Coix Seed Oil Alleviates Hyperuricemia in Mice by Ameliorating Oxidative Stress and Intestinal Microbial Composition
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Extraction, Esterification, and GC-MS Analysis of Fatty Acids from YRO
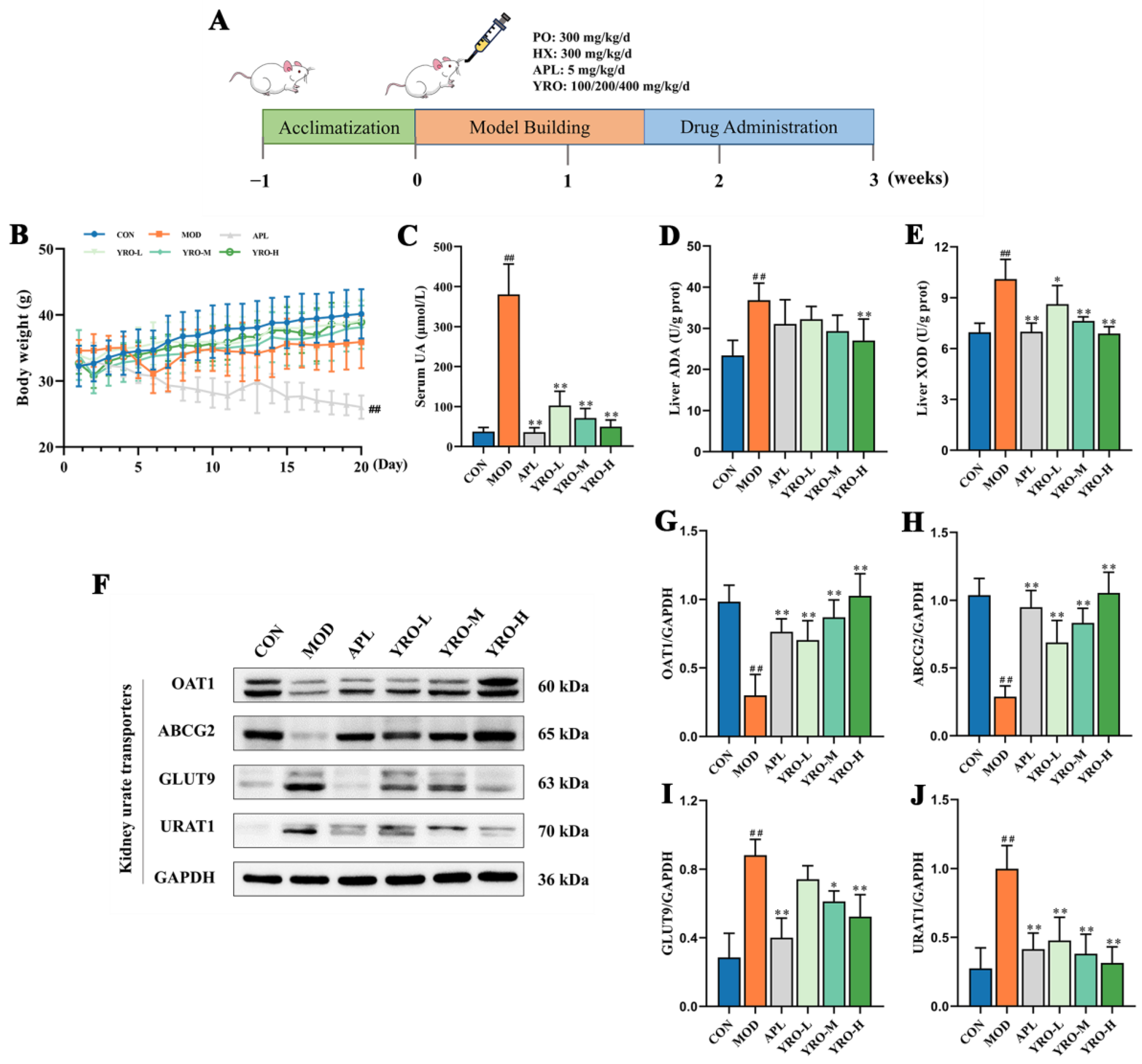
2.3. Animal Model and Experimental Design
2.4. Biochemical and Oxidative Stress Measurements
2.5. Western Blot Analysis
2.6. Histology, Immunohistochemistry (IHC), and Immunofluorescence (IF) Analysis
2.7. Microbial Community Composition and SCFAs Analysis
2.8. Lipid Metabolomics Analysis of Serum
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Fatty Acid Composition of YRO
3.2. YRO Modulated UA Metabolism in HUA Mice
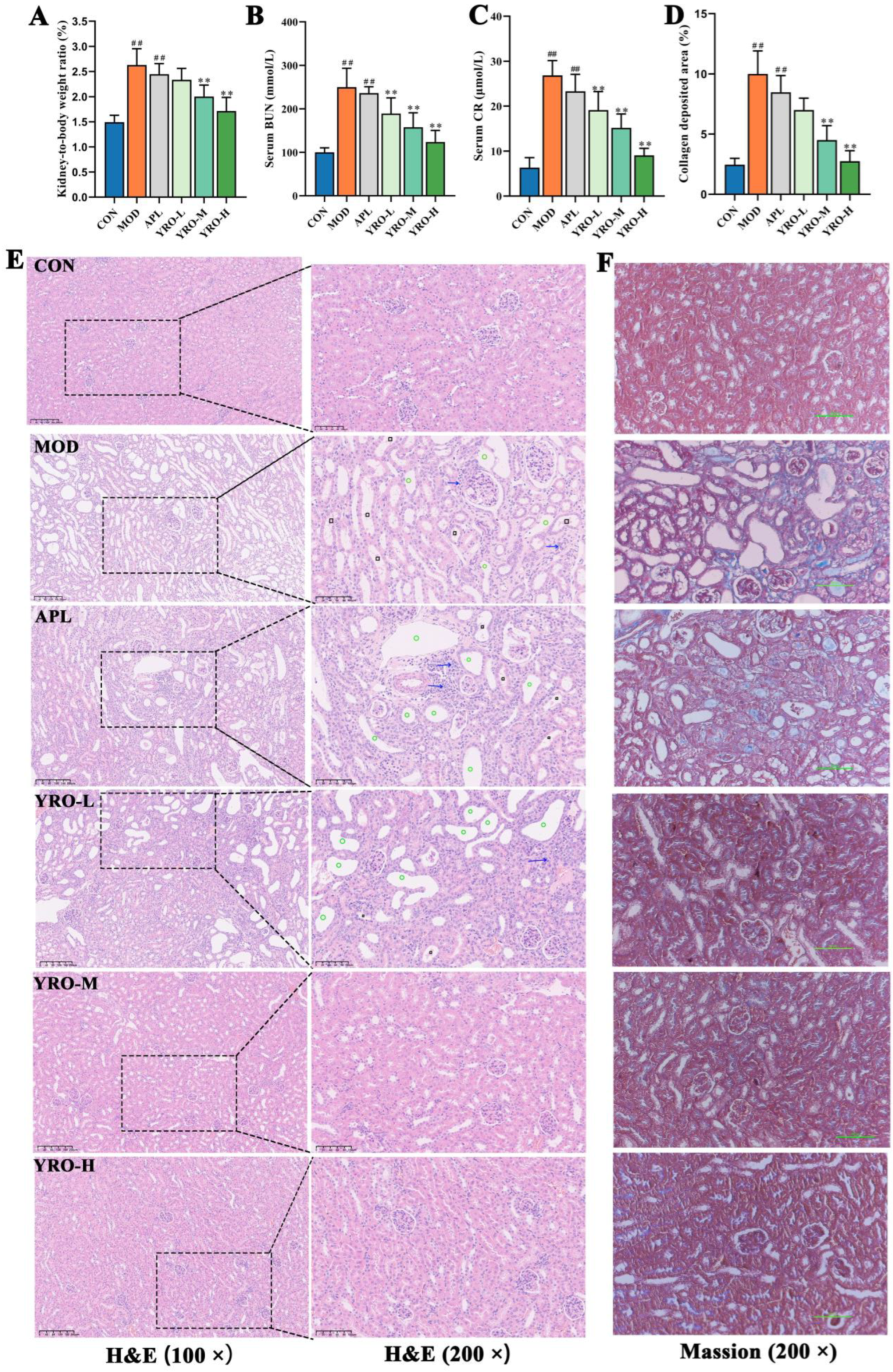
3.3. YRO Attenuated HUA-Induced Renal Injury in HUA Mice
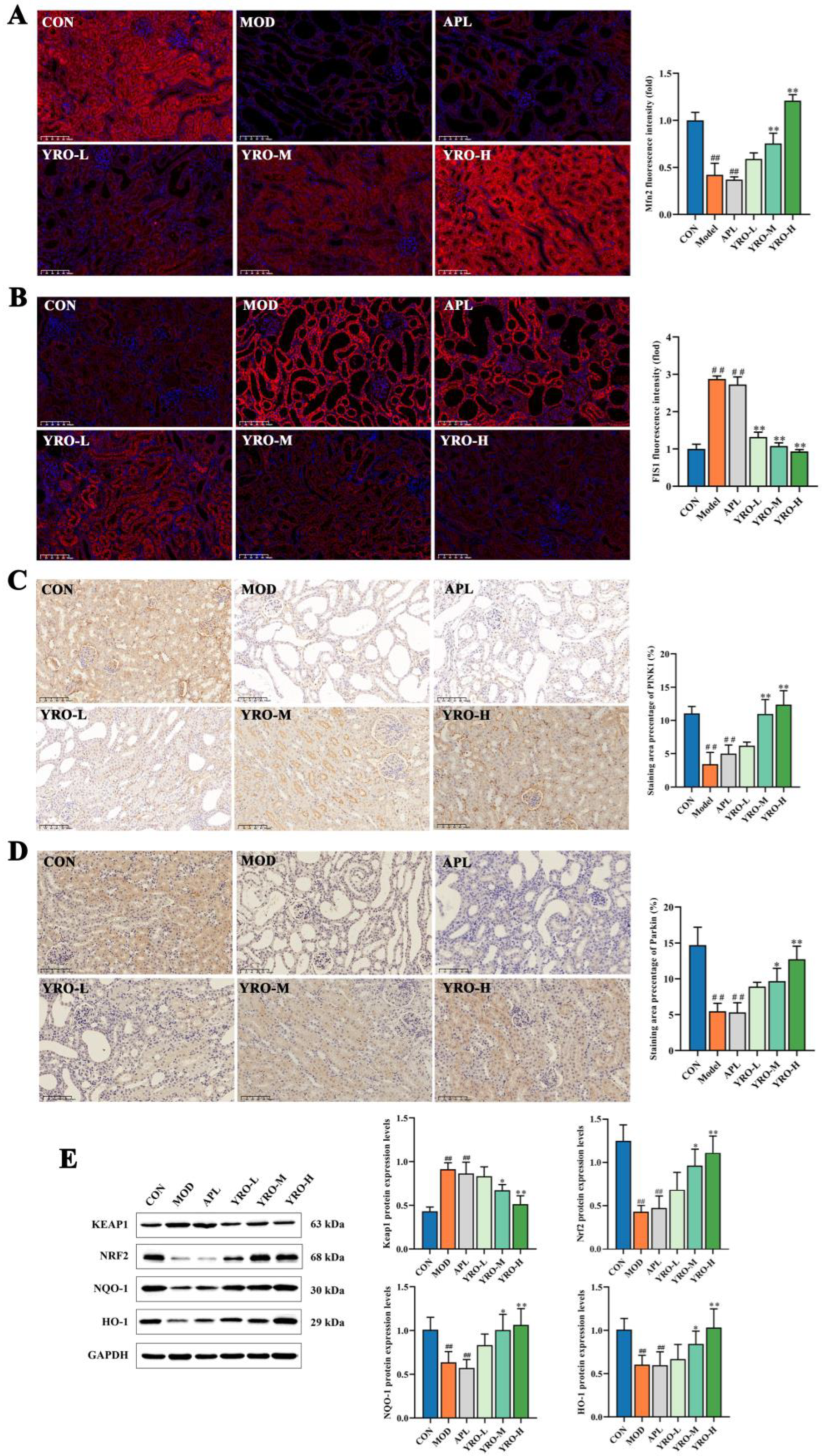
3.4. YRO Mitigated Oxidative Stress and Mitochondrial Dysfunction in HUA Mice
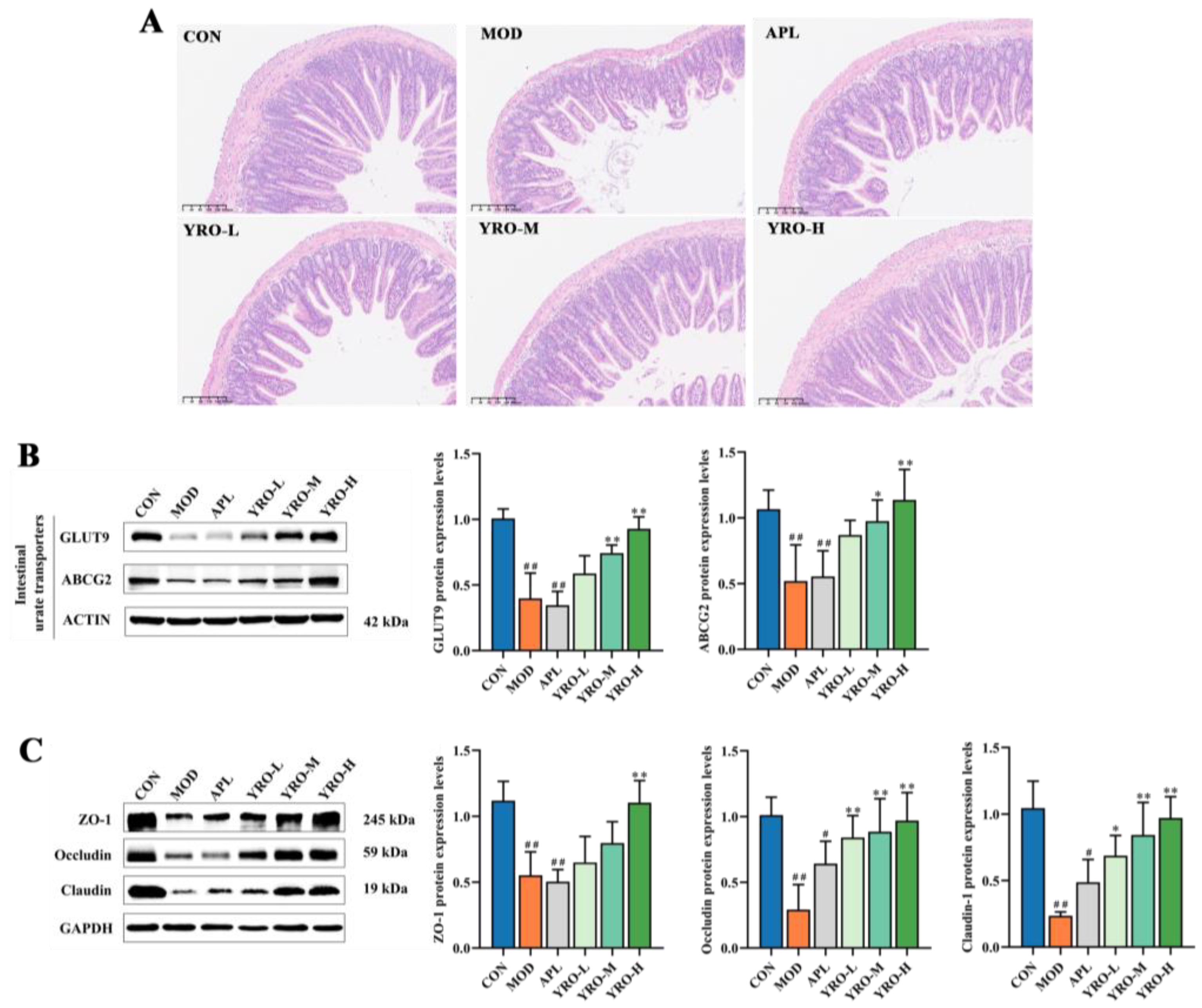
3.5. YRO Enhances Intestinal Barrier Integrity in HUA Mice
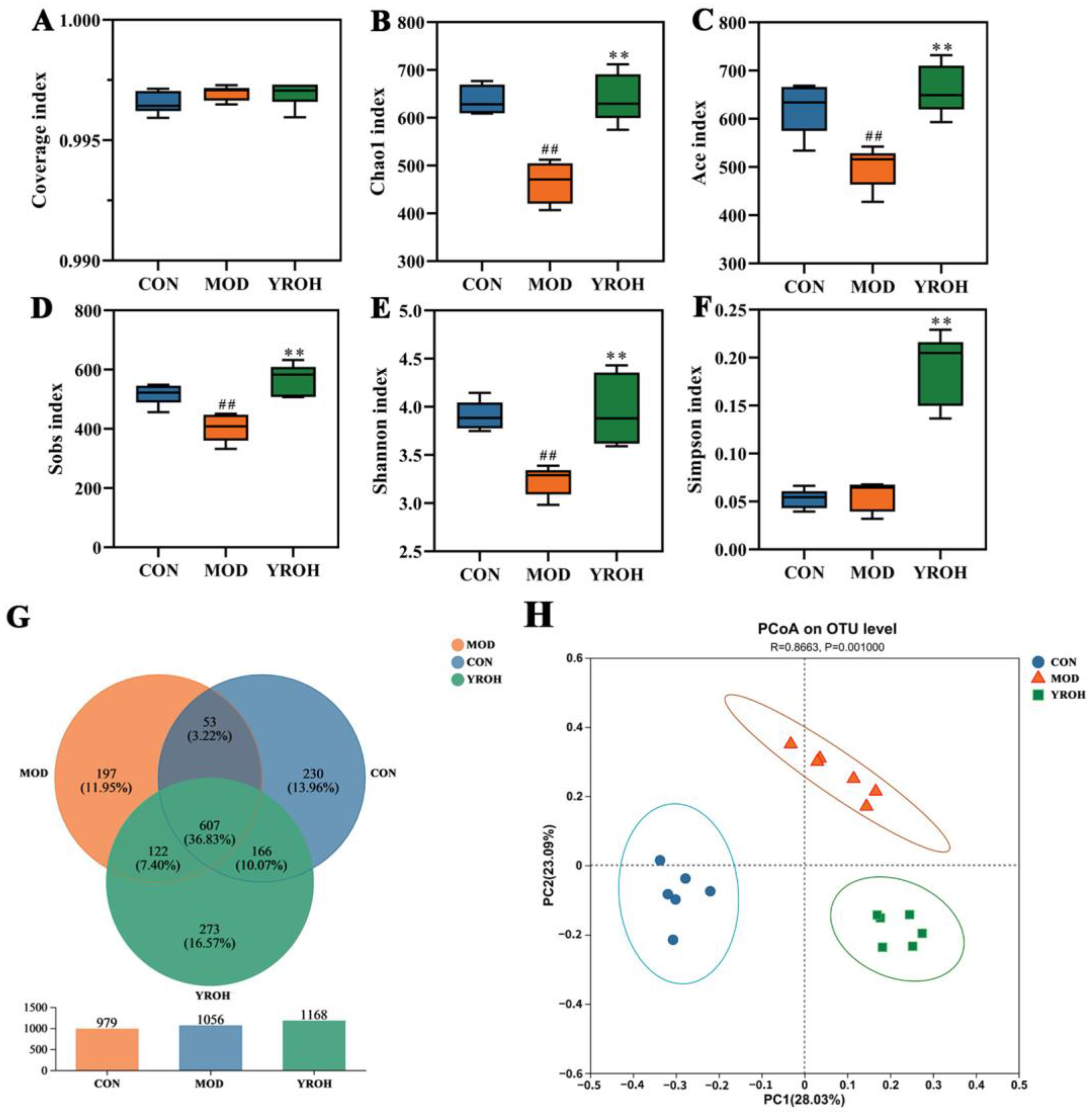
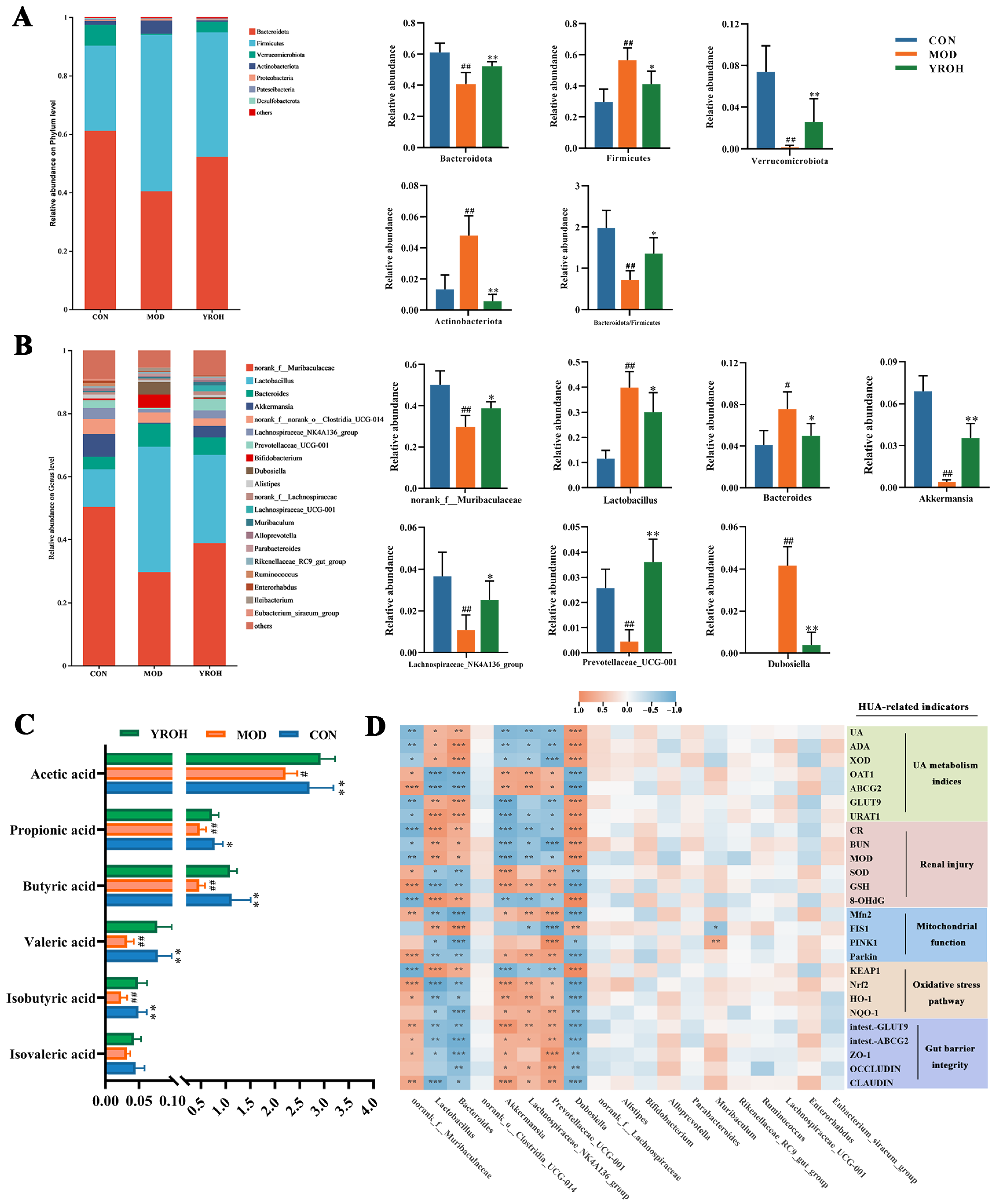
3.6. YRO Modulates Gut Microbiota Diversity and Composition in HUA Mice
3.7. YRO Enhanced SCFAs Production in HUA Mice
3.8. Correlation Between Intestinal Bacterial Abundances and HUA-Related Biomarkers
3.9. YRO Attenuated Lipid Metabolism Disorders in HUA Mice
3.9.1. YRO Modulated Serum Lipid Profile in HUA Mice
3.9.2. KEGG Pathway Enrichment Analysis
3.9.3. YRO Modulated the PI3K/AKT/mTOR Signaling Pathway
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sato, Y.; Feig, D.I.; Stack, A.G.; Kang, D.H.; Lanaspa, M.A.; Ejaz, A.A.; Sánchez-Lozada, L.G.; Kuwabara, M.; Borghi, C.; Johnson, R.J. The case for uric acid-lowering treatment in patients with hyperuricaemia and CKD. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2019, 15, 767–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Luo, L.Y.; Hu, S.S.; Gan, R.Y.; Zeng, L. The chemistry, processing, and preclinical anti-hyperuricemia potential of tea: A comprehensive review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 63, 7065–7090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalbeth, N.; Phipps-Green, A.; Frampton, C.; Neogi, T.; Taylor, W.J.; Merriman, T.R. Relationship between serum urate concentration and clinically evident incident gout: An individual participant data analysis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2018, 77, 1048–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.K.; Choe, J.Y.; Park, S.H.; Lee, H. SAT0542 oxidative stress by monosodium urate crystals promotes renal cell apoptosis through mitochondrial caspase-dependent pathway in human embryonic kidney 293 cells. