Non-Celiac Wheat Gluten Sensitivity Model: Effects on Hepatic Morphophysiology of Wistar Rats
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design
2.1.1. Animals
- G0: Gluten-free diet;
- G14: 14% wheat gluten (standard control diet);
- G42: 42% wheat gluten;
- G70: 70% wheat gluten;
- G70/0: 70 days on a high-gluten diet (70%) followed by 30 days on a gluten-free diet.
2.1.2. Feed Preparation
2.1.3. Food Consumption and Body Mass
| Ingredients (g/kg) | G0 | G14 | G42 | G70 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Corn grain | 614 | 614 | 334 | 0 |
| Soybean meal | 141 | 141 | 141 | 141 |
| Wheat flour | 0 | 140 | 420 | 700 |
| Rice bran | 140 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Soybean oil | 40 | 40 | 40 | 40 |
| Sodium chloride | 6.8 | 6.8 | 6.8 | 6.8 |
| Calcium carbonate | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 |
| Dicalcium phosphate | 11.4 | 11.4 | 11.4 | 11.4 |
| Vitamin premix | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| Mineral premix | 11.8 | 11.8 | 11.8 | 11.8 |
2.2. Biological Material Collection
2.3. Biochemical Analyses
2.4. Processing and Histological and Histochemical Analysis of the Liver
2.5. Oxidative State
2.5.1. Tissue Preparation
2.5.2. Oxidative State Parameters
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Food Consumption and Body Mass Progression
3.2. Biometric Parameters
3.3. Adipose Tissue
3.4. Biochemical Parameters
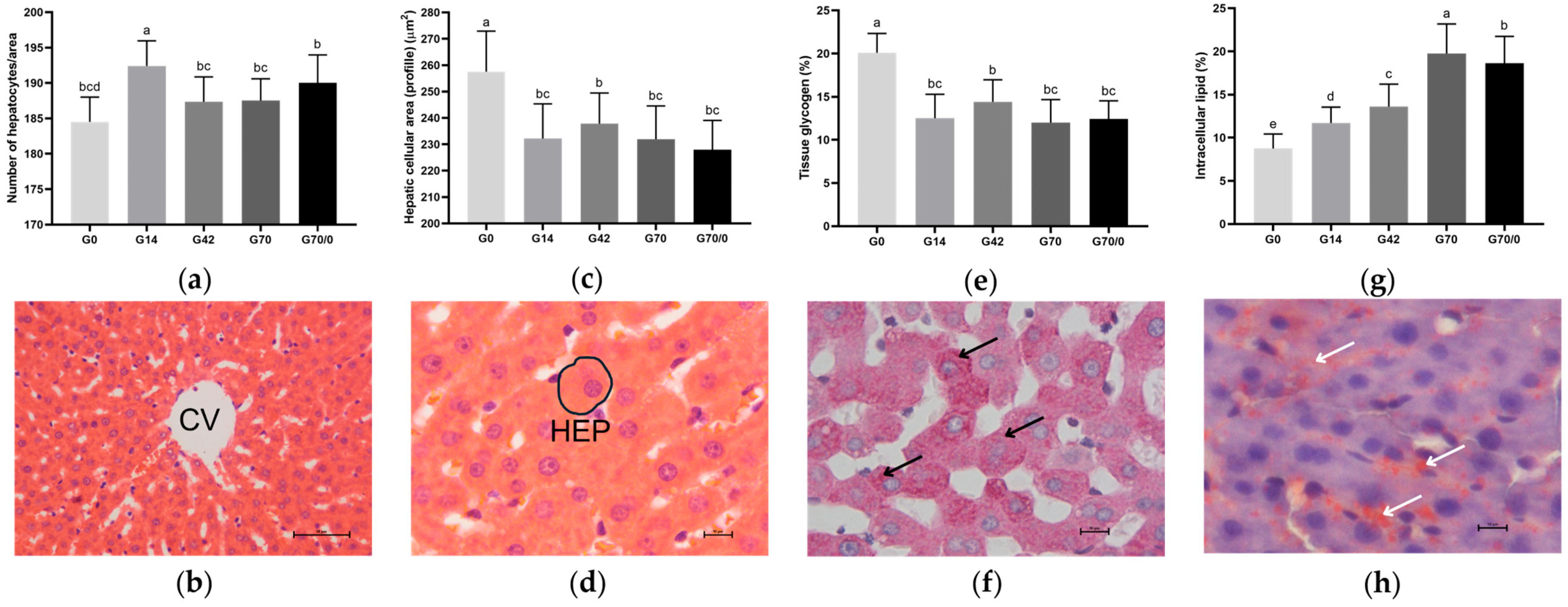
3.5. Morphological and Morphometric Analyses
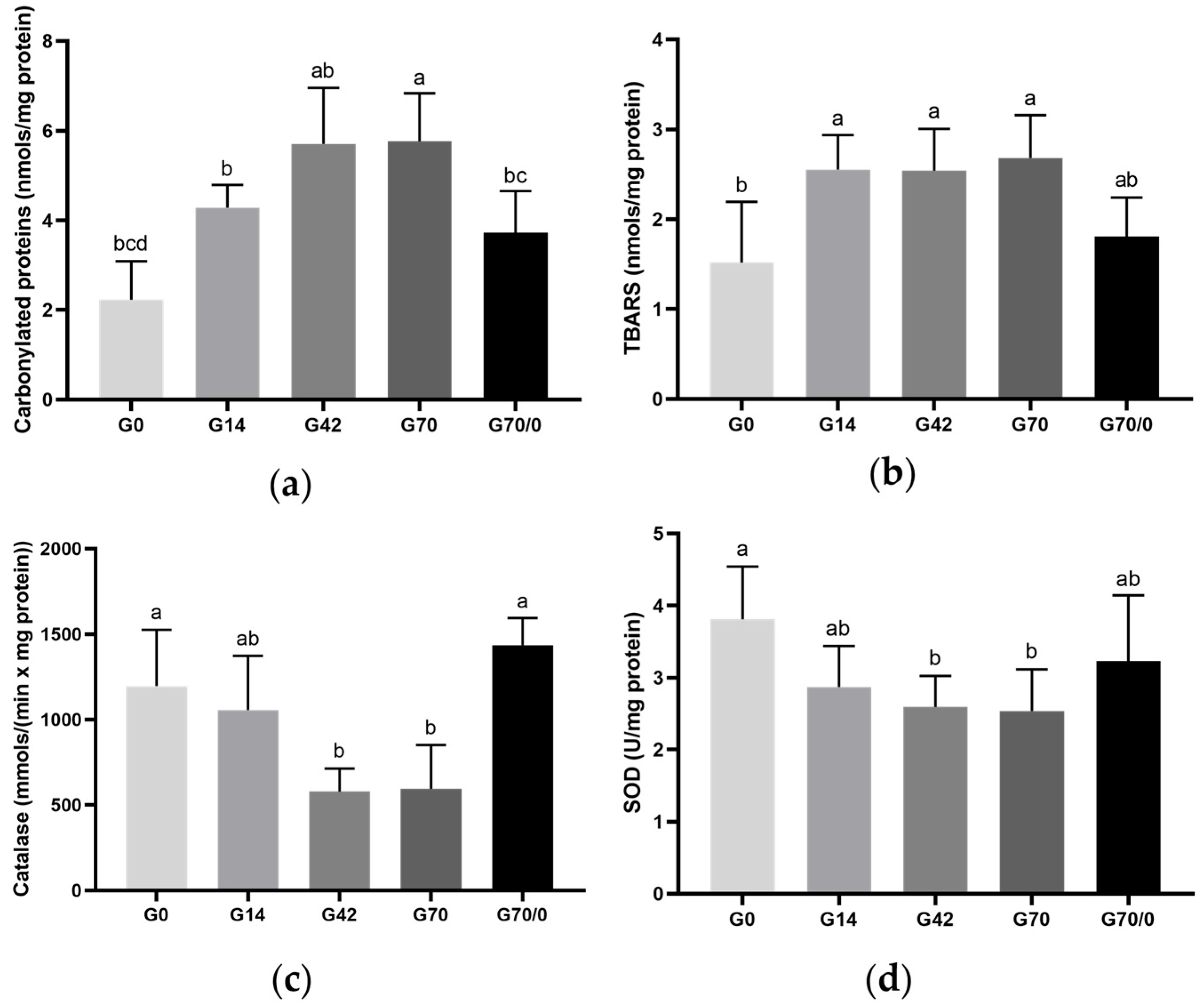
3.6. Oxidative State
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Balakireva, A.V.; Zamyatnin, A.A. Properties of Gluten Intolerance: Gluten Structure, Evolution, Pathogenicity and Detoxification Capabilities. Nutrients 2016, 8, 644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocha Garcez, D.; Ana, D.; Cerveira, C.; Almeida, C. O Papel Da Nutrição Nas Doenças Autoimunes. Master’s Thesis, Instituto de Ciências Biomédicas Abel Salazar-Universidade do Porto, Porto, Portugal, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Araújo, H.M.C.; Araújo, W.M.C.; Botelho, R.B.A.; Zandonadi, R.P. Celiac Disease, Eating Habits and Practices and Life Quality of Life. Nutr. Mag. 2010, 23, 467–474. [Google Scholar]
