Dietary Inflammatory Index and Blood Pressure Levels in Mexican Adults
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
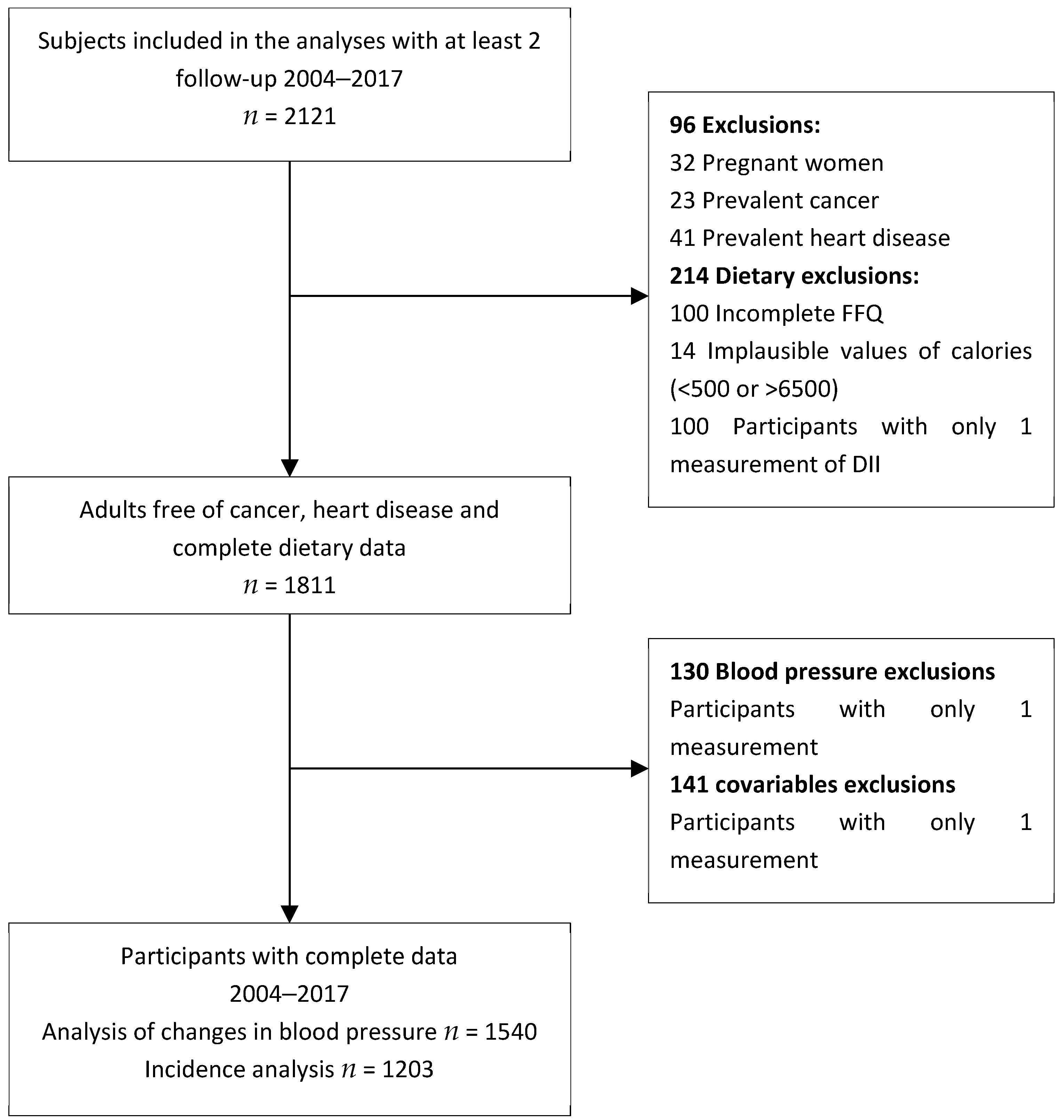
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Dietary Assessment
2.3. Dietary Inflammatory Index (DII)
2.4. Blood Pressure
2.5. Covariates
2.6. Statistical Analysis
2.6.1. Association between Changes in DII and Changes in Blood Pressure
2.6.2. Association between DII and the Incidence of Hypertension
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Study Population
3.2. Association between Changes in DII and Changes in Blood Pressure
3.3. Association between DII and the Incidence of Hypertension
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Keibel, A.; Singh, V.; Sharma, M.C. Inflammation, microenvironment, and the immune system in cancer progression. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2009, 15, 1949–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Nakayama, T. Inflammation, a link between obesity and cardiovascular disease. Mediat. Inflamm. 2010, 2010, 535918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buford, T.W. Hypertension and aging. Ageing Res. Rev. 2016, 26, 96–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bautista, L.E.; Lopez-Jaramillo, P.; Vera, L.M.; Casas, J.P.; Otero, A.P.; Guaracao, A.I. Is C-reactive protein an independent risk factor for essential hypertension? J. Hypertens. 2001, 19, 857–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bautista, L.E.; Vera, L.M.; Arenas, I.A.; Gamarra, G. Independent association between inflammatory markers (C-reactive protein, interleukin-6, and TNF-alpha) and essential hypertension. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2005, 19, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sesso, H.D.; Wang, L.; Buring, J.E.; Ridker, P.M.; Gaziano, J.M. Comparison of interleukin-6 and C-reactive protein for the risk of developing hypertension in women. Hypertension 2007, 49, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sesso, H.D.; Buring, J.E.; Rifai, N.; Blake, G.J.; Gaziano, J.M.; Ridker, P.M. C-reactive protein and the risk of developing hypertension. JAMA 2003, 290, 2945–2951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattace-Raso, F.U.; Verwoert, G.C.; Hofman, A.; Witteman, J.C. Inflammation and incident-isolated systolic hypertension in older adults: The Rotterdam study. J. Hypertens. 2010, 28, 892–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinh, Q.N.; Drummond, G.R.; Sobey, C.G.; Chrissobolis, S. Roles of inflammation, oxidative stress, and vascular dysfunction in hypertension. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 406960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collaboration, N.C.D.R.F. Worldwide trends in hypertension prevalence and progress in treatment and control from 1990 to 2019: A pooled analysis of 1201 population-representative studies with 104 million participants. Lancet 2021, 398, 957–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos-Nonato, I.; Oviedo-Solís, C.; Vargas-Meza, J.; Ramírez-Villalobos, D.; Medina-García, C.; Gómez-Álvarez, E.; Hernández-Barrera, L.; Barquera, S. Prevalencia, Tratamiento y Control de la Hipertensión Arterial en Adultos Mexicanos: Resultados de la Ensanut 2022. Salud Publica Mex [Internet]. 14 de junio de 2023; 65, s169–s180. Available online: https://saludpublica.mx/index.php/spm/article/view/14779 (accessed on 15 May 2024).
