Multi-Strain Probiotics Alleviate Food Allergy-Induced Neurobehavioral Abnormalities by Regulating Gut Microbiota and Metabolites
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
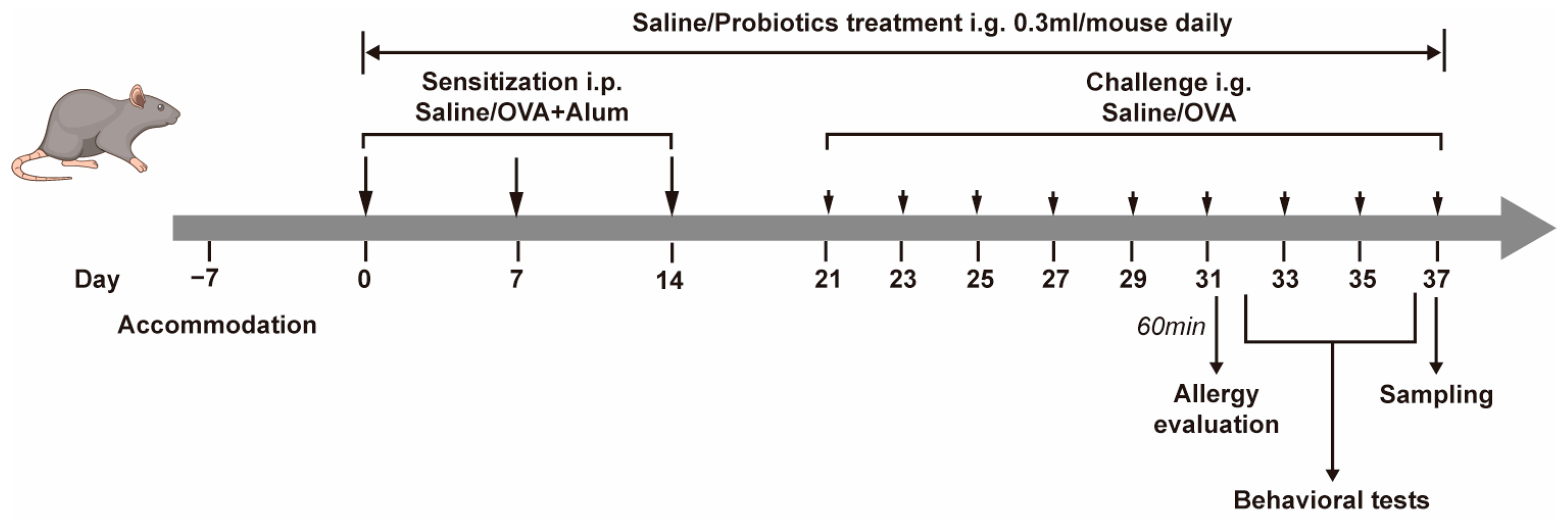
2.2. Experimental Protocol
3. Results
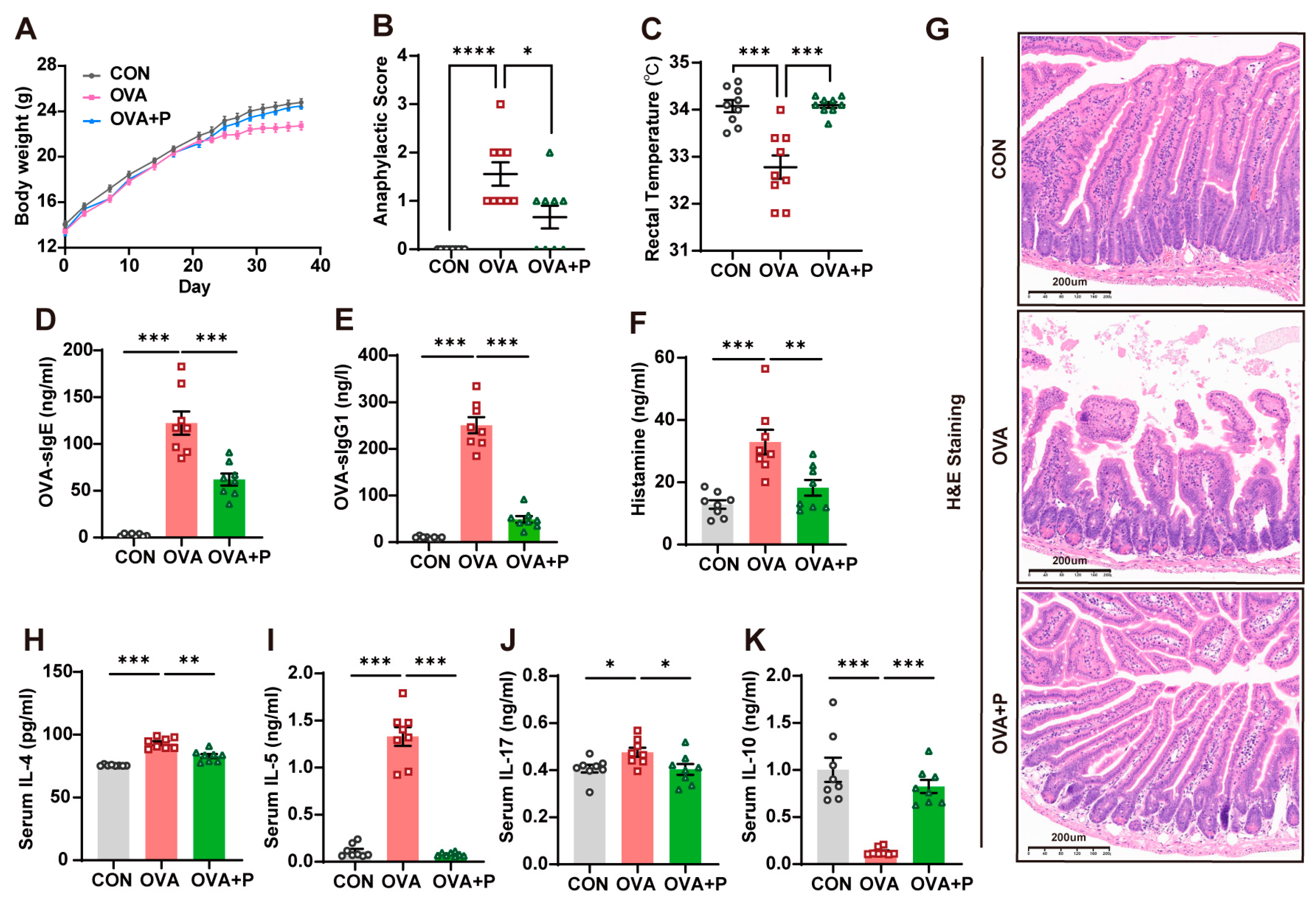
3.1. Multi-Strain Probiotics Attenuated Allergic Responses in OVA Mice
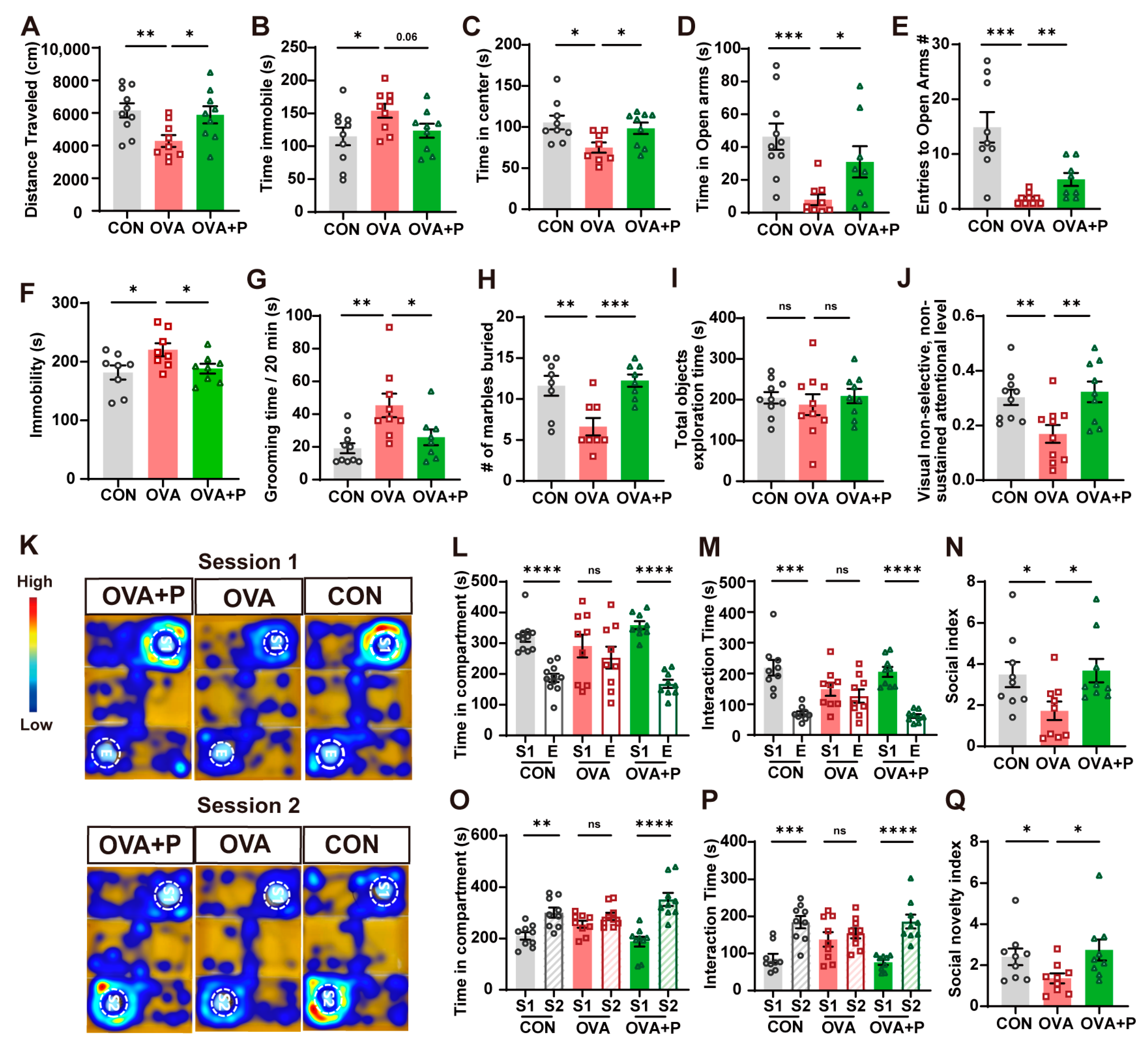
3.2. Multi-Strain Probiotics Partially Mitigated Neurobehavioral Abnormalities in OVA-Induced FA
3.3. Multi-Strain Probiotics Attenuated FA-Induced Neuroinflammation and Neuronal Injury
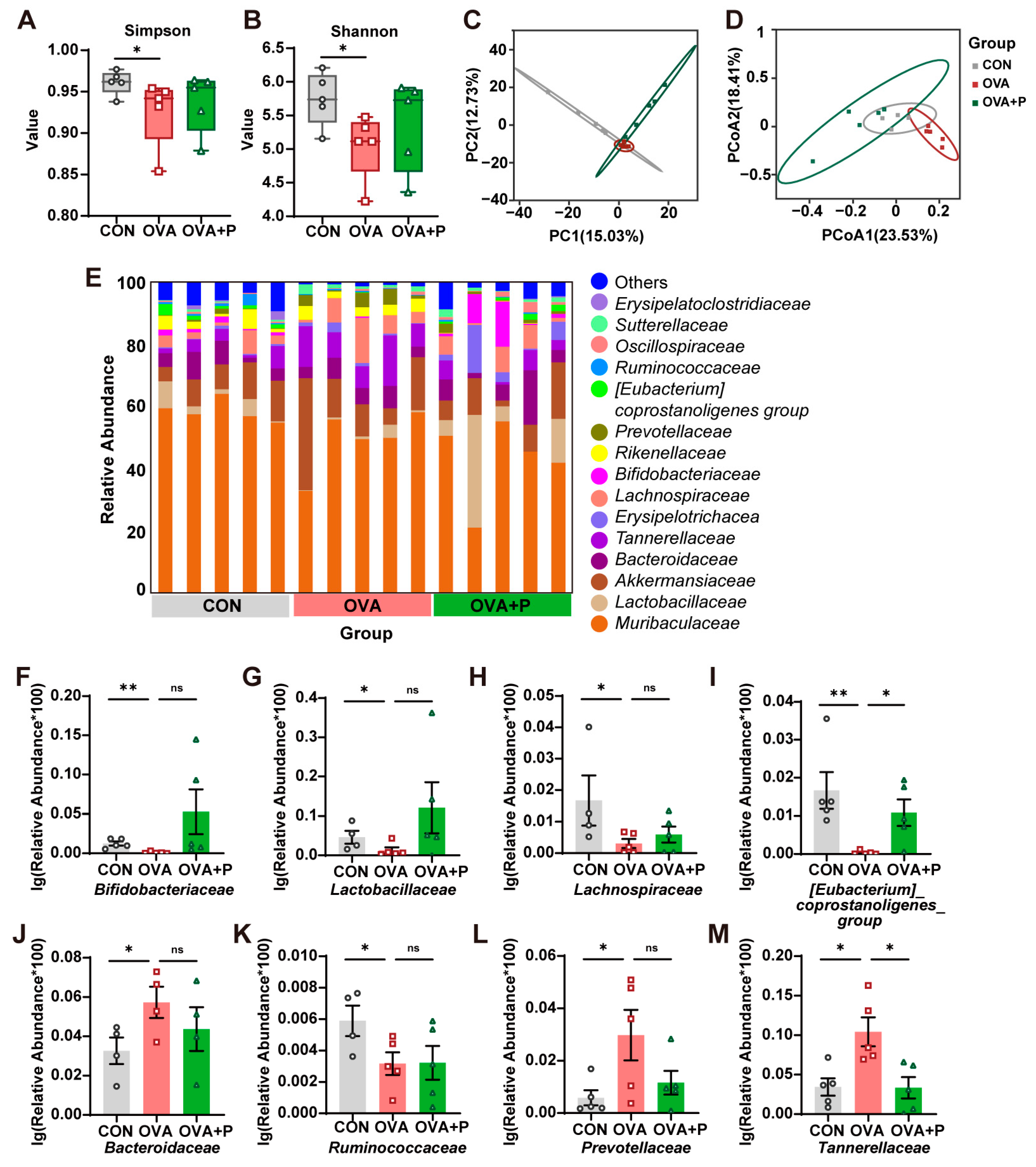
3.4. Multi-Strain Probiotics Partially Restored the Structure of Gut Microbiota
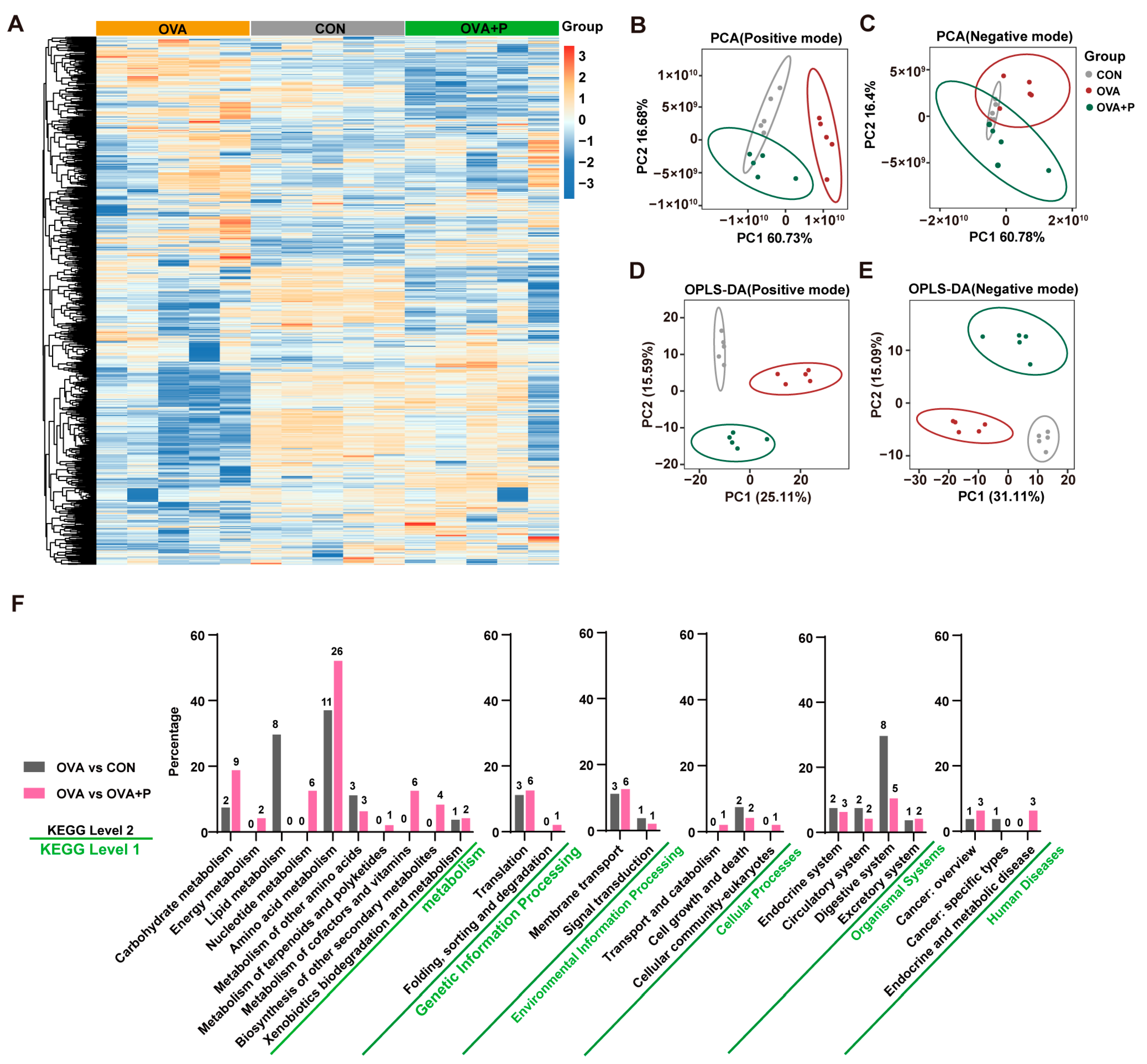
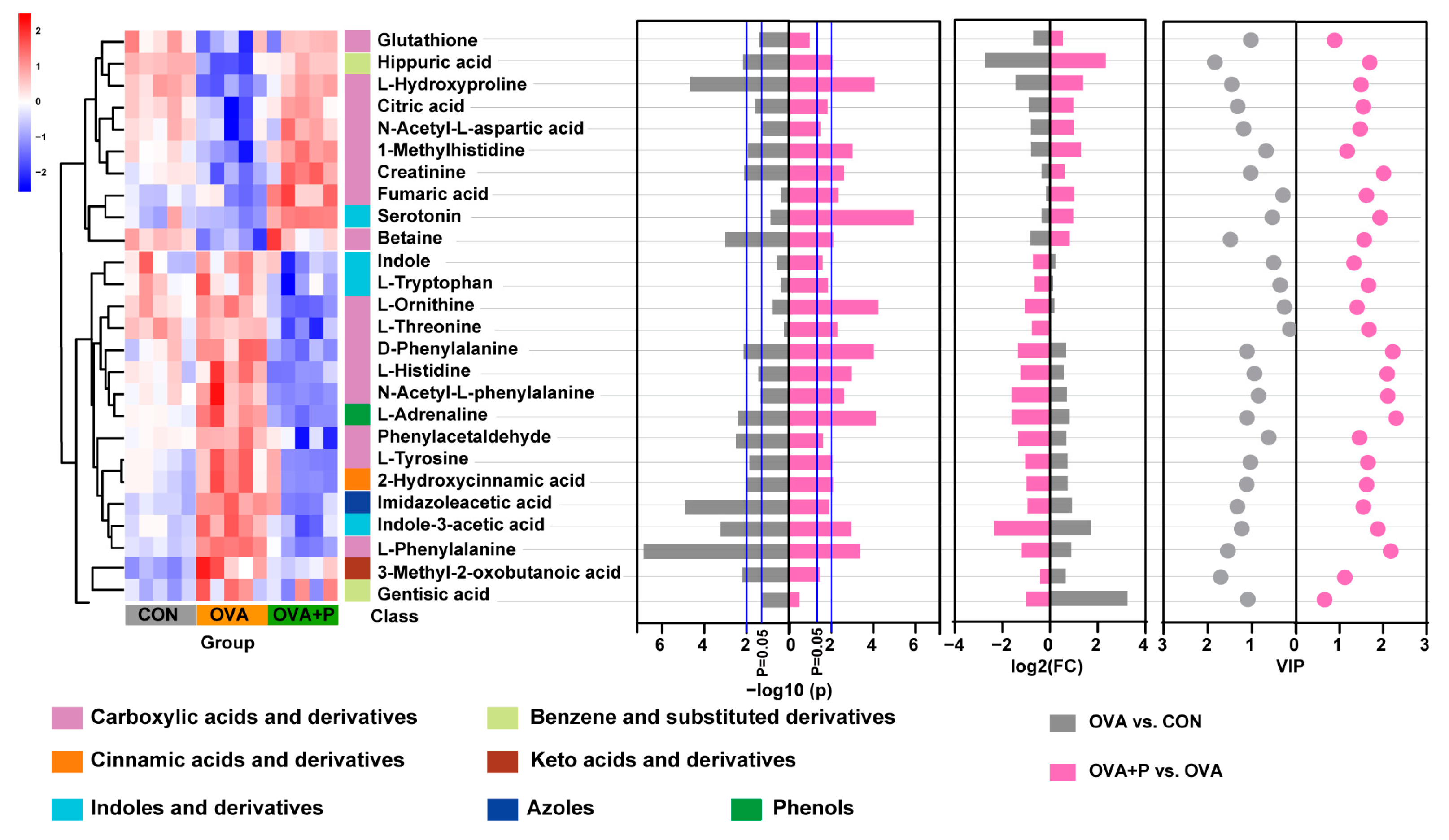
3.5. Multi-Strain Probiotics Altered Amino Acid Metabolism in OVA Mice
3.6. Correlation Between Altered Serum Amino Acid Metabolites and Gut Microbiota
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| FA | Food Allergy |
| OVA | Ovalbumin |
| FMT | Fecal microbiota transplantation |
| MGBA | Microbiota-gut-brain axis |
| OFT | Open field test |
| EPM | Elevated plus test |
| FST | Forced swimming test |
| MBT | Marbles berried test |
| TST | Three-chamber social test |
| NNAT | Non-selective, non-sustained visual attention test |
| SI | Social Index |
| SNI | Social Novelty Index |
References
- Muraro, A.; Werfel, T.; Hoffmann-Sommergruber, K.; Roberts, G.; Beyer, K.; Bindslev-Jensen, C.; Cardona, V.; Dubois, A.; duToit, G.; Eigenmann, P.; et al. EAACI food allergy and anaphylaxis guidelines: Diagnosis and management of food allergy. Allergy 2014, 69, 1008–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, R.S.; Warren, C.M.; Smith, B.M.; Jiang, J.; Blumenstock, J.A.; Davis, M.M.; Schleimer, R.P.; Nadeau, K.C. Prevalence and Severity of Food Allergies Among US Adults. JAMA Netw. Open 2019, 2, e185630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osborne, N.J.; Koplin, J.J.; Martin, P.E.; Gurrin, L.C.; Lowe, A.J.; Matheson, M.C.; Ponsonby, A.L.; Wake, M.; Tang, M.L.; Dharmage, S.C.; et al. Prevalence of challenge-proven IgE-mediated food allergy using population-based sampling and predetermined challenge criteria in infants. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011, 127, 668–676.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, W.; Freeland, D.M.H.; Nadeau, K.C. Food allergy: Immune mechanisms, diagnosis and immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 751–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferro, M.A.; Van Lieshout, R.J.; Ohayon, J.; Scott, J.G. Emotional and behavioral problems in adolescents and young adults with food allergy. Allergy 2016, 71, 532–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Liu, B.; Yang, W.; Snetselaar, L.G.; Chen, M.; Bao, W.; Strathearn, L. Association of Food Allergy, Respiratory Allergy, and Skin Allergy with Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder among Children. Nutrients 2022, 14, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Shen, W.; Yao, H.; Zheng, R.; Chen, W.; Zhang, W. Association between Autism Spectrum Disorder and Food Allergy: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Autism. Res. 2021, 14, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Li, L.