What Environmental Metrics Are Used in Scientific Research to Estimate the Impact of Human Diets?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
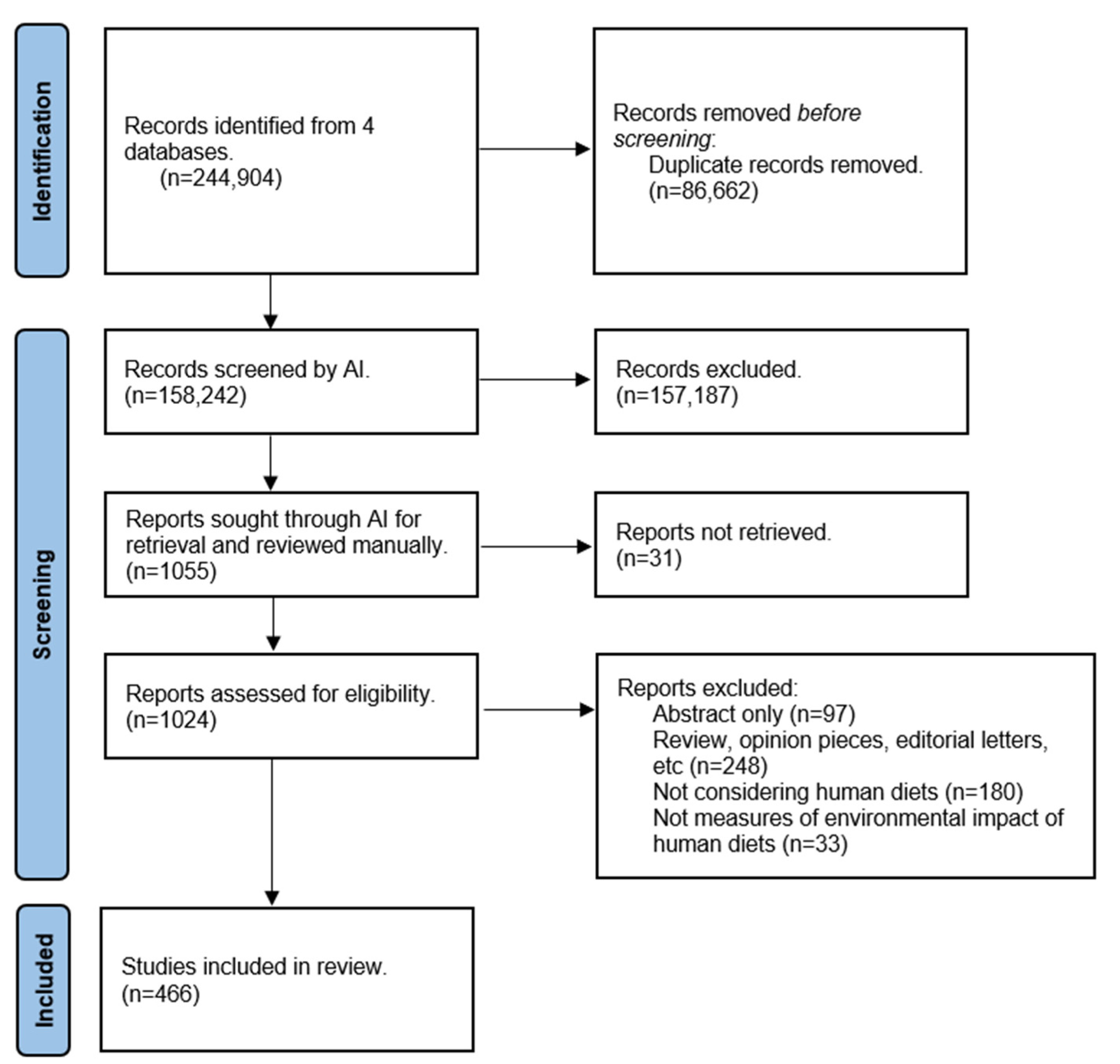
2.1. Searches
2.2. Screening
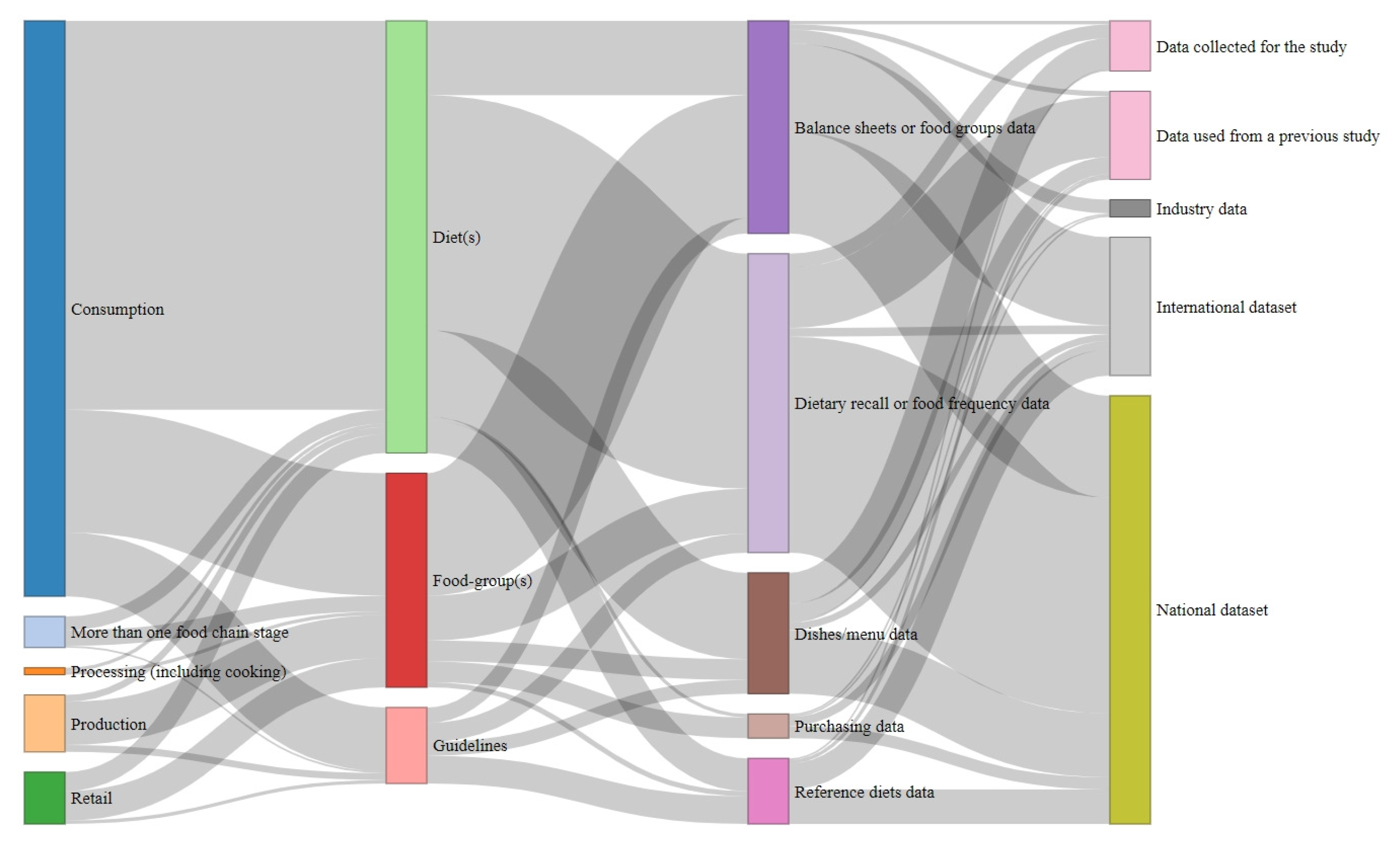
2.3. Data Extraction
2.4. Synthesis
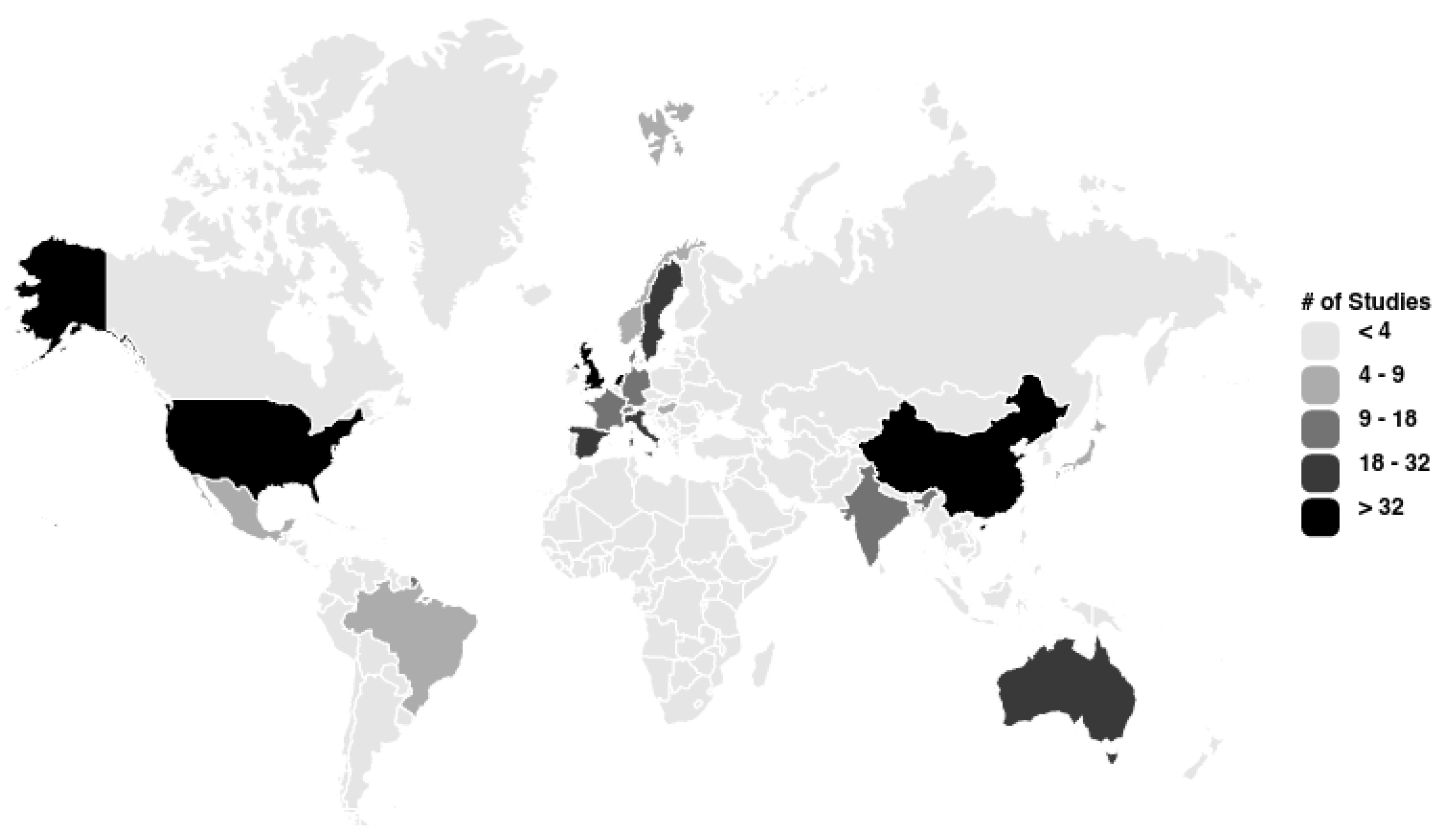
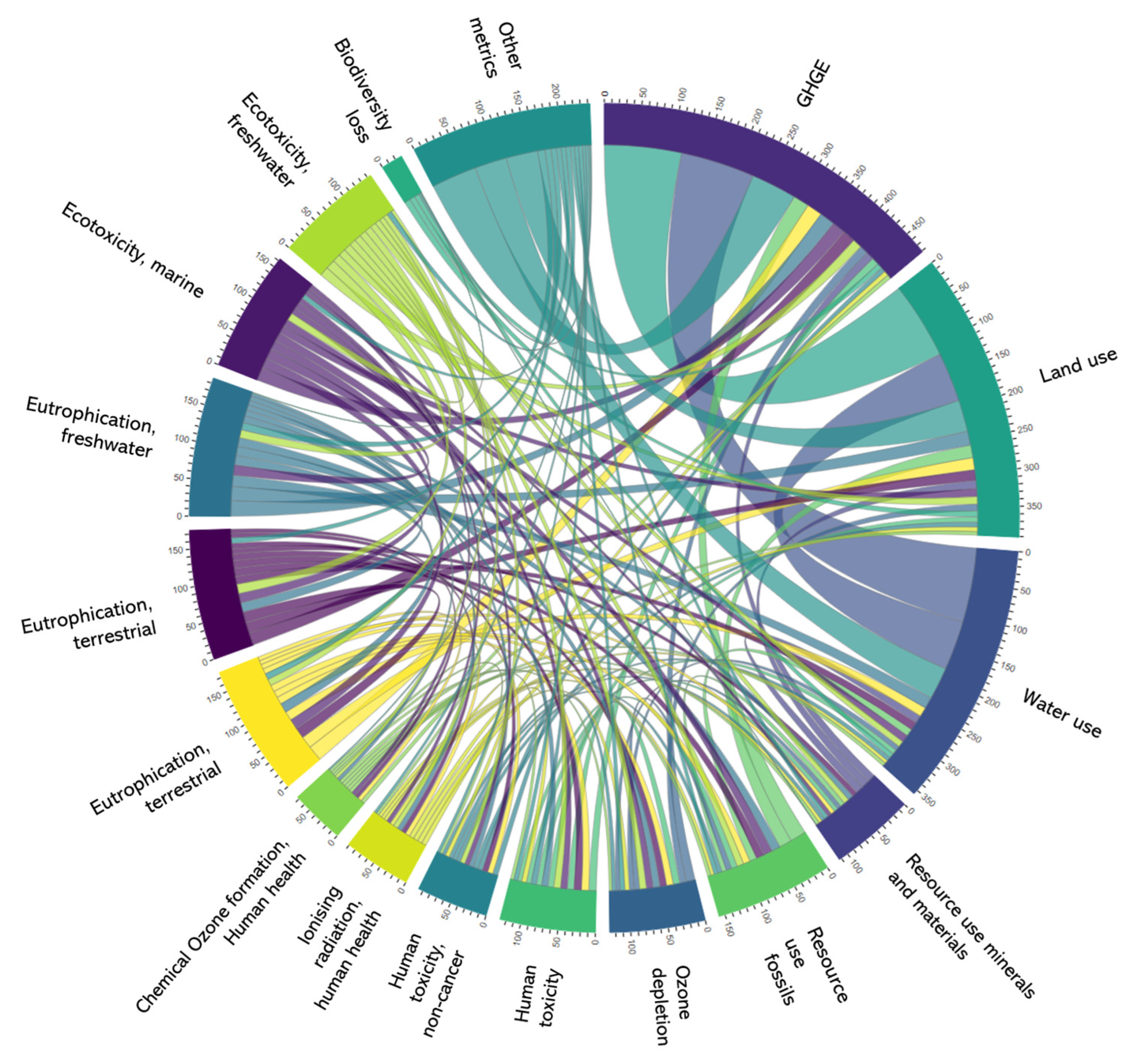
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khan, N.H.; Nafees, M.; ur Rahman, A.; Saeed, T. Ecodesigning for ecological sustainability. In Frontiers in Plant-Soil Interaction; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 589–616. [Google Scholar]
- Angeler, D.G.; Fried-Petersen, H.B.; Allen, C.R.; Garmestani, A.; Twidwell, D.; Chuang, W.C.; Donovan, V.M.; Eason, T.; Roberts, C.P.; Sundstrom, S.M.; et al. Adaptive capacity in ecosystems. In Advances in Ecological Research; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, S.T.; Batool, B.; Zhu, B.; Khan, I. Environmental complexity of globalization, education, and income inequalities: New insights of energy poverty. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 340, 130735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molotoks, A.; Smith, P.; Dawson, T.P. Impacts of land use, population, and climate change on global food security. Food Energy Secur. 2021, 10, e261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shackelford, B.B.; Cronk, R.; Behnke, N.; Cooper, B.; Tu, R.; D’Souza, M.; Bartram, J.; Schweitzer, R.; Jaff, D. Environmental health in forced displacement: A systematic scoping review of the emergency phase. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 714, 136553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faghmous, J.H.; Kumar, V. A big data guide to understanding climate change: The case for theory-guided data science. Big Data 2014, 2, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eme, P.E.; Douwes, J.; Kim, N.; Foliaki, S.; Burlingame, B. Review of methodologies for assessing sustainable diets and potential for development of harmonised indicators. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, P.; Westhoff, P.; Debnath, D. Biofuels, food security, and sustainability. In Biofuels, Bioenergy and Food Security; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 211–229. [Google Scholar]
