Differences in Lifestyle-Related Behaviors Among Healthy Weight, Overweight, and Obese Groups: A Secondary Analysis of Data on 4714 Adults in Poland
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Source and Study Participants
2.2. Measures
- How often do you check your weight (weigh yourself)?
- Which of the following methods do you use to track physical activity and diet?
- How many meals do you usually eat in a day?
- Which of the following statements best describes your daily eating habits?
- Which of the following statements best describes your physical activity?
- During the week (7 days), how much time do you usually spend in total on moderate physical activity such as cycling or walking?
- During the week (7 days), how much time do you usually spend in total on vigorous physical activity such as running?
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Participants—Descriptive Characteristics
3.2. Physicial Activity and Diet Monitoring Among Adults in Poland
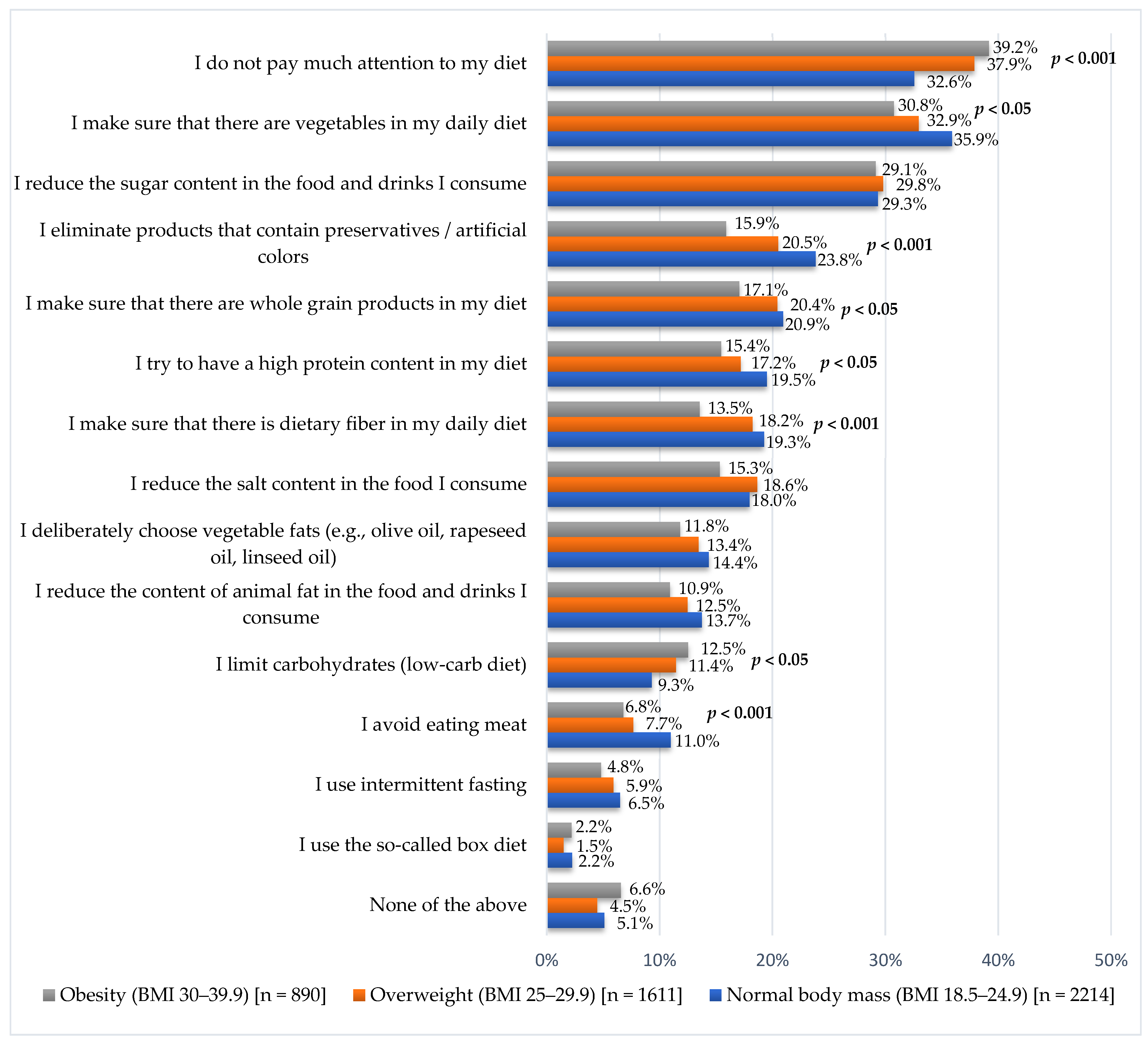
3.3. Diet-Related Habits Among Adults in Poland
3.4. Physicial Activity Undertaken by Adults in Poland
3.5. Factors Associated with Nutrition-Related Behaviors and Physical Activity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Safiri, S.; Grieger, J.A.; Ghaffari Jolfayi, A.; Mousavi, S.E.; Nejadghaderi, S.A.; Fazlollahi, A.; Sullman, M.J.M.; Karamzad, N.; Sahin, F.; Singh, K.; et al. Burden of diseases attributable to excess body weight in 204 countries and territories, 1990–2019. Nutr. J. 2025, 24, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Obesity and Overweight. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight (accessed on 29 May 2025).
