Artemisiae Iwayomogii Herba Protects Dopaminergic Neurons Against 1-Methyl-4-phenylpyridinium/1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine Neurotoxicity in Models of Parkinson’s Disease
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation and Standardization of AIK Extract
2.3. ABTS Radical Cation Scavenging Assay
2.4. DPPH Radical Scavenging Assay
2.5. Cell Culture and Drug Treatment
2.6. Measurement of Cell Viability
2.7. Western Blotting
2.8. Animals and Drug Treatment
2.9. Rotarod Test
2.10. Preparation of Brain Tissues
2.11. Immunohistochemistry and Immunofluorescence
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
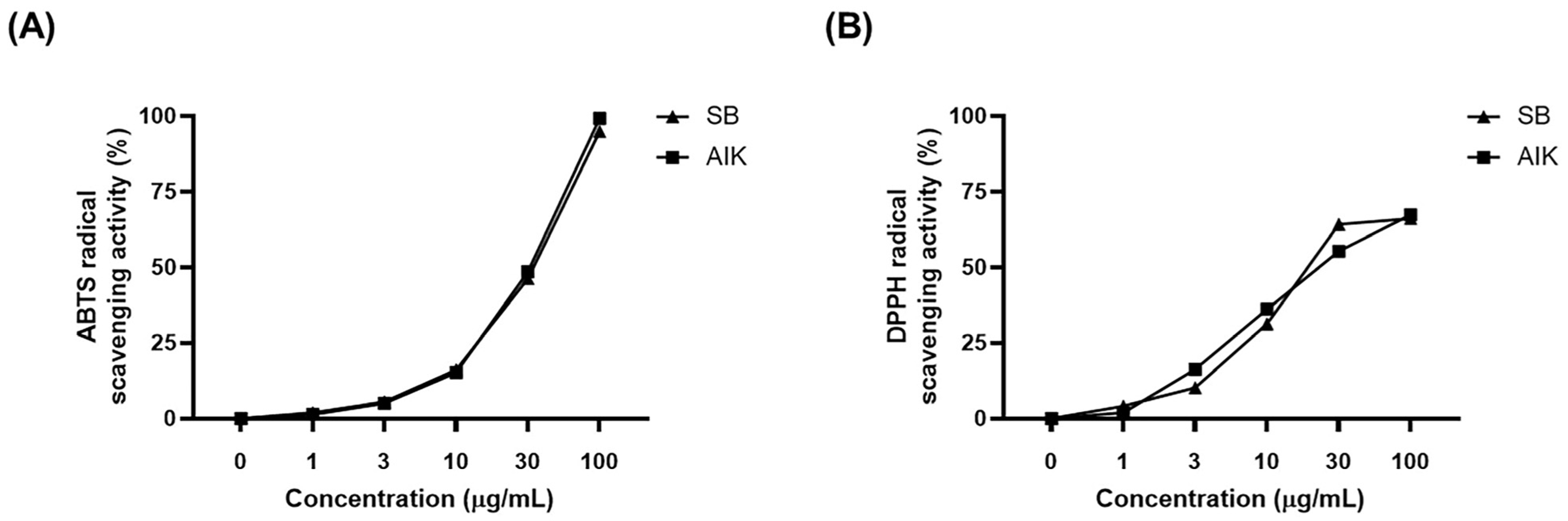
3.1. Effects of AIK on Free Radical Scavenging Activities
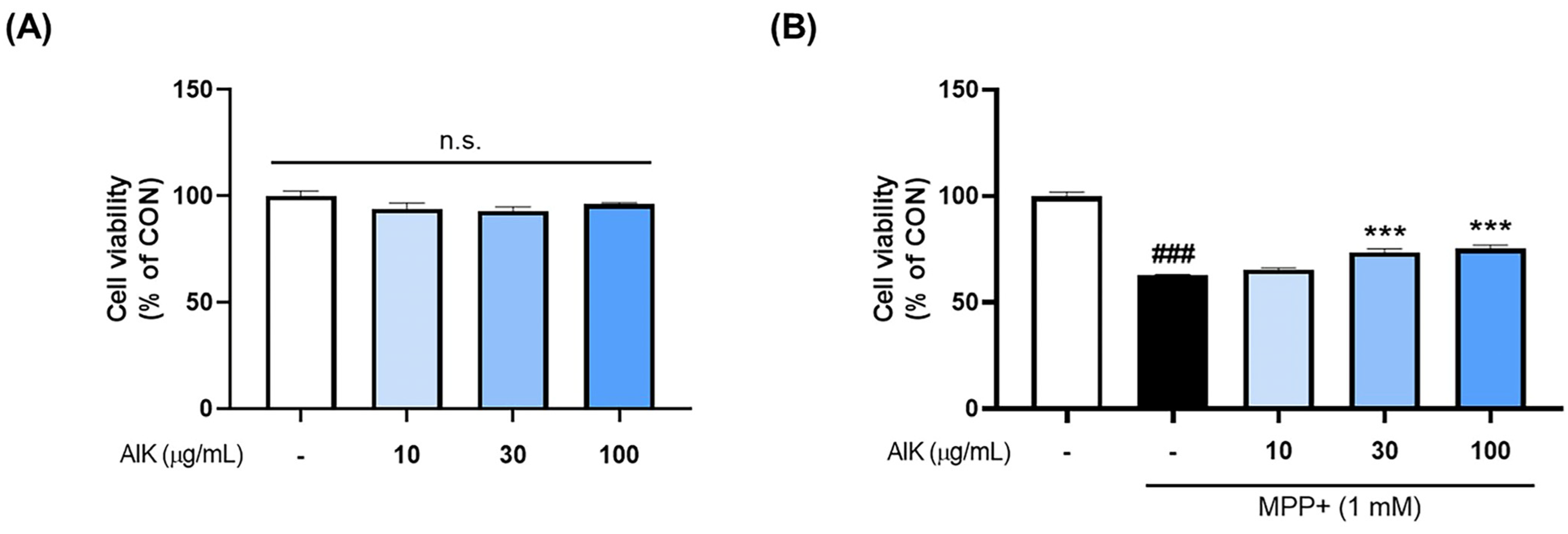
3.2. Effects of AIK on MPP+-Induced Cytotoxicity in PC12 Cells
3.3. Effects of AIK on Akt/GSK3β/Nrf2 Signaling Pathway in PC12 Cells
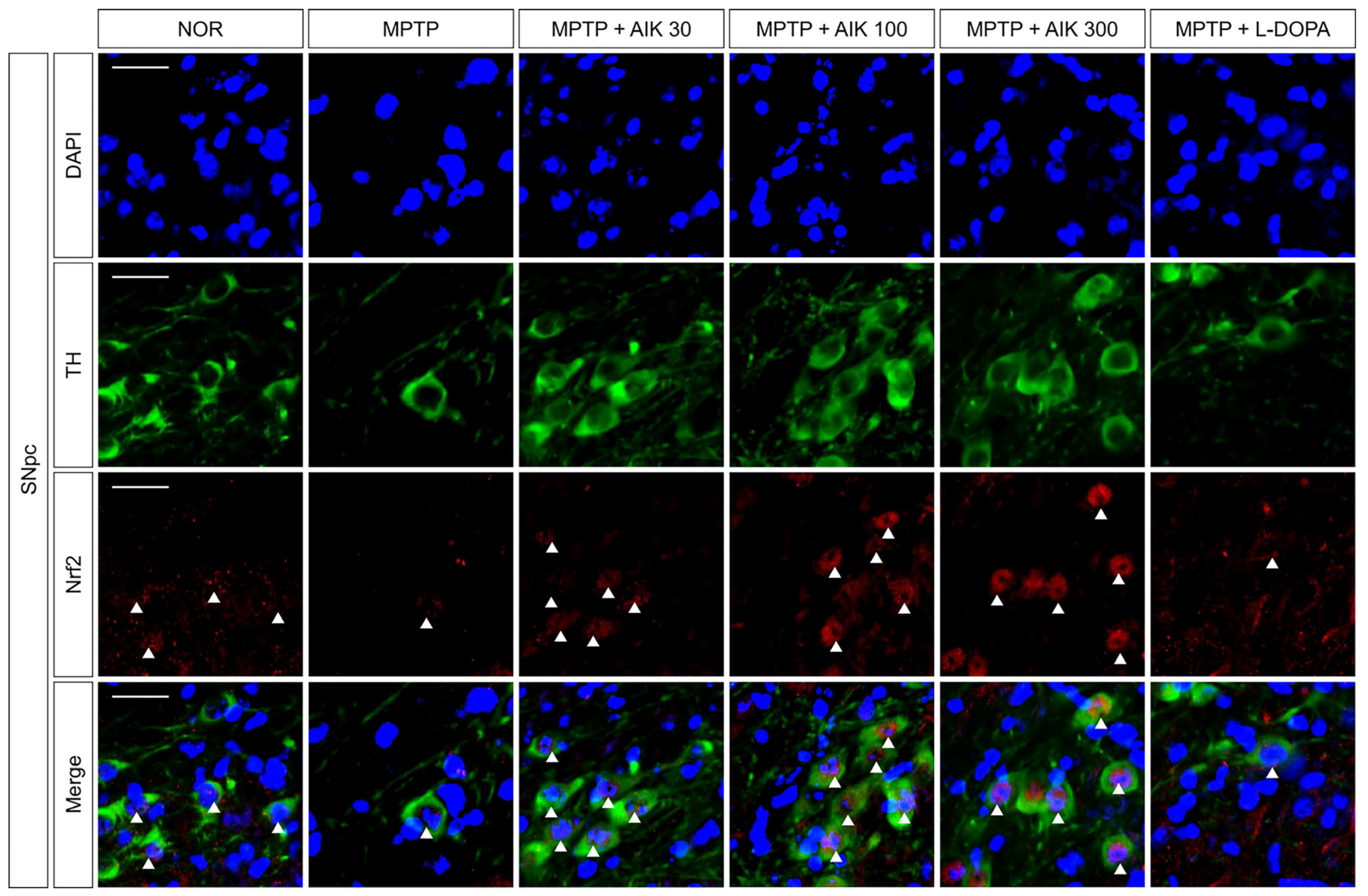
3.4. Effects of AIK on the Nuclear Translocation of Nrf2 in Dopaminergic Neurons in Mice with MPTP-Induced PD
3.5. Effects of AIK on Dopaminergic Neuronal Loss in Mice with MPTP-Induced PD
3.6. Effects of AIK on Behavioral Impairment in Mice with MPTP-Induced PD
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABC | avidin–biotin complex |
| ABTS | 2,2-azinobis-(3-ethyl-benzthiazolin-6-sulphonic acid) |
| AIK | aerial parts of Artemisia iwayomogi Kitamura |
| Akt | protein kinase B |
| ANOVA | analysis of variance |
| AREs | antioxidant response elements |
| BVR | biliverdin reductase |
| CON | control |
| DAB | 3,3′-diaminobenzidine |
| DAPI | 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole |
| DAT | dopamine transporter |
| DPPH | 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl |
| DRT | dopamine replacement therapy |
| GSK3β | glycogen synthase kinase-3β |
| HO-1 | heme oxygenase-1 |
| HRP | horseradish peroxidase |
| IC50 values | half-maximal inhibitory concentration |
| IgG | immunoglobulin G |
| Keap1 | Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 |
| L-DOPA | levodopa |
| LPS | lipopolysaccharide |
| MPP+ | 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium |
| MPTP | 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine |
| MTT | 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl-2H-tetrazolium bromide |
| Nrf2 | nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 |
| PBS | phosphate-buffered saline |
| PCNA | proliferating cell nuclear antigen |
| PD RIPA | Parkinson’s disease radio-immunoprecipitation assay lysis buffer |
| ROS | reactive oxygen species |
