The State of Weight in Cystic Fibrosis: Understanding Nutritional Status and Individualizing Nutritional Care in the Modulator Era
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Undernutrition in Cystic Fibrosis
3. Co-Morbid Conditions Associated with Undernutrition in PwCF
3.1. Celiac Disease and Non-Celiac Gluten Sensitivity
3.2. Eosinophilic Esophagitis
3.3. Inflammatory Bowel Disease
3.4. Cystic-Fibrosis-Related Diabetes (CFRD)
3.5. Advanced CF Liver Disease
4. Overnutrition in Cystic Fibrosis
4.1. Overnutrition in CF Prior to Widespread HEMT Use
4.2. Acceleration of Weight Trajectory with HEMT and Potential Mechanisms
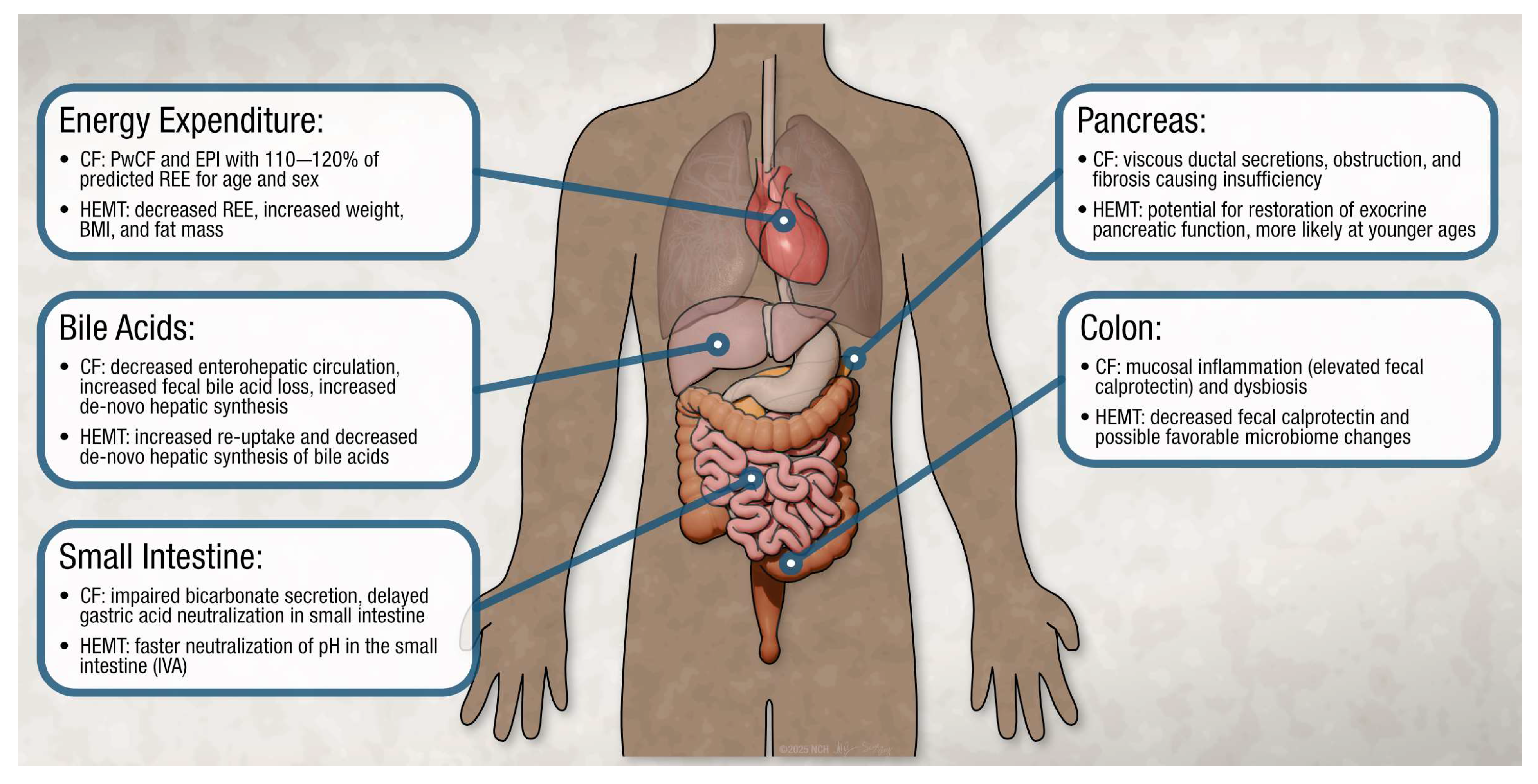
4.3. Changes in Energy Expenditure
4.4. Changes in Exocrine Pancreatic Function
4.5. Changes in Intestinal Absorption
4.6. Changes in Bile Acid Metabolism
4.7. Changes in Colonic Inflammation and Microbiome
4.8. HEMT and Body Composition
5. Impact of Overnutrition in PwCF
5.1. Overweight and Obesity and Pulmonary Function
5.2. Cardiovascular and Metabolic Disease in CF
5.3. CF Hepatobiliary Involvement
5.4. Type 2 Diabetes
6. Evolving Practices in Nutritional Care for PwCF
6.1. Weight Loss Medications in PwCF
6.2. Eating Disorders/ARFID
7. Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Andersen, D.H. Cystic fibrosis of the pancreas and its relation to celiac disease: A clinical and pathologic study. Am. J. Dis. Child. 1938, 56, 344–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bass, R.; Brownell, J.N.; Stallings, V.A. The Impact of Highly Effective CFTR Modulators on Growth and Nutrition Status. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szentpetery, S.; Fernandez, G.S.; Schechter, M.S.; Jain, R.; Flume, P.A.; Fink, A.K. Obesity in Cystic fibrosis: Prevalence, trends and associated factors data from the US cystic fibrosis foundation patient registry. J. Cyst. Fibros. Off. J. Eur. Cyst. Fibros. Soc. 2022, 21, 777–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corey, M.; McLaughlin, F.J.; Williams, M.; Levison, H. A comparison of survival, growth, and pulmonary function in patients with cystic fibrosis in Boston and Toronto. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 1988, 41, 583–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harindhanavudhi, T.; Wang, Q.; Dunitz, J.; Moran, A.; Moheet, A. Prevalence and factors associated with overweight and obesity in adults with cystic fibrosis: A single-center analysis. J. Cyst. Fibros. Off. J. Eur. Cyst. Fibros. Soc. 2020, 19, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moudiou, T.; Galli-Tsinopoulou, A.; Nousia-Arvanitakis, S. Effect of exocrine pancreatic function on resting energy expenditure in cystic fibrosis. Acta Paediatr. Oslo Nor. 1992 2007, 96, 1521–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, C.; Blackman, S.M.; Nelson, A.; Oberdorfer, E.; Wells, D.; Dunitz, J.; Thomas, W.; Moran, A. Diabetes-related mortality in adults with cystic fibrosis. Role of genotype and sex. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 191, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Psoter, K.J.; Dickinson, K.M.; Riekert, K.A.; Collaco, J.M. Early life growth trajectories in cystic fibrosis are associated with lung function at age six. J. Cyst. Fibros. Off. J. Eur. Cyst. Fibros. Soc. 2023, 22, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guimbellot, J.S.; Baines, A.; Paynter, A.; Heltshe, S.L.; VanDalfsen, J.; Jain, M.; Rowe, S.M.; Sagel, S.D.; GOAL-e2 Investigators. Long term clinical effectiveness of ivacaftor in people with the G551DCFTRmutation. J. Cyst. Fibros. Off. J. Eur. Cyst. Fibros. Soc. 2021, 20, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proud, D.; Duckers, J. Weight a minute: Exploring the effect on weight and body composition after the initiation of elexacaftor/tezacaftor/ivacaftor in adults with CF. J. Cyst. Fibros. Off. J. Eur. Cyst. Fibros. Soc. 2023, 22, 847–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonard, A.; Bailey, J.; Bruce, A.; Jia, S.; Stein, A.; Fulton, J.; Helmick, M.; Litvin, M.; Patel, A.; Powers, K.E.; et al. Nutritional considerations for a new era: A CF foundation position paper. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2023, 22, 788–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, V.K.; Schwarzenberg, S.J. Pancreatic insufficiency in Cystic Fibrosis. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2017, 16, S70–S78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brownell, J.N.; Bashaw, H.; Stallings, V.A. Growth and Nutrition in Cystic Fibrosis. Semin. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 40, 775–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darukhanavala, A.; Merjaneh, L.; Mason, K.; Le, T. Eating disorders and body image in cystic fibrosis. J. Clin. Transl. Endocrinol. 2021, 26, 100280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieni, G.; Faraci, S.; Collura, M.; Lombardo, M.; Traverso, G.; Cristadoro, S.; Termini, L.; Lucanto, M.C.; Furnari, M.L.; Trimarchi, G.; et al. Stunting is an independent predictor of mortality in patients with cystic fibrosis. Clin. Nutr. Edinb. Scotl. 2013, 32, 382–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Lindstrom, M.J.; Lai, H.J. Pubertal height velocity and associations with prepubertal and adult heights in cystic fibrosis. J. Pediatr. 2013, 163, 376–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, D.H.; Heltshe, S.L.; Borowitz, D.; Gelfond, D.; Kloster, M.; Heubi, J.E.; Stalvey, M.; Ramsey, B.W.; Baby Observational and Nutrition Study (BONUS) Investigators of the Cystic Fibrosis Foundation Therapeutics Development Network. Effects of Diagnosis by Newborn Screening for Cystic Fibrosis on Weight and Length in the First Year of Life. JAMA Pediatr. 2017, 171, 546–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marks, M.P.; Heltshe, S.L.; Baines, A.; Ramsey, B.W.; Hoffman, L.R.; Stalvey, M.S. Most Short Children with Cystic Fibrosis Do Not Catch Up by Adulthood. Nutrients 2021, 13, 4414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anton-Păduraru, D.