- Chooi, Y.C.; Ding, C.; Magkos, F. The epidemiology of obesity. Metabolism 2019, 92, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sweatt, K.; Garvey, W.T.; Martins, C. Strengths and Limitations of BMI in the Diagnosis of Obesity: What is the Path Forward? Curr. Obes. Rep. 2024, 13, 584–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khanna, D.; Peltzer, C.; Kahar, P.; Parmar, M.S. Body Mass Index (BMI): A Screening Tool Analysis. Cureus 2022, 14, e22119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esquivel, M.K. Energy Balance Dynamics: Exercise, Appetite, Diet, and Weight Control. Am. J. Lifestyle Med. 2021, 15, 220–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masood, B.; Moorthy, M. Causes of obesity: A review. Clin. Med. 2023, 23, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadden, T.A.; Tronieri, J.S.; Butryn, M.L. Lifestyle modification approaches for the treatment of obesity in adults. Am. Psychol. 2020, 75, 235–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romieu, I.; Dossus, L.; Barquera, S.; Blottière, H.M.; Franks, P.W.; Gunter, M.; Hwalla, N.; Hursting, S.D.; Leitzmann, M.; Margetts, B.; et al. Energy balance and obesity: What are the main drivers? Cancer Causes Control 2017, 28, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlesinger, S.; Neuenschwander, M.; Schwedhelm, C.; Hoffmann, G.; Bechthold, A.; Boeing, H.; Schwingshackl, L. Food Groups and Risk of Overweight, Obesity, and Weight Gain: A Systematic Review and Dose-Response Meta-Analysis of Prospective Studies. Adv. Nutr. 2019, 10, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moschonis, G.; Trakman, G.L. Overweight and Obesity: The Interplay of Eating Habits and Physical Activity. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, B.; Vahlhaus, J.; Pivovarova-Ramich, O. Meal timing and its role in obesity and associated diseases. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1359772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostendorf, D.M.; Caldwell, A.E.; Creasy, S.A.; Pan, Z.; Lyden, K.; Bergouignan, A.; MacLean, P.S.; Wyatt, H.R.; Hill, J.O.; Melanson, E.L.; et al. Physical Activity Energy Expenditure and Total Daily Energy Expenditure in Successful Weight Loss Maintainers. Obesity 2019, 27, 496–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oppert, J.M.; Ciangura, C.; Bellicha, A. Physical activity and exercise for weight loss and maintenance in people living with obesity. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2023, 24, 937–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Baak, M.A.; Pramono, A.; Battista, F.; Beaulieu, K.; Blundell, J.E.; Busetto, L.; Carraça, E.V.; Dicker, D.; Encantado, J.; Ermolao, A.; et al. Effect of different types of regular exercise on physical fitness in adults with overweight or obesity: Systematic review and meta-analyses. Obes. Rev. 2021, 22 (Suppl. S4), e13239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blüher, M. An overview of obesity-related complications: The epidemiological evidence linking body weight and other markers of obesity to adverse health outcomes. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2025, 27 (Suppl S2), 3–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephenson, J.; Smith, C.M.; Kearns, B.; Haywood, A.; Bissell, P. The association between obesity and quality of life: A retrospective analysis of a large-scale population-based cohort study. BMC Public Health 2021, 21, 1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, Z.J.; Bleich, S.N.; Long, M.W.; Gortmaker, S.L. Association of body mass index with health care expenditures in the United States by age and sex. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0247307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. The Heavy Burden of Obesity. Available online: https://www.oecd.org/en/publications/the-heavy-burden-of-obesity_67450d67-en.html (accessed on 29 May 2025).
