Dietary Influence on Drug Efficacy: A Comprehensive Review of Ketogenic Diet–Pharmacotherapy Interactions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. KD versus Antidiabetic Drugs
3.1. Metformin
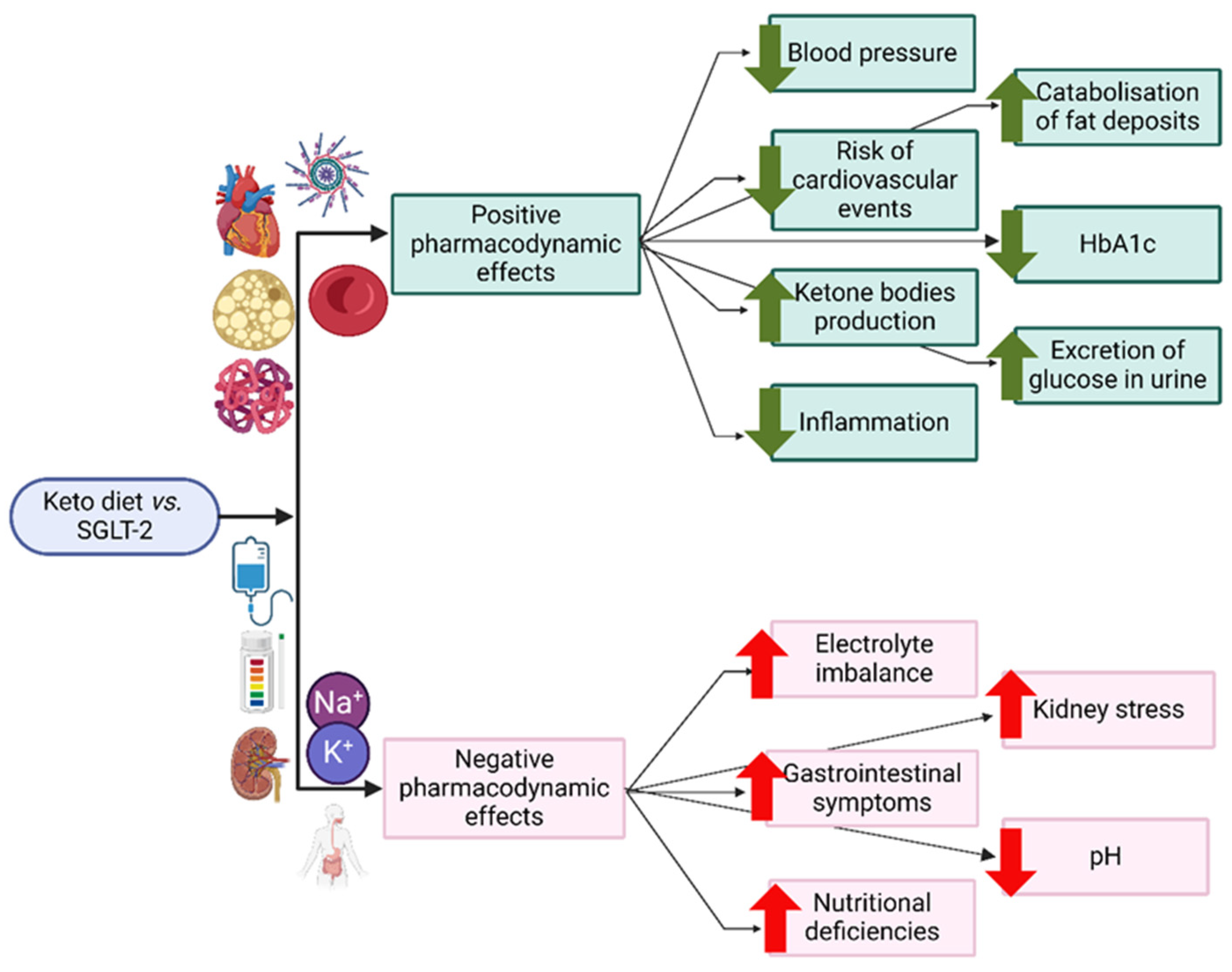
3.2. SGLT-2 Inhibitors
4. KD versus Cardiovascular Drugs
4.1. Agents Acting on the Renin-Angiotensin System
4.2. Beta-Blocking Agents
4.3. Diuretics
5. KD versus Haematological Agents
6. KD versus Anti-Inflammatory Agents
Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs
7. KD versus CNS Disorders
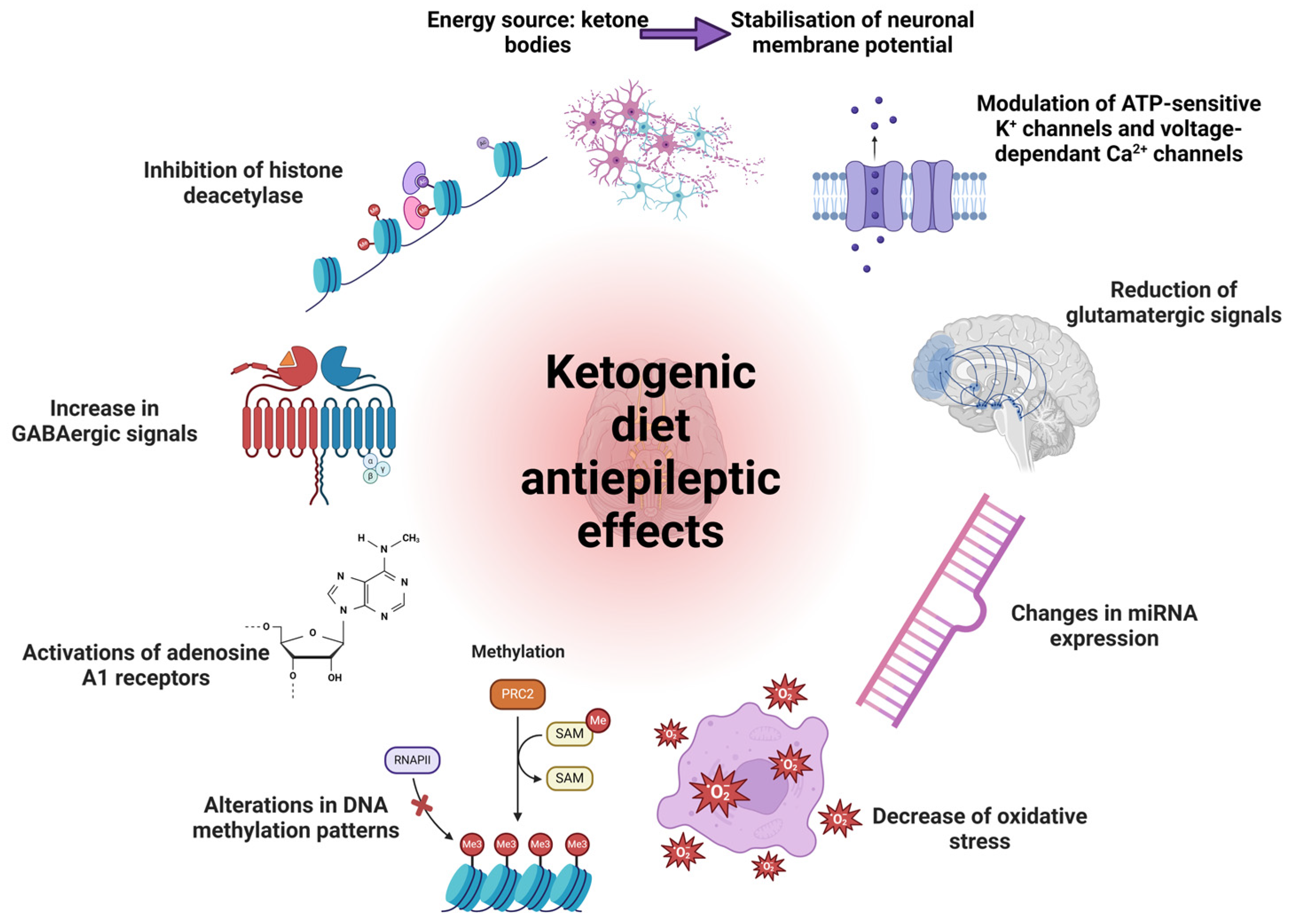
7.1. Antiepileptic Drugs
7.2. Antipsychotic Agents
7.3. Anxiolytics and Hypnotic Agents
7.4. Antidepressants
7.5. General Anaesthetics
7.6. Cannabidiol (CBD)
8. KD versus Cancer
9. KD on the Microbiome
10. Other Pharmacotherapeutic Interactions
10.1. Pharmacodynamics of Ketoacidosis-Inducing Agents
10.2. Pharmacokinetics of Lipophilic Drugs
10.3. Drugs Disrupting Ketosis
11. Identified Research Gaps and Future Perspectives
12. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO Noncommunicable Diseases. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/noncommunicable-diseases (accessed on 3 March 2024).
