Within- and Between-Individual Variations in Protein, Sodium, Potassium, and Phosphorus Intake Estimated from Urinary Biomarkers and Dietary Records in Individuals with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
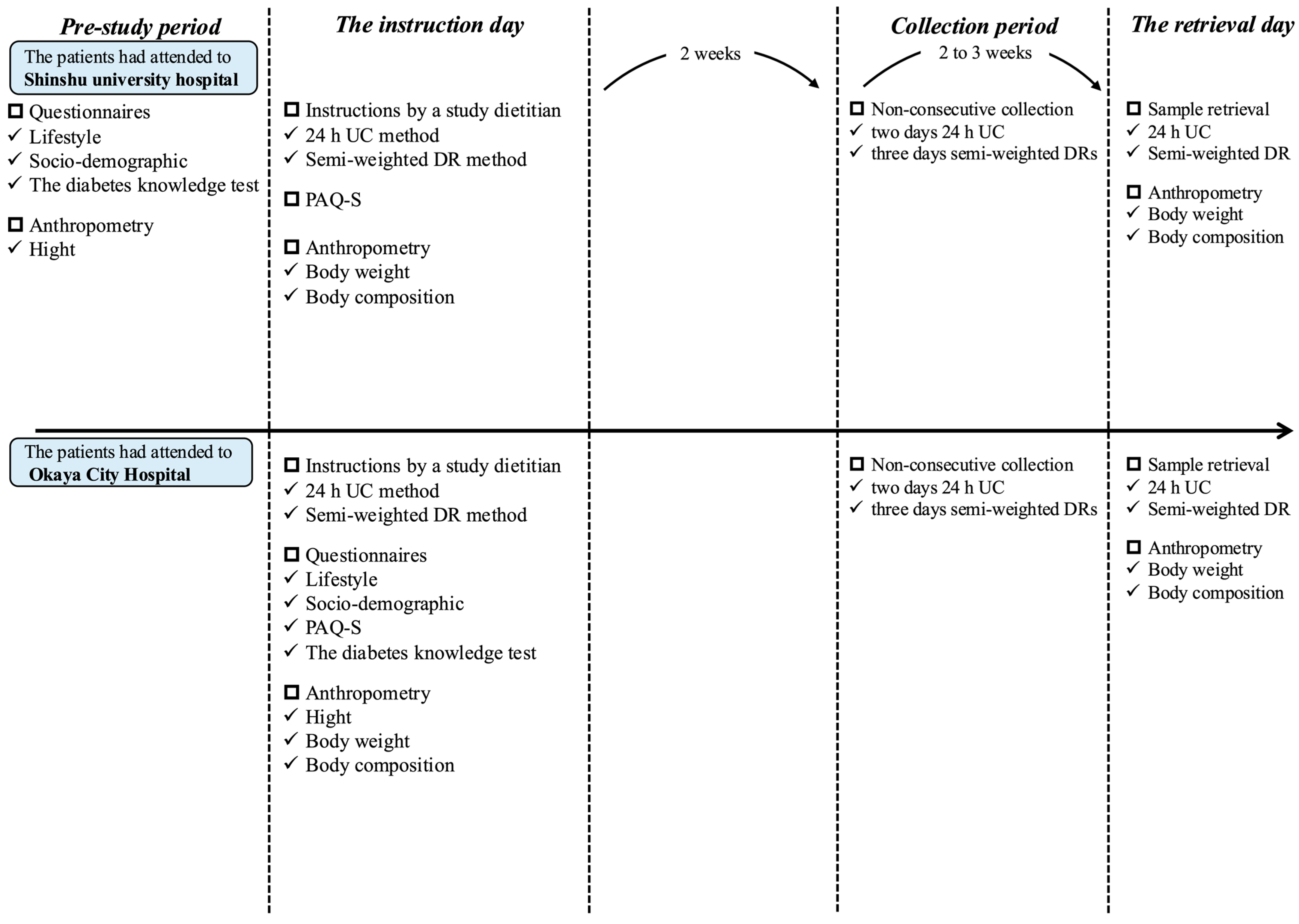
2.2. Measurement Schedule
2.3. Twenty-Four-Hour Urine Collection
2.4. Semi-Weighted Dietary Records
2.5. Other Measurements
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Study Participants
3.2. Mean Nutrient Intake and Within-to-Between-Individual Variance Ratios Estimated Using 24 h UC and DRs
3.3. Required Group Size for Estimating Mean Nutrient Intake Using 24 h UC and DRs
3.4. Days Required to Achieve a Specific Level of Correlation Between Observed and Unobserved Usual Nutrient Intake Using 24 h UC and DRs
3.5. Required Days for Estimating Mean Nutrient Intake Using 24 h UC and DRs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 24 h UC | 24 h urine collection |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| CVb | Between-individual coefficient of variation |
| CVw | Within-individual coefficient of variation |
| DR | Dietary record |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| STFC-J | Standard Tables of Foods Composition in Japan |
| T2DM | Type 2 diabetes mellitus |
| VR | Variance ratio |
References
- Evert, A.B.; Dennison, M.; Gardner, C.D.; Garvey, W.T.; Lau, K.H.K.; MacLeod, J.; Mitri, J.; Pereira, R.F.; Rawlings, K.; Robinson, S.; et al. Nutrition Therapy for Adults with Diabetes or Prediabetes: A Consensus Report. Diabetes Care 2019, 42, 731–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franz, M.J.; MacLeod, J.; Evert, A.; Brown, C.; Gradwell, E.; Handu, D.; Reppert, A.; Robinson, M. Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics Nutrition Practice Guideline for Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes in Adults: Systematic Review of Evidence for Medical Nutrition Therapy Effectiveness and Recommendations for Integration into the Nutrition Care Process. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2017, 117, 1659–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coppell, K.J.; Kataoka, M.; Williams, S.M.; Chisholm, A.W.; Vorgers, S.M.; Mann, J.I. Nutritional intervention in patients with type 2 diabetes who are hyperglycaemic despite optimised drug treatment–Lifestyle Over and Above Drugs in Diabetes (LOADD) study: Randomised controlled trial. BMJ 2010, 341, c3337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omura, Y.; Murakami, K.; Matoba, K.; Nishimura, R.; Sasaki, S. Effects of individualized dietary advice compared with conventional dietary advice for adults with type 2 diabetes: A randomized controlled trial. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2022, 32, 1035–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattisson, I.; Wirfält, E.; Aronsson, C.A.; Wallström, P.; Sonestedt, E.; Gullberg, B.; Berglund, G. Misreporting of energy: Prevalence, characteristics of misreporters and influence on observed risk estimates in the Malmo Diet and Cancer cohort. Br. J. Nutr. 2005, 94, 832–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinker, L.F.; Sarto, G.E.; Howard, B.V.; Huang, Y.; Neuhouser, M.L.; Mossavar-Rahmani, Y.; Beasley, J.M.; Margolis, K.L.; Eaton, C.B.; Phillips, L.S.; et al. Biomarker-calibrated dietary energy and protein intake associations with diabetes risk among postmenopausal women from the Women’s Health Initiative. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 94, 1600–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, Y.; Dodd, K.W.; Kipnis, V.; Thompson, F.E.; Potischman, N.; Schoeller, D.A.; Baer, D.J.; Midthune, D.; Troiano, R.P.; Bowles, H.; et al. Comparison of self-reported dietary intakes from the Automated Self-Administered 24-h recall, 4-d food records, and food-frequency questionnaires against recovery biomarkers. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 107, 80–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korth, A.L.; Bhutani, S.; Neuhouser, M.L.; Beresford, S.A.; Snetselaar, L.; Tinker, L.F.; Schoeller, D.A. Comparison of Methods Used to Correct Self-Reported Protein Intake for Systematic Variation in Reported Energy Intake Using Quantitative Biomarkers of Dietary Intake. J. Nutr. 2020, 150, 1330–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willett, W. Nutritional Epidemiology; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Shaar, L.; Yuan, C.; Rosner, B.; Dean, S.B.; Ivey, K.L.; Clowry, C.M.; Sampson, L.A.; Barnett, J.B.; Rood, J.; Harnack, L.J.; et al. Reproducibility and Validity of a Semiquantitative Food Frequency Questionnaire in Men Assessed by Multiple Methods. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2021, 190, 1122–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bingham, S.A. Biomarkers in nutritional epidemiology. Public Health Nutr. 2002, 5, 821–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekinci, E.I.; Clarke, S.; Thomas, M.C.; Moran, J.L.; Cheong, K.; MacIsaac, R.J.; Jerums, G. Dietary salt intake and mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2011, 34, 703–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaz, J.S.; Bittencourt, M.; Almeida, J.C.; Gross, J.L.; De Azevedo, M.J.; Zelmanovitz, T. Protein intake estimated by weighed diet records in patients with type 2 diabetes: Misreporting and intra-individual variability using 24-hour nitrogen output as criterion standard. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2008, 108, 867–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, D.; Machida, S.; Matsumoto, N.; Shibagaki, Y.; Sakurada, T. Age Modifies the Association of Dietary Protein Intake with All-Cause Mortality in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, A.; Takachi, R.; Ishihara, J.; Maruya, S.; Ishii, Y.; Kito, K.; Nakamura, K.; Tanaka, J.; Yamaji, T.; Iso, H.; et al. Urinary Biomarkers in Screening for the Usual Intake of Fruit and Vegetables, and Sodium, Potassium, and the Sodium-to-Potassium Ratio: Required Number and Accuracy of Measurements. Nutrients 2024, 16, 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukumoto, A.; Asakura, K.; Murakami, K.; Sasaki, S.; Okubo, H.; Hirota, N.; Notsu, A.; Todoriki, H.; Miura, A.; Fukui, M.; et al. Within- and between-individual variation in energy and nutrient intake in Japanese adults: Effect of age and sex differences on group size and number of records required for adequate dietary assessment. J. Epidemiol. 2013, 23, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokudome, Y.; Imaeda, N.; Nagaya, T.; Ikeda, M.; Fujiwara, N.; Sato, J.; Kuriki, K.; Kikuchi, S.; Maki, S.; Tokudome, S. Daily, weekly, seasonal, within- and between-individual variation in nutrient intake according to four season consecutive 7 day weighed diet records in Japanese female dietitians. J. Epidemiol. 2002, 12, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, D.; Nanri, H.; Yoshida, T.; Yamaguchi, M.; Sugita, M.; Nozawa, Y.; Okabe, Y.; Itoi, A.; Goto, C.; Yamada, Y.; et al. Validation of Energy and Nutrition Intake in Japanese Elderly Individuals Estimated Based on a Short Food Frequency Questionnaire Compared against a 7-day Dietary Record: The Kyoto-Kameoka Study. Nutrients 2019, 11, 688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, D.G.; Murayi, T.; Clemens, J.C.; Baer, D.J.; Sebastian, R.S.; Moshfegh, A.J. The USDA Automated Multiple-Pass Method accurately assesses population sodium intakes. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 97, 958–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, A.E.; Jebb, S.A.; Bingham, S.A.; Runswick, S.A.; Poppitt, S.D. The validation of energy and protein intakes by doubly labelled water and 24-hour urinary nitrogen excretion in post-obese subjects. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 2008, 8, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araki, E.; Goto, A.; Kondo, T.; Noda, M.; Noto, H.; Origasa, H.; Osawa, H.; Taguchi, A.; Tanizawa, Y.; Tobe, K.; et al. Japanese Clinical Practice Guideline for Diabetes 2019. Diabetol. Int. 2020, 11, 165–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunbar, S.B.; Clark, P.C.; Stamp, K.D.; Reilly, C.M.; Gary, R.A.; Higgins, M.; Kaslow, N. Family partnership and education interventions to reduce dietary sodium by patients with heart failure differ by family functioning. Heart Lung 2016, 45, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nerbass, F.B.; Pecoits-Filho, R.; McIntyre, N.J.; McIntyre, C.W.; Taal, M.W. Development of a formula for estimation of sodium intake from spot urine in people with chronic kidney disease. Nephron Clin. Pract. 2014, 128, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.-Y.; Cogswell, M.E.; Loria, C.M.; Chen, T.-C.; Pfeiffer, C.M.; Swanson, C.A.; Caldwell, K.L.; Perrine, C.G.; Carriquiry, A.L.; Liu, K.; et al. Urinary excretion of sodium, potassium, and chloride, but not iodine, varies by timing of collection in a 24-hour calibration study. J. Nutr. 2013, 143, 1276–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lachat, C.; Hawwash, D.; Ocké, M.C.; Berg, C.; Forsum, E.; Hörnell, A.; Larsson, C.; Sonestedt, E.; Wirfält, E.; Åkesson, A.; et al. Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology-Nutritional Epidemiology (STROBE-nut): An Extension of the STROBE Statement. PLoS Med. 2016, 13, e1002036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goios, A.C.; Severo, M.; Lloyd, A.J.; Magalhaes, V.P.; Lopes, C.; Torres, D.P. Validation of a new software eAT24 used to assess dietary intake in the adult Portuguese population. Public Health Nutr. 2020, 23, 3093–3103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, K.; Sasaki, S.; Takahashi, Y.; Uenishi, K.; Watanabe, T.; Kohri, T.; Yamasaki, M.; Watanabe, R.; Baba, K.; Shibata, K.; et al. Sensitivity and specificity of published strategies using urinary creatinine to identify incomplete 24-h urine collection. Nutrition 2008, 24, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bingham, S.A.; Williams, R.; Cole, T.J.; Price, C.P.; Cummings, J.H. Reference values for analytes of 24-h urine collections known to be complete. Ann. Clin. Biochem. 1988, 25 Pt 6, 610–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bingham, S.A.; Cummings, J.H. Urine nitrogen as an independent validatory measure of dietary intake: A study of nitrogen balance in individuals consuming their normal diet. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1985, 42, 1276–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holbrook, J.T.; Patterson, K.Y.; Bodner, J.E.; Douglas, L.W.; Veillon, C.; Kelsay, J.L.; Mertz, W.; Smith, J.C., Jr. Sodium and potassium intake and balance in adults consuming self-selected diets. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1984, 40, 786–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasevska, N.; Runswick, S.A.; Bingham, S.A. Urinary potassium is as reliable as urinary nitrogen for use as a recovery biomarker in dietary studies of free living individuals. J. Nutr. 2006, 136, 1334–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinozaki, N.; Murakami, K.; Asakura, K.; Uechi, K.; Kobayashi, S.; Masayasu, S.; Sasaki, S. Dietary phosphorus intake estimated by 4-day dietary records and two 24-hour urine collections and their associated factors in Japanese adults. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 72, 517–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Council for Science and Technology; Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology, Japan. Standard Tables of Food Composition in Japan. 7th ed. 2015. Available online: https://www.mext.go.jp/en/policy/science_technology/policy/title01/detail01/1374030.htm (accessed on 27 December 2024).
