The Adverse Impact of Bisphenol A Exposure on Optimal Cardiovascular Health as Measured by Life’s Essential 8 in U.S. Adults: Evidence from NHANES 2005 to 2016
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
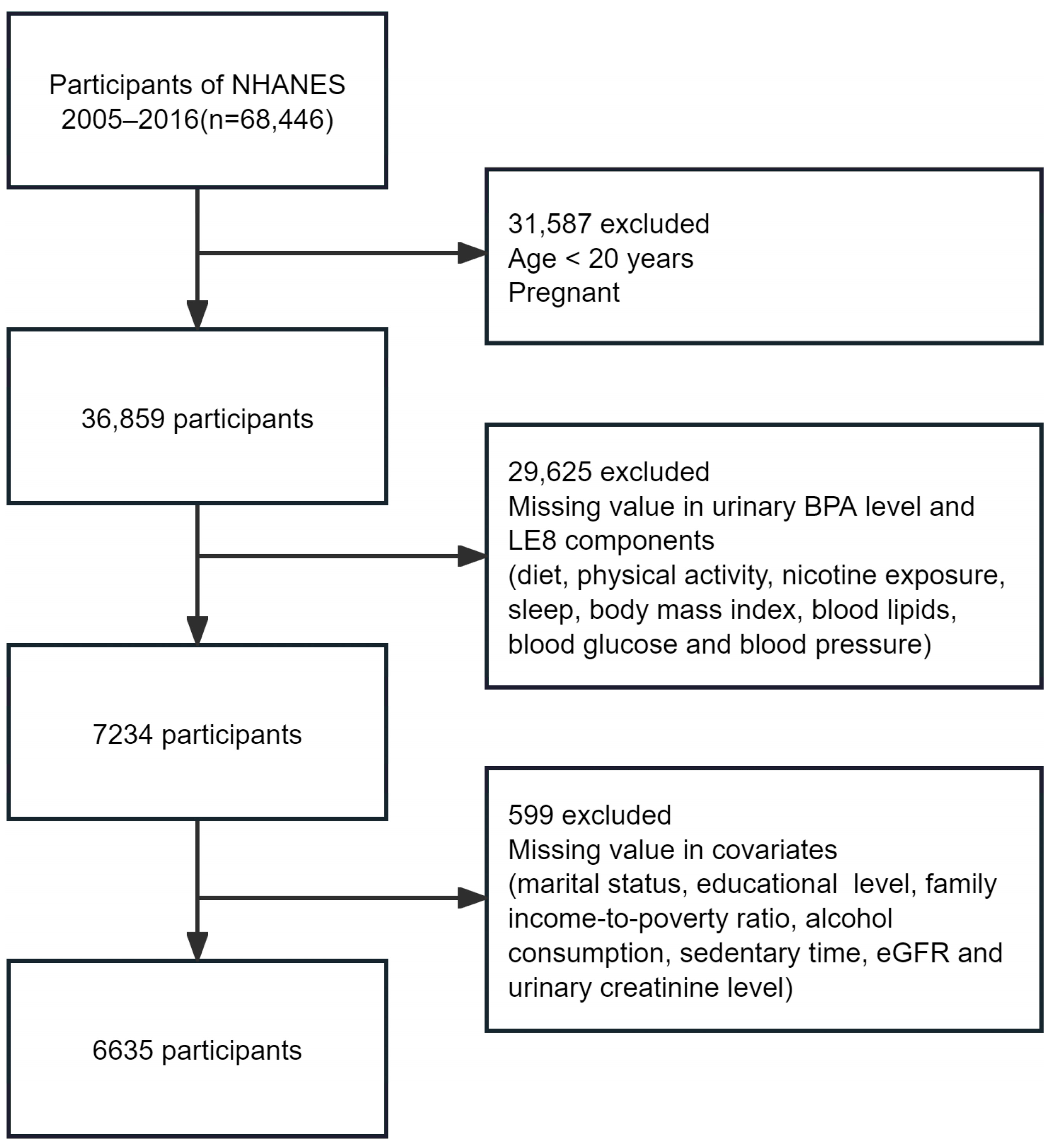
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Urinary BPA-Level Measurement
2.3. CVH Assessment (LE8 Score)
2.4. Assessment of Covariates
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
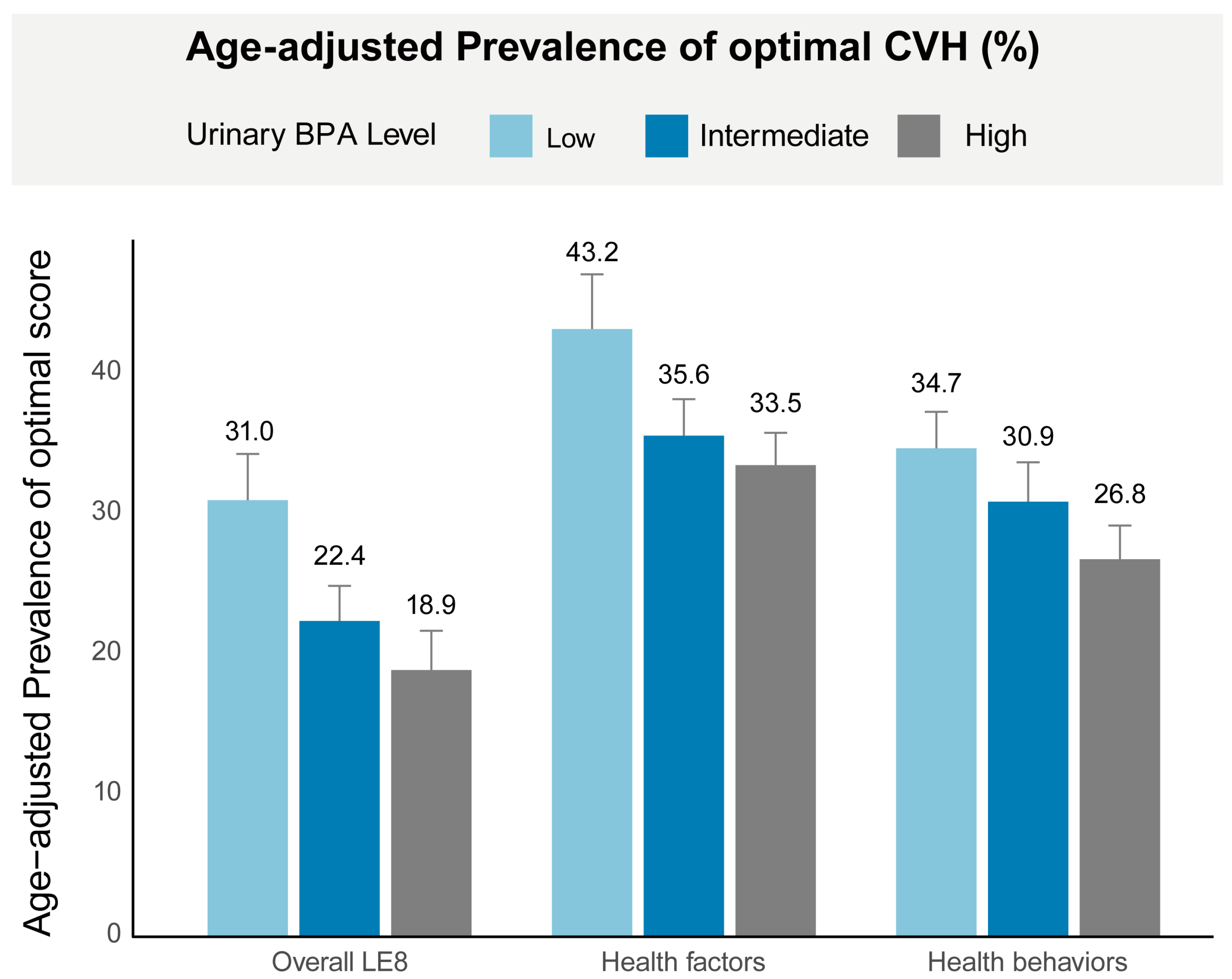
3.2. Age-Adjusted Prevalence of Optimal CVH
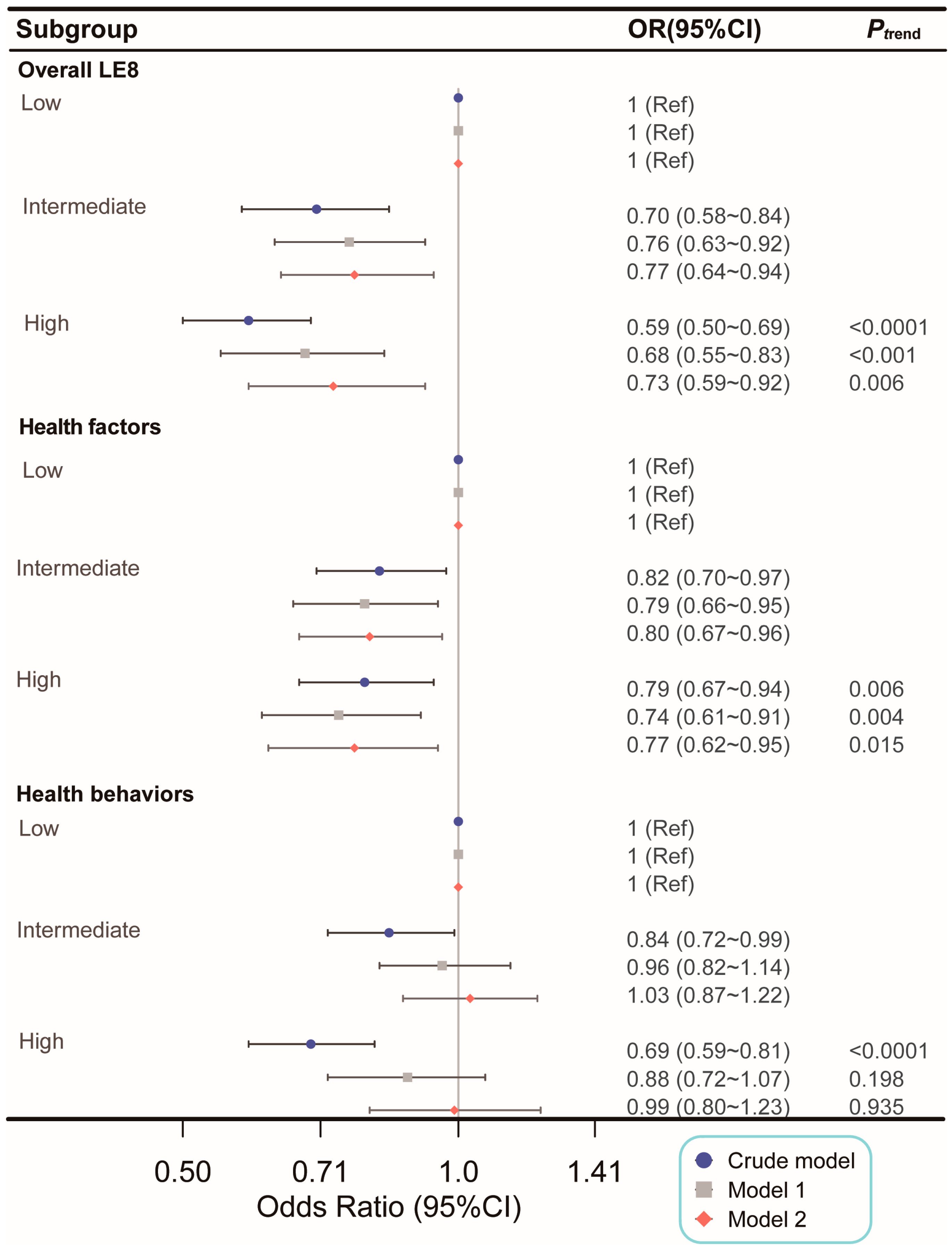
3.3. Association between Urinary BPA Levels and Optimal CVH
3.4. Subgroup and Sensitivity Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. BPA’s Negative Association with Optimal CVH
4.2. BPA’s Association with Health Factor and Behavior Scores
4.3. Strengths and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Roth, G.A.; Mensah, G.A.; Johnson, C.O.; Addolorato, G.; Ammirati, E.; Baddour, L.M.; Barengo, N.C.; Beaton, A.Z.; Benjamin, E.J.; Benziger, C.P.; et al. Global burden of cardiovascular diseases and risk factors, 1990–2019: Update from the GBD 2019 study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 76, 2982–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lloyd-Jones, D.M.; Allen, N.B.; Anderson, C.A.M.; Black, T.; Brewer, L.C.; Foraker, R.E.; Grandner, M.A.; Lavretsky, H.; Perak, A.M.; Sharma, G.; et al. Life’s essential 8: Updating and enhancing the American heart association’s construct of cardiovascular health: A presidential advisory from the American heart association. Circulation 2022, 146, e18–e43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lloyd-Jones, D.M.; Hong, Y.; Labarthe, D.; Mozaffarian, D.; Appel, L.J.; Van Horn, L.; Greenlund, K.; Daniels, S.; Nichol, G.; Tomaselli, G.F.; et al. Defining and setting national goals for cardiovascular health promotion and disease reduction: The American heart association’s strategic impact goal through 2020 and beyond. Circulation 2010, 121, 586–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younus, A.; Aneni, E.C.; Spatz, E.S.; Osondu, C.U.; Roberson, L.; Ogunmoroti, O.; Malik, R.; Ali, S.S.; Aziz, M.; Feldman, T.; et al. A systematic review of the prevalence and outcomes of ideal cardiovascular health in US and non-US populations. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2016, 91, 649–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radovanovic, M.; Jankovic, J.; Mandic-Rajcevic, S.; Dumic, I.; Hanna, R.D.; Nordstrom, C.W. Ideal cardiovascular health and risk of cardiovascular events or mortality: A systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective studies. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 4417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aneni, E.C.; Crippa, A.; Osondu, C.U.; Valero-Elizondo, J.; Younus, A.; Nasir, K.; Veledar, E. Estimates of mortality benefit from ideal cardiovascular health metrics: A dose response meta-analysis. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2017, 6, e006904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Li, Y.; Zhao, M.; Yu, X.; Zhang, C.; Magnussen, C.G.; Xi, B. Association of the american heart association’s new “life’s essential 8” with all-cause and cardi-ovascular disease-specific mortality: Prospective cohort study. BMC Med. 2023, 21, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, P.; Zhang, Y.; Ye, Z.; Li, H.; Liu, M.; Zhou, C.; Yang, S.; Gan, X.