- Zhu, H.; Bi, D.; Zhang, Y.; Kong, C.; Du, J.; Wu, X.; Wei, Q.; Qin, H. Ketogenic Diet for Human Diseases: The Underlying Mechanisms and Potential for Clinical Implementations. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masood, W.; Annamaraju, P.; Khan Suheb, M.Z.; Uppaluri, K.R. Ketogenic Diet; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Basolo, A.; Magno, S.; Santini, F.; Ceccarini, G. Ketogenic Diet and Weight Loss: Is There an Effect on Energy Expenditure? Nutrients 2022, 14, 1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.-M. Ketogenic Diet: Old Treatment, New Beginning. Clin. Neurophysiol. Pract. 2017, 2, 161–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Neill, B.; Raggi, P. The Ketogenic Diet: Pros and Cons. Atherosclerosis 2020, 292, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paoli, A. Ketogenic Diet for Obesity: Friend or Foe? Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2014, 11, 2092–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tragni, E.; Vigna, L.; Ruscica, M.; Macchi, C.; Casula, M.; Santelia, A.; Catapano, A.L.; Magni, P. Reduction of Cardio-Metabolic Risk and Body Weight through a Multiphasic Very-Low Calorie Ketogenic Diet Program in Women with Overweight/Obesity: A Study in a Real-World Setting. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rusek, M.; Pluta, R.; Ułamek-Kozioł, M.; Czuczwar, S.J. Ketogenic Diet in Alzheimer’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardinoglu, A.; Wu, H.; Bjornson, E.; Zhang, C.; Hakkarainen, A.; Räsänen, S.M.; Lee, S.; Mancina, R.M.; Bergentall, M.; Pietiläinen, K.H.; et al. An Integrated Understanding of the Rapid Metabolic Benefits of a Carbohydrate-Restricted Diet on Hepatic Steatosis in Humans. Cell Metab. 2018, 27, 559–571.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luukkonen, P.K.; Dufour, S.; Lyu, K.; Zhang, X.-M.; Hakkarainen, A.; Lehtimäki, T.E.; Cline, G.W.; Petersen, K.F.; Shulman, G.I.; Yki-Järvinen, H. Effect of a Ketogenic Diet on Hepatic Steatosis and Hepatic Mitochondrial Metabolism in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 7347–7354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volek, J.S.; LaFountain, R.A.; Dituro, P. Extended Ketogenic Diet and Physical Training Intervention in Military Personnel. Mil. Med. 2019, 184, 199–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domouzoglou, E.M.; Maratos-Flier, E. Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 Is a Metabolic Regulator That Plays a Role in the Adaptation to Ketosis. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 93, 901S–905S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veldhorst, M.A.; Westerterp-Plantenga, M.S.; Westerterp, K.R. Gluconeogenesis and Energy Expenditure after a High-Protein, Carbohydrate-Free Diet. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 90, 519–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, X.; Wang, J.; Yang, S.; Gao, M.; Cao, L.; Li, X.; Hong, D.; Tian, S.; Sun, C. Effect of the Ketogenic Diet on Glycemic Control, Insulin Resistance, and Lipid Metabolism in Patients with T2DM: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutr. Diabetes 2020, 10, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Athinarayanan, S.J.; Adams, R.N.; Hallberg, S.J.; McKenzie, A.L.; Bhanpuri, N.H.; Campbell, W.W.; Volek, J.S.; Phinney, S.D.; McCarter, J.P. Long-Term Effects of a Novel Continuous Remote Care Intervention Including Nutritional Ketosis for the Management of Type 2 Diabetes: A 2-Year Non-Randomized Clinical Trial. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gershuni, V.M.; Yan, S.L.; Medici, V. Nutritional Ketosis for Weight Management and Reversal of Metabolic Syndrome. Curr. Nutr. Rep. 2018, 7, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolla, A.M.; Caretto, A.; Laurenzi, A.; Scavini, M.; Piemonti, L. Low-Carb and Ketogenic Diets in Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes. Nutrients 2019, 11, 962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakanishi, S.; Hirukawa, H.; Shimoda, M.; Tatsumi, F.; Kohara, K.; Obata, A.; Okauchi, S.; Katakura, Y.; Sanada, J.; Fushimi, Y.; et al. Comparison of HbA1c Levels and Body Mass Index for Prevention of Diabetic Kidney Disease: A Retrospective Longitudinal Study Using Outpatient Clinical Data in Japanese Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2019, 155, 107807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stocker, R.K.; Reber Aubry, E.; Bally, L.; Nuoffer, J.-M.; Stanga, Z. Ketogene Diät: Evidenzbasierte Therapeutische Anwendung Bei Endokrinologischen Erkrankungen. Praxis 2019, 108, 541–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dehghan, P.; Abbasalizad Farhangi, M. Dietary Acid Load, Blood Pressure, Fasting Blood Sugar and Biomarkers of Insulin Resistance among Adults: Findings from an Updated Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2020, 74, e13471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruskin, D.N.; Masino, S.A. The Nervous System and Metabolic Dysregulation: Emerging Evidence Converges on Ketogenic Diet Therapy. Front. Neurosci. 2012, 6, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaManna, J.C.; Salem, N.; Puchowicz, M.; Erokwu, B.; Koppaka, S.; Flask, C.; Lee, Z. Ketones Suppress Brain Glucose Consumption. In Oxygen Transport to Tissue XXX; Springer: Boston, MA, USA; pp. 301–306.
- McNally, M.A.; Hartman, A.L. Ketone Bodies in Epilepsy. J. Neurochem. 2012, 121, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlin, M.; Elfving, Å.; Ungerstedt, U.; Åmark, P. The Ketogenic Diet Influences the Levels of Excitatory and Inhibitory Amino Acids in the CSF in Children with Refractory Epilepsy. Epilepsy Res. 2005, 64, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neal, E.G.; Cross, J.H. Efficacy of Dietary Treatments for Epilepsy. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 2010, 23, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanner, G.R.; Lutas, A.; Martinez-Francois, J.R.; Yellen, G. Single KATP Channel Opening in Response to Action Potential Firing in Mouse Dentate Granule Neurons. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 8689–8696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omote, H.; Miyaji, T.; Juge, N.; Moriyama, Y. Vesicular Neurotransmitter Transporter: Bioenergetics and Regulation of Glutamate Transport. Biochemistry 2011, 50, 5558–5565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, D.D.; Aminzadeh-Gohari, S.; Tulipan, J.; Catalano, L.; Feichtinger, R.G.; Kofler, B. Ketogenic Diet in the Treatment of Cancer—Where Do We Stand? Mol. Metab. 2020, 33, 102–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sargaço, B.; Oliveira, P.A.; Antunes, M.L.; Moreira, A.C. Effects of the Ketogenic Diet in the Treatment of Gliomas: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dal Bello, S.; Valdemarin, F.; Martinuzzi, D.; Filippi, F.; Gigli, G.L.; Valente, M. Ketogenic Diet in the Treatment of Gliomas and Glioblastomas. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crosby, L.; Davis, B.; Joshi, S.; Jardine, M.; Paul, J.; Neola, M.; Barnard, N.D. Ketogenic Diets and Chronic Disease: Weighing the Benefits Against the Risks. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 702802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasui, B.A.; Toth, A.; Popescu, C.A.; Penes, O.N.; Varlas, V.N.; Ungur, R.A.; Ciuciuc, N.; Silaghi, C.A.; Silaghi, H.; Pop, A.L. Comparative Study on Nutrition and Lifestyle of Information Technology Workers from Romania before and during COVID-19 Pandemic. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nettleton, J.A.; Brouwer, I.A.; Geleijnse, J.M.; Hornstra, G. Saturated Fat Consumption and Risk of Coronary Heart Disease and Ischemic Stroke: A Science Update. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2017, 70, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayele, G.M.; Atalay, R.T.; Mamo, R.T.; Hussien, S.; Nigussie, B.; Fissha, A.; Michael, M.B. Is Losing Weight Worth Losing Your Kidney: Keto Diet Resulting in Renal Failure. Cureus 2023, 15, e36546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraris, C.; Guglielmetti, M.; Tamagni, E.; Trentani, C.; De Giorgis, V.; Pasca, L.; Varesio, C.; Ferraro, O.E.; Tagliabue, A. Use of Remote Monitoring by E-Mail for Long-Term Management of the Classic Ketogenic Diet. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrea, L.; Caprio, M.; Camajani, E.; Verde, L.; Perrini, S.; Cignarelli, A.; Prodam, F.; Gambineri, A.; Isidori, A.M.; Colao, A.; et al. Ketogenic Nutritional Therapy (KeNuT)—A Multi-Step Dietary Model with Meal Replacements for the Management of Obesity and Its Related Metabolic Disorders: A Consensus Statement from the Working Group of the Club of the Italian Society of Endocrinology (SIE)-diet therapies in endocrinology and metabolism. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2024, 47, 487–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO Diabetes. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/diabetes (accessed on 5 March 2024).