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2014, 73, 787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharaf El Din, U.A.A.; Salem, M.M.; Abdulazim, D.O. Uric acid in the pathogenesis of metabolic, renal, and cardiovascular diseases: A review. J. Adv. Res. 2017, 8, 537–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.J.; Peng, L.X.; Yin, F.; Fang, J.H.; Cai, L.T.; Zhang, C.J.; Xiang, Z.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Zhang, S.F.; Sheng, H.D.; et al. Research on Coix seed as a food and medicinal resource, it’s chemical components and their pharmacological activities: A review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 319, 117309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, Y.L.; Xu, D.P.; Sun, X.L. Identification of anti-hyperuricemic components from Coix seed. Food Biosci. 2023, 52, 102461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.Q.; Kong, H.X.; Ren, S.; Meng, F.Y.; Liu, R.S.; Jin, H.X.; Zhang, J. Coix seed oil alleviates synovial angiogenesis through suppressing HIF-1α/VEGF-A signaling pathways via SIRT1 in collagen-induced arthritis rats. Chin. Med. 2023, 18, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.Y.; Zhu, A.R.; He, S.L.; Wu, M.J.; Mazhar, M.; Wen, A.Y.; Liu, N.; Qin, L.K.; Miao, S. Anti-lipid-oxidation effects and edible safety evaluation of the oil extracted by a supercritical CO2 process from coix seed fermented by Monascus purpureus. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2023, 12, 1119–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.S.; Li, L.L.; Rui, J.X.; Li, J.X.; Sun, Y.Y.; Cui, D.D.; Xu, B. Tomato seed oil attenuates hyperlipidemia and modulates gut microbiota in C57BL/6J mice. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 4275–4290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.M.; Chen, Z.H.; Li, W.Z.; Su, A.H.; Cui, C. Inquiry of modulatory role of sea buckthorn fruit oil on dyslipidemia and gut microbiota in hyperlipidemia mice. Food Sci. Hum. Wellnes 2025, 14, 9250098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, M.; Brooks, C.; Liu, F.Y.; Sun, L.; Dong, Z. Mitochondrial dynamics: Regulatory mechanisms and emerging role in renal pathophysiology. Kidney Int. 2013, 83, 568–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.Q.; Jian, T.Y.; Gai, Y.N.; Niu, G.T.; Liu, Y.; Meng, X.H.; Li, J.; Lyu, H.; Ren, B.R.; Chen, J. Chicoric acid attenuated renal tubular injury in HFD-induced chronic kidney disease mice through the promotion of mitophagy via the Nrf2/PINK/Parkin pathway. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 2923–2935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mubarak, B.R.; Bell, K.F.S.; Chowdhry, S.; Meakin, P.J.; Baxter, P.S.; McKay, S.; Dando, O.; Ashford, M.L.J.; Gazaryan, I.; Hayes, J.D.; et al. Non-canonical Keap1-independent activation of Nrf2 in astrocytes by mild oxidative stress. Redox Biol. 2021, 47, 102158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.U.H.; Rathore, M.G.; Allende-Vega, N.; Vo, D.N.; Belkhala, S.; Orecchioni, S.; Talarico, G.; Bertolini, F.; Cartron, G.; Lecellier, C.H.; et