From Mother to Child: Epigenetic Signatures of Hyperglycemia and Obesity during Pregnancy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Maternal Anthropometric, Clinical Data, and Sampling
Maternal Lifestyle Questionnaires
2.4. Perinatal Outcomes and Newborn’s Sampling
2.5. Molecular Studies
2.5.1. Genotyping
2.5.2. Placenta Tissue Sampling (DNA and Total RNA Extraction)
2.5.3. Epigenetic Analysis (DNA Methylation Analysis in Mothers, Newborns, and Placenta)
2.5.4. Gene Expression Analysis in Placenta
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Study Population
3.2. Anthropometric and Clinical Data of GDM versus Normoglycemic (NGT) Women
3.3. Anthropometric and Clinical Data of OB versus Normal Weight (NW) Pregnant Women
4. Neonatal Characteristics
4.1. Neonatal Outcomes Relative to GDM and NGT Pregnant Women
4.2. Neonatal Outcomes Relative to OB and NW Pregnant Women
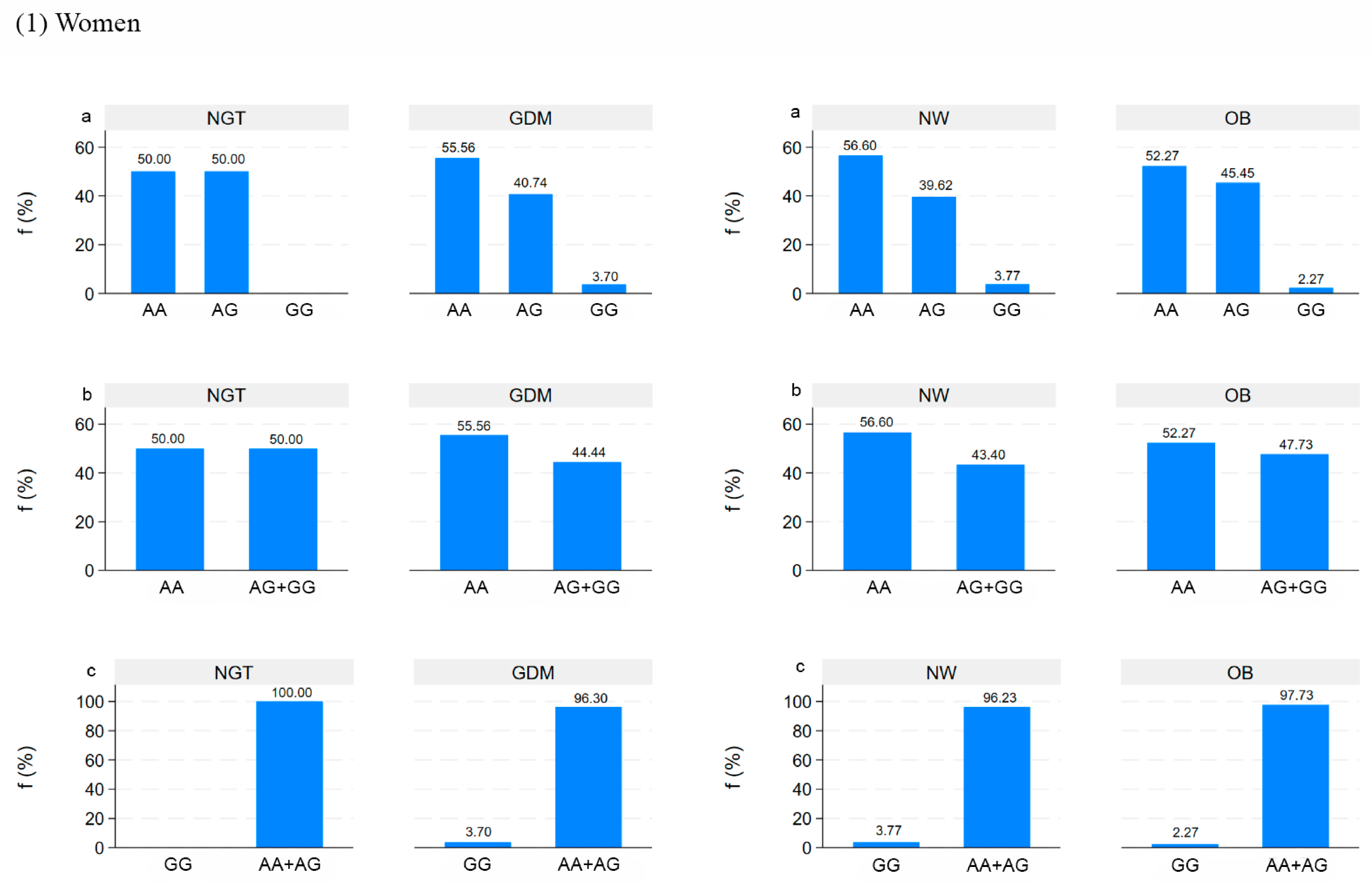
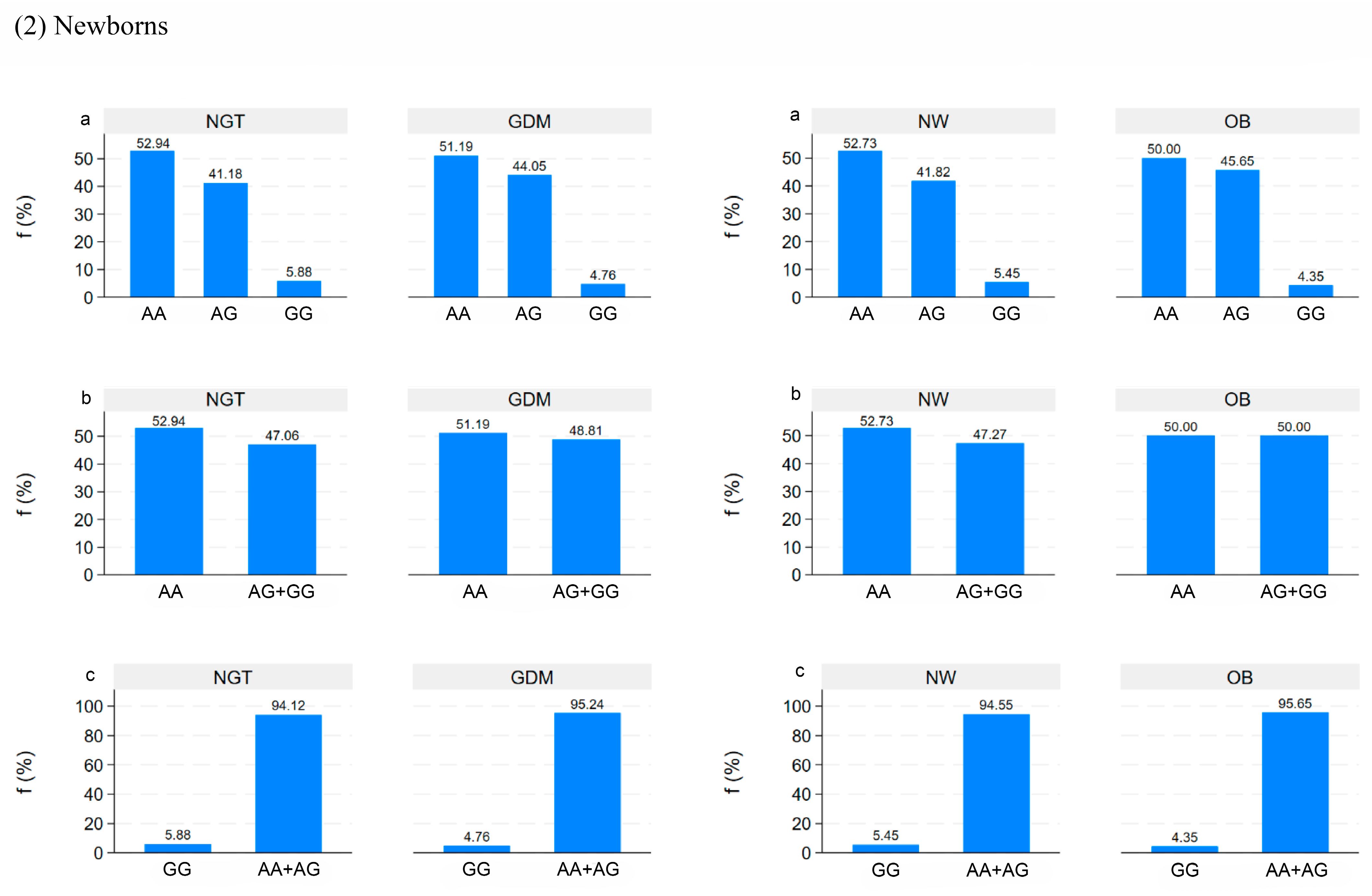
5. Genetic Analysis in Mothers and Newborns
5.1. Correlation between DNA Methylation and Clinical Data in Mothers and Newborns
5.2. Correlation between DNA Methylation in Placenta and Clinical Data in Mothers and Newborns
5.3. Correlation between Placental LPL and MC4R DNA Methylation and mRNA Expression Levels in Placenta
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Maguolo, A.; Gabbianelli, R.; Maffeis, C. Micronutrients in early life and offspring metabolic health programming: A promising target for preventing non-communicable diseases. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2023, 77, 1105–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heidari-Beni, M. Early Life Nutrition and Non Communicable Disease. In Primordial Prevention of Non Communicable Disease; Kelishadi, R., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Z.J.; Zhang, C.L.; Schatten, H.; Sun, Q.Y. Maternal diabetes mellitus and the origin of non-communicable diseases in offspring: The role of epigenetics. Biol. Reprod. 2014, 90, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franzago, M.; Fraticelli, F.; Stuppia, L.; Vitacolonna, E. Nutrigenetics, epigenetics, and gestational diabetes: Consequences in mother and child. Epigenetics 2019, 14, 215–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franzago, M.; Santurbano, D.; Vitacolonna, E.; Stuppia, L. Genes and diet in the prevention of chronic diseases in future generations. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cetin, I.; Bühling, K.; Demir, C.; Kortam, A.; Prescott, S.L.; Yamashiro, Y.; Yarmolinskaya, M.; Koletzko, B. Impact of Micronutrient Status during Pregnancy on Early Nutrition Programming. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2019, 74, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, M.; Fagier, Y.; Ahmed, B.C.; Konje, J. An overview of diabetes mellitus in pregnant women with obesity. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2024, 93, 102469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes: Standards of Care in Diabetes—2024. Diabetes Care. 2024, 47 (Suppl S1), S20–S42. [CrossRef]