- Lv, Z.; Guo, Y. Metformin and Its Benefits for Various Diseases. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 490991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pernicova, I.; Korbonits, M. Metformin—Mode of Action and Clinical Implications for Diabetes and Cancer. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2014, 10, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rena, G.; Hardie, D.G.; Pearson, E.R. The Mechanisms of Action of Metformin. Diabetologia 2017, 60, 1577–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foretz, M.; Guigas, B.; Bertrand, L.; Pollak, M.; Viollet, B. Metformin: From Mechanisms of Action to Therapies. Cell Metab. 2014, 20, 953–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakkar, B.; Aronis, K.N.; Vamvini, M.T.; Shields, K.; Mantzoros, C.S. Metformin and Sulfonylureas in Relation to Cancer Risk in Type II Diabetes Patients: A Meta-Analysis Using Primary Data of Published Studies. Metabolism 2013, 62, 922–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heckman-Stoddard, B.M.; DeCensi, A.; Sahasrabuddhe, V.V.; Ford, L.G. Repurposing Metformin for the Prevention of Cancer and Cancer Recurrence. Diabetologia 2017, 60, 1639–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misirkic Marjanovic, M.S.; Vucicevic, L.M.; Despotovic, A.R.; Stamenkovic, M.M.; Janjetovic, K.D. Dual Anticancer Role of Metformin: An Old Drug Regulating AMPK Dependent/Independent Pathways in Metabolic, Oncogenic/Tumorsuppresing and Immunity Context. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2021, 11, 5625–5643. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kalender, A.; Selvaraj, A.; Kim, S.Y.; Gulati, P.; Brûlé, S.; Viollet, B.; Kemp, B.E.; Bardeesy, N.; Dennis, P.; Schlager, J.J.; et al. Metformin, Independent of AMPK, Inhibits MTORC1 in a Rag GTPase-Dependent Manner. Cell Metab. 2010, 11, 390–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elgendy, M.; Cirò, M.; Hosseini, A.; Weiszmann, J.; Mazzarella, L.; Ferrari, E.; Cazzoli, R.; Curigliano, G.; DeCensi, A.; Bonanni, B.; et al. Combination of Hypoglycemia and Metformin Impairs Tumor Metabolic Plasticity and Growth by Modulating the PP2A-GSK3β-MCL-1 Axis. Cancer Cell 2019, 35, 798–815.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porper, K.; Shpatz, Y.; Plotkin, L.; Pechthold, R.G.; Talianski, A.; Champ, C.E.; Furman, O.; Shimoni-Sebag, A.; Symon, Z.; Amit, U.; et al. A Phase I Clinical Trial of Dose-Escalated Metabolic Therapy Combined with Concomitant Radiation Therapy in High-Grade Glioma. J. Neurooncol. 2021, 153, 487–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koutentakis, M.; Kuciński, J.; Świeczkowski, D.; Surma, S.; Filipiak, K.J.; Gąsecka, A. The Ketogenic Effect of SGLT-2 Inhibitors—Beneficial or Harmful? J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2023, 10, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frąk, W.; Hajdys, J.; Radzioch, E.; Szlagor, M.; Młynarska, E.; Rysz, J.; Franczyk, B. Cardiovascular Diseases: Therapeutic Potential of SGLT-2 Inhibitors. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halimi, S.; Vergès, B. Adverse Effects and Safety of SGLT-2 Inhibitors. Diabetes Metab. 2014, 40, S28–S34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douros, A.; Lix, L.M.; Fralick, M.; Dell’Aniello, S.; Shah, B.R.; Ronksley, P.E.; Tremblay, É.; Hu, N.; Alessi-Severini, S.; Fisher, A.; et al. Sodium–Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitors and the Risk for Diabetic Ketoacidosis. Ann. Intern. Med. 2020, 173, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrannini, E.; Solini, A. SGLT2 Inhibition in Diabetes Mellitus: Rationale and Clinical Prospects. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2012, 8, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO Cardiovascular Diseases. Available online: https://www.who.int/health-topics/cardiovascular-diseases#tab=tab_1 (accessed on 10 March 2024).
- Yancy, W.S.; Olsen, M.K.; Guyton, J.R.; Bakst, R.P.; Westman, E.C. A Low-Carbohydrate, Ketogenic Diet versus a Low-Fat Diet To Treat Obesity and Hyperlipidemia. Ann. Intern. Med. 2004, 140, 769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burén, J.; Ericsson, M.; Damasceno, N.; Sjödin, A. A Ketogenic Low-Carbohydrate High-Fat Diet Increases LDL Cholesterol in Healthy, Young, Normal-Weight Women: A Randomized Controlled Feeding Trial. Nutrients 2021, 13, 814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dyńka, D.; Kowalcze, K.; Charuta, A.; Paziewska, A. The Ketogenic Diet and Cardiovascular Diseases. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, X.; Yang, S.; Lu, J.; Wu, M. Small, Dense Low-Density Lipoprotein-Cholesterol and Atherosclerosis: Relationship and Therapeutic Strategies. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 8, 804214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yurista, S.R.; Chong, C.-R.; Badimon, J.J.; Kelly, D.P.; de Boer, R.A.; Westenbrink, B.D. Therapeutic Potential of Ketone Bodies for Patients with Cardiovascular Disease. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2021, 77, 1660–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bank, I.M.; Shemie, S.D.; Rosenblatt, B.; Bernard, C.; Mackie, A.S. Sudden Cardiac Death in Association with the Ketogenic Diet. Pediatr. Neurol. 2008, 39, 429–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, J.; Chen, H.; Wang, Y.-J.; Qiu, J.-X.; Meng, Q.-Q.; Zou, R.-J.; Li, L.; Huang, J.-G.; Zhao, Z.-K.; Huang, Y.-L.; et al. Ketogenic Diet Suppressed T-Regulatory Cells and Promoted Cardiac Fibrosis via Reducing Mitochondria-Associated Membranes and Inhibiting Mitochondrial Function. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 5512322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belany, P.; Kackley, M.L.; Zhao, S.; Kluwe, B.; Buga, A.; Crabtree, C.D.; Nedungadi, D.; Kline, D.; Brock, G.; Simonetti, O.P.; et al. Effects of Hypocaloric Low-Fat, Ketogenic, and Ketogenic and Ketone Supplement Diets on Aldosterone and Renin. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2023, 108, 1727–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yin, Y.; Ni, L.; Long, Q.; You, L.; Zhang, Q.; Lin, S.; Chen, J. Low-Protein Diet Supplemented with Ketoacids Ameliorates Proteinuria in 3/4 Nephrectomised Rats by Directly Inhibiting the Intrarenal Renin–Angiotensin System. Br. J. Nutr. 2016, 116, 1491–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vahed, Y.A.K.; Koeslag, J.H.; Lochner, J.d.V. β-Adrenergic Blockade Counteracts Starvational Ketosis, but Aggravates Post-Exercise Ketosis in Non-Athletes. J. Endocrinol. 1988, 119, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unwin, D.J.; Tobin, S.D.; Murray, S.W.; Delon, C.; Brady, A.J. Substantial and Sustained Improvements in Blood Pressure, Weight and Lipid Profiles from a Carbohydrate Restricted Diet: An Observational Study of Insulin Resistant Patients in Primary Care. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrea, L.; Verde, L.; Santangeli, P.; Lucà, S.; Docimo, A.; Savastano, S.; Colao, A.; Muscogiuri, G. Very Low-Calorie Ketogenic Diet (VLCKD): An Antihypertensive Nutritional Approach. J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dungan, K.; Merrill, J.; Long, C.; Binkley, P. Effect of Beta Blocker Use and Type on Hypoglycemia Risk among Hospitalized Insulin Requiring Patients. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2019, 18, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonseca, V.A. Effects of β-Blockers on Glucose and Lipid Metabolism. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2010, 26, 615–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mills, G.A.; Horn, J.R. β-Blockers and Glucose Control. Drug Intell. Clin. Pharm. 1985, 19, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dowis, K.; Banga, S. The Potential Health Benefits of the Ketogenic Diet: A Narrative Review. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unger, T.; Borghi, C.; Charchar, F.; Khan, N.A.; Poulter, N.R.; Prabhakaran, D.; Ramirez, A.; Schlaich, M.; Stergiou, G.S.; Tomaszewski, M.; et al. 2020 International Society of Hypertension Global Hypertension Practice Guidelines. Hypertension 2020, 75, 1334–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, R.; Mandalia, R. Diuretics and the Kidney. BJA Educ. 2022, 22, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duchowny, M.S. Food for Thought: The Ketogenic Diet and Adverse Effects in Children. Epilepsy Curr. 2005, 5, 152–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimitriadis, G.; Tegos, C.; Golfinopoulou, L.; Roboti, C.; Raptis, S. Furosemide-Induced Hyperglycaemia: The Implication of Glycolytic Kinases. Horm. Metab. Res. 1993, 25, 557–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornsby, L.B.; Hester, E.K.; Donaldson, A.R. Potential Interaction between Warfarin and High Dietary Protein Intake. Pharmacother. J. Hum. Pharmacol. Drug Ther. 2008, 28, 536–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, Y.; Murata, M.; Chiba, T.; Umegaki, K. A Systematic Review of the Acceptable Intake Level of Vitamin K among Warfarin Users. Food Hyg. Saf. Sci. (Shokuhin Eiseigaku Zasshi) 2015, 56, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Han, H. The Importance of Vitamin K Monitoring with Warfarin (Coumadin) Use in Chronic Kidney Disease Patients. J. Ren. Nutr. 2015, 25, e7–e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simes, D.C.; Viegas, C.S.B.; Araújo, N.; Marreiros, C. Vitamin K as a Diet Supplement with Impact in Human Health: Current Evidence in Age-Related Diseases. Nutrients 2020, 12, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shilpa, J.; Mohan, V. Ketogenic Diets: Boon or Bane? Indian J. Med. Res. 2018, 148, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cullingford, T.E. The Ketogenic Diet; Fatty Acids, Fatty Acid-Activated Receptors and Neurological Disorders. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fat. Acids 2004, 70, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, E.A.; Jeon, B.T.; Shin, H.J.; Kim, N.; Lee, D.H.; Kim, H.J.; Kang, S.S.; Cho, G.J.; Choi, W.S.; Roh, G.S. Ketogenic Diet-Induced Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor-γ Activation Decreases Neuroinflammation in the Mouse Hippocampus after Kainic Acid-Induced Seizures. Exp. Neurol. 2011, 232, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taggart, A.K.P.; Kero, J.; Gan, X.; Cai, T.-Q.; Cheng, K.; Ippolito, M.; Ren, N.; Kaplan, R.; Wu, K.; Wu, T.-J.; et al. (D)-β-Hydroxybutyrate Inhibits Adipocyte Lipolysis via the Nicotinic Acid Receptor PUMA-G. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 26649–26652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.; Muhammad, S.; Khan, M.A.; Chen, H.; Ridder, D.A.; Müller-Fielitz, H.; Pokorná, B.; Vollbrandt, T.; Stölting, I.; Nadrowitz, R.; et al. The β-Hydroxybutyrate Receptor HCA2 Activates a Neuroprotective Subset of Macrophages. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zandi-Nejad, K.; Takakura, A.; Jurewicz, M.; Chandraker, A.K.; Offermanns, S.; Mount, D.; Abdi, R. The Role of HCA2 (GPR109A) in Regulating Macrophage Function. FASEB J. 2013, 27, 4366–4374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi, H.; Mohri, I.; Okabe-Arahori, H.; Aritake, K.; Wada, K.; Kanekiyo, T.; Narumiya, S.; Nakayama, M.; Ozono, K.; Urade, Y.; et al. Prostaglandin D 2 Protects Neonatal Mouse Brain from Hypoxic Ischemic Injury. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 4303–4312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forsythe, C.E.; Phinney, S.D.; Fernandez, M.L.; Quann, E.E.; Wood, R.J.; Bibus, D.M.; Kraemer, W.J.; Feinman, R.D.; Volek, J.S. Comparison of Low Fat and Low Carbohydrate Diets on Circulating Fatty Acid Composition and Markers of Inflammation. Lipids 2008, 43, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Z.; Yin, X.; Wang, M.; Chen, T.; Wang, Y.; Gao, Z.; Wang, Z. Effects of Ketogenic Diet on Neuroinflammation in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Aging Dis. 2022, 13, 1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, T.; McQueen, A.; Chen, T.-C.; Wang, J.-C. Regulation of Glucose Homeostasis by Glucocorticoids. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2015, 872, 99–126. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Esteves, G.P.; Mazzolani, B.C.; Smaira, F.I.; Mendes, E.S.; de Oliveira, G.G.; Roschel, H.; Gualano, B.; Pereira, R.M.R.; Dolan, E. Nutritional Recommendations for Patients Undergoing Prolonged Glucocorticoid Therapy. Rheumatol. Adv. Pract. 2022, 6, rkac029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besemer, F.; Kramers, C.; Brinkman, K.; Hermus, A.R.M.M.; van Herwaarden, A.E.; Burger, D.M. Hypothalamic–Pituitary–Adrenal Axis Suppression by Inhaled or Nasal Corticosteroids in HIV-Infected Patients. Int. J. Clin. Pharm. 2020, 42, 347–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thio, L.L. Hypothalamic Hormones and Metabolism. Epilepsy Res. 2012, 100, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, K.K.; Packard, A.E.B.; Larson, K.R.; Stout, J.; Fourman, S.M.; Thompson, A.M.K.; Ludwick, K.; Habegger, K.M.; Stemmer, K.; Itoh, N.; et al. Dietary Manipulations That Induce Ketosis Activate the HPA Axis in Male Rats and Mice: A Potential Role for Fibroblast Growth Factor-21. Endocrinology 2018, 159, 400–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Andrea Meira, I.; Romão, T.T.; Pires do Prado, H.J.; Krüger, L.T.; Pires, M.E.P.; da Conceição, P.O. Ketogenic Diet and Epilepsy: What We Know So Far. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 434220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soltani, D.; Ghaffar Pour, M.; Tafakhori, A.; Sarraf, P.; Bitarafan, S. Nutritional Aspects of Treatment in Epileptic Patients. Iran. J. Child Neurol. 2016, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Marvanova, M. Pharmacokinetic Characteristics of Antiepileptic Drugs (AEDs). Ment. Health Clin. 2016, 6, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newmaster, K.; Zhu, Z.; Bolt, E.; Chang, R.J.; Day, C.; Mhanna, A.; Paudel, S.; Farooq, O.; Swaminathan, A.; Acharya, P.; et al. A Review of the Multi-Systemic Complications of a Ketogenic Diet in Children and Infants with Epilepsy. Children 2022, 9, 1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ułamek-Kozioł, M.; Czuczwar, S.J.; Januszewski, S.; Pluta, R. Ketogenic Diet and Epilepsy. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyczkowski, D.A.; Pfeifer, H.H.; Ghosh, S.; Thiele, E.A. Safety and Tolerability of the Ketogenic Diet in Pediatric Epilepsy: Effects of Valproate Combination Therapy. Epilepsia 2005, 46, 1533–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armeno, M.L.; Kossoff, E.H. Let Food Be Thy Medicine. The Interaction between Ketogenic Diet Therapy and Anti-seizure Medications: A Systematic Review. Epileptic Disord. 2023, 25, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heo, G.; Kim, S.H.; Chang, M.J. Effect of Ketogenic Diet and Other Dietary Therapies on Anti-Epileptic Drug Concentrations in Patients with Epilepsy. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 2017, 42, 758–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kverneland, M.; Taubøll, E.; Molteberg, E.; Veierød, M.B.; Selmer, K.K.; Nakken, K.O.; Iversen, P.O. Pharmacokinetic Interaction between Modified Atkins Diet and Antiepileptic Drugs in Adults with Drug-resistant Epilepsy. Epilepsia 2019, 60, 2235–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, A.; Kwon, H.E.; Kim, H.D. Updates on the Ketogenic Diet Therapy for Pediatric Epilepsy. Biomed. J. 2022, 45, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imdad, K.; Abualait, T.; Kanwal, A.; AlGhannam, Z.T.; Bashir, S.; Farrukh, A.; Khattak, S.H.; Albaradie, R.; Bashir, S. The Metabolic Role of Ketogenic Diets in Treating Epilepsy. Nutrients 2022, 14, 5074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murugan, M.; Boison, D. Ketogenic Diet, Neuroprotection, and Antiepileptogenesis. Epilepsy Res. 2020, 167, 106444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tayutivutikul, N.; Wanleenuwat, P.; Panapongvasin, T.; Klajing, R.; Iwanowski, P. Dietary Effects on Antiseizure Drug Metabolism and Management of Epilepsy. Seizure Eur. J. Epilepsy 2022, 102, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, Y.P.; Casazza, J.P.; Sohn, D.H.; Veech, R.L.; Song, B.J. Pretranslational Activation of Cytochrome P450IIE during Ketosis Induced by a High Fat Diet. Mol. Pharmacol. 1992, 41, 474–479. [Google Scholar]
