Starvation in Mice Induces Liver Damage Associated with Autophagy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Study Design
2.3. Locomotor Activity Determination
2.4. Biochemistry
2.5. Histology, Immunohistochemistry, and Image Analysis
2.6. Statistics
2.7. Literature Research
3. Results
3.1. Acute and Chronic Starvation Lead to Weight Loss and Hyperactivity
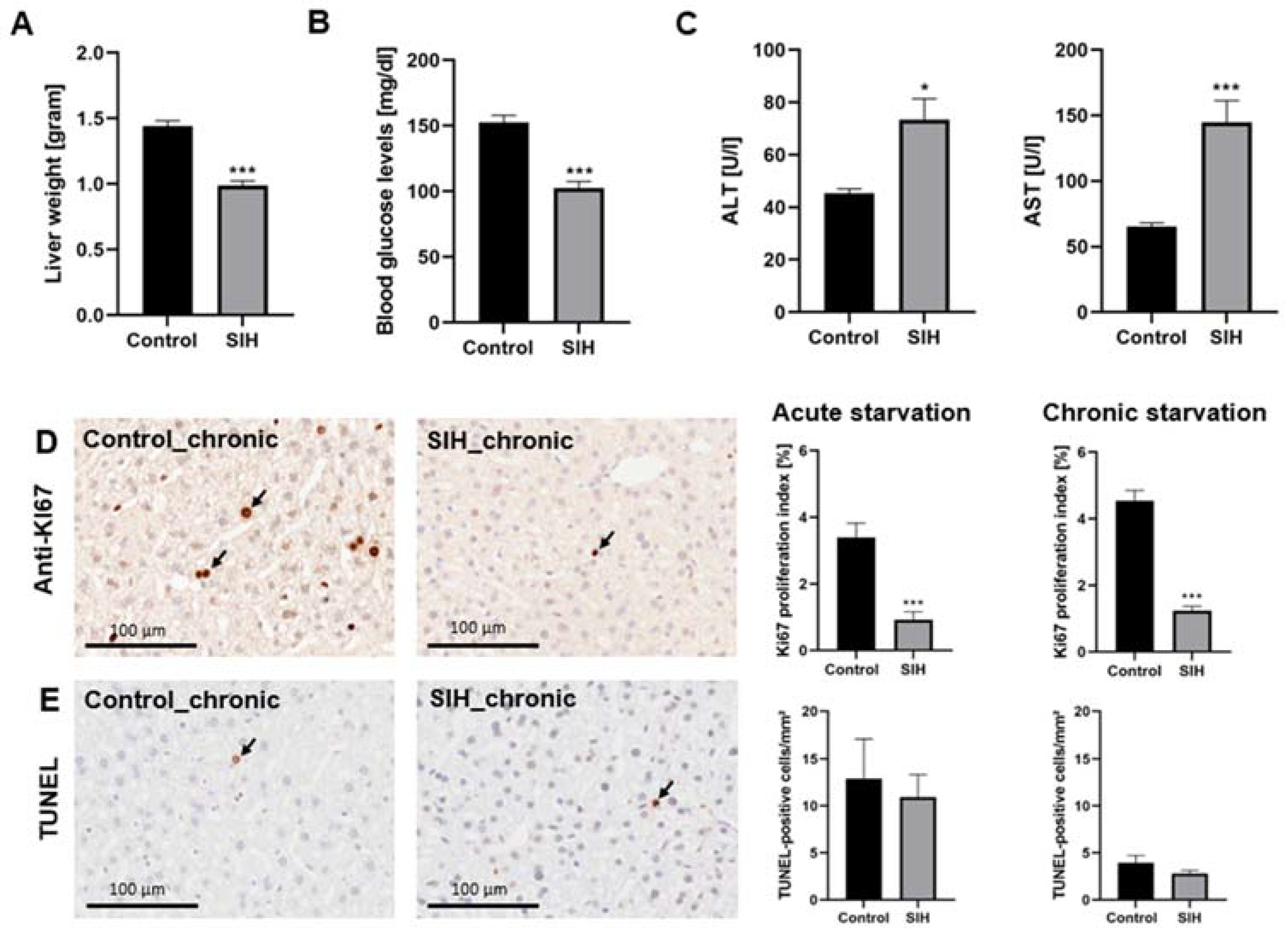
3.2. Starvation Can Induce Morphological Liver Damage, Reduced Liver Glycogen Deposits, and Reduced Liver Fat Content
3.3. Starvation Affects the Liver, Resulting in Increased Serum Transaminases and Decreased Proliferation Rate
3.4. Starvation Leads to a Reduction in Hepatic Macrophage Density and an Increase in Autophagy-Related Protein Staining
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Herpertz-Dahlmann, B. Adolescent eating disorders: Update on definitions, symptomatology, epidemiology, and comorbidity. Child. Adolesc. Psychiatr. Clin. N. Am. 2015, 24, 177–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rautou, P.E.; Cazals-Hatem, D.; Moreau, R.; Francoz, C.; Feldmann, G.; Lebrec, D.; Ogier-Denis, E.; Bedossa, P.; Valla, D.; Durand, F. Acute liver cell damage in patients with anorexia nervosa: A possible role of starvation-induced hepatocyte autophagy. Gastroenterology 2008, 135, 840–848.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaudiani, J.L.; Sabel, A.L.; Mascolo, M.; Mehler, P.S. Severe anorexia nervosa: Outcomes from a medical stabilization unit. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2012, 45, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosen, E.; Sabel, A.L.; Brinton, J.T.; Catanach, B.; Gaudiani, J.L.; Mehler, P.S. Liver dysfunction in patients with severe anorexia nervosa. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2016, 49, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanachi, M.; Melchior, J.C.; Crenn, P. Hypertransaminasemia in severely malnourished adult anorexia nervosa patients: Risk factors and evolution under enteral nutrition. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 32, 391–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, K.K.; Grinspoon, S.K.; Ciampa, J.; Hier, J.; Herzog, D.; Klibanski, A. Medical findings in outpatients with anorexia nervosa. Arch. Intern. Med. 2005, 165, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pratt, D.S.; Kaplan, M.M. Evaluation of abnormal liver-enzyme results in asymptomatic patients. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 342, 1266–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kheloufi, M.; Boulanger, C.M.; Durand, F.; Rautou, P.E. Liver autophagy in anorexia nervosa and acute liver injury. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 701064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizushima, N. Autophagy: Process and function. Genes. Dev. 2007, 21, 2861–2873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kheloufi, M.; Boulanger, C.M.; Codogno, P.; Rautou, P.E. Autosis occurs in the liver of patients with severe anorexia nervosa. Hepatology 2015, 62, 657–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeZwaan-McCabe, D.; Sheldon, R.D.; Gorecki, M.C.; Guo, D.F.; Gansemer, E.R.; Kaufman, R.J.; Rahmouni, K.; Gillum, M.P.; Taylor, E.B.; Teesch, L.M.; et