Controlling Nutritional Status (CONUT) Score as Prognostic Indicator in Stage IV Gastric Cancer with Chronic Intestinal Failure
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
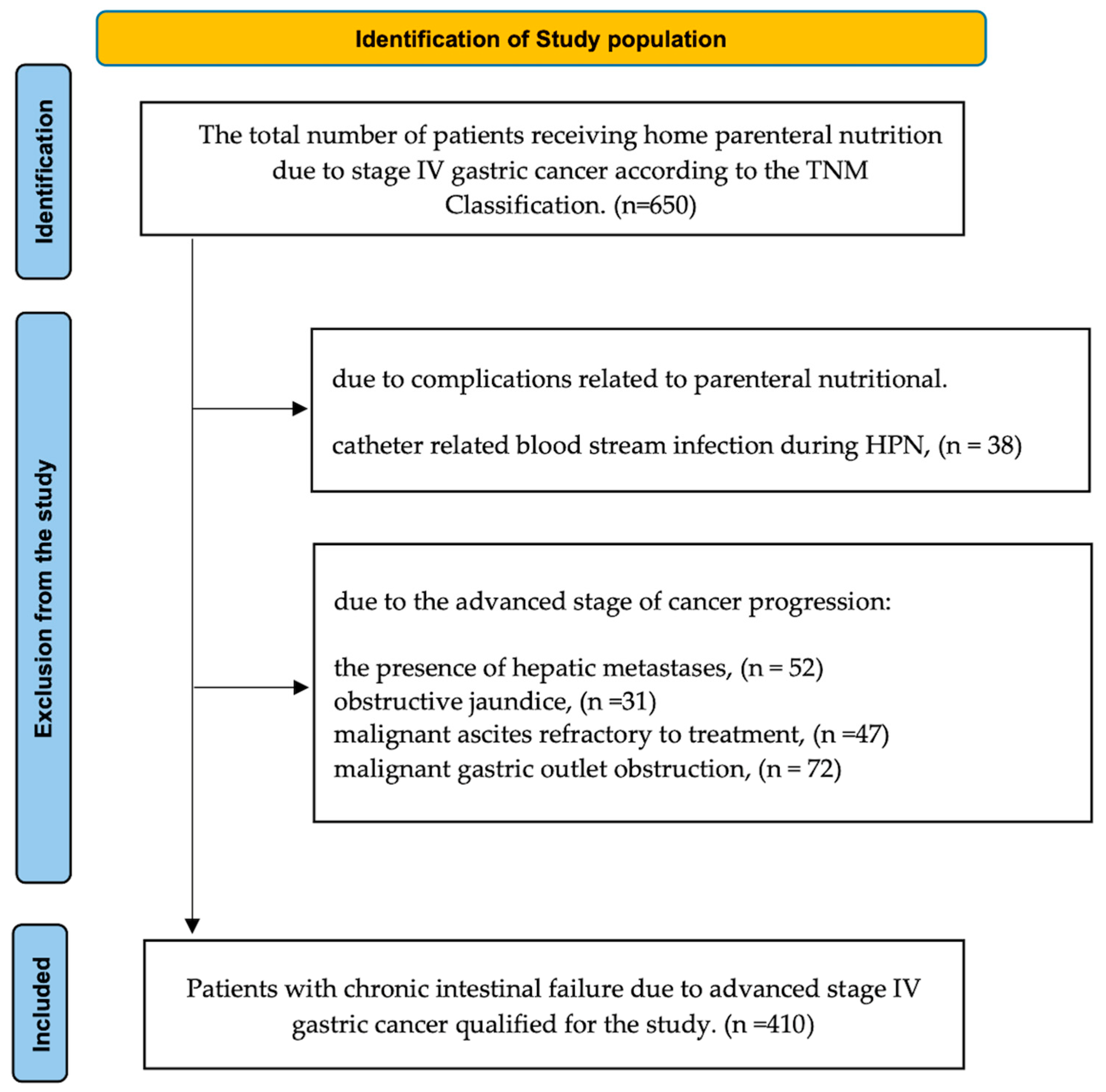
2.1. Study Population
- Advanced stage IV gastric cancer;
- Chronic intestinal failure preventing natural oral intake;
- The administration of HPN.