- Lebwohl, B.; Ludvigsson, J.F.; Green, P.H.R. For Personal Use Only Celiac Disease and Non-Celiac Gluten Sensitivity. BMJ 2015, 351, h4347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmanová, I.; Sánchez, D.; Tučková, L.; Tlaskalová-Hogenová, H. Celiac Disease and Liver Disorders: From Putative Pathogenesis to Clinical Implications. Nutrients 2018, 10, 892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, U.N.; Pervaiz, A.; Khan, Z.B.; Sultana, T. Diagnostic Dilemma, Possible Non-Celiac Gluten Sensitivity: Consideration in Approach and Management. Cureus 2022, 14, e25302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansueto, P.; Seidita, A.; D’Alcamo, A.; Carroccio, A. Non-Celiac Gluten Sensitivity: Literature Review. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2014, 33, 39–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Sabatino, A.; Lenti, M.V.; Giuffrida, P.; Vanoli, A.; Corazza, G.R. New Insights into Immune Mechanisms Underlying Autoimmune Diseases of the Gastrointestinal Tract. Autoimmun. Rev. 2015, 14, 1161–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moretti, S.; Mrakic-Sposta, S.; Roncoroni, L.; Vezzoli, A.; Dellanoce, C.; Monguzzi, E.; Branchi, F.; Ferretti, F.; Lombardo, V.; Doneda, L.; et al. Oxidative Stress as a Biomarker for Monitoring Treated Celiac Disease Article. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2018, 9, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remes-Troche, J.M.; de Cobos-Quevedo, O.J.; Rivera-Gutiérrez, X.; Hernández, G.; De La Cruz-Patiño, E.; Uscanga-Domínquez, L.F. Metabolic Effects in Patients with Celiac Disease, Patients with Nonceliac Gluten Sensitivity, and Asymptomatic Controls, after Six Months of a Gluten-Free Diet. Rev. Gastroenterol. Mex. 2020, 85, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozougwu, J.C.; Ozougwu, J.C. Physiology of the Liver. Int. J. Res. Pharm. Biosci. 2017, 4, 13–24. [Google Scholar]
- Reeves, P.G.; Nielsen, F.H.; Fahey, G.C. AIN-93 Purified Diets for Laboratory Rodents: Final Report of the American Institute of Nutrition Ad Hoc Writing Committee on the Reformulation of the AIN-76A Rodent Diet. J. Nutr. 1993, 123, 1939–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nistiar, F.; Racz, O.; Lukacinova, A.; Hubkova, B.; Novakova, J.; Lovasova, E.; Sedlakova, E. Age Dependency on Some Physiological and Biochemical Parameters of Male Wistar Rats in Controlled Environment. J. Environ. Sci. Health A Tox Hazard. Subst. Environ. Eng. 2012, 47, 1224–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarache, G.; Frez, F.L.V.; Rosa, A.C.S.; Pazinato, B.; da Silva, G.B.V.; Duarte, A.L.R.; Castilha, L.D.; Raniero, G.Z.; Natali, M.R.M.; Monteiro, A.R.G. Evaluation of the Physicochemical and Technological Characteristics of Extruded Feed for Rodents with Gluten. In Harmony of Knowledge: Exploring Interdisciplinary Synergie; Seven Editora: São José dos Pinhais, Brazil, 2024; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, M.