The Impact of Ten Days of Periodic Fasting on the Modulation of the Longevity Gene in Overweight and Obese Individuals: A Quasi-Experimental Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
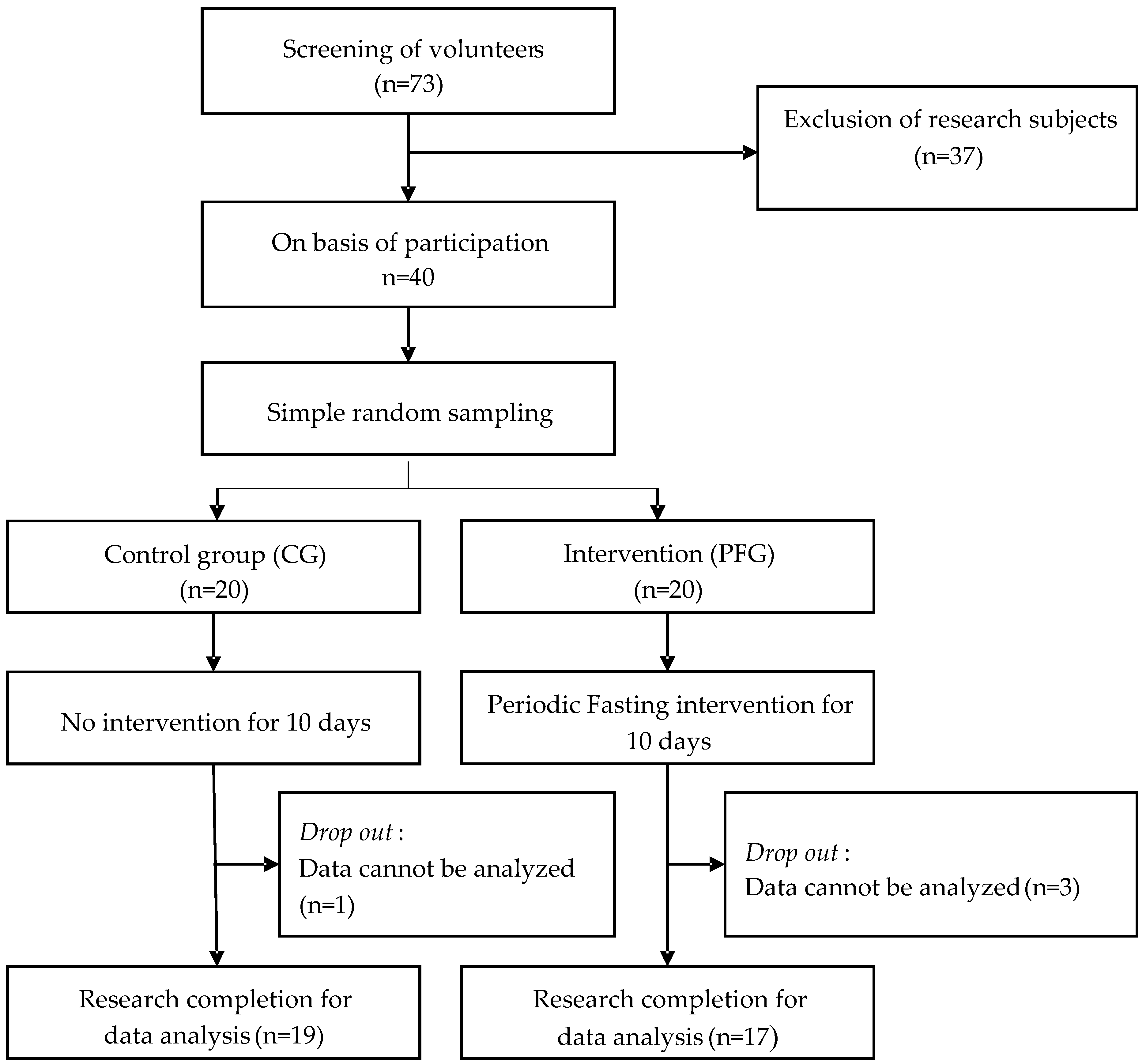
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Participants
2.3. Data Collection
2.4. Periodic Fasting Protocol
2.5. Physiological Parameter Measurements
2.5.1. Vital Sign Parameter Measurements
2.5.2. Anthropometric and Body Composition Parameter Measurements
2.5.3. Glucose and Lipids Profile Measurements
2.6. Blood Sample Collection and Storage
2.7. Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cell (PMBC) Extraction
2.8. RNA and DNA Extraction
2.9. FOXO and hTERT Expression Analysis
- ΔΔCT = ΔCT(test) − ΔCT(calibrator)
- ΔCT(test) = CT(target, test) − CT(reference, test)
- ΔCT(calibrator) = CT(target, calibrator) − CT(reference, calibrator)
- Targets = FOXO3, hTERT
- TEST = CG and PFG
- Calibrator = control group
- Reference = GADPH
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Physiological Characteristics of Participants
3.1.1. Age and Physical Activity of Participants
3.1.2. Effects of PF on Vital Signs, and Anthropometric and Body Composition of Participants
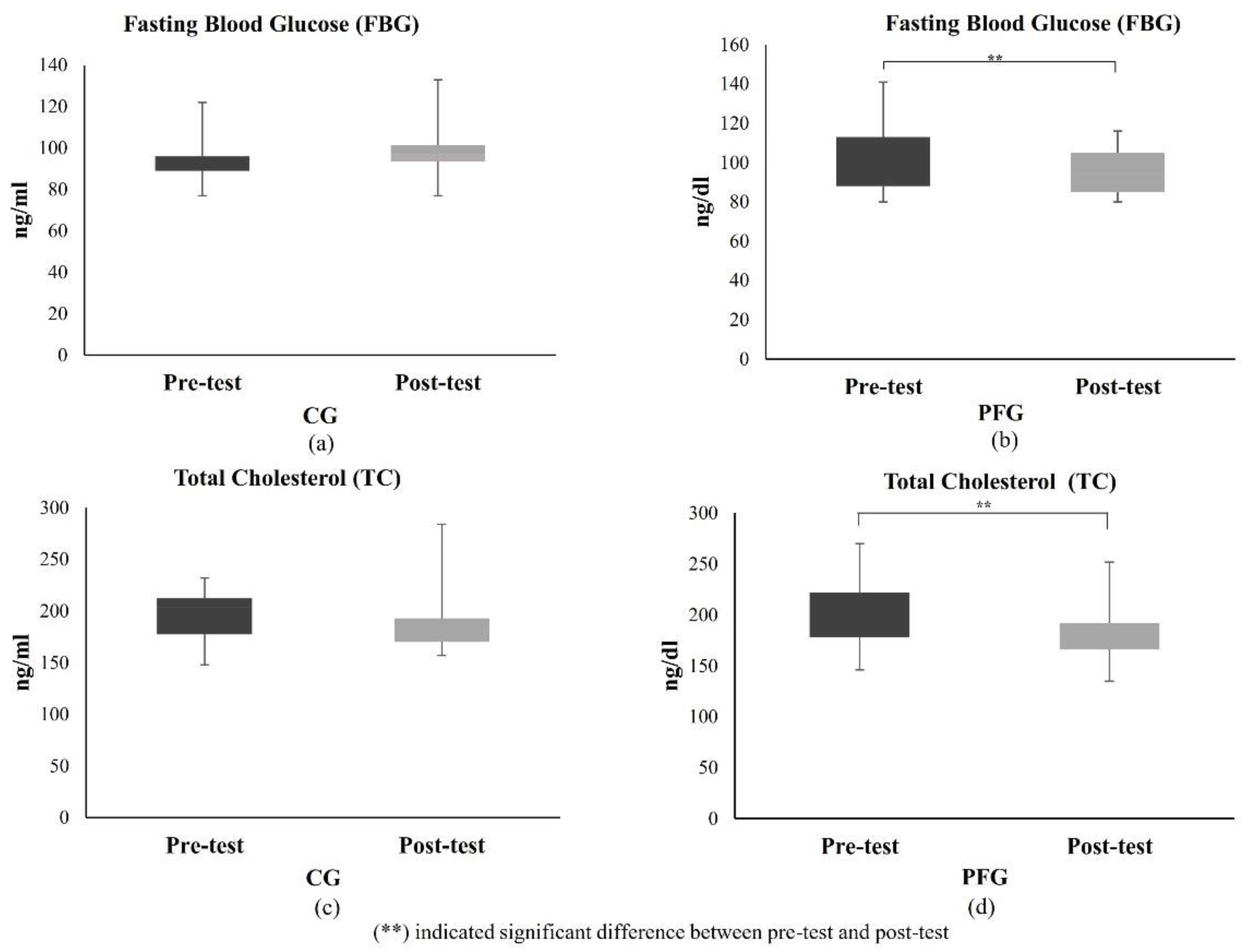
3.1.3. Effects of PF on Glucose and Lipid Profiles of Participants
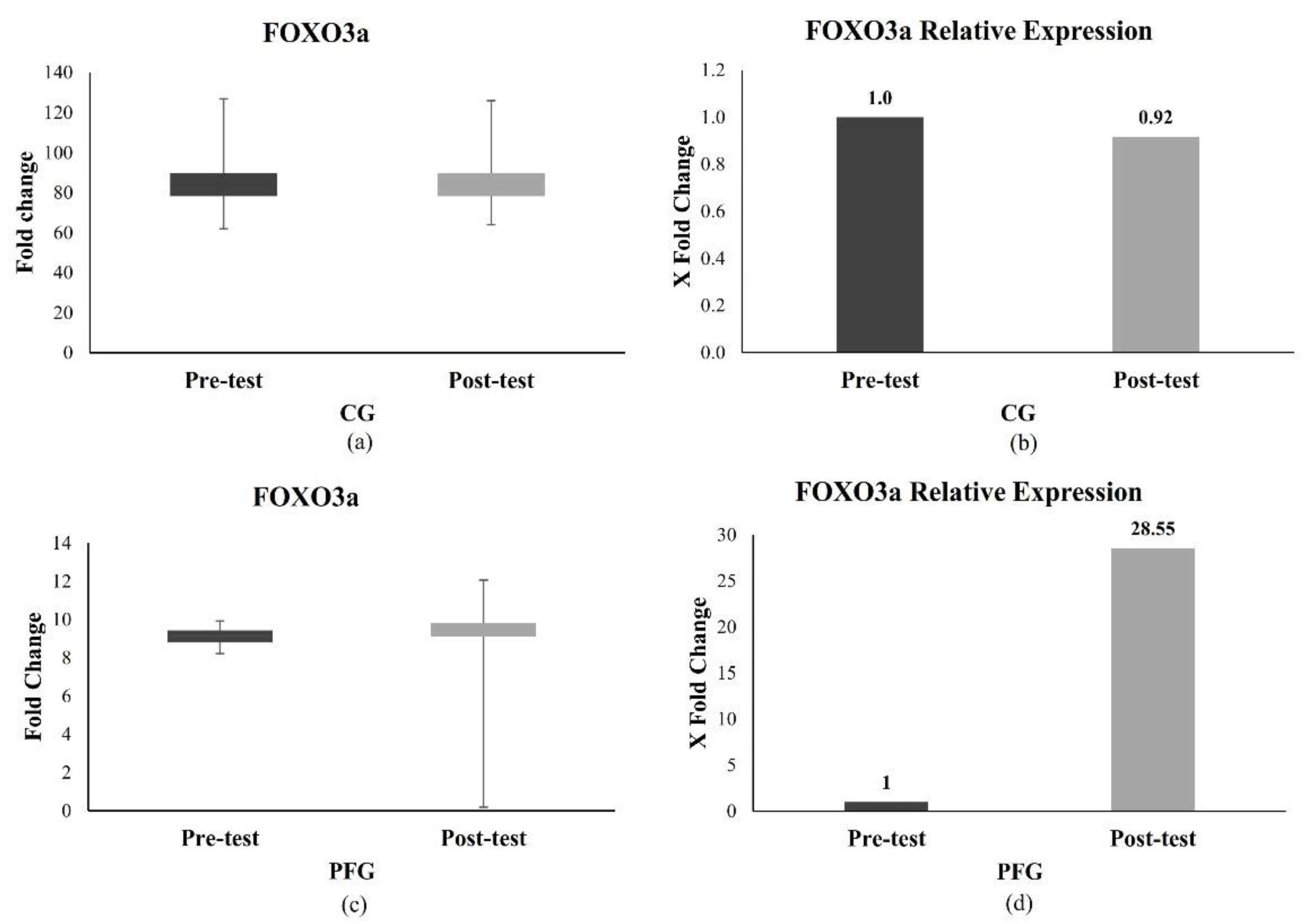
3.2. Effects of PF on the Longevity Gene Expression in the CG and PFG
3.2.1. Effect of PF on FOXO3a Expression
3.2.2. Effect of PF on hTERT Expression
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rebelo-Marques, A.; De Sousa Lages, A.; Andrade, R.; Ribeiro, C.F.; Mota-Pinto, A.; Carrilho, F.; Espregueira-Mendes, J. Aging hallmarks: The benefits of physical exercise. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Pitcher, L.E.; Yousefzadeh, M.J.; Niedernhofer, L.J.; Robbins, P.D.; Zhu, Y. Cellular senescence: A key therapeutic target in aging and diseases. J. Clin. Investig. 2022, 132, e158450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, W.; Muhammad, T.; Muneera, K. Prevalence of early and late onset of chronic diseases and multimorbidity and its association with physical, mental and functional health among older Indian adults. BMC Geriatr. 