- Fujii, H.; Yamamoto, S.; Takeda-Imai, F.; Inoue, M.; Tsugane, S.; Kadowaki, T.; Noda, M. Validity and applicability of a simple questionnaire for the estimation of total and domain-specific physical activity. Diabetol. Int. 2011, 2, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minami, T.; Shirakawa, J.; Hiiragi, H.; Yamada, T.; Suzuki, Y.; Shirabe, S.; Maeda, H.; Terauchi, Y. Validity and reliability of the Japanese version of the diabetes knowledge test among in-patients with type 2 diabetes. J. Diabetes Investig. 2022, 13, 580–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahns, L.; Carriquiry, A.; Arab, L.; Mroz, T.A.; Popkin, B.M. Within- and between-person variation in nutrient intakes of Russian and U.S. children differs by sex and age. J. Nutr. 2004, 134, 3114–3120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Manning, W.G. The logged dependent variable, heteroscedasticity, and the retransformation problem. J. Health Econ. 1998, 17, 283–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milner, J.; MCGuire, V.; Feather, T.E.; Little, J.A. Source of variance in 24-hour dietary recall data: Implications for nutrition study design and interpretation. Carbohydrate sources, vitamins, and minerals. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1983, 37, 986–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, M.; Black, A.E.; Morris, J.A.; Cole, T.J. Between- and within-subject variation in nutrient intake from infancy to old age: Estimating the number of days required to rank dietary intakes with desired precision. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1989, 50, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uechi, K.; Asakura, K.; Ri, Y.; Masayasu, S.; Sasaki, S. Advantage of multiple spot urine collections for estimating daily sodium excretion: Comparison with two 24-h urine collections as reference. J. Hypertens. 2016, 34, 204–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knuiman, J.T.; Hautvast, J.G.; Van Der Heyden, L.; Geboers, J.; Joossens, J.V.; Tornqvist, H.; Isaksson, B.; Pietinen, P.; Tuomilehto, J.; Poulsen, L. A multi-centre study on completeness of urine collection in 11 European centres. I. Some problems with the use of creatinine and 4-aminobenzoic acid as markers of the completeness of collection. Hum. Nutr. Clin. Nutr. 1986, 40, 229–237. [Google Scholar]
- Pendon-Ruiz de Mier, M.V.; Vergara, N.; Rodelo-Haad, C.; Lopez-Zamorano, M.D.; Membrives-Gonzalez, C.; Lopez-Baltanas, R.; Muñoz-Castañeda, J.R.; Caravaca, F.; Martín-Malo, A.; Felsenfeld, A.J.; et al. Assessment of Inorganic Phosphate Intake by the Measurement of the Phosphate/Urea Nitrogen Ratio in Urine. Nutrients 2021, 13, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLean, R.; Cameron, C.; Butcher, E.; Cook, N.R.; Woodward, M.; Campbell, N.R.C. Comparison of 24-hour urine and 24-hour diet recall for estimating dietary sodium intake in populations: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2019, 21, 1753–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asakura, K.; Uechi, K.; Masayasu, S.; Sasaki, S. Sodium sources in the Japanese diet: Difference between generations and sexes. Public Health Nutr. 2016, 19, 2011–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogawa, K.; Tsubono, Y.; Nishino, Y.; Watanabe, Y.; Ohkubo, T.; Watanabe, T.; Nakatsuka, H.; Takahashi, N.; Kawamura, M.; Tsuji, I.; et al. Inter- and intra-individual variation of food and nutrient consumption in a rural Japanese population. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 1999, 53, 781–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tsubota-Utsugi, M.; Imai, E.; Nakade, M.; Matsumoto, T.; Tsuboyama-Kasaoka, N.; Nishi, N.; Tsubono, Y. Evaluation of the prevalence of iodine intakes above the tolerable upper intake level from four 3-day dietary records in a Japanese population. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 2013, 59, 310–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshizawa, K.; Willett, W.C.; Yuan, C. Reliability of Repeated Measures of Nutrient Intake by Diet Records in Residents in the Western Region of Japan. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taguchi, C.; Kishimoto, Y.; Fukushima, Y.; Saita, E.; Tanaka, M.; Takahashi, Y.; Masuda, Y.; Goda, T.; Kondo, K. Dietary Polyphenol Intake Estimated by 7-Day Dietary Records among Japanese Male Workers: Evaluation of the Within- and Between-Individual Variation. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 2017, 63, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lombard, M.J.; Steyn, N.P.; Charlton, K.E.; Senekal, M. Application and interpretation of multiple statistical tests to evaluate validity of dietary intake assessment methods. Nutr. J. 2015, 14, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, K.; Shinozaki, N.; Kimoto, N.; Masayasu, S.; Sasaki, S. Relative Validity of Food Intake in Each Meal Type and Overall Food Intake Derived Using the Meal-Based Diet History Questionnaire against the 4-Day Weighed Dietary Record in Japanese Adults. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Health and Welfare Department Health Promotion Department Nagano Prefecture. Inhabitant of a Prefecture Health and Nutritional Investigation. 2010. Available online: https://www.pref.nagano.lg.jp/kenko-choju/kenko/kenko/kenko/chosa/chousa22.html (accessed on 5 January 2025).
- The Health and Welfare Department Health Promotion Department Nagano Prefecture. Inhabitant of a Prefecture Health and Nutritional Investigation. 2013. Available online: https://www.pref.nagano.lg.jp/kenko-choju/kenko/kenko/kenko/chosa/chousa25-2.html (accessed on 5 January 2025).
- The Health and Welfare Department Health Promotion Department Nagano Prefecture. Inhabitant of a Prefecture Health and Nutritional Investigation. 2016. Available online: https://www.pref.nagano.lg.jp/kenko-choju/kenko/kenko/kenko/chosa/chousa28.html (accessed on 5 January 2025).
- The Health and Welfare Department Health Promotion Department Nagano Prefecture. Inhabitant of a Prefecture Health and Nutritional Investigation. 2019. Available online: https://www.pref.nagano.lg.jp/kenko-choju/kenko/kenko/kenko/chosa/chousa-r1.html (accessed on 5 January 2025).
- The Health and Welfare Department Health Promotion Department Nagano Prefecture. Inhabitant of a Prefecture Health and Nutritional Investigation. 2022. Available online: https://www.pref.nagano.lg.jp/kenko-choju/kenko/kenko/kenko/chosa/chousar4.html (accessed on 5 January 2025).
- Nusser, S.M.; Carriquiry, A.L.; Dodd, K.W.; Fuller, W.A. A semiparametric transformation approach to estimating usual daily intake distributions. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1996, 91, 1440–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, K.; Livingstone, M.B.E.; Okubo, H.; Sasaki, S. Prevalence and characteristics of misreporting of energy intake in Japanese adults: The 2012 National Health and Nutrition Survey. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 27, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, K.; Livingstone, M.B. Prevalence and characteristics of misreporting of energy intake in US adults: NHANES 2003-2012. Br. J. Nutr. 2015, 114, 1294–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adachi, R.; Oono, F.; Matsumoto, M.; Yuan, X.; Murakami, K.; Sasaki, S.; Takimoto, H. Seasonal variation in the intake of food groups and nutrients in Japan: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Epidemiol. 2024, 35, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Total | Females | Males | |