-F.; Tian, S.; Song, Y.-G.; Li, C.-X.; Miao, M.-S.; Ren, Z.; Li, M. Effects of Total Flavonoids from Eucommia Ulmoides Oliv. Leaves on Polycystic Ovary Syndrome with Insulin Resistance Model Rats Induced by Letrozole Combined with a High-Fat Diet. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 273, 113947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smiderle, F.R.; Baggio, C.H.; Borato, D.G.; Santana-Filho, A.P.; Sassaki, G.L.; Iacomini, M.; Van Griensven, L.J.L.D. Anti-Inflammatory Properties of the Medicinal Mushroom Cordyceps Militaris Might Be Related to Its Linear (1→3)-β-D-Glucan. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e110266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azevedo, S.C.S.F.; Rosa, C.V.D.; Wunderlich, A.L.M.; Yamada, L.A.; Mariano, I.R.; Bataglini, C.; Branquinho, N.T.D.; Raposo, S.R.; Bazotte, R.B.; Baroni, E.A.; et al. Glutamine or Glutamine Dipeptide Supplementation Improves Gluconeogenesis and Liver Glycogenosis in Type 1 Diabetic Rats. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2019, 7, 398–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, R.L.; Garland, D.; Oliver, C.N.; Amici, A.; Climent, I.; Lenz, A.-G.; Ahn, B.-W.; Shaltiel, S.; Stadtman, E.R. Determination of Carbonyl Content in Oxidatively Modified Proteins. Methods Enzym. 1990, 186, 464–478. [Google Scholar]
- Buege, J.A.; Aust, S.D. Microsomal Lipid Peroxidation. Methods Enzym. 1978, 52, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmeyer, H.U. Methods of Enzymatic Analysis, 2nd ed.; Verlag Chemie-Academic Press: London, UK, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Marklund, S.; Marklund, G. Involvement of the Superoxide Anion Radical in the Autoxidation of Pyrogallol and a Convenient Assay for Superoxide Dismutase. Eur. J. Biochem. 1974, 47, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowry, O.H.; Rosebrough, N.J.; Farr, A.L.; Randall, R.J. Protein Measurement with the Folin Phenol Reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 1951, 193, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarpato, E.; Auricchio, R.; Penagini, F.; Campanozzi, A.; Zuccotti, G.V.; Troncone, R. Efficacy of the Gluten Free Diet in the Management of Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders: A Systematic Review on Behalf of the Italian Society of Paediatrics. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2019, 45, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niland, B.; Cash, B.D. Health Benefits and Adverse Effects of a Gluten-Free Diet in Non-Celiac Disease Patients. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 14, 82–91. [Google Scholar]