al. Human leukemic cells performing oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) generate an antioxidant response independently of reactive oxygen species (ROS) production. EBioMedicine 2016, 3, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehmood, A.; Zhao, L.; Wang, C.T.; Hossen, I.; Raka, R.N.; Zhang, H.M. Stevia residue extract increases intestinal uric acid excretion via interactions with intestinal urate transporters in hyperuricemic mice. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 7900–7912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Q.; Chen, Y.H.; Gao, X.X.; Wu, Y.J.; El-Seedi, H.R.; Cao, Y.; Zhao, C. Antihyperuricemic effect of green alga Ulva lactuca Ulvan through regulating urate transporters. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 11225–11235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.X.; Chen, X.L.; Zhou, K.; Wang, L.L.; Zhong, Y.Z.; Peng, J.; Ge, B.S.; Ho, C.T.; Lu, C.Y. Fucoidan dose-dependently alleviated hyperuricemia and modulated gut microbiota in mice. Food Med. Homol. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, B.X.; Chen, T.; Huang, B.X.; Liu, Y.; Chen, J. Untargeted metabolomics reveal the therapeutic effects of Ermiao wan categorized formulas on rats with hyperuricemia. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 281, 114545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Xiao, H.Z.; Zou, X.; Pan, L.; Song, Q.Z.; Hou, L.Y.; Zeng, Y.H.; Han, Y.; Zhou, Z.J. Mechanisms of levan in ameliorating hyperuricemia: Insight into levan on serum metabolites, gut microbiota, and function in hyperuricemia rats. Carbohydr. Polym. 2025, 347, 122665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manto, A.A.; Ramirez, I.F.T.; Arnado, L.M.; Damiotan, C.T.; Sumalpong, E.T.; Ido, A.L.; Arazo, R.O. Oil extraction from Calophyllum inophyllum L. seeds through ultrasonication with n-hexane and petroleum ether as solvents. Biomass Conv. Bioref. 2024, 14, 5423–5434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Wang, X.M.; Yang, Y.; Rong, R.; Gong, L.L.; Jiang, H.Q.; Han, B.B. Research on fusion-fingerprint of Coicis Semen oil. Chin. Tradit. Herbal Drugs. 2014, 45, 1698–1701. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, L.Q.; Lin, G.S.; Yu, Q.X.; Li, Q.P.; Mai, L.T.; Cheng, J.J.; Xie, J.H.; Liu, Y.H.; Su, Z.R.; Li, Y.C. Anti-hyperuricemic and nephroprotective effects of dihydroberberine in potassium oxonate- and hypoxanthine-induced hyperuricemic mice. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 645879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.F.; Xu, L.Q.; Jiang, L.Y.; Wu, Y.L.; Wei, L.; Wu, X.L.; Xiao, S.H.; Liu, Y.H.; Gao, C.J.; Cai, J.; et al. Sonneratia apetala seed oil attenuates potassium oxonate/hypoxanthine-induced hyperuricemia and renal injury in mice. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 9416–9431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Zhou, Q.; Zhou, L.F.; Sun, Y.S.; Han, X.; Cheng, X.L.; Wu, M.Y.; Lv, W.; Wang, J.; Zhao, W. Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd) bran saponins alleviate hyperuricemia and inhibit renal injury by regulating the PI3K/AKT/NFκB signaling pathway and uric acid transport. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 6635–6649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.Y.; Si, F.; Hao, R.L.; Zheng, J.Q.; Zhang, C. Nuciferine protects against obesity-induced nephrotoxicity through its hypolipidemic, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant effects. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 18769–18779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Zhang, X.Q.; Zheng, X.; Gao, J.R.; Shang, M.F.; Xu, J.H.; Liang, H. Folic acid protects against hyperuricemia in C57BL/6J mice via ameliorating gut–kidney axis dysfunction. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 15787–15803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.M.; Wang, P.; Teka, T.; Zhang, Y.C.; Yang, W.Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, T.; Liu, L.X.; Han, L.F.; Liu, C.X. 1H NMR and UHPLC/Q-Orbitrap-MS-based metabolomics combined with 16S rRNA gut microbiota analysis revealed the potential regulation mechanism of Nuciferine in hyperuricemia rats. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 14059–14070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Wahab, H.M.F.; Mohamed, M.A.; El Sayed, H.H.; Bauomy, A.E. Modulatory effects of rice bran and its oil on lipid metabolism in insulin resistance rats. J. Food Biochem. 2017, 41, e12318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Kamouni, S.; El Kebbaj, R.; Andreoletti, P.; El Ktaibi, A.; Rharrassi, I.; Essamadi, A.; El Kebbaj, M.S.; Mandard, S.; Latruffe, N.; Vamecq, J.; et al. Protective effect of argan and olive oils against LPS-induced oxidative stress and inflammation in mice livers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ait Eldjoudi, D.; Ruiz-Fernandez, C.; González-Rodriguez, M.; Ait Atmane, S.; Cordero-Barreal, A.; Farrag, Y.; Pino, J.; Sineiro, J.; Lago, F.; Conde-Aranda, J.; et al. Analgesic and antiinflammatory effects of Nigella orientalis L. seeds fixed oil: Pharmacological potentials and molecular mechanisms. Phytother. Res. 2022, 36, 1372–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, R.X.; Chen, Q.; Li, Z.; Wang, D.; Wu, Y.Z.; Liu, M.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, T. Eurycomanol alleviates hyperuricemia by promoting uric acid excretion and reducing purine synthesis. Phytomedicine 2022, 96, 153850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Fan, X.X.; Zhao, S.L.; Ishii, Y.; Yu, B.Y.; Li, R.S. Supplements extracted from Lophatherum Gracile Brongn. ameliorates hyperuricemia by regulating nucleotide metabolic enzymes and urate transporters. Food Med. Homol. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spoto, B.; Politi, C.; Pizzini, P.; Parlongo, R.M.; Testa, A.; Mobrici, M.; Tripepi, G.L.; Mallamaci, F.; Zoccali, C. 8-hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine, a biomarker of oxidative DNA injury, in diabetic kidney disease. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2024, 35, 103722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, G.X.; Huang, R.L.; Xie, J.H.; Zhong, L.J.; Wu, X.Y.; Qin, Z.H.; Su, Z.R.; Chen, J.N.; Yang, X.B.; Dou, Y.X. Hypouricemic and nephroprotective effects of palmatine from Cortex Phellodendri Amurensis: A uric acid modulator targeting Keap1-Nrf2/NLRP3 axis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023, 301, 115775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.F.; Ma, Y.F.; Guan, K.F.; Zhao, L.; Ma, Y.; Wang, R. Whey protein peptide Pro-Glu-Trp ameliorates hyperuricemia by enhancing intestinal uric acid excretion, modulating the gut microbiota, and protecting the intestinal barrier in rats. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 2573–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Wei, J.; Liu, P.D. Attacking the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway for targeted therapeutic treatment in human cancer. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2022, 85, 69–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.Q.; Zeng, Y.P.; Wang, R.J.; Pang, J.; Wang, X.; Pan, Z.J.; Jin, Y.F.; Chen, Y.; Yang, Y.; Ling, W.H. Resveratrol improves hyperuricemia and ameliorates renal injury by modulating the gut microbiota. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.Y.; Ji, H.W.; Song, W.K.; Peng, S.; Zhan, S.H.; Qu, Y.S.; Chen, M.; Zhang, D.; Liu, S.C. Hypouricemic, hepatoprotective and nephroprotective roles of oligopeptides derived from Auxis thazard protein in hyperuricemic mice. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 11838–11848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balal, A.; Obeidat, A.M.; Fadul, K.Y.; Sati, W.; Ahmed, S.M.I.; Elgassim, M.; Nahid, S.; Balal, A.; Obeidat, A.M.; Fadul, K.Y.; et al. Sepsis-induced coagulopathy: From pathophysiology to patient care. In Septic Shock—From Pathophysiology to Patient Care; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2024; ISBN 978-0-85014-708-7. [Google Scholar]