- The presence of hepatic metastases;
- Obstructive jaundice;
- Malignant ascites refractory to treatment;
- Catheter-related blood stream infection during HPN;
- Malignant gastric outlet obstruction (MGOO);
- Lack of patient consent.
- Inability to fulfil nutritional needs through oral and/or enteral routes;
- Confirmed metabolic stability;
- Health condition suitable for safe home-based management.
2.2. Data Collection
- The CONUT score [5], which was derived from the following:
- a.
- Serum albumin (g/L);
- b.
- Total cholesterol (mg/dL);
- c.
- Total lymphocyte count (TLC).
- TLC was calculated through a leukogram using the lymphocyte percentage and absolute lymphocyte count (mL).
- According to THE CONUT nutritional index, patients were classified as follows:
- a.
- Those scoring 0 and 1 points were classified as well-nourished;
- b.
- Those scoring from 2 to 4 points were classified as mildly malnourished;
- c.
- Those scoring from 5 to 8 points were classified as moderately malnourished;
- d.
- Those scoring from 9 to 12 points were classified as severely malnourished.
- BMI, which was calculated using Quetelet’s formula.
- Biochemical assessment, which was performed in a certified university hospital laboratory according to standardized procedures and good laboratory practice. The evaluation included the following:
- a.
- Complete blood count;
- b.
- Hemoglobin (g/dL);
- c.
- White blood cells (×109/L);
- d.
- Lymphocyte cells (×109/L);
- e.
- Percentage of lymphocytes (%);
- f.
- Total protein (g/dL);
- g.
- Albumin (g/L);
- h.
- Total cholesterol (mg/dL).
- The analysis included test results obtained on the day of hospital admission for qualification for home parenteral nutrition therapy.
2.3. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristic
3.2. Cox Regression Results
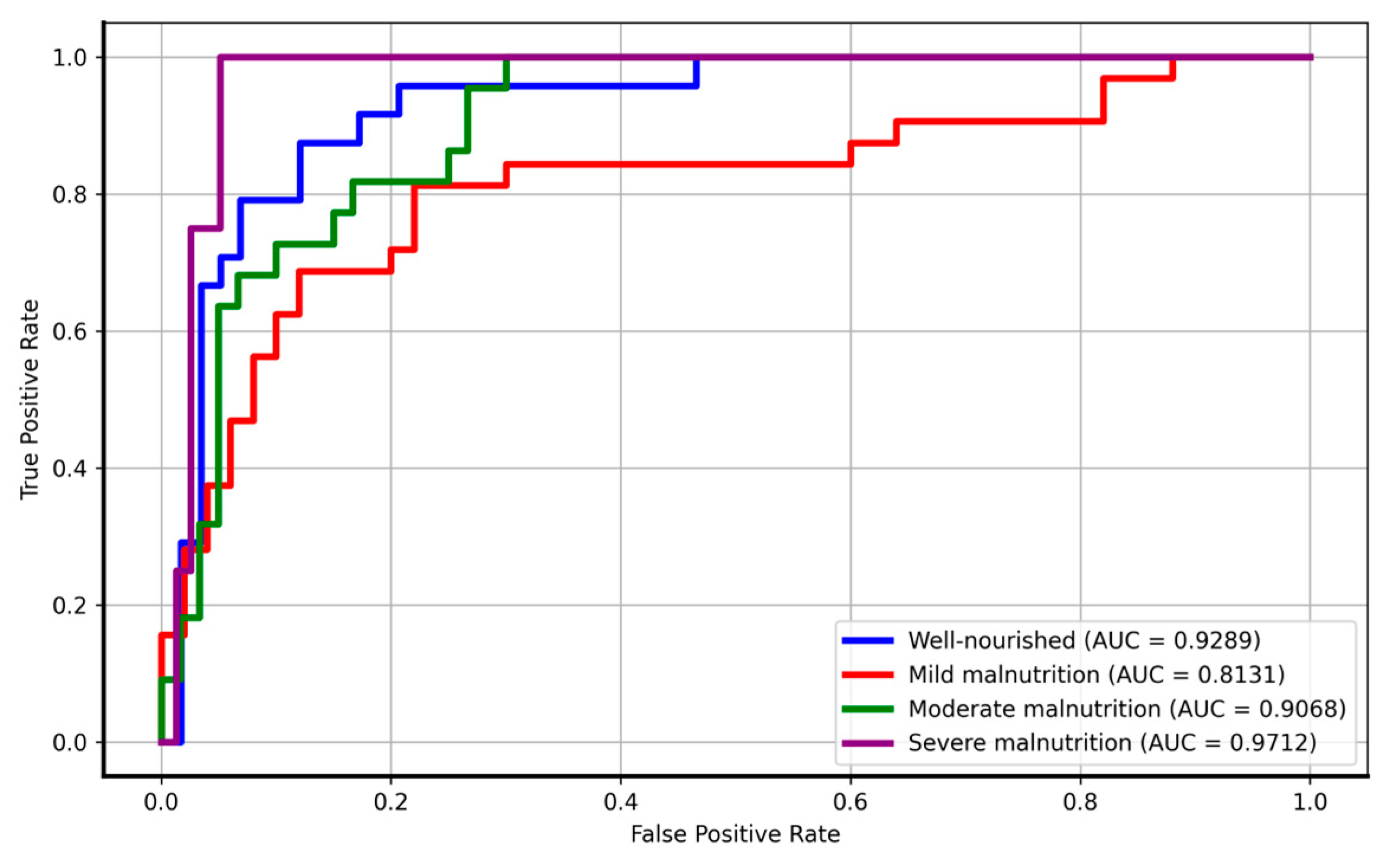
3.3. Logistic Regression Results
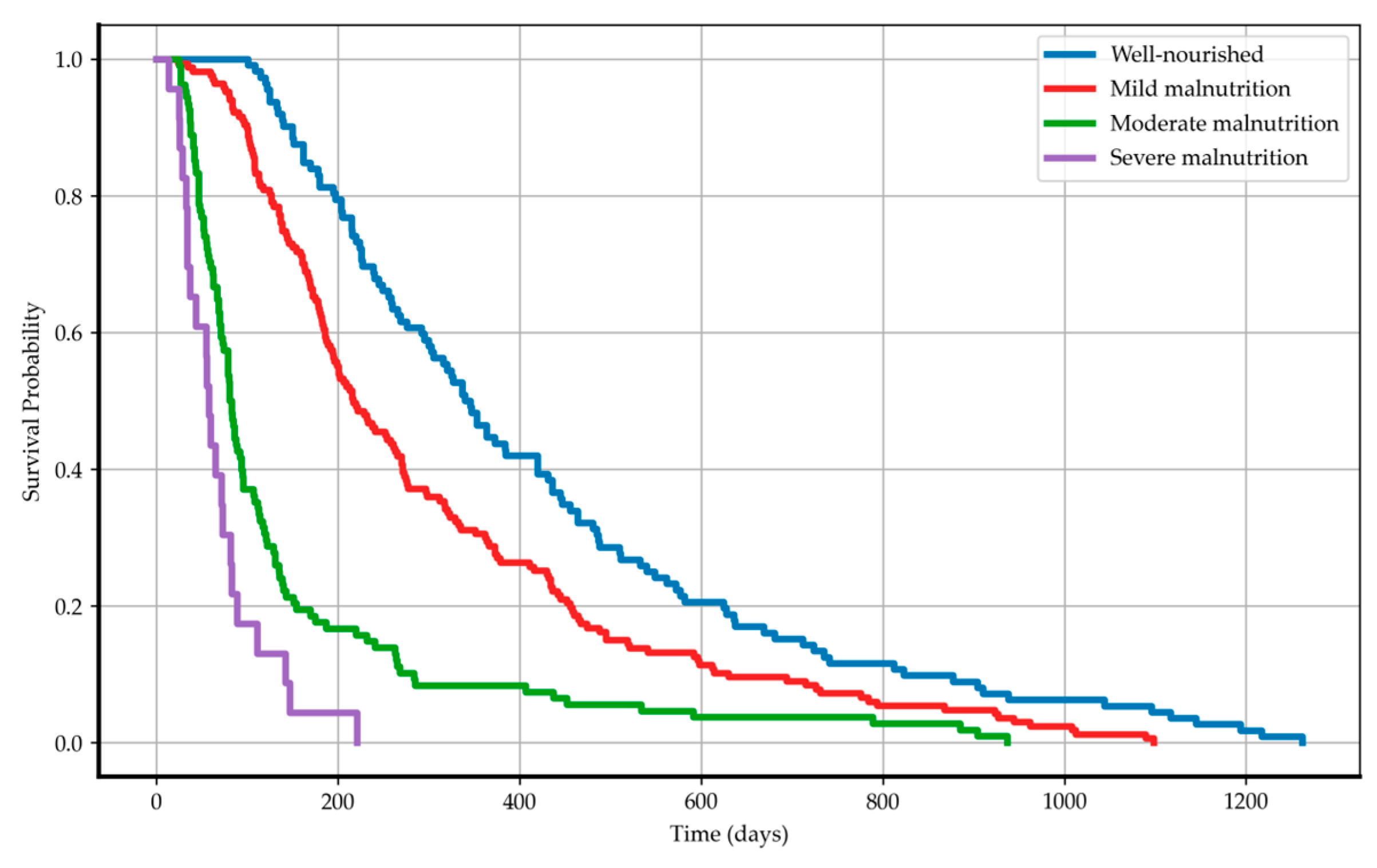
3.4. Kaplan–Meier Survival Curves and Log-Rank Test
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fearon, K.; Strasser, F.; Anker, S.D.; Bosaeus, I.; Bruera, E.; Fainsinger, R.L.; Jatoi, A.; Loprinzi, C.; MacDonald, N.; Mantovani, G.; et al. Definition and Classification of Cancer Cachexia: An International Consensus. Lancet Oncol. 