- Dennis, M.; Lee, A.R.; McCarthy, T. Nutritional Considerations of the Gluten-Free Diet. Gastroenterol. Clin. N. Am. 2019, 48, 53–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozuna, C.V.; Barro, F. Safety Evaluation of Transgenic Low-Gliadin Wheat in Sprague Dawley Rats: An Alternative to the Gluten Free Diet with No Subchronic Adverse Effects. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2017, 107, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bektaş, A.; Ulusoy, M.; Özsarı, L.; Özel, A.M. The Effects of Gluten on Weight Gain, Hematological, Biochemical, and Various Endocrinological Parameters. Turk. J. Gastroenterol. 2024, 35, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabença, C.; Ribeiro, M.; de Sousa, T.; Poeta, P.; Bagulho, A.S.; Igrejas, G. Wheat/Gluten-Related Disorders and Gluten-Free Diet Misconceptions: A Review. Foods 2021, 10, 1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christoffolete, M.A.; Moriscot, A.S. Hypercaloric Cafeteria-like Diet Induced UCP3 Gene Expression in Skeletal Muscle Is Impaired by Hypothyroidism. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2004, 37, 923–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura, A.M.A. Laboratory Rodent Nutrition: Paradigms and Challenges. RESBCAL 2014, 2, 288–296. [Google Scholar]
- Freire, R.H.; Fernandes, L.R.; Silva, R.B.; Coelho, B.S.L.; De Araújo, L.P.T.; Ribeiro, L.S.; Andrade, J.M.O.; Lima, P.M.A.; Araújo, R.S.; Santos, S.H.S.; et al. Wheat Gluten Intake Increases Weight Gain and Adiposity Associated with Reduced Thermogenesis and Energy Expenditure in an Animal Model of Obesity. Int. J. Obes. 2016, 40, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, T.T.; Tong, L.T.; Geng, D.H.; Wang, L.L.; Zhou, X.R.; Pu, H.Y.; Jia, W.; Wu, Q.P.; Huang, J.R. Wheat Gluten Regulates Cholesterol Metabolism by Modulating Gut Microbiota in Hamsters with Hyperlipidemia. J. Oleo Sci. 2019, 68, 909–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narwal, V.; Deswal, R.; Batra, B.; Kalra, V.; Hooda, R.; Sharma, M.; Rana, J.S. Cholesterol Biosensors: A Review. Steroids 2019, 143, 6–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, H.H.; Casas, G.A.; Abelilla, J.J.; Liu, Y.; Sulabo, R.C. Nutritional Value of High Fiber Co-Products from the Copra, Palm Kernel, and Rice Industries in Diets Fed to Pigs. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2015, 6, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dantas, J.A.; Ambiel, C.R.; Cuman, R.K.N.; Baroni, S.; Bersani-Amado, C.A. Reference Physiological Parameters for Rats Housed in the Central Animal Facility at the State University of Maringa, Parana, Brazil. Acta Sci. Health Sci. 2006, 28, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.-J.; Choi, Y.-K.; Im, H.-S.; Yarimaga, O.; Yoon, E.; Kim, H.-S. Aspartate Aminotransferase (AST/GOT) and Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT/GPT) Detection Techniques. Sensors 2006, 6, 756–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigorescu, M. Noninvasive Biochemical Markers of Liver Fibrosis. JGLD 2006, 45, 149–159. [Google Scholar]
- Giannini, E.G.; Testa, R.; Savarino, V. Liver Enzyme Alteration: A Guide for Clinicians. Can. Med. Assoc. J. 2005, 172, 367–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, R.J.; Robles-Díaz, M. Diagnostic and Prognostic Assessment of Suspected Drug-Induced Liver Injury in Clinical Practice. Liver Int. 2020, 40, 6–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnhold, J. The Dual Role of Myeloperoxidase in Immune Response. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, M.S.; Drewnowski, B.; Bueno, B.F.; Rickli, C.; Balzer, E.R.; Novak, R.S.; Vellosa, J.C.R. General Aspects of Myeloperoxidase and Its Involvement in Diseases: A Review. Braz. J. Dev. 2021, 7, 28677–28691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.Q.; Zou, J.-S.; Tu, L.; Yun, X.; Qin, Y.H. Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Involved in the Pathogenesis of IgA Vasculitis: Confirmed in Two IgAV Rat Models. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0288538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branquinho, N.T.D.; Loiola, M.S.M.; Crepaldi, L.D.; Yamada, L.A.; Azevedo, S.C.S.F.; Bataglini, C.; Brito, M.N.; Godoy, V.A.F.; Pedrosa, M.M.D.; Natali, M.R.M. Responses of the Adult Rat Glucose Metabolism to Early Life Feeding, Caloric Restriction and Refeeding. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2018, 6, 370–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Aguilar, E.C.; Fernandes-Braga, W.; Santos, E.A.; Leocádio, P.C.L.; dos Santos Aggum Capettini, L.; Orellano, L.A.A.; Campos, P.P.; Lemos, V.S.; Soares, F.L.P.; Navia-Pelaez, J.M.; et al. Gluten Worsens Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease by Affecting Lipogenesis and Fatty Acid Oxidation in Diet-Induced Obese Apolipoprotein E-Deficient Mice. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2024, 479, 1335–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chelikani, P.; Fita, I.; Loewen, P.C. Diversity of Structures and Properties among Catalases. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2004, 61, 192–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguilar, E.C.; Navia-Pelaez, J.M.; Fernandes-Braga, W.; Soares, F.L.P.; dos Santos, L.C.; Leonel, A.J.; dos Santos Aggum Capettini, L.; de Oliveira, R.P.; de Faria, A.M.C.; Lemos, V.S.; et al. Gluten Exacerbates Atherosclerotic Plaque Formation in ApoE–/– Mice with Diet-Induced Obesity. Nutrition 2020, 75–76, 110658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tovoli, F.; Negrini, G.; Farì, R.; Guidetti, E.; Faggiano, C.; Napoli, L.; Bolondi, L.; Granito, A. Increased Risk of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Patients with Coeliac Disease on a Gluten-Free Diet: Beyond Traditional Metabolic Factors. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 48, 538–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granito, A.; Zauli, D.; Muratori, P.; Muratori, L.; Grassi, A.; Bortolotti, R.; Petrolini, N.; Veronesi, L.; Gionchetti, P.; Bianchi, F.B.; et al. Anti-Saccharomyces Cerevisiae and Perinuclear Anti-Neutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibodies in Coeliac Disease before and after Gluten-Free Diet. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2005, 21, 881–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Nutritional Values | Standard Diet |
|---|---|
| (Kcal per 100 g of feed) * | 417 |
| Carbohydrates (%) | 75.4 |
| Proteins (%) | 14.1 |
| Fats (%) | 4 |
| Water (%) | 25 |
| G0 | G14 | G42 | G70 | G70/0 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FBM | 436.78 ± 23.75 ab | 403.50 ± 29.84 b | 436.90 ± 52.23 ab | 461.78 ± 39.73 a | 450.50 ± 21.62 a |
| NAL | 24.50 ± 0.35 a | 23.60 ± 0.84 b | 24.00 ± 0.58 ab | 24.39 ± 0.42 a | 24.40 ± 0.52 a |
| LM/100 g | 3.78 ± 0.29 a | 3.58 ± 0.18 ab | 3.54 ± 0.32 ab | 3.41 ± 0.21 b | 3.38 ± 0.15 b |
| LI | 3.09 ± 0.05 | 3.13 ± 0.06 | 3.16 ± 0.10 | 3.17 ± 0.09 | 3.14 ± 0.06 |
| G0 | G14 | G42 | G70 | G70/0 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ME | 0.98 ± 0.24 | 0.97 ± 0.27 | 0.89 ± 0.25 | 1.14 ± 0.33 | 1.17 ± 0.28 |
| RP | 3.02 ± 0.30 | 3.11 ± 0.32 | 3.00 ± 0.28 | 3.05 ± 0.29 | 3.27 ± 0.49 |
| PE | 2.42 ± 0.35 ab | 2.02 ± 0.55 b | 2.35 ± 0.37 ab | 2.64 ± 0.49 a | 2.79 ± 0.51 a |