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, X. A healthy lifestyle, life’s essential 8 scores and new-onset severe nafld: A prospective analysis in UK biobank. Metabolism 2023, 146, 155643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ma, H.; Li, X.; Heianza, Y.; Manson, J.E.; Franco, O.H.; Qi, L. Association of cardiovascular health with life expectancy free of cardiovascular disease, diabetes, cancer, and dementia in UK adults. JAMA Intern. Med. 2023, 183, 340–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Chen, S.; Tian, X.; Xu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, P.; Wu, S.; Lin, L.; Wang, A. Association of cardiovascular health assessed by the new life’s essential 8 metrics with years lived without cardiovascular disease. J. Am. Heart Assoc. Cardiovasc. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2023, 12, e029241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Sun, M.; Wang, Y.; Xu, T.; Ning, N.; Tong, L.; He, Y.; Jin, L.; Ma, Y. Association of cardiovascular health using life’s essential 8 with noncommunicable disease multimorbidity. Prev. Med. 2023, 174, 107607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Li, Y.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, C.; Bovet, P.; Xi, B. Using the new “life’s essential 8” metrics to evaluate trends in cardiovascular health among us adults from 2005 to 2018: Analysis of serial cross-sectional studies. JMIR Public Health Surveill. 2023, 9, e45521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lloyd-Jones, D.M.; Ning, H.; Labarthe, D.; Brewer, L.; Sharma, G.; Rosamond, W.; Foraker, R.E.; Black, T.; Grandner, M.A.; Allen, N.B.; et al. Status of cardiovascular health in us adults and children using the american heart association’s new “life’s essential 8” metrics: Prevalence estimates from the national health and nutrition examination survey (nhanes), 2013 through 2018. Circulation 2022, 146, 822–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariana, M.; Castelo-Branco, M.; Soares, A.M.; Cairrao, E. Phthalates’ exposure leads to an increasing concern on cardiovascular health. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 457, 131680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, W.-Y.; Sun, J.-N.; Liu, F.-H.; Shan, L.-S.; Yin, J.-L.; Li, Y.-Z.; Xu, H.-L.; Wei, Y.-F.; Liu, J.-X.; Zheng, W.-R.; et al. Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances and human health outcomes: An umbrella review of systematic reviews with meta-analyses of observational studies. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 472, 134556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlezinger, J.J.; Gokce, N. Perfluoroalkyl/polyfluoroalkyl substances: Links to cardiovascular disease risk. Circ. Res. 2024, 134, 1136–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Gong, T.; Liang, P. Heavy metal exposure and cardiovascular disease. Circ. Res. 2024, 134, 1160–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Liu, X.; Zhang, G. Identification of potential food sources affecting blood lead levels and their health hazards (CVD, respiratory diseases, cancer). Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 906, 167505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-F.; Shan, C.; Wang, Y.; Qian, L.-L.; Jia, D.-D.; Zhang, Y.-F.; Hao, X.-D.; Xu, H.-M. Cardiovascular toxicity and mechanism of bisphenol A and emerging risk of bisphenol S. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 723, 137952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, H.; Liu, S. Low-dose bisphenol a exposure: A seemingly instigating carcinogenic effect on breast cancer. Adv. Sci. Weinh. Baden-Wurtt. Ger. 2017, 4, 1600248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Liu, H.; Wu, J.; Yuan, L.; Wang, Y.; Du, X.; Wang, R.; Marwa, P.W.; Petlulu, P.; Chen, X.; et al. The adverse health effects of bisphenol A and related toxicity mechanisms. Environ. Res. 2019, 176, 108575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno-Gómez-Toledano, R.; Delgado-Marín, M.; Sánchez-Esteban, S.; Cook-Calvete, A.; Ortiz, S.; Bosch, R.J.; Saura, M. Combination of bisphenol a and its emergent substitute molecules is related to heart disease and exerts a differential effect on vascular endothelium. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 12188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno-Gómez-Toledano, R.; Sánchez-Esteban, S.; Cook, A.; Mínguez-Moratinos, M.; Ramírez-Carracedo, R.; Reventún, P.; Delgado-Marín, M.; Bosch, R.J.; Saura, M. Bisphenol a induces accelerated cell aging in murine endothelium. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, I.; Kaur, M.; Tyagi, D.; Singh, T.B.; Kaur, G.; Afzal, S.M.; Jauhar, M. Exploring novel insights into the molecular mechanisms underlying bisphenol a-induced toxicity: A persistent threat to human health. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2024, 108, 104467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, B.L.; Posnack, N.G. Characteristics of bisphenol cardiotoxicity: Impaired excitability, contractility, and relaxation. Cardiovasc. Toxicol. 2022, 22, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, S.; Yu, S.H.; Lee, C.B.; Park, Y.J.; Yoo, H.J.; Kim, D.S. Effects of bisphenol a on cardiovascular disease: An epidemiological study using national health and nutrition examination survey 2003–2016 and meta-analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 763, 142941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Lu, Y.; Yin, N.; Faiola, F. Transcriptomic integration analyses uncover common bisphenol a effects across species and tissues primarily mediated by disruption of JUN/FOS, EGFR, ER, PPARG, and P53 pathways. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 19156–19168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.; Huang, Y.; Chen, H.; Huang, J.; Zhang, L.; Wei, S.; Liu, F.; Chen, D.; Huang, W. BPA and its alternatives BPF and BPAF exaggerate hepatic lipid metabolism disorders in male mice fed a high fat diet. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 867, 161521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corre, L.L.; Besnard, P.; Chagnon, M.-C. BPA, an energy balance disruptor. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2015, 55, 769–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.