-T.; Murgu, A.M.; Bozomitu, L.I.; Mîndru, D.E.; Iliescu Halițchi, C.O.; Trofin, F.; Ciongradi, C.I.; Sârbu, I.; Eṣanu, I.M.; Azoicăi, A.N. Diagnosis and Management of Gastrointestinal Manifestations in Children with Cystic Fibrosis. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emiralioglu, N.; Ademhan Tural, D.; Hizarcioglu Gulsen, H.; Ergen, Y.M.; Ozsezen, B.; Sunman, B.; Saltık Temizel, İ.; Yalcin, E.; Dogru, D.; Ozcelik, U.; et al. Does cystic fibrosis make susceptible to celiac disease? Eur. J. Pediatr. 2021, 180, 2807–2813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villella, V.R.; Venerando, A.; Cozza, G.; Esposito, S.; Ferrari, E.; Monzani, R.; Spinella, M.C.; Oikonomou, V.; Renga, G.; Tosco, A.; et al. A pathogenic role for cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator in celiac disease. EMBO J. 2019, 38, e100101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hjelm, M.; Shaikhkhalil, A.K. Celiac Disease in Patients With Cystic Fibrosis on Ivacaftor: A Case Series. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2020, 71, 257–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cárdenas-Torres, F.I.; Cabrera-Chávez, F.; Figueroa-Salcido, O.G.; Ontiveros, N. Non-Celiac Gluten Sensitivity: An Update. Med. Kaunas Lith. 2021, 57, 526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goralski, J.L.; Lercher, D.M.; Davis, S.D.; Dellon, E.S. Eosinophilic esophagitis in cystic fibrosis: A case series and review of the literature. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2013, 12, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capucilli, P.; Cianferoni, A.; Grundmeier, R.W.; Spergel, J.M. Comparison of comorbid diagnoses in children with and without eosinophilic esophagitis in a large population. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. Off. Publ. Am. Coll. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2018, 121, 711–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaber, O.; Sabe, R.; Baez-Socorro, V.; Sankararaman, S.; Roesch, E.; Sferra, T.J. Epidemiology of Eosinophilic Esophagitis in Patients with Cystic Fibrosis: A Population-Based 5-Year Study. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Nutr. 2022, 25, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucendo, A.J.; Molina-Infante, J. Current treatment options and long-term outcomes in patients with eosinophilic esophagitis. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2022, 18, 859–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, M.-Y.A.; Chinnaratha, M.A.; Hancock, D.G.; Woodman, R.; Wong, G.R.; Cock, C.; Fraser, R.J. Topical Steroid Therapy for the Treatment of Eosinophilic Esophagitis (EoE): A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2015, 6, e82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K.; Ashby, D.; Smyth, R.L. Oral steroids for long-term use in cystic fibrosis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2011, CD000407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abel, E.; Stone, L.; Spoletini, G.; Etherington, C.; Clifton, I.; Peckham, D. P303 Prevalence and clinical presentation of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) in a large adult cystic fibrosis (CF) Unit. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2024, 23, S161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Zhang, Q.; Yuan, K.; Sazonovs, A.; Stevens, C.; Fachal, L.; The International Inflammatory Bowel Disease Genetics Consortium; Anderson, C.A.; Daly, M.J.; Huang, H. Cystic fibrosis risk variants confer protection against inflammatory bowel disease. medRxiv, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, N.; Miller, C.; Suskind, D.; Brown, M.; Pope, C.; Hayden, H.; McNamara, S.; Kanter, A.; Nay, L.; Hoffman, L.; et al. The impact of a whole foods dietary intervention on gastrointestinal symptoms, inflammation, and fecal microbiota in pediatric patients with cystic fibrosis: A pilot study. Clin. Nutr. 2024, 43, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patient Registry Annual Data Report; Cystic Fibrosis Foundation: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2023.
- Kaminski, B.A.; Goldsweig, B.K.; Sidhaye, A.; Blackman, S.M.; Schindler, T.; Moran, A. Cystic fibrosis related diabetes: Nutrition and growth considerations. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2019, 18, S32–S37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, A.; Brunzell, C.; Cohen, R.C.; Katz, M.; Marshall, B.C.; Onady, G.; Robinson, K.A.; Sabadosa, K.A.; Stecenko, A.; Slovis, B.; et al. Clinical care guidelines for cystic fibrosis-related diabetes: A position statement of the American Diabetes Association and a clinical practice guideline of the Cystic Fibrosis Foundation, endorsed by the Pediatric Endocrine Society. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 2697–2708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellers, Z.M.; Assis, D.N.; Paranjape, S.M.; Sathe, M.; Bodewes, F.; Bowen, M.; Cipolli, M.; Debray, D.; Green, N.; Hughan, K.S.; et al. Cystic fibrosis screening, evaluation, and management of hepatobiliary disease consensus recommendations. Hepatology 2024, 79, 1220–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drzymała-Czyż, S.; Krzyżanowska, P.; Koletzko, B.; Nowak, J.; Miśkiewicz-Chotnicka, A.; Moczko, J.; Lisowska, A.; Walkowiak, J. Determinants of Serum Glycerophospholipid Fatty Acids in Cystic Fibrosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Biervliet, S.; Van Biervliet, J.-P.; Robberecht, E.; Christophe, A. Fatty acid composition of serum phospholipids in cystic fibrosis (CF) patients with or without CF related liver disease. CCLM 2010, 48, 1751–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldámiz-Echevarría, L.; Prieto, J.A.; Andrade, F.; Elorz, J.; Sojo, A.; Lage, S.; Sanjurjo, P.; Vázquez, C.; Rodríguez-Soriano, J. Persistence of essential fatty acid deficiency in cystic fibrosis despite nutritional therapy. Pediatr. Res. 2009, 66, 585–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patient Registry Annual Data Report; Cystic Fibrosis Foundation: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2021.