2011, 12, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Xue, Z.; Yu, J.; Ma, Z.; Kang, W.; Ye, X.; Li, Z. Risk Factors for Cancer-Specific Survival in Elderly Gastric Cancer Patients after Curative Gastrectomy. Nutr. Res. Pract. 2022, 16, 604–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilic, M.; Ilic, I. Epidemiology of Stomach Cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 28, 1187–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantzorou, M.; Koutelidakis, A.; Theocharis, S.; Giaginis, C. Clinical Value of Nutritional Status in Cancer: What Is Its Impact and How It Affects Disease Progression and Prognosis? Nutr. Cancer 2017, 69, 1151–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ignacio de Ulíbarri, J.; González-Madroño, A.; de Villar, N.G.P.; González, P.; González, B.; Mancha, A.; Rodríguez, F.; Fernández, G. CONUT: A Tool for Controlling Nutritional Status. First Validation in a Hospital Population. Nutr. Hosp. 2005, 20, 38–45. [Google Scholar]
- Poziomyck, A.K.; Fruchtenicht, A.V.G.; Kabke, G.B.; Volkweis, B.S.; Antoniazzi, J.L.; Moreira, L.F. Reliability of Nutritional Assessment in Patients with Gastrointestinal Tumors. Rev. Col. Bras. Cir. 2016, 43, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.; Zhang, C.; Liu, Z.; Ai, S.; Guan, W.; Liu, S. Controlling Nutritional Status (CONUT) Score as a Predictive Marker for Short-Term Complications Following Gastrectomy of Gastric Cancer: A Retrospective Study. BMC Gastroenterol. 2021, 21, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Q.; Li, X.; Duan, B.; Li, X.; Liu, S.; Xu, B.; Shi, S.; Zhang, J.; Qin, H.; Duan, X.; et al. Clinical Significance of Controlling Nutritional Status Score (CONUT) in Evaluating Outcome of Postoperative Patients with Gastric Cancer. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Ma, F.; Wu, S. Controlling Nutritional Status Score Predict the Individualized Survival of Patients with Gastric Cancer. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 30, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, D.; Lin, E.; Chen, Y.; Li, W.; Chen, Y.; Sun, X.; Zhou, Z. Preoperative Controlling Nutritional Status (CONUT) Score as a Predictor of Long-Term Outcome after Curative Resection Followed by Adjuvant Chemotherapy in Stage II-III Gastric Cancer. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pironi, L.; Arends, J.; Baxter, J.; Bozzetti, F.; Peláez, R.B.; Cuerda, C.; Forbes, A.; Gabe, S.; Gillanders, L.; Holst, M.; et al. ESPEN Endorsed Recommendations. Definition and Classification of Intestinal Failure in Adults. Clin. Nutr. Edinb. Scotl. 