Is Obesity a Problem in New Cystic Fibrosis Treatments?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Data Collection
2.2. Clinical and Demographic Variables
- -
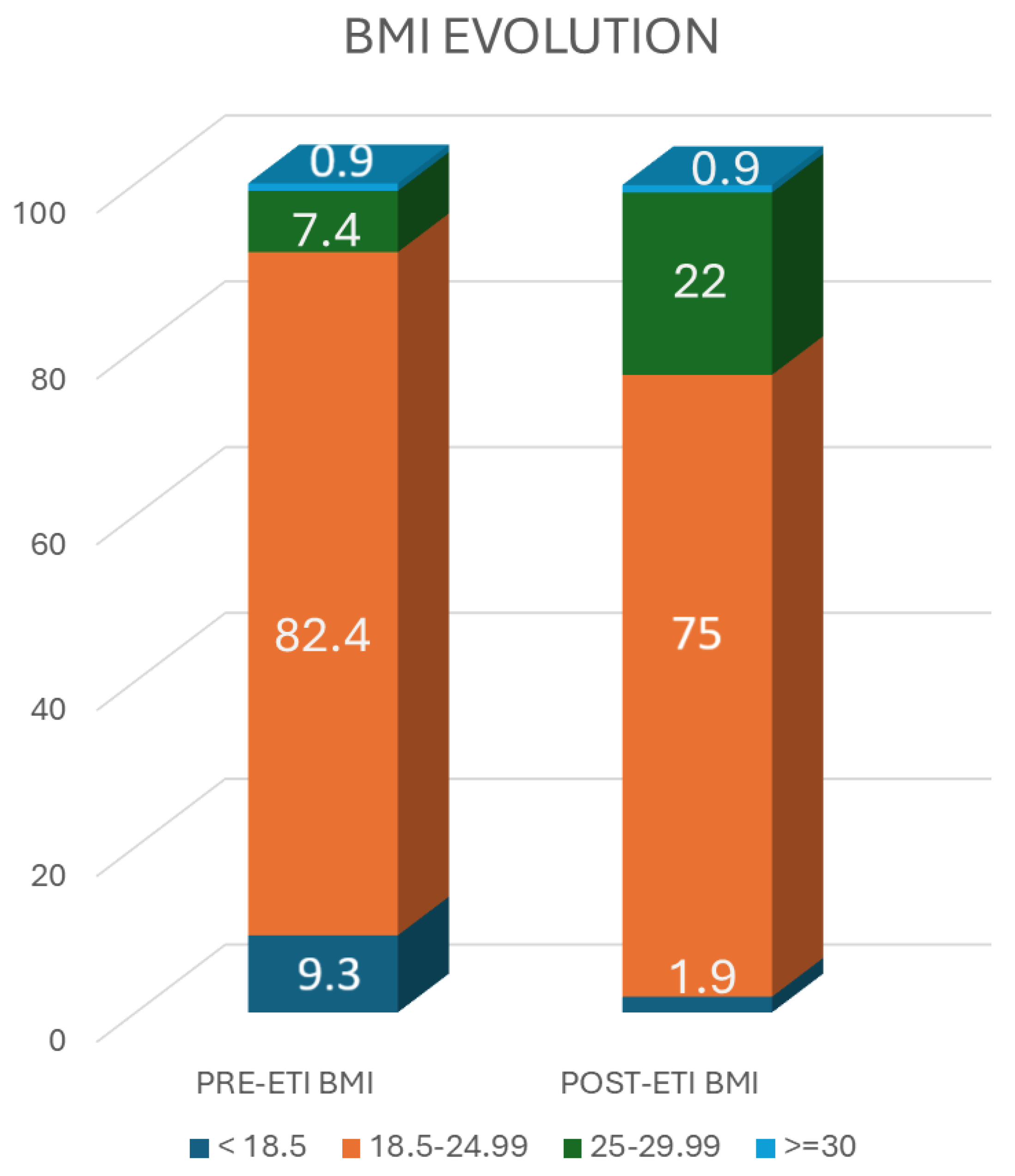
- BMI < 18.5 kg/m2 (underweight).
- -
- BMI 18.5–24.9 kg/m2 (target weight).
- -
- BMI 25–29.9 kg/m2 (overweight).
- -
- BMI > 30 kg/m2 (obese).
