Perfluoroalkyl and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) and Vitamin Metabolism: A Nutritional Perspective on an Emerging Environmental Health Issue
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Vitamin A
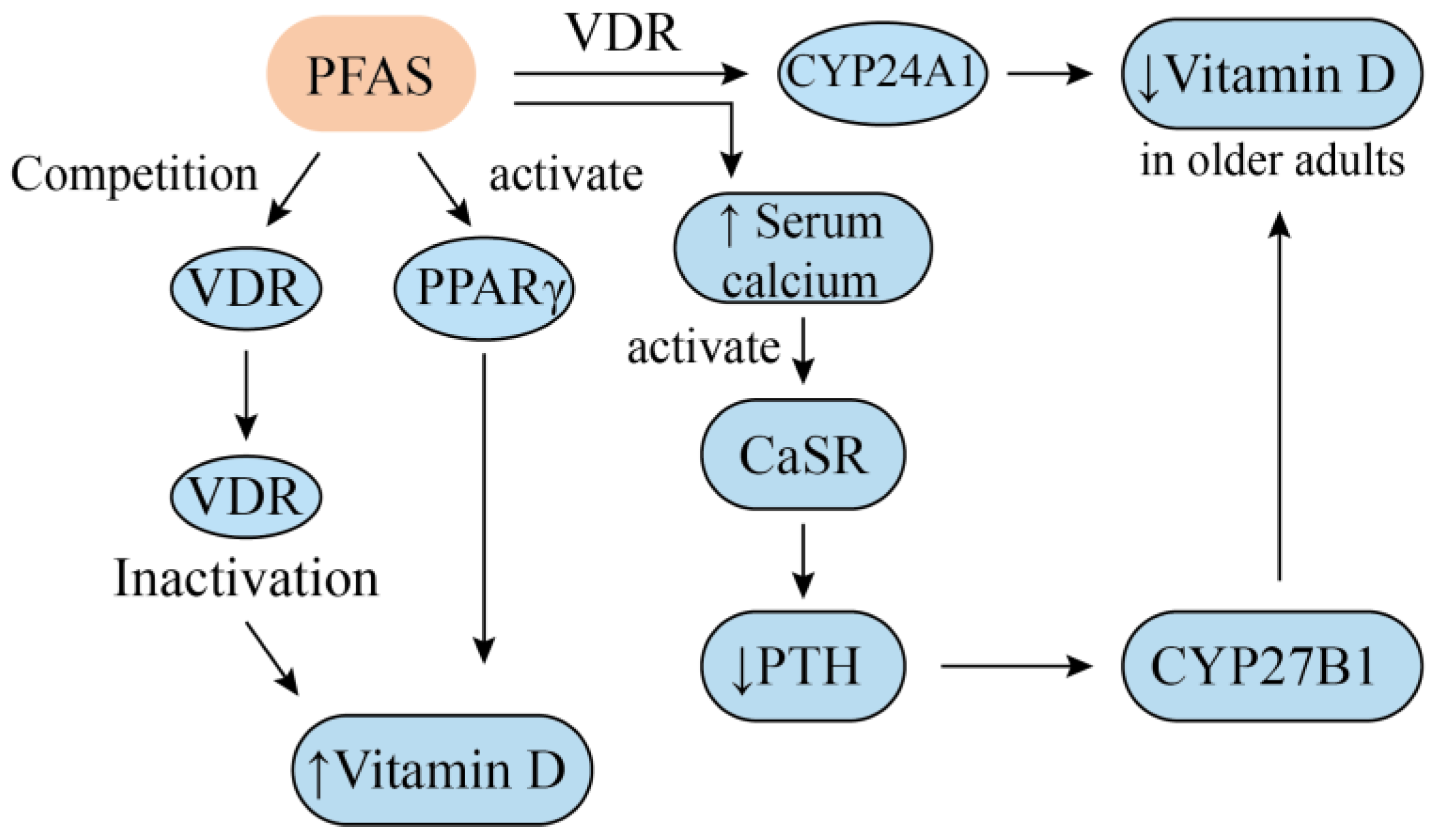
4. Vitamin D
5. Vitamin E
6. Vitamin B
6.1. Vitamin B3
6.2. Vitamin B6
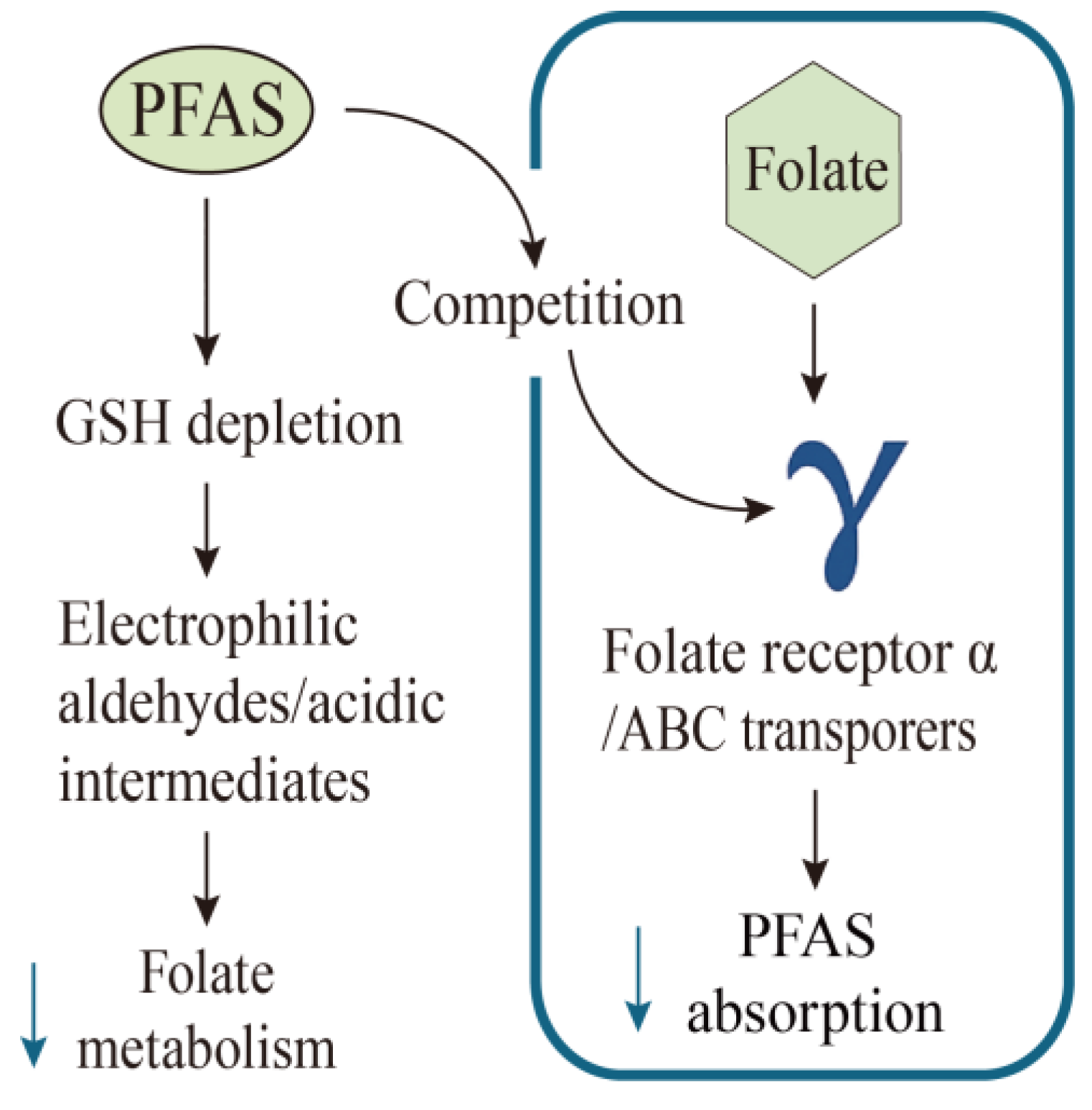
6.3. Vitamin B9
6.4. Vitamin B12
7. Vitamin C
8. Other Vitamins
9. Discussion
10. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Panieri, E.; Baralic, K.; Djukic-Cosic, D.; Buha Djordjevic, A.; Saso, L. PFAS Molecules: A Major Concern for the Human Health and the Environment. Toxics 2022, 10, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). Perfluorooctane Sulfonate (PFOS), Perfluorooctanoic Acid (PFOA) and Their Salts Scientific Opinion of the Panel on Contaminants in the Food Chain. EFSA J. 2008, 6, 653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunderland, E.M.; Hu, X.C.; Dassuncao, C.; Tokranov, A.K.; Wagner, C.C.; Allen, J.G. A Review of the Pathways of Human Exposure to Poly- and Perfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs) and Present Understanding of Health Effects. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2019, 29, 131–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, J.R.; Sáez, M.; Dolfing, J.; De Voogt, P. Biodegradation of Perfluorinated Compounds. In Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology; Whitacre, D.M., Ed.; Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2008; Volume 196, pp. 53–71. ISBN 978-0-387-78443-4. [Google Scholar]