al. ER Stress Inhibits Liver Fatty Acid Oxidation while Unmitigated Stress Leads to Anorexia-Induced Lipolysis and Both Liver and Kidney Steatosis. Cell Rep. 2017, 19, 1794–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabloffsky, T.; Gill, S.; Staffeld, A.; Salomon, R.; Power Guerra, N.; Joost, S.; Hawlitschka, A.; Kipp, M.; Frintrop, L. Food Restriction in Mice Induces Food-Anticipatory Activity and Circadian-Rhythm-Related Activity Changes. Nutrients 2022, 14, 5252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulukat, L.; Frintrop, L.; Liesbrock, J.; Heussen, N.; Johann, S.; Exner, C.; Kas, M.J.; Tolba, R.; Neulen, J.; Konrad, K.; et al. Memory impairment is associated with the loss of regular oestrous cycle and plasma oestradiol levels in an activity-based anorexia animal model. World J. Biol. Psychiatry 2016, 17, 274–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frintrop, L.; Trinh, S.; Liesbrock, J.; Paulukat, L.; Kas, M.J.; Tolba, R.; Konrad, K.; Herpertz-Dahlmann, B.; Beyer, C.; Seitz, J. Establishment of a chronic activity-based anorexia rat model. J. Neurosci. Methods 2018, 293, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frintrop, L.; Trinh, S.; Liesbrock, J.; Leunissen, C.; Kempermann, J.; Etdoger, S.; Kas, M.J.; Tolba, R.; Heussen, N.; Neulen, J.; et al. The reduction of astrocytes and brain volume loss in anorexia nervosa-the impact of starvation and refeeding in a rodent model. Transl. Psychiatry 2019, 9, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staffeld, A.; Gill, S.; Zimmermann, A.; Boge, N.; Schuster, K.; Lang, S.; Kipp, M.; Palme, R.; Frintrop, L. Establishment of a Murine Chronic Anorexia Nervosa Model. Cells 2023, 12, 1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keski-Rahkonen, A.; Mustelin, L. Epidemiology of eating disorders in Europe: Prevalence, incidence, comorbidity, course, consequences, and risk factors. Curr. Opin. Psychiatry 2016, 29, 340–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yakimov, V.; Schweiger, F.; Zhan, J.; Behrangi, N.; Horn, A.; Schmitz, C.; Hochstrasser, T.; Kipp, M. Continuous cuprizone intoxication allows active experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis induction in C57BL/6 mice. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2019, 152, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, J.; Yakimov, V.; Ruhling, S.; Fischbach, F.; Nikolova, E.; Joost, S.; Kaddatz, H.; Greiner, T.; Frenz, J.; Holzmann, C.; et al. High Speed Ventral Plane Videography as a Convenient Tool to Quantify Motor Deficits during Pre-Clinical Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis. Cells 2019, 8, 1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frintrop, L.; Liesbrock, J.; Paulukat, L.; Johann, S.; Kas, M.J.; Tolba, R.; Heussen, N.; Neulen, J.; Konrad, K.; Herpertz-Dahlmann, B.; et al. Reduced astrocyte density underlying brain volume reduction in activity-based anorexia rats. World J. Biol. Psychiatry 2018, 19, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashed, M. Rolling ball algorithm as a multitask filter for terrain conductivity measurements. J. Appl. Geophys. 