- Kalafut, K.C.; Mitchell, S.J.; MacArthur, M.R.; Mitchell, J.R. Short-Term Ketogenic Diet Induces a Molecular Response That Is Distinct From Dietary Protein Restriction. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 839341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johannessen, S.I.; Johannessen Landmark, C. Antiepileptic Drug Interactions—Principles and Clinical Implications. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2010, 8, 254–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kverneland, M.; Taubøll, E.; Selmer, K.K.; Iversen, P.O.; Nakken, K.O. Modified Atkins Diet May Reduce Serum Concentrations of Antiepileptic Drugs. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2015, 131, 187–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anghelescu, A. Late-Onset Epilepsy in the Elderly: Difficulties of Diagnosis and Personalized Pharmacological Management, with Particularities to COVID-19 Pandemic—Systematic Review of Literature. Farmacia 2022, 70, 184–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matran, I.M. Dietary and Pharmaco-Therapy in Skin Diseases. Farmacia 2022, 70, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, T. Effect of Aripiprazole Combined with Olanzapine on the Clinical Efficacy of Schizophrenia. Farmacia 2022, 70, 550–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danan, A.; Westman, E.C.; Saslow, L.R.; Ede, G. The Ketogenic Diet for Refractory Mental Illness: A Retrospective Analysis of 31 Inpatients. Front. Psychiatry 2022, 13, 951376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Włodarczyk, A.; Wiglusz, M.S.; Cubała, W.J. Ketogenic Diet for Schizophrenia: Nutritional Approach to Antipsychotic Treatment. Med. Hypotheses 2018, 118, 74–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillery, E.E.; Ellis, K.D.; Threatt, T.B.; Reyes, H.A.; Plummer, C.S.; Barney, L.R. The Use of the Ketogenic Diet in the Treatment of Psychiatric Disorders. Ment. Health Clin. 2021, 11, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamshoum, H.; Medak, K.D.; McKie, G.L.; Hahn, M.K.; Wright, D.C. Fasting or the Short-term Consumption of a Ketogenic Diet Protects against Antipsychotic-induced Hyperglycaemia in Mice. J. Physiol. 2022, 600, 2713–2728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, C.M.; Gilbert-Jaramillo, J.; Westman, E.C. The Ketogenic Diet and Remission of Psychotic Symptoms in Schizophrenia: Two Case Studies. Schizophr. Res. 2019, 208, 439–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herbert, M.R.; Buckley, J.A. Autism and Dietary Therapy. J. Child Neurol. 2013, 28, 975–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Włodarczyk, A.; Cubała, W.J.; Wielewicka, A. Ketogenic Diet: A Dietary Modification as an Anxiolytic Approach? Nutrients 2020, 12, 3822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Włodarczyk, A.; Cubała, W.J.; Stawicki, M. Ketogenic Diet for Depression: A Potential Dietary Regimen to Maintain Euthymia? Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2021, 109, 110257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichikawa, J.; Nishiyama, K.; Ozaki, K.; Ikeda, M.; Takii, Y.; Ozaki, M. Anesthetic Management of a Pediatric Patient on a Ketogenic Diet. J. Anesth. 2006, 20, 135–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto, A.; Bonucci, A.; Maggi, E.; Corsi, M.; Businaro, R. Anti-Oxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Ketogenic Diet: New Perspectives for Neuroprotection in Alzheimer’s Disease. Antioxidants 2018, 7, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conover, Z.R.; Talai, A.; Klockau, K.S.; Ing, R.J.; Chatterjee, D. Perioperative Management of Children on Ketogenic Dietary Therapies. Anesth. Analg. 2020, 131, 1872–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirikonda, N.S.; Patten, W.D.; Phillips, J.R.; Mullett, C.J. Ketogenic Diet: Rapid Onset of Selenium Deficiency-Induced Cardiac Decompensation. Pediatr. Cardiol. 2012, 33, 834–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidwell, R.; Tobias, J.D. Tobias Anesthetic Care of a Child Receiving a Ketogenic Diet. Pediatr. Anesth. Crit. Care J. 2021, 9, 85–93. [Google Scholar]
- Abu-Sawwa, R.; Busque, K.; Cokley, J. Parenteral Medication Considerations for the Ketogenic Diet. Am. J. Health Pharm. 2023, 80, 1357–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pietrafusa, N.; Ferretti, A.; Trivisano, M.; de Palma, L.; Calabrese, C.; Carfì Pavia, G.; Tondo, I.; Cappelletti, S.; Vigevano, F.; Specchio, N. Purified Cannabidiol for Treatment of Refractory Epilepsies in Pediatric Patients with Developmental and Epileptic Encephalopathy. Pediatr. Drugs 2019, 21, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, X.; Shi, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Lu, M.; Qu, D. Cannabidiol-Decorated Berberine-Loaded Microemulsions Improve IBS-D Therapy Through Ketogenic Diet-Induced Cannabidiol Receptors Overexpression. Int. J. Nanomed. 2023, 18, 2839–2853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagihara, K.; Kajimoto, K.; Osaga, S.; Nagai, N.; Shimosegawa, E.; Nakata, H.; Saito, H.; Nakano, M.; Takeuchi, M.; Kanki, H.; et al. Promising Effect of a New Ketogenic Diet Regimen in Patients with Advanced Cancer. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zhang, H.; Dai, Z. Cancer Treatment with the Ketogenic Diet: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Animal Studies. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 594408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrea, L.; Caprio, M.; Tuccinardi, D.; Moriconi, E.; Di Renzo, L.; Muscogiuri, G.; Colao, A.; Savastano, S. Could Ketogenic Diet “Starve” Cancer? Emerging Evidence. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 1800–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mundi, M.S.; Mohamed Elfadil, O.; Patel, I.; Patel, J.; Hurt, R.T. Ketogenic Diet and Cancer: Fad or Fabulous? J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2021, 45, S26–S32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jing, M.-X.; Jiang, L.; Jia, Y.-F.; Ying, E.; Cao, H.; Guo, X.-Y.; Sun, T. Does a Ketogenic Diet as an Adjuvant Therapy for Drug Treatment Enhance Chemotherapy Sensitivity and Reduce Target Lesions in Patients with Locally Recurrent or Metastatic Her-2-Negative Breast Cancer? Study Protocol for a Randomized Controlled Trial. Trials 2020, 21, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; TeSlaa, T.; Ng, S.; Nofal, M.; Wang, L.; Lan, T.; Zeng, X.; Cowan, A.; McBride, M.; Lu, W.; et al. Ketogenic Diet and Chemotherapy Combine to Disrupt Pancreatic Cancer Metabolism and Growth. Med 2022, 3, 119–136.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyikesici, M. Survival Outcomes of Metabolically Supported Chemotherapy Combined with Ketogenic Diet, Hyperthermia, and Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy in Advanced Gastric Cancer. Niger. J. Clin. Pract. 2020, 23, 734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Lv, J.; Li, T. Promoting the Anti-Tumor Activity of Radiotherapy on Lung Cancer through a Modified Ketogenic Diet and the AMPK Signaling Pathway. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2023, 117, e268–e269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klement, R.J.; Champ, C.E.; Kämmerer, U.; Koebrunner, P.S.; Krage, K.; Schäfer, G.; Weigel, M.; Sweeney, R.A. Impact of a Ketogenic Diet Intervention during Radiotherapy on Body Composition: III—Final Results of the KETOCOMP Study for Breast Cancer Patients. Breast Cancer Res. 2020, 22, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klement, R.J.; Schäfer, G.; Sweeney, R.A. A Ketogenic Diet Exerts Beneficial Effects on Body Composition of Cancer Patients during Radiotherapy: An Interim Analysis of the KETOCOMP Study. J. Tradit. Complement. Med. 2020, 10, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olson, C.A.; Vuong, H.E.; Yano, J.M.; Liang, Q.Y.; Nusbaum, D.J.; Hsiao, E.Y. The Gut Microbiota Mediates the Anti-Seizure Effects of the Ketogenic Diet. Cell 2018, 173, 1728–1741.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, C.; Nikpoor, N.; Tompkins, T.A.; Rho, J.M.; Scantlebury, M.H.; Shearer, J. Probiotics Counteract Hepatic Steatosis Caused by Ketogenic Diet and Upregulate AMPK Signaling in a Model of Infantile Epilepsy. eBioMedicine 2022, 76, 103838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, D.; Wang, A.C.; Parikh, I.; Green, S.J.; Hoffman, J.D.; Chlipala, G.; Murphy, M.P.; Sokola, B.S.; Bauer, B.; Hartz, A.M.S.; et al. Ketogenic Diet Enhances Neurovascular Function with Altered Gut Microbiome in Young Healthy Mice. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 6670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altayyar, M.; Nasser, J.A.; Thomopoulos, D.; Bruneau, M. The Implication of Physiological Ketosis on The Cognitive Brain: A Narrative Review. Nutrients 2022, 14, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engelking, L.R. Ketone Body Formation and Utilization. In Textbook of Veterinary Physiological Chemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 450–457. [Google Scholar]
- McPherson, P.A.C. Ketone Bodies. In Encyclopedia of Food and Health; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 483–489. [Google Scholar]