2023, 23, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, K.B. Chronic Conditions Among Adults Aged 18–34 Years—United States, 2019. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2022, 71, 964–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Obesity and Overweight. 2021, p. 1. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight (accessed on 20 June 2024).
- Jin, X.; Qiu, T.; Li, L.; Yu, R.; Chen, X.; Li, C.; Proud, C.G.; Jiang, T. Pathophysiology of obesity and its associated diseases. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2023, 13, 2403–2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hruby, A.; Hu, F.B. The Epidemiology of Obesity: A Big Picture. Pharmacoeconomics 2015, 33, 673–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvestrini, V.; Sell, C.; Lorenzini, A. Obesity may accelerate the aging process. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, S.G.; Misra, S.; Karmakar, P. Understanding the Impact of Obesity on Ageing in the Radiance of DNA Metabolism. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2023, 27, 314–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaiserman, A.; Krasnienkov, D. Telomere Length as a Marker of Biological Age: State-of-the-Art, Open Issues, and Future Perspectives. Front. Genet. 2021, 11, 630186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bär, C.; Blasco, M.A. Telomeres and telomerase as therapeutic targets to prevent and treat age-related diseases. F1000Research 2016, 5, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welendorf, C.; Nicoletti, C.F.; de Souza Pinhel, M.A.; Noronha, N.Y.; de Paula, B.M.F.; Nonino, C.B. Obesity, weight loss, and its influence on telomere length: New insights for personalized nutrition. Nutrition 2019, 66, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yik, M.Y.; Azlan, A.; Rajasegaran, Y.; Rosli, A.; Yusoff, N.M.; Moses, E.J. Mechanism of Human Telomerase Reverse Transcriptase (hTERT) Regulation and Clinical Impacts in Leukemia. Genes 2021, 12, 1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murtaza, G.; Khan, A.K.; Rashid, R.; Muneer, S.; Hasan, S.M.F.; Chen, J. FOXO Transcriptional Factors and Long-Term Living. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 3494289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tia, N.; Singh, A.K.; Pandey, P.; Azad, C.S.; Chaudhary, P. Role of Forkhead Box O (FOXO) transcription factor in aging and diseases. Gene 2018, 648, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, S.; Ogawa, K.; Ikei, T.; Fujiki, T.; Katakura, Y. FOXO3a potentiates hTERT gene expression by activating c-MYC and extends the replicative life-span of human fibroblast. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolb, H.; Kempf, K.; Röhling, M.; Lenzen-Schulte, M.; Schloot, N.C.; Martin, S. Ketone bodies: From enemy to friend and guardian angel. BMC Med. 2021, 19, 313–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pignatti, C.; D’adamo, S.; Stefanelli, C.; Flamigni, F.; Cetrullo, S. Nutrients and pathways that regulate health span and life span. Geriatrics 2020, 5, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anton, S.D.; Moehl, K.; Donahoo, W.T.; Marosi, K.; Lee, S.A.; Mainous, A.G., 3rd; Leeuwenburgh, C.; Mattson, M.P. Flipping the Metabolic Switch: Understanding and Applying the Health Benefits of Fasting. Obesity 2017, 26, 254–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattson, M.P.; Longo, V.D.; Harvie, M. Impact of Intermittent Fasting. Ageing Res. Rev. 2017, 39, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Toledo, F.W.; Grundler, F.; Bergouignan, A.; Drinda, S.; Michalsen, A. Safety, health improvement and well-being during a 4 to 21-day fasting period in an observational study including 1422 subjects. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0209353. [Google Scholar]
- Persynaki, A.; Karras, S.; Pichard, C. Unraveling the metabolic health benefits of fasting related to religious beliefs: A narrative review. Nutrition 2017, 35, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Toledo, F.W.; Grundler, F.; Goutzourelas, N.; Tekos, F.; Vassi, E.; Mesnage, R.; Kouretas, D. Influence of Long-Term Fasting on Blood Redox Status in Humans. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Otín, C.; Blasco, M.A.; Partridge, L.; Serrano, M.; Kroemer, G. The hallmarks of aging. Cell 2013, 153, 1194–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuliyanasari, N.; Rejeki, P.S.; Hidayati, H.B.; Subsomwong, P.; Miftahussurur, M. The effect of intermittent fasting on preventing obesity-related early aging from a molecular and cellular perspective. J. Med. Life 2024, 17, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wegman, M.P.; Guo, M.H.; Bennion, D.M.; Shankar, M.N.; Chrzanowski, S.M.; Goldberg, L.A.; Xu, J.; Williams, T.A.; Lu, X.; Hsu, S.I.; et al. Practicality of Intermittent Fasting in Humans and its Effect on Oxidative Stress and Genes Related to Aging and Metabolism. Rejuvenation Res. 2015, 18, 162–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamshed, H.; Beyl, R.A.; Della Manna, D.L.; Yang, E.S.; Ravussin, E.; Peterson, C.M. Early Time-Restricted Feeding Improves 24-Hour. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stekovic, S.; Hofer, S.J.; Tripolt, N.; Aon, M.A.; Royer, P.; Pein, L.; Stadler, J.T.; Pendl, T.; Prietl, B.; Url, J.; et al. Alternate Day Fasting Improves Physiological and Molecular Markers of Aging in Healthy, Non-obese Humans. Cell Metab. 2019, 30, 462–476.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO Western Pacific Region. The Asia-Pacific Perspective: Redefining Obesity and Its Treatment; Health Communication: Sydney, Australia, 2000; 55p. [Google Scholar]
- Rudolf, K.; Lammer, F.; Stassen, G.; Froböse, I.; Schaller, A. Show cards of the Global Physical Activity Questionnaire (GPAQ)—Do they impact validity? A crossover study. BMC Public Health 2020, 20, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mindikoglu, A.L.; Abdulsada, M.M.; Jain, A.; Choi, J.M.; Jalal, P.K.; Devaraj, S.; Mezzari, M.P.; Petrosino, J.F.; Opekun, A.R.; Jung, S.Y. Intermittent fasting from dawn to sunset for 30 consecutive days is associated with anticancer proteomic signature and upregulates key regulatory proteins of glucose and lipid metabolism, circadian clock, DNA repair, cytoskeleton remodeling, immune system. J. Proteom. 2020, 217, 103645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubrzycki, A.; Cierpka-Kmiec, K.; Kmiec, Z.; Wronska, A. The role of low-calorie diets and intermittent fasting in the treatment of obesity and type-2 diabetes. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2018, 69, 663–683. [Google Scholar]