- Paulo, M.S.; Abdo, N.M.; Bettencourt-Silva, R.; Al-Rifai, R.H. Gestational Diabetes Mellitus in Europe: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Prevalence Studies. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 691033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntyre, H.D.; Jensen, D.M.; Jensen, R.C.; Kyhl, H.B.; Jensen, T.K.; Glintborg, D.; Andersen, M. Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: Does One Size Fit All? A Challenge to Uniform Worldwide Diagnostic Thresholds. Diabetes Care 2018, 41, 1339–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzago, M.; Fraticelli, F.; Marchioni, M.; Di Nicola, M.; Di Sebastiano, F.; Liberati, M.; Stuppia, L.; Vitacolonna, E. Fat mass and obesity-associated (FTO) gene epigenetic modifications in gestational diabetes: New insights and possible pathophysiological connections. Acta Diabetol. 2021, 58, 997–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, R.A.; Kim, A.; Das, P.; Li, Y.; Choi, Y.K.; Thompson, A.T.; Douglas, E.; Subramanian, S.; Ramos, K.; Callahan, K.; et al. Prefrontal cortex melanocortin 4 receptors (MC4R) mediate food intake behavior in male mice. Physiol. Behav. 2023, 269, 114280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breton, C. The hypothalamus-adipose axis is a key target of developmental programming by maternal nutritional manipulation. J. Endocrinol. 2013, 216, R19–R31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wattez, J.S.; Delahaye, F.; Lukaszewski, M.A.; Risold, P.Y.; Eberlé, D.; Vieau, D.; Breton, C. Perinatal nutrition programs the hypothalamic melanocortin system in offspring. Horm. Metab. Res. 2013, 45, 980–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Widiker, S.; Karst, S.; Wagener, A.; Brockmann, G.A. High-fat diet leads to a decreased methylation of the Mc4r gene in the obese BFMI and the lean B6 mouse lines. J. Appl. Genet. 2010, 51, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heerwagen, M.J.; Miller, M.R.; Barbour, L.A.; Friedman, J.E. Maternal obesity and fetal metabolic programming: A fertile epigenetic soil. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2010, 299, R711–R722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Gagné-Ouellet, V.; Houde, A.-A.; Guay, S.-P.; Perron, P.; Gaudet, D.; Guérin, R.; Jean-Patrice, B.; Hivert, M.-F.; Brisson, D.; Bouchard, L. Placental lipoprotein lipase DNA methylation alterations are associated with gestational diabetes and body composition at 5 years of age. Epigenetics 2017, 12, 616–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Association of Diabetes and Pregnancy Study Groups Consensus Panel; Metzger, B.E.; Gabbe, S.G.; Persson, B.; Buchanan, T.A.; Catalano, P.A.; Damm, P.; Dyer, A.R.; de Leiva, A.; Hod, M.; et al. International association of diabetes and pregnancy study groups recommendations on the diagnosis and classification of hyperglycemia in pregnancy. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mannocci, A.; Di Thiene, D.; Del Cimmuto, A.; Masala, D.; Boccia, A.; De Vito, E.; La Torre, G. International physical activity questionnaire: Validation and assessment in an Italian sample. Ital. J. Public Health 2010, 7, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schröder, H.; Fitó, M.; Estruch, R.; Martínez-González, M.A.; Corella, D.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; Lamuela-Raventós, R.; Ros, E.; Salaverría, I.; Fiol, M.; et al. A short screener is valid for assessing Mediterranean diet adherence among older Spanish men and women. J. Nutr. 2011, 141, 1140–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-González, M.A.; García-Arellano, A.; Toledo, E.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; Buil-Cosiales, P.; Corella, D.; Covas, M.I.; Schröder, H.; Arós, F.; Gómez-Gracia, E.; et al. A 14-item Mediterranean diet assessment tool and obesity indexes among high-risk subjects: The PREDIMED trial. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e43134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornblath, M.; Hawdon, J.M.; Williams, A.F.; Aynsley-Green, A.; Ward-Platt, M.P.; Schwartz, R.; Kalhan, S.C. Controversies regarding definition of neonatal hypoglycemia: Suggested operational thresholds. Pediatrics 2000, 105, 1141–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, S.A.; Goodman, S.J.; MacIsaac, J.L.; Obradović, J.; Barr, R.G.; Boyce, W.T.; Kobor, M.S.; Islam, S.A.; Goodman, S.J.; MacIsaac, J.L.; et al. Integration of DNA methylation patterns and genetic variation in human pediatric tissues help inform EWAS design and interpretation. Epigenetics Chromatin 2019, 12, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, W.; Apostol, G.; Schreiner, P.J.; Jacobs, D.R., Jr.; Boerwinkle, E.; Fornage, M. Associations of lipoprotein lipase gene polymorphisms with longitudinal plasma lipid trends in young adults: The coronary artery risk development in young adults (CARDIA) study. Circ. Cardiovasc. Genet. 2010, 3, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zhou, D.; Zhang, Z.; Song, Y.; Zhang, D.; Zhao, T.; Chen, Z.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, D.; Yang, Y.; et al. Effects of genetic variants on lipid parameters and dyslipidemia in a Chinese population. J. Lipid Res. 2011, 52, 354–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzago, M.; Di Nicola, M.; Fraticelli, F.; Marchioni, M.; Stuppia, L.; Vitacolonna, E. Nutrigenetic variants and response to diet/lifestyle intervention in obese subjects: A pilot study. Acta Diabetol. 2022, 59, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franzago, M.; Porreca, A.; D’ardes, M.; Di Nicola, M.; Di Tizio, L.; Liberati, M.; Stuppia, L.; Vitacolonna, E. The Obesogenic Environment: Epigenetic Modifications in Placental Melanocortin 4 Receptor Gene Connected to Gestational Diabetes and Smoking. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 879526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreutz, M.; Schock, G.; Kaiser, J.; Hochstein, N.; Peist, R. PyroMark® Instruments, Chemistry, and Software for Pyrosequencing® Analysis. In Pyrosequencing. Methods in Molecular Biology; Lehmann, U., Tost, J., Eds.; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2015; Volume 1315. [Google Scholar]
