Diabetes-Related Dietary Patterns and Endometrial Cancer Risk and Survival in the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Dietary Information
2.3. Statistical Analysis
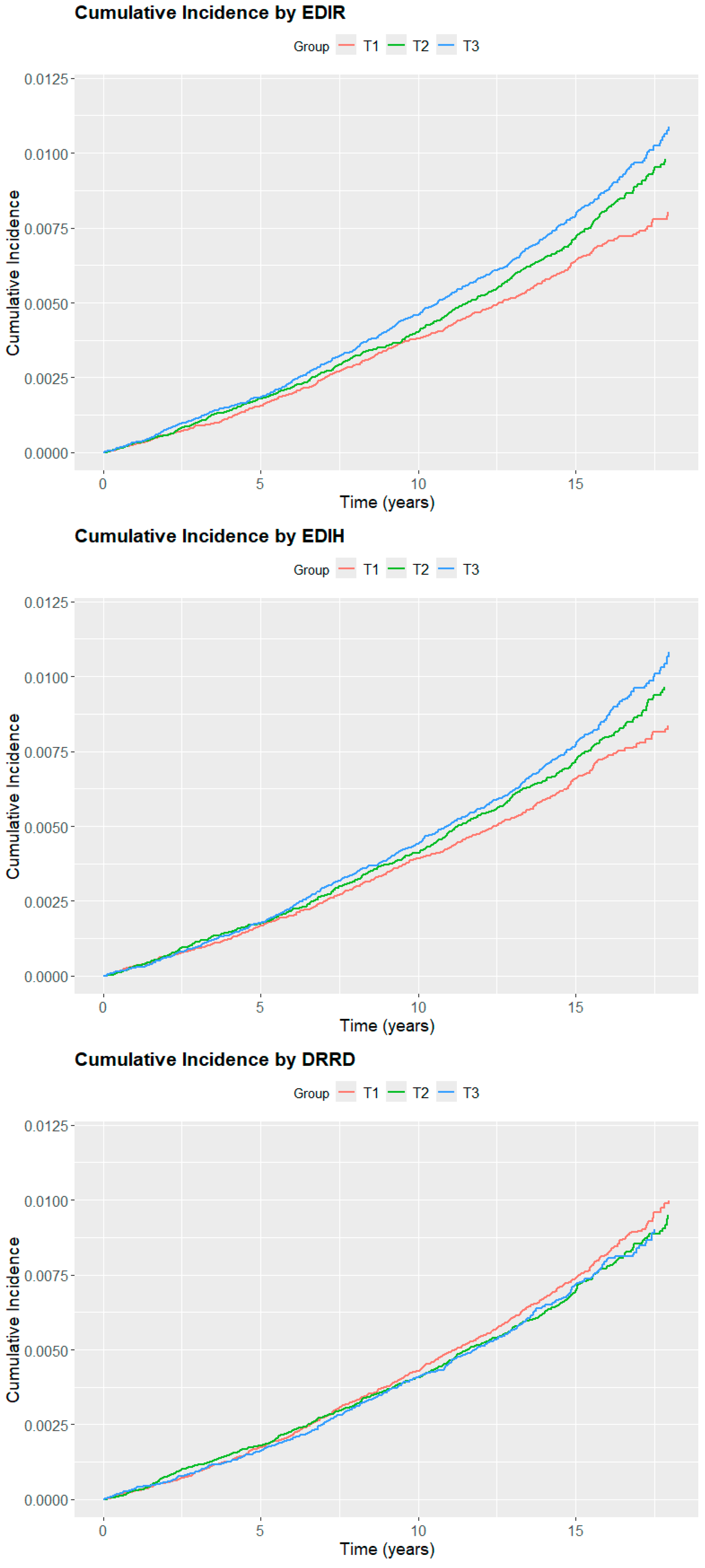
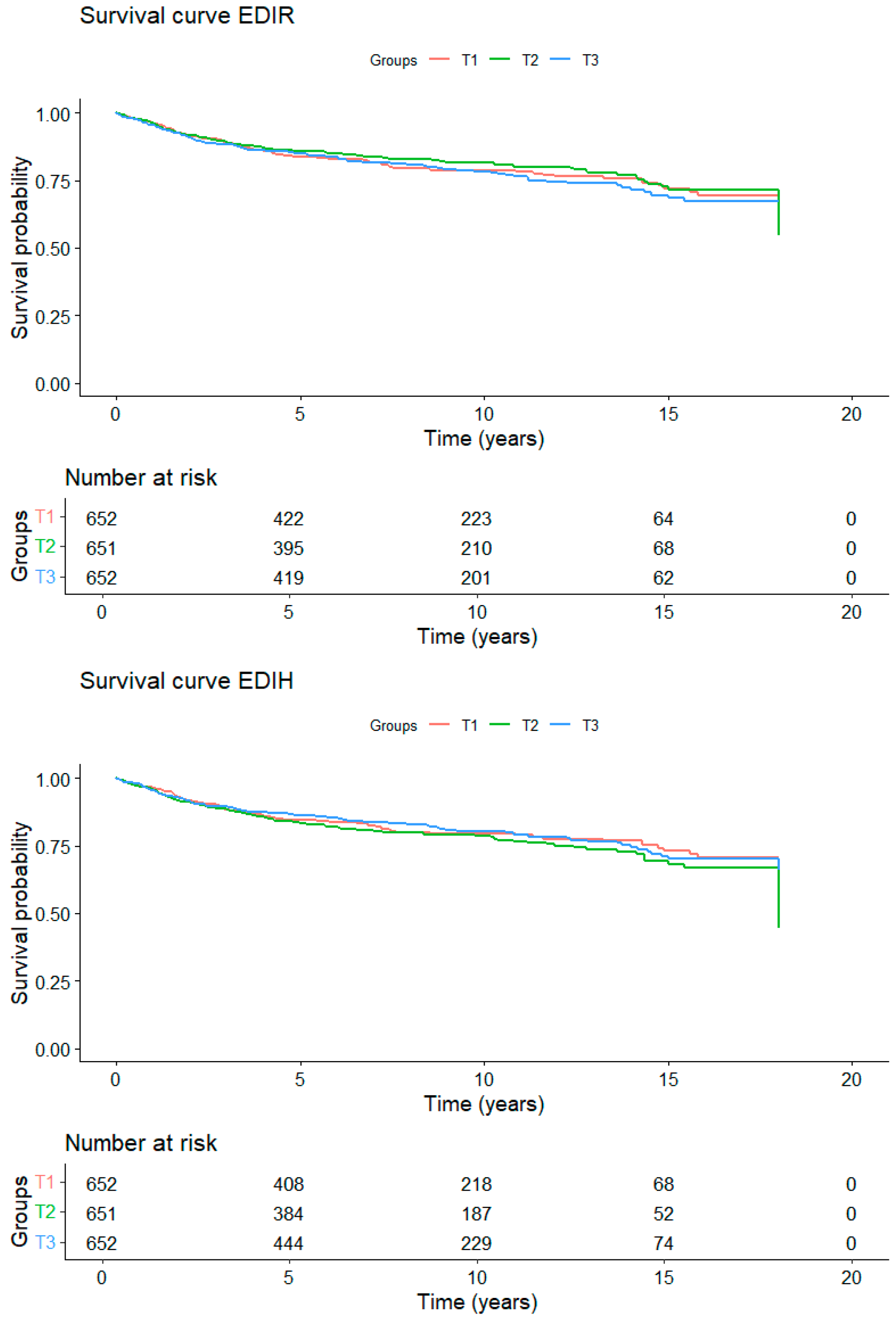
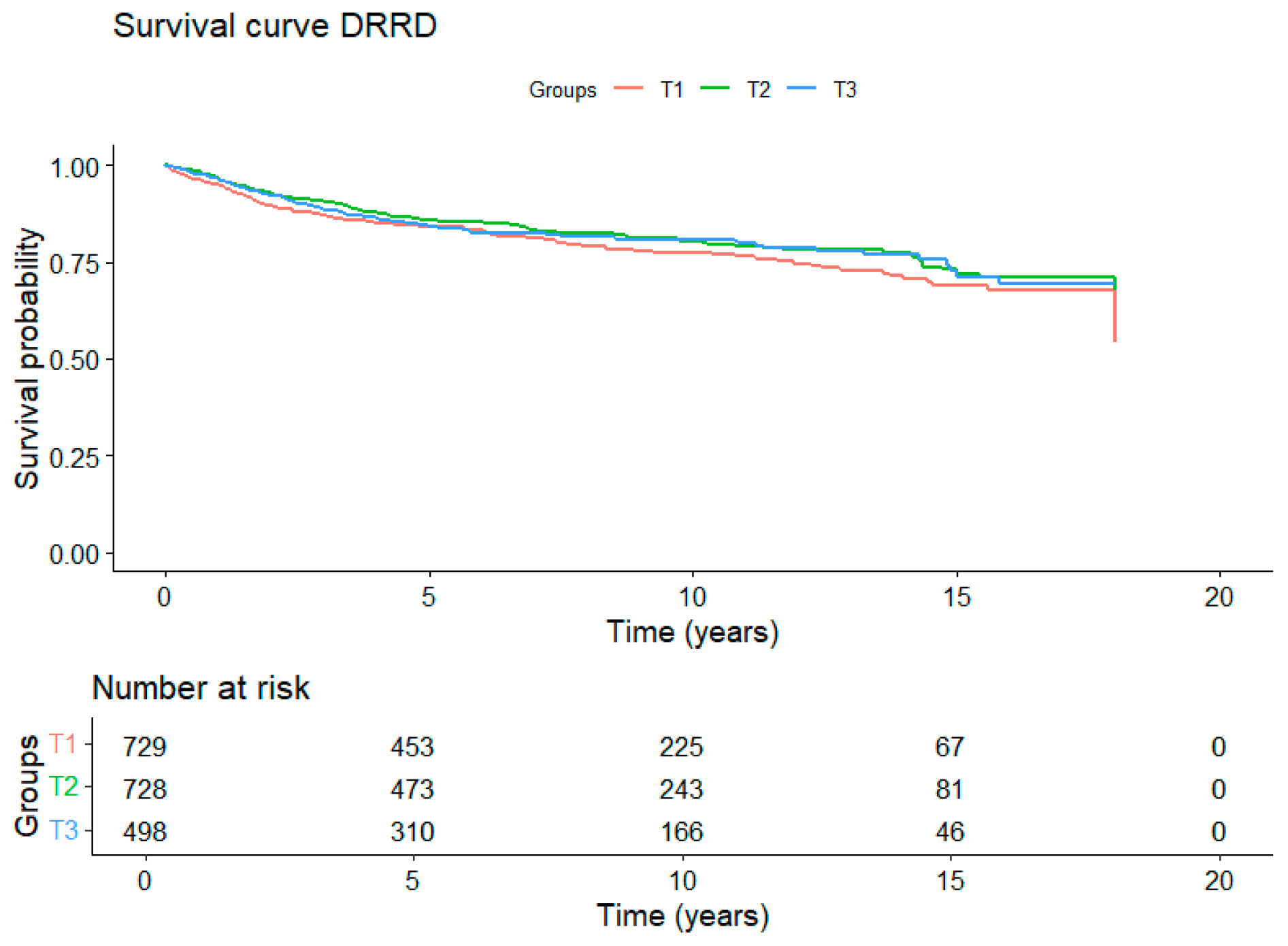
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
IARC Disclaimer
Abbreviations
| EC | Endometrial cancer |
| EPIC | European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition |
| EDIH | Empirical Dietary Index for Hyperinsulinemia |
| EDIR | Empirical Dietary Index for Insulin Resistance |
| DRRD | Diabetes Risk Reduction Diet |
| HR | Hazard ratio |
| CI | Confidence intervals |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| FFQ | Food frequency questionnaires |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| SHBG | Sex hormone-binding globulin |
References
- Lega, I.C.; Lipscombe, L.L. Review: Diabetes, Obesity, and Cancer—Pathophysiology and Clinical Implications. Endocr. Rev. 2020, 41, 33–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallagher, E.J.; LeRoith, D. Obesity and Diabetes: The Increased Risk of Cancer and Cancer-Related Mortality. Physiol. Rev. 2015, 95, 727–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howlader, N.; Noone, A.M.; Krapcho, M.; Miller, D.; Brest, A.; Yu, M.; Ruhl, J.; Tatalovich, Z.; Mariotto, A.; Lewis, D.R.; et al. SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975–2018; National Cancer Institute (NCI): Bethesda, MD, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Kaaks, R.; Lukanova, A.; Kurzer, M.S. Obesity, endogenous hormones, and endometrial cancer risk: A synthetic review. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2002, 11, 1531–1543. [Google Scholar]
- Henderson, M.B.E.; Bernstein, P.L.; Ross, M.R.K. Hormones and the Etiology of Cancer. In Cancer Medicine, 6th ed.; BC Decker Inc.: Hamilton, ON, Canada, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Harvey, S.V.; Wentzensen, N.; Bertrand, K.; Black, A.; Brinton, L.A.; Chen, C.; Costas, L.; Maso, L.D.; De Vivo, I.; Du, M.; et al. Associations of life course obesity with endometrial cancer in the Epidemiology of Endometrial Cancer Consortium (E2C2). Int. J. Epidemiol. 2023, 52, 1086–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Cancer Research Fund International. Diet, Nutrition, Physical Activity and Cancer: A Global Perspective; World Cancer Research Fund International: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe, Y.; Katagiri, R.; Goto, A.; Shimazu, T.; Yamaji, T.; Sawada, N.; Iwasaki, M.; Inoue, M.; Tsugane, S.; Japan Public Health Center-Based Prospective Study Group. Dietary glycemic index, glycemic load, and endometrial cancer risk: The Japan Public Health Center-based Prospective Study. Cancer Sci. 2021, 112, 3682–3690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Cancer Research Fund International. Diet, Nutrition, Physical Activity and Endometrial Cancer; World Cancer Research Fund International: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Steck, S.E.; Murphy, E.A. Dietary patterns and cancer risk. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2020, 20, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanos-Nanclares, A.; Tabung, F.K.; Sinnott, J.A.; Trabert, B.; De Vivo, I.; Playdon, M.C.; Eliassen, A.H. Inflammatory and insulinemic dietary patterns and risk of endometrial cancer among US women. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2023, 115, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Q.; Shi, N.; Lee, D.H.; Rexrode, K.M.; Manson, J.E.; Balasubramanian, R.; Zhang, X.; Neuhouser, M.L.; Lopez-Pentecost, M.; Thomson, C.A.; et al. Hyperinsulinemic and Pro-Inflammatory Dietary Patterns and Metabolomic Profiles Are Associated with Increased Risk of Total and Site-Specific Cancers among Postmenopausal Women. Cancers 2023, 15, 1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, G.; Bravi, F.; Serraino, D.; Parazzini, F.; Crispo, A.; Augustin, L.S.A.; Negri, E.; La Vecchia, C.; Turati, F. Diabetes Risk Reduction Diet and Endometrial Cancer Risk. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prescott, J.; Bao, Y.; Viswanathan, A.N.; Giovannucci, E.L.; Hankinson, S.E.; De Vivo, I. Dietary Insulin Index and Insulin Load in Relation to Endometrial Cancer Risk in the Nurses’ Health Study. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2014, 23, 1512–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartman, T.J.; McCullough, M.L.; Hodge, J.M.; Gaudet, M.M.; Wang, Y.; Gapstur, S.M. Dietary Energy Density, Glycemic Load, Glycemic Index, and Risk for Endometrial Cancer in the CPS-II Nutrition Cohort. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2018, 27, 113–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riboli, E.; Hunt, K.; Slimani, N.; Ferrari, P.; Norat, T.; Fahey, M.; Charrondière, U.; Hémon, B.; Casagrande, C.; Vignat, J.; et al. European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition (EPIC): Study populations and data collection. Public Health Nutr. 2002, 5, 1113–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haftenberger, M.; Lahmann, P.; Panico, S.; Gonzalez, C.; Seidell, J.; Boeing, H.; Giurdanella, M.; Krogh, V.; Bueno-De-Mesquita, H.; Peeters, P.; et al. Overweight, obesity and fat distribution in 50- to 64-year-old participants in the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition (EPIC). Public Health Nutr. 2002, 5, 1147–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabung, F.K.; Wang, W.; Fung, T.T.; Hu, F.B.; Smith-Warner, S.A.; Chavarro, J.E.; Fuchs, C.S.; Willett, W.C.; Giovannucci, E.L. Development