- Conder, J.M.; Hoke, R.A.; Wolf, W.D.; Russell, M.H.; Buck, R.C. Are PFCAs Bioaccumulative? A Critical Review and Comparison with Regulatory Criteria and Persistent Lipophilic Compounds. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 995–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trudel, D.; Horowitz, L.; Wormuth, M.; Scheringer, M.; Cousins, I.T.; Hungerbühler, K. Estimating Consumer Exposure to PFOS and PFOA. Risk Anal. 2008, 28, 251–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAdam, J.; Bell, E.M. Determinants of Maternal and Neonatal PFAS Concentrations: A Review. Environ. Health 2023, 22, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steenland, K.; Winquist, A. PFAS and Cancer, a Scoping Review of the Epidemiologic Evidence. Environ. Res. 2021, 194, 110690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.-I.D.; Cardenas, A.; Hauser, R.; Gold, D.R.; Kleinman, K.P.; Hivert, M.-F.; Calafat, A.M.; Webster, T.F.; Horton, E.S.; Oken, E. Temporal Trends of Concentrations of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances among Adults with Overweight and Obesity in the United States: Results from the Diabetes Prevention Program and NHANES. Environ. Int. 2021, 157, 106789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, N.; Chen, A.; Lee, M.; Czerwinski, S.A.; Ebert, J.R.; DeWitt, J.C.; Kannan, K. Association of Perfluoroalkyl Substances, Bone Mineral Density, and Osteoporosis in the U.S. Population in NHANES 2009–2010. Environ. Health Perspect. 2016, 124, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liew, Z.; Goudarzi, H.; Oulhote, Y. Developmental Exposures to Perfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs): An Update of Associated Health Outcomes. Curr. Environ. Health Rep. 2018, 5, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, J.; Qu, Y.; Hu, Q.; Ji, S.; Chang, X.; Zhao, F.; Lv, Y.; Pan, Y.; et al. Associations between Serum Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances and Thyroid Hormones in Chinese Adults: A Nationally Representative Cross-Sectional Study. Environ. Int. 2024, 184, 108459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Zhu, L.; Wang, M.; Sun, Q. Associations between Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances Exposures and Blood Lipid Levels among Adults—A Meta-Analysis. Environ. Health Perspect. 2023, 131, 56001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Hong, X.; Zhao, F.; Wu, J.; Wang, B. The Effects of Perfluoroalkyl and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances on Female Fertility: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Environ. Res. 2023, 216, 114718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency. FINAL: Human Health Toxicity Assessment for Perfluorooctanoic Acid (PFOA) and Related Salts; United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2024.
- United States Environmental Protection Agency. FINAL: Human Health Toxicity Assessment for Perfluorooctane Sulfonic Acid (PFOS) and Related Salts; United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2024.