-H.; Asai, D.; Toita, R. Bisphenol a (BPA) and cardiovascular or cardiometabolic diseases. J. Xenobiotics 2023, 13, 775–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, M.; Ferrini, M.G.; Han, G.; Jellyman, J.K.; Ross, M.G. In vivo maternal and in vitro BPA exposure effects on hypothalamic neurogenesis and appetite regulators. Environ. Res. 2018, 164, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Q.; Deng, P.; Lin, M.; Yang, L.; Li, L.; Guo, L.; Zhang, L.; He, M.; Lu, Y.; Pi, H.; et al. Long-term bisphenol a exposure exacerbates diet-induced prediabetes via TLR4-dependent hypothalamic inflammation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 402, 123926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beydoun, H.A.; Beydoun, M.A.; Jeng, H.A.; Zonderman, A.B.; Eid, S.M. Bisphenol-a and sleep adequacy among adults in the national health and nutrition examination surveys. Sleep 2016, 39, 467–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bigambo, F.M.; Sun, J.; Zhu, C.; Zheng, S.; Xu, Y.; Wu, D.; Xia, Y.; Wang, X. Gender- and obesity-specific association of co-exposure to personal care product and plasticizing chemicals and short sleep duration among adults: Evidence from the national health and nutrition examination survey 2011–2016. Toxics 2024, 12, 503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patisaul, H.B. Achieving CLARITY on bisphenol a, brain and behaviour. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2020, 32, e12730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesan, D.; Feighan, K.M.; Antle, M.C.; Kurrasch, D.M. Gestational low-dose BPA exposure impacts suprachiasmatic nucleus neurogenesis and circadian activity with transgenerational effects. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabd1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, T.; Huang, Z.; Zheng, C.; Quach, B.; Zhu, Y.; Li, F.; Liang, W.; Baker, J.; Reichetzeder, C.; Hocher, B.; et al. Associations of bisphenol A exposure with metabolic syndrome and its components: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes. Rev. 2024, 25, e13738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.-H.; Lee, C.-Y.; Chuang, Y.-S.; Shih, C.-L. Exposure to bisphenol a associated with multiple health-related outcomes in humans: An umbrella review of systematic reviews with meta-analyses. Environ. Res. 2023, 237 Pt 1, 116900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rancière, F.; Botton, J.; Slama, R.; Lacroix, M.Z.; Debrauwer, L.; Charles, M.A.; Roussel, R.; Balkau, B.; Magliano, D.J.; the D.E.S.I.R. Study Group. Exposure to bisphenol a and bisphenol S and incident type 2 diabetes: A case–cohort study in the french cohort D.E.S.I.R. Environ. Health Perspect. 2019, 127, 107013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Li, M.; Zhao, Z.; Lu, J.; Chen, Y.; Xu, Y.; Xu, M.; Wang, W.; Wang, T.; Bi, Y.; et al. Urinary bisphenol A concentration and glucose homeostasis in non-diabetic adults: A repeated-measures, longitudinal study. Diabetologia 2019, 62, 1591–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Liu, R.; Yang, Z.; Liu, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Sun, M.; Shen, C.; Liu, J.; Yu, P.; et al. Association of metals and bisphenols exposure with lipid profiles and dyslipidemia in Chinese adults: Independent, combined and interactive effects. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 946, 174315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Wang, S.; Zhao, Z.; Chen, Y.; Xu, Y.; Li, M.; Xu, M.; Wang, W.; Ning, G.; Bi, Y.; et al. Bisphenol a exposure in relation to altered lipid profile and dyslipidemia among Chinese adults: A repeated measures study. Environ. Res. 2020, 184, 109382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varshavsky, J.R.; Meeker, J.D.; Zimmerman, E.; Woodbury, M.L.; Aung, M.T.; Rosario-Pabon, Z.Y.; Cathey, A.L.; Vélez-Vega, C.M.; Cordero, J.; Alshawabkeh, A.; et al. Association of phenols, parabens, and their mixture with maternal blood pressure measurements in the PROTECT cohort. Environ. Health Perspect. 2024, 132, 87004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, S.; Rao, X.; Ye, J.; Ling, Y.; Mi, S.; Chen, H.; Fan, C.; Li, Y. Relationship between urinary bisphenol a levels and cardiovascular diseases in the U.S. adult population, 2003–2014. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 192, 110300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-M.; Liu, Z.-Y.; Chen, S.; Lu, X.-T.; Huang, Z.-H.; Wusiman, M.; Huang, B.-X.; Lan, Q.-Y.; Wu, T.; Huang, R.-Z.; et al. Mitigating the impact of bisphenol A exposure on mortality: Is diet the key? A cohort study based on NHANES. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 267, 115629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, W.; Liu, B.; Rong, S.; Dai, S.Y.; Trasande, L.; Lehmler, H.-J. Association between bisphenol A exposure and risk of all-cause and cause-specific mortality in US adults. JAMA Netw. Open 2020, 3, e2011620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salamanca-Fernández, E.; Rodríguez-Barranco, M.; Petrova, D.; Larrañaga, N.; Guevara, M.; Moreno-Iribas, C.; Chirlaque, M.D.; Colorado-Yohar, S.; Arrebola, J.P.; Vela, F.; et al. Bisphenol A exposure and risk of ischemic heart disease in the Spanish European Prospective Investigation into cancer and nutrition study. Chemosphere 2020, 261, 127697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, S.A.; Severo, M.; Lopes, C.; Torres, D. Association between bisphenol A exposure and cardiometabolic outcomes: A longitudinal approach. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 476, 135000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salamanca-Fernández, E.; Vela-Soria, F.; Rodríguez-Barranco, M.; Arrebola-Moreno, A.; Iribarne-Durán, L.M.; Olea, N.; Sánchez, M.J.; Arrebola, J.P. Serum levels of non-persistent environmental pollutants and risk of incident hypertension in a sub-cohort from the EPIC study. Environ. Res. 2021, 193, 110491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunder, L.; Lejonklou, M.H.; Lind, P.M.; Lind, L. Urinary bisphenol A and serum lipids: A meta-analysis of six NHANES examination cycles (2003–2014). J. Epidemiol. Community Health 2019, 73, 1012–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, C.W.; Wolfson, J.A.; Brandt, E.J.; Rimm, E.B. Disparities in cardiovascular health by food security status and supplemental nutrition assistance program participation using life’s essential 8 metrics. JAMA Netw. Open 2023, 6, e2321375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Wang, J.; Wang, M.; Hou, H.; Ding, X.; Ma, L.; Liu, M. Oxidative stress factors mediate the association between life’s essential 8 and accelerated phenotypic aging: NHANES 2005–2018. J. Gerontol. A. Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2023, 79, glad240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Yi, J.; Guo, X.; Ren, X. Associations between life’s essential 8 and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease among US adults. J. Transl. Med. 2022, 20, 616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granic, A.; Sayer, A.A.; Robinson, S.M. Dietary patterns, skeletal muscle health, and sarcopenia in older adults. Nutrients 2019, 11, 745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, G.; Xia, H.; Wang, X.; Wang, C.; Cai, M.; Gao, Y.; Lip, G.Y.H.; Lin, H. Associations of life’s essential 8 and fine particulate matter pollution with the incidence of atrial fibrillation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 459, 132114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krebs-Smith, S.M.; Pannucci, T.E.; Subar, A.F.; Kirkpatrick, S.I.; Lerman, J.L.; Tooze, J.A.; Wilson, M.M.; Reedy, J. Update of the healthy eating index: HEI-2015. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2018, 118, 1591–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, W.; Liu, B.; Simonsen, D.W.; Lehmler, H.-J. Association between exposure to pyrethroid insecticides and risk of all-cause and cause-specific mortality in the general US adult population. JAMA Intern. Med. 2020, 180, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.-Y.; Wang, C.; Huang, S.-Y.; Lu, X.-T.; Yang, Z.-J.; Lan, Q.-Y.; Huang, B.-X.; Chen, S.; Li, M.-C.; Zhu, H.-L. Does anti-inflammatory diet mitigate the deleterious effect of bisphenol A on mortality in US adults? Results from NHANES 2003–2016. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 253, 114706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levey, A.S.; Stevens, L.A.; Schmid, C.H.; Zhang, Y.L.; Castro, A.F.; Feldman, H.I.; Kusek, J.W.; Eggers, P.; Van Lente, F.; Greene, T.; et al. A new equation to estimate glomerular filtration rate. Ann. Intern. Med. 2009, 150, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reventun, P.; Sanchez-Esteban, S.; Cook, A.; Cuadrado, I.; Roza, C.; Moreno-Gomez-Toledano, R.; Muñoz, C.; Zaragoza, C.; Bosch, R.J.; Saura, M. Bisphenol A induces coronary endothelial cell necroptosis by activating RIP3/CamKII dependent pathway. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 4190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandi, M.L.; Marini, F.; Parri, S.; Bandinelli, S.; Iantomasi, T.; Giusti, F.; Talluri, E.; Sini, G.; Nannipieri, F.; Battaglia, S.; et al. Association of vitamin D and bisphenol a levels with cardiovascular risk in an elderly italian population: Results from the InCHIANTI study. GeroScience, 2024; Online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsén, L.; Lind, L.; Lind, P.M. Associations between circulating levels of bisphenol a and phthalate metabolites and coronary risk in the elderly. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2012, 80, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Lehmler, H.-J.; Sun, Y.; Xu, G.; Liu, Y.; Zong, G.; Sun, Q.; Hu, F.B.; Wallace, R.B.; Bao, W. Bisphenol A substitutes and obesity in US adults: Analysis of a population-based, cross-sectional study. Lancet Planet. Health 2017, 1, e114–e122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Dong, T.; Hu, W.; Wang, X.; Xu, B.; Lin, Z.; Hofer, T.; Stefanoff, P.