The Oral–Gut Microbiota Axis Across the Lifespan: New Insights on a Forgotten Interaction
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Overview of the Oral and Gut Microbiota Composition Across the Lifespan
3. Overview on the Interaction Between Oral and Gut Microbiota
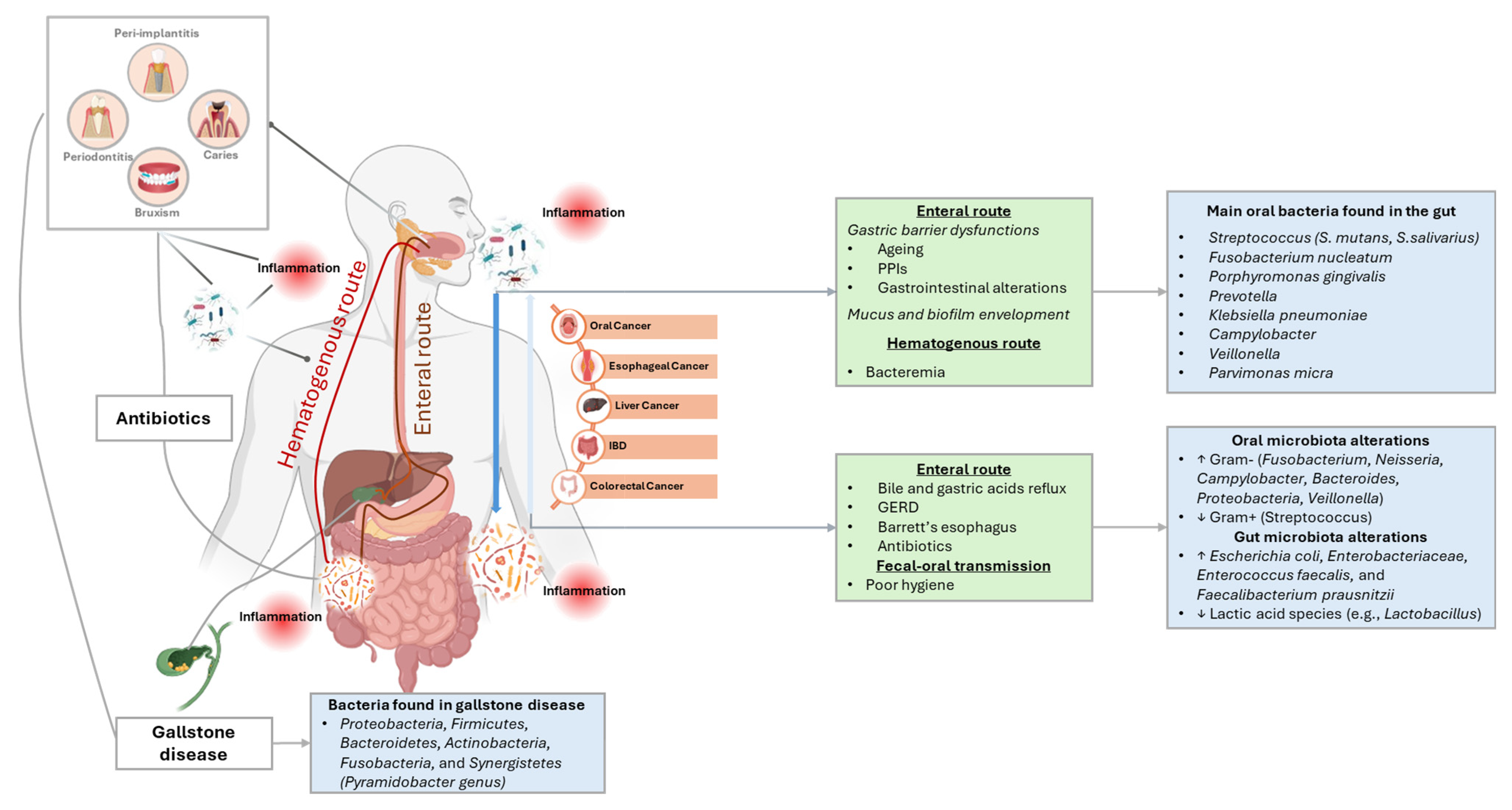
3.1. The Enteral Route
3.2. The Hematogenous Route
3.3. Fecal-Oral Route
3.4. Metabolite-Mediated Interactions Between Oral and Gut Microbiota
4. Dietary Strategies
5. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Peng, X.; Cheng, L.; You, Y.; Tang, C.; Ren, B.; Li, Y.; Xu, X.; Zhou, X. Oral microbiota in human systematic diseases. Int. J. Oral Sci. 2022, 14, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnbaugh, P.J.; Ley, R.E.; Hamady, M.; Fraser-Liggett, C.M.; Knight, R.; Gordon, J.I. The Human Microbiome Project. Nature 2007, 449, 804–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, J.W.; Roach, J.; Azcarate-Peril, M.A. Emerging Technologies for Gut Microbiome Research. Trends Microbiol. 2016, 24, 887–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, G.; Zhi, A.; Lai, P.F.H.; Wang, G.; Xia, Y.; Xiong, Z.; Zhang, H.; Che, N.; Ai, L. The oral microbiota—A mechanistic role for systemic diseases. Br. Dent. J. 2018, 224, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santacroce, L.; Passarelli, P.C.; Azzolino, D.; Bottalico, L.; Charitos, I.A.; Cazzolla, A.P.; Colella, M.; Topi, S.; Godoy, F.G.; D’Addona, A. Oral microbiota in human health and disease: A perspective. Exp. Biol. Med. 2023, 248, 1288–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Yang, X.; Li, C.; Song, Z. The Oral Microbiota: Community Composition, Influencing Factors, Pathogenesis, and Interventions. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 895537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, H.-C.; Colditz, G.; Joshipura, K.J. The association between tooth loss and the self-reported intake of selected CVD-related nutrients and foods among US women. Community Dent. Oral Epidemiol. 2005, 33, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil-Montoya, J.A.; Ferreira de Mello, A.L.; Barrios, R.; Gonzalez-Moles, M.A.; Bravo, M. Oral health in the elderly patient and its impact on general well-being: A nonsystematic review. Clin. Interv. Aging 2015, 10, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, J.-L.P.; Milledge, K.L.; O’Leary, F.; Cumming, R.; Eberhard, J.; Hirani, V. Poor dietary intake of nutrients and food groups are associated with increased risk of periodontal disease among community-dwelling older adults: A systematic literature review. Nutr. Rev. 2020, 78, 175–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casati, M.; Ferri, E.; Azzolino, D.; Cesari, M.; Arosio, B. Gut microbiota and physical frailty through the mediation of sarcopenia. Exp. Gerontol. 2019, 124, 110639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Wang, W.; Li, Y.; Cui, J.; Zhu, M.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y. The oral-gut microbiota axis: A link in cardiometabolic diseases. Npj Biofilms Microbiomes 2025, 11, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultan, A.S.; Kong, E.F.; Rizk, A.M.; Jabra-Rizk, M.A. The oral microbiome: A Lesson in coexistence. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1006719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HOMD: Human Oral Microbiome Database. Available online: https://www.homd.org/ (accessed on 24 January 2023).
