Analysis of the Combined Effects of a Novel Combination of Hypersmin, Pumpkin Seed and Amaranthus Extracts in an In Vitro Model of Chronic Venous Insufficiency
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Agent Preparation
2.2. Cell Cultures
2.3. Experimental Protocol
2.4. In Vitro Model of Intestinal Barrier
2.5. MTT Cell Viability Assay
2.6. ROS Production Assay
2.7. Tumour Necrosis Factor α (TNFα) ELISA Kit
2.8. Interleukin 1β (IL-1β) ELISA Kit
2.9. Analysis of NO Production
2.10. eNOS ELISA Kit
2.11. Endothelin-1 ELISA Kit
2.12. Apoptosis Analysis
2.13. MMPs Analysis
2.14. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Absorption Rate Analysis in an In Vitro Intestinal Barrier Model
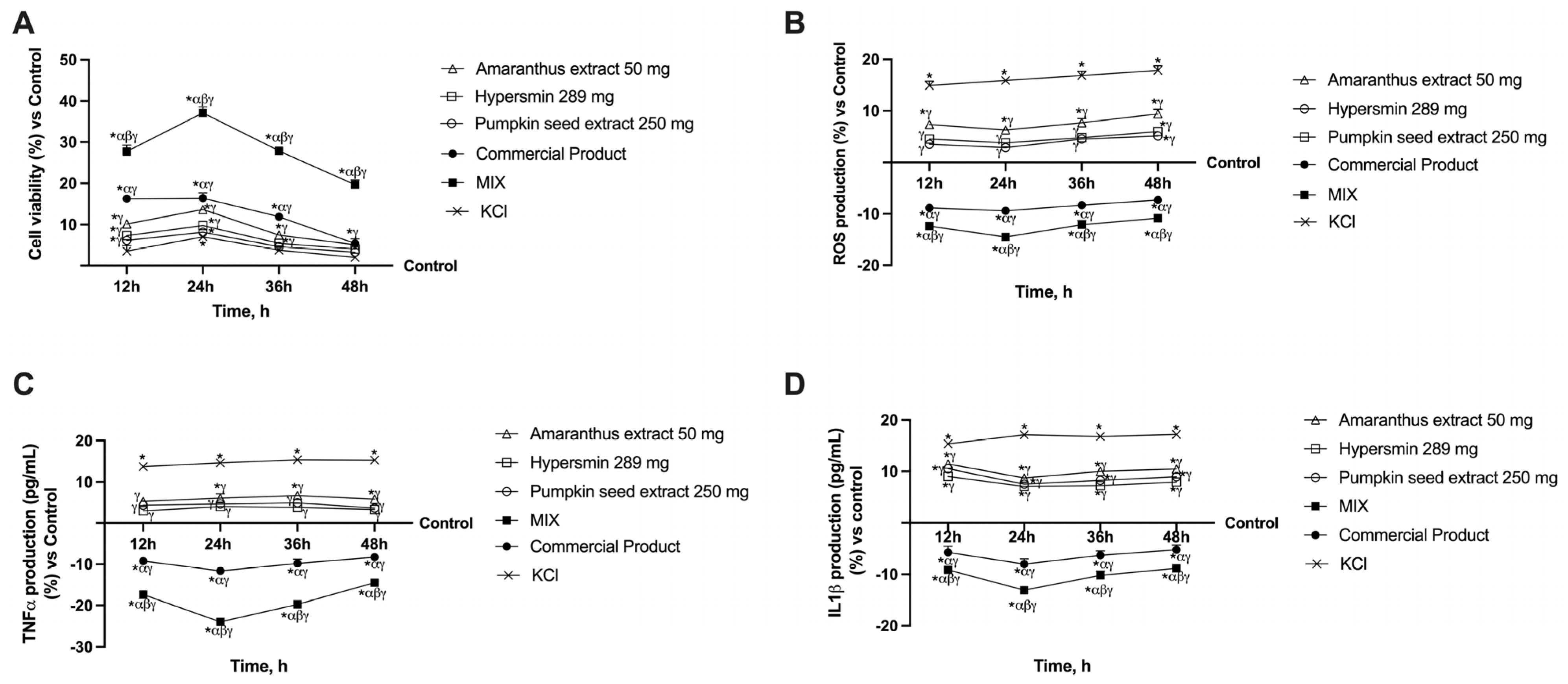
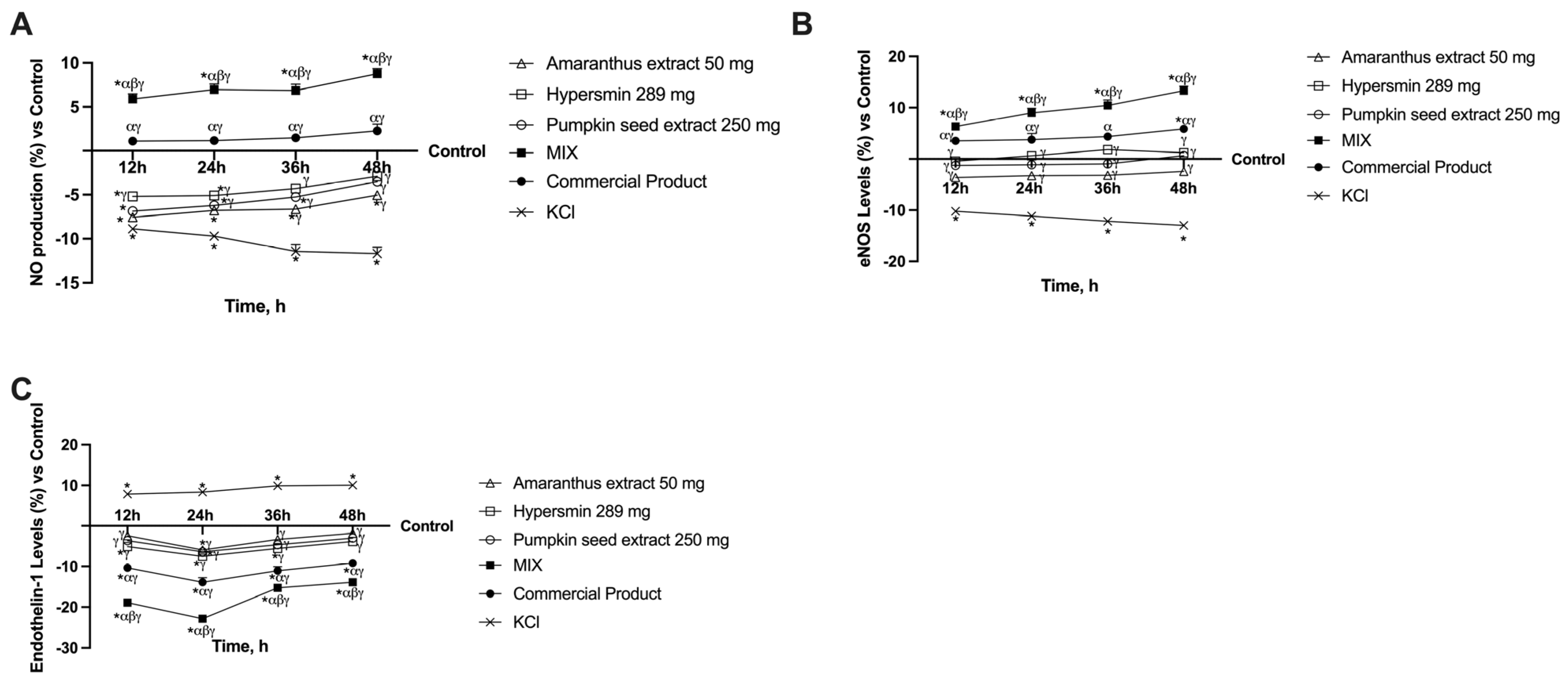
3.2. Effect of Single Agents and Their Combination on a 3D Vein Model
3.3. Effects of Single Agents and Their Combination on Apoptosis in CVI Condition
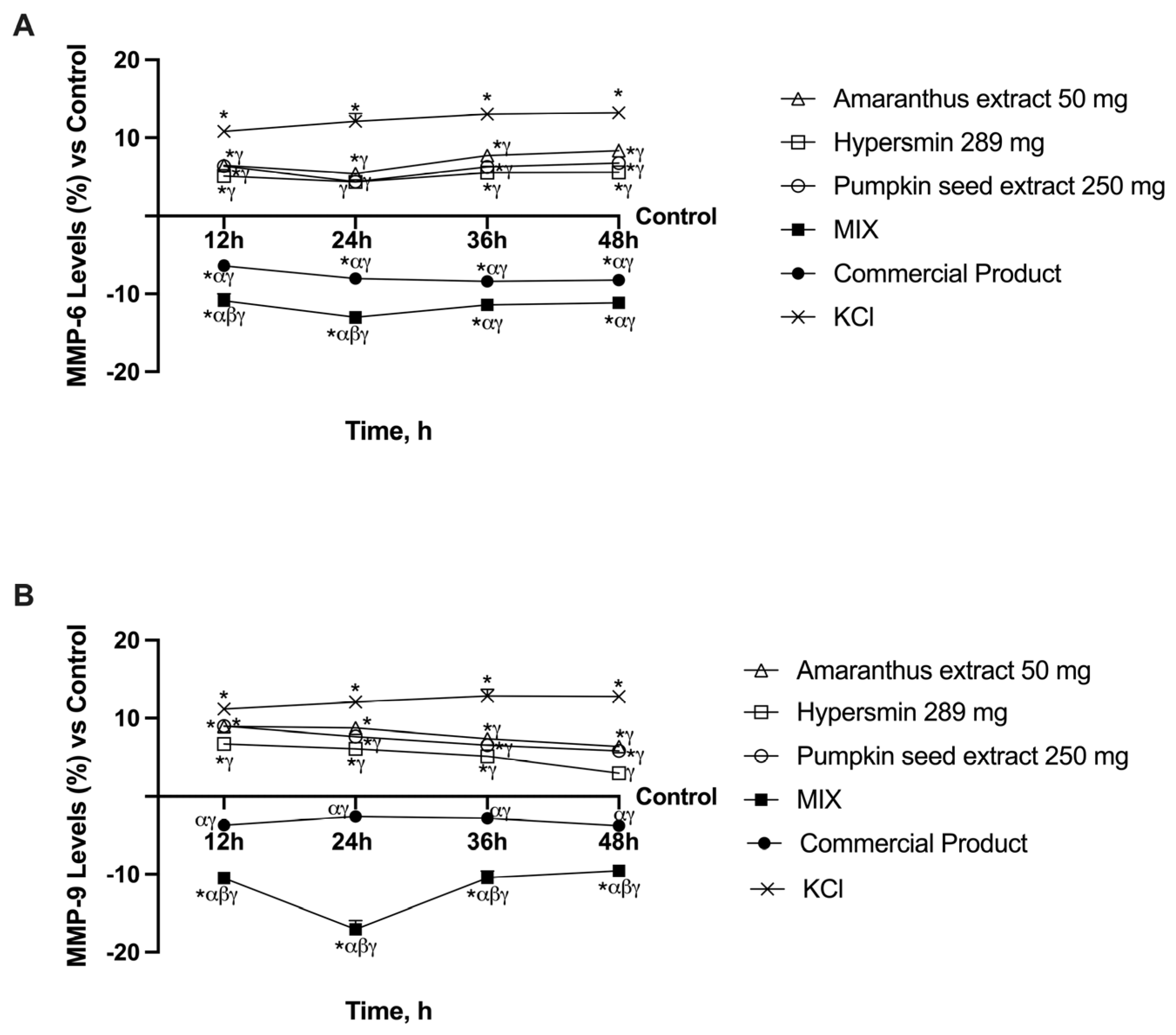
3.4. Ability of Single Agents and Their Combination to Decrease MMPs Levels in CVI Condition
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ATCC | American Type Culture Collection |
| CVI | Chronic venous insufficiency |
| DMEM-Adv | DMEM Advance |
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle’s Medium |
| EGM-2 | Endothelial Growth Medium-2 |
| EMA | European Medicines Agency |
| eNOS | Endothelial nitric oxide synthase |
| FBS | Foetal bovine serum |
| FDA | Food and Drug Delivery |
| IL-1β | Interleukin 1β |
| MMP | Metalloproteases |
| NO | Nitric oxide |
| PAF | Platelet-activating factor |
| Papp | Apparent permeability coefficient |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| SOD | Superoxide dismutase |
| TEER | Trans-epithelial electrical resistance |
| TNFα | Tumour necrosis factor α |