- EFSA Panel on Contaminants in the Food Chain (EFSA CONTAM Panel); Schrenk, D.; Bignami, M.; Bodin, L.; Chipman, J.K.; del Mazo, J.; Grasl-Kraupp, B.; Hogstrand, C.; Hoogenboom, L.; Leblanc, J.; et al. Risk to Human Health Related to the Presence of Perfluoroalkyl Substances in Food. EFSA J. 2020, 18, e06223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berntsen, H.F.; Bjørklund, C.G.; Audinot, J.-N.; Hofer, T.; Verhaegen, S.; Lentzen, E.; Gutleb, A.C.; Ropstad, E. Time-Dependent Effects of Perfluorinated Compounds on Viability in Cerebellar Granule Neurons: Dependence on Carbon Chain Length and Functional Group Attached. Neurotoxicology 2017, 63, 70–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Mustieles, V.; Wang, Y.-X.; Sun, Y.; Agudelo, J.; Bibi, Z.; Torres, N.; Oulhote, Y.; Slitt, A.; Messerlian, C. Folate Concentrations and Serum Perfluoroalkyl and Polyfluoroalkyl Substance Concentrations in Adolescents and Adults in the USA (National Health and Nutrition Examination Study 2003–16): An Observational Study. Lancet Planet. Health 2023, 7, e449–e458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Park, H.Y.; Jeon, J.D.; Kho, Y.; Kim, S.-K.; Park, M.-S.; Hong, Y.-C. The Modifying Effect of Vitamin C on the Association between Perfluorinated Compounds and Insulin Resistance in the Korean Elderly: A Double-Blind, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Crossover Trial. Eur. J. Nutr. 2016, 55, 1011–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, L.; Yang, Z.; Qin, X.; Lai, K.P.; Qin, J.; Yang, B.; Su, M. Vitamin C Protects the Spleen against PFOA-Induced Immunotoxicity. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 865, 161266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carazo, A.; Macáková, K.; Matoušová, K.; Krčmová, L.K.; Protti, M.; Mladěnka, P. Vitamin a Update: Forms, Sources, Kinetics, Detection, Function, Deficiency, Therapeutic Use and Toxicity. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azhagiya Singam, E.R.; Durkin, K.A.; La Merrill, M.A.; Furlow, J.D.; Wang, J.-C.; Smith, M.T. The Vitamin D Receptor as a Potential Target for the Toxic Effects of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs): An in-Silico Study. Environ. Res. 2023, 217, 114832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Weiskirchen, S.; Weiskirchen, R. Vitamin a: Too Good to Be Bad? Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1186336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Lu, X.; Yu, N.; Li, A.; Zhuang, T.; Du, L.; Tang, S.; Shi, W.; Yu, H.; Song, M.; et al. Exposure to Legacy and Novel Perfluoroalkyl Substance Disturbs the Metabolic Homeostasis in Pregnant Women and Fetuses: A Metabolome-Wide Association Study. Environ. Int. 2021, 156, 106627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingsley, S.L.; Walker, D.I.; Calafat, A.M.; Chen, A.; Papandonatos, G.D.; Xu, Y.; Jones, D.P.; Lanphear, B.P.; Pennell, K.D.; Braun, J.M. Metabolomics of Childhood Exposure to Perfluoroalkyl Substances: A Cross-Sectional Study. Metabolomics 2019, 15, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Luo, T.; Liu, Y.; Huo, X.; Mo, C.; Huang, B.; Li, Y.; Feng, L.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, J.; et al. Multi-Omics Reveal Disturbance of Glucose Homeostasis in Pregnant Rats Exposed to Short-Chain Perfluorobutanesulfonic Acid. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 278, 116402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.K.; Lam, T.K.Y.; Tang, H.C.; Ho, T.C.; Wan, H.T.; Wong, C.K.C. PFOS-Elicited Metabolic Perturbation in Liver and Fatty Acid Metabolites in Testis of Adult Mice. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1302965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalil, S.; Bardawil, T.; Stephan, C.; Darwiche, N.; Abbas, O.; Kibbi, A.G.; Nemer, G.; Kurban, M. Retinoids: A Journey from the Molecular Structures and Mechanisms of Action to Clinical Uses in Dermatology and Adverse Effects. J. Dermatol. Treat. 2017, 28, 684–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botelho, J.; Machado, V.; Proença, L.; Delgado, A.S.; Mendes, J.J. Vitamin D Deficiency and Oral Health: A Comprehensive Review. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouillon, R.; Marcocci, C.; Bikle, D.; White, J.H.; Dawson-Hughes, B.; Lips, P.; Munns, C.F.; Lazaretti-Castro, M.; Giustina, A.; Bilezikian, J. Skeletal and Extraskeletal Actions of Vitamin D: Current Evidence and Outstanding Questions. Endocr. Rev. 2019, 40, 1109–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wimalawansa, S.J. Infections and Autoimmunity—The Immune System and Vitamin D: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charoenngam, N.; Holick, M.F. Immunologic Effects of Vitamin D on Human Health and Disease. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khundmiri, S.J.; Murray, R.D.; Lederer, E. PTH and Vitamin D. In Comprehensive Physiology; Prakash, Y.S., Ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 561–601. ISBN 978-0-470-65071-4. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Huang, Y.; Pan, Y.; Cheng, R.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Lu, S.; Zhou, A.; Dai, J.; Xu, S. Associations between per and Polyfluoroalkyl Ether Sulfonic Acids and Vitamin D Biomarker Levels in Chinese Newborns. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 866, 161410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.-J.; Barr, D.B.; Zhang, Q.; Dunlop, A.L.; Smarr, M.M.; Kannan, K.; Panuwet, P.; Tangpricha, V.; Shi, L.; Liang, D.; et al. Associations of Single and Multiple Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substance (PFAS) Exposure with Vitamin D Biomarkers in African American Women during Pregnancy. Environ. Res. 2021, 202, 111713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etzel, T.M.; Braun, J.M.; Buckley, J.P. Associations of Serum Perfluoroalkyl Substance and Vitamin D Biomarker Concentrations in NHANES, 2003–2010. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2019, 222, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Ren, Y.; Ni, J.; Fang, L.; Zhang, T.; Wang, M.; Cai, G.; Ma, Y.; Pan, F. Sex-Specific Association of per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) Exposure with Vitamin D Concentrations in Older Adults in the USA: An Observational Study. Environ. Health 2024, 23, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, E.; Sanchez-Solis, M.; Garcia-Marcos, L. Vitamin D Metabolism Genes in Asthma and Atopy. Mini-Rev. Med. Chem. 2015, 15, 913–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellavia, D.; Costa, V.; De Luca, A.; Maglio, M.; Pagani, S.; Fini, M.; Giavaresi, G. Vitamin D Level between Calcium-Phosphorus Homeostasis and Immune System: New Perspective in Osteoporosis. Curr. Osteoporos. Rep. 2024, 22, 599–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Nisio, A.; Rocca, M.S.; De Toni, L.; Sabovic, I.; Guidolin, D.; Dall’Acqua, S.; Acquasaliente, L.; De Filippis, V.; Plebani, M.; Foresta, C. Endocrine Disruption of Vitamin D Activity by Perfluoro-Octanoic Acid (PFOA). Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, G.; Prosser, D.E.; Kaufmann, M. 25-Hydroxyvitamin D-24-Hydroxylase (CYP24A1): Its Important Role in the Degradation of Vitamin D. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2012, 523, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cakmak, S.; Lukina, A.; Karthikeyan, S.; Atlas, E.; Dales, R. The Association between Blood PFAS Concentrations and Clinical Biochemical Measures of Organ Function and Metabolism in Participants of the Canadian Health Measures Survey (CHMS). Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 827, 153900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goltzman, D.; Mannstadt, M.; Marcocci, C. Physiology of the Calcium-Parathyroid Hormone-Vitamin D Axis. Front. Horm. Res. 2018, 50, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Roof, B.S.; Piel, C.F.; Hansen, J.; Fudenberg, H.H. Serum Parathyroid Hormone Levels and Serum Calcium Levels from Birth to Senescence. Mech. Ageing Dev. 1976, 5, 289–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, A.; Kattoor, A.J.; Saldeen, T.; Mehta, J.L. Vitamin E and Its Anticancer Effects. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, 2831–2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Z.; Liu, L.; Jian, Z.; Ma, Y.; Li, H.; Jin, X.; Liao, B.; Wang, K. Vitamin E and Multiple Health Outcomes: An Umbrella Review of Meta-Analyses. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Liu, L.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, J.; Du, X.; Huang, Q.; Tian, M.; Shen, H. Serum Metabolome Biomarkers Associate Low-Level Environmental Perfluorinated Compound Exposure with Oxidative /Nitrosative Stress in Humans. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 229, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pope, S.A.S.; Burtin, G.E.; Clayton, P.T.; Madge, D.J.; Muller, D.P.R. Synthesis and Analysis of Conjugates of the Major Vitamin e Metabolite, α-CEHC. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2002, 33, 807–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasperi, V.; Sibilano, M.; Savini, I.; Catani, M.V. Niacin in the Central Nervous System: An Update of Biological Aspects and Clinical Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alegre, G.F.S.; Pastore, G.M. NAD+ Precursors Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN) and Nicotinamide Riboside (NR): Potential Dietary Contribution to Health. Curr. Nutr. Rep. 2023, 12, 445–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alderete, T.L.; Jin, R.; Walker, D.I.; Valvi, D.; Chen, Z.; Jones, D.P.; Peng, C.; Gilliland, F.D.; Berhane, K.; Conti, D.V.; et al. Perfluoroalkyl Substances, Metabolomic Profiling, and Alterations in Glucose Homeostasis among Overweight and Obese Hispanic Children: A Proof-of-Concept Analysis. Environ. Int. 2019, 126, 445–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhamad, R.; Akrivaki, A.; Papagiannopoulou, G.; Zavridis, P.; Zis, P. The Role of Vitamin B6 in Peripheral Neuropathy: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stach, K.; Stach, W.; Augoff, K. Vitamin B6 in Health and Disease. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, D.; Taibl, K.R.; Dunlop, A.L.; Barr, D.B.; Ryan, P.B.; Everson, T.; Huels, A.; Tan, Y.; Panuwet, P.; Kannan, K.; et al. Metabolic Perturbations Associated with an Exposure Mixture of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in the Atlanta African American Maternal-Child Cohort. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 16206–16218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viswanathan, M.; Urrutia, R.P.; Hudson, K.N.; Middleton, J.C.; Kahwati, L.C. Folic Acid Supplementation to Prevent Neural Tube Defects Updated Evidence Report and Systematic Review for the US Preventive Services Task Force. Obstet. Anesth. Dig. 2024, 44, 63–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggini, S.; Pierre, A.; Calder, P.C. Immune Function and Micronutrient Requirements Change over the Life Course. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oulhote, Y.; Lanphear, B.; Braun, J.M.; Webster, G.M.; Arbuckle, T.E.; Etzel, T.; Forget-Dubois, N.; Seguin, J.R.; Bouchard, M.F.; MacFarlane, A.; et al. Gestational Exposures to Phthalates and Folic Acid, and Autistic Traits in Canadian Children. Environ. Health Perspect. 2020, 128, 27004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Mustieles, V.; Wang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Bibi, Z.; Slitt, A.; Messerlian, C. Dietary Intake and Blood Concentrations of Folate and Folic Acid in Relation to Serum Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) Concentrations. ISEE Conf. Abstr. 2021, 2021, 618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Luan, M.; Zhang, J.; Yang, H.; Wang, Y.; Chen, H. Associations of Single and Multiple Perfluoroalkyl Substances Exposure with Folate among Adolescents in NHANES 2007–2010. Chemosphere 2022, 307, 135995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, R.B. Impact of the Increasing Concentrations of Selected Perfluoroalkyl Acids on the Observed Concentrations of Red Blood Cell Folate among US Adults Aged ≥20 Years. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 52357–52369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pompella, A.; Corti, A. Editorial: The Changing Faces of Glutathione, a Cellular Protagonist. Front. Pharmacol. 2015, 6, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rand, A.A.; Mabury, S.A. Is There a Human Health Risk Associated with Indirect Exposure to Perfluoroalkyl Carboxylates (PFCAs)? Toxicology 2017, 375, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, J.B. Biomarkers of Nutrient Exposure and Status in One-Carbon (Methyl) Metabolism. J. Nutr. 2003, 133, 941S–947S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannon, R.E.; Richards, A.C.; Trexler, A.W.; Juberg, C.T.; Sinha, B.; Knudsen, G.A.; Birnbaum, L.S. Effect of GenX on P-Glycoprotein, Breast Cancer Resistance Protein, and Multidrug Resistance–Associated Protein 2 at the Blood–Brain Barrier. Environ. Health Perspect. 