and validation of empirical indices to assess the insulinaemic potential of diet and lifestyle. Br. J. Nutr. 2016, 116, 1787–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.H.; Peng, C.; Rhee, J.J.; Farvid, M.S.; Willett, W.C.; Hu, F.B.; Rosner, B.A.; Tamimi, R.; Eliassen, A.H. Prospective study of a diabetes risk reduction diet and the risk of breast cancer. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 112, 1492–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leighton, E.; Sainsbury, C.A.; Jones, G.C. A Practical Review of C-Peptide Testing in Diabetes. Diabetes Ther. 2017, 8, 475–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unger, G.; Benozzi, S.F.; Perruzza, F.; Pennacchiotti, G.L. Índice triglicéridos y glucosa: Un indicador útil de insulinorresistencia. Endocrinol. Nutr. 2014, 61, 533–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhee, J.J.; Mattei, J.; Hughes, M.D.; Hu, F.B.; Willett, W.C. Dietary Diabetes Risk Reduction Score, Race and Ethnicity, and Risk of Type 2 Diabetes in Women. Diabetes Care 2015, 38, 596–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ElHafeez, S.A.; D’Arrigo, G.; Leonardis, D.; Fusaro, M.; Tripepi, G.; Roumeliotis, S. Methods to Analyze Time-to-Event Data: The Cox Regression Analysis. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 1302811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevo, D.; Liao, X.; Spiegelman, D. Estimation and Inference for the Mediation Proportion. Int. J. Biostat. 2017, 13, 20170006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, P.C.; Fine, J.P. Practical recommendations for reporting Fine-Gray model analyses for competing risk data. Stat. Med. 2017, 36, 4391–4400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- dos Santos Silva, I. Chapter 9—Case–control studies. In Cancer Epidemiology: Principles and Methods; International Agency for Research on Cancer IARC: Lyon, France, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Zhao, L.; Christopher, C.N.; Tabung, F.K.; Bao, W.; Garcia, D.O.; Shadyab, A.H.; Saquib, N.; Neuhouser, M.L.; Tinker, L.F.; et al. Association of dietary insulinemic and inflammatory potential with risk of liver cancer and chronic liver disease mortality in postmenopausal women: A prospective cohort study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2023, 118, 530–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Q.; Gheeya, J.; Nepal, S.; Shi, N.; Folefac, E.; Webb, M.Z.; Grainger, E.M.; Wei, L.; Prosek, J.M.; Focht, B.C.; et al. Associations of dietary patterns with kidney cancer risk, kidney cancer-specific mortality and all-cause mortality among postmenopausal women. Br. J. Cancer 2023, 129, 1978–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanos-Nanclares, A.; Tabung, F.K.; Willett, W.C.; Rosner, B.; Holmes, M.D.; Chen, W.Y.; Tamimi, R.M.; Eliassen, A.H. Insulinemic potential of diet and risk of total and subtypes of breast cancer among US females. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 116, 1530–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Y.; Hur, J.; Cao, Y.; Tabung, F.; Wang, M.; Wu, K.; Song, M.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Y.; Meyerhardt, J.; et al. Prospective evaluation of dietary and lifestyle pattern indices with risk of colorectal cancer in a cohort of younger women. Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, 778–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Song, M.; Eliassen, A.H.; Wang, M.; Giovannucci, E.L. Dietary patterns and risk of colorectal cancer: A comparative analysis. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2023, 52, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadirad, H.; Teymoori, F.; Nateghi, R.; Shabanian, A.; Mirmiran, P. The Association of Empirical Dietary Index for Hyperinsulinemia with the Risk of Cancer and Cancer Mortality: A Meta-analysis of Observational Studies. Nutr. Cancer 2023, 75, 1399–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Sui, J.; Zhao, L.; Ma, Y.; Tabung, F.K.; Simon, T.G.; Lee, D.H.; Zeng, X.; Nguyen, L.H.; Meyerhardt, J.A.; et al. Association of Inflammatory and Insulinemic Potential of Diet and Lifestyle with Risk of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2021, 30, 789–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, L.; Liu, X.; Petrick, J.; Liu, W.; Lee, J.K.; Liao, L.; Lai, M.J.; Yang, W.; Libermann, T.A.; Roberts, L.R.; et al. Dietary inflammatory and insulinemic potential, risk of hepatocellular carcinoma, and chronic liver disease mortality. JNCI Cancer Spectr. 2023, 7, pkad023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Q.; Hart, P.A.; Shi, N.; Joseph, J.J.; Donneyong, M.; Conwell, D.L.; Clinton, S.K.; Cruz-Monserrate, Z.; Brasky, T.M.; Tinker, L.F.; et al. Dietary Patterns of Insulinemia, Inflammation and Glycemia, and Pancreatic Cancer Risk: Findings from the Women’s Health Initiative. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2021, 30, 1229–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhao, L.; Jung, S.Y.; Pichardo, M.S.; Lopez-Pentecost, M.; Rohan, T.E.; Saquib, N.; Sun, Y.; Tabung, F.K.; Zheng, T.; et al. Diabetes risk reduction diet and risk of liver cancer and chronic liver disease mortality: A prospective cohort study. J. Intern. Med. 2024, 296, 410–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Zhang, Y.; Kim, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Giovannucci, E. A Comparative Study of Healthy Dietary Patterns for Incident and Fatal Digestive System Cancer. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2023, 118, 2061–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, L.; Xiao, Y.; Xu, Z.; Luo, H.; Ren, X.; Wei, Q.; Zhu, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Tang, Y.; He, H.; et al. Association of diabetes risk reduction diet with renal cancer risk in 101,755 participants: A prospective study. J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, E.; Zhang, S.; Ou, F.-S.; Mullen, B.; Ng, K.; Saltz, L.B.; Niedzwiecki, D.; Mayer, R.J.; Mowat, R.B.; Whittom, R.; et al. The Diet of Higher Insulinemic Potential Is Not Associated with Worse Survival in Patients with Stage III Colon Cancer (Alliance). Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2020, 29, 1692–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabung, F.K.; Noonan, A.; Lee, D.H.; Song, M.; Clinton, S.K.; Spakowicz, D.; Wu, K.; Cheng, E.; Meyerhardt, J.A.; Fuchs, C.S.; et al. Post-diagnosis dietary insulinemic potential and survival outcomes among colorectal cancer patients. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Tabung, F.K.; Lee, D.H.; Fung, T.T.; Willett, W.C.; Giovannucci, E.L. Dietary Insulinemic Potential and Risk of Total and Cause-Specific Mortality in the Nurses’ Health Study and the Health Professionals Follow-up Study. Diabetes Care 2022, 45, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Espin, C.; Bonet, C.; Crous-Bou, M.; Katzke, V.; Le Cornet, C.; Jannasch, F.; Schulze, M.B.; Olsen, A.; Tjønneland, A.; Dahm, C.C.; et al. Dietary patterns related to biological mechanisms and survival after breast cancer diagnosis: Results from a cohort study. Br. J. Cancer 2023, 128, 1301–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Key, T.J.; Allen, N.E.; Verkasalo, P.K.; Banks, E. Energy balance and cancer: The role of sex hormones. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2001, 60, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunter, M.J.; Hoover, D.R.; Yu, H.; Wassertheil-Smoller, S.; Manson, J.E.; Li, J.; Harris, T.G.; Rohan, T.E.; Xue, X.; Ho, G.Y.F.; et al. A Prospective Evaluation of Insulin and Insulin-like Growth Factor-I as Risk Factors for Endometrial Cancer. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2008, 17, 921–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallagher, E.J.; LeRoith, D. The proliferating role of insulin and insulin-like growth factors in cancer. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 21, 610–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Ke, K.; Liu, Z.; Yang, L.; Wang, L.; Zhou, J.; Dong, Q. Body Mass Index and Cancer Risk: An Umbrella Review of Meta-Analyses of Observational Studies. Nutr. Cancer 2023, 75, 1051–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cust, A.E.; Allen, N.E.; Rinaldi, S.; Dossus, L.; Friedenreich, C.; Olsen, A.; Tjønneland, A.; Overvad, K.; Clavel-Chapelon, F.; Boutron-Ruault, M.