| SB | Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi root |
| S.E.M | standard error of the mean |
| SN | substantia nigra |
| SNpc | substantia nigra pars compacta |
| ST | striatum |
| TH | tyrosine hydroxylase |
References
- Ramesh, S.; Arachchige, A. Depletion of dopamine in Parkinson’s disease and relevant therapeutic options: A review of the literature. AIMS Neurosci. 2023, 10, 200–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moustafa, A.A.; Chakravarthy, S.; Phillips, J.R.; Gupta, A.; Keri, S.; Polner, B.; Frank, M.J.; Jahanshahi, M. Motor symptoms in Parkinson’s disease: A unified framework. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2016, 68, 727–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Dai, L.; Chen, S.; Zhang, Z.; Fang, X.; Zhang, Z. Protein-protein interactions regulating alpha-synuclein pathology. Trends Neurosci. 2024, 47, 209–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrazzoli, D.; Carter, A.; Ustun, F.S.; Palamara, G.; Ortelli, P.; Maestri, R.; Yucel, M.; Frazzitta, G. Dopamine Replacement Therapy, Learning and Reward Prediction in Parkinson’s Disease: Implications for Rehabilitation. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, V.L.; Dawson, T.M. Promising disease-modifying therapies for Parkinson’s disease. Sci. Transl. Med. 2019, 11, eaba1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aryal, S.; Skinner, T.; Bridges, B.; Weber, J.T. The Pathology of Parkinson’s Disease and Potential Benefit of Dietary Polyphenols. Molecules 2020, 25, 4382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, H.E.; Paek, S.H. Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Parkinson’s Disease. Exp. Neurobiol. 2015, 24, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, V.; Junn, E.; Mouradian, M.M. The role of oxidative stress in Parkinson’s disease. J. Parkinsons Dis. 2013, 3, 461–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabisiak, T.; Patel, M. Crosstalk between neuroinflammation and oxidative stress in epilepsy. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 976953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.D.; Zhao, X.; Li, Y.; Li, G.R.; Liu, X.L. Damage to dopaminergic neurons by oxidative stress in Parkinson’s disease (Review). Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 41, 1817–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salim, S. Oxidative Stress and the Central Nervous System. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2017, 360, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loeffler, D.A.; DeMaggio, A.J.; Juneau, P.L.; Havaich, M.K.; LeWitt, P.A. Effects of enhanced striatal dopamine turnover in vivo on glutathione oxidation. Clin. Neuropharmacol. 