- Meller, M.; Vadachkoria, S.; Luthy, D.A.; Williams, M.A. Evaluation of housekeeping genes in placental comparative expression studies. Placenta 2005, 26, 601–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzago, M.; La Rovere, M.; Guanciali, F.P.; Vitacolonna, E.; Stuppia, L. Epigenetics and human reproduction: The primary prevention of the noncommunicable diseases. Epigenomics 2019, 11, 1441–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, D.A.; McDaniel, L.N.; Yin, T.; Khan, M.; Jiang, J.; Acevedo, M.R.; Walsh, S.A.; Ponto, L.L.B.; Norris, A.W.; Lutter, M.; et al. Regulation of glucose tolerance and sympathetic activity by MC4R signaling in the lateral hypothalamus. Diabetes 2015, 64, 1976–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaisse, C.; Clement, K.; Durand, E.; Hercberg, S.; Guy-Grand, B.; Froguel, P. Melanocortin-4 receptor mutations are a frequent and heterogeneous cause of morbid obesity. J. Clin. Investig. 2000, 106, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, J.; Balthasar, N.; Olson, D.; Scott, M.; Berglund, E.; Lee, C.E.; Choi, M.J.; Lauzon, D.; Lowell, B.B.; Elmquist, J.K. Melanocortin-4 receptors expressed by cholinergic neurons regulate energy balance and glucose homeostasis. Cell Metab. 2011, 13, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berthoud, H.R.; Morrison, C. The brain, appetite, and obesity. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2008, 59, 55–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mul, J.D.; van Boxtel, R.; Bergen, D.J.; Brans, M.A.; Brakkee, J.H.; Toonen, P.W.; Garner, K.M.; Adan, R.A.; Cuppen, E. Melanocortin receptor 4 deficiency affects body weight regulation, grooming behavior, and substrate preference in the rat. Obesity 2012, 20, 612–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fani, L.; Bak, S.; Delhanty, P.; van Rossum, E.F.; van den Akker, E.L. The melanocortin-4 receptor as target for obesity treatment: A systematic review of emerging pharmacological therapeutic options. Int. J. Obes. 2014, 38, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, E.J.; Lee, H.A.; You, Y.A.; Yoo, J.Y.; Park, H.; Park, E.A.; Ha, E.H.; Kim, Y.J. MC4R and HNF4α promoter methylation at birth contribute to triglyceride levels in childhood: A prospective cohort study. Medicine 2019, 98, e16424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wild, R.; Feingold, K.R. Effect of Pregnancy on Lipid Metabolism and Lipoprotein Levels. Endotext [Internet] 2023. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK498654/ (accessed on 3 March 2024).