- Duraimani, S.; Schneider, R.H.; Randall, O.S.; Nidich, S.I.; Xu, S.; Ketete, M.; Rainforth, M.A.; Gaylord-King, C.; Salerno, J.W.; Fagan, J. Effects of lifestyle modification on telomerase gene expression in hypertensive patients: A pilot trial of stress reduction and health education programs in African Americans. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0142689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.-Z.; Zhang, J.-J.; Gao, C.-C.; Zhao, M.; Liu, S.-Y.; Gao, G.-M.; Zheng, Z.-H. Expression of autophagy related genes mTOR, Becline-1, LC3 and p62 in the peripheral blood mononuclear cells of systemic lupus erythematosus. Am. J. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2017, 6, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardiany, N.S.; Remifta Putra, M.A.; Penantian, R.M.; Antarianto, R.D. Effects of fasting on FOXO3 expression as an anti-aging biomarker in the liver. Heliyon 2023, 9, e13144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arciero, P.J.; Arciero, K.M.; Poe, M.; Mohr, A.E.; Ives, S.J.; Arciero, A.; Boyce, M.; Zhang, J.; Haas, M.; Valdez, E.; et al. Intermittent fasting two days versus one day per week, matched for total energy intake and expenditure, increases weight loss in overweight/obese men and women. Nutr. J. 2022, 21, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dote-Montero, M.; Sanchez-Delgado, G.; Ravussin, E. Effects of Intermittent Fasting on Cardiometabolic Health: An Energy Metabolism Perspective. Nutrients 2022, 14, 489–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, K.; Chan, V.; Chan, S.; Wong, M.M.H.; Chung, G.K.K.; Cheng, W.Y.; Lo, K.; Zeng, F. Effect of Intermittent Fasting on Cardiometabolic Health in the Chinese Population: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Nutrients 2024, 16, 357–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A.K.; Webb, A.E. Regulation of FOXO Factors in Mammalian Cells. Curr. Top. Dev. Biol. 2018, 127, 165–192. [Google Scholar]