- Salvatore, D.; Padoan, R.; Amato, A.; Salvatore, M.; Campagna, G.; On Behalf of the Italian Cf Registry Working Group. Nutritional Trends in Cystic Fibrosis: Insights from the Italian Cystic Fibrosis Patient Registry. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 3652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Childhood Obesity Facts; CDC: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2024. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/obesity/childhood-obesity-facts/childhood-obesity-facts.html (accessed on 21 July 2025).
- Sheikh, S.; Zemel, B.S.; Stallings, V.A.; Rubenstein, R.C.; Kelly, A. Body composition and pulmonary function in cystic fibrosis. Front. Pediatr. 2014, 2, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomezsko, J.L.; Stallings, V.A.; Kawchak, D.A.; Goin, J.E.; Diamond, G.; Scanlin, T.F. Energy Expenditure and Genotype of Children with Cystic Fibrosis. Pediatr. Res. 1994, 35, 451–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Frantzen, T.; Barsky, S.; LaVecchia, G.; Marowitz, M.; Wang, J. Evolving Nutritional Needs in Cystic Fibrosis. Life Basel Switz. 2023, 13, 1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gur, M.; Bar–Yoseph, R.; Hanna, M.; Abboud, D.; Keidar, Z.; Palchan, T.; Toukan, Y.; Masarweh, K.; Alisha, I.; Zuckerman-Levin, N.; et al. Effect of Trikafta on bone density, body composition and exercise capacity in CF: A pilot study. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2023, 58, 577–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freswick, P.N.; Reid, E.K.; Mascarenhas, M.R. Pancreatic Enzyme Replacement Therapy in Cystic Fibrosis. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durie, P.R. The pathophysiology of the pancreatic defect in cystic fibrosis. Acta Paediatr. Scand. Suppl. 1989, 363, 41–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trang, T.; Chan, J.; Graham, D.Y. Pancreatic enzyme replacement therapy for pancreatic exocrine insufficiency in the 21st century. World J. Gastroenterol. WJG 2014, 20, 11467–11485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munce, D.; Lim, M.; Akong, K. Persistent recovery of pancreatic function in patients with cystic fibrosis after ivacaftor. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2020, 55, 3381–3383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nichols, A.L.; Davies, J.C.; Jones, D.; Carr, S.B. Restoration of exocrine pancreatic function in older children with cystic fibrosis on ivacaftor. Paediatr. Respir. Rev. 2020, 35, 99–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenfeld, M.; Wainwright, C.E.; Higgins, M.; Wang, L.T.; McKee, C.; Campbell, D.; Tian, S.; Schneider, J.; Cunningham, S.; Davies, J.C.; et al. Ivacaftor treatment of cystic fibrosis in children aged 12 to <24 months and with a CFTR gating mutation (ARRIVAL): A phase 3 single-arm study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2018, 6, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stastna, N.; Kunovsky, L.; Svoboda, M.; Pokojova, E.; Homola, L.; Mala, M.; Gracova, Z.; Jerabkova, B.; Skrickova, J.; Trna, J. Improved Nutritional Outcomes and Gastrointestinal Symptoms in Adult Cystic Fibrosis Patients Treated with Elexacaftor/Tezacaftor/Ivacaftor. Dig. Dis. 2024, 42, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delchier, J.C.; Vidon, N.; Saint-Marc Girardin, M.F.; Soule, J.C.; Moulin, C.; Huchet, B.; Zylberberg, P. Fate of orally ingested enzymes in pancreatic insufficiency: Comparison of two pancreatic enzyme preparations. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 1991, 5, 365–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wacklin, H.P. Interfacial mechanism of phospholipase A2: pH-dependent inhibition and Me-beta-cyclodextrin activation. Biochemistry 2009, 48, 5874–5881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, C.C.; Weber, A.M.; Lepage, G.; Smith, L.; Levy, E. Digestive and Absorptive Phase Anomalies Associated with the Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency of Cystic Fibrosis. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 1988, 7, S1–S7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelfond, D.; Heltshe, S.; Ma, C.; Rowe, S.M.; Frederick, C.; Uluer, A.; Sicilian, L.; Konstan, M.; Tullis, E.; Roach, C.R.N.; et al. Impact of CFTR Modulation on Intestinal pH, Motility, and Clinical Outcomes in Patients With Cystic Fibrosis and the G551D Mutation. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2017, 8, e81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, N.; Chan, C.; Ooi, C.Y. The gastrointestinal microbiome, small bowel bacterial overgrowth, and microbiome modulators in cystic fibrosis. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2024, 59, S70–S80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van De Peppel, I.P.; Bodewes, F.A.J.A.; Verkade, H.J.; Jonker, J.W. Bile acid homeostasis in gastrointestinal and metabolic complications of cystic fibrosis. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2019, 18, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camilleri, M. Advances in understanding of bile acid diarrhea. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 8, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagar, N.M.; Cree, I.A.; Covington, J.A.; Arasaradnam, R.P. The interplay of the gut microbiome, bile acids, and volatile organic compounds. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2015, 2015, 398585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernhard, W. Choline in cystic fibrosis: Relations to pancreas insufficiency, enterohepatic cycle, PEMT and intestinal microbiota. Eur. J. Nutr. 2021, 60, 1737–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnell, A.; Jüngert, J.; Klett, D.; Hober, H.; Kaiser, N.; Ruppel, R.; Geppert, A.; Tremel, C.; Sobel, J.; Plattner, E.; et al. Increase of liver stiffness and altered bile acid metabolism after triple CFTR modulator initiation in children and young adults with cystic fibrosis. Liver Int. Off. J. Int. Assoc. Study Liver 2023, 43, 878–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, E.Y.T.; Yang, N.; Quinton, P.M.; Chin, W.-C. A new role for bicarbonate in mucus formation. Am. J. Physiol.-Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2010, 299, L542–L549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonnell, L.; Gilkes, A.; Ashworth, M.; Rowland, V.; Harries, T.H.; Armstrong, D.; White, P. Association between antibiotics and gut microbiome dysbiosis in children: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1870402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.M.; Leach, S.T.; Katz, T.; Day, A.S.; Jaffe, A.; Ooi, C.Y. Update of Faecal Markers of Inflammation in Children with Cystic Fibrosis. Mediat. Inflamm. 2012, 2012, 948367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruzzese, E.; Raia, V.; Gaudiello, G.; Polito, G.; Buccigrossi, V.; Formicola, V.; Guarino, A. Intestinal inflammation is a frequent feature of cystic fibrosis and is reduced by probiotic administration. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2004, 20, 813–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hevilla, F.; Porras, N.; Girón, M.V.; García-Olivares, M.; Padial, M.; Sánchez-Torralvo, F.J.; Olveira, C.; Olveira, G. Impact of Elexacaftor–Tezacaftor–Ivacaftor Therapy on Body Composition, Dietary Intake, Biomarkers, and Quality of Life in People with Cystic Fibrosis: A Prospective Observational Study. Nutrients 2024, 16, 3293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, S.J.; Nyulasi, I.B.; Strauss, B.J.G.; Kotsimbos, T.; Bailey, M.; Wilson, J.W. Fat-free mass depletion in cystic fibrosis: Associated with lung disease severity but poorly detected by body mass index. Nutr. Burbank Los Angel. Cty. Calif 2010, 26, 753–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, A.; Hutcheon, D.; Ziegler, J. Association Between Fat-Free Mass and Pulmonary Function in Patients With Cystic Fibrosis: A Narrative Review. Nutr. Clin. Pract. Off. Publ. Am. Soc. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2019, 34, 715–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, J.A.; Ziegler, T.R.; Millson, E.C.; Stecenko, A.A. Body composition and lung function in cystic fibrosis and their association with adiposity and normal-weight obesity. Nutrition 2016, 32, 447–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stallings, V.A.; Sainath, N.; Oberle, M.; Bertolaso, C.; Schall, J.I. Energy Balance and Mechanisms of Weight Gain with Ivacaftor Treatment of Cystic Fibrosis Gating Mutations. J. Pediatr. 2018, 201, 229–237.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouzaki, M.; Dupuis, A.; Avolio, J.; Griffin, K.; Ratjen, F.; Tullis, E.; Gonska, T. Weight increase in people with cystic fibrosis on CFTR modulator therapy is mainly due to increase in fat mass. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1157459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merino Sánchez-Cañete, A.; López Cárdenes, C.M.; Vicente Santamaría, S.; Gutiérrez Martínez, J.R.; Suárez González, M.; Álvarez Merino, M.; González Jiménez, D. Increased fat mass and obesity risk after elexacaftor-tezacaftor-ivacaftor therapy in young adults with cystic fibrosis. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1477674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, S.J.; Tierney, A.C.; Edgeworth, D.; Keating, D.; Williams, E.; Kotsimbos, T.; Button, B.M.; Wilson, J.W. Body composition and weight changes after ivacaftor treatment in adults with cystic fibrosis carrying the G551 D cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator mutation: A double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized, crossover study with open-label extension. Nutrition 2021, 85, 111124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López Cárdenes, C.M.; Merino Sánchez-Cañete, A.; Vicente Santamaría, S.; Gascón Galindo, C.; Merino Sanz, N.; Tabares González, A.; Blitz Castro, E.; Morales Tirado, A.; Garriga García, M.; López Rozas, M.; et al. Effects on growth, weight and body composition after CFTR modulators in children with cystic fibrosis. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2024, 59, 3632–3640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westhölter, D.; Haubold, J.; Welsner, M.; Salhöfer, L.; Wienker, J.; Sutharsan, S.; Straßburg, S.; Taube, C.; Umutlu, L.; Schaarschmidt, B.M.; et al. Elexacaftor/tezacaftor/ivacaftor influences body composition in adults with cystic fibrosis: A fully automated CT-based analysis. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 9465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frost, F.; Nazareth, D.; Fauchier, L.; Wat, D.; Shelley, J.; Austin, P.; Walshaw, M.J.; Lip, G.Y.H. Prevalence, risk factors and outcomes of cardiac disease in cystic fibrosis: A multinational retrospective cohort study. Eur. Respir. J. 2023, 62, 2300174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, B.; Nash, E.F.; Tullis, E.; Pencharz, P.B.; Brotherwood, M.; Dupuis, A.; Stephenson, A. Prevalence of dyslipidemia in adults with cystic fibrosis. J. Cyst. Fibros. Off. J. Eur. Cyst. Fibros. Soc. 2010, 9, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandouk, Z.; Nachawi, N.; Simon, R.; Wyckoff, J.; Putman, M.S.; Kiel, S.; Soltman, S.; Moran, A.; Moheet, A. Coronary artery disease in patients with cystic fibrosis—A case series and review of the literature. J. Clin. Transl. Endocrinol. 2022, 30, 100308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bass, R.; Stalvey, M.; Solomon, G.; Rowe, S.; Nichols, D.; Schwarzenberg, S.J.; Freedman, S.; Walega, R.; Kelly, A. Cholesterol and triglyceride concentrations following 12–18 months of clinically prescribed elexacaftor-tezacaftor-ivacaftor-PROMISE sub-study. J. Clin. Transl. Endocrinol. 