- Umekar, S.; Joshi, A. Obesity and Preventive Intervention Among Children: A Narrative Review. Cureus 2024, 16, e54520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heerman, W.J.; Kenney, E.; Block, J.P.; Fiechtner, L.; McMahon, E.; Kruse, L.; Sharifi, M.; Edmondson, E.K.; Virudachalam, S.A. Narrative Review of Public Health Interventions for Childhood Obesity. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2024, 13, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taillie, L.S.; Busey, E.; Stoltze, F.M.; Dillman Carpentier, F.R. Governmental policies to reduce unhealthy food marketing to children. Nutr. Rev. 2019, 77, 787–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, E.; Zhang, A.; Shogbesan, O.; Gudzune, K.A.; Wilson, R.F.; Kharrazi, H.; Cheskin, L.J.; Bass, E.B.; Bennett, W.L. Effectiveness of Policies and Programs to Combat Adult Obesity: A Systematic Review. J. Gen. Intern. Med. 2018, 33, 1990–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bellicha, A.; van Baak, M.A.; Battista, F.; Beaulieu, K.; Blundell, J.E.; Busetto, L.; Carraça, E.V.; Dicker, D.; Encantado, J.; Ermolao, A.; et al. Effect of exercise training on weight loss, body composition changes, and weight maintenance in adults with overweight or obesity: An overview of 12 systematic reviews and 149 studies. Obes. Rev. 2021, 22 (Suppl. S4), e13256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradley, T.; Campbell, E.; Dray, J.; Bartlem, K.; Wye, P.; Hanly, G.; Gibson, L.; Fehily, C.; Bailey, J.; Wynne, O.; et al. Systematic review of lifestyle interventions to improve weight, physical activity and diet among people with a mental health condition. Syst. Rev. 2022, 11, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, N.R.; Zivich, P.N.; Frerichs, L. Social Influences on Obesity: Current Knowledge, Emerging Methods, and Directions for Future Research and Practice. Curr. Nutr. Rep. 2020, 9, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traczyk, I.; Kucharska, A.; Sińska, B.I.; Panczyk, M.; Samel-Kowalik, P.; Kłak, A.; Raciborski, F.; Wyleżoł, M.; Samoliński, B.; Szostak-Węgierek, D. Prevalence of Overweight, Obesity, and Abdominal Obesity in Polish Adults: Sociodemographic Analysis from the 2016-2020 National Health Program. Nutrients 2024, 16, 4248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traczyk, I.; Kucharska, A.; Sińska, B.I.; Panczyk, M.; Wronka, L.; Raciborski, F.; Szostak-Węgierek, D.; Samoliński, B. Every second adult inhabitant of Poland (aged 18–64) is overweight-results of representative cross-sectional studies conducted in 2017–2020. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2023, 30, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Observatory on Health Systems and Policies. Obesity in Poland. Available online: https://eurohealthobservatory.who.int/publications/i/obesity-in-poland#:~:text=For%20many%20years%2C%20obesity%20was%20not%20recognised%20as,financial%20resources%20to%20tackle%20the%20burden%20of%20obesity (accessed on 29 May 2025).
- Centre for Health Policy and Health Inequalities of the Cardinal Stefan Wyszynski University. Research Report: Health Prophylaxis and Health Inequalities. Available online: https://ncpz.uksw.edu.pl/badania-i-projekty-naukowe/ (accessed on 29 May 2025).
- ARC Rynek i Opinia. About Us. Available online: https://arc.com.pl/en/main-2/ (accessed on 29 May 2025).