-C.; et al. Serum levels of C-peptide, IGFBP-1 and IGFBP-2 and endometrial cancer risk; Results from the European prospective investigation into cancer and nutrition. Int. J. Cancer 2007, 120, 2656–2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augustin, L.S.A.; Kendall, C.W.C.; Jenkins, D.J.A.; Willett, W.C.; Astrup, A.; Barclay, A.W.; Björck, I.; Brand-Miller, J.C.; Brighenti, F.; Buyken, A.E.; et al. Glycemic index, glycemic load and glycemic response: An International Scientific Consensus Summit from the International Carbohydrate Quality Consortium (ICQC). Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2015, 25, 795–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Participants (n = 285,418) | % | EC Cases (n = 1955) | % | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Country | The Netherlands | 22,175 | 7.8 | 153 | 7.8 |
| Spain | 22,780 | 8.0 | 176 | 9.0 | |
| Germany | 23,303 | 8.2 | 98 | 5.0 | |
| Denmark | 24,471 | 8.6 | 281 | 14.4 | |
| Sweden | 25,702 | 9.0 | 241 | 12.3 | |
| Italy | 27,761 | 9.7 | 199 | 10.2 | |
| Norway | 32,416 | 11.4 | 222 | 11.4 | |
| United Kingdom | 46,079 | 16.1 | 275 | 14.1 | |
| France | 60,731 | 21.3 | 310 | 15.9 | |
| Age at recruitment (years) | <40 | 38,089 | 13.3 | 50 | 2.6 |
| 40 to <50 | 98,005 | 32.3 | 436 | 22.3 | |
| 50 to <60 | 103,904 | 36.4 | 973 | 49.8 | |
| ≥60 | 45,420 | 15.9 | 496 | 25.4 | |
| mean (SD) | 50.13 (9.8) | 54.75 (7.6) | |||
| Age at Diagnosis (years) | <50 | / | / | 84 | 4.3 |
| 50 to <60 | / | / | 574 | 39.4 | |
| 60 to <70 | / | / | 866 | 44.3 | |
| ≥70 | / | / | 431 | 22.0 | |
| mean (SD) | / | / | 63.51 (8.2) | ||
| Educational level | None | 10,097 | 3.6 | 98 | 5.0 |
| Primary | 63,920 | 22.7 | 538 | 27.5 | |
| Technical | 62,792 | 22.0 | 449 | 23.0 | |
| Secondary | 69,494 | 24.7 | 438 | 22.4 | |
| Longer (University) | 68,320 | 24.3 | 350 | 17.9 | |
| Unknown | 10,795 | 3.8 | 82 | 4.2 | |
| BMI (kg/m2) | <18.5 | 6185 | 2.2 | 19 | 1.0 |
| 18.5 to <25 | 168,506 | 59.0 | 824 | 42.1 | |
| 25 to <30 | 79,302 | 27.8 | 655 | 33.5 | |
| >30 | 31,425 | 11.0 | 457 | 23.4 | |
| mean (SD) | 24.68 (4.3) | 26.85 (5.3) | |||
| Waits circumference (cm) | <88 | 157,784 | 55.3 | 917 | 46.9 |
| ≥88 | 40,670 | 14.2 | 505 | 25.8 | |
| Unknown | 86,964 | 30.5 | 533 | 27.3 | |
| mean (SD) | 79.25 (11.1) | 84.26 (12.6) | |||
| Alcohol consumption (g/day) | Non-consumers | 44,149 | 15.5 | 351 | 18.0 |
| >0–3 | 90,629 | 31.8 | 631 | 32.3 | |
| >3–12 | 86,858 | 30.4 | 560 | 28.6 | |
| >12–24 | 38,858 | 13.6 | 259 | 13.2 | |
| >24 | 24,924 | 8.7 | 154 | 7.9 | |
| mean (SD) | 8.10 (11.7) | 7.53 (11.1) | |||
| Smoke status | Never | 156,085 | 54.7 | 1194 | 61.1 |
| Former | 66,275 | 23.2 | 422 | 21.6 | |