- Du, S.; Zheng, H. Role of FoxO transcription factors in aging and age-related metabolic and neurodegenerative diseases. Cell Biosci. 2021, 11, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davy, P.M.C.; Willcox, D.C.; Shimabukuro, M.; A Donlon, T.; Torigoe, T.; Suzuki, M.; Higa, M.; Masuzaki, H.; Sata, M.; Chen, R.; et al. Minimal shortening of leukocyte telomere length across age groups in a cross-sectional study for carriers of a longevity-associated FOXO3 allele. J. Gerontol. Ser. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2018, 73, 1448–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torigoe, T.H.; Willcox, D.C.; Shimabukuro, M.; Higa, M.; Gerschenson, M.; Andrukhiv, A.; Suzuki, M.; Morris, B.J.; Chen, R.; Gojanovich, G.S.; et al. Novel protective effect of the FOXO3 longevity genotype on mechanisms of cellular aging in Okinawans. Npj Aging 2024, 10, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mustofa, M.S.; Suyatna, F.D.; Sadikin, M.; Pujianto, D.A.; Royhan, A.; Suwardji, K. Soybean extract increases telomerase reverse transcriptase protein expression in pancreatic β-cells of diabetes mellitus-induced rats. Med. J. Indones. 2019, 28, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.; Devkota, S.; Roh, J.I.; Lee, J.; Lee, H.W. Telomerase reverse transcriptase induces basal and amino acid starvation-induced autophagy through mTORC1. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 478, 1198–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weichhart, T. mTOR as Regulator of Lifespan, Aging, and Cellular Senescence: A Mini-Review. Gerontology 2018, 64, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tulsian, R.; Velingkaar, N.; Kondratov, R. Caloric restriction effects on liver mTOR signaling are time-of-day dependent. Aging 2018, 10, 1640–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wardi, L.; Alaaeddine, N.; Raad, I.; Sarkis, R.; Serhal, R.; Khalil, C.; Hilal, G. Glucose restriction decreases telomerase activity and enhances its inhibitor response on breast cancer cells: Possible extra-telomerase role of BIBR 1532. Cancer Cell Int. 2014, 14, 60–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leão, R.; Apolónio, J.D.; Lee, D.; Figueiredo, A.; Tabori, U.; Castelo-Branco, P. Mechanisms of human telomerase reverse transcriptase (hTERT) regulation: Clinical impacts in cancer. J. Biomed. Sci. 2018, 25, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colebatch, A.J.; Dobrovic, A.; Cooper, W.A. TERT gene: Its function and dysregulation in cancer. J. Clin. Pathol. 