2020, 128, 37002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bangma, J.; Guillette, T.C.; Bommarito, P.A.; Ng, C.; Reiner, J.L.; Lindstrom, A.B.; Strynar, M.J. Understanding the Dynamics of Physiological Changes, Protein Expression, and PFAS in Wildlife. Environ. Int. 2022, 159, 107037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forsthuber, M.; Kaiser, A.M.; Granitzer, S.; Hassl, I.; Hengstschläger, M.; Stangl, H.; Gundacker, C. Albumin Is the Major Carrier Protein for PFOS, PFOA, PFHxS, PFNA and PFDA in Human Plasma. Environ. Int. 2020, 137, 105324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducatman, A.; Luster, M.; Fletcher, T. Perfluoroalkyl Substance Excretion: Effects of Organic Anion-Inhibiting and Resin-Binding Drugs in a Community Setting. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2021, 85, 103650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taleb, R.; Hafez, B.; El Kassir, N.; El Achkar, H.; Mourad, M. Role of Vitamin B12 in Treating Recurrent Aphthous Stomatitis: A Review. Int. J. Vitam. Nutr. Res. 2020, 92, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giedyk, M.; Goliszewska, K.; Gryko, D. Vitamin B12 Catalysed Reactions. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 3391–3404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halczuk, K.; Kaźmierczak-Barańska, J.; Karwowski, B.T.; Karmańska, A.; Cieślak, M. Vitamin B12—Multifaceted In Vivo Functions and In Vitro Applications. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-Y.; Lee, H.-L.; Wang, C.; Sung, F.-C.; Su, T.-C. Examining the Impact of Polyfluoroalkyl Substance Exposure on Erythrocyte Profiles and Its Related Nutrients: Insights from a Prospective Study on Young Taiwanese. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 359, 124576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payne, K.A.P.; Quezada, C.P.; Fisher, K.; Dunstan, M.S.; Collins, F.A.; Sjuts, H.; Levy, C.; Hay, S.; Rigby, S.E.J.; Leys, D. Reductive Dehalogenase Structure Suggests a Mechanism for B12-Dependent Dehalogenation. Nature 2015, 517, 513–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochoa-Herrera, V.; Sierra-Alvarez, R.; Somogyi, A.; Jacobsen, N.E.; Wysocki, V.H.; Field, J.A. Reductive Defluorination of Perfluorooctane Sulfonate. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 3260–3264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Zenobio, J.E.; Lee, L.S. Perfluorooctane Sulfonate (PFOS) Removal with Pd0/nFe0 Nanoparticles: Adsorption or Aqueous Fe-Complexation, Not Transformation? J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 342, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koval, A.M.; Jenness, G.R.; Shukla, M.K. Structural Investigation of the Complexation between Vitamin B12 and Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances: Insights into Degradation Using Density Functional Theory. Chemosphere 2024, 364, 143213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farasati Far, B.; Behnoush, A.H.; Ghondaghsaz, E.; Habibi, M.A.; Khalaji, A. The Interplay between Vitamin C and Thyroid. Endocrinol. Diabetes Metab. 2023, 6, e432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lykkesfeldt, J.; Carr, A.C. Vitamin C. Adv. Nutr. 2024, 15, 100155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Guo, C.; Lin, X.; Chan, T.F.; Su, M.; Zhang, Z.; Lai, K.P. Integrative Omics Analysis Reveals the Protective Role of Vitamin C on Perfluorooctanoic Acid-Induced Hepatoxicity. J. Adv. Res. 2022, 35, 279–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, M.; Liang, X.; Xu, X.; Wu, X.; Yang, B. Hepatoprotective Benefits of Vitamin C against Perfluorooctane Sulfonate-Induced Liver Damage in Mice through Suppressing Inflammatory Reaction and ER Stress. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2019, 65, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Guo, C.; Li, Y.; Liang, X.; Su, M. Functional Benefit and Molecular Mechanism of Vitamin C against Perfluorooctanesulfonate-Associated Leukemia. Chemosphere 2021, 263, 128242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Shen, Z.; Wang, W.; Ma, Z.; Bi, S.; Sun, H.; Bu, Y. The Capture of ˙H and ˙OH Radicals by Vitamin C and Implications for the New Source for the Formation of the Anion Free Radical. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2010, 12, 5256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paschalis, V.; Theodorou, A.A.; Kyparos, A.; Dipla, K.; Zafeiridis, A.; Panayiotou, G.; Vrabas, I.S.; Nikolaidis, M.G. Low Vitamin C Values Are Linked with Decreased Physical Performance and Increased Oxidative Stress: Reversal by Vitamin C Supplementation. Eur. J. Nutr. 2016, 55, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Vitamins | PFAS | Association Direction | Type of Study | Sample Size | Number of Studies | Reference | Strength of Evidence |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vitamin A | PFOA | ↓ | Metabolomics | 84 | 1 | [25] | limited |
| PFOS | ↓ | Animal (mouse) | N/A | 1 | [28] | weak | |
| PFHxS | ↓ | Metabolomics | 84 | 1 | [25] | limited | |
| PFNA | ↓ | Metabolomics | 114 | 1 | [26] | limited | |
| PFBS | ↓ | Animal (rat) | 33 | 1 | [27] | weak | |
| Vitamin D | PFOA | ↓ | Cross-sectional | 3853 | 1 | [38] | limited |
| PFOS | Mixed (↑/↓) | Cross-sectional, Cohort | 12,327 | 4 | [35,36,37,38] | moderate | |
| PFHxS | ↑ | Cross-sectional, Cohort | 8474 | 3 | [35,36,37] | strong | |
| PFNA | ↓ | Cross-sectional | 3853 | 1 | [38] | limited | |
| PFDA | ↑ | Cohort | 442 | 1 | [36] | limited | |
| PFTrDA | ↑ | Cohort | 992 | 1 | [35] | limited | |
| PFPeA | ↓ | Cohort | 442 | 1 | [36] | limited | |
| NMeFOSAA | Mixed (↑/↓) | Cross-sectional, Cohort | 4295 | 2 | [36,38] | moderate | |
| Vitamin E | PFOA | ↓ | Metabolomics, Animal (rat) | 181 (human) N/A (animal) | 2 | [18,48] | moderate |
| PFOS | ↓ | Animal (rat) | N/A | 1 | [18] | weak | |
| PFNA | ↓ | Animal (rat) | N/A | 1 | [18] | weak | |
| Vitamin B3 | PFOA | ↓ | Metabolomics | 154 | 2 | [26,52] | limited |
| PFOS | ↓ | Metabolomics | 154 | 2 | [26,52] | limited | |
| PFHxS | ↓ | Metabolomics | 154 | 2 | [52] | limited | |
| PFNA | ↓ | Metabolomics | 114 | 1 | [26] | limited | |
| Vitamin B6 | PFOS | ↓ | Metabolomics | 268 | 1 | [55] | limited |
| PFNA | ↓ | Metabolomics | 268 | 1 | [55] | limited | |
| Vitamin B9 | PFOA | ↓ | Cross-sectional | 16,908 | 3 | [19,59,61] | strong |
| PFOS | ↓ | Cross-sectional | 20776 | 4 | [19,59,60,61] | strong | |
| PFHxS | ↓ | Cross-sectional | 16,908 | 2 | [19,61] | moderate | |
| PFNA | ↓ | Cross-sectional | 20,055 | 3 | [19,59,61] | strong | |
| PFDA | ↓ | Cross-sectional | 7012 | 2 | [60,61] | moderate | |
| PFUnDA | ↓ | Cross-sectional | 6291 | 1 | [61] | limited | |
| Vitamin B12 | PFOA | ↓ | Cohort | 502 | 1 | [72] | limited |
| PFOS | ↓ | Cohort | 502 | 1 | [72] | limited | |
| Vitamin C | PFOA | ↓ | Animal (mouse) | 56 | 2 | [21,79] | weak |
| PFOS | ↓ | Animal (mouse), Cell, RCT | 141 (human) 40 (animal) | 3 | [20,80,81] | moderate | |
| PFDoDA | ↓ | RCT | 141 | 1 | [20] | moderate |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, C.; Zhou, B.; Huang, L.; Han, D.; He, M.; Zhou, M.; Xu, P.; Zhang, R. Perfluoroalkyl and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) and Vitamin Metabolism: A Nutritional Perspective on an Emerging Environmental Health Issue. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1660. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17101660
Liu C, Zhou B, Huang L, Han D, He M, Zhou M, Xu P, Zhang R. Perfluoroalkyl and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) and Vitamin Metabolism: A Nutritional Perspective on an Emerging Environmental Health Issue. Nutrients. 2025; 17(10):1660. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17101660
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Chen, Biao Zhou, Lichun Huang, Dan Han, Mengjie He, Mengyi Zhou, Peiwei Xu, and Ronghua Zhang. 2025. "Perfluoroalkyl and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) and Vitamin Metabolism: A Nutritional Perspective on an Emerging Environmental Health Issue" Nutrients 17, no. 10: 1660. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17101660
APA StyleLiu, C., Zhou, B., Huang, L., Han, D., He, M., Zhou, M., Xu, P., & Zhang, R. (2025). Perfluoroalkyl and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) and Vitamin Metabolism: A Nutritional Perspective on an Emerging Environmental Health Issue. Nutrients, 17(10), 1660. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17101660