| VEGF | Vascular endothelial growth factor |
Appendix A

References
- Orhurhu, V.; Chu, R.; Xie, K.; Kamanyi, G.N.; Salisu, B.; Salisu-Orhurhu, M.; Urits, I.; Kaye, R.J.; Hasoon, J.; Viswanath, O.; et al. Management of lower extremity pain from chronic venous insufficiency: A comprehensive review. Cardiol. Ther. 2021, 10, 111–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonkemeyer Millan, S.; Gan, R.; Townsend, P.E. Venous Ulcers: Diagnosis and Treatment. Am. Fam. Physician 2019, 100, 298–305. [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan, R.M.; Criqui, M.H.; Denenberg, J.O.; Bergan, J.; Fronek, A. Quality of life in patients with chronic venous disease: San Diego population study. J. Vasc. Surg. 2003, 37, 1047–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, M.A.; Fraile-Martínez, O.; García-Montero, C.; Álvarez-Mon, M.A.; Chaowen, C.; Ruiz-Grande, F.; Pekarek, L.; Monserrat, J.; Asúnsolo, A.; García-Honduvilla, N.; et al. Understanding Chronic Venous Disease: A Critical Overview of Its Pathophysiology and Medical Management. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukaya, E.; Flores, A.M.; Lindholm, D.; Gustafsson, S.; Zanetti, D.; Ingelsson, E.; Leeper, N.J. Clinical and genetic determinants of varicose veins: Prospective, community-based study of ≈500,000 individuals. Circulation 2018, 138, 2869–2880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eberhardt, R.T.; Raffetto, J.D. Chronic venous insufficiency. Circulation 2014, 130, 333–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, S.R. The post-thrombotic syndrome. Hematol. Am. Soc. Hematol. Educ. Program. 2016, 2016, 413–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raffetto, J.D. Pathophysiology of Chronic Venous Disease and Venous Ulcers. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2018, 98, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansilha, A.; Sousa, J. Pathophysiological Mechanisms of Chronic Venous Disease and Implications for Venoactive Drug Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, M.A.; Romero, B.; Asúnsolo, Á.; Sola, M.; Álavrez-Rocha, M.J.; Sainz, F.; Álavrez-Mon, M.; Buján, J.; García-Honduvilla, N. Patients with incompetent valves in chronic venous insufficiency show increased systematic lipid peroxidation and cellular oxidative stress markers. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 5164576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, J.; Sultan, D.L.; Waqas, B.; Ellison, T.; Kwong, J.; Kim, C.; Hassan, A.; Rabbani, P.S.; Ceradini, D.J. Nrf2-activating Therapy Accelerates Wound Healing in a Model of Cutaneous Chronic Venous Insufficiency. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2020, 8, e3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horecka, A.; Biernacka, J.; Hordyjewska, A.; Dąbrowski, W.; Terlecki, P.; Zubilewicz, T.; Musik, I.; Kurzepa, J. Antioxidative mechanism in the course of varicose veins. Phlebology 2018, 33, 464–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casili, G.; Lanza, M.; Campolo, M.; Messina, S.; Scuderi, S.; Ardizzone, A.; Filippone, A.; Paterniti, I.; Cuzzocrea, S.; Esposito, E. Therapeutic potential of flavonoids in the treatment of chronic venous insufficiency. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2021, 137, 106825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raffetto, J.D.; Khalil, R.A. Mechanisms of lower extremity vein dysfunction in chronic venous disease and implications in management of varicose veins. Vessel. Plus 2021, 5, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrin, M.; Ramelet, A.A. Pharmacological treatment of primary chronic venous disease: Rationale, results and unanswered questions. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2011, 41, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imam, F.; Al-Harbi, N.O.; Al-Harbi, M.M.; Ansari, M.A.; Zoheir, K.M.A.; Iqbal, M.; Anwer, M.K.; Hoshani, A.A.R.; Attia, S.M.; Ahmad, S.F. Pharmacological Research. Pharmacol. Res. 2015, 102, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasain, J.K.; Arabshahi, A.; Taub, P.R.; Sweeney, S.; Moore, R.; Sharer, J.D.; Barnes, S. Simultaneous quantification of F2-isoprostanes and prostaglandins in human urine by liquid chromatography tandem-mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B 2012, 913–914, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huwait, E.; Mobashir, M. Potential and Therapeutic Roles of Diosmin in Human Diseases. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lurie, F.; Branisteanu, D.E. Improving Chronic Venous Disease Management with Micronised Purified Flavonoid Fraction: New Evidence from Clinical Trials to Real Life. Clin. Drug Investig. 2023, 43, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacatusu, I.; Arsenie, L.V.; Badea, G.; Popa, O.; Oprea, O.; Badea, N. New cosmetic formulations with broad photoprotective and antioxidative activities designed by amaranth and pumpkin seed oils nanocarriers. Ind. Crops Prod. 2018, 123, 424–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacatusu, I.; Badea, G.; Popescu, M.; Bordei, N.; Istrati, D.; Moldovan, L.; Seciuc, A.M.; Pantelid, M.I.; Rasitd, I.; Badea, N. Marigold extract, azelaic acid and black caraway oil into lipid nanocarriers provides a strong anti-inflammatory effect in vivo. Ind. Crops Prod. 2017, 109, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ionescu, N.; Neagu, A.M.; Raiciu, A.D.; Popescu, M.; Livadariu, O. Characterization of some vegetable oils in order to use them in the treatment of the varicose veins. Rom. Biotechnol. Lett. 2021, 26, 2370–2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruzmetova, S.; Abrorova, M. Amaranth: Chemical Composition and Use Prospects. Sci. Innov. 2022, 1, 94–96. [Google Scholar]
- Gandhi, S.V.; Nilgar, N.M.; Bhalekar, M.R. Formulation and evaluation of phytoconstituents cream for the treatment of varicose veins. World J. Pharm. Res. SJIF Impact Factor. 2018, 7, 733. [Google Scholar]
- Nardo, A.E.; Suárez, S.; Quiroga, A.V.; Añón, M.C. Amaranth as a source of antihypertensive peptides. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.B.; Jones, C.D.; Nguyen, E. Correlating in vitro and in vivo pharmacokinetics: Establishing dosage equivalence. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2015, 130, 234–242. [Google Scholar]
- EMA. Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP). Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/committees/committee-medicinal-products-human-use-chmp (accessed on 14 May 2024).
- Galla, R.; Grisenti, P.; Farghali, M.; Saccuman, L.; Ferraboschi, P.; Uberti, F. Ovotransferrin Supplementation Improves the Iron Absorption: An In Vitro Gastro-Intestinal Model. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EMA. International Council on Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Registration of Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH). Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/partners-networks/international-activities/multilateral-coalitions-initiatives/international-council-harmonisation-technical-requirements-registration-pharmaceuticals-human-use-ich (accessed on 14 May 2024).