- Accorsi, R. Planning sustainable food supply chains to meet growing demands. In Encyclopedia of Food Security and Sustainability; Ferranti, P., Berry, E.M., Anderson, J.R., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 45–53. [Google Scholar]
- Hallström, E.; Carlsson-Kanyama, A.; Börjesson, P. Environmental impact of dietary change: A systematic review. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 91, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, A.D.; Hoey, L.; Blesh, J.; Miller, L.; Green, A.; Shapiro, L.F. A Systematic Review of the Measurement of Sustainable Diets. Adv. Nutr. 2016, 7, 641–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berrang-Ford, L.; Sietsma, A.J.; Callaghan, M.; Minx, J.C.; Scheelbeek, P.; Haddaway, N.R.; Haines, A.; Belesova, K.; Dangour, A.D. Mapping global research on climate and health using machine learning (a systematic evidence map). Wellcome Open Res. 2021, 6, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berrang-Ford, L.; Sietsma, A.J.; Callaghan, M.; Minx, J.C.; Scheelbeek, P.F.D.; Haddaway, N.R.; Haines, A.; Dangour, A.D. Systematic mapping of global research on climate and health: A machine learning review. Lancet Planet. Health 2021, 5, e514–e525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bornmann, L.; Mutz, R. Growth rates of modern science: A bibliometric analysis based on the number of publications and cited references. J. Assoc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2015, 66, 2215–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaizot, A.; Veettil, S.K.; Saidoung, P.; Moreno-Garcia, C.F.; Wiratunga, N.; Aceves-Martins, M.; Lai, N.M.; Chaiyakunapruk, N. Using artificial intelligence methods for systematic review in health sciences: A systematic review. Res. Synth. Methods 2022, 13, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno-Garcia, C.F.; Jayne, C.; Elyan, E.; Aceves-Martins, M. A novel application of machine learning and zero-shot classification methods for automated abstract screening in systematic reviews. Decis. Anal. J. 2023, 6, 100162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ofori-Boateng, R.; Aceves-Martins, M.; Wiratunga, N.; Moreno-Garcia, C.F. Towards automation of systematic reviews using natural language processing, machine learning, and deep learning: A comprehensive review. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2024, 57, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aceves-Martins, M.; Lofstedt, A.; De Roos, B. How is the environmental impact of human diets being measured in scientific research? Protocol for a systematic review aided by artificial intelligence. OSFRegistries 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amico, S.; Bodin, P.; Delpech, M.; Noteborn, R. Prisma. In Distributed Space Missions for Earth System Monitoring; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 599–637. [Google Scholar]
- Van De Schoot, R.; De Bruin, J.; Schram, R.; Zahedi, P.; De Boer, J.; Weijdema, F.; Kramer, B.; Huijts, M.; Hoogerwerf, M.; Ferdinands, G.; et al. An open source machine learning framework for efficient and transparent systematic reviews. Nat. Mach. Intell. 2021, 3, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. Product Environmental Footprint Category Rules Guidance; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2018.
- Mackie, C.; Wemhoff, A.P. Comparing greenhouse gas emissions associated with food away from home versus food at home in the United States. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 260, 120930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxe, H. The New Nordic Diet is an effective tool in environmental protection: It reduces the associated socioeconomic cost of diets. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 99, 1117–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saxe, H.; Jensen, J.D.; Laugesen, S.M.B.; Bredie, W.L.P. Environmental impact of meal service catering for dependent senior citizens in Danish municipalities. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2019, 24, 654–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, R.; Gunasekaran, A.; Childe, S.J.; Papadopoulos, T.; Luo, Z.; Wamba, S.F.; Roubaud, D. Can big data and predictive analytics improve social and environmental sustainability? Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2019, 144, 534–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schau, E.M.; Fet, A.M. LCA studies of food products as background for environmental product declarations. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2008, 13, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clune, S.; Crossin, E.; Verghese, K. Systematic review of greenhouse gas emissions for different fresh food categories. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 140, 766–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rancilio, G.; Gibin, D.; Blaco, A.; Casagrandi, R. Low-GHG culturally acceptable diets to reduce individual carbon footprint by 20%. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 338, 130623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rippin, H.L.; Cade, J.E.; Berrang-Ford, L.; Benton, T.G.; Hancock, N.; Greenwood, D.C. Variations in greenhouse gas emissions of individual diets: Associations between the greenhouse gas emissions and nutrient intake in the United Kingdom. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0259418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, A.R.; Costa, J.; Reis, J. Using a systematic literature review to build a framework for University-Industry linkages using open innovation. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2021, 181, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrieta, E.M.; Fischer, C.G.; Aguiar, S.; Geri, M.; Fernández, R.J.; Coquet, J.B.; Scavuzzo, C.M.; Rieznik, A.; León, A.; González, A.D.; et al. The health, environmental, and economic dimensions of future dietary transitions in Argentina. Sustain. Sci. 2022, 15, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arrieta, E.M.; Geri, M.; Coquet, J.B.; Scavuzzo, C.M.; Zapata, M.E.; González, A.D. Quality and environmental footprints of diets by socio-economic status in Argentina. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 801, 149686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrieta, E.M. and A.D. Gonzalez, Impact of current, National Dietary Guidelines and alternative diets on greenhouse gas emissions in Argentina. Food Policy 2018, 79, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugimoto, M.; Murakami, K.; Asakura, K.; Masayasu, S.; Sasaki, S. Diet-related greenhouse gas emissions and major food contributors among Japanese adults: Comparison of different calculation methods. Public Health Nutr. 2021, 24, 973–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandjean, A.C. Dietary intake data collection: Challenges and limitations. Nutr. Rev. 2012, 70 (Suppl. 2), S101–S104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baroni, L.; Berati, M.; Candilera, M.; Tettamanti, M. Total environmental impact of three main dietary patterns in relation to the content of animal and plant food. Foods 2014, 3, 443–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankowska, A.; Jeswani, H.K.; Azapagic, A. Life cycle environmental impacts of fruits consumption in the UK. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 248, 109111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frankowska, A.; Jeswani, H.K.; Azapagic, A. Environmental impacts of vegetables consumption in the UK. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 682, 80–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aceves-Martins, M.; Denton, P.; de Roos, B. Ready meals, especially those that are animal-based and cooked in an oven, have lower nutritional quality and higher greenhouse gas emissions and are more expensive than equivalent home-cooked meals. Public Health Nutr. 2023, 26, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Laurentiis, V.; Hunt, D.V.; Lee, S.E.; Rogers, C.D. EATS: A life cycle-based decision support tool for local authorities and school caterers. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2019, 24, 1222–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, J.G.; Collins, J. Fisheries Information in Developing Countries: Support to the Implementation of the 1995 FAO Code of Conduct for Responsible Fisheries; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Climate Change Committee. Government’s Food Strategy ‘a Missed Opportunity’ for the Climate. 2022. Available online: https://www.theccc.org.uk/2022/06/13/governments-food-strategy-a-missed-opportunity-for-the-climate/ (accessed on 13 March 2024).