- Dimasuay, K.G.; Boeuf, P.; Powell, T.L.; Jansson, T. Placental Responses to Changes in the Maternal Environment Determine Fetal Growth. Front. Physiol. 2016, 7, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, B.; Wilker, E.H.; Willis-Owen, S.A.G.; Byun, H.-M.; Wong, K.C.C.; Motta, V.; Baccarelli, A.A.; Schwartz, J.; Cookson, W.O.C.M.; Khabbaz, K.; et al. Predicting DNA methylation level across human tissues. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 3515–3528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabak, L.A. A revolution in biomedical assessment: The development of salivary diagnostics. J. Dent. Educ. 2001, 65, 1335–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, D.A.; Lesseur, C.; Conradt, E.; Lester, B.M.; Marsit, C.J. Global and gene-specific DNA methylation across multiple tissues in early infancy: Implications for children's health research. FASEB J. 2014, 28, 2088–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrettini, S.; Caroli, A.; Torlone, E. Nutrition and Metabolic Adaptations in Physiological and Complicated Pregnancy: Focus on Obesity and Gestational Diabetes. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 611929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alba-Linares, J.J.; Pérez, R.F.; Tejedor, J.R.; Bastante-Rodríguez, D.; Ponce, F.; Carbonell, N.G.; Zafra, R.G.; Fernández, A.F.; Fraga, M.F.; Lurbe, E. Maternal obesity and gestational diabetes reprogram the methylome of offspring beyond birth by inducing epigenetic signatures in metabolic and developmental pathways. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2023, 22, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
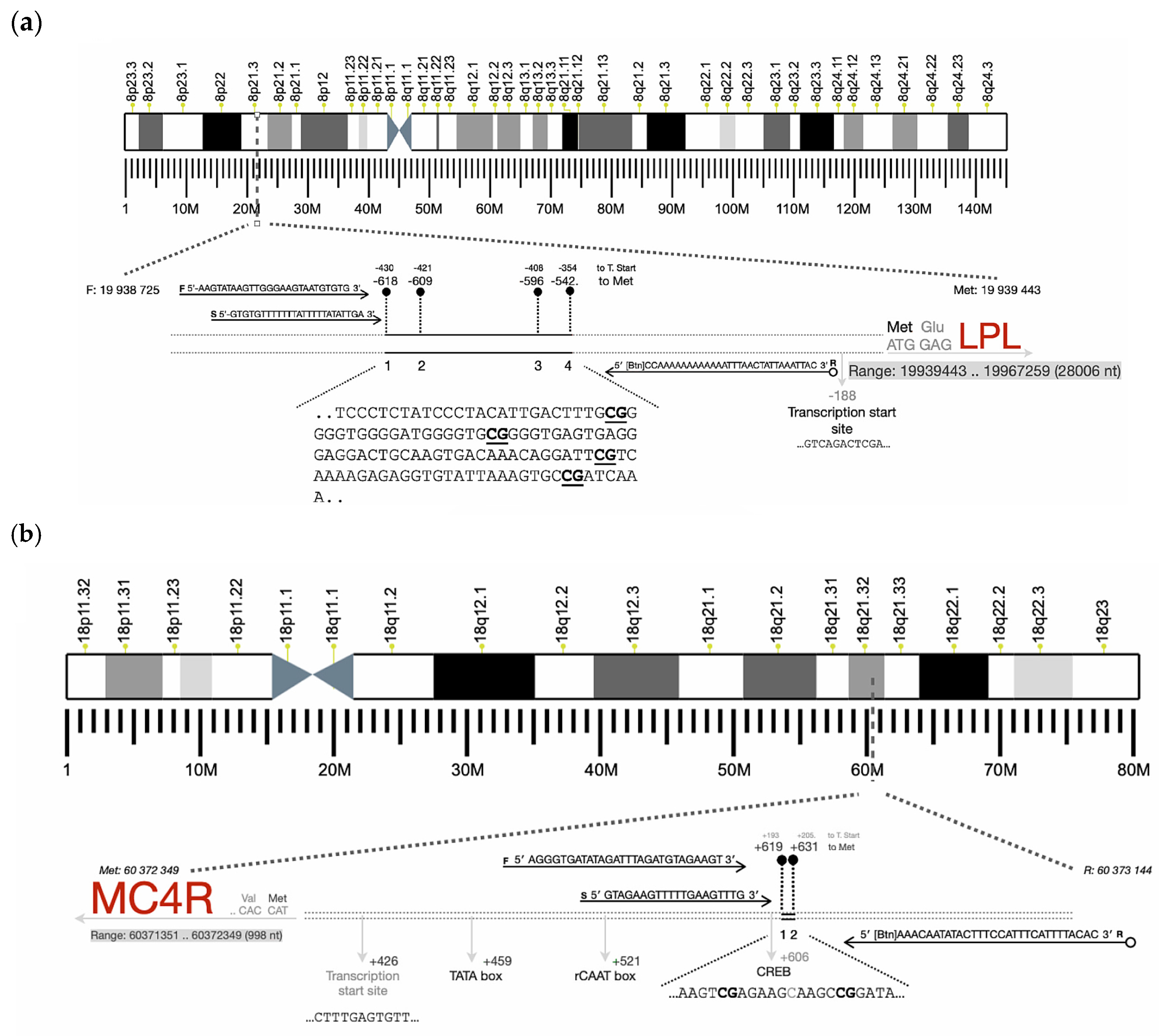
| Gene | Primers | Product Size (pb) | Number of CpGs Analyzed |
|---|---|---|---|
| MC4R | F: 5′-AGGGTGATATAGATTTAGATGTAGAAGT-3′ R:5′-[Btn]AAACAATATACTTTCCATTTCATTTTACAC-3′ Seq: 5′-GTAGAAGTTTTTGAAGTTTG-3′ | 202 | 2 |
| LPL | F: 5′-AAGTATAAGTTGGGAAGTAATGTGTG-3′ R: 5′bio-CCAAAAAAAAAAAATTTAACTATTAAATTAC-3′ Seq: 5′-GTGTGTTTTTTTATTTTTATATTGA-3′ | 177 | 4 |
| Characteristics | NGT (n = 17) | GDM (n = 84) | p-Value | NW (n = 55) | OB (n = 46) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 33.7 (5.3) | 35.3 (4.9) | 0.221 + | 35.6 (4.3) | 34.4 (5.6) | 0.208 + |
| Systolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 112.2 (11.58) | 117.5 (14.4) | 0.186 + | 112.2 (11.6) | 121.2 (15.1) | 0.005 + |
| Diastolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 68.1 (7.0) | 70.8 (9.0) | 0.273 + | 67.7 (7.9) | 73.3 (8.6) | 0.005 + |
| PREDIMED | 8.0 (7–9) | 9.0 (8–10) | 0.037 $ | 9.5 (9–10) | 9.0 (8–10) | 0.004 $ |
| PREDIMED CLASS * | 0.061 § | 0.013 § | ||||
| No adherence | 2 (13.3%) | 2 (2.6%) | 0 (0.0%) | 4 (9.3%) | ||
| Medium adherence | 10 (66.7%) | 42 (53.8%) | 25 (50.0%) | 27 (62.8%) | ||
| Maximum adherence | 3 (20.0%) | 34 (43.6%) | 25 (50.0%) | 12 (27.9%) | ||
| IPAQ * | 0.824 § | 0.427 § | ||||
| Low | 3 (20.0%) | 21 (26.9%) | 13 (26.0%) | 11 (25.6%) | ||
| Moderate | 5 (33.3%) | 28 (35.9%) | 15 (30.0%) | 18 (41.9%) | ||
| High | 7 (46.7%) | 29 (37.2%) | 22 (44.0%) | 14 (32.6%) | ||
| Smoking history * | 0.339 § | 0.118 § | ||||
| Non-smoker | 5 (41.7%) | 48 (60.0%) | 33 (66.0%) | 20 (47.6%) | ||
| Smoker | 0 (0.0%) | 3 (3.8%) | 2 (4.0%) | 1 (2.4%) | ||
| Ex-smoker | 7 (58.3%) | 29 (36.2%) | 15 (30.0%) | 21 (50.0%) | ||
| Pre-pregnancy weight (Kg) | 80.3 (23.8) | 70.9 (19.5) | 0.083 + | 58.2 (6.3) | 89.5 (18.3) | <0.001 + |
| Weight at the end of pregnancy (Kg) | 92.5 (22.0) | 80.5 (17.8) | 0.019 + | 70.0 (7.7) | 97.0 (17.8) | <0.001 + |
| Pre-pregnancy BMI (Kg/m2) | 29.2 (7.8) | 26.6 (7.6) | 0.202 + | 21.8 (1.9) | 33.3 (7.3) | <0.001 + |
| BMI at the end of pregnancy (Kg/m2) | 33.6 (7.2) | 30.2 (6.9) | 0.072 + | 26.2 (2.4) | 36.1 (6.9) | <0.001 + |
| Weight variation (Kg) | 10.7 (5.8) | 9.6 (6.7) | 0.562 + | 11.7 (5.9) | 7.5 (6.6) | <0.001 § |
| Delivery * | 0.964 § | 0.163 § | ||||
| Vaginal delivery | 10 (62.5%) | 53 (63.1%) | 38 (69.1%) | 17 (30.9%) | ||
| Cesarean section | 6 (37.5%) | 31 (36.9%) | 25 (55.6%) | 20 (44.4%) | ||
| Third-trimester TC (mg/dL) | 225.6 (30.3) | 254.3 (46.3) | 0.049 + | 249.9 (45.9) | 251.6 (45.4) | 0.865 + |
| Third-trimester HDL-C (mg/dL) | 60.6 (11.5) | 64.7 (13.2) | 0.336 + | 68.1 (12.7) | 59.2 (11.7) | 0.001 + |
| Third-trimester TG (mg/dL) | 187.8 (86.1) | 230.8 (126.1) | 0.278 + | 207.5 (103.6) | 247.9 (140.4) | 0.128 + |