- Kuramitsu, H.K.; He, X.; Lux, R.; Anderson, M.H.; Shi, W. Interspecies interactions within oral microbial communities. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2007, 71, 653–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewhirst, F.E.; Chen, T.; Izard, J.; Paster, B.J.; Tanner, A.C.R.; Yu, W.-H.; Lakshmanan, A.; Wade, W.G. The human oral microbiome. J. Bacteriol. 2010, 192, 5002–5017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemos, J.A.; Palmer, S.R.; Zeng, L.; Wen, Z.T.; Kajfasz, J.K.; Freires, I.A.; Abranches, J.; Brady, L.J. The Biology of Streptococcus mutans. Microbiol. Spectr. 2019, 7, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, H.; Ni, C.; Du, Z.; Yan, F. Human oral microbiota and its modulation for oral health. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 99, 883–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C. Human Microbiome, Actinobacteria in. In Encyclopedia of Metagenomics; Nelson, K.E., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 1–7. ISBN 978-1-4614-6418-1. [Google Scholar]
- Aas, J.A.; Paster, B.J.; Stokes, L.N.; Olsen, I.; Dewhirst, F.E. Defining the normal bacterial flora of the oral cavity. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 5721–5732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, G.; Garg, N.; Hasan, S.; Shirodkar, S. Prevotella: An insight into its characteristics and associated virulence factors. Microb. Pathog. 2022, 169, 105673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dashper, S.G.; Seers, C.A.; Tan, K.H.; Reynolds, E.C. Virulence Factors of the Oral Spirochete Treponema denticola. J. Dent. Res. 2011, 90, 691–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sztukowska, M.N.; Dutton, L.C.; Delaney, C.; Ramsdale, M.; Ramage, G.; Jenkinson, H.F.; Nobbs, A.H.; Lamont, R.J. Community Development between Porphyromonas gingivalis and Candida albicans Mediated by InlJ and Als3. MBio 2018, 9, e00202-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zou, T.; Ding, G.; Jiang, S. Findings and methodologies in oral phageome research: A systematic review. J. Oral Microbiol. 2024, 16, 2417099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santacroce, L.; Di Cosola, M.; Bottalico, L.; Topi, S.; Charitos, I.A.; Ballini, A.; Inchingolo, F.; Cazzolla, A.P.; Dipalma, G. Focus on HPV Infection and the Molecular Mechanisms of Oral Carcinogenesis. Viruses 2021, 13, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santacroce, L.; Sardaro, N.; Topi, S.; Pettini, F.; Bottalico, L.; Cantore, S.; Cascella, G.; Del Prete, R.; Dipalma, G.; Inchingolo, F. The pivotal role of oral microbiota in health and disease. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2020, 34, 733–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poehlein, A.; Seedorf, H. Draft Genome Sequences of Methanobrevibacter curvatus DSM11111, Methanobrevibacter cuticularis DSM11139, Methanobrevibacter filiformis DSM11501, and Methanobrevibacter oralis DSM7256. Genome Announc. 2016, 4, e00617-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, H.T.T.; Nkamga, V.D.; Drancourt, M.; Aboudharam, G. Genetic variants of dental plaque Methanobrevibacter oralis. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2015, 34, 1097–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bringuier, A.; Khelaifia, S.; Richet, H.; Aboudharam, G.; Drancourt, M. Real-Time PCR Quantification of Methanobrevibacter oralis in Periodontitis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 993–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksen, C.; Boustedt, K.; Sonne, S.B.; Dahlgren, J.; Kristiansen, K.; Twetman, S.; Brix, S.; Roswall, J. Early life factors and oral microbial signatures define the risk of caries in a Swedish cohort of preschool children. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 8463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agostoni, C.; Kim, K.S. Nutrition and the microbiome 2015. Pediatr. Res. 2015, 77, 113–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kageyama, S.; Takeshita, T. Development and establishment of oral microbiota in early life. J. Oral Biosci. 2024, 66, 300–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlHarbi, S.G.; Almushayt, A.S.; Bamashmous, S.; Abujamel, T.S.; Bamashmous, N.O. The oral microbiome of children in health and disease—A literature review. Front. Oral Health 2024, 5, 1477004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veenman, F.; van Dijk, A.; Arredondo, A.; Medina-Gomez, C.; Wolvius, E.; Rivadeneira, F.; Àlvarez, G.; Blanc, V.; Kragt, L. Oral microbiota of adolescents with dental caries: A systematic review. Arch. Oral Biol. 2024, 161, 105933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarafidou, K.; Alexakou, E.; Talioti, E.; Bakopoulou, A.; Anastassiadou, V. The oral microbiome in older adults—A state-of-the-art review. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. Plus 2024, 1, 100061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazarina, A.; Kuzmicka, J.; Bortkevica, S.; Zayakin, P.; Kimsis, J.; Igumnova, V.; Sadovska, D.; Freimane, L.; Kivrane, A.; Namina, A.; et al. Oral microbiome variations related to ageing: Possible implications beyond oral health. Arch. Microbiol. 2023, 205, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Donnell, L.E.; Robertson, D.; Nile, C.J.; Cross, L.J.; Riggio, M.; Sherriff, A.; Bradshaw, D.; Lambert, M.; Malcolm, J.; Buijs, M.J.; et al. The Oral Microbiome of Denture Wearers Is Influenced by Levels of Natural Dentition. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0137717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asakawa, M.; Takeshita, T.; Furuta, M.; Kageyama, S.; Takeuchi, K.; Hata, J.; Ninomiya, T.; Yamashita, Y. Tongue Microbiota and Oral Health Status in Community-Dwelling Elderly Adults. mSphere 2018, 3, e00332-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekundo, C.; Langowski, E.; Wolff, D.; Boutin, S.; Frese, C. Maintaining oral health for a hundred years and more?—An analysis of microbial and salivary factors in a cohort of centenarians. J. Oral Microbiol. 2022, 14, 2059891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckburg, P.B.; Bik, E.M.; Bernstein, C.N.; Purdom, E.; Dethlefsen, L.; Sargent, M.; Gill, S.R.; Nelson, K.E.; Relman, D.A. Diversity of the human intestinal microbial flora. Science 2005, 308, 1635–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajilić-Stojanović, M.; de Vos, W.M. The first 1000 cultured species of the human gastrointestinal microbiota. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2014, 38, 996–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yatsunenko, T.; Rey, F.E.; Manary, M.J.; Trehan, I.; Dominguez-Bello, M.G.; Contreras, M.; Magris, M.; Hidalgo, G.; Baldassano, R.N.; Anokhin, A.P.; et al. Human gut microbiome viewed across age and geography. Nature 2012, 486, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, C.J.; Lynch, D.B.; Murphy, K.; Ulaszewska, M.; Jeffery, I.B.; O’Shea, C.A.; Watkins, C.; Dempsey, E.; Mattivi, F.; Tuohy, K.; et al. Evolution of gut microbiota composition from birth to 24 weeks in the INFANTMET Cohort. Microbiome 2017, 5, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Human Microbiome Project Consortium; Huttenhower, C.; Gevers, D.; Knight, R.; Abubucker, S.; Badger, J.H.; Chinwalla, A.T.; Creasy, H.H.; Earl, A.M.; FitzGerald, M.G.; et al. Structure, function and diversity of the healthy human microbiome. Nature 2012, 486, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenhalgh, K.; Meyer, K.M.; Aagaard, K.M.; Wilmes, P. The human gut microbiome in health: Establishment and resilience of microbiota over a lifetime. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 18, 2103–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biagi, E.; Candela, M.; Fairweather-Tait, S.; Franceschi, C.; Brigidi, P. Aging of the human metaorganism: The microbial counterpart. Age 2012, 34, 247–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claesson, M.J.; Jeffery, I.B.; Conde, S.; Power, S.E.; O’Connor, E.M.; Cusack, S.; Harris, H.M.B.; Coakley, M.; Lakshminarayanan, B.; O’Sullivan, O.; et al. Gut microbiota composition correlates with diet and health in the elderly. Nature 2012, 488, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langille, M.G.; Meehan, C.J.; Koenig, J.E.; Dhanani, A.S.; Rose, R.A.; Howlett, S.E.; Beiko, R.G. Microbial shifts in the aging mouse gut. Microbiome 2014, 2, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rampelli, S.; Candela, M.; Turroni, S.; Biagi, E.; Collino, S.; Franceschi, C.; O’Toole, P.W.; Brigidi, P. Functional metagenomic profiling of intestinal microbiome in extreme ageing. Aging 2013, 5, 902–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haran, J.P.; McCormick, B.A. Aging, Frailty, and the Microbiome—How Dysbiosis Influences Human Aging and Disease. Gastroenterology 2021, 160, 507–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biagi, E.; Nylund, L.; Candela, M.; Ostan, R.; Bucci, L.; Pini, E.; Nikkïla, J.; Monti, D.; Satokari, R.; Franceschi, C.; et al. Through Ageing, and Beyond: Gut Microbiota and Inflammatory Status in Seniors and Centenarians. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e10667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monira, S.; Nakamura, S.; Gotoh, K.; Izutsu, K.; Watanabe, H.; Alam, N.H.; Endtz, H.P.; Cravioto, A.; Ali, S.I.; Nakaya, T.; et al. Gut microbiota of healthy and malnourished children in bangladesh. Front. Microbiol. 2011, 2, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Xie, X.; Li, Y.; Liang, T.; Zhong, H.; Yang, L.; Xi, Y.; Zhang, J.; Ding, Y.; Wu, Q. Gut microbiota as an antioxidant system in centenarians associated with high antioxidant activities of gut-resident Lactobacillus. npj Biofilms Microbiomes 2022, 8, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Zeng, T.; Zinellu, A.; Rubino, S.; Kelvin, D.J.; Carru, C. A Cross-Sectional Study of Compositional and Functional Profiles of Gut Microbiota in Sardinian Centenarians. mSystems 2019, 4, e00325-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Yu, T.; Huang, G.; Cai, D.; Liang, X.; Su, H.; Zhu, Z.; Li, D.; Yang, Y.; Shen, P.; et al. Gut Microbiota Community and Its Assembly Associated with Age and Diet in Chinese Centenarians. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 25, 1195–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Candela, M.; Biagi, E.; Brigidi, P.; O’Toole, P.W.; De Vos, W.M. Maintenance of a healthy trajectory of the intestinal microbiome during aging: A dietary approach. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2014, 136–137, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Cobas, A.E.; Gosalbes, M.J.; Friedrichs, A.; Knecht, H.; Artacho, A.; Eismann, K.; Otto, W.; Rojo, D.; Bargiela, R.; von Bergen, M.; et al. Gut microbiota disturbance during antibiotic therapy: A multi-omic approach. Gut 2013, 62, 1591–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodmansey, E.J.; McMurdo, M.E.T.; Macfarlane, G.T.; Macfarlane, S. Comparison of compositions and metabolic activities of fecal microbiotas in young adults and in antibiotic-treated and non-antibiotic-treated elderly subjects. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 6113–6122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Wang, Y.; Gong, T. The interplay between oral microbiota, gut microbiota and systematic diseases. J. Oral Microbiol. 2023, 15, 2213112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.-Y.; Hwang, B.-O.; Lim, M.; Ok, S.-H.; Lee, S.-K.; Chun, K.-S.; Park, K.-K.; Hu, Y.; Chung, W.-Y.; Song, N.-Y. Oral-Gut Microbiome Axis in Gastrointestinal Disease and Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mammen, M.J.; Scannapieco, F.A.; Sethi, S. Oral-lung microbiome interactions in lung diseases. Periodontol. 2000 2020, 83, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santacroce, L.; Man, A.; Charitos, I.A.; Haxhirexha, K.; Topi, S. Current knowledge about the connection between health status and gut microbiota from birth to elderly. A narrative review. Front. Biosci. 2021, 26, 135–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, C.F.F.A.; Correia-de-Sá, T.; Araujo, R.; Barbosa, F.; Burnet, P.W.J.; Ferreira-Gomes, J.; Sampaio-Maia, B. The oral-gut microbiota relationship in healthy humans: Identifying shared bacteria between environments and age groups. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1475159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Zhai, Z.; Ding, Y.; Wei, J.; Wei, Z.; Cao, H. The oral-gut microbiome axis in inflammatory bowel disease: From inside to insight. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1430001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunath, B.J.; De Rudder, C.; Laczny, C.C.; Letellier, E.; Wilmes, P. The oral-gut microbiome axis in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2024, 22, 791–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imhann, F.; Bonder, M.J.; Vich Vila, A.; Fu, J.; Mujagic, Z.; Vork, L.; Tigchelaar, E.F.; Jankipersadsing, S.A.; Cenit, M.C.; Harmsen, H.J.M.; et al. Proton pump inhibitors affect the gut microbiome. Gut 2016, 65, 740–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwauchi, M.; Horigome, A.; Ishikawa, K.; Mikuni, A.; Nakano, M.; Xiao, J.-Z.; Odamaki, T.; Hironaka, S. Relationship between oral and gut microbiota in elderly people. Immun. Inflamm. Dis. 2019, 7, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odamaki, T.; Kato, K.; Sugahara, H.; Hashikura, N.; Takahashi, S.; Xiao, J.-Z.; Abe, F.; Osawa, R. Age-related changes in gut microbiota composition from newborn to centenarian: A cross-sectional study. BMC Microbiol. 2016, 16, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitamoto, S.; Nagao-Kitamoto, H.; Hein, R.; Schmidt, T.M.; Kamada, N. The Bacterial Connection between the Oral Cavity and the Gut Diseases. J. Dent. Res. 2020, 99, 1021–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, S.; Chopra, A.; Karmakar, S.; Bhat, S.G. Periodontitis increases the risk of gastrointestinal dysfunction: An update on the plausible pathogenic molecular mechanisms. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2025, 51, 187–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Könönen, E.; Gursoy, U.K. Oral Prevotella Species and Their Connection to Events of Clinical Relevance in Gastrointestinal and Respiratory Tracts. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 798763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, N.; Wang, J.; Liao, B.; Cheng, L.; Ren, B. The interactions between oral-gut axis microbiota and Helicobacter pylori. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 914418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Kudo, Y.; Baker, J.L.; LaBonte, S.; Jordan, P.A.; McKinnie, S.M.K.; Guo, J.; Huan, T.; Moore, B.S.; Edlund, A. Cariogenic Streptococcus mutans Produces Tetramic Acid Strain-Specific Antibiotics That Impair Commensal Colonization. ACS Infect. Dis. 2020, 6, 563–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Angelis, P.; Gasparini, G.; Manicone, P.F.; Passarelli, P.C.; Azzolino, D.; Rella, E.; De Rosa, G.; Papi, P.; Pompa, G.; De Angelis, S.; et al. The Effect of an Optimized Diet as an Adjunct to Non-Surgical Periodontal Therapy in Subjects with Periodontitis: A Prospective Study. Healthcare 2022, 10, 583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thayer, M.L.T.; Ali, R. The dental demolition derby: Bruxism and its impact-part 1: Background. Br. Dent. J. 2022, 232, 515–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, C.; Minty, M.; Vinel, A.; Canceill, T.; Loubières, P.; Burcelin, R.; Kaddech, M.; Blasco-Baque, V.; Laurencin-Dalicieux, S. Oral Microbiota: A Major Player in the Diagnosis of Systemic Diseases. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haraga, H.; Sato, T.; Watanabe, K.; Hamada, N.; Tani-Ishii, N. Effect of the Progression of Fusobacterium nucleatum-induced Apical Periodontitis on the Gut Microbiota. J. Endod. 2022, 48, 1038–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abed, J.; Maalouf, N.; Manson, A.L.; Earl, A.M.; Parhi, L.; Emgård, J.E.M.; Klutstein, M.; Tayeb, S.; Almogy, G.; Atlan, K.A.; et al. Colon Cancer-Associated Fusobacterium nucleatum May Originate from the Oral Cavity and Reach Colon Tumors via the Circulatory System. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arimatsu, K.; Yamada, H.; Miyazawa, H.; Minagawa, T.; Nakajima, M.; Ryder, M.I.; Gotoh, K.; Motooka, D.; Nakamura, S.; Iida, T.; et al. Oral pathobiont induces systemic inflammation and metabolic changes associated with alteration of gut microbiota. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 4828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Huang, L.; Zhou, X.; Zhao, D.; Wang, Y.; Min, H.; Song, S.; Sun, W.; Gao, Q.; Hu, Q.; et al. Experimental Periodontitis Deteriorated Atherosclerosis Associated with Trimethylamine N-Oxide Metabolism in Mice. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 820535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedghi, L.; DiMassa, V.; Harrington, A.; Lynch, S.V.; Kapila, Y.L. The oral microbiome: Role of key organisms and complex networks in oral health and disease. Periodontol. 2000 2021, 87, 107–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atarashi, K.; Suda, W.; Luo, C.; Kawaguchi, T.; Motoo, I.; Narushima, S.; Kiguchi, Y.; Yasuma, K.; Watanabe, E.; Tanoue, T.; et al. Ectopic colonization of oral bacteria in the intestine drives TH1 cell induction and inflammation. Science 2017, 358, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Chen, X.; Chu, C.H.; Yu, O.Y.; He, J.; Li, M. Roles of Streptococcus mutans in human health: Beyond dental caries. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1503657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Wang, B.; Gao, H.; He, C.; Hua, R.; Liang, C.; Xin, S.; Wang, Y.; Xu, J. Insight into the Relationship between Oral Microbiota and the Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strauss, J.; Kaplan, G.G.; Beck, P.L.; Rioux, K.; Panaccione, R.; Devinney, R.; Lynch, T.; Allen-Vercoe, E. Invasive potential of gut mucosa-derived Fusobacterium nucleatum positively correlates with IBD status of the host. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2011, 17, 1971–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kostic, A.D.; Chun, E.; Robertson, L.; Glickman, J.N.; Gallini, C.A.; Michaud, M.; Clancy, T.E.; Chung, D.C.; Lochhead, P.; Hold, G.L.; et al. Fusobacterium nucleatum Potentiates Intestinal Tumorigenesis and Modulates the Tumor-Immune Microenvironment. Cell Host Microbe 2013, 14, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castellarin, M.; Warren, R.L.; Freeman, J.D.; Dreolini, L.; Krzywinski, M.; Strauss, J.; Barnes, R.; Watson, P.; Allen-Vercoe, E.; Moore, R.A.; et al. Fusobacterium nucleatum infection is prevalent in human colorectal carcinoma. Genome Res. 2012, 22, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitamoto, S.; Kamada, N. The oral-gut axis: A missing piece in the IBD puzzle. Inflamm. Regen. 2023, 43, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Gu, Y.; Li, L.; Liu, T.; Song, X.; Sun, Y.; Cao, X.; Wang, B.; Jiang, K.; Cao, H. Bile Acid-Gut Microbiota Axis in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: From Bench to Bedside. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, V.d.S.M.; Azevedo, J.; Leal, H.F.; Queiroz, A.T.L.d.; Filho, H.P.d.S.; Reis, J.N. Bacterial diversity and prevalence of antibiotic resistance genes in the oral microbiome. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0239664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, H.; Ebrahimi, A.; Ahmadi, F. Antibiotic Therapy in Dentistry. Int. J. Dent. 2021, 2021, 6667624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antibiotic Prophylaxis. Available online: https://www.ada.org/resources/ada-library/oral-health-topics/antibiotic-prophylaxis (accessed on 20 February 2025).
- Wilson, W.R.; Gewitz, M.; Lockhart, P.B.; Bolger, A.F.; DeSimone, D.C.; Kazi, D.S.; Couper, D.J.; Beaton, A.; Kilmartin, C.; Miro, J.M.; et al. Prevention of Viridans Group Streptococcal Infective Endocarditis: A Scientific Statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2021, 143, e963–e978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naghavi, M.; Vollset, S.E.; Ikuta, K.S.; Swetschinski, L.R.; Gray, A.P.; Wool, E.E.; Aguilar, G.R.; Mestrovic, T.; Smith, G.; Han, C.; et al. Global burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance 1990–2021: A Ssystematic analysis with forecasts to 2050. Lancet 2024, 404, 1199–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surveillance of Antimicrobial Resistance in Europe, 2023 Data—Executive Summary. Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/publications-data/surveillance-antimicrobial-resistance-europe-2023-data-executive-summary (accessed on 21 February 2025).
