Ultrasound-Derived Skinfolds in Anthropometric Predictive Equations Overestimate Fat Mass: A Validation Study Using a Four-Component Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
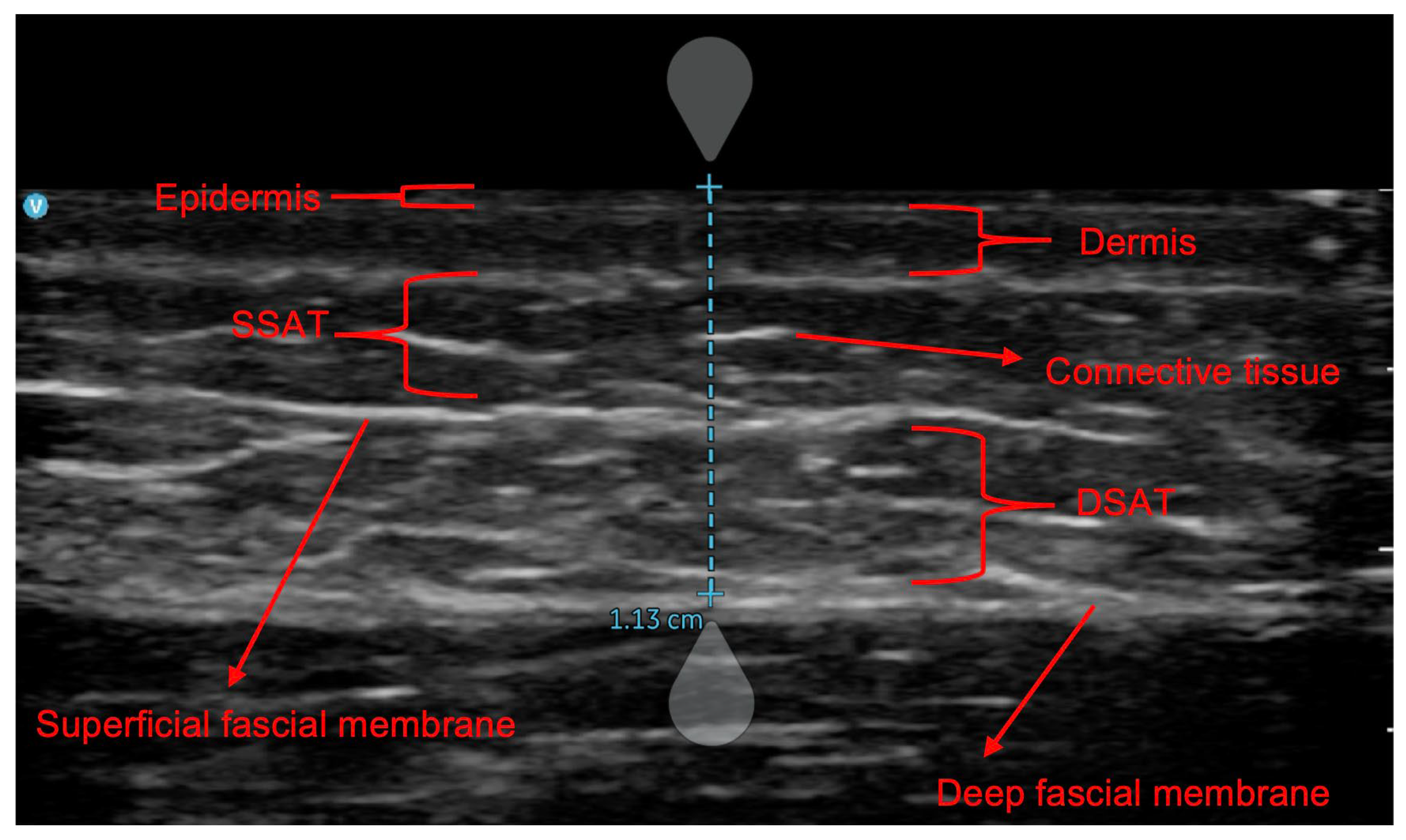
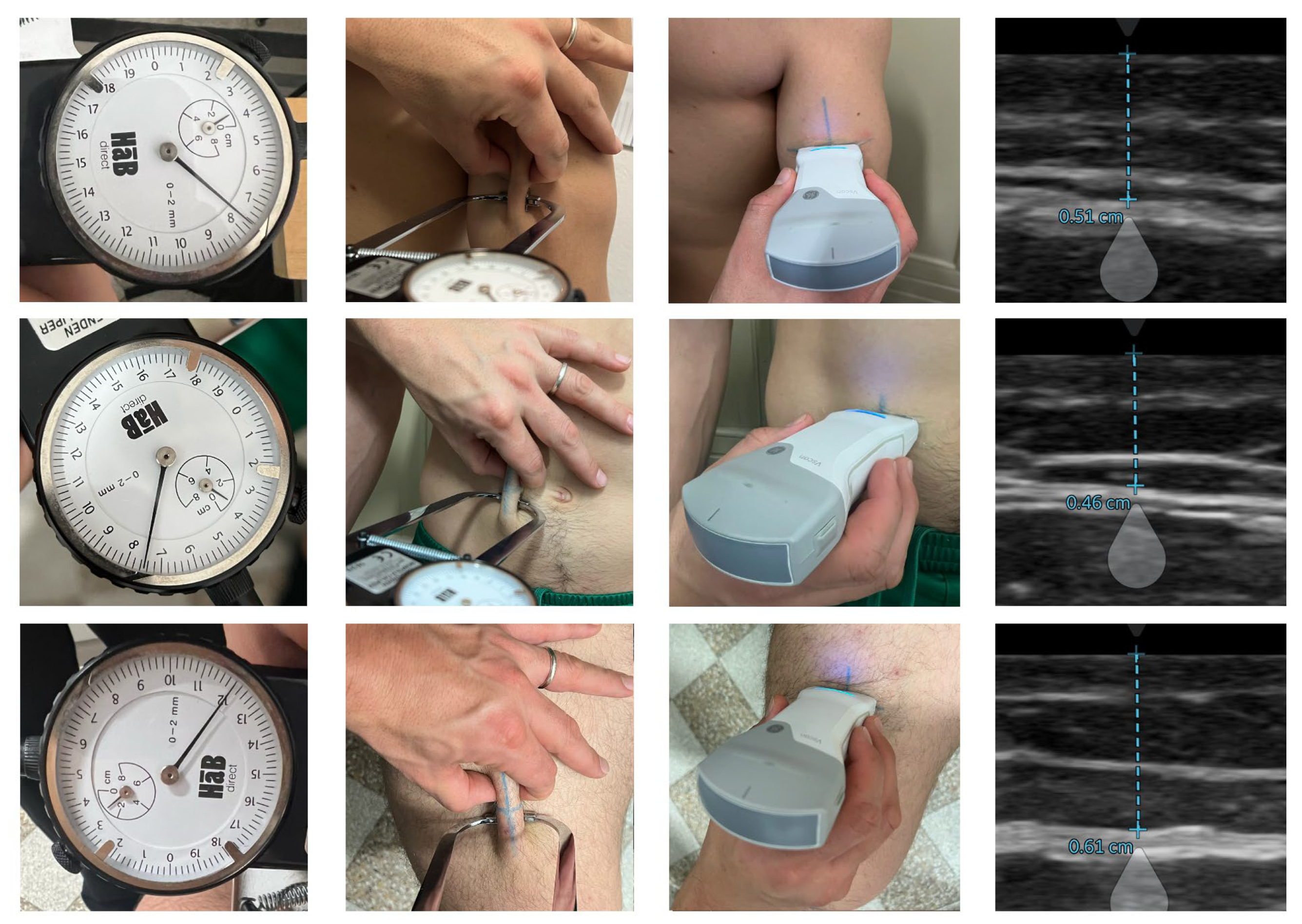
2.2. Procedures
2.3. Statistical Analysis
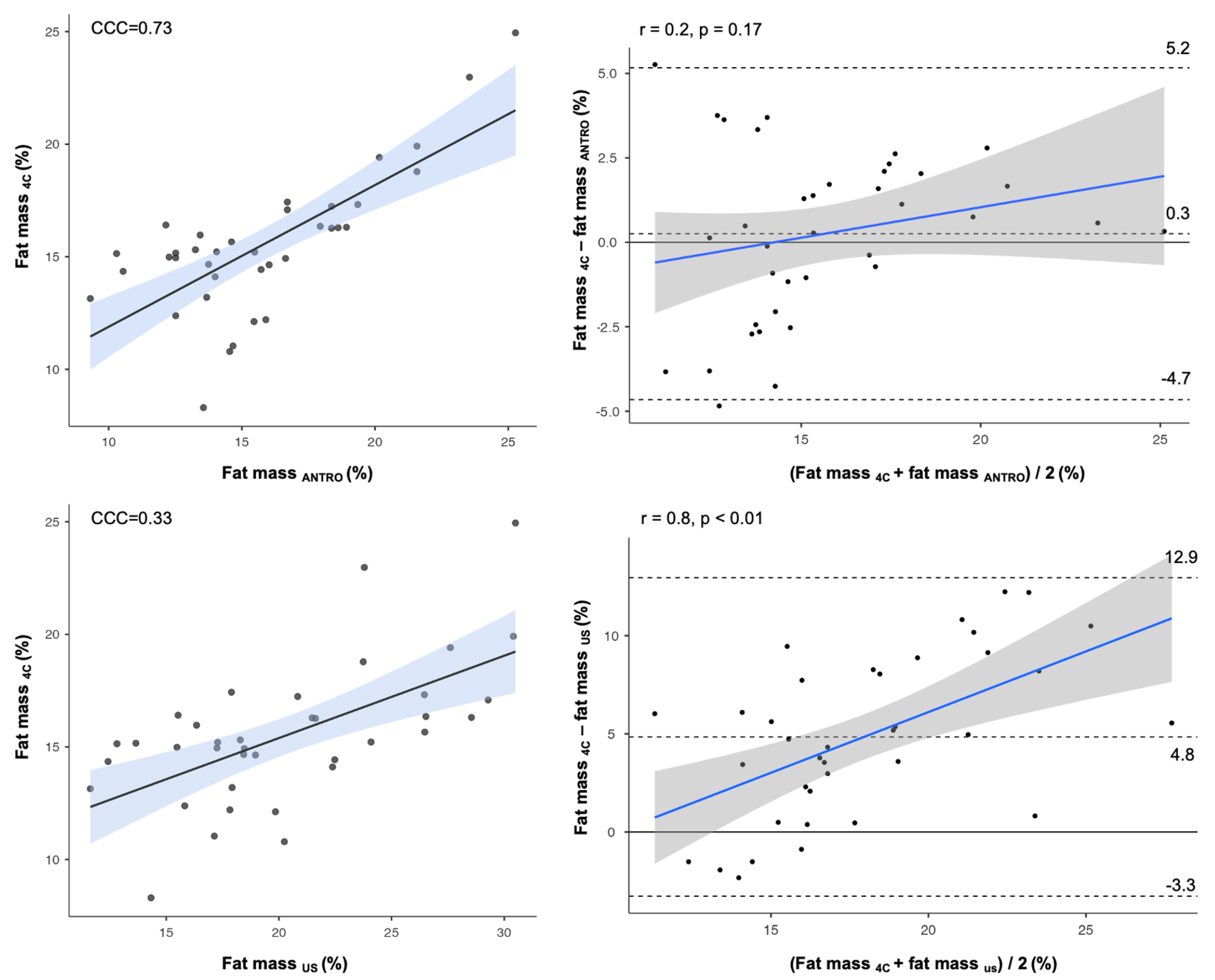
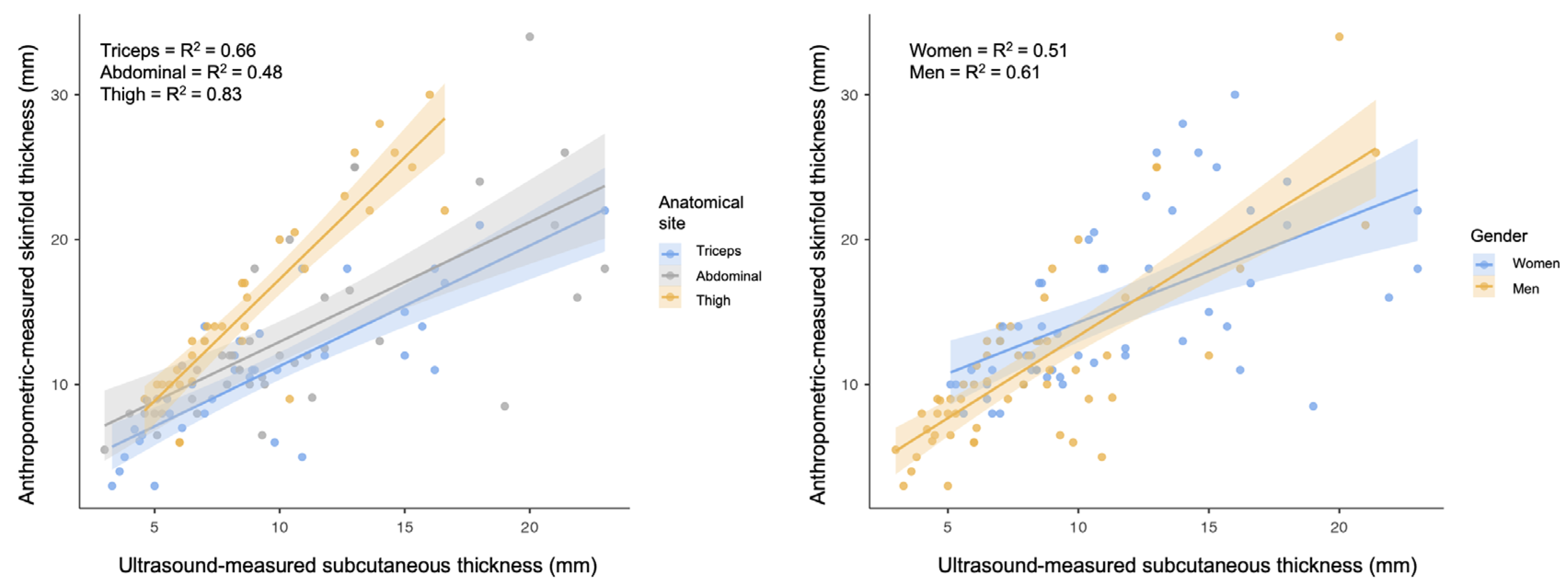
3. Results
4. Discussion
Nutritional Perspectives
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BIA | Bioelectrical impedance analysis |
| BIVA | Bioelectrical impedance vector analysis |
| DSAT | Deep subcutaneous adipose tissue |
| FM | Fat mass |
| R | Resistance |
| SSAT | Superficial subcutaneous adipose tissue |
| US | Ultrasound |
| Xc | Reactance |
References
- Holmes, C.J.; Racette, S.B. The Utility of Body Composition Assessment in Nutrition and Clinical Practice: An Overview of Current Methodology. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martín-Rodríguez, A.; Belinchón-deMiguel, P.; Rubio-Zarapuz, A.; Tornero-Aguilera, J.F.; Martínez-Guardado, I.; Villanueva-Tobaldo, C.V.; Clemente-Suárez, V.J. Advances in Understanding the Interplay between Dietary Practices, Body Composition, and Sports Performance in Athletes. Nutrients 2024, 16, 571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gotsman, I.; Keren, A.; Amir, O.; Zwas, D.R. Increased Estimated Fat-free Mass and Fat Mass Associated with Improved Clinical Outcome in Heart Failure. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2022, 52, e13655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tur, J.A.; Bibiloni, M.D.M. Anthropometry, Body Composition and Resting Energy Expenditure in Human. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toselli, S.; Campa, F. Anthropometry and Functional Movement Patterns in Elite Male Volleyball Players of Different Competitive Levels. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2018, 32, 2601–2611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berná, G.; López-Bermudo, L.; Escudero-López, B.; Martín, F. We Are What We Eat: The Role of Lipids in Metabolic Diseases. Adv. Food Nutr. Res. 2023, 105, 173–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohman, T.G.; Milliken, L.A. ACSM’s Body Composition Assessment; Human Kinetics: Champaign, IL, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Paoli, A.; Campa, F. Problems and Opportunities in the Use of Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis for Assessing Body Composition During Ketogenic Diets: A Scoping Review. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2024, 13, 496–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Almeida, J.M.; García-García, C.; Vegas-Aguilar, I.M.; Ballesteros Pomar, M.D.; Cornejo-Pareja, I.M.; Fernández Medina, B.; de Luis Román, D.A.; Bellido Guerrero, D.; Bretón Lesmes, I.; Tinahones Madueño, F.J. Nutritional Ultrasound®: Conceptualisation, Technical Considerations and Standardisation. Endocrinol. Diabetes Nutr. 2023, 70 (Suppl. S1), 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokura, Y.; Nishioka, S.; Maeda, K.; Wakabayashi, H. Ultrasound Utilized by Registered Dietitians for Body Composition Measurement, Nutritional Assessment, and Nutritional Management. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2023, 57, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Socorro, C.R.; Ruiz-Santana, S. Role of Ultrasound in the Nutritional Assessment of Critically Ill Patients. Med. Intensiva 2024, 48, 235–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranger, B.J.; Lombardi, A.; Kwon, S.; Loeb, M.; Cho, H.; He, K.; Wei, D.; Park, J. Ultrasound for Assessing Paediatric Body Composition and Nutritional Status: Scoping Review and Future Directions. Acta Paediatr. 2025, 114, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umbrello, M.; Guglielmetti, L.; Formenti, P.; Antonucci, E.; Cereghini, S.; Filardo, C.; Montanari, G.; Muttini, S. Qualitative and Quantitative Muscle Ultrasound Changes in Patients with COVID-19–Related ARDS. Nutrition 2021, 91–92, 111449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wischmeyer, P.E.; Bear, D.E.; Berger, M.M.; De Waele, E.; Gunst, J.; McClave, S.A.; Prado, C.M.; Puthucheary, Z.; Ridley, E.J.; Van den Berghe, G.; et al. Personalized Nutrition Therapy in Critical Care: 10 Expert Recommendations. Crit. Care 2023, 27, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franchi, M.V.; Raiteri, B.J.; Longo, S.; Sinha, S.; Narici, M.V.; Csapo, R. Muscle Architecture Assessment: Strengths, Shortcomings and New Frontiers of in vivo Imaging Techniques. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2018, 44, 2492–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franchi, M.V.; Narici, M.V. Imaging of Skeletal Muscle Mass: Ultrasound. In Neuromuscular Assessments of Form and Function; Atherton, P.J., Wilkinson, D.J., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2023; pp. 65–84. ISBN 978-1-0716-3315-1. [Google Scholar]
- Sengeis, M.; Müller, W.; Störchle, P.; Führhapter-Rieger, A. Body Weight and Subcutaneous Fat Patterning in Elite Judokas. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2019, 29, 1774–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, N.; Quinton, A.; Brown, C.; Peek, M.J.; Benzie, R.; Nanan, R. Changes in Maternal Abdominal Subcutaneous Fat Layers Using Ultrasound: A Longitudinal Study. Obes. Res. Clin. Pract. 2017, 11, 655–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Perez, S.L.; Zhang, Y.; Mourtzakis, M.; Tussing-Humphreys, L.; Ridlon, J.; Gaskins, H.R.; Mutlu, E. Comparison between Handheld Ultrasound and Regional and Whole-Body Dual Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry (DXA) for Body Fat Assessment. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2021, 46, 386–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, J.; Thiele, J.; Kwast, S.; Borger, M.A.; Schröter, T.; Falz, R.; Busse, M. Measurement of Subcutaneous Fat Tissue: Reliability and Comparison of Caliper and Ultrasound via Systematic Body Mapping. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 15798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopinski, S.; Engel, T.; Cassel, M.; Fröhlich, K.; Mayer, F.; Carlsohn, A. Ultrasound Applied to Subcutaneous Fat Tissue Measurements in International Elite Canoeists. Int. J. Sports Med. 2015, 36, 1134–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, J.N.; Ducker, K.J.; Furzer, B.J.; Dymock, M.; Landers, G.J. Food and Fluid Intake and Hydration Status Does Not Affect Ultrasound Measurements of Subcutaneous Adipose Tissue in Active Adults. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2022, 25, 548–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, D.R.; Cotter, J.D. Ultrasound Measurements of Subcutaneous Fat Thickness Are Robust Against Hydration Changes. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2021, 31, 244–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campa, F.; Gatterer, H.; Lukaski, H.; Toselli, S. Stabilizing Bioimpedance-Vector-Analysis Measures with a 10-Minute Cold Shower After Running Exercise to Enable Assessment of Body Hydration. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2019, 14, 1006–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietrobelli, A.; Wang, Z.; Formica, C.; Heymsfield, S.B. Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry: Fat Estimation Errors Due to Variation in Soft Tissue Hydration. Am. J. Physiol. 1998, 274, E808–E816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, W.; Lohman, T.G.; Stewart, A.D.; Maughan, R.J.; Meyer, N.L.; Sardinha, L.B.; Kirihennedige, N.; Reguant-Closa, A.; Risoul-Salas, V.; Sundgot-Borgen, J.; et al. Subcutaneous Fat Patterning in Athletes: Selection of Appropriate Sites and Standardisation of a Novel Ultrasound Measurement Technique: Ad Hoc Working Group on Body Composition, Health and Performance, under the Auspices of the IOC Medical Commission. Br. J. Sports Med. 2016, 50, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serafini, S.; Charrier, D.; Izzicupo, P.; Esparza-Ros, F.; Vaquero-Cristóbal, R.; Petri, C.; Mecherques-Carini, M.; Baglietto, N.; Holway, F.; Tinsley, G.; et al. Anthropometric-Based Predictive Equations Developed with Multi-Component Models for Estimating Body Composition in Athletes. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2024, 125, 595–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, D.C.; Cronin, O.; O’Neill, S.B.; Woods, T.; Keohane, D.M.; Molloy, M.G.; Falvey, E.C. Application of a Sub-Set of Skinfold Sites for Ultrasound Measurement of Subcutaneous Adiposity and Percentage Body Fat Estimation in Athletes. Int. J. Sports Med. 2016, 37, 359–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiebaud, R.S.; Abe, T.; Loenneke, J.P.; Fujita, E.; Akamine, T. Body Fat Percentage Assessment by Ultrasound Subcutaneous Fat Thickness Measurements in Middle-Aged and Older Adults. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 38, 2659–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petri, C.; Campa, F.; Holway, F.; Pengue, L.; Arrones, L.S. ISAK-Based Anthropometric Standards for Elite Male and Female Soccer Players. Sports 2024, 12, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, K.; Metoyer, C.J.; Winchester, L.J.; Esco, M.R.; Fedewa, M.V. Agreement between Ultrasound Protocols for the Estimation of Body Fat Percentage: Comparison to a Four-Compartment Model. Clin. Physiol. Funct. Imaging 2023, 43, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, J.J.; Smith, R.W.; Stratton, M.T.; Harty, P.S.; Rodriguez, C.; Siedler, M.R.; White, S.J.; Williams, A.D.; Dellinger, J.R.; Keith, D.S.; et al. Cross-Sectional and Longitudinal Associations between Subcutaneous Adipose Tissue Thickness and Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry Fat Mass. Clin. Physiol. Funct. Imaging 2021, 41, 514–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinsley, G.M.; Rodriguez, C.; White, S.J.; Williams, A.D.; Stratton, M.T.; Harty, P.S.; Smith, R.W.; Dellinger, J.R.; Johnson, B.A. A Field-Based Three-Compartment Model Derived from Ultrasonography and Bioimpedance for Estimating Body Composition Changes. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2021, 53, 658–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandler, A.J.; Cintineo, H.P.; Sanders, D.J.; McFadden, B.A.; Arent, M.A.; Monaco, R.; Arent, S.M. Agreement between B-Mode Ultrasound and Air Displacement Plethysmography in Preprofessional Ballet Dancers. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2021, 53, 653–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, D.R. Oversimplification of the Relationship between Ultrasound and Skinfold Measurements of Subcutaneous Fat Thickness. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2022, 54, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, W.; Horn, M.; Fürhapter-Rieger, A.; Kainz, P.; Kröpfl, J.M.; Maughan, R.J.; Ahammer, H. Body Composition in Sport: A Comparison of a Novel Ultrasound Imaging Technique to Measure Subcutaneous Fat Tissue Compared with Skinfold Measurement. Br. J. Sports Med. 2013, 47, 1028–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nösslinger, H.; Mair, E.; Toplak, H.; Hörmann-Wallner, M. Measuring Subcutaneous Fat Thickness Using Skinfold Calipers vs. High-Resolution B-Scan Ultrasonography in Healthy Volunteers: A Pilot Study. Clin. Nutr. Open Sci. 2022, 41, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selkow, N.M.; Pietrosimone, B.G.; Saliba, S.A. Subcutaneous Thigh Fat Assessment: A Comparison of Skinfold Calipers and Ultrasound Imaging. J. Athl. Train. 