2019, 72, 281–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fragkiadaki, P.; Renieri, E.; Kalliantasi, K.; Kouvidi, E.; Apalaki, E.; Vakonaki, E.; Mamoulakis, C.; Spandidos, D.A.; Tsatsakis, A. Τelomerase inhibitors and activators in aging and cancer: A systematic review. Mol. Med. Rep. 2022, 25, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razgonova, M.P.; Zakharenko, A.M.; Golokhvast, K.S.; Thanasoula, M.; Sarandi, E.; Nikolouzakis, K.; Fragkiadaki, P.; Tsoukalas, D.; Spandidos, D.A.; Tsatsakis, A. Telomerase and telomeres in aging theory and chronographic aging theory (Review). Mol. Med. Rep. 2020, 22, 1679–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmati-Yamchi, M.; Zarghami, N.; Rahbani, M.; Montazeri, A. Plasma leptin, hTERT gene expression, and anthropometric measures in obese and non-obese women with breast cancer. Breast Cancer Basic Clin. Res. 2011, 5, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gadde, K.M.; Martin, C.K.; Berthoud, H.R.; Heymsfield, S.B. Obesity: Pathophysiology and Management. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 71, 69–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Parameters | CG (n = 19) | PFG (n = 17) | p-Value of the Difference Parameters between Groups (Δ) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-Test | Post-Test | p-Value | Pre-Test | Post-Test | p-Value | ||
| SBP (mmHG) | 125.26 (±10.07) | 123.05 (±10.37) | † 0.32 | 121.06 (±9.03) | 117.06 (±9.30) | ‡ 0.02 * | ⸼ 0.51 |
| DBP (mmHG) | 86.32 (±10.65) | 84.74 (±8.41) | ‡ 0.38 | 85.88 (±7.95) | 82.35 (±9.70) | † 0.19 | ⸼ 0.40 |
| HR (x/minute) | 83.95 (±12.40) | 86.37 (±14.51) | † 0.46 | 87.59 (±8.59) | 87.06 (±13.04) | † 0.88 | ⸸ 0.54 |
| RR (x/minute) | 18.84 (±1.54) | 18.84 (±1.80) | ‡ 1.00 | 18.12 (±2.29) | 18.47 (±2.29) | † 0.53 | ⸸ 0.80 |
| BW (kg) | 85.42 (±14.82) | 85.81 (±14.67) | † 0.18 | 82.85 (±10.22) | 80.44 (±10.77) | † 0.00 * | ⸸ 0.00 * |
| BH (m) | 170.05 (±6.62) | - | - | 169.59 (±6.60) | - | - | - |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 29.57 (±5.17) | 29.85 (±4.94) | ‡ 0.17 | 28.69 (±2.19) | 27.88 (±2.42) | † 0.00 * | ⸼ 0.00 * |