2.3. Statistical Study
3. Results
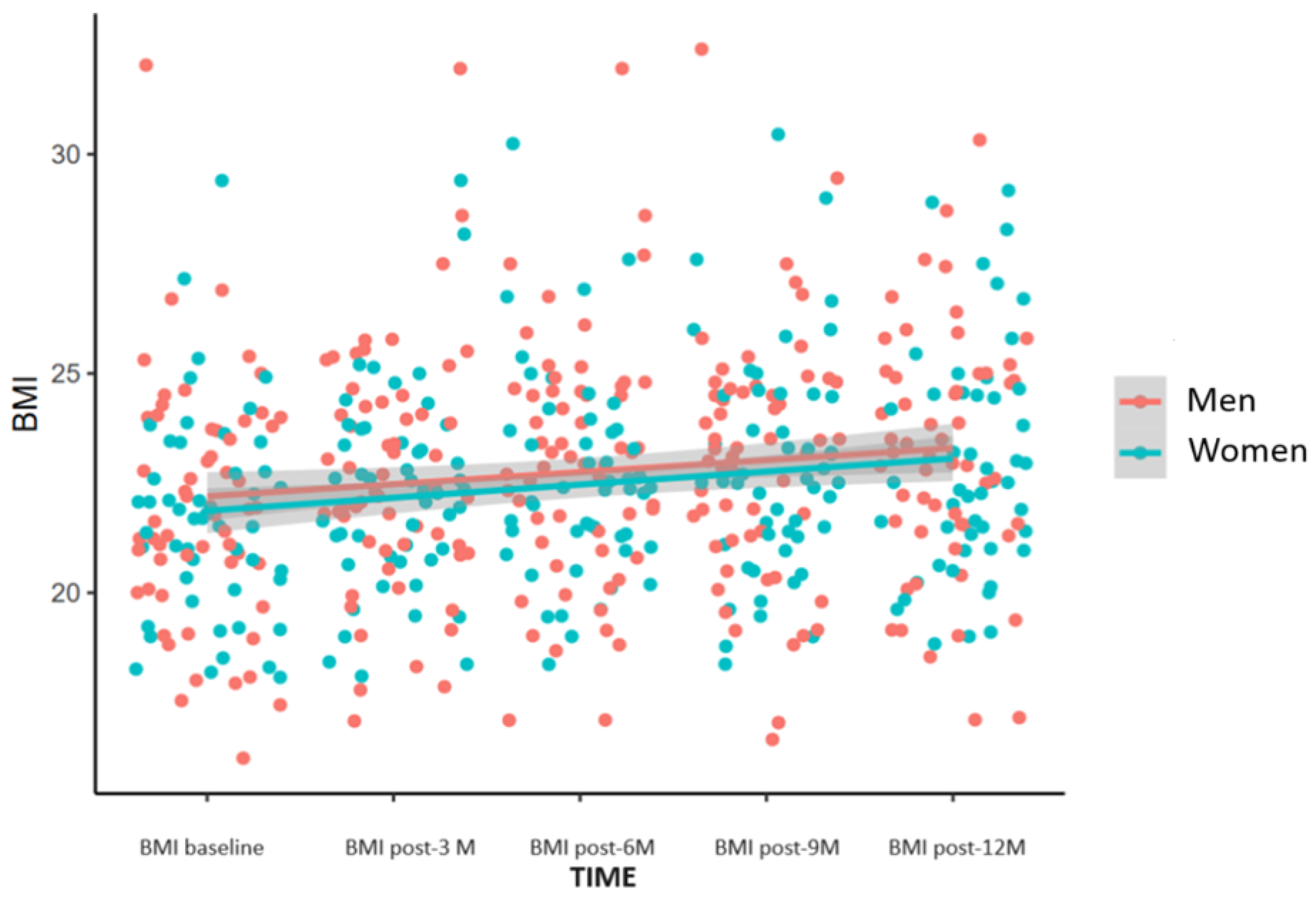
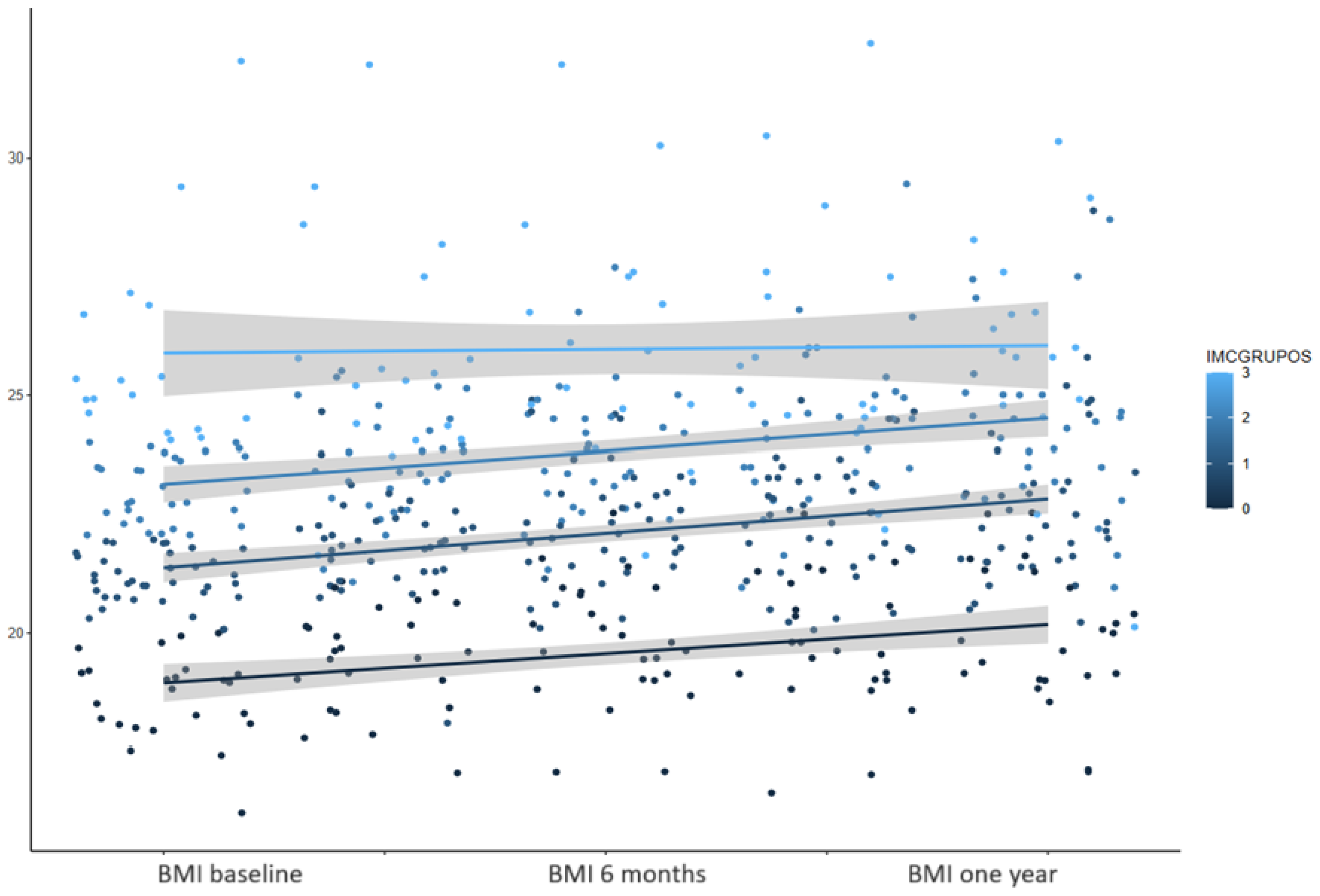
3.1. BMI
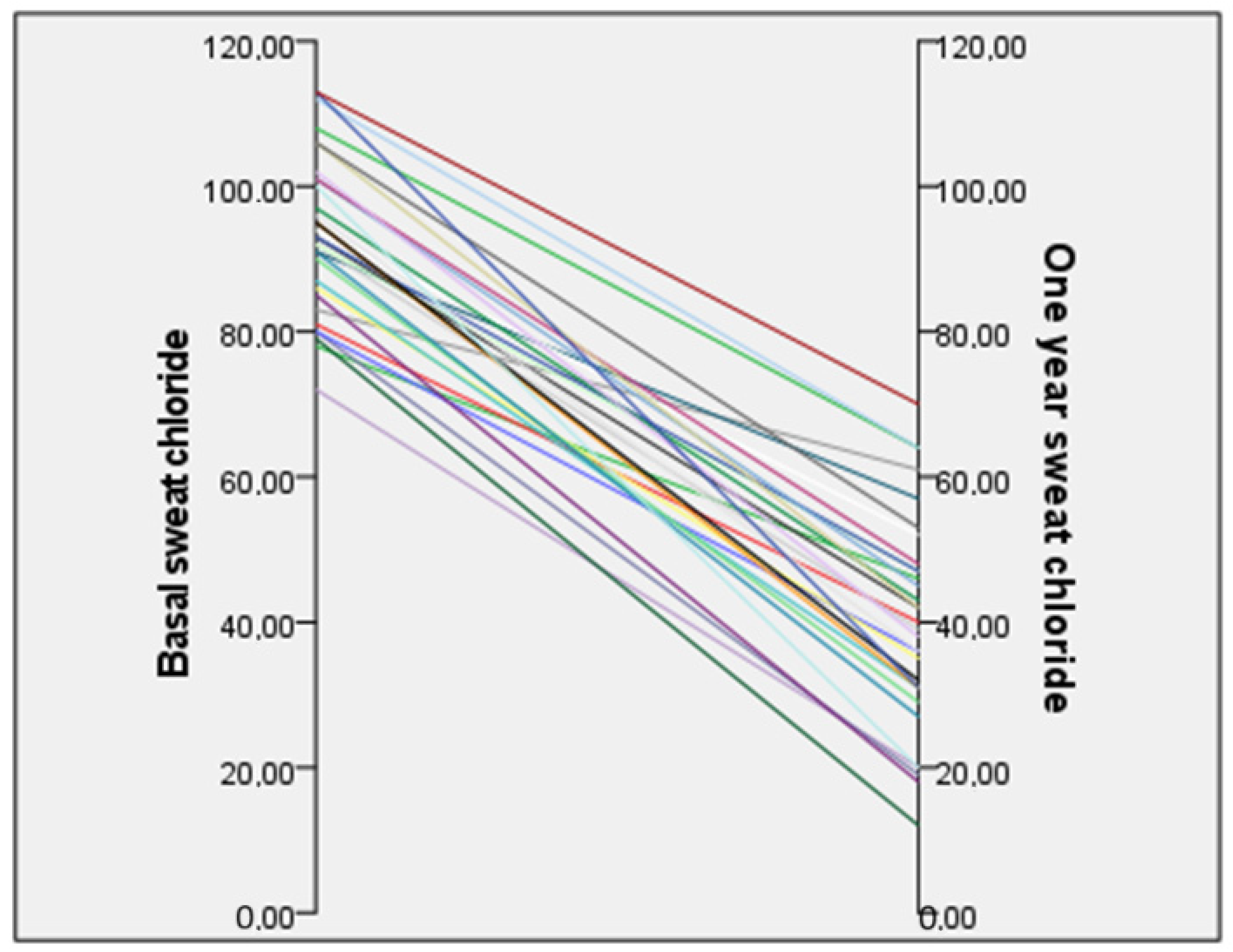
3.2. Sweat Chloride Test
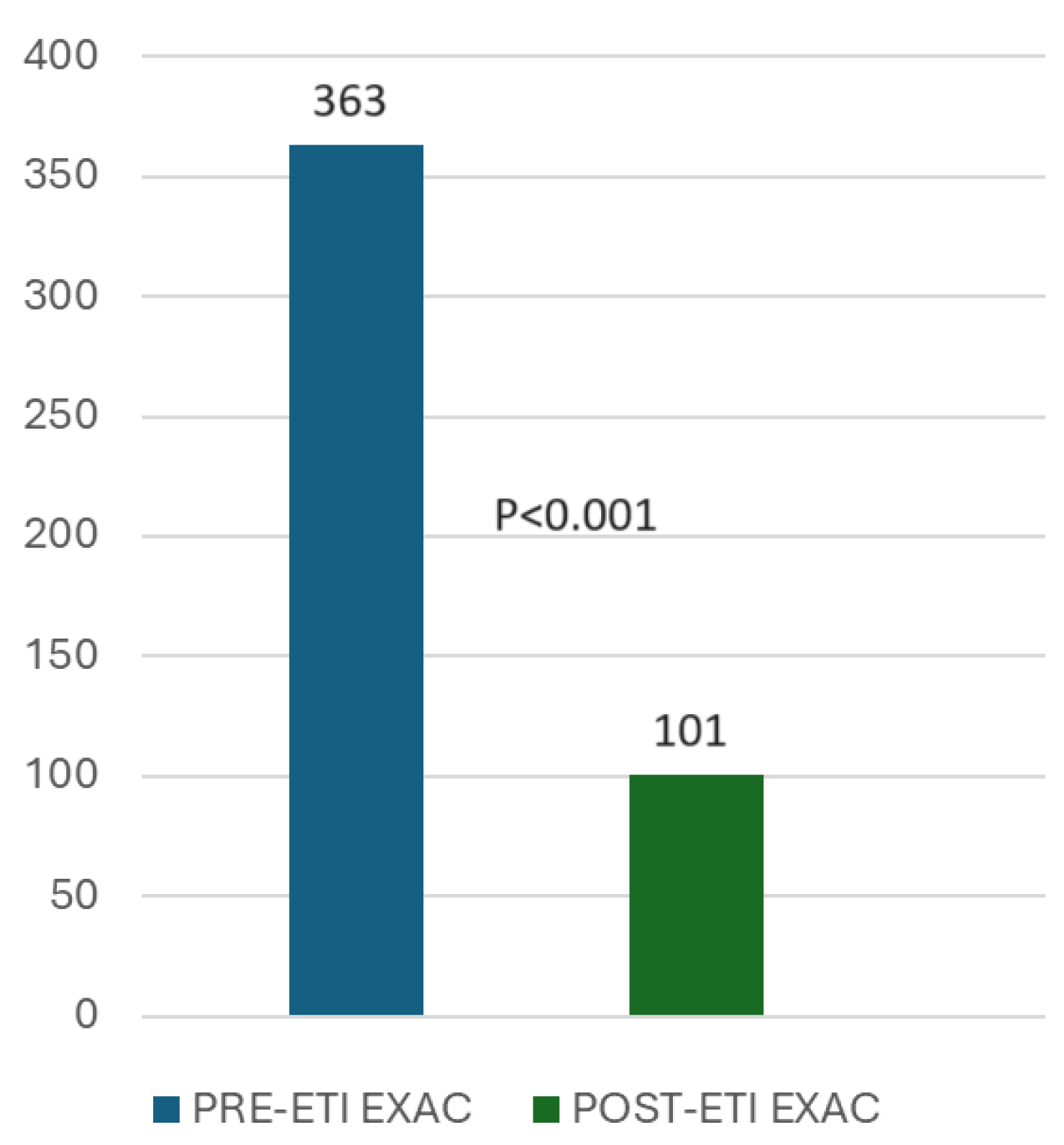
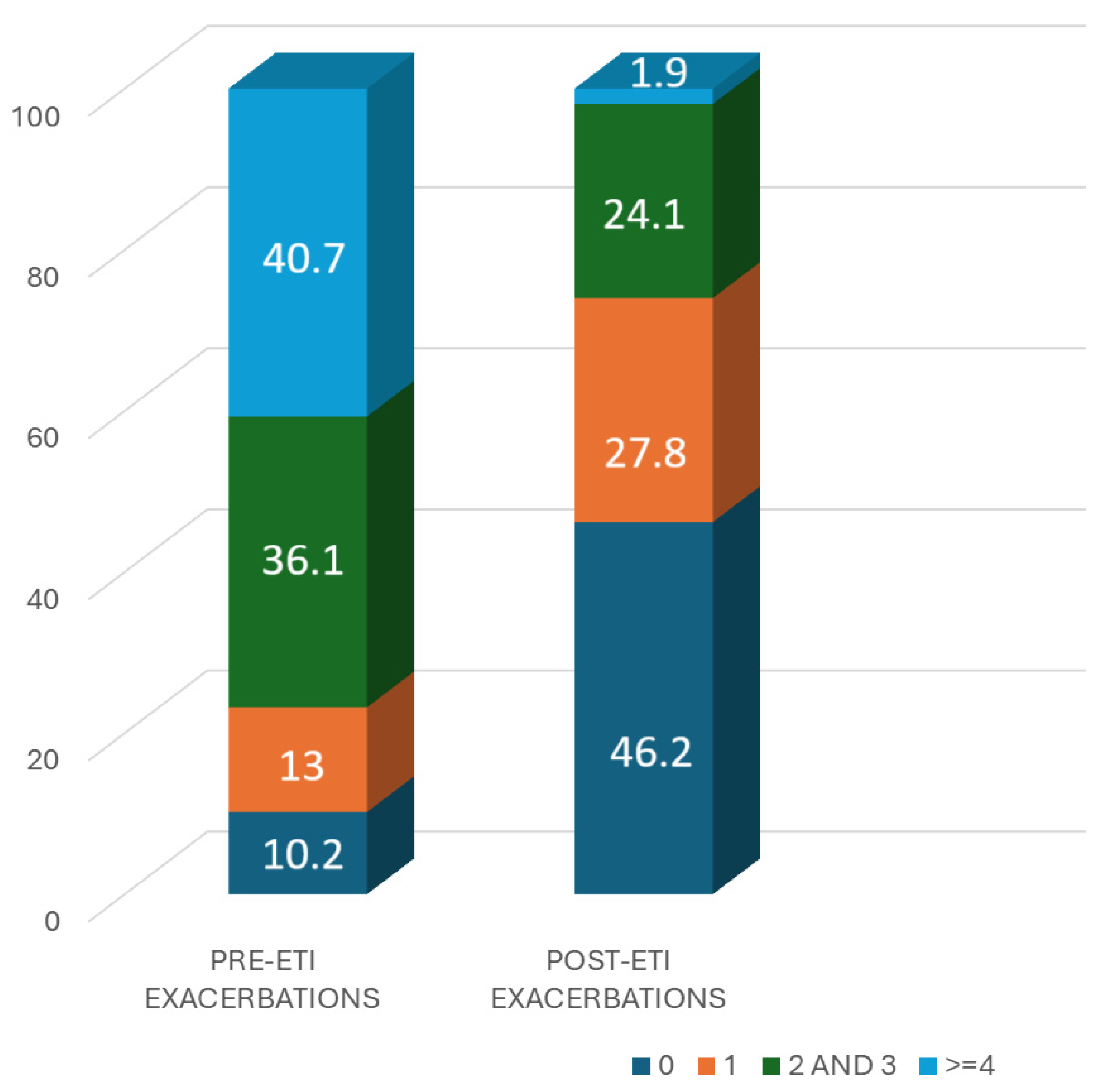
3.3. Exacerbations
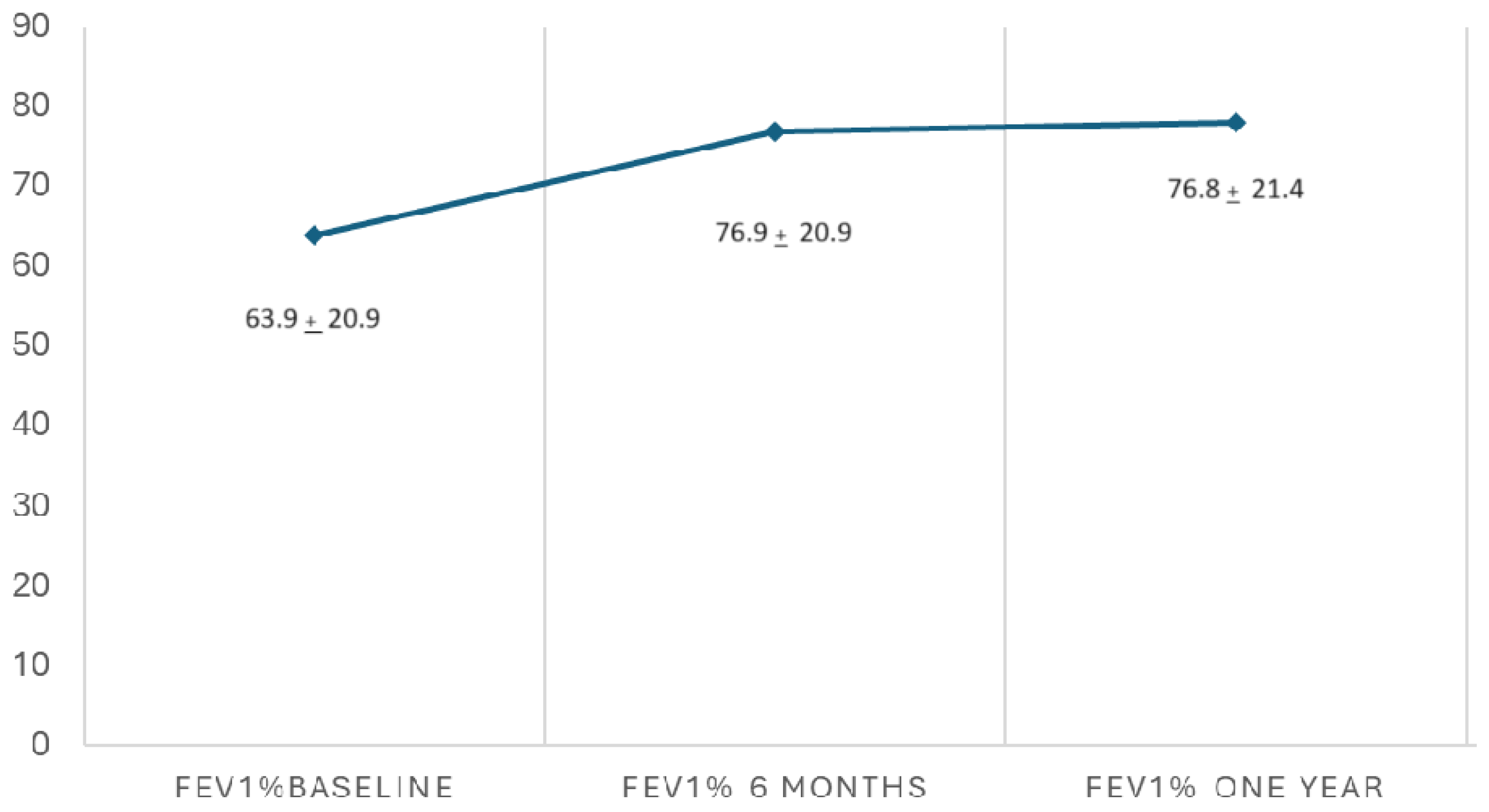
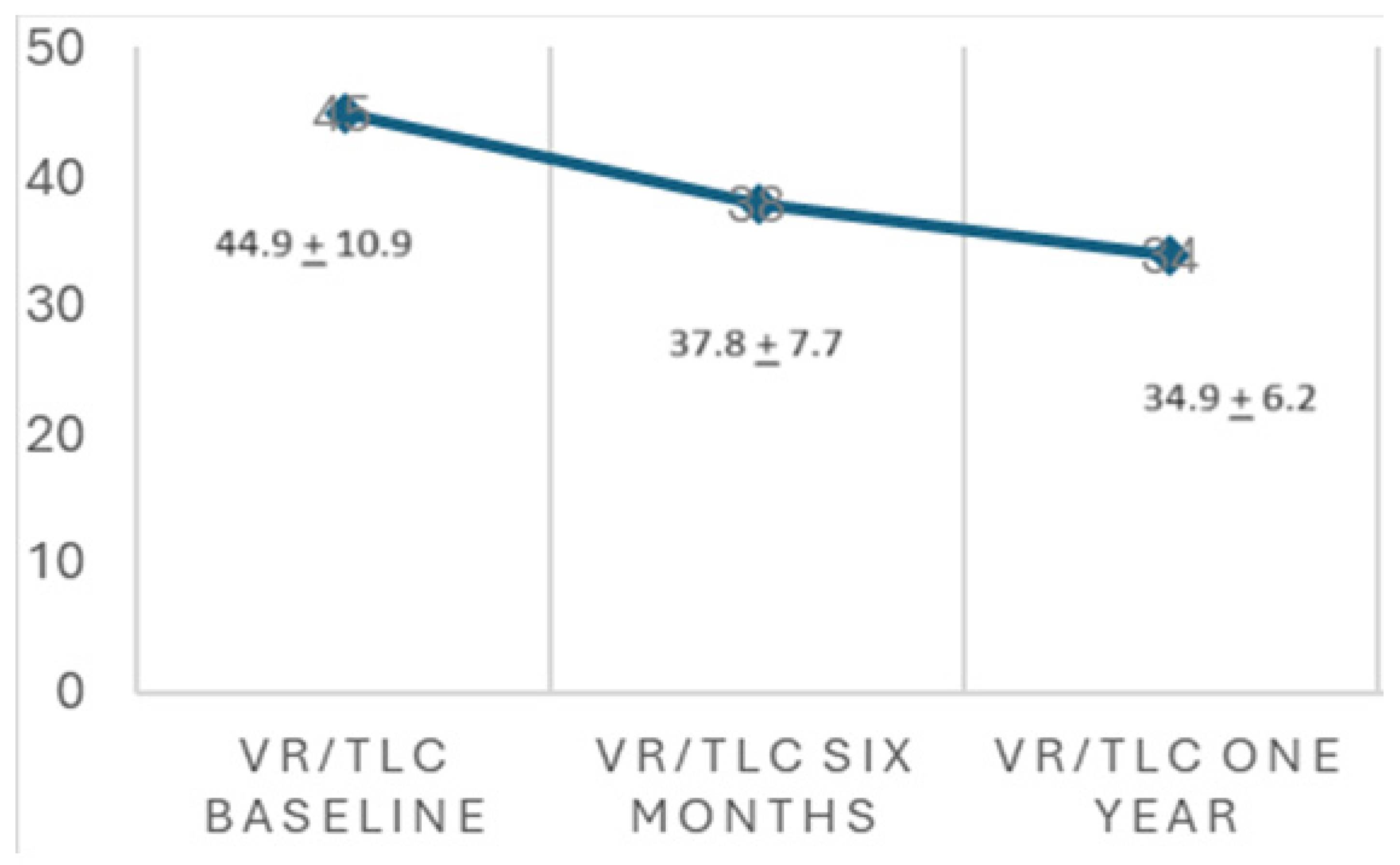
3.4. Lung Function
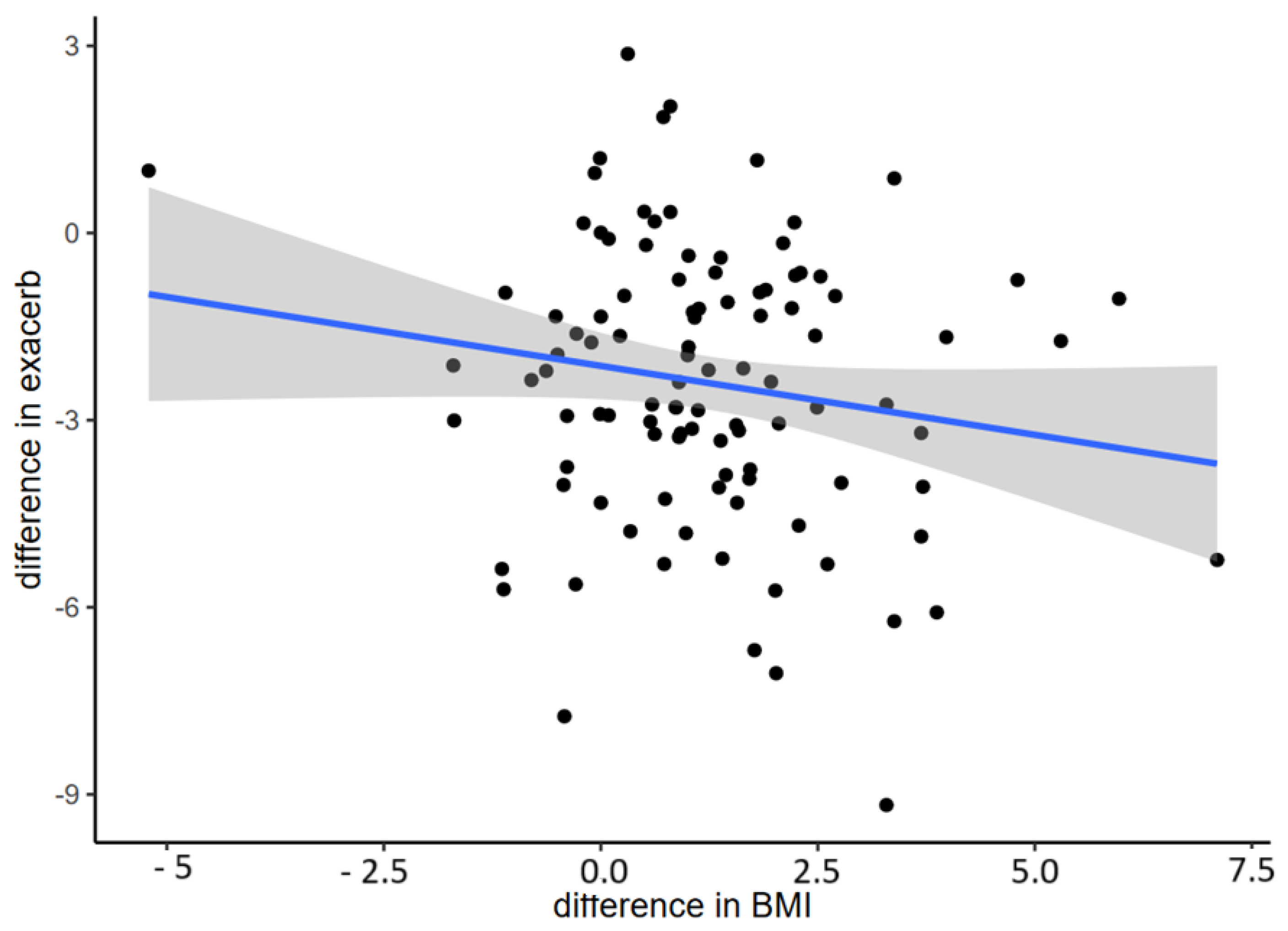
3.5. BMI Change during the Study Period
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sutharsan, S.; Dillenhoefer, S.; Welsner, M.; Stehling, F.; Brinkmann, F.; Burkhart, M.; Ellemunter, H.; Dittrich, A.M.; Smaczny, C.; Eickmeier, O.; et al. Registry of the