2016, 132, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bankhead, P.; Loughrey, M.B.; Fernandez, J.A.; Dombrowski, Y.; McArt, D.G.; Dunne, P.D.; McQuaid, S.; Gray, R.T.; Murray, L.J.; Coleman, H.G.; et al. QuPath: Open source software for digital pathology image analysis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, A.; Choe, M.; Birkness, J.E.; Limketkai, B.; Chen, P.H. Two Acute Liver Injuries in a Patient with Malnutrition. J. Med. Cases 2021, 12, 315–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faragalla, K.; So, J.; Chan, P.C.; Wang, H.L.; Liu, J. Value of liver biopsy in anorexia nervosa-related transaminitis: A case study and literature review. Hepatol. Res. 2022, 52, 652–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Risi, R.; Tuccinardi, D.; Mariani, S.; Lubrano, C.; Manfrini, S.; Donini, L.M.; Watanabe, M. Liver disease in obesity and underweight: The two sides of the coin. A narrative review. Eat. Weight. Disord. 2021, 26, 2097–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakada, M.; Tanaka, A.; Ohta, D.; Takayanagi, M.; Kodama, T.; Suzuki, K.; Inoue, K.; Fujita, Y.; Maruyama, M. Severe steatosis resulted from anorexia nervosa leading to fatal hepatic failure. J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 41, 714–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosen, E.; Bakshi, N.; Watters, A.; Rosen, H.R.; Mehler, P.S. Hepatic Complications of Anorexia Nervosa. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2017, 62, 2977–2981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tessitore, L. Apoptosis and cell proliferation are involved in the initiation of liver carcinogenesis by a subnecrogenic dose of diethylnitrosamine in refed rats. J. Nutr. 2000, 130, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobis, S.; Goichon, A.; Achamrah, N.; Guerin, C.; Azhar, S.; Chan, P.; Morin, A.; Bole-Feysot, C.; do Rego, J.C.; Vaudry, D.; et al. Alterations of proteome, mitochondrial dynamic and autophagy in the hypothalamus during activity-based anorexia. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 7233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizushima, N.; Yamamoto, A.; Matsui, M.; Yoshimori, T.; Ohsumi, Y. In vivo analysis of autophagy in response to nutrient starvation using transgenic mice expressing a fluorescent autophagosome marker. Mol. Biol. Cell 2004, 15, 1101–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deter, R.L.; Baudhuin, P.; De Duve, C. Participation of lysosomes in cellular autophagy induced in rat liver by glucagon. J. Cell Biol. 1967, 35, C11–C16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruan, H.B.; Ma, Y.; Torres, S.; Zhang, B.; Feriod, C.; Heck, R.M.; Qian, K.; Fu, M.; Li, X.; Nathanson, M.H.; et al. Calcium-dependent O-GlcNAc signaling drives liver autophagy in adaptation to starvation. Genes. Dev. 2017, 31, 1655–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mortimore, G.E.; Poso, A.R. Intracellular protein catabolism and its control during nutrient deprivation and supply. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 1987, 7, 539–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabinowitz, J.D.; White, E. Autophagy and metabolism. Science 2010, 330, 1344–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filaire, E.; Rouveix, M.; Massart, A.; Gladine, C.; Davicco, M.J.; Durand, D. Lipid peroxidation and antioxidant status in rat: Effect of food restriction and wheel running. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2009, 107, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, H.; Zhai, W.; Lu, X.; Wang, G. The Cross-Links of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress, Autophagy, and Neurodegeneration in Parkinson’s Disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2021, 13, 691881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rashid, H.O.; Yadav, R.K.; Kim, H.R.; Chae, H.J. ER stress: Autophagy induction, inhibition and selection. Autophagy 2015, 11, 1956–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mickley, D.; Greenfeld, D.; Quinlan, D.M.; Roloff, P.; Zwas, F. Abnormal liver enzymes in outpatients with eating disorders. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 1996, 20, 325–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montagnese, C.; Scalfi, L.; Signorini, A.; De Filippo, E.; Pasanisi, F.; Contaldo, F. Cholinesterase and other serum liver enzymes in underweight outpatients with eating disorders. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2007, 40, 746–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, H.-F.; DiVasta, A.D.; DiFabio, D.; Ringelheim, J.; Jonas, M.M.; Gordon, C.M. Prevalence and predictors of abnormal liver enzymes in young women with anorexia nervosa. J. Pediatr. 2008, 153, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukamoto, M.; Tanaka, A.; Arai, M.; Ishii, N.; Ohta, D.; Horiki, N.; Fujita, Y. Hepatocellular injuries observed in patients with an eating disorder prior to nutritional treatment. Intern. Med. 2008, 47, 1447–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagata, J.M.; Park, K.; Colditz, K.; Golden, N.H. Associations of elevated liver enzymes among hospitalized adolescents with anorexia nervosa. J. Pediatr. 2015, 166, 439–443.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fanin, A.; Miele, L.; Bertolini, E.; Giorgini, A.; Pontiroli, A.E.; Benetti, A. Liver alterations in anorexia nervosa are not caused by insulin resistance. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2019, 15, 337–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuntz, U.; Voderholzer, U. Liver Damage Is Related to the Degree of Being Underweight in Anorexia Nervosa and Improves Rapidly with Weight Gain. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaryura-Tobias, J.A.; Pinto, A.; Neziroglu, F. Anorexia nervosa, diabetes mellitus, brain atrophy, and fatty liver. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2001, 30, 350–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Caprio, C.; Alfano, A.; Senatore, I.; Zarrella, L.; Pasanisi, F.; Contaldo, F. Severe acute liver damage in anorexia nervosa: Two case reports. Nutrition 2006, 22, 572–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, R.H.; Sasson, G.; Mehler, P.S. Elevation of liver function tests in severe anorexia nervosa. Int. J. Eat Disord. 