2015, 34, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 Statement: An Updated Guideline for Reporting Systematic Reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arends, J.; Bachmann, P.; Baracos, V.; Barthelemy, N.; Bertz, H.; Bozzetti, F.; Fearon, K.; Hütterer, E.; Isenring, E.; Kaasa, S.; et al. ESPEN Guidelines on Nutrition in Cancer Patients. Clin. Nutr. Edinb. Scotl. 2017, 36, 11–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, H.-L.; Lu, J.; Li, P.; Xie, J.-W.; Wang, J.-B.; Lin, J.-X.; Chen, Q.-Y.; Cao, L.-L.; Lin, M.; Tu, R.; et al. Effects of Preoperative Malnutrition on Short- and Long-Term Outcomes of Patients with Gastric Cancer: Can We Do Better? Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2017, 24, 3376–3385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grenader, T.; Waddell, T.; Peckitt, C.; Oates, J.; Starling, N.; Cunningham, D.; Bridgewater, J. Prognostic Value of Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio in Advanced Oesophago-Gastric Cancer: Exploratory Analysis of the REAL-2 Trial. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27, 687–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.C.; Jia, Z.F.; Cao, D.H.; Wu, Y.H.; Jiang, J.; Wen, S.M.; Zhao, D.; Zhang, S.L.; Cao, X.Y. Preoperative Lymphocyte-to-Monocyte Ratio (LMR) Could Independently Predict Overall Survival of Resectable Gastric Cancer Patients. Medicine 2018, 97, e13896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.-J.; Li, Q.-Y.; Yuan, Z.; Zhang, D.-C.; Xu, H.; Yang, L.; Gu, X.-H.; Xu, Z.-K. Prognostic Value of Preoperative Immune-Nutritional Scoring Systems in Remnant Gastric Cancer Patients Undergoing Surgery. World J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2023, 15, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsushita, H.; Vesely, M.D.; Koboldt, D.C.; Rickert, C.G.; Uppaluri, R.; Magrini, V.J.; Arthur, C.D.; White, J.M.; Chen, Y.-S.; Shea, L.K.; et al. Cancer Exome Analysis Reveals a T-Cell-Dependent Mechanism of Cancer Immunoediting. Nature 2012, 482, 400–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fridman, W.H.; Pagès, F.; Sautès-Fridman, C.; Galon, J. The Immune Contexture in Human Tumours: Impact on Clinical Outcome. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Fang, T.; Yin, X.; Lou, S.; Han, B.; Gao, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, D.; Wang, Y.; et al. Prognostic Importance of the Preoperative New-Naples Prognostic Score for Patients with Gastric Cancer. Cancer Med. 2023, 12, 1358–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, S.; Kanaji, S.; Yamamoto, M.; Oshikiri, T.; Nakamura, T.; Kakeji, Y. Controlling Nutritional Status (CONUT) Score Predicts Outcomes of Curative Resection for Gastric Cancer in the Elderly. World J. Surg. 2019, 43, 1076–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuroda, D.; Sawayama, H.; Kurashige, J.; Iwatsuki, M.; Eto, T.; Tokunaga, R.; Kitano, Y.; Yamamura, K.; Ouchi, M.; Nakamura, K.; et al. Controlling Nutritional Status (CONUT) Score Is a Prognostic Marker for Gastric Cancer Patients after Curative Resection. Gastric Cancer 2018, 21, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boicean, A.; Boeras, I.; Birsan, S.; Ichim, C.; Todor, S.B.; Onisor, D.M.; Brusnic, O.; Bacila, C.; Dura, H.; Roman-Filip, C.; et al. In Pursuit of Novel Markers: Unraveling the Potential of miR-106, CEA and CA 19-9 in Gastric Adenocarcinoma Diagnosis and Staging. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 7898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.-F.; Nie, R.-C.; Wu, T.; Li, S.-M.; Chen, S.; Wang, W.; Chen, X.-J.; Chen, G.-M.; Chen, Y.-B.; Zhou, Z.-W.; et al. Prognostic Value of the Nutritional Risk Screening 2002 Scale in Metastatic Gastric Cancer: A Large-Scale Cohort Study. J. Cancer 2019, 10, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.W.; Youn, J.; Kim, E.M.; Choi, M.-G.; Lee, J.E. Associations of Patient-Generated Subjective Global Assessment (PG-SGA) and NUTRISCORE with Survival in Gastric Cancer Patients: Timing Matters, a Retrospective Cohort Study. BMC Gastroenterol. 2022, 22, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Nutritional Status According to CONUT Score | Well Nourished (n = 112) | Malnutrition | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mild (n = 167) | Moderate (n = 108) | Severe (n = 23) | |||
| Chemotherapy | 26 | 45 | 23 | 2 | 0.240 |
| Gastrectomy and chemotherapy | 20 | 25 | 26 | 3 | 0.250 |
| Parenteral nutrition only | 66 | 97 | 59 | 18 | 0.223 |