- Lockhart, P.B.; Tampi, M.P.; Abt, E.; Aminoshariae, A.; Durkin, M.J.; Fouad, A.F.; Gopal, P.; Hatten, B.W.; Kennedy, E.; Lang, M.S.; et al. Evidence-based clinical practice guideline on antibiotic use for the urgent management of pulpal- and periapical-related dental pain and intra-oral swelling. J. Am. Dent. Assoc. 2019, 150, 906–921.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Éliás, A.J.; Barna, V.; Patoni, C.; Demeter, D.; Veres, D.S.; Bunduc, S.; Erőss, B.; Hegyi, P.; Földvári-Nagy, L.; Lenti, K. Probiotic supplementation during antibiotic treatment is unjustified in maintaining the gut microbiome diversity: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Med. 2023, 21, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szajewska, H.; Scott, K.P.; de Meij, T.; Forslund-Startceva, S.K.; Knight, R.; Koren, O.; Little, P.; Johnston, B.C.; Łukasik, J.; Suez, J.; et al. Antibiotic-perturbed microbiota and the role of probiotics. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2025, 22, 155–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaffer, M.; Lozupone, C. Prevalence and Source of Fecal and Oral Bacteria on Infant, Child, and Adult Hands. mSystems 2018, 3, e00192-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuurhuis, J.M.; Stokman, M.A.; Witjes, M.J.H.; Langendijk, J.A.; van Winkelhoff, A.J.; Vissink, A.; Spijkervet, F.K.L. Head and neck intensity modulated radiation therapy leads to an increase of opportunistic oral pathogens. Oral Oncol. 2016, 58, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaetti-Jardim, E.; Jardim, E.C.G.; Schweitzer, C.M.; da Silva, J.C.L.; Oliveira, M.M.; Masocatto, D.C.; Dos Santos, C.M. Supragingival and subgingival microbiota from patients with poor oral hygiene submitted to radiotherapy for head and neck cancer treatment. Arch. Oral Biol. 2018, 90, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotwal, G.; Cannon, J.L. Environmental persistence and transfer of enteric viruses. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2014, 4, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahaei, S.M.E.; Mohebbi, S.R.; Zali, M.R. Enteric hepatitis viruses. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Bed Bench 2012, 5, 7–15. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Huang, F.; Ling, Z.; Liu, S.; Liu, J.; Fan, J.; Yu, J.; Wang, W.; Jin, X.; Meng, Y.; et al. Altered faecal microbiota on the expression of Th cells responses in the exacerbation of patients with hepatitis E infection. J. Viral Hepat. 2020, 27, 1243–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karst, S.M. The influence of commensal bacteria on infection with enteric viruses. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 14, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Schryver, A.; Van Winckel, M.; Cornelis, K.; Moens, G.; Devlies, G.; De Backer, G. Helicobacter pylori infection: Further evidence for the role of feco-oral transmission. Helicobacter 2006, 11, 523–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonov, G.E.; Varaeva, Y.R.; Livantsova, E.N.; Starodubova, A.V. The Complicated Relationship of Short-Chain Fatty Acids and Oral Microbiome: A Narrative Review. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.N.; Yao, Y.; Ju, S.Y. Short Chain Fatty Acids and Fecal Microbiota Abundance in Humans with Obesity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.-T.; Sun, C.-L.; Lai, T.-T.; Liou, C.-W.; Lin, Y.-Y.; Xue, J.-Y.; Wang, H.-W.; Chai, L.M.X.; Lee, Y.-J.; Chen, S.-L.; et al. Oral short-chain fatty acids administration regulates innate anxiety in adult microbiome-depleted mice. Neuropharmacology 2022, 214, 109140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, X.; Li, W.; Meng, H. A double-edged sword: Role of butyrate in the oral cavity and the gut. Mol. Oral Microbiol. 2021, 36, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asai, S.; Nakamura, Y.; Yamamura, M.; Ikezawa, H.; Namikawa, I. Quantitative analysis of the Epstein-Barr virus-inducing properties of short-chain fatty acids present in the culture fluids of oral bacteria. Arch. Virol. 1991, 119, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; He, J.; Wang, L.; Zhou, S.; Peng, X.; Huang, S.; Zheng, L.; Cheng, L.; Hao, Y.; Li, J.; et al. Ecological Effect of Arginine on Oral Microbiota. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 7206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuda, H.; Ochiai, K.; Suzuki, N.; Otsuka, K. Butyrate, a bacterial metabolite, induces apoptosis and autophagic cell death in gingival epithelial cells. J. Periodontal Res. 2010, 45, 626–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoer, S.; Shilo, S.; Godneva, A.; Ben-Yacov, O.; Rein, M.; Wolf, B.C.; Lotan-Pompan, M.; Bar, N.; Weiss, E.I.; Houri-Haddad, Y.; et al. Impact of dietary interventions on pre-diabetic oral and gut microbiome, metabolites and cytokines. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 5384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayorga-Ramos, A.; Barba-Ostria, C.; Simancas-Racines, D.; Guamán, L.P. Protective role of butyrate in obesity and diabetes: New insights. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 1067647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Yin, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, W. Gut Microbiota-Derived Components and Metabolites in the Progression of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD). Nutrients 2019, 11, 1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Li, Y.; Cai, Z.; Li, S.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, F.; Liang, S.; Zhang, W.; Guan, Y.; Shen, D.; et al. A metagenome-wide association study of gut microbiota in type 2 diabetes. Nature 2012, 490, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwiertz, A.; Taras, D.; Schäfer, K.; Beijer, S.; Bos, N.A.; Donus, C.; Hardt, P.D. Microbiota and SCFA in lean and overweight healthy subjects. Obesity 2010, 18, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nandy, D.; Craig, S.J.C.; Cai, J.; Tian, Y.; Paul, I.M.; Savage, J.S.; Marini, M.E.; Hohman, E.E.; Reimherr, M.L.; Patterson, A.D.; et al. Metabolomic profiling of stool of two-year old children from the INSIGHT study reveals links between butyrate and child weight outcomes. Pediatr. Obes. 2022, 17, e12833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patil, D.P.; Dhotre, D.P.; Chavan, S.G.; Sultan, A.; Jain, D.S.; Lanjekar, V.B.; Gangawani, J.; Shah, P.S.; Todkar, J.S.; Shah, S.; et al. Molecular analysis of gut microbiota in obesity among Indian individuals. J. Biosci. 2012, 37, 647–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, K.; Dong, W.; Luo, T.; Tang, H.; Zhu, W.; Huang, Y.; Yang, X. Butyrate and obesity: Current research status and future prospect. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1098881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Yin, J.; Zhang, J.; Ward, R.E.; Martin, R.J.; Lefevre, M.; Cefalu, W.T.; Ye, J. Butyrate improves insulin sensitivity and increases energy expenditure in mice. Diabetes 2009, 58, 1509–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, T.; Tremaroli, V. Therapeutic Potential of Butyrate for Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 761834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; He, M.; Yi, X.; Lu, X.; Zhu, M.; Xue, M.; Tang, Y.; Zhu, Y. Short-chain fatty acids in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: New prospects for short-chain fatty acids as therapeutic targets. Heliyon 2024, 10, e26991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canfora, E.E.; Jocken, J.W.; Blaak, E.E. Short-chain fatty acids in control of body weight and insulin sensitivity. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2015, 11, 577–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pant, K.; Venugopal, S.K.; Lorenzo Pisarello, M.J.; Gradilone, S.A. The Role of Gut Microbiome-Derived Short-Chain Fatty Acid Butyrate in Hepatobiliary Diseases. Am. J. Pathol. 2023, 193, 1455–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Y.; Chen, M.; Wang, Z.; Han, J.-D.J. Oral microbiota in aging and diseases. Life Med. 2024, 3, lnae024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Shao, Y. Role of the oral-gut microbiota axis in pancreatic cancer: A new perspective on tumor pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment. Mol. Med. 2025, 31, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adil, N.A.; Omo-Erigbe, C.; Yadav, H.; Jain, S. The Oral–Gut Microbiome–Brain Axis in Cognition. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzolino, D.; Coelho-Junior, H.J.; Proietti, M.; Manzini, V.M.; Cesari, M. Fatigue in older persons: The role of nutrition. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2023, 82, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Feng, Q. Linking Periodontitis with Inflammatory Bowel Disease through the Oral–Gut Axis: The Potential Role of Porphyromonas gingivalis. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, J.; Lu, J.; Huang, Y.; Wang, M.; Chen, B.; Bao, J.; Wang, L.; Cui, D.; Luo, B.; Yan, F. Periodontitis Salivary Microbiota Worsens Colitis. J. Dent. Res. 2022, 101, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanwar, H.; Gnanasekaran, J.M.; Allison, D.; Chuang, L.-S.; He, X.; Aimetti, M.; Baima, G.; Costalonga, M.; Cross, R.K.; Sears, C.; et al. Unravelling the Oral-Gut Axis: Interconnection Between Periodontitis and Inflammatory Bowel Disease, Current Challenges, and Future Perspective. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2024, 18, 1319–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodaii, Z.; Mehrabani, M.; Rafieian, N.; Najafi-Parizi, G.A.; Mirzaei, A.; Akbarzadeh, R. Altered levels of salivary biochemical markers in periodontitis. Am. J. Dent. 2019, 32, 183–186. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Li, Q.; Wang, L.; Ding, H.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Gong, T. The interaction between oral microbiota and gut microbiota in atherosclerosis. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2024, 11, 1406220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- L’Heureux, J.E.; van der Giezen, M.; Winyard, P.G.; Jones, A.M.; Vanhatalo, A. Localisation of nitrate-reducing and highly abundant microbial communities in the oral cavity. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0295058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundberg, J.O.; Weitzberg, E.; Gladwin, M.T. The nitrate-nitrite-nitric oxide pathway in physiology and therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2008, 7, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundberg, J.O.; Carlström, M.; Larsen, F.J.; Weitzberg, E. Roles of dietary inorganic nitrate in cardiovascular health and disease. Cardiovasc. Res. 2011, 89, 525–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanhatalo, A.; Blackwell, J.R.; L’Heureux, J.E.; Williams, D.W.; Smith, A.; van der Giezen, M.; Winyard, P.G.; Kelly, J.; Jones, A.M. Nitrate-responsive oral microbiome modulates nitric oxide homeostasis and blood pressure in humans. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2018, 124, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fennema, D.; Phillips, I.R.; Shephard, E.A. Trimethylamine and Trimethylamine N-Oxide, a Flavin-Containing Monooxygenase 3 (FMO3)-Mediated Host-Microbiome Metabolic Axis Implicated in Health and Disease. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2016, 44, 1839–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrea, L.; Annunziata, G.; Muscogiuri, G.; Di Somma, C.; Laudisio, D.; Maisto, M.; de Alteriis, G.; Tenore, G.C.; Colao, A.; Savastano, S. Trimethylamine-N-oxide (TMAO) as Novel Potential Biomarker of Early Predictors of Metabolic Syndrome. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Qiu, J.; Lian, J.; Yang, X.; Zhou, J. Gut Metabolite Trimethylamine-N-Oxide in Atherosclerosis: From Mechanism to Therapy. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 723886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caradonna, E.; Abate, F.; Schiano, E.; Paparella, F.; Ferrara, F.; Vanoli, E.; Difruscolo, R.; Goffredo, V.M.; Amato, B.; Setacci, C.; et al. Trimethylamine-N-Oxide (TMAO) as a Rising-Star Metabolite: Implications for Human Health. Metabolites 2025, 15, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Xue, J.; Shan, J.; Hong, Y.; Zhu, W.; Nie, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Ji, N.; Luo, X.; Zhang, T.; et al. Gut-Flora-Dependent Metabolite Trimethylamine-N-Oxide Promotes Atherosclerosis-Associated Inflammation Responses by Indirect ROS Stimulation and Signaling Involving AMPK and SIRT1. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Kwek, E.; Hao, W.; Zhu, H.; Liu, J.; Ma, K.Y.; Chen, Z.-Y. Hawthorn fruit extract reduced trimethylamine-N-oxide (TMAO)-exacerbated atherogenesis in mice via anti-inflammation and anti-oxidation. Nutr. Metab. 2021, 18, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Shui, Y.; Cui, Y.; Tang, C.; Wang, X.; Qiu, X.; Hu, W.; Fei, L.; Li, Y.; Zhang, S.; et al. Gut microbiota dependent trimethylamine N-oxide aggravates angiotensin II-induced hypertension. Redox Biol. 2021, 46, 102115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scannapieco, F.A.; Cantos, A. Oral inflammation and infection, and chronic medical diseases: Implications for the elderly. Periodontol. 2000 2016, 72, 153–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, R.; Xu, C.; Feng, B.; Gao, X.; Liu, Z. Critical roles of bile acids in regulating intestinal mucosal immune responses. Ther. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2021, 14, 17562848211018098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dosedělová, V.; Laštovičková, M.; Ayala-Cabrera, J.F.; Dolina, J.; Konečný, Š.; Schmitz, O.J.; Kubáň, P. Quantification and identification of bile acids in saliva by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry: Possible non-invasive diagnostics of Barrett’s esophagus? J. Chromatogr. A 2022, 1676, 463287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, K.; Saha, P.K.; Chan, L.; Moore, D.D. Farnesoid X receptor is essential for normal glucose homeostasis. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 1102–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taoka, H.; Yokoyama, Y.; Morimoto, K.; Kitamura, N.; Tanigaki, T.; Takashina, Y.; Tsubota, K.; Watanabe, M. Role of bile acids in the regulation of the metabolic pathways. World J. Diabetes 2016, 7, 260–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.-X.; Shen, W.; Sun, H. Effects of nuclear receptor FXR on the regulation of liver lipid metabolism in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatol. Int. 2010, 4, 741–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Xie, C.; Nichols, R.G.; Chan, S.H.J.; Jiang, C.; Hao, R.; Smith, P.B.; Cai, J.; Simons, M.N.; Hatzakis, E.; et al. Farnesoid X Receptor Signaling Shapes the Gut Microbiota and Controls Hepatic Lipid Metabolism. mSystems 2016, 1, e00070-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cariou, B.; Duran-Sandoval, D.; Kuipers, F.; Staels, B. Farnesoid X Receptor: A New Player in Glucose Metabolism? Endocrinology 2005, 146, 981–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, C.; Gioiello, A.; Noriega, L.; Strehle, A.; Oury, J.; Rizzo, G.; Macchiarulo, A.; Yamamoto, H.; Mataki, C.; Pruzanski, M.; et al. TGR5-mediated bile acid sensing controls glucose homeostasis. Cell Metab. 2009, 10, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, G.; Ma, X.; Fu, X.; Meng, Z.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Y.-D.; Ness, C.V.; Yu, D.; Xu, R.; Huang, W. GPBAR1/TGR5 Mediates Bile Acid-Induced Cytokine Expression in Murine Kupffer Cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e93567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, K.C.P.; Ma, J.; Loiola, R.A.; Chen, X.; Jia, W. Bile acid-activated receptors in innate and adaptive immunity: Targeted drugs and biological agents. Eur. J. Immunol. 2023, 53, 2250299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernstein, H.; Bernstein, C. Bile acids as carcinogens in the colon and at other sites in the gastrointestinal system. Exp. Biol. Med. 2023, 248, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vakil, N.; van Zanten, S.V.; Kahrilas, P.; Dent, J.; Jones, R.; Global Consensus Group. The Montreal definition and classification of gastroesophageal reflux disease: A global evidence-based consensus. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 101, 1900–1920; quiz 1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nehra, D.; Howell, P.; Williams, C.P.; Pye, J.K.; Beynon, J. Toxic bile acids in gastro-oesophageal reflux disease: Influence of gastric acidity. Gut 1999, 44, 598–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kauer, W.K.H.; Peters, J.H.; DeMeester, T.R.; Feussner, H.; Ireland, A.P.; Stein, H.J.; Siewert, R.J. Composition and concentration of bile acid reflux into the esophagus of patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease. Surgery 1997, 122, 874–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milani, D.C.; Borba, M.; Farré, R.; Grando, L.G.R.; Bertol, C.; Fornari, F. Gastroesophageal reflux disease and dental erosion: The role of bile acids. Arch. Oral Biol. 2022, 139, 105429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larabi, A.B.; Masson, H.L.P.; Bäumler, A.J. Bile acids as modulators of gut microbiota composition and function. Gut Microbes 2023, 15, 2172671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahlström, A.; Sayin, S.I.; Marschall, H.