1994, 17, 370–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abad, M.J.; Bedoya, L.M.; Apaza, L.; Bermejo, P. The artemisia L. Genus: A review of bioactive essential oils. Molecules 2012, 17, 2542–2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryu, S.H.; Jo, H.; Kim, J.W.; Youn, H.J.; Kim, K.B. Four-Week Repeated Oral Toxicity Study of AIP1, a Water-soluble Carbohydrate Fraction from Artemisia iwayomogi in Mice. Toxicol. Res. 2011, 27, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, T.Y.; Park, J.S.; Kim, S.H. Artemisia iwayomogi inhibits immediate-type allergic reaction and inflammatory cytokine secretion. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 2006, 28, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, E.J.; Nan, J.X.; Kim, J.Y.; Kang, H.C.; Choi, J.H.; Lee, S.J.; Lee, B.H.; Kim, S.J.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, Y.C.; et al. The ethanol-soluble part of a hot-water extract from Artemisia iwayomogi inhibits liver fibrosis induced by carbon tetrachloride in rats. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2000, 52, 875–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.M.; Vetrivel, P.; Kim, H.H.; Ha, S.E.; Saralamma, V.V.G.; Kim, G.S. Artemisia iwayomogi (Dowijigi) inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation in RAW264.7 macrophages by suppressing the NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 19, 2161–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Narayan, V.P.; Hong, E.Y.; Whang, W.K.; Park, T. Artemisia iwayomogi Extract Attenuates High-Fat Diet-Induced Hypertriglyceridemia in Mice: Potential Involvement of the Adiponectin-AMPK Pathway and Very Low Density Lipoprotein Assembly in the Liver. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Ding, Y.; Yan, X.T.; Kim, Y.H.; Jang, H.D. Scopoletin and scopolin isolated from Artemisia iwayomogi suppress differentiation of osteoclastic macrophage RAW 264.7 cells by scavenging reactive oxygen species. J. Nat. Prod. 2013, 76, 615–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, I.G.; Huh, E.; Kim, N.; Lee, S.; Choi, J.G.; Hong, J.; Oh, M.S. Artemisiae Iwayomogii Herba inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced neuroinflammation by regulating NF-kappaB and MAPK signaling pathways. Phytomedicine 2021, 84, 153501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Zhu, H.; Liu, Z.; He, X.; Sun, J.; Li, Y.; Wu, X.; Pehrsson, P.