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xuan, J.; Xu, X.; Qiu, H.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; et al. Effects of allergic diseases on social-emotional development in children at 12 months of age: A Prospective Cohort Study. J. Affect. Disord. 2025, 374, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunyavanich, S.; Berin, M.C. Food allergy and the microbiome: Current understandings and future directions. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 144, 1468–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharon, G.; Cruz, N.J.; Kang, D.W.; Gandal, M.J.; Wang, B.; Kim, Y.M.; Zink, E.M.; Casey, C.P.; Taylor, B.C.; Lane, C.J.; et al. Human Gut Microbiota from Autism Spectrum Disorder Promote Behavioral Symptoms in Mice. Cell 2019, 177, 1600–1618.e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavzy, S.J.; Kensiski, A.; Lee, Z.L.; Mongodin, E.F.; Ma, B.; Bromberg, J.S. Bifidobacterium mechanisms of immune modulation and tolerance. Gut Microbes. 2023, 15, 2291164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, R.; Wu, F.; Zhou, Q.; Wei, W.; Yue, J.; Xiao, B.; Luo, Z. Lactobacillus and intestinal diseases: Mechanisms of action and clinical applications. Microbiol. Res. 2022, 260, 127019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Li, N.; Yang, J.J.; Zhao, D.M.; Chen, B.; Zhang, G.Q.; Chen, S.; Cao, R.F.; Yu, H.; Zhao, C.Y.; et al. Probiotics and fructo-oligosaccharide intervention modulate the microbiota-gut brain axis to improve autism spectrum reducing also the hyper-serotonergic state and the dopamine metabolism disorder. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 157, 104784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Santa, F.; Strimpakos, G.; Marchetti, N.; Gargari, G.; Torcinaro, A.; Arioli, S.; Mora, D.; Petrella, C.; Farioli-Vecchioli, S. Effect of a multi-strain probiotic mixture consumption on anxiety and depression symptoms induced in adult mice by postnatal maternal separation. Microbiome 2024, 12, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germundson, D.L.; Smith, N.A.; Vendsel, L.P.; Kelsch, A.V.; Combs, C.K.; Nagamoto-Combs, K. Oral sensitization to whey proteins induces age- and sex-dependent behavioral abnormality and neuroinflammatory responses in a mouse model of food allergy: A potential role of mast cells. J. Neuroinflamm. 2018, 15, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczepanski, S.M.; Knight, R.T. Insights into human behavior from lesions to the prefrontal cortex. Neuron 2014, 83, 1002–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colonna, M.; Butovsky, O. Microglia Function in the Central Nervous System During Health and Neurodegeneration. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 35, 441–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.T.; Walsh, R.F.L.; Sheehan, A.E. Prebiotics and probiotics for depression and anxiety: A systematic review and meta-analysis of controlled clinical trials. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2019, 102, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaub, A.C.; Schneider, E.; Vazquez-Castellanos, J.F.; Schweinfurth, N.; Kettelhack, C.; Doll, J.P.K.; Yamanbaeva, G.; Mählmann, L.; Brand, S.; Beglinger, C.; et al. Clinical, gut microbial and neural effects of a probiotic add-on therapy in depressed patients: A randomized controlled trial. Transl. Psychiatry 2022, 12, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Zhang, D.; Yu, H.; Yuan, H.; Shen, H.; Lan, X.; Liu, H.; Chen, X.; Meng, F.; Wu, X.; et al. Gut microbiota regulates chronic ethanol exposure-induced depressive-like behavior through hippocampal NLRP3-mediated neuroinflammation. Mol. Psychiatry 2023, 28, 919–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, J.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Q.; Yu, H.; Yuan, H.; Guo, Y.; Shen, H.; Liu, H.; Wang, C.; Meng, F.; et al. Probiotics alleviate chronic ethanol exposure-induced anxiety-like behavior and hippocampal neuroinflammation in male mice through gut microbiota-derived extracellular vesicles. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2024, 22, 730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, P.; Zou, R.; Wang, L.; Chen, Y.; Qian, X.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Qian, L.; Wang, Q.; Wang, G.; et al. Multi-Probiotics ameliorate Major depressive disorder and accompanying gastrointestinal syndromes via serotonergic system regulation. J. Adv. Res. 2023, 45, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murack, M.; Kadamani, A.K.; Guindon-Riopel, A.; Traynor, O.H.; Iqbal, U.H.; Bronner, S.; Messier, C.; Ismail, N. The effect of probiotic supplementation on sleep, depression-like behaviour, and central glucose and lactate metabolism in male and female pubertal mice exposed to chronic sleep disruption. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2024, 168, 107146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, Y.J.; Ma, X.; Joo, M.K.; Baek, J.S.; Kim, D.H. Lactococcus lactis and Bifidobacterium bifidum alleviate postmenopausal symptoms by suppressing NF-κB signaling and microbiota dysbiosis. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 31675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emge, J.R.; Huynh, K.; Miller, E.N.; Kaur, M.; Reardon, C.; Barrett, K.E.; Gareau, M.G. Modulation of the microbiota-gut-brain axis by probiotics in a murine model of inflammatory bowel disease. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2016, 310, G989–G998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qing, L.; Qian, X.; Zhu, H.; Wang, J.; Sun, J.; Jin, Z.; Tang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, G.; Zhao, J.; et al. Maternal-infant probiotic transmission mitigates early-life stress-induced autism in mice. Gut Microbes. 2025, 17, 2456584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.M.; Wu, C.C.; Kim, Y.; Hsu, W.Y.; Tsai, Y.C.; Chiu, S.L. Enhancing social behavior in an autism spectrum disorder mouse model: Investigating the underlying mechanisms of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum intervention. Gut Microbes. 