- Ramos-Lopez, O.; Martinez-Urbistondo, D.; Vargas-Nunez, J.A.; Martinez, J.A. The Role of Nutrition on Meta-inflammation: Insights and Potential Targets in Communicable and Chronic Disease Management. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2022, 11, 305–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz-Teno, C.; Perez-Martinez, P.; Delgado-Lista, J.; Yubero-Serrano, E.M.; Garcia-Rios, A.; Marin, C.; Gomez, P.; Jimenez-Gomez, Y.; Camargo, A.; Rodriguez-Cantalejo, F.; et al. Dietary fat modifies the postprandial inflammatory state in subjects with metabolic syndrome: The LIPGENE study. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2012, 56, 854–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neale, E.P.; Batterham, M.J.; Tapsell, L.C. Consumption of a healthy dietary pattern results in significant reductions in C-reactive protein levels in adults: A meta-analysis. Nutr. Res. 2016, 36, 391–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, P.K.; Park, S.J.; Kim, M.S.; Kwon, D.Y.; Kim, M.J.; Kim, K.; Chun, S.; Lee, H.J.; Choi, S.W. A Traditional Korean Diet with a Low Dietary Inflammatory Index Increases Anti-Inflammatory IL-10 and Decreases Pro-Inflammatory NF-kappaB in a Small Dietary Intervention Study. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonaccio, M.; Costanzo, S.; Di Castelnuovo, A.; Gialluisi, A.; Ruggiero, E.; De Curtis, A.; Persichillo, M.; Cerletti, C.; Donati, M.B.; de Gaetano, G.; et al. Increased Adherence to a Mediterranean Diet Is Associated with Reduced Low-Grade Inflammation after a 12.7-Year Period: Results from the Moli-sani Study. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2023, 123, 783–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Garcia, E.; Schulze, M.B.; Fung, T.T.; Meigs, J.B.; Rifai, N.; Manson, J.E.; Hu, F.B. Major dietary patterns are related to plasma concentrations of markers of inflammation and endothelial dysfunction. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 80, 1029–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shivappa, N.; Steck, S.E.; Hurley, T.G.; Hussey, J.R.; Hebert, J.R. Designing and developing a literature-derived, population-based dietary inflammatory index. Public Health Nutr. 2014, 17, 1689–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhangi, M.A.; Najafi, M. Dietary inflammatory index: A potent association with cardiovascular risk factors among patients candidate for coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) surgery. Nutr. J. 2018, 17, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zucchetto, A.; Serraino, D.; Shivappa, N.; Hebert, J.R.; Stocco, C.; Puppo, A.; Falcini, F.; Panato, C.; Dal Maso, L.; Polesel, J. Dietary inflammatory index before diagnosis and survival in an Italian cohort of women with breast cancer. Br. J. Nutr. 2017, 117, 1456–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivappa, N.; Bosetti, C.; Zucchetto, A.; Montella, M.; Serraino, D.; La Vecchia, C.; Hebert, J.R. Association between dietary inflammatory index and prostate cancer among Italian men. Br. J. Nutr. 2015, 113, 278–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Merchant, A.T.; Wirth, M.D.; Zhang, J.; Antwi, S.O.; Shoaibi, A.; Shivappa, N.; Stolzenberg-Solomon, R.Z.; Hebert, J.R.; Steck, S.E. Inflammatory potential of diet and risk of pancreatic cancer in the Prostate, Lung, Colorectal and Ovarian (PLCO) Cancer Screening Trial. Int. J. Cancer 2018, 142, 2461–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sokol, A.; Wirth, M.D.; Manczuk, M.; Shivappa, N.; Zatonska, K.; Hurley, T.G.; Hebert, J.R. Association between the dietary inflammatory index, waist-to-hip ratio and metabolic syndrome. Nutr. Res. 2016, 36, 1298–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laouali, N.; Mancini, F.R.; Hajji-Louati, M.; El Fatouhi, D.; Balkau, B.; Boutron-Ruault, M.C.; Bonnet, F.; Fagherazzi, G. Dietary inflammatory index and type 2 diabetes risk in a prospective cohort of 70,991 women followed for 20 years: The mediating role of BMI. Diabetologia 2019, 62, 