- Grigoriadis, V.; Nugent, A.; Brereton, P. Working towards a combined measure for describing environmental impact and nutritive value of foods: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 112, 298–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Population/problem | Studies considering human diets or human food production, retail, or consumption, in any geographical area. |
| Interest | Identification of metrics and definitions of the environmental impact of human diets. |
| Context | Climate change and the environmental impact of human diets and food consumption. |
| Scope and Time | Scientific publications published in academic journals between January 2012 and July 2022 were included to focus on the contemporary study of the environmental impact of diets. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aceves-Martins, M.; Lofstedt, A.; Godina Flores, N.L.; Ortiz Hernández, D.M.; de Roos, B. What Environmental Metrics Are Used in Scientific Research to Estimate the Impact of Human Diets? Nutrients 2024, 16, 3166. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16183166
Aceves-Martins M, Lofstedt A, Godina Flores NL, Ortiz Hernández DM, de Roos B. What Environmental Metrics Are Used in Scientific Research to Estimate the Impact of Human Diets? Nutrients. 2024; 16(18):3166. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16183166
Chicago/Turabian StyleAceves-Martins, Magaly, Anneli Lofstedt, Naara Libertad Godina Flores, Danielle Michelle Ortiz Hernández, and Baukje de Roos. 2024. "What Environmental Metrics Are Used in Scientific Research to Estimate the Impact of Human Diets?" Nutrients 16, no. 18: 3166. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16183166
APA StyleAceves-Martins, M., Lofstedt, A., Godina Flores, N. L., Ortiz Hernández, D. M., & de Roos, B. (2024). What Environmental Metrics Are Used in Scientific Research to Estimate the Impact of Human Diets? Nutrients, 16(18), 3166. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16183166