- Ingels, J.S.; Misra, R.; Stewart, J.; Lucke-Wold, B.; Shawley-Brzoska, S. The Effect of Adherence to Dietary Tracking on Weight Loss: Using HLM to Model Weight Loss over Time. J. Diabetes Res. 2017, 2017, 6951495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, S.H.; Tan, Z.Y.A.; Cheng, L.J.; Lau, S.T. Wearable technology-delivered lifestyle intervention amongst adults with overweight and obese: A systematic review and meta-regression. Int. J. Nurs. Stud. 2022, 127, 104163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristoffersen, E.; Hjort, S.L.; Thomassen, L.M.; Arjmand, E.J.; Perillo, M.; Balakrishna, R.; Onni, A.T.; Sletten, I.S.K.; Lorenzini, A.; Fadnes, L.T. Umbrella Review of Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses on the Consumption of Different Food Groups and the Risk of Overweight and Obesity. Nutrients 2025, 17, 662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nour, M.; Lutze, S.A.; Grech, A.; Allman-Farinelli, M. The Relationship between Vegetable Intake and Weight Outcomes: A Systematic Review of Cohort Studies. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pol, K.; Christensen, R.; Bartels, E.M.; Raben, A.; Tetens, I.; Kristensen, M. Whole grain and body weight changes in apparently healthy adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled studies. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 98, 872–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansilla-Obando, K.; Llanos, G.; Gómez-Sotta, E.; Buchuk, P.; Ortiz, F.; Aguirre, M.; Ahumada, F. Eco-Innovation in the Food Industry: Exploring Consumer Motivations in an Emerging Market. Foods 2023, 13, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, N.M.; Sigurdsson, V.; Gunnarsson, D. Environmental cues for healthy food marketing: The importance of in-store research into three conversions. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 1078672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ndahimana, D.; Kim, E.K. Measurement Methods for Physical Activity and Energy Expenditure: A Review. Clin. Nutr. Res. 2017, 6, 68–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, C.E. Role of Physical Activity for Weight Loss and Weight Maintenance. Diabetes Spectr. 2017, 30, 157–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nosrani, S.E.; Tartibian, B.; Eslami, R.; Farinha, C.; Serrano, J.; Ferreira, J.P.; Texeira, A.M. The Effects of Combined Aquatic Exercise on Physical Performance and Metabolic Indices in Overweight Healthy Older Adults. Int. J. Exerc. Sci. 2024, 16, 1499–1513. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, X.; Yang, G.; Li, X.; Fu, J.; Mohedaner, M.; Danzengzhuoga; Høj Jørgensen, T.S.; Agogo, G.O.; Wang, L.; Zhang, X.; et al. Weight change across adulthood and accelerated biological aging in middle-aged and older adults. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2023, 117, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warshaw, H.; Edelman, S.V. Practical Strategies to Help Reduce Added Sugars Consumption to Support Glycemic and Weight Management Goals. Clin. Diabetes 2021, 39, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayib, M.; Larson, J.; Slavin, J. Dietary fibers reduce obesity-related disorders: Mechanisms of action. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2020, 23, 445–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Healthy Weight (BMI 18.5–24.9) | Overweight (BMI 25–29.9) | Obesity (BMI 30–39.9) | Overall | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n = 2214 | n = 1611 | n = 890 | n = 4714 | |
| Gender | ||||
| men | 992 (44.8) | 915 (56.8) | 505 (56.8) | 2412 (51.2) |
| women | 1221 (55.2) | 696 (43.2) | 384 (43.2) | 2301 (48.8) |
| Age | ||||
| 18–24 | 355 (16) | 82 (5.1) | 42 (4.7) | 479 (10.2) |
| 25–34 | 564 (25.5) | 238 (14.8) | 113 (12.7) | 915 (19.4) |
| 35–44 | 586 (26.5) | 432 (26.8) | 241 (27) | 1259 (26.7) |
| 45–64 | 709 (32) | 860 (53.3) | 495 (55.6) | 2064 (43.8) |
| Educational level | ||||
| primary or vocationals | 598 (27) | 543 (33.7) | 340 (38.2) | 1481 (31.4) |
| secondary | 829 (37.4) | 608 (37.7) | 352 (39.6) | 1789 (38.0) |
| higher | 787 (35.5) | 460 (28.6) | 197 (22.2) | 1444 (30.6) |
| Place of residence | ||||
| Rural area | 838 (37.9) | 674 (41.8) | 400 (45) | 1912 (40.6) |
| city <100,000 residents | 724 (32.7) | 507 (31.5) | 273 (30.7) | 1504 (31.9) |