2024, 16, 2359501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Z.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H. Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis Probio-M8 alleviates abnormal behavior and regulates gut microbiota in a mouse model suffering from autism. mSystems 2024, 9, e0101323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabouy, L.; Getselter, D.; Ziv, O.; Karpuj, M.; Tabouy, T.; Lukic, I.; Maayouf, R.; Werbner, N.; Ben-Amram, H.; Nuriel-Ohayon, M.; et al. Dysbiosis of microbiome and probiotic treatment in a genetic model of autism spectrum disorders. Brain Behav. Immun. 2018, 73, 310–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, P.; Wang, N.; Yu, Y.; Zhu, J.; Zuo, Z.; Zhang, B.; Zhao, F. Single-cell delineation of the microbiota-gut-brain axis: Probiotic intervention in Chd8 haploinsufficient mice. Cell Genom. 2025, 5, 100768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Wang, L.; Yang, L.; Tao, S.; Xia, R.; Fan, W. Long-term effect of early-life supplementation with probiotics on preventing atopic dermatitis: A meta-analysis. J. Dermatolog. Treat. 2015, 26, 537–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bresnahan, M.; Hornig, M.; Schultz, A.F.; Gunnes, N.; Hirtz, D.; Lie, K.K.; Magnus, P.; Reichborn-Kjennerud, T.; Roth, C.; Schjølberg, S.; et al. Association of maternal report of infant and toddler gastrointestinal symptoms with autism: Evidence from a prospective birth cohort. JAMA Psychiatry 2015, 72, 466–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Restrepo, B.; Angkustsiri, K.; Taylor, S.L.; Rogers, S.J.; Cabral, J.; Heath, B.; Hechtman, A.; Solomon, M.; Ashwood, P.; Amaral, D.G.; et al. Developmental-behavioral profiles in children with autism spectrum disorder and co-occurring gastrointestinal symptoms. Autism. Res. 2020, 13, 1778–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevens, B.R.; Goel, R.; Seungbum, K.; Richards, E.M.; Holbert, R.C.; Pepine, C.J.; Raizada, M.K. Increased human intestinal barrier permeability plasma biomarkers zonulin and FABP2 correlated with plasma LPS and altered gut microbiome in anxiety or depression. Gut 2018, 67, 1555–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballou, S.; Katon, J.; Singh, P.; Rangan, V.; Lee, H.N.; McMahon, C.; Iturrino, J.; Lembo, A.; Nee, J. Chronic Diarrhea and Constipation Are More Common in Depressed Individuals. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 17, 2696–2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barberio, B.; Zamani, M.; Black, C.J.; Savarino, E.V.; Ford, A.C. Prevalence of symptoms of anxiety and depression in patients with inflammatory bowel disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 6, 359–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Theije, C.G.; Koelink, P.J.; Korte-Bouws, G.A.; Lopes da Silva, S.; Korte, S.M.; Olivier, B.; Garssen, J.; Kraneveld, A.D. Intestinal inflammation in a murine model of autism spectrum disorders. Brain Behav. Immun. 