|---|---|---|---|
| (n = 39) | (n = 13) | (n = 26) | |
| Age, years | 64.6 (8.4) | 66.2 (5.8) | 63.8 (9.4) |
| Height, cm | 163.6 (9.4) | 154.8 (8.5) | 168.1 (6.2) |
| Body weight, kg | 68.3 (15.3) | 59.9 (10.3) | 72.5 (15.9) |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 25.3 (4.0) | 24.9 (2.9) | 25.5 (4.5) |
| Education, n (%) | |||
| <10 years | 4 (10.3) | 0 (0.0) | 4 (15.4) |
| 10 to 12 years | 10 (25.6) | 8 (61.5) | 2 (7.7) |
| ≥13 years | 25 (64.1) | 5 (38.5) | 20 (76.9) |
| Marital status, n (%) | |||
| Single | 7 (17.9) | 0 (0.0) | 7 (26.9) |
| Married | 30 (76.9) | 12 (92.3) | 18 (69.2) |
| Divorced or widowed | 2 (5.1) | 1 (7.7) | 1 (3.8) |
| Living status, n (%) | |||
| Lives alone | 7 (17.9) | 0 (0.0) | 7 (26.9) |
| Lives with others | 31 (79.5) | 13 (100.0) | 18 (69.2) |
| Occasionally lives with others | 1 (2.6) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (3.8) |
| Employment status, n (%) | |||
| Employed | 29 (74.4) | 8 (61.5) | 21 (80.8) |
| Unemployed/retired | 10 (25.6) | 5 (38.5) | 5 (19.2) |
| Current smoker, n (%) | 4 (10.3) | 0 (0.0) | 4 (15.4) |
| Household income, JPY/year, n (%) | |||
| <2 million | 7 (17.9) | 5 (38.5) | 2 (7.7) |
| 2–6 million | 24 (61.5) | 5 (38.5) | 19 (73.1) |
| ≥6 million | 6 (15.4) | 1 (7.7) | 5 (19.2) |
| Unknown | 2 (5.1) | 2 (15.4) | 0 (0.0) |
| Physical activity, MET-h/day | 40.7 (4.2) | 41.4 (3.9) | 40.4 (4.4) |
| HbA1c, % | 7.0 (0.8) | 7.0 (0.5) | 7.0 (0.9) |
| Fasting plasma glucose, mg/dL | 129 (44) | 117 (19) | 135 (52) |
| eGFR, mL/min/1.73 m2 | 71(17) | 73 (16) | 70 (17) |
| Duration of diabetes, years | 17.8 (10.1) | 15.2 (9.5) | 19.1 (10.3) |
| Diabetes treatment, n (%) | |||
| Oral hypoglycemic agents | 33 (84.6) | 10 (76.9) | 23 (88.5) |
| Sulphonylureas | 5 (12.8) | 2 (15.4) | 3 (11.5) |
| Glinides | 4 (10.3) | 1 (7.7) | 3 (11.5) |
| DPP-4 inhibitors | 12 (30.8) | 4 (30.8) | 8 (30.8) |
| Biguanides | 28 (71.8) | 10 (76.9) | 18 (69.2) |
| SGLT2 inhibitors | 21 (53.8) | 6 (46.2) | 15 (57.7) |
| α-Glucosidase inhibitors | 3 (7.7) | 0 (0.0) | 3 (11.5) |
| GLP-1 receptor agonist | 8 (20.5) | 4 (30.8) | 4 (15.4) |
| Imeglimin | 1 (2.6) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (3.8) |
| Insulin | 19 (48.7) | 6 (46.2) | 13 (50.0) |
| Anti-hypertensive agents, n (%) | 29 (74.4) | 10 (76.9) | 19 (73.1) |
| Lipid lowering drug, n (%) | 25 (64.1) | 9 (69.2) | 16 (61.5) |
| Diuretics without loop diuretics, n (%) | 1 (2.6) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (3.8) |
| J-DKT score, points | 5.3 (1.4) | 5.3 (1.3) | 5.2 (1.4) |
| Energy intake, kcal/day | 2061 (557) | 1760 (335) | 2211 (585) |
| Protein (g/day) | Sodium (mg/day) | Potassium (mg/day) | Phosphorus (mg/day) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 24 h UC 1 | DR 2 | Difference 3 | 24 h UC 1 | DR 2 | Difference 3 | 24 h UC 1 | DR 2 | Difference 3 | 24 h UC 1 | DR 2 | Difference 3 | |
| Total (n = 39) | ||||||||||||
| Mean 4 | 77.8 | 77.0 | 0.8 (−4.7 to 6.3) | 5315 | 4530 | 784 (312 to 1257) * | 2796 | 2868 | −72 (−314 to 171) | 1060 | 1151 | −91 (−194 to 12) |