2025, 40, 100391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Despotes, K.A.; Ceppe, A.S.; Goralski, J.L.; Donaldson, S.H. New era, new GOALs: Cardiovascular screening and lipid management in cystic fibrosis. Ther. Adv. Respir. Dis. 2025, 19, 17534666251317200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goetz, D.M.; Brown, R.F.; Filigno, S.S.; Bichl, S.L.; Nelson, A.L.; Merlo, C.A.; Juel, R.; Lomas, P.; Hempstead, S.E.; Tran, Q.; et al. Cystic fibrosis foundation position paper: Redefining the CF care model. J. Cyst. Fibros. Off. J. Eur. Cyst. Fibros. Soc. 2024, 23, 1055–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobato, A.O.; Vasques, A.C.J.; Ribeiro, A.F.; Yamada, R.M.; Hessel, G. Prevalence of hepatic steatosis among children and adolescents with cystic fibrosis and its association with nutritional status. Rev. Paul. Pediatr. 2019, 37, 435–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernhard, W.; Lange, R.; Graepler-Mainka, U.; Engel, C.; Machann, J.; Hund, V.; Shunova, A.; Hector, A.; Riethmüller, J. Choline Supplementation in Cystic Fibrosis-The Metabolic and Clinical Impact. Nutrients 2019, 11, 656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The InterAct Consortium. The link between family history and risk of type 2 diabetes is not explained by anthropometric, lifestyle or genetic risk factors: The EPIC-InterAct study. Diabetologia 2013, 56, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granados, A.; Chan, C.L.; Ode, K.L.; Moheet, A.; Moran, A.; Holl, R. Cystic fibrosis related diabetes: Pathophysiology, screening and diagnosis. J. Cyst. Fibros. Off. J. Eur. Cyst. Fibros. Soc. 2019, 18 (Suppl. S2), S3–S9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, C.M.; Alvarez, J.A.; Bailey, J.; Bowser, E.K.; Farnham, K.; Mangus, M.; Padula, L.; Porco, K.; Rozga, M. Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics: 2020 Cystic Fibrosis Evidence Analysis Center Evidence-Based Nutrition Practice Guideline. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2021, 121, 1591–1636.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Jain, R.; Mirfakhraee, S. Glucagon-like-peptide-1 agonist therapy in adults with cystic fibrosis. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2025, 24, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.; Ankireddypalli, A.; Harindhanavudhi, T.; Moran, A.; Moheet, A. Glucagon-like peptide1 receptor agonist treatment of cystic fibrosis-related diabetes complicated by obesity: A cases series and literature review. J. Clin. Transl. Endocrinol. 2024, 38, 100375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quick, V.M.; Byrd-Bredbenner, C.; Neumark-Sztainer, D. Chronic Illness and Disordered Eating: A Discussion of the Literature. Adv. Nutr. 2013, 4, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, D.; Shan, A.; Mathews, S.; Sathe, M. Understanding Cystic Fibrosis Comorbidities and Their Impact on Nutritional Management. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khemka, S.; Hunter, S.; Jones, J.; Valentín-Martínez, K.; Chadwick, C.B.; Bass, R. The State of Weight in Cystic Fibrosis: Understanding Nutritional Status and Individualizing Nutritional Care in the Modulator Era. Nutrients 2025, 17, 2533. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17152533
Khemka S, Hunter S, Jones J, Valentín-Martínez K, Chadwick CB, Bass R. The State of Weight in Cystic Fibrosis: Understanding Nutritional Status and Individualizing Nutritional Care in the Modulator Era. Nutrients. 2025; 17(15):2533. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17152533
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhemka, Sapna, Stacie Hunter, Jessica Jones, Keishla Valentín-Martínez, Christina B. Chadwick, and Rosara Bass. 2025. "The State of Weight in Cystic Fibrosis: Understanding Nutritional Status and Individualizing Nutritional Care in the Modulator Era" Nutrients 17, no. 15: 2533. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17152533
APA StyleKhemka, S., Hunter, S., Jones, J., Valentín-Martínez, K., Chadwick, C. B., & Bass, R. (2025). The State of Weight in Cystic Fibrosis: Understanding Nutritional Status and Individualizing Nutritional Care in the Modulator Era. Nutrients, 17(15), 2533. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17152533