2014, 37, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Xi, H.; Xue, X.; Sun, X.; Huang, H.; Fu, D.; Mi, Y.; He, Y.; Yang, P.; Tang, Y.; et al. Clostridium butyricum regulates intestinal barrier function via trek1 to improve behavioral abnormalities in mice with autism spectrum disorder. Cell Biosci. 2024, 14, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, H.M.; Lee, K.E.; Kim, D.H. The Preventive and Curative Effects of Lactobacillus reuteri NK33 and Bifidobacterium adolescentis NK98 on Immobilization Stress-Induced Anxiety/Depression and Colitis in Mice. Nutrients 2019, 11, 819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, J.W.; Shin, Y.J.; Ma, X.; Son, Y.H.; Jang, H.M.; Lee, C.K.; Kim, D.H. The Alleviation of Gut Microbiota-Induced Depression and Colitis in Mice by Anti-Inflammatory Probiotics NK151, NK173, and NK175. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, H.; Qing, W.; Liu, F.; Zeng, N.; Wu, F.; Shi, Y.; Gao, X.; Cheng, M.; Li, H.; et al. Congenitally underdeveloped intestine drives autism-related gut microbiota and behavior. Brain Behav. Immun. 2022, 105, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Kang, H.; Zhang, W.; Wang, J.; Liu, Z.; Jing, J.; Han, L.; Gao, A. Probiotics ameliorate benzene-induced systemic inflammation and hematopoietic toxicity by inhibiting Bacteroidaceae-mediated ferroptosis. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 899, 165678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Ye, Z.; Li, J.; Wang, L.; Chen, Y.; Yu, M.; Han, J.; Huang, J.; Li, D.; Lv, Y.; et al. Gut bacteria Prevotellaceae related lithocholic acid metabolism promotes colonic inflammation. J. Transl. Med. 2025, 23, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, T.S.; Guan, M.; Mayer, E.A.; Stains, J.; Liu, C.; Vora, P.; Jacobs, J.P.; Lagishetty, V.; Chang, L.; Barry, R.L.; et al. Obesity is associated with a distinct brain-gut microbiome signature that connects Prevotella and Bacteroides to the brain’s reward center. Gut Microbes 2022, 14, 2051999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, Y.W.; Tung, Y.T.; Yang, S.C.; Shirakawa, H.; Su, L.H.; Loe, P.Y.; Chiu, W.C. The Effects of Rice Bran on Neuroinflammation and Gut Microbiota in Ovariectomized Mice Fed a Drink with Fructose. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, M.; Kou, G.; Li, Y. The relationship between gut microbiota and inflammatory response, learning and memory in mice by sleep deprivation. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1159771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Y.; Mu, C.; Wang, H.; Shen, J.; Zoetendal, E.G.; Zhu, W. Amino acid utilization allows intestinal dominance of Lactobacillus amylovorus. ISME J. 2022, 16, 2491–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laursen, M.F.; Sakanaka, M.; von Burg, N.; Mörbe, U.; Andersen, D.; Moll, J.M.; Pekmez, C.T.; Rivollier, A.; Michaelsen, K.F.; Mølgaard, C.; et al. Bifidobacterium species associated with breastfeeding produce aromatic lactic acids in the infant gut. Nat. Microbiol. 