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, L. Chemical Compositions of Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi. (Huangqin) Extracts and Their Effects on ACE2 Binding of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein, ACE2 Activity, and Free Radicals. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, N.; Choi, J.G.; Park, S.; Lee, J.K.; Oh, M.S. Butterbur Leaves Attenuate Memory Impairment and Neuronal Cell Damage in Amyloid Beta-Induced Alzheimer’s Disease Models. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju, I.G.; Lee, S.; Im, H.; Kim, J.H.; Eo, H.; Oh, M.S. Artemisiae Iwayomogii Herba mitigates excessive neuroinflammation and Abeta accumulation by regulating the pro-inflammatory response and autophagy-lysosomal pathway in microglia in 5xFAD mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Geroscience 2025, 47, 1957–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, W.; Chen, C.; Zhong, Y.; An, J.; Zhang, X.; Yu, Y.; Yu, Z.; Fu, J. PI3K/Akt pathway mediates Nrf2/ARE activation in human L02 hepatocytes exposed to low-concentration HBCDs. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 12434–12440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loboda, A.; Damulewicz, M.; Pyza, E.; Jozkowicz, A.; Dulak, J. Role of Nrf2/HO-1 system in development, oxidative stress response and diseases: An evolutionarily conserved mechanism. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 73, 3221–3247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustapha, M.; Mat Taib, C.N. MPTP-induced mouse model of Parkinson’s disease: A promising direction of therapeutic strategies. Bosn. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2021, 21, 422–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zawada, W.M.; Banninger, G.P.; Thornton, J.; Marriott, B.; Cantu, D.; Rachubinski, A.L.; Das, M.; Griffin, W.S.; Jones, S.M. Generation of reactive oxygen species in 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium (MPP+) treated dopaminergic neurons occurs as an NADPH oxidase-dependent two-wave cascade. J. Neuroinflamm. 2011, 8, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Yang, J.; Li, Y.; Xie, J.; Wang, J. Heme oxygenase-1: The roles of both good and evil in neurodegenerative diseases. J. Neurochem. 2023, 167, 347–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, S.K.; Chen, S.E.; Chang, L.C. The Role of HO-1 and Its Crosstalk with Oxidative Stress in Cancer Cell Survival. Cells 2021, 10, 2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhayay, S.; Mehan, S. Targeting Nrf2/HO-1 anti-oxidant signaling pathway in the progression of multiple sclerosis and influences on neurological dysfunctions. Brain Disord. 