| Smoker | 56,531 | 19.2 | 298 | 15.2 | |
| Unknown | 6527 | 2.3 | 41 | 2.1 | |
| Physical activity | Inactive | 154,608 | 54.2 | 1152 | 58.9 |
| Active | 125,497 | 44.0 | 767 | 39.2 | |
| Unknown | 5313 | 1.9 | 36 | 1.8 | |
| Age at menarche (years) | <12 | 41,017 | 14.4 | 320 | 16.4 |
| 12 | 58,727 | 20.6 | 417 | 21.3 | |
| 13 | 71,924 | 25.2 | 452 | 23.1 | |
| >13 | 103,538 | 36.6 | 703 | 36.0 | |
| Unknown | 10,212 | 3.6 | 63 | 3.2 | |
| Menopausal status | Perimenopause | 52,144 | 18.3 | 389 | 19.9 |
| Premenopause | 108,603 | 38.1 | 414 | 21.2 | |
| Postmenopause | 124,671 | 43.7 | 1152 | 58.9 | |
| Age at menopause (years) | <45 | 9675 | 3.4 | 47 | 2.4 |
| 45 to 50 | 29,226 | 10.2 | 183 | 9.4 | |
| 50 to 55 | 44,410 | 15.6 | 477 | 24.4 | |
| ≥55 | 8427 | 3.0 | 151 | 7.7 | |
| Unknown | 193,680 | 67.9 | 1097 | 56.1 | |
| Standard Menstrual Cycle (years) | <20 | 46,227 | 16.2 | 74 | 3.8 |
| 20 to 30 | 70,761 | 24.8 | 293 | 15.0 | |
| 30 to 40 | 93,599 | 32.8 | 946 | 48.4 | |
| >40 | 8236 | 2.9 | 173 | 8.8 | |
| Unknown | 66,595 | 23.3 | 469 | 24.0 | |
| Number of live births | 0 | 41,971 | 14.7 | 311 | 15.9 |
| 1 | 42,260 | 14.8 | 309 | 15.8 | |
| 2 | 108,384 | 38.0 | 733 | 37.5 | |
| 3 | 50,681 | 17.8 | 355 | 18.2 | |
| 4 or more | 20,836 | 7.3 | 132 | 6.8 | |
| Unknown | 21,286 | 7.5 | 115 | 5.9 | |
| Ever use of hormonal treatment for menopause | No | 200,814 | 70.4 | 1203 | 61.5 |
| Yes | 64,045 | 22.4 | 610 | 31.1 | |
| Unknown | 20,559 | 7.2 | 142 | 7.3 | |
| Ever use of contraceptive pill | No | 104,972 | 36.8 | 1091 | 55.8 |
| Yes | 172,250 | 60.4 | 815 | 41.7 | |
| Unknown | 8196 | 2.9 | 49 | 2.5 | |
| Diabetes Mellitus | Yes | 5327 | 1.9 | 68 | 3.5 |
| No | 258,034 | 90.4 | 1658 | 84.8 | |
| Don’t know | 916 | 0.3 | 12 | 0.6 | |
| Unknown | 21,141 | 7.4 | 217 | 11.1 | |
| Dietary Patterns | Models | T1 | T2 | T3 | Ptrend |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR (95% CI) | HR (95% CI) | HR (95% CI) | |||
| EDIR | n (events) | 95,140 (568) | 95,139 (661) | 95,139 (726) | |
| Model 1 | 1.00 (Reference) | 1.05 (0.93 to 1.18) | 1.17 (1.04 to 1.31) | 0.008 | |
| Model 2 | 1.00 (Reference) | 0.98 (0.87 to 1.10) | 1.03 (0.91 to 1.16) | 0.61 | |
| EDIH | n (events) | 95,140 (729) | 95,139 (728) | 95,139 (498) | |
| Model 1 | 1.00 (Reference) | 1.03 (0.92 to 1.16) | 1.12 (0.99 to 1.26) | 0.07 | |
| Model 2 | 1.00 (Reference) | 0.97 (0.86 to 1.09) | 1.00 (0.88 to 1.12) | 0.95 | |
| DRRD | n (events) | 102,497 (593) | 109,437 (660) | 73,484 (702) | |
| Model 1 | 1.00 (Reference) | 0.95 (0.85 to 1.06) | 0.96 (0.85 to 1.09) | 0.51 | |
| Model 2 | 1.00 (Reference) | 0.98 (0.88 to 1.09) | 1.02 (0.91 to 1.16) | 0.76 |
| Mortality | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | T2 | T3 | Ptrend | ||||