| Third-trimester LDL-C (mg/dL) | 127.4 (22.0) | 145.8 (35.3) | 0.097 + | 140.3 (35.3) | 147.5 (33.0) | 0.344 + |
| OGTT (mg/dL) at baseline (min) | 83.0 (4.4) | 90.8 (9.3) | <0.001 + | 86.6 (9.2) | 93.0 (7.8) | <0.001 + |
| OGTT (mg/dL) after 60 min | 131.5 (25.7) | 162.4 (34.0) | <0.001 + | 155.6 (37.3) | 158.8 (31.4) | 0.646 + |
| OGTT (mg/dL) after 120 min | 115.9 (20.0) | 135.7 (33.2) | 0.019 | 132.7 (34.1) | 131.9 (30.1) | 0.908 |
| First quarter fasting blood glucose (mg/dL) | 86.6 (11.6) | 85.9 (8.9) | 0.801 + | 86.0 (8.6) | 85.9 (10.1) | 0.980 + |
| Characteristics | NGT (n = 17) | GDM (n = 84) | p-Value | NW (n = 55) | OB (n = 46) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gestational week | 39.1 (1.4) | 38.5 (1.2) | 0.047 + | 38.9 (1.3) | 38.2 (1.0) | 0.014+ |
| Gender * | 0.300 § | 0.503 § | ||||
| Male | 11 (68.8%) | 46 (54.8%) | 33 (60.0%) | 24 (53.3%) | ||
| Female | 5 (31.2%) | 38 (45.2%) | 22 (40.0%) | 21 (46.7%) | ||
| Birth weight (grams) | 3348.8 (289.5) | 3190.4 (454.7) | 0.183 + | 3191.8 (453.5) | 3244.9 (415.0) | 0.546 + |
| One-minute Apgar scores | 7.9 (1.7) | 8.8 (0.7) | <0.001 + | 8.8 (0.5) | 8.4 (1.3) | 0.028 + |
| Five-minute Apgar scores | 9.2 (0.9) | 9.73 (0.7) | <0.001 + | 9.8 (0.5) | 9.6 (0.7) | 0.061 + |
| Birth head circumference (cm) | 34.5 (1.6) | 34.7(1.8) | 0.689 + | 34.6 (1.8) | 34.0 (1.7) | 0.124 + |
| Birth length (cm) | 50.2 (1.3) | 49.6 (2.0) | 0.222 + | 49.9 (2.0) | 49.5 (1.7) | 0.374 + |
| Hypoglycemia * | 0.050 § | 0.993 § | ||||
| No | 13 (81.2%) | 43 (55.1%) | 31 (59.6%) | 25 (59.5%) | ||
| Yes | 3 (18.8%) | 35 (44.9%) | 21 (40.4%) | 17 (40.5%) |
| DNA Methylation% | NGT (n = 17) | GDM (n = 84) | p-Value | NW (n = 55) | OB (n = 46) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MC4R Women | ||||||
| CpG1 | 9.4 (6.3) | 8.4 (5.8) | 0.541 | 8.3 (4.7) | 8.8 (7.1) | 0.674 |
| CpG2 | 15.2 (9.46) | 13.5 (4.6) | 0.254 | 13.6 (4.6) | 13.9 (6.9) | 0.839 |
| Mean methylation levels | 12.1 (7.9) | 10.9 (4.7) | 0.426 | 11.0 (4.5) | 11.3 (6.3) | 0.778 |
| Newborns | ||||||
| CpG1 | 6.9 (6.2) | 2.8 (3.0) | <0.001 | 3.4 (3.4) | 3.7 (4.5) | 0.672 |
| CpG2 | 6.8 (5.6) | 3.8 (3.3) | 0.003 | 4.2 (3.8) | 4.3 (4.1) | 0.917 |
| Mean methylation levels | 6.8 (5.8) | 3.4 (3.0) | <0.001 | 3.8 (3.4) | 4.1 (4.4) | 0.690 |