Mukoviszidose e.V. and participating CF sites. Impact of elexacaftor/tezacaftor/ivacaftor on lung function, nutritional status, pulmonary exacerbation frequency and sweat chloride in people with cystic fibrosis: Real-world evidence from the German CF Registry. Lancet Reg. Health Eur. 2023, 32, 100690. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Garratt, A.; Hill, A. Worldwide rates of diagnosis and effective treatment for cystic fibrosis. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2022, 21, 456–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birket, S.E.; Chu, K.K.; Liu, L.; Houser, G.H.; Diephuis, B.J.; Wilsterman, E.J.; Dierksen, G.; Mazur, M.; Shastry, S.; Li, Y.; et al. A functional anatomic defect of the cystic fibrosis airway. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2014, 190, 421–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, K.L.; Szczesniak, R.; Liou, T.G. Predicting weight gain in patients with cystic fibrosis on triple combination modulator. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2024, 59, 1724–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barry, P.J.; Jones, A.M. Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator Modulators: Real-World Evidence Highlights Need for Worldwide Access. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2024, 21, 1003–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, M.C.; Begnel, L.; Wallendorf, M.; Litvin, M. Effect of elexacaftor-tezacaftor-ivacaftor on body weight and metabolic parameters in adults with cystic fibrosis. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2022, 21, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liou, T.G.; Kartsonaki, C.; Keogh, R.H.; Adler, F.R. Evaluation of a five-year predicted survival model for cystic fibrosis in later time periods. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 6602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, J.; Krick, S.; Fontaine, K.R. The Changing Landscape of Nutrition in Cystic Fibrosis: The Emergence of Overweight and Obesity. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stallings, V.A.; Stark, L.J.; Robinson, K.A.; Feranchak, A.P.; Quinton, H. Clinical Practice Guidelines on Growth and Nutrition Subcommittee; Ad Hoc Working Group. Evidence-based practice recommendations for nutrition-related management of children and adults with cystic fibrosis and pancreatic insufficiency: Results of a systematic review. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2008, 108, 832–839. [Google Scholar]
- Cystic Fibrosis Foundation. Patient Registry 2021 Annual Data Report; Cystic Fibrosis Foundation: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2022; Available online: http://www.cff.org/Our-Research/CF-Patient-Registry/ (accessed on 12 September 2024).