2021, 6, 1367–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, Y.; Yang, H. Xanthan gum modified fish gelatin and binary culture modulates the metabolism of probiotics in fermented milk mainly via amino acid metabolism pathways. Food Res. Int. 2022, 161, 111844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Yu, Y.; Chen, X.; Gao, S.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, C. Bifidobacterium breve M-16V alters the gut microbiota to alleviate OVA-induced food allergy through IL-33/ST2 signal pathway. J. Cell. Physiol. 2020, 235, 9464–9473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xu, H.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, W.; Li, S.; Gao, J. Bifidobacterium breve Protects the Intestinal Epithelium and Mitigates Inflammation in Colitis via Regulating the Gut Microbiota-Cholic Acid Pathway. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 3572–3583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.; Dong, P.; Liu, C.; Xu, Y.; Zheng, M.; Cheng, L.; Wang, J.; Raghavan, V. Lactobacillus rhamnosus Probio-M9 alleviates OVA-sensitized food allergy through modulating gut microbiota and its metabolism. Food Funct. 2023, 14, 10784–10795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ta, L.D.H.; Chan, J.C.Y.; Yap, G.C.; Purbojati, R.W.; Drautz-Moses, D.I.; Koh, Y.M.; Tay, C.J.X.; Huang, C.H.; Kioh, D.Y.Q.; Woon, J.Y.; et al. A compromised developmental trajectory of the infant gut microbiome and metabolome in atopic eczema. Gut Microbes 2020, 12, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Song, L.; Wang, Y.; Liu, C.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, S.; Liu, S.; Duan, L. Beneficial effect of butyrate-producing Lachnospiraceae on stress-induced visceral hypersensitivity in rats. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 34, 1368–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noval Rivas, M.; Burton, O.T.; Wise, P.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Hobson, S.A.; Garcia Lloret, M.; Chehoud, C.; Kuczynski, J.; DeSantis, T.; Warrington, J.; et al. A microbiota signature associated with experimental food allergy promotes allergic sensitization and anaphylaxis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 131, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, T.S.; Lærke, H.N.; Theil, P.K.; Sørensen, J.F.; Saarinen, M.; Forssten, S.; Knudsen, K.E. Diets high in resistant starch and arabinoxylan modulate digestion processes and SCFA pool size in the large intestine and faecal microbial composition in pigs. Br. J. Nutr. 2014, 112, 1837–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Jiang, W.; Tian, Z.; Wu, H.; Ning, H.; Yan, G.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Z.; Dong, F.; Sun, Y.; et al. Fecal g. Streptococcus and g. Eubacterium_coprostanoligenes_group combined with sphingosine to modulate the serum dyslipidemia in high-fat diet mice. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 4234–4245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Li, H.; Liang, J.; Lv, C.; Zhao, K.; Niu, M.; Li, Z.; Zeng, L.; Xu, K. Assessment of oral ciprofloxacin impaired gut barrier integrity on gut bacteria in mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 83, 106460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Ye, Y.; Ji, J.; Sun, J.; Wang, J.S.; Sun, X. Untargeted Metabolomic Profiling Reveals Changes in Gut Microbiota and Mechanisms of Its Regulation of Allergy in OVA-Sensitive BALB/c Mice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 3344–3356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, R.; Wang, J.; Li, A.; Wang, Y.; Fan, D.; Zhang, B.; Fu, W.; Liu, J.; Fu, H.; Wang, S. 2′-Fucosyllactose alleviates OVA-induced food allergy in mice by ameliorating intestinal microecology and regulating the imbalance of Th2/Th1 proportion. Food Funct. 2023, 14, 10924–10940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Chen, B.; Luo, M.; Xie, L.; Lu, M.; Lu, X.; Zhang, S.; Wei, L.; Zhou, X.; Yao, B.; et al. Microbiota-indole 3-propionic acid-brain axis mediates abnormal synaptic pruning of hippocampal microglia and susceptibility to ASD in IUGR offspring. Microbiome 2023, 11, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Wang, H.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Xie, P. Gut microbiota and its metabolites in depression: From pathogenesis to treatment. eBioMedicine 2023, 90, 104527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erny, D.; Hrabě de Angelis, A.L.; Jaitin, D.; Wieghofer, P.; Staszewski, O.; David, E.; Keren-Shaul, H.; Mahlakoiv, T.; Jakobshagen, K.; Buch, T.; et al. Host microbiota constantly control maturation and function of microglia in the CNS. Nat. Neurosci. 2015, 18, 965–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Sun, G.; Feng, T.; Zhang, J.; Huang, X.; Wang, T.; Xie, Z.; Chu, X.; Yang, J.; Wang, H.; et al. Sodium oligomannate therapeutically remodels gut microbiota and suppresses gut bacterial amino acids-shaped neuroinflammation to inhibit Alzheimer’s disease progression. Cell Res. 2019, 29, 787–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soheili, M.; Alinaghipour, A.; Salami, M. Good bacteria, oxidative stress and neurological disorders: Possible therapeutical considerations. Life Sci. 2022, 301, 120605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoyama, K. Glutathione in the Brain. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, J.; Liu, Y.; Gui, S.; Tian, L.; Yu, Y.; Song, X.; Zhong, X.; Chen, X.; Chen, W.; Zheng, P.; et al. Metabolomic changes in animal models of depression: A systematic analysis. Mol. Psychiatry 2021, 26, 7328–7336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiteside, S.P.; Abramowitz, J.S.; Port, J.D. The effect of behavior therapy on caudate N-acetyl-l-aspartic acid in adults with obsessive-compulsive disorder. Psychiatry Res. 2012, 201, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, N.; Wegner, A. N-acetyl-aspartate metabolism at the interface of cancer, immunity, and neurodegeneration. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2024, 85, 103051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.X.; Li, M.Y.; Lei, J.X.; Wu, Y.Z.; Li, Z.H.; Chen, L.M.; Zhou, C.L.; Su, J.Y.; Huang, G.X.; Huang, X.Q.; et al. Huangqin decoction ameliorates DSS-induced ulcerative colitis: Role of gut microbiota and amino acid metabolism, mTOR pathway and intestinal epithelial barrier. Phytomedicine 2022, 100, 154052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Hou, Y.; Dai, Z.; Hu, C.A.; Wu, G. Metabolism, Nutrition, and Redox Signaling of Hydroxyproline. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2019, 30, 674–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, Y.; Dai, Z.; Sun, S.; Ma, X.; Yang, Y.; Tso, P.; Wu, G.; Wu, Z. Hydroxyproline Attenuates Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Colitis in Mice: Involvment of the NF-κB Signaling and Oxidative Stress. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2018, 62, e1800494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalueff, A.V.; Stewart, A.M.; Song, C.; Berridge, K.C.; Graybiel, A.M.; Fentress, J.C. Neurobiology of rodent self-grooming and its value for translational neuroscience. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2016, 17, 45–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartzer, J.J.; Careaga, M.; Chang, C.; Onore, C.E.; Ashwood, P. Allergic fetal priming leads to developmental, behavioral and neurobiological changes in mice. Transl. Psychiatry 2015, 5, e543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Jiao, X.; Xu, M.; Wang, B.; Li, J.; Yang, F.; Zhang, L.; Xu, L.; Yu, X. Effects of circulating vitamin D concentrations on emotion, behavior and attention: A cross-sectional study in preschool children with follow-up behavior experiments in juvenile mice. J. Affect. Disord. 2020, 275, 290–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millecamps, M.; Etienne, M.; Jourdan, D.; Eschalier, A.; Ardid, D. Decrease in non-selective, non-sustained attention induced by a chronic visceral inflammatory state as a new pain evaluation in rats. Pain 2004, 109, 214–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, S.; Li, L.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, X. Multi-Strain Probiotics Alleviate Food Allergy-Induced Neurobehavioral Abnormalities by Regulating Gut Microbiota and Metabolites. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1955. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17121955
Hu S, Li L, Zhou C, Zhang Y, Yu X. Multi-Strain Probiotics Alleviate Food Allergy-Induced Neurobehavioral Abnormalities by Regulating Gut Microbiota and Metabolites. Nutrients. 2025; 17(12):1955. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17121955
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Shouxun, Luanluan Li, Chunyan Zhou, Yue Zhang, and Xiaodan Yu. 2025. "Multi-Strain Probiotics Alleviate Food Allergy-Induced Neurobehavioral Abnormalities by Regulating Gut Microbiota and Metabolites" Nutrients 17, no. 12: 1955. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17121955
APA StyleHu, S., Li, L., Zhou, C., Zhang, Y., & Yu, X. (2025). Multi-Strain Probiotics Alleviate Food Allergy-Induced Neurobehavioral Abnormalities by Regulating Gut Microbiota and Metabolites. Nutrients, 17(12), 1955. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17121955





