyanto, E.; Abdul Majid, F.A.; Kumar Jaganathan, S.; Jamil, S.; Hamzehalipour Almaki, J.; Nasiri, R. Antioxidant Activity and ROS-Dependent Apoptotic Effect of Scurrula ferruginea (Jack) Danser Methanol Extract in Human Breast Cancer Cell MDA-MB-231. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0158942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massaoka, M.H.; Matsuo, A.L.; Figueiredo, C.R.; Farias, C.F.; Girola, N.; Arruda, D.C.; Scutti, J.A.; Romoff, P.; Favero, O.A.; Ferreira, M.J. Jacaranone induces apoptosis in melanoma cells via ROS-mediated downregulation of Akt and p38 MAPK activation and displays antitumor activity in vivo. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e38698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duymuş, H.; Çiftçi, G.A.; Yıldırım, Ş.U.; Demirci, B.; Kırımer, N. The cytotoxic activity of Vitex agnus castus L. essential oils and their biochemical mechanisms. Ind. Crops Prod. 2014, 55, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-J.; Wang, C.-J.; Kuo, H.-C.; Chou, F.-P.; Jean, L.-F.; Tseng, T.-H. Induction apoptosis of luteolin in human hepatoma HepG2 cells involving mitochondria translocation of Bax/Bak and activation of JNK. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2005, 203, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Liu, Y.E.; Cao, J.; Zeng, G.; Shen, C.; Li, Y.; Zhou, M.; Chen, Y.; Pu, W.; Potters, L.; et al. Vitexins, nature-derived lignan compounds, induce apoptosis and suppress tumor growth. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 5161–5169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilhan, S. Essential Oils from Vitex agnus castus L. Leaves Induces Caspase-Dependent Apoptosis of Human Multidrug-Resistant Lung Carcinoma Cells through Intrinsic and Extrinsic Pathways. Nutr. Cancer 2021, 73, 694–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, L.; Yuan, X.; Ou, Y.; Zhu, X.; Cheng, Z.; Zhang, P.; Wu, X.; Meng, Y.; Zhang, L. The relationship between the Bcl-2/Bax proteins and the mitochondria-mediated apoptosis pathway in the differentiation of adipose-derived stromal cells into neurons. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0163327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Li, X.; Xie, R.; Chen, Y.; Hu, X.; Liu, Y.; Ma, H. Expression levels of microRNA-300/BCL2L11 in papillary thyroid cancer and their clinical diagnostic values. Eur. Surg. Res. 2023, 64, 342–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Duan, J.; Qu, Y.; Deng, T.; Liu, R.; Zhang, L.; Bai, M.; Li, J.; Ning, T.; Ge, S.; et al. Onco-miR-24 regulates cell growth and apoptosis by targeting BCL2L11 in gastric cancer. Protein Cell 2016, 7, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Y.; Sai, Y.; Zhou, L.; Liu, Z.; Du, P.; Wu, J.; Zhang, J. Current insights into the regulation of programmed cell death by TP53 mutation in cancer. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zou, H.; Yang, R.; Hao, J.; Wang, J.; Sun, C.; Fesik, S.W.; Wu, J.C.; Tomaselli, K.J.; Armstrong, R.C. Regulation of the Apaf-1/Caspase-9 apoptosome by caspase-3 and XIAP. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 8091–8098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dietz, L.; Ellison, C.J.; Riechmann, C.; Cassidy, C.K.; Felfoldi, F.D.; Pinto-Fernández, A.; Kessler, B.M.; Elliott, P.R. Structural basis for SMAC-mediated antagonism of caspase inhibition by the giant ubiquitin ligase BIRC6. Science 2023, 379, 1112–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiozaki, E.N.; Chai, J.; Rigotti, D.J.; Riedl, S.J.; Li, P.; Srinivasula, S.M.; Alnemri, E.S.; Fairman, R.; Shi, Y. Mechanism of XIAP-mediated inhibition of caspase-9. Mol. Cell 2003, 11, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanley, R.F.; Piszczatowski, R.T.; Bartholdy, B.; Mitchell, K.; McKimpson, W.M.; Narayanagari, S.; Walter, D.; Todorova, T.I.; Hirsch, C.; Makishima, H.; et al. A myeloid tumor