- Taylor-Cousar, J.L.; Munck, A.; McKone, E.F.; van der Ent, C.K.; Moeller, A.; Simard, C.; Wang, L.T.; Ingenito, E.P.; McKee, C.; Lu, Y.; et al. Tezacaftor-Ivacaftor in Patients with Cystic Fibrosis Homozygous for Phe508del. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 2013–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrasco Hernández, L.; Girón Moreno, R.M.; Balaguer Cartagena, M.N.; Peláez, A.; Sole, A.; Álvarez Fernández, A.; Felipe Montiel, A.; Olveira, C.; Olveira, G.; Gómez Bonilla, A.; et al. Experience with Elexacaftor/Tezacaftor/Ivacaftor in Patients with Cystic Fibrosis and Advanced Disease. Arch. Bronconeumol. 2023, 59, 556–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Middleton, P.G.; Mall, M.A.; Dřevínek, P.; Lands, L.C.; McKone, E.F.; Polineni, D.; Ramsey, B.W.; Taylor-Cousar, J.L.; Tullis, E.; Vermeulen, F.; et al. Elexacaftor-Tezacaftor-Ivacaftor for Cystic Fibrosis with a Single Phe508del Allele. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 1809–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carnovale, V.; Iacotucci, P.; Terlizzi, V.; Colangelo, C.; Ferrillo, L.; Pepe, A.; Francalanci, M.; Taccetti, G.; Buonaurio, S.; Celardo, A.; et al. Elexacaftor/Tezacaftor/Ivacaftor in Patients with Cystic Fibrosis Homozygous for the F508del Mutation and Advanced Lung Disease: A 48-Week Observational Study. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvatore, D.; Padoan, R.; Amato, A.; Salvatore, M.; Campagna, G.; On Behalf of The Italian Cf Registry Working Group. Nutritional Trends in Cystic Fibrosis: Insights from the Italian Cystic Fibrosis Patient Registry. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 3652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna, R.M.; Weiner, D.J. Overweight and obesity in patients with cystic fibrosis: A center-based analysis. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2015, 50, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stallings, V.A.; Sainath, N.; Oberle, M.; Bertolaso, C.; Schall, J.I. Energy Balance and Mechanisms of Weight Gain with Ivacaftor Treatment of Cystic Fibrosis Gating Mutations. J. Pediatr. 2018, 201, 229–237.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gould, M.J.; Smith, H.; Rayment, J.H.; Machida, H.; Gonska, T.; Galante, G.J. CFTR modulators increase risk of acute pancreatitis in pancreatic insufficient patients with cystic fibrosis. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2022, 21, 600–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gramegna, A.; Majo, F.; Alicandro, G.; Leonardi, G.; Cristiani, L.; Amati, F.; Contarini, M.; Aliberti, S.; Fiocchi, A.G.; Blasi, F. Heterogeneity of weight gain after initiation of Elexacaftor/Tezacaftor/Ivacaftor in people with cystic fibrosis. Respir. Res. 2023, 24, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichols, D.P.; Paynter, A.C.; Heltshe, S.L.; Donaldson, S.H.; Frederick, C.A.; Freedman, S.D.; Gelfond, D.; Hoffman, L.R.; Kelly, A.; Narkewicz, M.R.; et al. Clinical Effectiveness of Elexacaftor/Tezacaftor/Ivacaftor in People with Cystic Fibrosis: A Clinical Trial. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2022, 205, 529–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harindhanavudhi, T.; Wang, Q.; Dunitz, J.; Moran, A.; Moheet, A. Prevalence and factors associated with overweight and obesity in adults with cystic fibrosis: A single-center analysis. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2020, 19, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephenson, A.L.; Mannik, L.A.; Walsh, S.; Brotherwood, M.; Robert, R.; Darling, P.B.; Nisenbaum, R.; Moerman, J.; Stanojevic, S. Longitudinal trends in nutritional status and the relation between lung function and BMI in cystic fibrosis: A population-based cohort study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 97, 872–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González Jiménez, D.; Muñoz-Codoceo, R.; Garriga-García, M.; Molina-Arias, M.; Álvarez-Beltrán, M.; García-Romero, R.; Martínez-Costa, C.; Meavilla-Olivas, S.M.; Peña-Quintana, L.R.; Gallego Gutiérrez, S.; et al. Excess weight in patients with cystic fibrosis: Is it always beneficial? Nutr. Hosp. 2017, 34, 578–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Madde, A.; Okoniewski, W.; Sanders, D.B.; Ren, C.L.; Weiner, D.J.; Forno, E. Nutritional status and lung function in children with pancreatic-sufficient cystic fibrosis. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2022, 21, 769–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, A.; Moran, A. Update on cystic fibrosis-related diabetes. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2013, 12, 318–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Worgall, T.S. Lipid metabolism in cystic fibrosis. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2009, 12, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bass, R.; Alvarez, J.A. Nutritional status in the era of highly effective CFTR modulators. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2024, 59, S6–S16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristics | |
|---|---|
| Age (mean ± SD) | 29.5 ± 9.4 (18–59) |
| Sex, female | 50/108 (46.3%) |
| BMI baseline | 21.9 ± 2.5 |
| Type of mutation | |
| F508del homozygous | 49/108 (45.4%) |
| F508del heterozygous | 59/108 (54.6%) |
| Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency | 91/108 (84.3%) |
| Endocrine pancreatic insufficiency | 45/108 (41.7%) |
| Previous treatment with a modulator | 46/108 (42.6%) |
| Total number of exacerbations in the previous year | 3.4 ± 2.3 (0–10) |
| Treated with oral antibiotics | 2.7 ± 1.9 (0–9) |
| Treated with intravenous antibiotics | 0.6 ± 1.1 (0–8) |
| Total number of admissions in the previous year | 0.3 ± 0.6 (0–4) |
| FVC% baseline | 80.1% (SD 16.9) |
| FEV1% baseline | 64.3% (SD 20.9) |
| VR% baseline | 181 ± 67 (94–352) |
| VR/TLC baseline | 44.9 ± 10.9 (27.4–61.6) |
| Sweat chloride test | 93.5 ± 10.8 (72–113) |
| Weight | BMI | |
|---|---|---|
| Baseline | 59.6 kg (9.8) | 21.9 (2.5) |
| 3 months | 61.7 kg (10.0) | 22.5 (2.5) |
| 6 months | 62.4 kg (10.2) | 22.8 (2.6) |
| 9 months | 62.9 kg (10.4) | 22.9 (2.7) |
| 12 months | 62.6 kg (10.2) | 23.0 (2.7) |
| p-values | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| Exacerbations | Oral Antibiotics | IV Antibiotics | Admissions | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Previous year | 3.36 ± 2.33 (0–10) | 2.73 ± 1.90 (0–9) | 0.58 ± 1.15 (0–8) | 0.26 ± 0.59 (0–4) |
| One year post-ETI | 0.94 ± 1.16 (0–7) | 0.83 ± 1.09 (0–7) | 0.09 ± 0.44 (0–3) | 0.06 ± 0.33 (0–3) |
| p-values | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Characteristics | Correlation Coefficient | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| Sex | −0.01 (−0.25; 0.28) | 0.98 |
| Type of mutation | 0.19 (−0.19; 0.64) | 0.37 |
| Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency | −0.05 (−0.41; 0.33) | 0.75 |
| Endocrine pancreatic insufficiency | 0.08 (−0.17; 0.37) | 0.91 |
| Previous treatment with a modulator | −0.04 (−0.28; 0.21) | 0.76 |
| Age at the start of the triple treatment | −0.03 (−0.16; 0.11) | 0.79 |
| Total number of exacerbations in the previous year | 0.16 (0.06; 0.26) | 0.01 |
| Total number of admissions in the previous year | 0.09 (−0.12; 0.28) | 0.37 |
| FVC %, baseline | −0.10 (−0.32; 0.11) | 0.29 |
| FEV 1%, baseline | −0.20 (−0.37; −0.02) | 0.04 |
| Baseline BMI | −0.25 (−0.41; −0.05) | 0.01 |
| Baseline VRTLC | 0.33 (0.11; 0.68) | 0.03 |
| Pulmonary Function Test, Changes | Correlation Coefficient with Changes in BMI | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| Changes in FEV1, % | 0.22 (0.03; 0.41) | 0.02 |
| Changes in FVC, % | 0.27 (0.07; 0.44) | 0.006 |
| Changes in VR/TLC | −0.45 (−0.75; −0.04) | 0.03 |
| Changes in VR, % | −0.39 (−0.77; 0.08) | 0.07 |
| Changes in TLC, % | −0.22 (−0.63; 0.22) | 0.31 |
| Multivariate Mixed Model | p-Value |
|---|---|
| Time | <0.001 |
| BMI at baseline | <0.001 |
| Baseline FEV1, % | 0.001 |
| Baseline FVC, % | 0.03 |
| Baseline VR/TLC | 0.02 |
| Exacerbations | 0.02 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Solís-García, M.; García-Clemente, M.M.; Madrid-Carbajal, C.J.; Peláez, A.; Gómez Punter, R.M.; Eiros Bachiller, J.M.; Girón Moreno, R.M. Is Obesity a Problem in New Cystic Fibrosis Treatments? Nutrients 2024, 16, 3103. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16183103
Solís-García M, García-Clemente MM, Madrid-Carbajal CJ, Peláez A, Gómez Punter RM, Eiros Bachiller JM, Girón Moreno RM. Is Obesity a Problem in New Cystic Fibrosis Treatments? Nutrients. 2024; 16(18):3103. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16183103
Chicago/Turabian StyleSolís-García, Marta, Marta María García-Clemente, Claudia Janeth Madrid-Carbajal, Adrián Peláez, Rosa Mar Gómez Punter, Jose María Eiros Bachiller, and Rosa María Girón Moreno. 2024. "Is Obesity a Problem in New Cystic Fibrosis Treatments?" Nutrients 16, no. 18: 3103. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16183103
APA StyleSolís-García, M., García-Clemente, M. M., Madrid-Carbajal, C. J., Peláez, A., Gómez Punter, R. M., Eiros Bachiller, J. M., & Girón Moreno, R. M. (2024). Is Obesity a Problem in New Cystic Fibrosis Treatments? Nutrients, 16(18), 3103. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16183103