- Iizuka, K. The Role of Carbohydrate Response Element–Binding Protein in the Development of Liver Diseases. In Dietary Interventions in Liver Disease; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 263–274. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, R.W. Diabetic Ketoacidosis. In Canine and Feline Endocrinology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 315–347. [Google Scholar]
- Elendu, C.; David, J.A.; Udoyen, A.-O.; Egbunu, E.O.; Ogbuiyi-Chima, I.C.; Unakalamba, L.O.; Temitope, A.I.; Ibhiedu, J.O.; Ibhiedu, A.O.; Nwosu, P.U.; et al. Comprehensive Review of Diabetic Ketoacidosis: An Update. Ann. Med. Surg. 2023, 85, 2802–2807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perilli, G.; Saraceni, C.; Daniels, M.N.; Ahmad, A. Diabetic Ketoacidosis: A Review and Update. Curr. Emerg. Hosp. Med. Rep. 2013, 1, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Voss, T.S.; Vendelbo, M.H.; Kampmann, U.; Pedersen, S.B.; Nielsen, T.S.; Johannsen, M.; Svart, M.V.; Jessen, N.; Møller, N. Substrate Metabolism, Hormone and Cytokine Levels and Adipose Tissue Signalling in Individuals with Type 1 Diabetes after Insulin Withdrawal and Subsequent Insulin Therapy to Model the Initiating Steps of Ketoacidosis. Diabetologia 2019, 62, 494–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanikarla-Marie, P.; Jain, S.K. Hyperketonemia and Ketosis Increase the Risk of Complications in Type 1 Diabetes. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2016, 95, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segerer, H.; Wurm, M.; Grimsmann, J.M.; Karges, B.; Neu, A.; Sindichakis, M.; Warncke, K.; Dost, A.; Holl, R.W. Diabetic Ketoacidosis at Manifestation of Type 1 Diabetes in Childhood and Adolescence. Dtsch. Arztebl. Int. 2021, 118, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, A.; Al-Robeh, H.; Sharma, H.; Ammari, Z.; Khan, M.S.; Jaume, J.C. Steroid-Induced Diabetic Ketoacidosis in a Patient with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. AACE Clin. Case Rep. 2018, 4, 131–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Takahashi, K.; Anno, T.; Takenouchi, H.; Iwamoto, H.; Horiya, M.; Kimura, Y.; Kawasaki, F.; Kaku, K.; Tomoda, K.; Kaneto, H. Serious Diabetic Ketoacidosis Induced by Insulin Allergy and Anti-insulin Antibody in an Individual with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. J. Diabetes Investig. 2022, 13, 1788–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panicker Rajeev, S.; Wilding, J.P. SGLT2 Inhibition and Ketoacidosis—Should We Be Concerned? Br. J. Diabetes 2015, 15, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musso, G.; Saba, F.; Cassader, M.; Gambino, R. Diabetic Ketoacidosis with SGLT2 Inhibitors. BMJ 2020, 371, m4147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, B.F.; Clegg, D.J. Euglycemic Ketoacidosis as a Complication of SGLT2 Inhibitor Therapy. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2021, 16, 1284–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warner, E.A.; Greene, G.S.; Buchsbaum, M.S.; Cooper, D.S.; Robinson, B.E. Diabetic Ketoacidosis Associated with Cocaine Use. Arch. Intern. Med. 1998, 158, 1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsch, T.M. Diabetic Ketoacidosis. JAAPA 2017, 30, 46–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Remessy, A.B. Diabetic Ketoacidosis Management: Updates and Challenges for Specific Patient Population. Endocrines 2022, 3, 801–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, R.; Syeda, J.; Saber, S. PSUN274 Chlorthalidone-Induced Diabetic Ketoacidosis. J. Endocr. Soc. 2022, 6, A401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, X.; Moses, L. An Interesting Cause of Diabetic Ketoacidosis: Case Report, Review of Literature and Possible Pathophysiology of Thiazide Diuretics-Induced Dka. Chest 2018, 154, 265A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberti, K.G.M.M.; Hockaday, T.D.R. Thiazides and Hypokalaemia in Diabetic Ketoacidosis. Postgrad. Med. J. 1973, 49, 29–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavataio, M.M.; Packer, C.D. Steroid-Induced Diabetic Ketoacidosis: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. Cureus 2022, 14, e24372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alakkas, Z.; Alzaedi, O.A.; Somannavar, S.S.; Alfaifi, A. Steroid-Induced Diabetes Ketoacidosis in an Immune Thrombocytopenia Patient: A Case Report and Literature Review. Am. J. Case Rep. 2020, 21, e923372-1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hailu, W.; Tesfaye, T.; Tadesse, A. Hyperglycemia After Dolutegravir-Based Antiretroviral Therapy. Int. Med. Case Rep. J. 2021, 14, 503–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horikawa, M.; Toyoda, M.; Saito, N.; Kimura, M.; Kobayashi, T.; Takagi, A.; Fukagawa, M. Raltegravir-Associated Diabetic Ketoacidosis in a Patient with HIV Infection: A Case Report. Tokai J. Exp. Clin. Med. 2018, 43, 19–23. [Google Scholar]
- O’Halloran, J.A.; Sahrmann, J.; Parra-Rodriguez, L.; Vo, D.T.; Butler, A.M.; Olsen, M.A.; Powderly, W.G. Integrase Strand Transfer Inhibitors Are Associated with Incident Diabetes Mellitus in People with Human Immunodeficiency Virus. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2022, 75, 2060–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Sá-Ferreira, C.O.; da Costa, C.H.M.; Guimarães, J.C.W.; Sampaio, N.S.; de Silva, L.M.L.; de Mascarenhas, L.P.; Rodrigues, N.G.; dos Santos, T.L.; Campos, S.; Young, E.C. Diabetic Ketoacidosis and COVID-19: What Have We Learned so Far? Am. J. Physiol. Metab. 2022, 322, E44–E53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porntharukchareon, T.; Tontivuthikul, B.; Sintawichai, N.; Srichomkwun, P. Pembrolizumab- and Ipilimumab-Induced Diabetic Ketoacidosis and Isolated Adrenocorticotropic Hormone Deficiency: A Case Report. J. Med. Case Rep. 2020, 14, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tzoulis, P.; Corbett, R.W.; Ponnampalam, S.; Baker, E.; Heaton, D.; Doulgeraki, T.; Stebbing, J. Nivolumab-Induced Fulminant Diabetic Ketoacidosis Followed by Thyroiditis. Endocrinol. Diabetes Metab. Case Rep. 2018, 2018, 18-0111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, A.R.; Yoon, J.H.; Kim, H.K.; Kang, H.-C. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor-Induced Diabetic Ketoacidosis: A Report of Four Cases and Literature Review. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.H.; Shafiq, I. Diabetic Ketoacidosis Following PEG-Asparaginase Therapy. Endocrinol. Diabetes Metab. Case Rep. 2018, 2018, 18-0064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, R.; Nandi, M.; Tiwari, A.; Chakravorti, S. Diabetic Ketoacidosis with L-Asparaginase Therapy. Indian Pediatr. 2011, 48, 735–736. [Google Scholar]
- Jameel, P.Z.; Lohiya, S.; Dongre, A.; Damke, S.; Lakhkar, B.B. Concurrent Diabetic Ketoacidosis and Pancreatitis in Paediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Receiving L-Asparaginase. BMC Pediatr. 2020, 20, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatti, A.; McGarrity, T.J.; Gabbay, R. Diabetic Ketoacidosis Induced by Alpha Interferon and Ribavirin Treatment in A Patient with Hepatitis C. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2001, 96, 604–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soultati, A.S. Simultaneous Development of Diabetic Ketoacidosis and Hashitoxicosis in a Patient Treated with Pegylated Interferon-Alpha for Chronic Hepatitis C. World J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 13, 1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sharma, S.K.; Doval, D.; Khandelwal, V.; Kumar, M.; Choudhary, D. Tacrolimus Induced Diabetic Ketoacidosis Following Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. Indian J. Hematol. Blood Transfus. 2019, 35, 711–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, K.; Chujo, D. Tacrolimus-Induced Diabetic Ketoacidosis with Subsequent Rapid Recovery of Endogenous Insulin Secretion after Cessation of Tacrolimus. Medicine 2019, 98, e16992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pham, A.Q.T.; Xu, L.H.R.; Moe, O.W. Drug-Induced Metabolic Acidosis. F1000Research 2015, 4, 1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gosmanov, A.R.; Gosmanova, E.; Dillard-Cannon, E. Management of Adult Diabetic Ketoacidosis. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. Targets Ther. 2014, 7, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morton, A. Diabetic Ketoacidosis with Severe Hypokalaemia and Valproate-associated Fanconi Syndrome. Intern. Med. J. 2023, 53, 155–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamba, N.G.; Amour, A.A.; Sadiq, A.M.; Lyamuya, T.R.; Assey, E.V.; Sadiq, A.M.; Howlett, W.P. Status Epilepticus and Diabetes Ketoacidosis: Uncommon Clinical Presentations of Acromegaly. Endocrinol. Diabetes Metab. Case Rep. 2021, 2021, 20-0156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guenette, M.D.; Hahn, M.; Cohn, T.A.; Teo, C.; Remington, G.J. Atypical Antipsychotics and Diabetic Ketoacidosis: A Review. Psychopharmacology 2013, 226, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuk, A.; Baretic, M.; Osvatic, M.M.; Filipcic, I.; Jovanovic, N.; Kuzman, M.R. Treatment of Diabetic Ketoacidosis Associated with Antipsychotic Medication. J. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2017, 37, 584–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okosieme, O.E.; Campbell, A.; Patton, K.; Evans, M.L. Transient Diabetes Associated with Withdrawal of Lithium Therapy. Diabetes Care 2006, 29, 1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kondziela, J.R.; Kaufmann, M.W.; Klein, M.J. Diabetic Ketoacidosis Associated with Lithium: Case Report. J. Clin. Psychiatry 1985, 46, 492–493. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, K.-Y.; Chang, S.-Y.; Wang, S.-H.; Su, H.-Y.; Tsai, C.-L. Short-Term Starvation with a near-Fatal Asthma Attack Induced Ketoacidosis in a Nondiabetic Pregnant Woman. Medicine 2016, 95, e4042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Philipson, L.H. β-Agonists and Metabolism. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2002, 110, S313–S317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, G.S.; Saliba, W.R.; Cohen, L. Diabetic Ketoacidosis Associated with Oral Salbutamol Overdose. Am. J. Med. 2002, 113, 701–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, V.; Arnould, L.; Martin, P.; Monnot, M.-C.; Pineau, T.; Besnard, P.; Niot, I. Chronic High-Fat Diet Affects Intestinal Fat Absorption and Postprandial Triglyceride Levels in the Mouse. J. Lipid Res. 2007, 48, 278–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, J.P.; Brocks, D.R. The Effect of Oral Lipids and Circulating Lipoproteins on the Metabolism of Drugs. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2009, 5, 1385–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gershkovich, P.; Hoffman, A. Effect of a High-Fat Meal on Absorption and Disposition of Lipophilic Compounds: The Importance of Degree of Association with Triglyceride-Rich Lipoproteins. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2007, 32, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markovic, M.; Ben-Shabat, S.; Aponick, A.; Zimmermann, E.M.; Dahan, A. Lipids and Lipid-Processing Pathways in Drug Delivery and Therapeutics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eastep, J.; Chen, G. The Relationships of High-Fat Diet and Metabolism of Lipophilic Vitamins. Integr. Food Nutr. Metab. 2015, 2, 174–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javaid, J.I. Clinical Pharmacokinetics of Antipsychotics. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1994, 34, 286–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.K.; Shah, J.C.; Hwang, S.S. Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Characterization of OROS® and Immediate-release Amitriptyline. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1999, 48, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzinski, M.; Lindner, E.; Pendley, B.; Chaum, E. Electrochemical Sensor for Tricyclic Antidepressants with Low Nanomolar Detection Limit: Quantitative Determination of Amitriptyline and Nortriptyline in Blood. Talanta 2022, 239, 123072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maślanka, A.; Krzek, J.; Stolarczyk, M.; Walczak, M.; Głogowska, A. Stability Studies of Clonazepam, Diazepam, Haloperidol, and Doxepin with Diverse Polarities in an Acidic Environment. J. AOAC Int. 2011, 94, 1791–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, C.E.; Kaye, A.M.; Bueno, F.R.; Kaye, A.D. Benzodiazepine Pharmacology and Central Nervous System-Mediated Effects. Ochsner J. 2013, 13, 214–223. [Google Scholar]
- Weersink, R.A.; Drenth, J.P.H.; Borgsteede, S.D. Why Zolpidem Increases the Risk of Falls and Fractures in Patients with Cirrhosis. JHEP Rep. 2022, 4, 100528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenblatt, D.J.; Harmatz, J.S.; Roth, T.; Singh, N.N.; Moline, M.L.; Harris, S.C.; Kapil, R.P. Comparison of Pharmacokinetic Profiles of Zolpidem Buffered Sublingual Tablet and Zolpidem Oral Immediate-Release Tablet: Results from a Single-Center, Single-Dose, Randomized, Open-Label Crossover Study in Healthy Adults. Clin. Ther. 2013, 35, 604–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Widanapathirana, L.; Tale, S.; Reineke, T.M. Dissolution and Solubility Enhancement of the Highly Lipophilic Drug Phenytoin via Interaction with Poly(N-Isopropylacrylamide-Co-Vinylpyrrolidone) Excipients. Mol. Pharm. 2015, 12, 2537–2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karaman, K.; Türkdoğan, K.A.; Deniz, A.T.; Çanakçı, S.E. Which Is the Best in Carbamazepine Overdose? Clin. Case Rep. 2017, 5, 1612–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lafuente-Lafuente, C.; Alvarez, J.; Leenhardt, A.; Mouly, S.; Extramiana, F.; Caulin, C.; Funck-Brentano, C.; Bergmann, J. Amiodarone Concentrations in Plasma and Fat Tissue during Chronic Treatment and Related Toxicity. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2009, 67, 511–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mortlock, R.; Smith, V.; Nesci, I.; Bertoldi, A.; Ho, A.; El Mekkawi, Z.; Kakuzada, L.; Williams, K.; Pont, L.; De Rubis, G.; et al. A Comparative Evaluation of Propranolol Pharmacokinetics in Obese versus Ideal Weight Individuals: A Blueprint towards a Personalised Medicine. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2023, 371, 110351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Climent, E.; Benaiges, D.; Pedro-Botet, J. Hydrophilic or Lipophilic Statins? Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 687585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warhurst, D.C. Hydroxychloroquine Is Much Less Active than Chloroquine against Chloroquine-Resistant Plasmodium Falciparum, in Agreement with Its Physicochemical Properties. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2003, 52, 188–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira, J.L.F.; Rivera, J.G.B.; de Sena, L.W.P.; Ferreira, M.V.D. Association of Lipid Levels with Mefloquine and Carboxy-Mefloquine Concentrations in Patients with Uncomplicated Falciparum Malaria. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2020, 64, e01731-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Troke, P.F.; Andrews, R.J.; Pye, G.W.; Richardson, K. Fluconazole and Other Azoles: Translation of in Vitro Activity to in Vivo and Clinical Efficacy. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1990, 12, S276–S280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljurbui, S.J.; Hussain, A.; Yusuf, M.; Ramzan, M.; Afzal, O.; Almohaywi, B.; Yasmin, S.; Altamimi, A.S.A. Impact of Composition and Morphology of Ketoconazole-Loaded Solid Lipid Nanoparticles on Intestinal Permeation and Gastroplus-Based Prediction Studies. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 22406–22420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.S.; Kim, D.H.; Lee, S.M.; Han, N.Y.; Oh, J.M.; Ha, J.; Kim, Y.S. Pharmacokinetics of Tacrolimus According to Body Composition in Recipients of Kidney Transplants. Kidney Res. Clin. Pract. 2012, 31, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Law, D.; Krill, S.L.; Schmitt, E.A.; Fort, J.J.; Qiu, Y.; Wang, W.; Porter, W.R. Physicochemical Considerations in the Preparation of Amorphous Ritonavir–Poly(Ethylene Glycol) 8000 Solid Dispersions. J. Pharm. Sci. 2001, 90, 1015–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefanidou, M.; Herrera, C.; Armanasco, N.; Shattock, R.J. Saquinavir Inhibits Early Events Associated with Establishment of HIV-1 Infection: Potential Role for Protease Inhibitors in Prevention. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 4381–4390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sunilkumar, M.; Lockman, K. Practical Pharmacology of Methadone: A Long-Acting Opioid. Indian J. Palliat. Care 2018, 24, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C. Physicochemical, Pharmacological and Pharmacokinetic Properties of the Zwitterionic Antihistamines Cetirizine and Levocetirizine. Curr. Med. Chem. 2008, 15, 2173–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamaddon, L.; Mohamadi, N.; Bavarsad, N. Preparation and Characterization of Mucoadhesive Loratadine Nanoliposomes for Intranasal Administration. Turkish J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 18, 492–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaccour, C.; Hammann, F.; Rabinovich, N.R. Ivermectin to Reduce Malaria Transmission I. Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Considerations Regarding Efficacy and Safety. Malar. J. 2017, 16, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ermondi, G.; Vallaro, M.; Saame, J.; Toom, L.; Leito, I.; Ruiz, R.; Caron, G. Rifampicin as an Example of Beyond-Rule-of-5 Compound: Ionization beyond Water and Lipophilicity beyond Octanol/Water. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 161, 105802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dołowy, M.; Pyka, A. Lipophilicity Assessment of Spironolactone by Means of Reversed Phase Liquid Chromatography and by Newly Developed Calculation Procedures. Acta Pol. Pharm. 2015, 72, 235–244. [Google Scholar]