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X.; et al. Association between exposure to a mixture of phenols, pesticides, and phthalates and obesity: Comparison of three statistical models. Environ. Int. 2019, 123, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Cho, Y.H.; Hong, Y.-C. MicroRNA expression in response to bisphenol A is associated with high blood pressure. Environ. Int. 2020, 141, 105791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Liu, H.; Zhou, S.; Zhang, X.; Peng, C.; Zhou, H.; Tong, Y.; Lu, Q. Association of bisphenol A and its alternatives bisphenol S and F exposure with hypertension and blood pressure: A cross-sectional study in china. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 257, 113639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.Y.; Lee, J.; Huh, D.-A.; Moon, K.W. Urinary bisphenol concentrations and its association with metabolic disorders in the US and Korean populations. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 295, 118679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Cornelis, M.C.; Townsend, M.K.; Tobias, D.K.; Eliassen, A.H.; Franke, A.A.; Hauser, R.; Hu, F.B. Association of urinary concentrations of bisphenol A and phthalate metabolites with risk of type 2 diabetes: A prospective investigation in the Nurses’ Health Study (NHS) and NHSII cohorts. Environ. Health Perspect. 2014, 122, 616–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Zhang, L.; Yan, J.; Sun, Y.; Jiang, H. Association of sleep problems with urinary concentrations of personal care and consumer product chemicals: A nationally representative, population-based study. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 14533–14544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Characteristics | Overall (n = 6635) | Life’s Essential 8 Score b | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Optimal (n = 1300) | Suboptimal (n = 5335) | |||
| Mean (SE) | 68.44 (0.30) | 86.81 (0.18) | 62.84 (0.22) | <0.0001 |
| Age (years) | 47.59 (0.34) | 42.04 (0.61) | 49.28 (0.33) | <0.0001 |
| Sex (%) | <0.0001 | |||
| Male | 48.94 (0.02) | 39.93 (1.59) | 51.68 (0.88) | |
| Female | 51.06 (0.02) | 60.07 (1.59) | 48.32 (0.88) | |
| Race/ethnicity (%) | <0.0001 | |||
| Non-Hispanic White | 71.90 (0.03) | 75.15 (1.55) | 70.90 (1.56) | |
| Non-Hispanic Black | 9.98 (0.01) | 5.66 (0.60) | 11.30 (0.88) | |
| Mexican American | 7.43 (0.01) | 6.26 (0.76) | 7.78 (0.73) | |
| Other | 10.69 (0.01) | 12.92 (1.07) | 10.01 (0.69) | |
| Educational level (%) | <0.0001 | |||
| Less than high school | 14.47 (0.01) | 6.35 (0.74) | 16.94 (0.85) | |
| High school or equivalent | 22.87 (0.01) | 10.93 (1.08) | 26.52 (1.02) | |
| College or above | 62.66 (0.02) | 82.72 (1.34) | 56.54 (1.41) | |
| Marital status (%) | <0.0001 | |||
| Married/living with partner | 66.08 (0.03) | 67.12 (1.78) | 65.76 (1.07) | |
| Widowed/divorce/separated | 17.67 (0.01) | 9.75 (0.92) | 20.08 (0.63) | |
| Never married | 16.25 (0.01) | 23.14 (1.68) | 14.15 (0.84) | |
| FITPR, (%) | <0.0001 | |||
| <1.3 | 17.96 (0.01) | 11.93 (1.21) | 19.80 (0.93) | |
| 1.3–3.5 | 36.30 (0.01) | 29.23 (1.60) | 38.46 (1.01) | |
| >3.5 | 45.74 (0.02) | 58.84 (1.86) | 41.74 (1.30) | |