| n (Deaths) | HR (95% CI) | n (Deaths) | HR (95% CI) | n (Deaths) | HR (95% CI) | ||
| EDIR | 652 (130) | 1.00 (Reference) | 651 (116) | 0.83 (0.60 to 1.16) | 652 (134) | 1.03 (0.74 to 1.42) | 0.95 |
| EDIH | 652 (123) | 1.00 (Reference) | 651 (131) | 1.27 (0.92 to 1.73) | 652 (126) | 0.99 (0.70 to 1.41) | 0.88 |
| DRRD | 729 (154) | 1.00 (Reference) | 728 (133) | 0.98 (0.71 to 1.34) | 498 (93) | 0.87 (0.62 to 1.22) | 0.42 |
| Endometrial Cancer Specific Mortality | |||||||
| T1 | T2 | T3 | Ptrend | ||||
| n (Deaths) | HR (95% CI) | n (Deaths) | HR (95% CI) | n (Deaths) | HR (95% CI) | ||
| EDIR | 652 (44) | 1.00 (Reference) | 651 (42) | 0.86 (0.51 to 1.45) | 652 (47) | 0.99 (0.58 to 1.68) | 0.92 |
| EDIH | 652 (47) | 1.00 (Reference) | 651 (47) | 0.94 (0.57 to 1.54) | 652 (39) | 0.74 (0.42 to 1.30) | 0.31 |
| DRRD | 729 (49) | 1.00 (Reference) | 728 (48) | 0.91 (0.54 to 1.54) | 498 (36) | 0.90 (0.53 to 1.55) | 0.72 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Torres-Laiton, L.; Luján-Barroso, L.; Nadal-Zaragoza, N.; Castro-Espin, C.; Jakszyn, P.; Panico, C.; Le Cornet, C.; Dahm, C.C.; Petrova, D.; Rodríguez-Palacios, D.Á.; et al. Diabetes-Related Dietary Patterns and Endometrial Cancer Risk and Survival in the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition Study. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1645. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17101645
Torres-Laiton L, Luján-Barroso L, Nadal-Zaragoza N, Castro-Espin C, Jakszyn P, Panico C, Le Cornet C, Dahm CC, Petrova D, Rodríguez-Palacios DÁ, et al. Diabetes-Related Dietary Patterns and Endometrial Cancer Risk and Survival in the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition Study. Nutrients. 2025; 17(10):1645. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17101645
Chicago/Turabian StyleTorres-Laiton, Luisa, Leila Luján-Barroso, Núria Nadal-Zaragoza, Carlota Castro-Espin, Paula Jakszyn, Camilla Panico, Charlotte Le Cornet, Christina C. Dahm, Dafina Petrova, Daniel Ángel Rodríguez-Palacios, and et al. 2025. "Diabetes-Related Dietary Patterns and Endometrial Cancer Risk and Survival in the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition Study" Nutrients 17, no. 10: 1645. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17101645
APA StyleTorres-Laiton, L., Luján-Barroso, L., Nadal-Zaragoza, N., Castro-Espin, C., Jakszyn, P., Panico, C., Le Cornet, C., Dahm, C. C., Petrova, D., Rodríguez-Palacios, D. Á., Jannasch, F., Masala, G., Dossus, L., Padroni, L., Guevara, M., Schulze, M. B., Fortner, R. T., Tumino, R., & Crous-Bou, M. (2025). Diabetes-Related Dietary Patterns and Endometrial Cancer Risk and Survival in the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition Study. Nutrients, 17(10), 1645. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17101645