- Pietrzak, D.; Kasperek, K.; Rękawek, P.; Piątkowska-Chmiel, I. The Therapeutic Role of Ketogenic Diet in Neurological Disorders. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shendurse, A.M.; Khedkar, C.D. Lactose. In Encyclopedia of Food and Health; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 509–516. [Google Scholar]
- Kaur, A.P.; Bhardwaj, S.; Dhanjal, D.S.; Nepovimova, E.; Cruz-Martins, N.; Kuča, K.; Chopra, C.; Singh, R.; Kumar, H.; Șen, F.; et al. Plant Prebiotics and Their Role in the Amelioration of Diseases. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di, X.; Liang, X.; Shen, C.; Pei, Y.; Wu, B.; He, Z. Carbohydrates Used in Polymeric Systems for Drug Delivery: From Structures to Applications. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, H.; Jain, A.; Laghate, G.; Prabhudesai, D. Pharmaceutical Excipients. In Remington; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 633–643. [Google Scholar]
- García Ibarra, V.; Sendón, R.; Rodríguez-Bernaldo de Quirós, A. Antimicrobial Food Packaging Based on Biodegradable Materials. In Antimicrobial Food Packaging; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 363–384. [Google Scholar]
- Kar, M.; Chourasiya, Y.; Maheshwari, R.; Tekade, R.K. Current Developments in Excipient Science. In Basic Fundamentals of Drug Delivery; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 29–83. [Google Scholar]
- Dhaneshwar, S.; Bhilare, N.; Roy, S. Dextran Pharmaceutical Applications. In Polysaccharides of Microbial Origin; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 1–28. [Google Scholar]
- Kadirvel, V.; Narayana, G.P. Edible Gums—An Extensive Review on Its Diverse Applications in Various Food Sectors. Food Bioeng. 2023, 2, 384–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, G.; Tiwari, R.; Rai, A. Cyclodextrins in Delivery Systems: Applications. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2010, 2, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, J.B.; Owusu, K.; Nussbaum, I.; Beekman, R.; DeFilippo, N.A.; Gilmore, E.J.; Hirsch, L.J.; Cervenka, M.C.; Maciel, C.B. Pearls and Pitfalls of Introducing Ketogenic Diet in Adult Status Epilepticus: A Practical Guide for the Intensivist. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| ATC | Therapeutics | Chemical/Pharmacological Class | Compounds | Observations | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A10 | DRUGS USED IN DIABETES | Insulin and analogues | Insulin | Improper administration or incorrect handling | [153] |
| Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) Inhibitors | Canagliflozin, dapagliflozin, empagliflozin | Because of their ability to promote increased breakdown of fats and elevated levels of glucagon | [154,155,156] | ||
| C01 | CARDIAC THERAPY | Sympathomimetics | Epinephrine, norepinephrine, terbutaline | [157,158,159] | |
| C02DA | DIURETICS | Thiazides | Hydrochlorothiazide, chlorthalidone | [160,161,162] | |
| H02 | CORTICOSTEROIDS FOR SYSTEMIC USE | Glucocorticosteroids | Prednisone, dexamethasone | At high concentrations, such as those used to alleviate intracranial tumours | [152,163,164] |
| J05 | ANTIVIRALS FOR SYSTEMIC USE | Integrase Strand Transfer Inhibitor (INSTI) | Raltegravir, elvitegravir, dolutegravir | The usage of INSTI was linked to a higher risk of developing new-onset diabetes mellitus or hyperglycaemia within the first 6 months after starting antiretroviral therapy | [165,166,167] |
| J05 | HIV Protease inhibitors | Ritonavir | [168] | ||
| L01 | ANTINEOPLASTIC AGENTS | Checkpoint Inhibitors | Pembrolizumab, nivolumab, ipilimumab | [169,170,171] | |
| Chemotherapy drugs | L-asparaginase | [172,173,174] | |||
| L03 | IMMUNOSTIMULANTS | Interferons | Interferon alpha | [175,176] | |
| L04 | IMMUNOSUPPRESSANTS | Calcineurin inhibitors | Tacrolimus | Immunosuppressive medicines administered post-transplantation are a primary risk factors for diabetic ketoacidosis. | [177,178] |
| N02B | ANALGESICS AND ANTIPYRETICS | Salicylates | Salicylic acid derivates | High anion gap acidosis is a common symptom of paediatric overdose, whereas adults may experience a combination of respiratory alkalosis and metabolic acidosis | [179] |
| N03 | ANTIEPILEPTICS | Anticonvulsivants | Valproate, phenytoin | [180,181,182] | |
| N05A | ANTIPSYCHOTICS | Atypical Antipsychotics | Clozapine, olanzapine | DKA can manifest suddenly and without weight increase | [183,184] |
| Mood stabilisers | Lithium | [185,186] | |||
| R03A | ADRENERGICS, INHALANTS | Beta-adrenergic agonists | Albuterol, salmeterol | Although insulin secretion is enhanced due to specific beta(2)-agonist actions on pancreatic beta cells, overall serum glucose levels are raised and insulin sensitivity appears to be decreased due to other mechanisms, such as increased glucagon production and hepatic effects | [187,188,189] |
| Chemical/Pharmacological Class | Compounds | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Antipsychotics | Olanzapine, clozapine | [195] |
| Antidepressants | Amitriptyline, nortriptyline, doxepin | [196,197,198] |
| Benzodiazepines | Diazepam, midazolam | [199] |
| Sedatives | Zolpidem, zopiclone | [200,201] |
| Antiepileptics | Phenytoin, carbamazepine, valproic acid, gabapentin, pregabalin | [202,203] |
| Antiarrhythmic drugs | Amiodarone | [204] |
| Beta-blocking agents | Propranolol, metoprolol | [205] |
| Statins | Simvastatin, fluvastatin, lovastatin, pitavastatin, and atorvastatin | [206] |
| Antimalarian drugs | Chloroquine, mefloquine | [207,208] |
| Antifungal drugs | Ketoconazole, itraconazole | [209,210] |
| Immunosuppressants | Tacrolimus | [211] |
| Antivirals | Ritonavir, saquinavir | [212,213] |
| Opioids | Methadone | [214] |
| Antihistamines | Cetirizine, loratadine | [215,216] |
| Antiparasitic drugs | Ivermectin | [217] |
| Antituberculosis | Rifampicin | [218] |
| Diuretics | Spironolactone | [219] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marinescu, S.C.; Apetroaei, M.-M.; Nedea, M.I.; Arsene, A.L.; Velescu, B.Ș.; Hîncu, S.; Stancu, E.; Pop, A.L.; Drăgănescu, D.; Udeanu, D.I. Dietary Influence on Drug Efficacy: A Comprehensive Review of Ketogenic Diet–Pharmacotherapy Interactions. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1213. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16081213
Marinescu SC, Apetroaei M-M, Nedea MI, Arsene AL, Velescu BȘ, Hîncu S, Stancu E, Pop AL, Drăgănescu D, Udeanu DI. Dietary Influence on Drug Efficacy: A Comprehensive Review of Ketogenic Diet–Pharmacotherapy Interactions. Nutrients. 2024; 16(8):1213. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16081213
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarinescu, Simona Cristina (Nicolescu), Miruna-Maria Apetroaei, Marina Ionela (Ilie) Nedea, Andreea Letiția Arsene, Bruno Ștefan Velescu, Sorina Hîncu, Emilia Stancu, Anca Lucia Pop, Doina Drăgănescu, and Denisa Ioana Udeanu. 2024. "Dietary Influence on Drug Efficacy: A Comprehensive Review of Ketogenic Diet–Pharmacotherapy Interactions" Nutrients 16, no. 8: 1213. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16081213
APA StyleMarinescu, S. C., Apetroaei, M.-M., Nedea, M. I., Arsene, A. L., Velescu, B. Ș., Hîncu, S., Stancu, E., Pop, A. L., Drăgănescu, D., & Udeanu, D. I. (2024). Dietary Influence on Drug Efficacy: A Comprehensive Review of Ketogenic Diet–Pharmacotherapy Interactions. Nutrients, 16(8), 1213. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16081213