- Uberti, F.; Lattuada, D.; Morsanuto, V.; Nava, U.; Bolis, G.; Vacca, G.; Squarzanti, D.F.; Cisari, C.; Molinari, C. Vitamin D protects human endothelial cells from oxidative stress through the autophagic and survival pathways. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 99, 1367–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FDA. M9 Biopharmaceutics Classification System-Based Biowaivers. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/117974/download (accessed on 14 May 2024).
- EMA. ICH Guideline M9 on Biopharmaceutics Classification 5 System Based Biowaivers. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/scientific-guideline/ich-m9-biopharmaceutics-classification-system-based-biowaivers-step-2b-first-version_en.pdf (accessed on 14 May 2024).
- Galla, R.; Ruga, S.; Ferrari, S.; Saccone, S.; Saccuman, L.; Invernizzi, M.; Uberti, F. In vitro analysis of the effects of plant-derived chondroitin sulfate from intestinal barrier to chondrocytes. J. Funct. Foods 2022, 98, 105285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konishi, Y.; Hagiwara, K.; Shimizu, M. Transepithelial transport of fluorescein in Caco-2 cell monolayers and use of such transport in in vitro evaluation of phenolic acid availability. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2002, 66, 2449–2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinari, C.; Morsanuto, V.; Ghirlanda, S.; Ruga, S.; Notte, F.; Gaetano, L.; Uberti, F. Role of combined lipoic acid and vitamin D3 on astrocytes as a way to prevent brain ageing by induced oxidative stress and iron accumulation. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 2843121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruga, S.; Galla, R.; Ferrari, S.; Invernizzi, M.; Uberti, F. Novel Approach to the Treatment of Neuropathic Pain Using a Combination with Palmitoylethanolamide and Equisetum arvense L. in an In Vitro Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinari, C.; Ruga, S.; Farghali, M.; Galla, R.; Bassiouny, A.; Uberti, F. Preventing c2c12 muscular cells damage combining magnesium and potassium with vitamin D3 and curcumin. J. Tradit. Complement. Med. 2021, 11, 532–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lattuada, D.; Uberti, F.; Colciaghi, B.; Morsanuto, V.; Maldi, E.; Squarzanti, D.F.; Molinari, C.; Boldorini, R.; Bulfoni, A.; Colombo, P.; et al. Fimbrial Cells Exposure to Catalytic Iron Mimics Carcinogenic Changes. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 2015, 25, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaihara, J.N.S.; Minami, C.K.; Peraçoli, M.T.S.; Romão-Veiga, M.; Ribeiro-Vasques, V.R.; Peraçoli, J.C.; Palei, A.C.T.; Cavalli, R.C.; Nunes, P.R.; Luizon, M.R.; et al. Plasma eNOS Concentration in Healthy Pregnancy and in Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy: Evidence of Reduced Concentrations in Pre-Eclampsia from Two Independent Studies. Diseases 2023, 11, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marey, M.A.; Yousef, M.S.; Liu, J.; Morita, K.; Sasaki, M.; Hayakawa, H. Endothelin-1 downregulates sperm phagocytosis by neutrophils in vitro: A physiological implication in bovine oviduct immunity. J. Reprod. Dev. 2016, 62, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partan, R.U.; Putra, K.M.; Kusuma, N.F.; Darma, S.; Reagan, M.; Muthia, P.; Radiandina, A.S.; Saleh, M.I.; Salim, E.M. Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cell Secretome Improves Clinical Outcomes and Changes Biomarkers in Knee Osteoarthritis. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 7138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, E.J.; Zheng, M.; Craft, C.M.; Jeong, S. Matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases 1 (TIMP-1) are localized in the nucleus of retinal Müller glial cells and modulated by cytokines and oxidative stress. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0253915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filis, K.; Kavantzas, N.; Isopoulos, T.; Antonakis, P.; Sigalas, P.; Vavouranakis, E.; Sigala, F. Increased vein wall apoptosis in varicose vein disease is related to venous hypertension. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2011, 41, 533–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfisterer, L.; König, G.; Hecker, M.; Korff, T. Pathogenesis of varicose veins—Lessons from biomechanics. Vasa 2014, 43, 88–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miguel, C.B.; Andrade, R.d.S.; Mazurek, L.; Martins-de-Abreu, M.C.; Miguel-Neto, J.; Barbosa, A.d.M.; Silva, G.P.; Góes-Neto, A.; Soares, S.d.C.; Lazo-Chica, J.E.; et al. Emerging Pharmacological Interventions for Chronic Venous Insufficiency: A Comprehensive Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Efficacy, Safety, and Therapeutic Advances. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olszanecki, R.; Gebska, A.; Kozlovski, V.I.; Gryglewski, R.J. Flavonoids and nitric oxide synthase. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2002, 53, 571–584. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Q.; Zhang, Y.-h. Flavonoids with Anti-Angiogenesis Function in Cancer. Molecules 2024, 29, 1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feldo, M.; Wójciak-Kosior, M.; Sowa, I.; Kocki, J.; Bogucki, J.; Zubilewicz, T.; Kęsik, J.; Bogucka-Kocka, A. Effect of Diosmin Administration in Patients with Chronic Venous Disorders on Selected Factors Affecting Angiogenesis. Molecules 2019, 24, 3316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira, J.F.L.; Teixeira-Viana, F.C.; Barboza-Silva, B.L.; Mendes-Pinto, D.; Rodrigues-Machad, M.D.G. Advanced Levels of Chronic Venous Insufficiency are Related to an Increased in Arterial Stiffness. Ann. Vasc. Surg. 2023, 96, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Hu, C.; Li, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Li, Q.; Fang, C. Pumpkin seed oil: A comprehensive review of extraction methods, nutritional constituents, and health benefits. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2024, 104, 572–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, H.S.; Kim, G.; Ahn, M.A.; Chung, J.W.; Hyun, T.K. Comparison of the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of leaf extracts from grain amaranths (Amaranthus spp.). J. Plant Biotechnol. 2022, 49, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzdağlı, Y.; Eyipınar, C.D.; Kacı, F.N.; Tekin, A. Effects of Hesperidin on Anti-Inflammatory and Antioxidant Response in Healthy People: A Meta-Analysis and Meta-Regression. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2023, 33, 1390–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riaz, B.; Sohn, S. Neutrophils in Inflammatory Diseases: Unraveling the Impact of Their Derived Molecules and Heterogeneity. Cells 2023, 12, 2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, I.; Barale, C.; Melchionda, E.; Penna, C.; Pagliaro, P. Platelets and Cardioprotection: The Role of Nitric Oxide and Carbon Oxide. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Immanuel, J.; Yun, S. Vascular Inflammatory Diseases and Endothelial Phenotypes. Cells 2023, 12, 1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apaijit, K.; Pakdeechote, P.; Maneesai, P.; Meephat, S.; Prasatthong, P.; Bunbupha, S. Hesperidin alleviates vascular dysfunction and remodelling in high-fat/high-fructose diet-fed rats by modulating oxidative stress, inflammation, AdipoR1, and eNOS expression. Tissue Cell 2022, 78, 101901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wójciak, M.; Feldo, M.; Borowski, G.; Kubrak, T.; Płachno, B.J.; Sowa, I. Antioxidant Potential of Diosmin and Diosmetin against Oxidative Stress in Endothelial Cells. Molecules 2022, 27, 8232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarafdar, A.; Pula, G. The Role of NADPH Oxidases and Oxidative Stress in Neurodegenerative Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Böhm, F.; Pernow, J. The importance of endothelin-1 for vascular dysfunction in cardiovascular disease. Cardiovasc. Res. 2007, 76, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gwozdzinski, L.; Bernasinska-Slomczewska, J.; Hikisz, P.; Wiktorowska-Owczarek, A.; Kowalczyk, E.; Pieniazek, A. The Effect of Diosmin, Escin, and Bromelain on Human Endothelial Cells Derived from the Umbilical Vein and the Varicose Vein—A Preliminary Study. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iriz, E.; Vural, C.; Ereren, E.; Poyraz, A.; Erer, D.; Oktar, L.; Gokgoz, L.; Halit, V.; Soncul, H. Effects of calcium dobesilate and diosmin-hesperidin on apoptosis of venous wall in primary varicose veins. Vasa 2008, 37, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filis, K.; Kavantzas, N.; Dalainas, I.; Galyfos, G.; Karanikola, E.; Toutouzas, K. Evaluation of apoptosis in varicose vein disease complicated by superficial vein thrombosis. Vasa 2014, 43, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Peng, W.; Raffetto, J.D.; Khalil, R.A. Matrix Metalloproteinases in Remodeling of Lower Extremity Veins and Chronic Venous Disease. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2017, 147, 267–299. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.J.; Im, A.R.; Kim, S.M.; Kang, H.S.; Lee, J.D.; Chae, S. The flavonoid hesperidin exerts anti-photoaging effect by downregulating matrix metalloproteinase (mmp)-9 expression via mitogen activated protein kinase (mapk)-dependent signaling pathways. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 18, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldo, M.; Wójciak-Kosior, M.; Sowa, I.; Kocki, J.; Bogucki, J.; Zubilewicz, T.; Bogucka-Kocka, A. Monitoring of endostatin, TNF-a VEGFs, MMP-9, and cathepsin-L during three months of diosmin treatment in patients with chronic venous disease (CVD). Acta Angiol. 2019, 25, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna, P.S.; Kumar, N.R.; Swathi; Rani, S. Amaranthus viridis methanolic extract and its active compound kaempferol ameliorate myocardial infarction induced by isoproterenol through decreasing oxidative stress and cell death via Nrf-2/HO-1 and MMP/Bax/Bcl-2/TLR-4 pathways in rats. Comp. Clin. Pathol. 2023, 32, 661–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santini, A.; Novellino, E. To Nutraceuticals and Back: Rethinking a Concept. Foods 2017, 6, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komala, M.G.; Ong, S.G.; Qadri, M.U.; Elshafie, L.M.; Pollock, C.A.; Saad, S. Investigating the Regulatory Process, Safety, Efficacy and Product Transparency for Nutraceuticals in the USA, Europe and Australia. Foods 2023, 12, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Compound | Characterisation | Extract Solvent |
|---|---|---|
| Pumpkin seeds from Curcubita maxima |
|
|
| Amaranthus from Amaranthus caudatus L. |
|
|
| Hypersmin |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ferrari, S.; Galla, R.; Mulè, S.; Molinari, C.; Uberti, F. Analysis of the Combined Effects of a Novel Combination of Hypersmin, Pumpkin Seed and Amaranthus Extracts in an In Vitro Model of Chronic Venous Insufficiency. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1807. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17111807
Ferrari S, Galla R, Mulè S, Molinari C, Uberti F. Analysis of the Combined Effects of a Novel Combination of Hypersmin, Pumpkin Seed and Amaranthus Extracts in an In Vitro Model of Chronic Venous Insufficiency. Nutrients. 2025; 17(11):1807. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17111807
Chicago/Turabian StyleFerrari, Sara, Rebecca Galla, Simone Mulè, Claudio Molinari, and Francesca Uberti. 2025. "Analysis of the Combined Effects of a Novel Combination of Hypersmin, Pumpkin Seed and Amaranthus Extracts in an In Vitro Model of Chronic Venous Insufficiency" Nutrients 17, no. 11: 1807. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17111807
APA StyleFerrari, S., Galla, R., Mulè, S., Molinari, C., & Uberti, F. (2025). Analysis of the Combined Effects of a Novel Combination of Hypersmin, Pumpkin Seed and Amaranthus Extracts in an In Vitro Model of Chronic Venous Insufficiency. Nutrients, 17(11), 1807. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17111807