| LPL Women | ||||||
| CpG1 | 23.8 (10.7) | 23.2 (6.9) | 0.768 | 23.7 (6.9) | 22.8 (8.4) | 0.570 |
| CpG2 | 15.7 (7.7) | 14.0 (6.6) | 0.381 | 14.3 (6.8) | 14.3 (6.8) | 0.957 |
| CpG3 | 20.8 (9.0) | 25.1 (12.3) | 0.182 | 24.4 (13.2) | 24.4 (10.3) | 0.990 |
| CpG4 | 45.9 (15.6) | 43.5 (14.1) | 0.543 | 42.6 (13.9) | 45.5 (14.8) | 0.328 |
| Mean methylation levels | 26.5 (7.0) | 26.5 (7.6) | 0.985 | 26.2 (7.9) | 26.8 (7.0) | 0.728 |
| Newborns | ||||||
| CpG1 | 12.6 (5.0) | 13.8 (5.4) | 0.431 | 13.5 (5.4) | 13.7 (5.4) | 0.877 |
| CpG2 | 9.1 (4.7) | 10.6 (8.0) | 0.472 | 10.7 (7.3) | 9.8 (7.9) | 0.559 |
| CpG3 | 12.6 (8.5) | 13.9 (10.2) | 0.613 | 13.5 (9.5) | 13.9 (10.5) | 0.839 |
| CpG4 | 26.2 (17.0) | 25.0 (12.0) | 0.718 | 24.6 (11.2) | 25.8 (14.8) | 0.637 |
| Mean methylation levels | 15.1 (5.9) | 15.8 (7.5) | 0.704 | 15.6 (6.8) | 15.8 (7.7) | 0.934 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Franzago, M.; Borrelli, P.; Di Nicola, M.; Cavallo, P.; D’Adamo, E.; Di Tizio, L.; Gazzolo, D.; Stuppia, L.; Vitacolonna, E. From Mother to Child: Epigenetic Signatures of Hyperglycemia and Obesity during Pregnancy. Nutrients 2024, 16, 3502. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16203502
Franzago M, Borrelli P, Di Nicola M, Cavallo P, D’Adamo E, Di Tizio L, Gazzolo D, Stuppia L, Vitacolonna E. From Mother to Child: Epigenetic Signatures of Hyperglycemia and Obesity during Pregnancy. Nutrients. 2024; 16(20):3502. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16203502
Chicago/Turabian StyleFranzago, Marica, Paola Borrelli, Marta Di Nicola, Pierluigi Cavallo, Ebe D’Adamo, Luciano Di Tizio, Diego Gazzolo, Liborio Stuppia, and Ester Vitacolonna. 2024. "From Mother to Child: Epigenetic Signatures of Hyperglycemia and Obesity during Pregnancy" Nutrients 16, no. 20: 3502. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16203502
APA StyleFranzago, M., Borrelli, P., Di Nicola, M., Cavallo, P., D’Adamo, E., Di Tizio, L., Gazzolo, D., Stuppia, L., & Vitacolonna, E. (2024). From Mother to Child: Epigenetic Signatures of Hyperglycemia and Obesity during Pregnancy. Nutrients, 16(20), 3502. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16203502