| IG | 3.06 ± 0.29 | 2.52 ± 0.26 | 2.58 ± 0.62 | 2.69 ± 0.75 | 2.72 ± 0.44 |
| AI | 9.48 ± 0.76 | 8.62 ± 1.12 | 8.82 ± 1.20 | 9.52 ± 1.71 | 9.96 ± 1.53 |
| G0 | G14 | G42 | G70 | G70/0 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TP | 5.68 ± 0.42 | 5.59 ± 0.34 | 5.63 ± 0.24 | 5.82 ± 0.92 | 5.65 ± 0.23 |
| ALB | 2.62 ± 0.21 | 2.43 ± 0.22 | 2.49 ± 0.23 | 2.41 ± 0.19 | 2.54 ± 0.22 |
| TC | 140 ± 38.77 a | 107.40 ± 11.37 b | 119.5 ± 34.40 ab | 115.3 ± 24.33 ab | 100.70 ± 14.33 b |
| TG | 209.50 ± 50.17 ab | 179.29 ± 68.31 b | 268.71 ± 81.27 a | 244.50 ± 102.92 ab | 241.50 ± 72.07 ab |
| AST | 81.29 ± 11.80 | 96 ± 22.63 | 93.86 ± 11.98 | 88.29 ± 35.90 | 78.57 ±11.44 |
| ALT | 45 ± 13.56 | 61.29 ± 13.03 | 54.57 ± 15.06 | 48.71 ± 16.06 | 61 ± 17.74 |
| GGT | 2.14 ± 1.46 | 2.14 ± 1.46 | 1.14 ± 1.07 | 2.29 ± 2.06 | 1.43 ± 0.98 |
| MPO | 0.21 ± 0.04 a | 0.07 ± 0.02 bc | 0.09 ± 0.01 b | 0.15 ± 0.08 ab | 0.12 ± 0.03 b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Duarte, A.L.R.; Silva, G.B.V.d.; Santa Rosa, A.C.; Raniero, G.Z.; Monteiro, A.R.G.; de Souza, G.H.; Sá-Nakanishi, A.B.d.; Comar, J.F.; Cuman, R.K.N.; Natali, M.R.M. Non-Celiac Wheat Gluten Sensitivity Model: Effects on Hepatic Morphophysiology of Wistar Rats. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1842. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17111842
Duarte ALR, Silva GBVd, Santa Rosa AC, Raniero GZ, Monteiro ARG, de Souza GH, Sá-Nakanishi ABd, Comar JF, Cuman RKN, Natali MRM. Non-Celiac Wheat Gluten Sensitivity Model: Effects on Hepatic Morphophysiology of Wistar Rats. Nutrients. 2025; 17(11):1842. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17111842
Chicago/Turabian StyleDuarte, Ana Luiza Russo, Gabriela Barone Volce da Silva, Anne Caroline Santa Rosa, Ghiovani Zanzotti Raniero, Antonio Roberto Giriboni Monteiro, Gustavo Henrique de Souza, Anacharis Babeto de Sá-Nakanishi, Jurandir Fernando Comar, Roberto Kenji Nakamura Cuman, and Maria Raquel Marçal Natali. 2025. "Non-Celiac Wheat Gluten Sensitivity Model: Effects on Hepatic Morphophysiology of Wistar Rats" Nutrients 17, no. 11: 1842. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17111842
APA StyleDuarte, A. L. R., Silva, G. B. V. d., Santa Rosa, A. C., Raniero, G. Z., Monteiro, A. R. G., de Souza, G. H., Sá-Nakanishi, A. B. d., Comar, J. F., Cuman, R. K. N., & Natali, M. R. M. (2025). Non-Celiac Wheat Gluten Sensitivity Model: Effects on Hepatic Morphophysiology of Wistar Rats. Nutrients, 17(11), 1842. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17111842