- Ponticelli, C.; Podestà, M.A.; Moroni, G. Hyperuricemia as a trigger of immune response in hypertension and chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2020, 98, 1149–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; He, L.; Liu, J.; Dong, Z. Mitophagy: Mitophagy: Mitophagy: Basic mechanism and potential role in kidney diseases. Kidney Dis. 2015, 1, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovira-Llopis, S.; Bañuls, C.; Diaz-Morales, N.; Hernandez-Mijares, A.; Rocha, M.; Victor, V.M. Mitochondrial dynamics in type 2 diabetes: Pathophysiological implications. Redox Biol. 2017, 11, 637–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.W.; Zheng, L.S.; Zhang, J.; Liu, X.J.; Wu, Z.M. Inhibition of ferroptosis by up-regulating Nrf2 delayed the progression of diabetic nephropathy. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2021, 162, 435–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Lin, X.; Yang, X.M.; Yang, Y.L. Research progress on related mechanisms of uric acid activating NLRP3 inflammasome in chronic kidney disease. Ren. Fail. 2022, 44, 615–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, T.; Wang, S.F.; Zhang, X.Y.; Zai, W.J.; Fan, J.J.; Chen, W.; Bian, Q.; Luan, J.Y.; Shen, Y.L.; Zhang, Y.D.; et al. Kidney protection effects of dihydroquercetin on diabetic nephropathy through duppressing ROS and NLRP3 inflammasome. Phytomedicine 2018, 41, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.Q.; Huang, Y.M.; Lu, G.D.; Sun, N.; Wang, R.; Lu, C.Y.; Ding, L.J.; Han, J.J.; Zhou, J.; Li, Y.; et al. Novel anti-hyperuricemic hexapeptides derived from Apostichopus japonicus hydrolysate and their modulation effects on the gut microbiota and host microRNA profile. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 3865–3878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.Q.; Ruan, F.K.; Chen, Z.Y.; Han, J.R.; Ding, X.Y.; Han, C.S.; Ye, L.X.; Yang, C.; Yu, Y.; Zuo, Z.H.; et al. Phenanthrene-induced hyperuricemia with intestinal barrier damage and the protective role of theabrownin: Modulation by gut microbiota-mediated bile acid metabolism. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 949, 174923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, M.J.; Cao, X.Q.; Liang, Y.H.; Li, Q.Y.; Chen, S.M.; Zhou, L.P.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Guo, Y. Neuroprotection of rhubarb extract against cerebral ischaemia-reperfusion injury via the gut-brain axis pathway. Phytomedicine 2024, 126, 155254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.N.; Li, F.F.; Quan, C.H.; Jin, D. Intestinal flora: A potential pathogenesis mechanism and treatment strategy for type 1 diabetes mellitus. Gut Microbes. 2024, 16, 2423024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crovesy, L.; Masterson, D.; Rosado, E.L. Profile of the gut microbiota of adults with obesity: A systematic review. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 74, 1251–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.H.; Zhou, J.X.; Zhao, L.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, S.R.; Zhang, L.B.; Zhou, F. Ferulic acid supplementation alleviates hyperuricemia in high-fructose/fat diet-fed rats via promoting uric acid excretion and mediating the gut microbiota. Food Funct. 