2013, 46, 369–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Restellini, S.; Spahr, L.; Brandt, L.R. Severe Starvation-Induced Hepatocyte Autophagy as a Cause of Acute Liver Injury in Anorexia Nervosa: A Case Report. Case Rep. Hepatol. 2013, 2013, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramsoekh, D.; Taimr, P.; Vanwolleghem, T. Reversible severe hepatitis in anorexia nervosa: A case report and overview. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 26, 473–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takata, K.; Nagata, T.; Uchida, Y.; Kitaguchi, T.; Higashi, T.; Fukuda, H.; Yamauchi, R.; Tsuchiya, N.; Tanaka, T.; Yokoyama, K.; et al. Gastroesophageal Varices and Hyperplastic Nodules of the Liver in a Patient with Anorexia Nervosa. Intern. Med. 2021, 60, 3107–3112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakata, M.; Takaki, A.; Oyama, A.; Adachi, T.; Wada, N.; Takeuchi, Y.; Yasunaka, T.; Onishi, H.; Shiraha, H.; Okada, H. Pathogenesis of Severe Liver Injury in Patients with Anorexia Nervosa: A Report of Two Cases and a Literature Review. Kurume Med. J. 2020, 67, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, J.-A.M.; Udquim, K.-I.T.; Starnes, T.A.; Radhakrishnan, N.S. A Hepatic Manifestation of Anorexia Nervosa. Eur. J. Case Rep. Intern. Med. 2023, 10, 003675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Antigen | Species | Dilution | Purchase Number | RRID | Supplier |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Antibodies | |||||
| Ki67 | Rabbit polyclonal | 1:500 | ab15580 | AB_443209 | Abcam, Cambridge, UK |
| F4/80 | Rat monoclonal | 1:100 | MCA497 | AB_2098196 | Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA |
| LC3B | Rabbit polyclonal | 1:500 | ab48394 | AB_881433 | Abcam, UK |
| Secondary Antibodies | |||||
| Anti-rabbit IgG | Goat | 1:200 | BA9400 | AB_2313606 | Vector Laboratories, USA |
| Anti-rat IgG | Goat | 1:200 | BA1000 | AB_2336202 | Vector Laboratories, USA |
| Isotype Controls | |||||
| IgG2b | Rat | 1:100 | 02-9288 | AB_2532966 | Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schuster, K.; Staffeld, A.; Zimmermann, A.; Böge, N.; Lang, S.; Kuhla, A.; Frintrop, L. Starvation in Mice Induces Liver Damage Associated with Autophagy. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1191. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16081191
Schuster K, Staffeld A, Zimmermann A, Böge N, Lang S, Kuhla A, Frintrop L. Starvation in Mice Induces Liver Damage Associated with Autophagy. Nutrients. 2024; 16(8):1191. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16081191
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchuster, Katharina, Anna Staffeld, Annelie Zimmermann, Natalie Böge, Stephan Lang, Angela Kuhla, and Linda Frintrop. 2024. "Starvation in Mice Induces Liver Damage Associated with Autophagy" Nutrients 16, no. 8: 1191. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16081191
APA StyleSchuster, K., Staffeld, A., Zimmermann, A., Böge, N., Lang, S., Kuhla, A., & Frintrop, L. (2024). Starvation in Mice Induces Liver Damage Associated with Autophagy. Nutrients, 16(8), 1191. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16081191