| SD | 23.0 | 23.0 | 2238 | 1648 | 995 | 917 | 376 | 346 | ||||
| CVw (%) 5 | 15.6 | 25.4 | −9.8 | 24.0 | 27.9 | −3.9 | 17.5 | 20.0 | −2.5 | 17.4 | 24.1 | −6.7 |
| CVb (%) 6 | 38.9 | 37.3 | 1.6 | 54.8 | 49.4 | 5.4 | 47.4 | 47.9 | −0.5 | 47.3 | 39.7 | 7.6 |
| VR 7 | 0.16 | 0.46 | −0.30 | 0.19 | 0.32 | −0.13 | 0.14 | 0.17 | −0.03 | 0.14 | 0.37 | −0.19 |
| r 8 | 0.56 * | 0.61 * | 0.63 * | 0.47 * | ||||||||
| Females (n = 13) | ||||||||||||
| Mean 4 | 65.9 | 69.5 | −3.6 (−13.4 to 6.2) | 4553 | 4052 | 501 (−191 to 1194) | 2638 | 2769 | −131 (−504 to 243) | 968 | 1065 | −97 (−242 to 47) |
| SD | 23.8 | 18.5 | 1532 | 1342 | 846 | 775 | 329 | 263 | ||||
| CVw (%) 5 | 20.0 | 22.3 | −2.3 | 27.9 | 23.0 | 5.0 | 19.3 | 16.0 | 3.3 | 17.8 | 20.9 | −3.0 |
| CVb (%) 6 | 47.7 | 34.1 | 13.6 | 38.9 | 48.2 | −9.4 | 41.7 | 43.9 | −2.2 | 45.5 | 31.3 | 14.1 |
| VR 7 | 0.18 | 0.43 | −0.25 | 0.52 | 0.23 | 0.29 | 0.21 | 0.13 | 0.08 | 0.15 | 0.44 | −0.26 |
| r 8 | 0.83 * | 0.48 | 0.75 * | 0.49 | ||||||||
| Males (n = 26) | ||||||||||||
| Mean 4 | 83.8 | 80.8 | 3.0 (−4.0 to 10.0) | 5696 | 4769 | 927 (284 to 1570) * | 2876 | 2918 | −43 (−373 to 287) | 1106 | 1194 | −88 (−231 to 56) |
| SD | 20.3 | 24.2 | 2443 | 1741 | 1061 | 981 | 392 | 375 | ||||
| CVw (%) 5 | 13.9 | 26.4 | −12.5 | 22.4 | 29.4 | −7.0 | 16.7 | 21.5 | −4.8 | 17.2 | 25.2 | −8.0 |
| CVb (%) 6 | 31.5 | 36.1 | −4.6 | 56.8 | 48.1 | 8.7 | 49.9 | 50.2 | −0.3 | 47.5 | 41.6 | 5.9 |
| VR 7 | 0.19 | 0.53 | −0.34 | 0.16 | 0.37 | −0.21 | 0.11 | 0.18 | −0.07 | 0.13 | 0.37 | −0.19 |
| r 8 | 0.39 * | 0.58 * | 0.58 * | 0.33 | ||||||||
| Protein | Sodium | Potassium | Phosphorus | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D0 | 24 h UC 2 | DR 3 | Difference 4 | 24 h UC 2 | DR 3 | Difference 4 | 24 h UC 2 | DR 3 | Difference 4 | 24 h UC 2 | DR 3 | Difference 4 |
| Total (n = 39) | ||||||||||||
| 20% | 17 | 20 | −3 | 35 | 31 | 4 | 25 | 26 | −1 | 25 | 21 | 4 |
| 10% | 68 | 79 | −11 | 138 | 124 | 14 | 99 | 104 | −5 | 98 | 83 | 15 |
| 5% | 271 | 313 | −42 | 550 | 496 | 54 | 394 | 415 | −21 | 391 | 331 | 60 |
| 2.5% | 1081 | 1252 | −171 | 2199 | 1981 | 218 | 1573 | 1659 | −86 | 1561 | 1323 | 238 |
| Females (n = 13) | ||||||||||||
| 20% | 26 | 16 | 10 | 23 | 28 | −5 | 21 | 21 | 0 | 23 | 14 | 9 |
| 10% | 103 | 64 | 39 | 89 | 110 | −21 | 82 | 84 | −2 | 92 | 55 | 37 |
| 5% | 412 | 256 | 156 | 353 | 439 | −86 | 325 | 336 | −11 | 367 | 218 | 149 |
| 2.5% | 1647 | 1022 | 625 | 1410 | 1756 | −346 | 1298 | 1341 | −43 | 1467 | 871 | 596 |
| Males (n = 26) | ||||||||||||
| 20% | 12 | 20 | −8 | 36 | 31 | 5 | 27 | 29 | −2 | 25 | 23 | 2 |
| 10% | 46 | 77 | −31 | 144 | 122 | 22 | 107 | 115 | −8 | 98 | 91 | 7 |
| 5% | 183 | 308 | −125 | 574 | 488 | 86 | 425 | 459 | −34 | 392 | 363 | 29 |
| 2.5% | 730 | 1231 | −501 | 2294 | 1950 | 344 | 1699 | 1833 | −134 | 1567 | 1452 | 115 |
| Protein | Sodium | Potassium | Phosphorus | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| r | 24 h UC 2 | DR 3 | Difference 4 | 24 h UC 2 | DR 3 | Difference 4 | 24 h UC 2 | DR 3 | Difference 4 | 24 h UC 2 | DR 3 | Difference 4 |
| Total (n = 39) | ||||||||||||
| 0.75 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 0.8 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 0.9 | 1 | 2 | −1 | 1 | 2 | −1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | −1 |
| 0.95 | 2 | 5 | −3 | 2 | 3 | −1 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 4 | −2 |
| Females (n = 13) | ||||||||||||
| 0.75 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 0.8 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 0.9 | 1 | 2 | −1 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | −1 |