| city 100,000–499,999 residents | 365 (16.5) | 251 (15.6) | 121 (13.6) | 737 (15.6) |
| city ≥ 500,000 residents | 287 (13) | 179 (11.1) | 95 (10.7) | 561 (11.9) |
| Factors Associated with Assigment to Overveight Group | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | Response | p | OR (95% CI) |
| I do not track physical activity, body composition, or diet | yes | p < 0.05 | 1.22 (1.02–1.45) |
| no | Ref. | Ref. | |
| I track the number of steps I take during the day | yes | p < 0.001 | 1.42 (1.19–1.71) |
| no | Ref. | Ref. | |
| I track my progress in losing weight or building muscle mass using an app or journal | yes | p < 0.05 | 1.3 (1–1.7) |
| no | Ref. | Ref. | |
| I reduce the sugar content in the food and drinks I consume | yes | p < 0.05 | 1.21 (1.02–1.44) |
| no | Ref. | Ref. | |
| I avoid eating meat | yes | p = 0.059 | 0.79 (0.62–1.01) |
| no | Ref. | Ref. | |
| I limit carbohydrates (low-carb diet) | yes | p < 0.01 | 1.39 (1.1–1.75) |
| no | Ref. | Ref. | |
| I eliminate products that contain preservatives/artificial colors | yes | p < 0.01 | 0.76 (0.63–0.91) |
| no | Ref. | Ref. | |
| I do no physical activity | yes | p < 0.05 | 1.21 (1.02–1.44) |
| no | Ref. | Ref. | |
| I do home exercises such as yoga or pilates | yes | p < 0.001 | 0.68 (0.55–0.84) |
| no | Ref. | Ref. | |
| I go to the swimming pool | yes | p < 0.05 | 1.33 (1.04–1.71) |
| no | Ref. | Ref. | |
| Gender | men | p < 0.001 | 1.69 (1.47–1.95) |
| women | Ref. | Ref. | |
| Education | vocational | p < 0.05 | 1.27 (1.05–1.53) |
| secondary | p < 0.01 | 1.24 (1.06–1.45) | |
| other | Ref. | Ref. | |
| Age | 18–24 years | Ref. | Ref. |
| 25–34 years | p < 0.001 | 1.94 (1.45–2.6) | |
| 35–44 years | p < 0.001 | 3.55 (2.69–4.7) | |
| 45–64 years | p < 0.001 | 5.7 (4.34–7.49) | |
| Location of the place of residence | rural | p < 0.01 | 1.21 (1.05–1.39) |
| urban | Ref. | Ref. | |
| Factors Associated with Assigment to Obesity Group | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | Response | p | OR (95% CI) |
| I track my progress in losing weight or building muscle mass using an app or journal | yes | p < 0.05 | 0.67 (0.49–0.92) |
| no | Ref. | Ref. | |
| I don’t pay much attention to my diet | yes | p < 0.05 | 1.23 (1–1.5) |
| no | Ref. | Ref. | |
| I limit carbohydrates (low-carb diet) | yes | p < 0.05 | 0.74 (0.56–0.97) |
| no | Ref. | Ref. | |
| I make sure that my daily diet includes dietary fiber | yes | p < 0.05 | 1.35 (1.04–1.75) |
| no | Ref. | Ref. | |
| I eliminate products that contain preservatives/artificial colors | yes | p = 0.054 | 1.27 (1–1.62) |
| no | Ref. | Ref. | |
| I don’t do any physical activity | yes | p < 0.001 | 0.62 (0.5–0.75) |
| no | Ref. | Ref. | |
| I exercise regularly at least 3 times a week | yes | p < 0.05 | 1.5 (1.09–2.06) |
| no | Ref. | Ref. | |
| I exercise occasionally, once or twice a month | yes | p = 0.055 | 0.78 (0.6–1.01) |
| no | Ref. | Ref. | |
| Education | primary | p < 0.001 | 0.51 (0.35–0.72) |
| vocational | p < 0.05 | 0.78 (0.62–0.99) | |
| secondary | p < 0.01 | 0.74 (0.6–0.92) | |
| higher | Ref. | Ref. | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sierpiński, R.; Jankowski, M.; Raciborski, F. Differences in Lifestyle-Related Behaviors Among Healthy Weight, Overweight, and Obese Groups: A Secondary Analysis of Data on 4714 Adults in Poland. Nutrients 2025, 17, 2083. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17132083
Sierpiński R, Jankowski M, Raciborski F. Differences in Lifestyle-Related Behaviors Among Healthy Weight, Overweight, and Obese Groups: A Secondary Analysis of Data on 4714 Adults in Poland. Nutrients. 2025; 17(13):2083. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17132083
Chicago/Turabian StyleSierpiński, Radosław, Mateusz Jankowski, and Filip Raciborski. 2025. "Differences in Lifestyle-Related Behaviors Among Healthy Weight, Overweight, and Obese Groups: A Secondary Analysis of Data on 4714 Adults in Poland" Nutrients 17, no. 13: 2083. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17132083
APA StyleSierpiński, R., Jankowski, M., & Raciborski, F. (2025). Differences in Lifestyle-Related Behaviors Among Healthy Weight, Overweight, and Obese Groups: A Secondary Analysis of Data on 4714 Adults in Poland. Nutrients, 17(13), 2083. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17132083