| Alcohol consumption (%) | 0.03 | |||
| Non-drinker | 21.32 (0.01) | 18.68 (1.40) | 22.13 (0.81) | |
| Low-to-moderate drinker | 68.51 (0.02) | 72.22 (1.49) | 67.38 (0.95) | |
| Heavy drinker | 10.16 (0.01) | 9.10 (1.00) | 10.48 (0.61) | |
| Sedentary time, minutes/day | 341.29 (4.49) | 342.23 (7.40) | 341.00 (4.84) | 0.87 |
| Urinary creatinine level (mg/dL) | 120.35 (1.47) | 106.24 (2.77) | 124.65 (1.62) | <0.0001 |
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) | 93.89 (0.42) | 98.54 (0.71) | 92.47 (0.43) | <0.0001 |
| Urinary BPA level (ng/mL) | 1.50 (0.70, 3.00) | 1.20 (0.60, 2.50) | 1.60 (0.80, 3.20) | <0.0001 |
| OR (95% CI) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Optimal LE8 | Optimal Health Factors | Optimal Health Behaviors | |
| Propensity score matching a | |||
| Low | 1.00 (Reference) | 1.00 (Reference) | 1.00 (Reference) |
| Intermediate | 0.77 (0.64, 0.94) | 0.80 (0.67, 0.96) | 1.03 (0.87, 1.22) |
| High | 0.73 (0.59, 0.92) | 0.77 (0.62, 0.95) | 0.99 (0.80, 1.23) |
| Excluding participants with CVD history b | |||
| Low | 1.00 (Reference) | 1.00 (Reference) | 1.00 (Reference) |
| Intermediate | 0.76 (0.62, 0.93) | 0.79 (0.65, 0.96) | 0.99 (0.83, 1.19) |
| High | 0.71 (0.56, 0.90) | 0.77 (0.61, 0.97) | 0.98 (0.79, 1.21) |
| Including the survey cycle b | |||
| Low | 1.00 (Reference) | 1.00 (Reference) | 1.00 (Reference) |
| Intermediate | 0.82 (0.68, 1.00) | 0.80 (0.67, 0.97) | 1.09 (0.91, 1.31) |
| High | 0.79 (0.63, 1.00) | 0.77 (0.62, 0.95) | 1.06 (0.85, 1.32) |
| BPA level categorized by quartiles b | |||
| Quartile 1 | 1.00 (Reference) | 1.00 (Reference) | 1.00 (Reference) |
| Quartile 2 | 0.80 (0.65, 0.98) | 0.77 (0.64, 0.94) | 1.02 (0.83, 1.26) |
| Quartile 3 | 0.74 (0.58, 0.94) | 0.69 (0.55, 0.87) | 1.05 (0.85, 1.28) |
| Quartile 4 | 0.69 (0.54, 0.87) | 0.73 (0.58, 0.91) | 0.95 (0.75, 1.20) |
| Log-transformed BPA b | 0.89 (0.82, 0.95) | 0.91 (0.85, 0.98) | 1.00 (0.93, 1.09) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Y.; Xu, C.; Huang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zou, J.; Zhu, H. The Adverse Impact of Bisphenol A Exposure on Optimal Cardiovascular Health as Measured by Life’s Essential 8 in U.S. Adults: Evidence from NHANES 2005 to 2016. Nutrients 2024, 16, 3253. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16193253
Chen Y, Xu C, Huang Y, Liu Z, Zou J, Zhu H. The Adverse Impact of Bisphenol A Exposure on Optimal Cardiovascular Health as Measured by Life’s Essential 8 in U.S. Adults: Evidence from NHANES 2005 to 2016. Nutrients. 2024; 16(19):3253. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16193253
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Yemei, Chao Xu, Ying Huang, Zhaoyan Liu, Jiupeng Zou, and Huilian Zhu. 2024. "The Adverse Impact of Bisphenol A Exposure on Optimal Cardiovascular Health as Measured by Life’s Essential 8 in U.S. Adults: Evidence from NHANES 2005 to 2016" Nutrients 16, no. 19: 3253. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16193253
APA StyleChen, Y., Xu, C., Huang, Y., Liu, Z., Zou, J., & Zhu, H. (2024). The Adverse Impact of Bisphenol A Exposure on Optimal Cardiovascular Health as Measured by Life’s Essential 8 in U.S. Adults: Evidence from NHANES 2005 to 2016. Nutrients, 16(19), 3253. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16193253