2222–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramallal, R.; Toledo, E.; Martinez, J.A.; Shivappa, N.; Hebert, J.R.; Martinez-Gonzalez, M.A.; Ruiz-Canela, M. Inflammatory potential of diet, weight gain, and incidence of overweight/obesity: The SUN cohort. Obesity 2017, 25, 997–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frith, E.; Shivappa, N.; Mann, J.R.; Hebert, J.R.; Wirth, M.D.; Loprinzi, P.D. Dietary inflammatory index and memory function: Population-based national sample of elderly Americans. Br. J. Nutr. 2018, 119, 552–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivappa, N.; Godos, J.; Hebert, J.R.; Wirth, M.D.; Piuri, G.; Speciani, A.F.; Grosso, G. Dietary Inflammatory Index and Cardiovascular Risk and Mortality-A Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2018, 10, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhangi, M.A.; Nikniaz, L.; Nikniaz, Z.; Dehghan, P. Dietary inflammatory index potentially increases blood pressure and markers of glucose homeostasis among adults: Findings from an updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Public Health Nutr. 2020, 23, 1362–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denova-Gutierrez, E.; Flores, Y.N.; Gallegos-Carrillo, K.; Ramirez-Palacios, P.; Rivera-Paredez, B.; Munoz-Aguirre, P.; Velazquez-Cruz, R.; Torres-Ibarra, L.; Meneses-Leon, J.; Mendez-Hernandez, P.; et al. Health workers cohort study: Methods and study design. Salud Publica Mex. 2016, 58, 708–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Avila, M.; Romieu, I.; Parra, S.; Hernandez-Avila, J.; Madrigal, H.; Willett, W. Validity and reproducibility of a food frequency questionnaire to assess dietary intake of women living in Mexico City. Salud Publica Mex. 1998, 40, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera-Paredez, B.; Quezada-Sanchez, A.D.; Robles-Rivera, K.; Hidalgo-Bravo, A.; Denova-Gutierrez, E.; Leon-Reyes, G.; Flores, Y.N.; Salmeron, J.; Velazquez-Cruz, R. Dietary inflammatory index and bone mineral density in Mexican population. Osteoporos. Int. 2022, 33, 1969–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. WHO Technical Specifications for Automated Non-Invasive Blood Pressure Measuring Devices with Cuff; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. A Global Brief on Hypertension: Silent Killer, Global Public Health Crisis: World Health Day 2013; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, S.R.; Lambrinoudaki, I.; Lumsden, M.; Mishra, G.D.; Pal, L.; Rees, M.; Santoro, N.; Simoncini, T. Menopause. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2015, 1, 15004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, A.M.; Hunter, D.J.; Colditz, G.A.; Manson, J.E.; Stampfer, M.J.; Corsano, K.A.; Rosner, B.; Kriska, A.; Willett, W.C. Reproducibility and validity of a self-administered physical activity questionnaire. Int. J. Epidemiol. 1994, 23, 991–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Gonzalez, M.A.; Lopez-Fontana, C.; Varo, J.J.; Sanchez-Villegas, A.; Martinez, J.A. Validation of the Spanish version of the physical activity questionnaire used in the Nurses’ Health Study and the Health Professionals’ Follow-up Study. Public Health Nutr. 2005, 8, 920–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ainsworth, B.E.; Haskell, W.L.; Whitt, M.C.; Irwin, M.L.; Swartz, A.M.; Strath, S.J.; O’Brien, W.L.; Bassett, D.R., Jr.; Schmitz, K.H.; Emplaincourt, P.O.; et al. Compendium of physical activities: An update of activity codes and MET intensities. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2000, 32, S498–S504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohman, T.; Roche, A.; Martorell, R. Anthropometric Standardization Reference Manual; Human Kinetics: Champaign, IL, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Obesidad y Sobrepeso [Internet]; World Health Organization WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- American Diabetes Association. 