2021, 3, 100019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojo, A.I.; Sagarra, M.R.; Cuadrado, A. GSK-3beta down-regulates the transcription factor Nrf2 after oxidant damage: Relevance to exposure of neuronal cells to oxidative stress. J. Neurochem. 2008, 105, 192–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Kim, K.M.; Jeong, J.U.; Shin, J.H.; Shin, J.M.; Bang, K.T. Nrf2-Heme oxygenase-1 modulates autophagy and inhibits apoptosis triggered by elevated glucose levels in renal tubule cells. Kidney Res. Clin. Pract. 2019, 38, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Li, Y.; Wang, X. TDAG51-Deficiency Podocytes are Protected from High-Glucose-Induced Damage Through Nrf2 Activation via the AKT-GSK-3beta Pathway. Inflammation 2022, 45, 1520–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Li, H.; Bai, S.; Xu, Z.; Jiao, Y. Loss of serine/threonine protein kinase 25 in retinal ganglion cells ameliorates high glucose-elicited damage through regulation of the AKT-GSK-3beta/Nrf2 pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2022, 600, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funes, S.C.; Rios, M.; Fernandez-Fierro, A.; Covian, C.; Bueno, S.M.; Riedel, C.A.; Mackern-Oberti, J.P.; Kalergis, A.M. Naturally Derived Heme-Oxygenase 1 Inducers and Their Therapeutic Application to Immune-Mediated Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo, J.A.; Zhang, M.; Yin, F. Heme oxygenase-1, oxidation, inflammation, and atherosclerosis. Front. Pharmacol. 2012, 3, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consoli, V.; Sorrenti, V.; Grosso, S.; Vanella, L. Heme Oxygenase-1 Signaling and Redox Homeostasis in Physiopathological Conditions. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Guo, S.; Wang, J.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wu, Q. Nrf2/HO-1 mediates the neuroprotective effect of mangiferin on early brain injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage by attenuating mitochondria-related apoptosis and neuroinflammation. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.L.; Park, S.Y.; Kim, Y.H.; Park, G.; Lee, S.J. Acanthopanax senticosus exerts neuroprotective effects through HO-1 signaling in hippocampal and microglial cells. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2013, 35, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morroni, F.; Sita, G.; Graziosi, A.; Turrini, E.; Fimognari, C.; Tarozzi, A.; Hrelia, P. Neuroprotective Effect of Caffeic Acid Phenethyl Ester in A Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease Involves Nrf2/HO-1 Pathway. Aging Dis. 2018, 9, 605–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, S.K. Does the Interdependence between Oxidative Stress and Inflammation Explain the Antioxidant Paradox? Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2016, 2016, 5698931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kempuraj, D.; Thangavel, R.; Natteru, P.A.; Selvakumar, G.P.; Saeed, D.; Zahoor, H.; Zaheer, S.; Iyer, S.S.; Zaheer, A. Neuroinflammation Induces Neurodegeneration. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Spine 2016, 1, 1003. [Google Scholar]
- Kishore Kumar, S.N.; Deepthy, J.; Prema, V.; Ashokkumar, S.; Thangarajeswari, M.; Bhavani, R.D.; Saraswathi, U.; Yogesh Kanna, S.; Rajasekaran, N.S.; Kalaiselvi, P. Scopoletin Augments DJ1/Nrf2 Signalling and Prevents Protein Aggregation in Parkinson’s disease. bioRxiv 2018, 260521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, H.; Ju, I.G.; Kim, J.H.; Choi, Y.; Lee, S.; Park, H.-J.; Oh, M.S. Artemisiae Iwayomogii Herba Protects Dopaminergic Neurons Against 1-Methyl-4-phenylpyridinium/1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine Neurotoxicity in Models of Parkinson’s Disease. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1672. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17101672
Lee H, Ju IG, Kim JH, Choi Y, Lee S, Park H-J, Oh MS. Artemisiae Iwayomogii Herba Protects Dopaminergic Neurons Against 1-Methyl-4-phenylpyridinium/1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine Neurotoxicity in Models of Parkinson’s Disease. Nutrients. 2025; 17(10):1672. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17101672
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Hanbyeol, In Gyoung Ju, Jin Hee Kim, Yujin Choi, Seungmin Lee, Hi-Joon Park, and Myung Sook Oh. 2025. "Artemisiae Iwayomogii Herba Protects Dopaminergic Neurons Against 1-Methyl-4-phenylpyridinium/1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine Neurotoxicity in Models of Parkinson’s Disease" Nutrients 17, no. 10: 1672. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17101672
APA StyleLee, H., Ju, I. G., Kim, J. H., Choi, Y., Lee, S., Park, H.-J., & Oh, M. S. (2025). Artemisiae Iwayomogii Herba Protects Dopaminergic Neurons Against 1-Methyl-4-phenylpyridinium/1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine Neurotoxicity in Models of Parkinson’s Disease. Nutrients, 17(10), 1672. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17101672