2011, 46, 50–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizukoshi, K.; Kurosumi, M.; Hamanaka, Y. Age-Related Changes in the Fiber Structure around Adipocytes in the Subcutaneous Fat Layer and Their Association with Skin Viscoelasticity. Skin Res. Technol. 2024, 30, e13566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranauskas, M.N.; Johnson, K.E.; Juvancic-Heltzel, J.A.; Kappler, R.M.; Richardson, L.; Jamieson, S.; Otterstetter, R. Seven-Site versus Three-Site Method of Body Composition Using BodyMetrix Ultrasound Compared to Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry. Clin. Physiol. Funct. Imaging 2017, 37, 317–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, A.S.; Pollock, M.L. Generalized Equations for Predicting Body Density of Men. Br. J. Nutr. 1978, 40, 497–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.S.; Lim, S.; Kim, H.; Kim, K.M. Comparison of Two DXA Systems, Hologic Horizon W and GE Lunar Prodigy, for Assessing Body Composition in Healthy Korean Adults. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 36, 1219–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Arellanes, R.; Urquidez-Romero, R.; Rodríguez-Tadeo, A.; Esparza-Romero, J.; Méndez-Estrada, R.O.; Ramírez-López, E.; Robles-Sardin, A.E.; Pacheco-Moreno, B.I.; Alemán-Mateo, H. Agreement between Laboratory Methods and the 4-Compartment Model in Assessing Fat Mass in Obese Older Hispanic-American Adults. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 3592–3600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campa, F.; Toselli, S.; Mazzilli, M.; Gobbo, L.A.; Coratella, G. Assessment of Body Composition in Athletes: A Narrative Review of Available Methods with Special Reference to Quantitative and Qualitative Bioimpedance Analysis. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, E.M.; Rowe, D.A.; Misic, M.M.; Prior, B.M.; Arngrímsson, S.A. Skinfold Prediction Equation for Athletes Developed Using a Four-Component Model. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2005, 37, 2006–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esparza Ros, F.; Vaquero-Cristòbal, R.; Marfell-Jones, M. International Standars for Anthropometric Assessment, 2019; International Society for the Advancement od Kinanthropometry: Potchefstroom, South Africa, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Schröder, H.; Covas, M.I.; Marrugat, J.; Vila, J.; Pena, A.; Alcántara, M.; Masiá, R. Use of a Three-Day Estimated Food Record, a 72-Hour Recall and a Food-Frequency Questionnaire for Dietary Assessment in a Mediterranean Spanish Population. Clin. Nutr. 2001, 20, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Society for Advancement of Kinanthropometry. International Standards for Anthropometric Assessment; International Society for the Advancement of Kinanthropometry: Potchefstroom, South Africa, 2001; ISBN 0868037125, 9780868037127. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Pi-Sunyer, F.X.; Kotler, D.P.; Wielopolski, L.; Withers, R.T.; Pierson, R.N.J.; Heymsfield, S.B. Multicomponent Methods: Evaluation of New and Traditional Soft Tissue Mineral Models by in vivo Neutron Activation Analysis. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2002, 76, 968–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heymsfield, S.B.; Smith, B.; Wong, M.; Bennett, J.; Ebbeling, C.; Wong, J.M.W.; Strauss, B.J.G.; Shepherd, J. Multicomponent Density Models for Body Composition: Review of the Dual Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry Volume Approach. Obes. Rev. 2021, 22, e13274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matias, C.N.; Santos, D.A.; Júdice, P.B.; Magalhães, J.P.; Minderico, C.S.; Fields, D.A.; Lukaski, H.C.; Sardinha, L.B.; Silva, A.M. Estimation of Total Body Water and Extracellular Water with Bioimpedance in Athletes: A Need for Athlete-Specific Prediction Models. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 35, 468–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelman, A.; Hill, J. Data Analysis Using Regression and Multilevel/Hierarchical Models; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2006; ISBN 9780521867061. [Google Scholar]
- Cancello, R.; Zulian, A.; Gentilini, D.; Maestrini, S.; Della Barba, A.; Invitti, C.; Corà, D.; Caselle, M.; Liuzzi, A.; Di Blasio, A.M. Molecular and Morphologic Characterization of Superficial- and Deep-Subcutaneous Adipose Tissue Subdivisions in Human Obesity. Obesity 2013, 21, 2562–2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosaka, K.; Kubota, Y.; Adachi, N.; Akita, S.; Sasahara, Y.; Kira, T.; Kuroda, M.; Mitsukawa, N.; Bujo, H.; Satoh, K. Human Adipocytes from the Subcutaneous Superficial Layer Have Greater Adipogenic Potential and Lower PPAR-γ DNA Methylation Levels than Deep Layer Adipocytes. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2016, 311, C322–C329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.M. Structural and Functional Body Components in Athletic Health and Performance Phenotypes. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 73, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donini, L.M.; Savina, C.; Rosano, A.; Cannella, C. Systematic Review of Nutritional Status Evaluation and Screening Tools in the Elderly. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2007, 11, 421–432. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dávalos-Yerovi, V.; Marco, E.; Sánchez-Rodríguez, D.; Duran, X.; Meza-Valderrama, D.; Rodríguez, D.A.; Muñoz, E.; Tejero-Sánchez, M.; Muns, M.D.; Guillén-Solà, A.; et al. Malnutrition According to GLIM Criteria Is Associated with Mortality and Hospitalizations in Rehabilitation Patients with Stable Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Nutrients 2021, 13, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozturk, Y.; Deniz, O.; Coteli, S.; Unsal, P.; Dikmeer, A.; Burkuk, S.; Koca, M.; Cavusoglu, C.; Dogu, B.B.; Cankurtaran, M.; et al. Global Leadership Initiative on Malnutrition Criteria with Different Muscle Assessments Including Muscle Ultrasound with Hospitalized Internal Medicine Patients. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2022, 46, 936–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nijholt, W.; Scafoglieri, A.; Jager-Wittenaar, H.; Hobbelen, J.S.M.; van der Schans, C.P. The Reliability and Validity of Ultrasound to Quantify Muscles in Older Adults: A Systematic Review. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2017, 8, 702–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akazawa, N.; Kishi, M.; Hino, T.; Tsuji, R.; Tamura, K.; Moriyama, H. Using GLIM Criteria, Cutoff Value for Low BMI in Asian Populations Discriminates High or Low Muscle Mass: A Cross-Sectional Study. Nutrition 2021, 81, 110928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahreis, T.; Kretschmann, J.; Weidner, N.; Volk, T.; Meiser, A.; Groesdonk, H.V. Sonographic Evaluation of Gastric Residual Volume during Enteral Nutrition in Critically Ill Patients Using a Miniaturized Ultrasound Device. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 4859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cederholm, T.; Jensen, G.L.; Correia, M.I.T.D.; Gonzalez, M.C.; Fukushima, R.; Higashiguchi, T.; Baptista, G.; Barazzoni, R.; Blaauw, R.; Coats, A.; et al. GLIM Criteria for the Diagnosis of Malnutrition—A Consensus Report from the Global Clinical Nutrition Community. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 38, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokura, Y.; Kato, M.; Kimoto, K.; Okada, Y.; Habu, D. Relationship between Energy Intake and Changes in Thigh Echo Intensity during the Acute Phase of Stroke in Older Patients with Hemiplegia. Med. Princ. Pract. 2021, 30, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokura, Y.; Kato, M.; Taniguchi, Y.; Kimoto, K.; Okada, Y. Energy Intake during the Acute Phase and Changes in Femoral Muscle Thickness in Older Hemiplegic Inpatients with Stroke. Nutrition 2020, 70, 110582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fetterplace, K.; Deane, A.M.; Tierney, A.; Beach, L.J.; Knight, L.D.; Presneill, J.; Rechnitzer, T.; Forsyth, A.; Gill, B.M.T.; Mourtzakis, M.; et al. Targeted Full Energy and Protein Delivery in Critically Ill Patients: A Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial (FEED Trial). J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2018, 42, 1252–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melin, A.K.; Heikura, I.A.; Tenforde, A.; Mountjoy, M. Energy Availability in Athletics: Health, Performance, and Physique. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2019, 29, 152–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Men (n = 19) Mean ± SD | Women (n = 18) Mean ± SD | |
|---|---|---|
| Body mass (kg) | 79.1 ± 9.7 | 57.4 ± 5.7 |
| Height (cm) | 178.7 ± 6.3 | 164.9 ± 5.4 |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 24.8 ± 2.7 | 21.1 ± 1.3 |
| Triceps SKF (mm) | 8.4 ± 4.7 | 13.4 ± 4.2 |
| Abdominal SKF (mm) | 14.2 ± 8.0 | 13.1 ± 4.2 |
| Thigh SKF (mm) | 11.3 ± 3.9 | 19.3 ± 6.3 |
| US-derived triceps SKF (mm) | 14.9 ± 7.4 | 23.4 ± 9.5 |
| US-derived abdominal SKF (mm) | 20.5 ± 11.0 | 23.7 ± 10.5 |
| US-derived thigh SKF (mm) | 13.7 ± 3.8 | 21.6 ± 7.6 |
| Triceps SKF/Raw US measure | 1.0 ± 0.4 | 1.2 ± 0.3 |
| Abdominal SKF/Raw US measure | 1.4 ± 0.4 | 1.2 ± 0.4 |
| Thigh SKF/Raw US measure | 1.7 ± 0.4 | 1.8 ± 0.2 |
| Total body water (l) | 50.1 ± 5.3 | 32.4 ± 2.9 |
| Body volume (l) | 75.3 ± 9.8 | 55.1 ± 5.1 |
| Bone mineral content (kg) | 2.8 ± 0.4 | 2.1 ± 0.4 |
| Lean soft mass (kg) | 60.6 ± 6.9 | 40.7 ± 6.9 |
| Fat mass 4C (%) | 15.6 ± 4.1 | 15.4 ± 1.6 |
| Fat mass DXA (%) | 19.4 ± 5.4 | 24.9 ± 6.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cerullo, G.; Franchi, M.V.; Sampieri, A.; Campa, F.; Paoli, A. Ultrasound-Derived Skinfolds in Anthropometric Predictive Equations Overestimate Fat Mass: A Validation Study Using a Four-Component Model. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1881. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17111881
Cerullo G, Franchi MV, Sampieri A, Campa F, Paoli A. Ultrasound-Derived Skinfolds in Anthropometric Predictive Equations Overestimate Fat Mass: A Validation Study Using a Four-Component Model. Nutrients. 2025; 17(11):1881. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17111881
Chicago/Turabian StyleCerullo, Giuseppe, Martino V. Franchi, Alessandro Sampieri, Francesco Campa, and Antonio Paoli. 2025. "Ultrasound-Derived Skinfolds in Anthropometric Predictive Equations Overestimate Fat Mass: A Validation Study Using a Four-Component Model" Nutrients 17, no. 11: 1881. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17111881
APA StyleCerullo, G., Franchi, M. V., Sampieri, A., Campa, F., & Paoli, A. (2025). Ultrasound-Derived Skinfolds in Anthropometric Predictive Equations Overestimate Fat Mass: A Validation Study Using a Four-Component Model. Nutrients, 17(11), 1881. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17111881