| Nutritional Status According to CONUT Score | Well Nourished (n = 112) | Malnutrition | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mild (n = 167) | Moderate (n = 108) | Severe (n = 23) | |||
| White blood cells (×109/L) | 8 (4) | 8 (5) | 8 (7) | 11 (7.5) | 0.208 |
| Lymphocyte cells (×109/L) | 2 (0.8) | 1.5 (0.8) | 1.1 (0.8) | 1.1 (0.5) | <0.001 |
| % Lymphocytes | 26.6 (10.7) | 17.8 (12.7) | 11.9 (11.3) | 7.7 (6.6) | <0.001 |
| Cholesterol total (mg/dL) | 184 (43.4) | 148 (52.5) | 134 (37) | 110 (41) | <0.001 |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 4 (0.6) | 3.7 (0.7) | 3.1 (0.6) | 2.4 (0.4) | <0.001 |
| Protein total (g/dL) | 7 (0.9) | 6.8 (0.8) | 6.2 (1) | 5.4 (1) | <0.001 |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 11.7 (1.9) | 11.3 (2.1) | 10.4 (1.9) | 9.4 (0.9) | 0.633 |
| TLC cells/m3 | 1974 (806) | 1400 (878) | 960 (714) | 889 (589) | <0.001 |
| BMI kg/m2 | 20.2 (5.4) | 19.9 (7.9) | 19.1 (4.8) | 21.3 (4.7) | 0.283 |
| Covariate | HR | 95% CI | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lower–Upper | |||
| Age (years) | 0.992 | 0.983–1.001 | 0.084 |
| Sex | 1.112 | 0.898–1.376 | 0.329 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 0.984 | 0.958–1.010 | 0.225 |
| CONUT Stage | 2.073 | 1.815–2.369 | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Matysiak, K.; Hojdis, A.; Szewczuk, M. Controlling Nutritional Status (CONUT) Score as Prognostic Indicator in Stage IV Gastric Cancer with Chronic Intestinal Failure. Nutrients 2024, 16, 4052. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16234052
Matysiak K, Hojdis A, Szewczuk M. Controlling Nutritional Status (CONUT) Score as Prognostic Indicator in Stage IV Gastric Cancer with Chronic Intestinal Failure. Nutrients. 2024; 16(23):4052. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16234052
Chicago/Turabian StyleMatysiak, Konrad, Aleksandra Hojdis, and Magdalena Szewczuk. 2024. "Controlling Nutritional Status (CONUT) Score as Prognostic Indicator in Stage IV Gastric Cancer with Chronic Intestinal Failure" Nutrients 16, no. 23: 4052. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16234052
APA StyleMatysiak, K., Hojdis, A., & Szewczuk, M. (2024). Controlling Nutritional Status (CONUT) Score as Prognostic Indicator in Stage IV Gastric Cancer with Chronic Intestinal Failure. Nutrients, 16(23), 4052. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16234052





