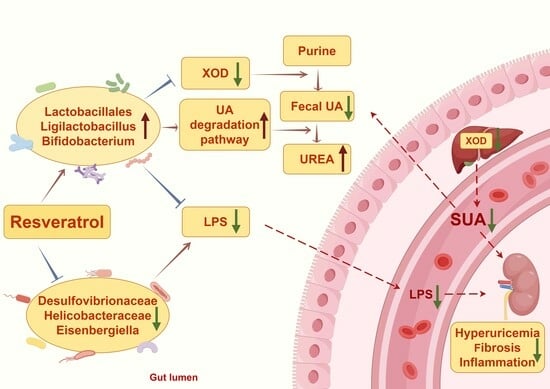
Resveratrol Improves Hyperuricemia and Ameliorates Renal Injury by Modulating the Gut Microbiota
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
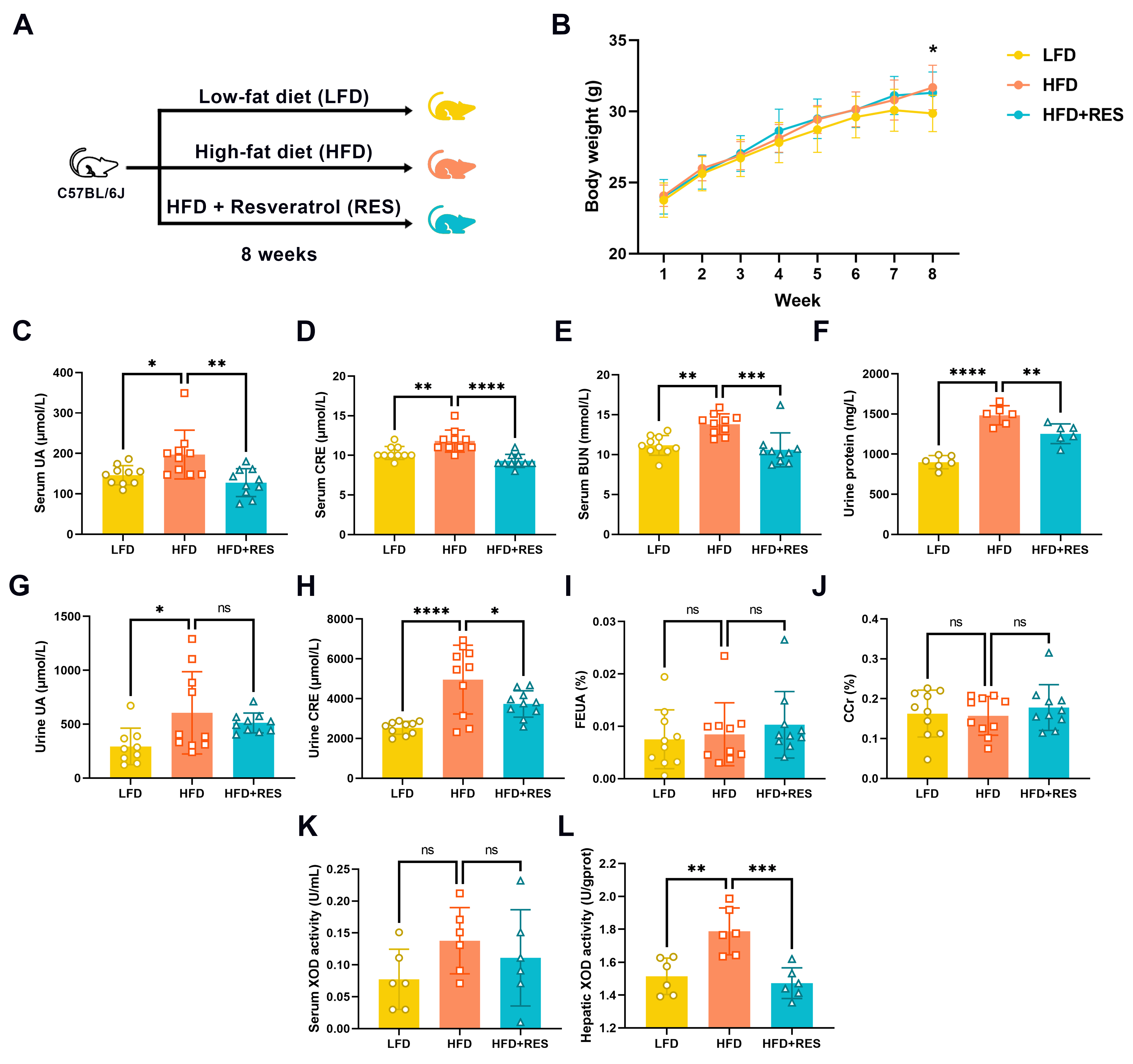
2.1. Design of the Intervention Experiments
2.2. Fecal Microbiota Transplantation
2.3. Metagenomic Sequencing
2.4. 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing
2.5. Biochemical Parameter Detection
2.6. XOD Activity Detection
2.7. Renal Histological Analysis
2.8. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.9. Determination of the UA Degradation Capacity of Cecum Contents
2.10. Statistical and Bioinformatics Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effect of RES on HFD-Induced HUA
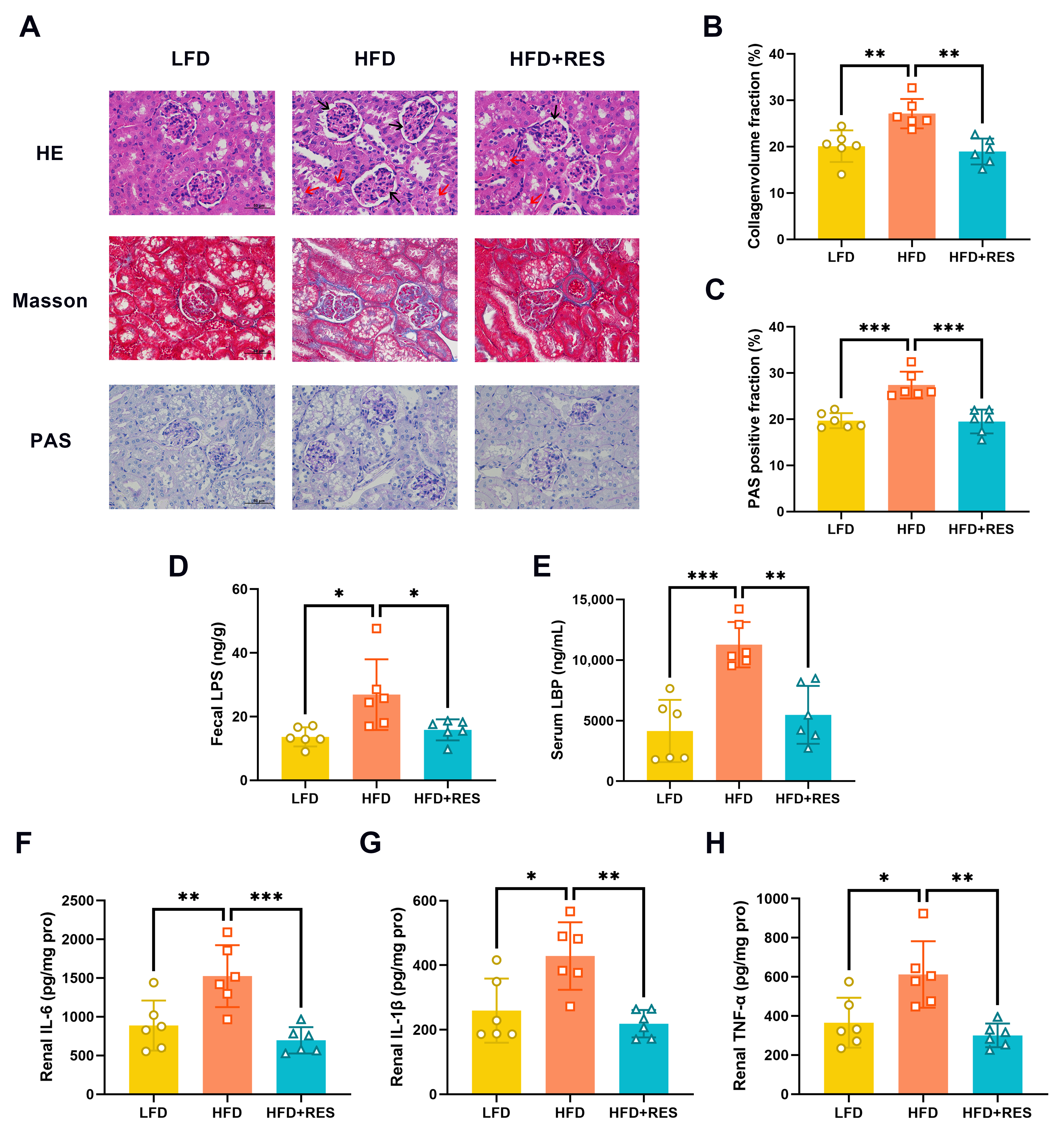
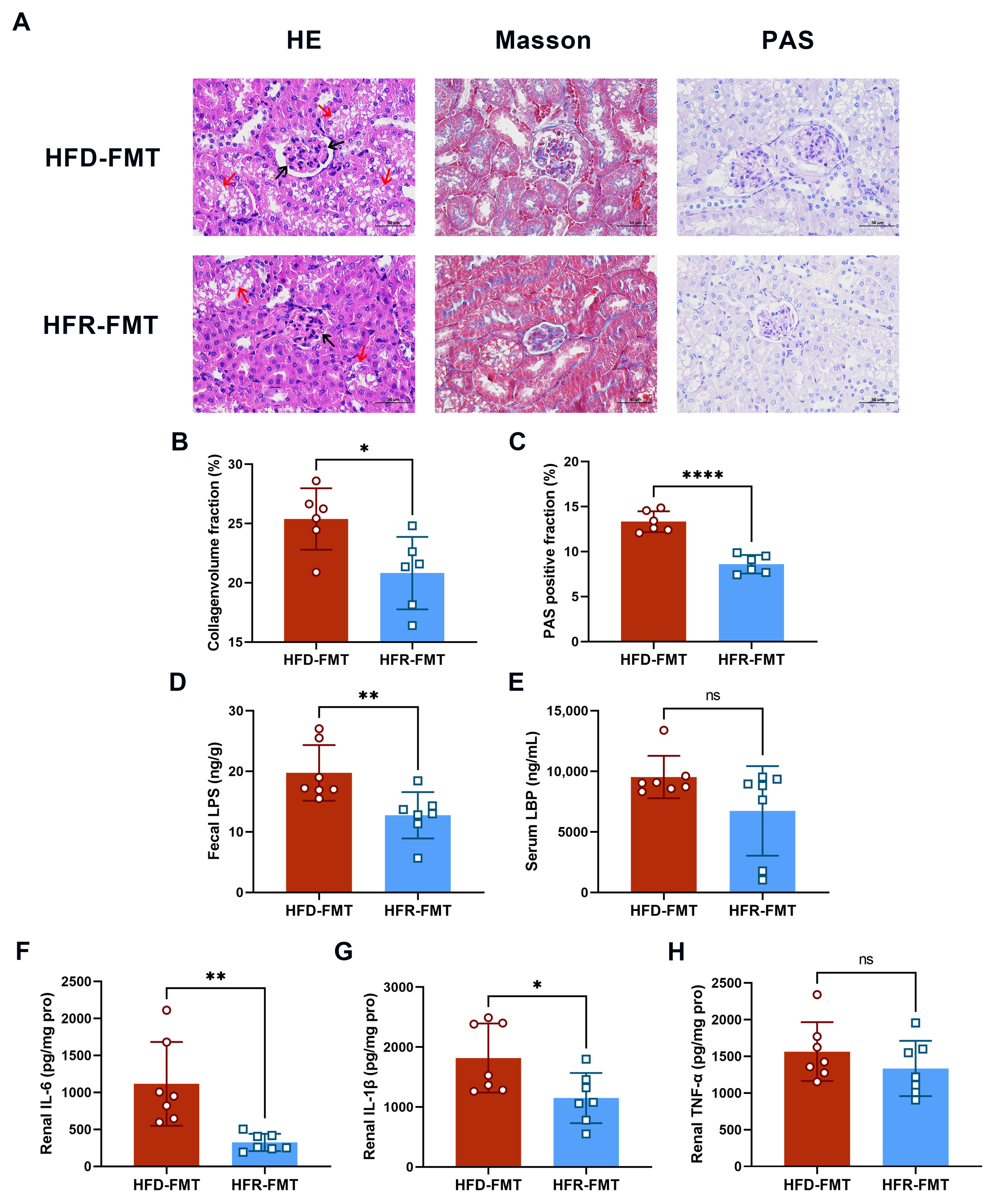
3.2. Effect of RES on Renal Injury and Inflammation
3.3. Effect of RES on Intestinal UA Metabolism
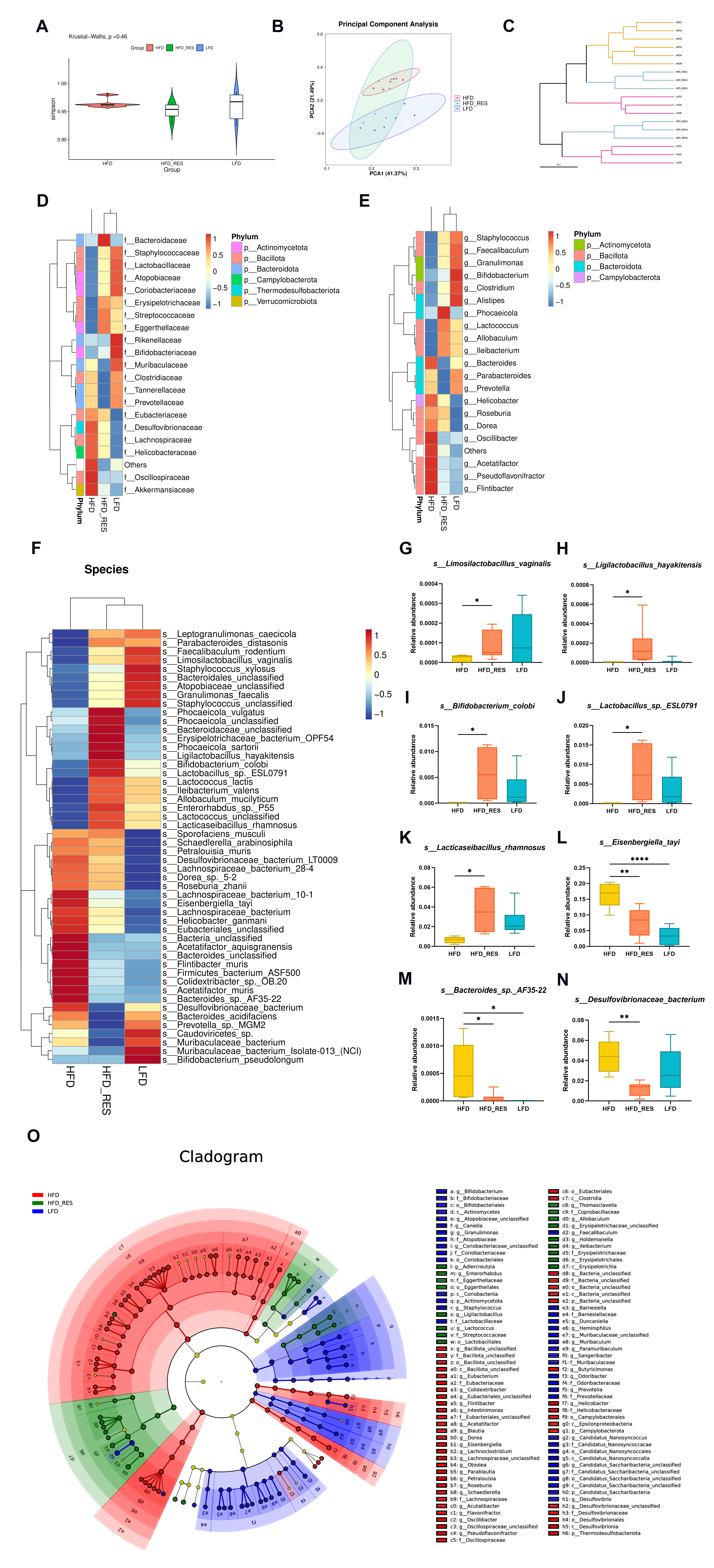
3.4. Effects of RES on the Structural Dysregulation of the Intestinal Flora
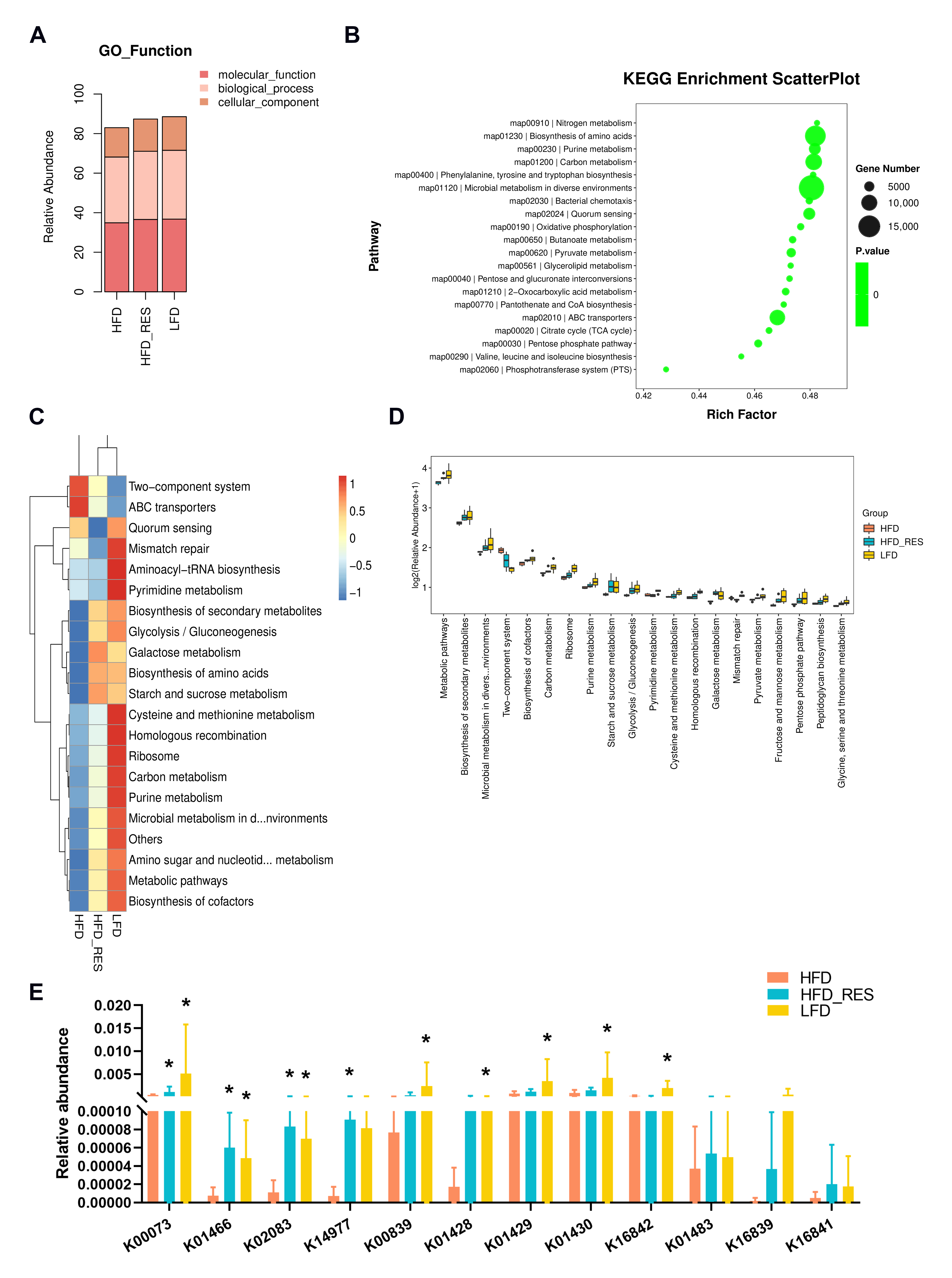
3.5. Effect of RES on the Function of the Gut Microbiota
3.6. The Intestinal Flora Is the Key to RES-Mediated HUA Regulation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Q.; Zhao, H.; Gao, Y.; Lu, J.; Xie, D.; Yu, W.; He, F.; Liu, W.; Hisatome, I.; Yamamoto, T.; et al. Uric acid inhibits HMGB1-TLR4-NF-κB signaling to alleviate oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation injury of microglia. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2021, 540, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, R.J.; Bakris, G.L.; Borghi, C.; Chonchol, M.B.; Feldman, D.; Lanaspa, M.A.; Merriman, T.R.; Moe, O.W.; Mount, D.B.; Sanchez Lozada, L.G.; et al. Hyperuricemia, Acute and Chronic Kidney Disease, Hypertension, and Cardiovascular Disease: Report of a Scientific Workshop Organized by the National Kidney Foundation. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2018, 71, 851–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, K.; Yamazaki, K.; Kato, T.; Nakanishi, Y.; Tsuzuno, T.; Yokoji-Takeuchi, M.; Yamada-Hara, M.; Miura, N.; Okuda, S.; Ohno, H.; et al. Obesity-Related Gut Microbiota Aggravates Alveolar Bone Destruction in Experimental Periodontitis through Elevation of Uric Acid. Mbio 2021, 12, e0077121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, Y.; Sun, S.; Huang, Y.; Gao, Q.; Xie, X.; Wang, P.; Li, J.; Liang, L.; He, X.; Jiang, Y.; et al. Metagenomic analysis revealed the potential role of gut microbiome in gout. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes 2021, 7, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Liu, Q.; Li, H.; Wen, C.; He, Z. Alterations of the Gut Microbiome Associated with the Treatment of Hyperuricaemia in Male Rats. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhong, H.; Chen, F.; Regenstein, J.; Hu, X.; Cai, L.; Feng, F. The gut microbiota as a target to control hyperuricemia pathogenesis: Potential mechanisms and therapeutic strategies. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 3979–3989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Lu, Z.; Lu, Y. The potential of probiotics in the amelioration of hyperuricemia. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 2394–2414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, B.; Liu, J. Resveratrol: A review of plant sources, synthesis, stability, modification and food application. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, 100, 1392–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szkudelska, K.; Okulicz, M.; Hertig, I.; Szkudelski, T. Resveratrol ameliorates inflammatory and oxidative stress in type 2 diabetic Goto-Kakizaki rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 125, 110026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.N.; Hou, C.Y.; Tain, Y.L. Preventive Aspects of Early Resveratrol Supplementation in Cardiovascular and Kidney Disease of Developmental Origins. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Pan, Z.; Jin, Y.; Li, Q.; Pang, J.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Yang, Y.; Ling, W. A Randomized Trial on Resveratrol Supplement Affecting Lipid Profile and Other Metabolic Markers in Subjects with Dyslipidemia. Nutrients 2023, 15, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; Yu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Wang, L.; Ma, J.; Bai, X.; Sun, Y.; Wang, D. Effects of β-carotin and Green Tea Powder Diets on Alleviating the Symptoms of Gouty Arthritis and Improving Gut Microbiota in C57BL/6 Mice. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 837182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, X.Q.; Jian, T.Y.; Gai, Y.N.; Niu, G.T.; Liu, Y.; Meng, X.H.; Li, J.; Lyu, H.; Ren, B.R.; Chen, J. Chicoric Acid Attenuated Renal Tubular Injury in HFD-Induced Chronic Kidney Disease Mice through the Promotion of Mitophagy via the Nrf2/PINK/Parkin Pathway. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 2923–2935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, S.E.; Li, L.; Fazzari, M.; Salvatore, S.R.; Li, J.; Hileman, E.A.; Maxwell, B.A.; Schopfer, F.J.; Arteel, G.E.; Khoo, N.K.H.; et al. Obese female mice do not exhibit overt hyperuricemia despite hepatic steatosis and impaired glucose tolerance. Adv. Redox Res. 2022, 6, 100051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reagan-Shaw, S.; Nihal, M.; Ahmad, N. Dose translation from animal to human studies revisited. Faseb J. 2008, 22, 659–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, J.; Raka, F.; Heirali, A.A.; Shao, W.; Liu, D.; Gu, J.; Feng, J.N.; Mineo, C.; Shaul, P.W.; Qian, X.; et al. Resveratrol intervention attenuates chylomicron secretion via repressing intestinal FXR-induced expression of scavenger receptor SR-B1. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 2656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, S.; Xiong, Q.; Tian, C.; Li, L.; Zhao, J.; Lin, X.; Guo, X.; He, Y.; Liang, W.; Zuo, X.; et al. Inulin-type prebiotics reduce serum uric acid levels via gut microbiota modulation: A randomized, controlled crossover trial in peritoneal dialysis patients. Eur. J. Nutr. 2022, 61, 665–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Li, W.; Yin, J. The intestinal-hepatic axis: A comprehensive review on fructose metabolism and its association with mortality and chronic metabolic diseases. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.; Zhang, Y.; Dalbeth, N.; Terkeltaub, R.; Yang, T.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Li, J.; Wu, Z.; Zeng, C.; et al. Association between Gut Microbiota and Elevated Serum Urate in Two Independent Cohorts. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022, 74, 682–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagami, Y.; Suzuki, S.; Espinoza, J.L.; Vu, L.; Enomoto, M.; Takasugi, S.; Nakamura, A.; Nakayama, T.; Hanamura, I.; Tani, H.; et al. Immunomodulatory and Metabolic Changes after Gnetin-C Supplementation in Humans. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2019, 41, 125. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, K.; Liu, S.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, X.; Fu, X.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, K.; Miao, L.; Li, Z.; Li, Y.; et al. Treating hyperuricemia related non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in rats with resveratrol. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 110, 844–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.T.; Chang, L.C.; Liu, C.W.; Wu, P.F. Negative correlation between serum uric acid and kidney URAT1 mRNA expression caused by resveratrol in rats. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2017, 61, 1601030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Liu, Y.; Wang, C.; Guo, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Qian, H.; Zhao, Y. Lycopene-Loaded Bilosomes Ameliorate High-Fat Diet-Induced Chronic Nephritis in Mice through the TLR4/MyD88 Inflammatory Pathway. Foods 2022, 11, 3042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, B.; Zheng, J.; Zheng, G.; Tian, X.; Zhang, W.; Yuan, F.; Yang, Z. Using Collagen Peptides from the Skin of Monkfish (Lophius litulon) to Ameliorate Kidney Damage in High-Fat Diet Fed Mice by Regulating the Nrf2 Pathway and NLRP3 Signaling. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 798708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.M.; Nie, Q.; Zhang, Z.M.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, F.X.; Wang, C.; Wang, X.; Song, G.Y. Resveratrol affects the expression of uric acid transporter by improving inflammation. Mol. Med. Rep. 2021, 24, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Chen, H.; Sun, C.; Wu, B.; Bai, B.; Liu, H.; Shan, X.; Liang, G.; Zhang, Y. A novel resveratrol analog PA19 attenuates obesity-induced cardiac and renal injury by inhibiting inflammation and inflammatory cell infiltration. Mol. Med. Rep. 2019, 19, 4770–4778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andre, D.M.; Calixto, M.C.; Sollon, C.; Alexandre, E.C.; Leiria, L.O.; Tobar, N.; Anhe, G.F.; Antunes, E. Therapy with resveratrol attenuates obesity-associated allergic airway inflammation in mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2016, 38, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.S.; Zhang, Z.S.; Yang, B.; He, W. Resveratrol attenuates oxidative damage and ameliorates cognitive impairment in the brain of senescence-accelerated mice. Life Sci. 2012, 91, 872–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Li, Y.; Luo, J.; Jiang, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Chen, Y.; Huang, Q.; Zhang, L.; Wu, T.; Pang, J. Resveratrol, a novel inhibitor of GLUT9, ameliorates liver and kidney injuries in a D-galactose-induced ageing mouse model via the regulation of uric acid metabolism. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 8274–8287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhu, X.X.; Liu, L.; Xue, Y.; Yang, X.; Zou, H.J. SIRT1 prevents hyperuricemia via the PGC-1alpha/PPARgamma-ABCG2 pathway. Endocrine 2016, 53, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, G.; Nie, Y.; Chang, Y.; Zeng, S.; Liang, C.; Zheng, X.; Xiao, D.; Zhan, S.; Zheng, Q. Protective effects of Rhizoma smilacis glabrae extracts on potassium oxonate- and monosodium urate-induced hyperuricemia and gout in mice. Phytomedicine 2019, 59, 152772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.W.; Wang, C.P.; Liu, L.; Liu, Y.L.; Wang, X.; Hong, Y.; Li, Z.; Kong, L.D. Antihyperuricemic and nephroprotective effects of resveratrol and its analogues in hyperuricemic mice. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2012, 56, 1433–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konno, H.; Kanai, Y.; Katagiri, M.; Watanabe, T.; Mori, A.; Ikuta, T.; Tani, H.; Fukushima, S.; Tatefuji, T.; Shirasawa, T. Melinjo (Gnetum gnemon L.) Seed Extract Decreases Serum Uric Acid Levels in Nonobese Japanese Males: A Randomized Controlled Study. Evid-Based Compl Alt. 2013, 2013, 589169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, Z.; Liu, X.; Cheng, Y.; Yan, X.; Wu, S. Gut microbiota and aging. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 3509–3534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adak, A.; Khan, M.R. An insight into gut microbiota and its functionalities. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2019, 76, 473–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Yang, Q.; Liu, X. The microbiota-gut-brain axis and neurodevelopmental disorders. Protein Cell 2023, 14, 762–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.Y.; Zhou, D.D.; Gan, R.Y.; Huang, S.Y.; Zhao, C.N.; Shang, A.; Xu, X.Y.; Li, H.B. Effects and Mechanisms of Probiotics, Prebiotics, Synbiotics, and Postbiotics on Metabolic Diseases Targeting Gut Microbiota: A Narrative Review. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulangé, C.L.; Neves, A.L.; Chilloux, J.; Nicholson, J.K.; Dumas, M.E. Impact of the gut microbiota on inflammation, obesity, and metabolic disease. Genome Med. 2016, 8, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, H.; Liu, N.; Chen, J. The Role of the Intestine in the Development of Hyperuricemia. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 845684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Wen, S.; Zhou, L. Effect of Intestinal Flora on Hyperuricemia-Induced Chronic Kidney Injury in Type 2 Diabetic Patients and the Therapeutic Mechanism of New Anti-Diabetic Prescription Medications. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2023, 16, 3029–3044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crane, J.K. Role of host xanthine oxidase in infection due to enteropathogenic and Shiga-toxigenic Escherichia coli. Gut Microbes 2013, 4, 388–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Wu, X.; Guo, Z.; Gao, R.; Ni, Z.; Cui, H.; Zong, M.; Van Bockstaele, F.; Lou, W. Lactiplantibacillus plantarum enables blood urate control in mice through degradation of nucleosides in gastrointestinal tract. Microbiome 2023, 11, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, N.; Iwamoto, C.; Kano, H.; Yamaoka, N.; Fukuuchi, T.; Kaneko, K.; Asami, Y. Evaluation of purine utilization by Lactobacillus gasseri strains with potential to decrease the absorption of food-derived purines in the human intestine. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids 2016, 35, 670–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, C.Y.; Lin, H.J.; Chen, C.H.; Lai, E.C.; Yang, Y.K. Chronic kidney disease and stroke. Lancet Neurol. 2014, 13, 1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhao, M.; Pu, Z.; Xu, G.; Li, X. Relationship between oxidative stress and inflammation in hyperuricemia: Analysis based on asymptomatic young patients with primary hyperuricemia. Medicine 2018, 97, e13108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Liao, W.; Huang, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, Z.; Tang, J. Gut microbiota remodeling: A promising therapeutic strategy to confront hyperuricemia and gout. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 935723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tawfick, M.M.; Xie, H.; Zhao, C.; Shao, P.; Farag, M.A. Inulin fructans in diet: Role in gut homeostasis, immunity, health outcomes and potential therapeutics. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 208, 948–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomova, A.; Bukovsky, I.; Rembert, E.; Yonas, W.; Alwarith, J.; Barnard, N.D.; Kahleova, H. The Effects of Vegetarian and Vegan Diets on Gut Microbiota. Front. Nutr. 2019, 6, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bian, M.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Nie, A.; Zhu, C.; Sun, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, B. Chicory ameliorates hyperuricemia via modulating gut microbiota and alleviating LPS/TLR4 axis in quail. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 131, 110719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Mei, L.; Deng, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wei, X.; Liu, M.; Zhou, J.; Ma, H.; Zheng, P.; Yuan, J.; et al. Lactobacillus brevis DM9218 ameliorates fructose-induced hyperuricemia through inosine degradation and manipulation of intestinal dysbiosis. Nutrition 2019, 62, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Chen, X.; Zhang, L.; Meng, F.; Zhou, L.; Pang, X.; Lu, Z.; Lu, Y. Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus Fmb14 prevents purine induced hyperuricemia and alleviate renal fibrosis through gut-kidney axis. Pharmacol. Res. 2022, 182, 106350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieuwdorp, M.; Gilijamse, P.W.; Pai, N.; Kaplan, L.M. Role of the microbiome in energy regulation and metabolism. Gastroenterology 2014, 146, 1525–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zhang, B.; Zhao, X.; Lin, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Hu, N.; Wang, S. Chlorogenic acid supplementation ameliorates hyperuricemia, relieves renal inflammation, and modulates intestinal homeostasis. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 5637–5649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, H.; Han, J.; Tang, S.; Bao, W.; Lu, C.; Zhou, J.; Ming, T.; Li, Y.; Su, X. Comparisons of protective effects between two sea cucumber hydrolysates against diet induced hyperuricemia and renal inflammation in mice. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 1074–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.E.; Lee, S.M.; Jung, J. Integrated omics analysis unraveled the microbiome-mediated effects of Yijin-Tang on hepatosteatosis and insulin resistance in obese mouse. Phytomedicine 2020, 79, 153354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, K.; Zhang, H.; Chen, C.; Ho, C.T.; Kang, M.; Zhu, S.; Xu, J.; Deng, X.; Huang, Q.; Cao, Y. Heptamethoxyflavone Alleviates Metabolic Syndrome in High-Fat Diet-Fed Mice by Regulating the Composition, Function, and Metabolism of Gut Microbiota. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 10050–10064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chu, L.; Liu, S.; Zhang, W.; Lin, L.; Zheng, G. Smilax china L. flavonoid alleviates HFHS-induced inflammation by regulating the gut-liver axis in mice. Phytomedicine 2022, 95, 153728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Q.; Zhou, J.; Wang, C.; Yang, X.; Han, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Yao, R.; Sui, A. A dynamics association study of gut barrier and microbiota in hyperuricemia. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1287468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Zhou, J.; Zhao, L.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, S.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, F. Ferulic acid supplementation alleviates hyperuricemia in high-fructose/fat diet-fed rats via promoting uric acid excretion and mediating the gut microbiota. Food Funct. 2023, 14, 1710–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, F.; Huang, R.; Lin, D.; Wang, Y.; Yang, X.; Huang, X.; Zheng, B.; Chen, Z.; Huang, Y.; Wang, X.; et al. Resveratrol Improves Liver Steatosis and Insulin Resistance in Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Association with the Gut Microbiota. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 611323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Quintela, A.; Macarulla, M.T.; Gómez-Zorita, S.; González, M.; Milton-Laskibar, I.; Portillo, M.P. Relationship between changes in microbiota induced by resveratrol and its anti-diabetic effect on type 2 diabetes. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 1084702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Gao, J.; Ke, W.; Wang, J.; Li, D.; Liu, R.; Jia, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, X.; Chen, F.; et al. Resveratrol reduces obesity in high-fat diet-fed mice via modulating the composition and metabolic function of the gut microbiota. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2020, 156, 83–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parizadeh, M.; Arrieta, M.C. The global human gut microbiome: Genes, lifestyles, and diet. Trends Mol. Med. 2023, 29, 789–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paripati, N.; Nesi, L.; Sterrett, J.D.; Dawud, L.M.; Kessler, L.R.; Lowry, C.A.; Perez, L.J.; DeSipio, J.; Phadtare, S. Gut Microbiome and Lipidome Signatures in Irritable Bowel Syndrome Patients from a Low-Income, Food-Desert Area: A Pilot Study. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Wang, R.; Pang, J.; Wang, X.; Pan, Z.; Jin, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yang, Y.; Ling, W. Resveratrol Improves Hyperuricemia and Ameliorates Renal Injury by Modulating the Gut Microbiota. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1086. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16071086
Zhou Y, Zeng Y, Wang R, Pang J, Wang X, Pan Z, Jin Y, Chen Y, Yang Y, Ling W. Resveratrol Improves Hyperuricemia and Ameliorates Renal Injury by Modulating the Gut Microbiota. Nutrients. 2024; 16(7):1086. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16071086
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Yuqing, Yupeng Zeng, Ruijie Wang, Juan Pang, Xin Wang, Zhijun Pan, Yufeng Jin, Yu Chen, Yan Yang, and Wenhua Ling. 2024. "Resveratrol Improves Hyperuricemia and Ameliorates Renal Injury by Modulating the Gut Microbiota" Nutrients 16, no. 7: 1086. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16071086
APA StyleZhou, Y., Zeng, Y., Wang, R., Pang, J., Wang, X., Pan, Z., Jin, Y., Chen, Y., Yang, Y., & Ling, W. (2024). Resveratrol Improves Hyperuricemia and Ameliorates Renal Injury by Modulating the Gut Microbiota. Nutrients, 16(7), 1086. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16071086