| HC (cm) | 98.37 (±10.10) | 98.55 (±10.11) | ‡ 0.55 | 99.21 (±10.25) | 93.91 (±9.77) | † 0.76 | ⸼ 0.26 |
| AC (cm) | 96.87 (±11.36) | 96.92 (±11.57) | ‡ 0.97 | 94.62 (±7.62) | 92.76 (±7.58) | † 0.00 * | ⸼ 0.02 * |
| WC (cm) | 90.53 (±9.01) | 90.45 (±9.52) | † 0.88 | 88.15 (±6.89) | 86.18 (±6.22) | † 0.00 * | ⸸ 0.02 * |
| UAC (cm) | 33.42 (±3.89) | 32.87 (±3.62) | ‡ 0.13 | 32.56 (±2.38) | 32.56 (±2.37) | ‡ 8.86 | ⸼ 0.38 |
| BF (%) | 25.64 (±5.47) | 25.87 (±5.36) | † 0.42 | 26.57 (±3.34) | 26.03 (±3.42) | ‡ 0.16 | ⸼ 0.09 |
| TBW (%) | 49.68 (±4.60) | 49.40 (±4.40) | † 0.46 | 47.80 (±3.52) | 47.48 (±3.44) | † 0.43 | ⸸ 0.99 |
| MM (kg) | 57.88 (±6.80) | 58.54 (±6.02) | ‡ 0.81 | 56.57 (±6.58) | 55.65 (±6.65) | † 0.00 * | ⸼ 0.02 * |
| BM (kg) | 3.19 (±0.34) | 3.19 (±0.32) | ‡ 1.00 | 3.08 (±0.35) | 3.05 (±0.34) | ‡ 0.06 | ⸼ 0.43 |
| VFL (level) | 10.91 (±3.13) | 10.96 (±3.04) | ‡ 0.63 | 10.62 (±1.85) | 10.41 (±1.96) | ‡ 0.02 * | ⸼ 0.15 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yuliyanasari, N.; Zamri, E.N.; Rejeki, P.S.; Miftahussurur, M. The Impact of Ten Days of Periodic Fasting on the Modulation of the Longevity Gene in Overweight and Obese Individuals: A Quasi-Experimental Study. Nutrients 2024, 16, 3112. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16183112
Yuliyanasari N, Zamri EN, Rejeki PS, Miftahussurur M. The Impact of Ten Days of Periodic Fasting on the Modulation of the Longevity Gene in Overweight and Obese Individuals: A Quasi-Experimental Study. Nutrients. 2024; 16(18):3112. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16183112
Chicago/Turabian StyleYuliyanasari, Nurma, Eva Nabiha Zamri, Purwo Sri Rejeki, and Muhammad Miftahussurur. 2024. "The Impact of Ten Days of Periodic Fasting on the Modulation of the Longevity Gene in Overweight and Obese Individuals: A Quasi-Experimental Study" Nutrients 16, no. 18: 3112. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16183112
APA StyleYuliyanasari, N., Zamri, E. N., Rejeki, P. S., & Miftahussurur, M. (2024). The Impact of Ten Days of Periodic Fasting on the Modulation of the Longevity Gene in Overweight and Obese Individuals: A Quasi-Experimental Study. Nutrients, 16(18), 3112. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16183112