2023, 14, 1710–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.F.; Zhang, B.W.; Zhao, X.L.; Zhang, P.X.; Guo, J.T.; Zhuang, Y.; Wang, S. Coffee leaf tea extracts improve hyperuricemia nephropathy and its associated negative effect in gut microbiota and amino acid metabolism in rats. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 17775–17787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Q.; Lai, Y.; Zhang, D.; Lei, H.; Wang, F.; Guo, X.R.; Song, C. Gut microbiota regulation and prebiotic properties of polysaccharides from Oudemansiella raphanipes mushroom. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2023, 39, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.P.; Zhang, F.; Ding, X.Y.; Wu, G.J.; Lam, Y.Y.; Wang, X.J.; Fu, H.Q.; Xue, X.H.; Lu, C.H.; Ma, J.L.; et al. Gut bacteria selectively promoted by dietary fibers alleviate type 2 diabetes. Science 2018, 359, 1151–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, C.; Dong, K.; Shen, Y.; Sun, Y.L.; Li, W.Y.; Man, C.X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Q.Y.; Jiang, Y.J. Mechanism of Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus JY027 alleviating hyperuricemia in mice through gut-kidney axis. Food Biosci. 2024, 61, 104757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilstrup, M.; Hammer, K.; Ruhdal Jensen, P.; Martinussen, J. Nucleotide metabolism and its control in lactic acid bacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2005, 29, 555–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.J.; Werlinger, P.; Suh, J.W.; Cheng, J.H. Potential probiotic Lacticaseibacillus paracasei MJM60396 prevents hyperuricemia in a multiple way by absorbing purine, suppressing xanthine oxidase and regulating urate excretion in mice. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.T.; Xiu, W.J.; Liu, J.K.; Yang, Y.; Hou, X.G.; Zheng, Y.Y.; Wu, T.T.; Wu, C.X.; Xie, X. Gut microbiota characterization in patients with asymptomatic hyperuricemia: Probiotics increased. Bioengineered 2021, 121, 7263–7275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Yang, J.L.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, Y.F.; Tang, Y.Y.; Xu, X.D.; He, H.D. Alterations of gut microbiota and metabolome in early chronic kidney disease patients complicated with hyperuricemia. Heliyon 2023, 9, e20328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, X.; Guo, Z.T.; Ao, L.; Yang, Y.L.; Liu, C.Y.; Gu, Z.H.; Xin, Y.; Li, M.Y.; Zhang, L. Integrated cell metabolomics and serum metabolomics to reveal the mechanism of hypouricemic effect of Inonotus hispidus. J. Funct. Foods 2023, 105, 105572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.X.; Li, B.W.; Lam, S.M.; Shui, G.H. Integration of lipidomics and metabolomics for in-depth understanding of cellular mechanism and disease progression. J. Genet. Genomics 2020, 47, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Zhao, K.L.; Luo, J.; Tian, J.H.; Zheng, F.X.; Lin, X.M.; Xie, Z.J.; Jiang, H.Y.; Li, Y.M.; Zhao, Z.A.; et al. Piperine improves hyperuricemic nephropathy by inhibiting URAT1/GLUT9 and the AKT-mTOR pathway. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 6565–6574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.Z.; Zhong, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, Y.Y.; Huang, Q.L.; Huang, Z.; Wang, Y.C.; Ye, H.; Zeng, X.B.; Zheng, X.B. Acetylshikonin inhibits colorectal cancer growth via PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. Chin. Med. 2018, 9, 126–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhao, X.; Zhu, J.X.; Mo, S.F.; Pan, Y.; Kong, L.D. Effects of cassia oil on serum and hepatic uric acid levels in oxonate-induced mice and xanthine dehydrogenase and xanthine oxidase activities in mouse liver. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2006, 103, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.H.; Liang, M.L.; Su, W.J.; Yang, J.L.; Pu, F.X.; Xie, Z.F.; Jin, K.L.; Polyakov, N.E.; Dushkin, A.V.; Su, W.K. Self-assembled nanocapsules of celery (Apium graveolens Linn) seed oil: Mechanochemical preparation, characterization and urate-lowering activity. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Tec. 2021, 66, 102810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F. Coix: Chemical composition and health effects. Trends Food Sci. Tech. 2017, 61, 160–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Qi, Q.; Liu, Z.H.; Zhang, M.; Liu, H.Q. Soy consumption and serum uric acid levels: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 975718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, G.; Wang, X.; Dong, H.; Yu, J.; Li, T.; Wang, X. Coix Seed Oil Alleviates Hyperuricemia in Mice by Ameliorating Oxidative Stress and Intestinal Microbial Composition. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1679. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17101679
Wu G, Wang X, Dong H, Yu J, Li T, Wang X. Coix Seed Oil Alleviates Hyperuricemia in Mice by Ameliorating Oxidative Stress and Intestinal Microbial Composition. Nutrients. 2025; 17(10):1679. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17101679
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Guozhen, Xinming Wang, Hongjing Dong, Jinqian Yu, Tao Li, and Xiao Wang. 2025. "Coix Seed Oil Alleviates Hyperuricemia in Mice by Ameliorating Oxidative Stress and Intestinal Microbial Composition" Nutrients 17, no. 10: 1679. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17101679
APA StyleWu, G., Wang, X., Dong, H., Yu, J., Li, T., & Wang, X. (2025). Coix Seed Oil Alleviates Hyperuricemia in Mice by Ameliorating Oxidative Stress and Intestinal Microbial Composition. Nutrients, 17(10), 1679. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17101679