-U.; Bäckhed, F. Intestinal Crosstalk between Bile Acids and Microbiota and Its Impact on Host Metabolism. Cell Metab. 2016, 24, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shansky, Y.; Bespyatykh, J. Bile Acids: Physiological Activity and Perspectives of Using in Clinical and Laboratory Diagnostics. Molecules 2022, 27, 7830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocvirk, S.; O’Keefe, S.J.D. Dietary fat, bile acid metabolism and colorectal cancer. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2021, 73, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzior, D.V.; Quinn, R.A. Review: Microbial transformations of human bile acids. Microbiome 2021, 9, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, A.J.; Greytak, M.; Kessler, M.; Yadlapati, R. Pilot study evaluating salivary bile acids as a diagnostic biomarker of laryngopharyngeal reflux. Dis. Esophagus 2024, 37, doae021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vageli, D.P.; Doukas, S.G.; Doukas, P.G.; Judson, B.L. Bile reflux and hypopharyngeal cancer (Review). Oncol. Rep. 2021, 46, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleaver, L.M.; Carda-Diéguez, M.; Moazzez, R.; Carpenter, G.H. Novel bacterial proteolytic and metabolic activity associated with dental erosion-induced oral dysbiosis. Microbiome 2023, 11, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boisen, G.; Davies, J.R.; Neilands, J. Acid tolerance in early colonizers of oral biofilms. BMC Microbiol. 2021, 21, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dipalma, G.; Inchingolo, A.D.; Inchingolo, F.; Charitos, I.A.; Di Cosola, M.; Cazzolla, A.P. Focus on the cariogenic process: Microbial and biochemical interactions with teeth and oral environment. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2021, 35, 429–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Liu, Y.; Yi, J.; Fang, Y.; Guo, Q.; Cheng, L.; He, J.; Li, M. Imbalance of oral microbiome homeostasis: The relationship between microbiota and the occurrence of dental caries. BMC Microbiol. 2025, 25, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Chu, W.; Luo, J.; Yang, J.; He, L.; Li, J. Dental Materials for Oral Microbiota Dysbiosis: An Update. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 900918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawar, N.; Park, S.G.; Schwartz, J.L.; Callahan, N.; Obrez, A.; Yang, B.; Chen, Z.; Adami, G.R. Salivary microbiome with gastroesophageal reflux disease and treatment. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Curran, G.; Altinok Dindar, D.; Wu, Y.; Wu, H.; Sharpton, T.; Zhao, L.; Lieberman, D.; Otaki, F. Insights into the Oral Microbiome and Barrett’s Esophagus Early Detection: A Narrative Review. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2021, 12, e00390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wang, S.; Zhang, N.; Li, P. The oral microbiome and oral and upper gastrointestinal diseases. J. Oral Microbiol. 2024, 16, 2355823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snider, E.J.; Freedberg, D.E.; Abrams, J.A. Potential Role of the Microbiome in Barrett’s Esophagus and Esophageal Adenocarcinoma. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2016, 61, 2217–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigor’eva, I.N.; Romanova, T.I. Gallstone Disease and Microbiome. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, F.; Shen, H.; Li, Z.; Meng, F.; Li, L.; Yang, J.; Chen, Y.; Bo, X.; Zhang, X.; Ni, M. Influence of the Biliary System on Biliary Bacteria Revealed by Bacterial Communities of the Human Biliary and Upper Digestive Tracts. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0150519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandari, S.; Reddy, M.; Shahzad, G. Association between oral hygiene and ultrasound-confirmed gallstone disease in US population. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 29, 861–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melander, R.J.; Minvielle, M.J.; Melander, C. Controlling bacterial behavior with indole-containing natural products and derivatives. Tetrahedron 2014, 70, 6363–6372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Tan, L.; Wu, L.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, Z.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, C.; Gao, L. Regulation of tryptophan-indole metabolic pathway in Porphyromonas gingivalis virulence and microbiota dysbiosis in periodontitis. npj Biofilms Microbiomes 2025, 11, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-H.; Lee, J. Indole as an intercellular signal in microbial communities. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2010, 34, 426–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, B.; Hu, Y.; Zhao, Y. New Insights into Gut-Bacteria-Derived Indole and Its Derivatives in Intestinal and Liver Diseases. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 769501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Lee, J.-H.; Lee, J. Diverse roles of microbial indole compounds in eukaryotic systems. Biol. Rev. 2021, 96, 2522–2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chimerel, C.; Emery, E.; Summers, D.K.; Keyser, U.; Gribble, F.M.; Reimann, F. Bacterial metabolite indole modulates incretin secretion from intestinal enteroendocrine L cells. Cell Rep. 2014, 9, 1202–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelante, T.; Iannitti, R.G.; Cunha, C.; De Luca, A.; Giovannini, G.; Pieraccini, G.; Zecchi, R.; D’Angelo, C.; Massi-Benedetti, C.; Fallarino, F.; et al. Tryptophan catabolites from microbiota engage aryl hydrocarbon receptor and balance mucosal reactivity via interleukin-22. Immunity 2013, 39, 372–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexeev, E.E.; Lanis, J.M.; Kao, D.J.; Campbell, E.L.; Kelly, C.J.; Battista, K.D.; Gerich, M.E.; Jenkins, B.R.; Walk, S.T.; Kominsky, D.J.; et al. Microbiota-Derived Indole Metabolites Promote Human and Murine Intestinal Homeostasis through Regulation of Interleukin-10 Receptor. Am. J. Pathol. 2018, 188, 1183–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natividad, J.M.; Agus, A.; Planchais, J.; Lamas, B.; Jarry, A.C.; Martin, R.; Michel, M.-L.; Chong-Nguyen, C.; Roussel, R.; Straube, M.; et al. Impaired Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Ligand Production by the Gut Microbiota Is a Key Factor in Metabolic Syndrome. Cell Metab. 2018, 28, 737–749.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, S.; Ding, Y.; Saedi, N.; Choi, M.; Sridharan, G.V.; Sherr, D.H.; Yarmush, M.L.; Alaniz, R.C.; Jayaraman, A.; Lee, K. Gut Microbiota-Derived Tryptophan Metabolites Modulate Inflammatory Response in Hepatocytes and Macrophages. Cell Rep. 2018, 23, 1099–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, M.; Mukherjee, S.; Wang, H.; Li, H.; Sun, K.; Benechet, A.P.; Qiu, Z.; Maher, L.; Redinbo, M.R.; Phillips, R.S.; et al. Symbiotic Bacterial Metabolites Regulate Gastrointestinal Barrier Function via the Xenobiotic Sensor PXR and Toll-like Receptor 4. Immunity 2014, 41, 296–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abildgaard, A.; Elfving, B.; Hokland, M.; Wegener, G.; Lund, S. The microbial metabolite indole-3-propionic acid improves glucose metabolism in rats, but does not affect behaviour. Arch. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 124, 306–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.Z.; Shan, W.; Guo, L.; Chu, C.H.; Zhang, J. Quorum sensing in Porphyromonas gingivalis and oral microbial interactions: A scoping review. Front. Oral Health 2025, 6, 1573863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; He, X.; Shi, W. Intercellular communications in multispecies oral microbial communities. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rickard, A.H.; Palmer, R.J.; Blehert, D.S.; Campagna, S.R.; Semmelhack, M.F.; Egland, P.G.; Bassler, B.L.; Kolenbrander, P.E. Autoinducer 2: A concentration-dependent signal for mutualistic bacterial biofilm growth. Mol. Microbiol. 2006, 60, 1446–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scardina, G.A.; Messina, P. Good Oral Health and Diet. BioMed Res. Int. 2012, 2012, 720692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azzolino, D.; Felicetti, A.; Santacroce, L.; Lucchi, T.; Garcia-Godoy, F.; Passarelli, P.C. The emerging role of oral microbiota: A key driver of oral and systemic health. Am. J. Dent. 2025, 38, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- de Vrese, M.; Schrezenmeir, J. Probiotics, prebiotics, and synbiotics. In Food Biotechnology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; Volume 111, pp. 1–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ticinesi, A.; Lauretani, F.; Milani, C.; Nouvenne, A.; Tana, C.; Del Rio, D.; Maggio, M.; Ventura, M.; Meschi, T. Aging Gut Microbiota at the Cross-Road between Nutrition, Physical Frailty, and Sarcopenia: Is There a Gut–Muscle Axis? Nutrients 2017, 9, 1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurtshuk, P. Bacterial Metabolism. In Medical Microbiology, 4th ed.; Baron, S., Ed.; University of Texas Medical Branch at Galveston: Galveston, TX, USA, 1996; ISBN 978-0-9631172-1-2. [Google Scholar]