| 0.95 | 2 | 4 | −2 | 5 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 5 | −3 |
| Males (n = 26) | ||||||||||||
| 0.75 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 0.8 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 0.9 | 1 | 3 | −2 | 1 | 2 | −1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | −1 |
| 0.95 | 2 | 5 | −3 | 2 | 4 | −2 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 4 | −2 |
| Protein | Sodium | Potassium | Phosphorus | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D1 | 24 h UC 2 | DR 3 | Difference 4 | 24 h UC 2 | DR 3 | Difference 4 | 24 h UC 2 | DR 3 | Difference 4 | 24 h UC 2 | DR 3 | Difference 4 |
| Total (n = 39) | ||||||||||||
| 30% | 2 | 3 | −1 | 3 | 4 | −1 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 3 | −1 |
| 20% | 3 | 7 | −4 | 6 | 8 | −2 | 3 | 4 | −1 | 3 | 6 | −3 |
| 10% | 10 | 25 | −15 | 23 | 30 | −7 | 12 | 16 | −4 | 12 | 23 | −11 |
| 5% | 38 | 100 | −62 | 89 | 120 | −31 | 48 | 62 | −14 | 47 | 89 | −42 |
| Females (n = 13) | ||||||||||||
| 30% | 2 | 3 | −1 | 4 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 0 |
| 20% | 4 | 5 | −1 | 8 | 6 | 2 | 4 | 3 | 1 | 4 | 5 | −1 |
| 10% | 16 | 20 | −4 | 30 | 21 | 9 | 15 | 10 | 5 | 13 | 17 | −4 |
| 5% | 62 | 77 | −15 | 120 | 82 | 38 | 58 | 40 | 18 | 49 | 67 | −18 |
| Males (n = 26) | ||||||||||||
| 30% | 1 | 3 | −2 | 3 | 4 | −1 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 3 | −1 |
| 20% | 2 | 7 | −5 | 5 | 9 | −4 | 3 | 5 | −2 | 3 | 7 | −4 |
| 10% | 8 | 27 | −19 | 20 | 34 | −14 | 11 | 18 | −7 | 12 | 25 | −13 |
| 5% | 30 | 107 | −77 | 78 | 133 | −55 | 43 | 72 | −29 | 46 | 98 | −52 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Takaoka, T.; Watanabe, D.; Hosokawa, M.; Hosokawa, K.; Kubota, S.; Kawai, Y.; Oono, F.; Inoue, Y.; Zakoji, C.; Oiwa, A.; et al. Within- and Between-Individual Variations in Protein, Sodium, Potassium, and Phosphorus Intake Estimated from Urinary Biomarkers and Dietary Records in Individuals with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1757. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17111757
Takaoka T, Watanabe D, Hosokawa M, Hosokawa K, Kubota S, Kawai Y, Oono F, Inoue Y, Zakoji C, Oiwa A, et al. Within- and Between-Individual Variations in Protein, Sodium, Potassium, and Phosphorus Intake Estimated from Urinary Biomarkers and Dietary Records in Individuals with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Nutrients. 2025; 17(11):1757. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17111757
Chicago/Turabian StyleTakaoka, Tomoya, Daiki Watanabe, Manami Hosokawa, Kana Hosokawa, Satoshi Kubota, Yuko Kawai, Fumi Oono, Yumiko Inoue, Chieko Zakoji, Ako Oiwa, and et al. 2025. "Within- and Between-Individual Variations in Protein, Sodium, Potassium, and Phosphorus Intake Estimated from Urinary Biomarkers and Dietary Records in Individuals with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus" Nutrients 17, no. 11: 1757. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17111757
APA StyleTakaoka, T., Watanabe, D., Hosokawa, M., Hosokawa, K., Kubota, S., Kawai, Y., Oono, F., Inoue, Y., Zakoji, C., Oiwa, A., Sato, A., Yamazaki, M., & Komatsu, M. (2025). Within- and Between-Individual Variations in Protein, Sodium, Potassium, and Phosphorus Intake Estimated from Urinary Biomarkers and Dietary Records in Individuals with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Nutrients, 17(11), 1757. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17111757