suppressor role for NOL3. J. Exp. Med. 2017, 214, 753–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lugli, E.; Troiano, L.; Ferraresi, R.; Roat, E.; Prada, N.; Nasi, M.; Pinti, M.; Cooper, E.L.; Cossarizza, A. Characterization of cells with different mitochondrial membrane potential during apoptosis. Cytom. A 2005, 68, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Takeyama, N.; Brady, G.; Watson, A.J.M.; Dive, C. Blood cells with reduced mitochondrial membrane potential and cytosolic cytochrome C can survive and maintain clonogenicity given appropriate signals to suppress apoptosis. Blood 1998, 92, 4545–4553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottlieb, E.; Armour, S.M.; Harris, M.H.; Thompson, C.B. Mitochondrial membrane potential regulates matrix configuration and cytochrome c release during apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 2003, 10, 709–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, H.K.; Bertoli, C.; de Bruin, R.A. Cell cycle control in cancer. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2022, 23, 74–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nehme, J.; Varela-Eirin, M.; Demaria, M. Molecular mechanisms of cellular senescence. In Regenerative Nephrology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2022; pp. 221–230. [Google Scholar]
- Winter, E.; Chiaradia, L.D.; Silva, A.H.; Nunes, R.J.; Yunes, R.A.; Creczynski-Pasa, T.B. Involvement of extrinsic and intrinsic apoptotic pathways together with endoplasmic reticulum stress in cell death induced by naphthylchalcones. Toxicol. In Vitro 2014, 28, 769–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoka, V.; Vasiljeva, O.; Nakanishi, H.; Turk, V. The role of cysteine protease cathepsins B, H, C, and X/Z in neurodegenerative diseases and cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linders, D.G.J.; Bijlstra, O.D.; Fallert, L.C.; Hilling, D.E.; Walker, E.; Straight, B.; March, T.L.; Valentijn, A.R.P.M.; Pool, M.; Burggraaf, J.; et al. Cysteine cathepsins in breast cancer: Promising targets for fluorescence-guided surgery. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2023, 25, 58–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Droga-Mazovec, G.; Bojic, L.; Petelin, A.; Ivanova, S.; Romih, R.; Repnik, U.; Salvesen, G.S.; Stoka, V.; Turk, V.; Turk, B.; et al. Cysteine cathepsins trigger caspase-dependent cell death through cleavage of Bid and antiapoptotic Bcl-2 homologues. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 19140–19150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoka, V.; Turk, B.; Schendel, S.L.; Kim, T.H.; Cirman, T.; Snipas, S.J.; Ellerby, L.M.; Bredesen, D.; Freeze, H.; Abrahamson, M.; et al. Lysosomal protease pathways to apoptosis: Cleavage of Bid, not pro-caspases, is the most likely route. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 3149–3157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, B.; Wang, M.Y.; Fei, M.; Wei, Y.; Chen, B.; Deng, G. ATP5A1 participates in transcriptional and posttranscriptional regulation of cancer-associated genes. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2021, 20, 15330338211039126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Yin, L.; Duan, T.; Niu, M.; He, Z.; Chen, X.; Zhang, X.; Li, J.; Geng, Z.; Zuo, L. High expression of ATP5A1 in gastric carcinoma correlates with poor prognosis and enhanced glucose metabolism. Nan Fang. Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao 2024, 44, 974–980. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ying, J.; Srivastava, G.; Hsieh, W.-S.; Gao, Z.; Murray, P.; Liao, S.-K.; Ambinder, R.; Tao, Q. The stress-responsive gene GADD45G is a functional tumor suppressor. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 6442–6449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, W.; Dong, Z.; Guo, Y.; Chen, Z.; Kuang, G.; Yang, Z. Methylation-mediated repression of GADD45A and GADD45G expression. Int. J. Cancer 2013, 133, 2043–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaks, V.; Kong, N.; Werb, Z. The cancer stem cell niche: How essential is the niche? Cell Stem Cell 2015, 16, 225–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, S.; Devi, G.R. Three-dimensional culture systems in cancer research: Focus on tumor spheroid model. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 163, 94–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hairuddin, O.N.; Yahaya, B.H.; Ibahim, M.J.; Verakumarasivam, A.; Choy, C.S.; Mazlan, M.; Rahim, N.A.; Dzulkarnain, S.M.H.; Mansor, S.F. Comparison of cancer stem cell enrichment in spheroids. Biomed. Res. Ther. 2023, 10, 5810–5830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasti, A.; Mehrazma, M.; Madjd, Z.; Abolhasani, M.; Saeednejad Zanjani, L.; Asgari, M. Co-expression of OCT4 and NANOG predicts poor prognosis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 11739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basati, G.; Mohammadpour, H.; Emami Razavi, A. High expression of SOX2, NANOG, and OCT4 in gastric cancer. Iran. Biomed. J. 2020, 51, 41–47. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, S.; Nawshad, A. Interpreting embryonic EMT in response to TGF-beta. Cells Tissues Organs 2007, 185, 131–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, M.A.; Kraut, N.; Beug, H. Molecular requirements for epithelial–mesenchymal transition. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2005, 17, 548–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Massagué, J. Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions: Twist in development and metastasis. Cell 2004, 118, 277–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolós, V.; Peinado, H.; Pérez-Moreno, M.A.; Fraga, M.F.; Esteller, M.; Cano, A. Slug represses E-cadherin and induces EMT. J. Cell Sci. 2003, 116, 499–511. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Rahman, M.A.; Chen, Z.G.; Shin, D.M. Multiple biological functions of Twist1. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 20380–20393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mrozik, K.M.; Blaschuk, O.W.; Cheong, C.M.; Zannettino, A.C.W.; Vandyke, K. N-cadherin in metastasis and blood cancers. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 939. [Google Scholar]


| ACTINB | ATP5A1 | CASP3 | CDH2 | GADD45G | SLUG |
| TWIST1 | BCL2L11 | CASP7 | CASP8 | NANOG | SNAIL |
| ADM | BIRC3 | CASP9 | CFLAR | NOL3 | TP53 |
| APAF1 | BMI1 | CDC37 | FASLG | POU5F1 | XIAP |
| Vitex agnus-castus Seed Extract | |
| DPPH (IC50 µg/mL) | 68.19 ± 4.68 |
| ABTS (mg/100 g BHT) | 323.529 ± 0.33 |
| Total Phenolic Content (mg/100 g GAE) | 1700.77 ± 163.37 |
| Total Flavonoid Content (mg/100 g RE) | 5765.86 ± 74.35 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Türksoy-Terzioğlu, Ö.; Tosya, F.; Çelik, A.B.; Bölek, S.; Gülüm, L.; Terzioğlu, G.; Tutar, Y. Anticancer Activity of Vitex agnus-castus Seed Extract on Gastric Cancer Cells. Nutrients 2025, 17, 2564. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17152564
Türksoy-Terzioğlu Ö, Tosya F, Çelik AB, Bölek S, Gülüm L, Terzioğlu G, Tutar Y. Anticancer Activity of Vitex agnus-castus Seed Extract on Gastric Cancer Cells. Nutrients. 2025; 17(15):2564. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17152564
Chicago/Turabian StyleTürksoy-Terzioğlu, Özlem, Feyza Tosya, Ayşe Büşranur Çelik, Sibel Bölek, Levent Gülüm, Gökhan Terzioğlu, and Yusuf Tutar. 2025. "Anticancer Activity of Vitex agnus-castus Seed Extract on Gastric Cancer Cells" Nutrients 17, no. 15: 2564. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17152564
APA StyleTürksoy-Terzioğlu, Ö., Tosya, F., Çelik, A. B., Bölek, S., Gülüm, L., Terzioğlu, G., & Tutar, Y. (2025). Anticancer Activity of Vitex agnus-castus Seed Extract on Gastric Cancer Cells. Nutrients, 17(15), 2564. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17152564