- Wade, W.G. The oral microbiome in health and disease. Pharmacol. Res. 2013, 69, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowden, G.H.; Li, Y.H. Nutritional influences on biofilm development. Adv. Dent. Res. 1997, 11, 81–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furman, D.; Campisi, J.; Verdin, E.; Carrera-Bastos, P.; Targ, S.; Franceschi, C.; Ferrucci, L.; Gilroy, D.W.; Fasano, A.; Miller, G.W.; et al. Chronic inflammation in the etiology of disease across the life span. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 1822–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millen, A.E.; Dahhan, R.; Freudenheim, J.L.; Hovey, K.M.; Li, L.; McSkimming, D.I.; Andrews, C.A.; Buck, M.J.; LaMonte, M.J.; Kirkwood, K.L.; et al. Dietary carbohydrate intake is associated with the subgingival plaque oral microbiome abundance and diversity in a cohort of postmenopausal women. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, K.; Ishikado, A.; Morino, K.; Nishio, Y.; Ugi, S.; Kajiwara, S.; Kurihara, M.; Iwakawa, H.; Nakao, K.; Uesaki, S.; et al. A high-fiber, low-fat diet improves periodontal disease markers in high-risk subjects: A pilot study. Nutr. Res. 2014, 34, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altun, E.; Walther, C.; Borof, K.; Petersen, E.; Lieske, B.; Kasapoudis, D.; Jalilvand, N.; Beikler, T.; Jagemann, B.; Zyriax, B.-C.; et al. Association between Dietary Pattern and Periodontitis-A Cross-Sectional Study. Nutrients 2021, 13, 4167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagli, N.; Dagli, R.; Darwish, S.; Baroudi, K. Oral Microbial Shift: Factors affecting the Microbiome and Prevention of Oral Disease. J. Contemp. Dent. Pract. 2016, 17, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Yu, W.-H.; Izard, J.; Baranova, O.V.; Lakshmanan, A.; Dewhirst, F.E. The Human Oral Microbiome Database: A web accessible resource for investigating oral microbe taxonomic and genomic information. Database 2010, 2010, baq013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samaranayake, L.; Matsubara, V.H. Normal Oral Flora and the Oral Ecosystem. Dent. Clin. N. Am. 2017, 61, 199–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, T.H.; Kern, T.; Bak, E.G.; Kashani, A.; Allin, K.H.; Nielsen, T.; Hansen, T.; Pedersen, O. Impact of a vegan diet on the human salivary microbiota. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, A.; Agrawal, M.; Savin-Shalom, E.; Wong, E.C.L.; Levinson, C.; Gold, S.; Narula, N.; Colombel, J.-F.; Carbonnel, F. Impact of diet on inflammatory bowel disease risk: Systematic review, meta-analyses and implications for prevention. eClinicalMedicine 2025, 86, 103353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cronin, P.; Joyce, S.A.; O’Toole, P.W.; O’Connor, E.M. Dietary Fibre Modulates the Gut Microbiota. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malesza, I.J.; Malesza, M.; Walkowiak, J.; Mussin, N.; Walkowiak, D.; Aringazina, R.; Bartkowiak-Wieczorek, J.; Mądry, E. High-Fat, Western-Style Diet, Systemic Inflammation, and Gut Microbiota: A Narrative Review. Cells 2021, 10, 3164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinashi, Y.; Hase, K. Partners in Leaky Gut Syndrome: Intestinal Dysbiosis and Autoimmunity. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 673708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, S.; Chinda, D.; Iino, C.; Sawada, K.; Mikami, T.; Nakaji, S.; Sakuraba, H.; Fukuda, S. A Cohort Study of the Influence of the 12-Component Modified Japanese Diet Index on Oral and Gut Microbiota in the Japanese General Population. Nutrients 2024, 16, 524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eremenko, M.; Pink, C.; Biffar, R.; Schmidt, C.O.; Ittermann, T.; Kocher, T.; Meisel, P. Cross-sectional association between physical strength, obesity, periodontitis and number of teeth in a general population. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2016, 43, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santonocito, S.; Giudice, A.; Polizzi, A.; Troiano, G.; Merlo, E.M.; Sclafani, R.; Grosso, G.; Isola, G. A Cross-Talk between Diet and the Oral Microbiome: Balance of Nutrition on Inflammation and Immune System’s Response during Periodontitis. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidel, D.V.; Azcárate-Peril, M.A.; Chapkin, R.S.; Turner, N.D. Shaping functional gut microbiota using dietary bioactives to reduce colon cancer risk. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2017, 46, 191–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riboli, E.; Norat, T. Epidemiologic evidence of the protective effect of fruit and vegetables on cancer risk. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2003, 78, 559S–569S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terry, P.; Giovannucci, E.; Michels, K.B.; Bergkvist, L.; Hansen, H.; Holmberg, L.; Wolk, A. Fruit, vegetables, dietary fiber, and risk of colorectal cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2001, 93, 525–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trock, B.; Lanza, E.; Greenwald, P. Dietary fiber, vegetables, and colon cancer: Critical review and meta-analyses of the epidemiologic evidence. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1990, 82, 650–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kris-Etherton, P.M.; Hecker, K.D.; Bonanome, A.; Coval, S.M.; Binkoski, A.E.; Hilpert, K.F.; Griel, A.E.; Etherton, T.D. Bioactive compounds in foods: Their role in the prevention of cardiovascular disease and cancer. Am. J. Med. 2002, 113 (Suppl. 9B), 71S–88S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzola, G.; Cattaneo, C.; Patta, E.; Alalwan, T.A.; Azzolino, D.; Perna, S.; Rondanelli, M. Sustainable Plant-Based Diets and Food Allergies: A Scoping Review Inspired by EAT-Lancet. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 7296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzola, L.G.; Fankhauser, N.; Srinivasan, M. Influence of the vegan, vegetarian and omnivore diet on the oral health status in adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Evid. Based Dent. 2023, 24, 43–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerstens, R.; Ng, Y.Z.; Pettersson, S.; Jayaraman, A. Balancing the Oral–Gut–Brain Axis with Diet. Nutrients 2024, 16, 3206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandya, V.S.; Fiorillo, L.; Kalpe, S.; Mehta, V.; Meto, A.; Certo, A.D.; Russo, D.; Gorassini, F.; Mancini, M.; Mancini, A.; et al. Veganism and Oral Health—An Overview through the Perspective. Eur. J. Gen. Dent. 2023, 12, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzolino, D.; Bertoni, C.; De Cosmi, V.; Spolidoro, G.C.I.; Agostoni, C.; Lucchi, T.; Mazzocchi, A. Omega-3 polyunsatured fatty acids and physical performance across the lifespan: A narrative review. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1414132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-T.; Tribble, G.D. Roles of specialized pro-resolving mediators and omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids in periodontal inflammation and impact on oral microbiota. Front. Oral Health 2023, 4, 1217088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awoyemi, A.; Trøseid, M.; Arnesen, H.; Solheim, S.; Seljeflot, I. Effects of dietary intervention and n-3 PUFA supplementation on markers of gut-related inflammation and their association with cardiovascular events in a high-risk population. Atherosclerosis 2019, 286, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.B.; Ebersole, J.L. A novel bioactivity of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and their ester derivatives. Mol. Oral Microbiol. 2010, 25, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, M.; Zhou, Z.; Dong, J.; Zhang, J.; Xia, Y.; Shu, R. Antibacterial and antibiofilm activities of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) and eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) against periodontopathic bacteria. Microb. Pathog. 2016, 99, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stańdo-Retecka, M.; Piatek, P.; Namiecinska, M.; Bonikowski, R.; Lewkowicz, P.; Lewkowicz, N. Clinical and microbiological outcomes of subgingival instrumentation supplemented with high-dose omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids in periodontal treatment—A randomized clinical trial. BMC Oral Health 2023, 23, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shama, S.; Liu, W. Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Gut Microbiota: A Reciprocal Interaction in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2020, 65, 906–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Peters, B.A.; Jacobs, E.J.; Gapstur, S.M.; Purdue, M.P.; Freedman, N.D.; Alekseyenko, A.V.; Wu, J.; Yang, L.; Pei, Z.; et al. Drinking alcohol is associated with variation in the human oral microbiome in a large study of American adults. Microbiome 2018, 6, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, C.; Guarner, F.; Reid, G.; Gibson, G.R.; Merenstein, D.J.; Pot, B.; Morelli, L.; Canani, R.B.; Flint, H.J.; Salminen, S.; et al. The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics consensus statement on the scope and appropriate use of the term probiotic. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 11, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, G.R.; Hutkins, R.; Sanders, M.E.; Prescott, S.L.; Reimer, R.A.; Salminen, S.J.; Scott, K.; Stanton, C.; Swanson, K.S.; Cani, P.D.; et al. Expert consensus document: The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics (ISAPP) consensus statement on the definition and scope of prebiotics. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 14, 491–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slomka, V.; Herrero, E.R.; Boon, N.; Bernaerts, K.; Trivedi, H.M.; Daep, C.; Quirynen, M.; Teughels, W. Oral prebiotics and the influence of environmental conditions in vitro. J. Periodontol. 2018, 89, 708–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hemarajata, P.; Versalovic, J. Effects of probiotics on gut microbiota: Mechanisms of intestinal immunomodulation and neuromodulation. Ther. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2013, 6, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santacroce, L.; Charitos, I.A.; Bottalico, L. A successful history: Probiotics and their potential as antimicrobials. Expert Rev. Anti-Infect. Ther. 2019, 17, 635–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clifford, M.N. Diet-derived phenols in plasma and tissues and their implications for health. Planta Med. 2004, 70, 1103–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cueva, C.; Silva, M.; Pinillos, I.; Bartolomé, B.; Moreno-Arribas, M.V. Interplay between Dietary Polyphenols and Oral and Gut Microbiota in the Development of Colorectal Cancer. Nutrients 2020, 12, 625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaymaz, K.; Hensel, A.; Beikler, T. Polyphenols in the prevention and treatment of periodontal disease: A systematic review of in vivo, ex vivo and in vitro studies. Fitoterapia 2019, 132, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majewska, M.; Lewandowska, U. The chemopreventive and anticancer potential against colorectal cancer of polyphenol-rich fruit extracts. Food Rev. Int. 2018, 34, 390–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costea, T.; Hudiță, A.; Ciolac, O.-A.; Gălățeanu, B.; Ginghină, O.; Costache, M.; Ganea, C.; Mocanu, M.-M. Chemoprevention of Colorectal Cancer by Dietary Compounds. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteban-Fernández, A.; Zorraquín-Peña, I.; González de Llano, D.; Bartolomé, B.; Moreno-Arribas, M.V. The role of wine and food polyphenols in oral health. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 69, 118–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palaska, I.; Papathanasiou, E.; Theoharides, T.C. Use of polyphenols in periodontal inflammation. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 720, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, M.C.; Ribeiro-Vidal, H.; Esteban-Fernández, A.; Bartolomé, B.; Figuero, E.; Moreno-Arribas, M.V.; Sanz, M.; Herrera, D. Antimicrobial activity of red wine and oenological extracts against periodontal pathogens in a validated oral biofilm model. BMC Complement Altern. Med. 2019, 19, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cano, R.; Bermúdez, V.; Galban, N.; Garrido, B.; Santeliz, R.; Gotera, M.P.; Duran, P.; Boscan, A.; Carbonell-Zabaleta, A.-K.; Durán-Agüero, S.; et al. Dietary Polyphenols and Gut Microbiota Cross-Talk: Molecular and Therapeutic Perspectives for Cardiometabolic Disease: A Narrative Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 9118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
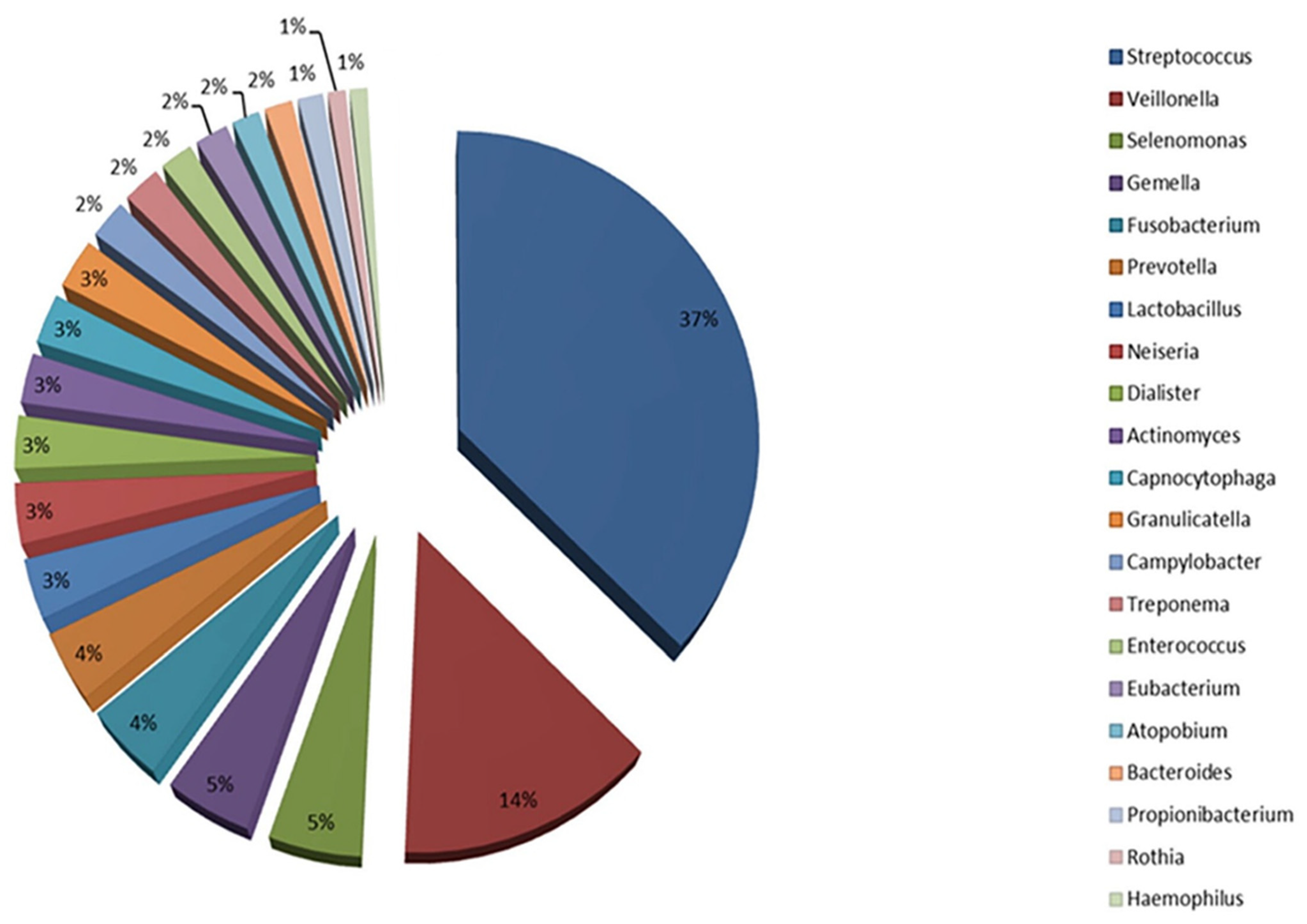
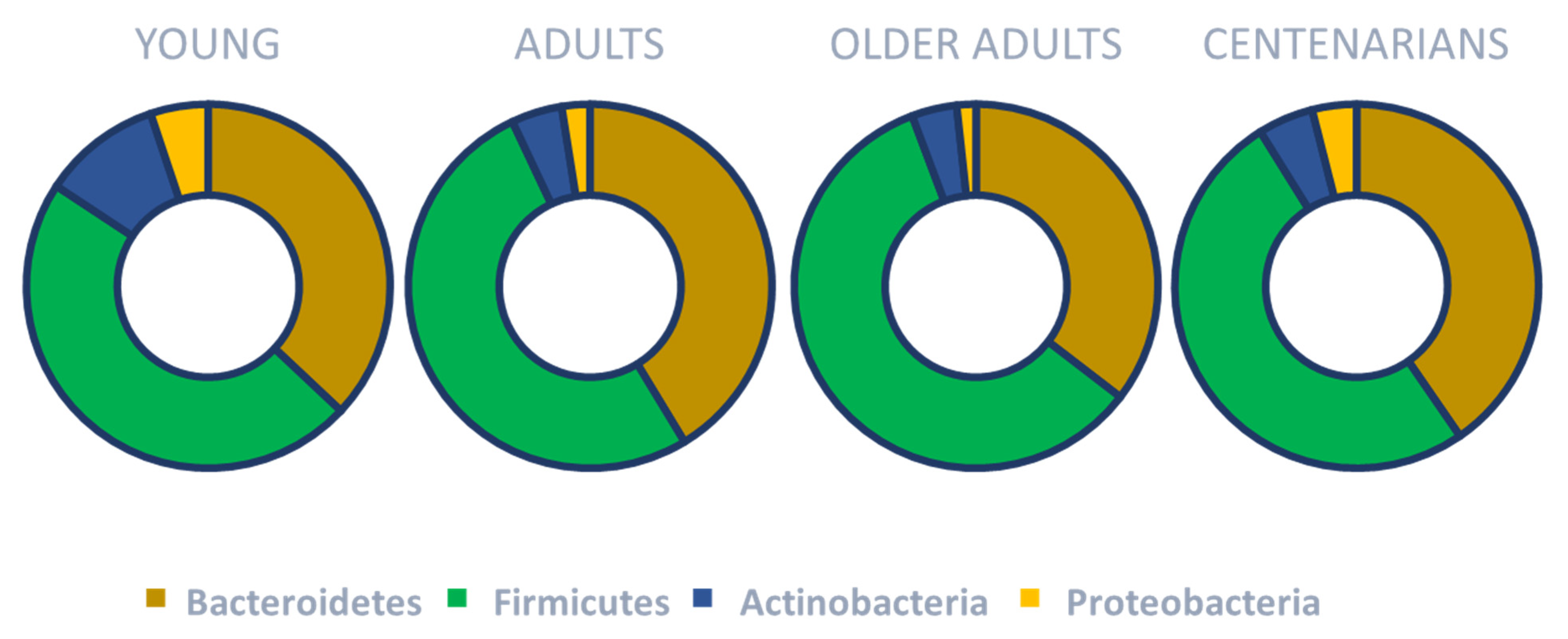
| Infancy (0–2 years) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Oral Microbiota | Gut Microbiota | |
| Main composition | Streptococcus, Staphylococcus, Neisseria | Enterobacteriaceae, Bifidobacterium, Lactobacillus |
| Characteristics and influencing factors |
|
|
| Childhood (2–12 years) | ||
| Oral Microbiota | Gut Microbiota | |
| Main composition | Streptococcus, Veillonella, Actinomyces, Fusobacterium | Bacillota (e.g., Clostridium), Bacteroidota, Prevotella |
| Characteristics and influencing factors |
|
|
| Adolescence (13–18 years) | ||
| Oral Microbiota | Gut Microbiota | |
| Main composition | Streptococcus, Fusobacterium, Neisseria, Prevotella | Bacillota, Bacteroidota, Actinobacteria |
| Characteristics and influencing factors |
|
|
| Adulthood (18–65 years) | ||
| Oral Microbiota | Gut Microbiota | |
| Main composition | Streptococcus, Veillonella, Actinomyces, Prevotella, Haemophilus | Firmicutes (e.g., Clostridia), Bacteroidetes, Actinobacteria, Proteobacteria |
| Characteristics and influencing factors |
|
|
| Older People (>65 years) | ||
| Oral Microbiota | Gut Microbiota | |
| Main composition | ↑ Lactobacillaceae, Streptococcus anginosus, and Gemella sanguinis ↓ Neisseria | ↓ Bacillota/Bacteroidota ratio, Bifidobacteriaceae ↑ Pseudomonadota (Escherichia coli, Klebsiella, Acquabacterium) |
| Main composition | Denture users: ↑ Bacillota and Actinomycetota | - |
| Main composition | Edentulous: ↑Prevotella histicola, Veillonella atypica, Streptococcus salivarius, and Streptococcus parasanguinis | - |
| Characteristics and influencing factors |
|
|
| Centenarians (100+ years) | ||
| Oral Microbiota | Gut Microbiota | |
| Main composition | Toothy centenarians | ↑ Pseudomonadota (Escherichia coli et rel., Haemophilus spp., Klebsiella pneumoniae et rel., Leminorella spp., Proteus et rel., Pseudomonas, Serratia spp., Vibrio spp., and Yersinia et rel.), Bacillota (Bacillus spp., Staphylococcus spp.) ↑ Methanobrevibacter smithii, Bifidobacterium adolescentis, Clostridium leptum ↑ Lactic acid species (Lactobacillaceae) ↓ Bacillota/Bacteroidota ratio ↓ Faecalibacterium prausnitzii, Agathobacter rectalis |
| Dental plaque and saliva: ↑ Spirochaetota and Synergistota (at phylum level), Aggregatibacter spp., Prevotella spp., Campylobacter spp., Anaeroglobus spp., Selenomonas spp., Fusobacterium spp., and Porphyromonas endodontalis (at genus level) | ||
| Dental plaque: ↑ Bifidobacterium and Scardovia (at genus level), Porphyromonas gingivalis, Tannerella forsythia, and Prevotella intermedia (at species level) | ||
| Edentulous | ||
| Dental plaque and saliva: ↑ Bacillota and Actinomycetota (at phylum level), Streptococcus spp. (at genus level) | ||
| Characteristics and influencing factors |
|
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Azzolino, D.; Carnevale-Schianca, M.; Santacroce, L.; Colella, M.; Felicetti, A.; Terranova, L.; Castrejón-Pérez, R.C.; Garcia-Godoy, F.; Lucchi, T.; Passarelli, P.C. The Oral–Gut Microbiota Axis Across the Lifespan: New Insights on a Forgotten Interaction. Nutrients 2025, 17, 2538. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17152538
Azzolino D, Carnevale-Schianca M, Santacroce L, Colella M, Felicetti A, Terranova L, Castrejón-Pérez RC, Garcia-Godoy F, Lucchi T, Passarelli PC. The Oral–Gut Microbiota Axis Across the Lifespan: New Insights on a Forgotten Interaction. Nutrients. 2025; 17(15):2538. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17152538
Chicago/Turabian StyleAzzolino, Domenico, Margherita Carnevale-Schianca, Luigi Santacroce, Marica Colella, Alessia Felicetti, Leonardo Terranova, Roberto Carlos Castrejón-Pérez, Franklin Garcia-Godoy, Tiziano Lucchi, and Pier Carmine Passarelli. 2025. "The Oral–Gut Microbiota Axis Across the Lifespan: New Insights on a Forgotten Interaction" Nutrients 17, no. 15: 2538. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17152538
APA StyleAzzolino, D., Carnevale-Schianca, M., Santacroce, L., Colella, M., Felicetti, A., Terranova, L., Castrejón-Pérez, R. C., Garcia-Godoy, F., Lucchi, T., & Passarelli, P. C. (2025). The Oral–Gut Microbiota Axis Across the Lifespan: New Insights on a Forgotten Interaction. Nutrients, 17(15), 2538. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17152538