2. Classification and diagnosis of diabetes: Standards of medical care in diabetes 2018. Diabetes Care 2018, 41, S13–S27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrell, C.H.; Brant, L.J.; Ferrucci, L. Model choice can obscure results in longitudinal studies. J. Gerontol. Ser. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2009, 64, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, C.J.; Laouali, N.; Madika, A.L.; Mancini, F.R.; Boutron-Ruault, M.C. Dietary inflammatory index, risk of incident hypertension, and effect modification from BMI. Nutr. J. 2020, 19, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neufcourt, L.; Assmann, K.E.; Fezeu, L.K.; Touvier, M.; Graffouillere, L.; Shivappa, N.; Hebert, J.R.; Wirth, M.D.; Hercberg, S.; Galan, P.; et al. Prospective association between the dietary inflammatory index and metabolic syndrome: Findings from the SU.VI.MAX study. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. NMCD 2015, 25, 988–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vissers, L.E.T.; Waller, M.; van der Schouw, Y.T.; Hebert, J.R.; Shivappa, N.; Schoenaker, D.; Mishra, G.D. A pro-inflammatory diet is associated with increased risk of developing hypertension among middle-aged women. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. NMCD 2017, 27, 564–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, J.S.; Dyer, K.A.; Davis, C.R.; Shivappa, N.; Hebert, J.R.; Woodman, R.; Hodgson, J.M.; Murphy, K.J. Adherence to a Mediterranean Diet for 6 Months Improves the Dietary Inflammatory Index in a Western Population: Results from the MedLey Study. Nutrients 2023, 15, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabe-Hesketh, S.; Skrondal, A. Multilevel and Longitudinal Modeling Using Stata; Stata Press: College Station, TX, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Pocock, S.J.; Ware, J.H. Translating statistical findings into plain English. Lancet 2009, 373, 1926–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Twisk, J.W.R. Applied Longitudinal Data Analysis for Epidemiology: A Practical Guide; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Singer, J.D.; Willett, J.B. Applied Longitudinal Data Analysis: Modeling Change and Event Occurrence; Oxford University Press: Oxrord, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Kleinbaum, D.G.; Klein, M. Survival Analysis: A Self-Learning Text; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Barton, M.; Meyer, M.R. Postmenopausal hypertension: Mechanisms and therapy. Hypertension 2009, 54, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franklin, S.S.; Gustin, W.t.; Wong, N.D.; Larson, M.G.; Weber, M.A.; Kannel, W.B.; Levy, D. Hemodynamic patterns of age-related changes in blood pressure. The Framingham Heart Study. Circulation 1997, 96, 308–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimenta, E.; Oparil, S. Management of hypertension in the elderly. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2012, 9, 286–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kay, C.D.; Hooper, L.; Kroon, P.A.; Rimm, E.B.; Cassidy, A. Relative impact of flavonoid composition, dose and structure on vascular function: A systematic review of randomised controlled trials of flavonoid-rich food products. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2012, 56, 1605–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivappa, N.; Steck, S.E.; Hurley, T.G.; Hussey, J.R.; Ma, Y.; Ockene, I.S.; Tabung, F.; Hebert, J.R. A population-based dietary inflammatory index predicts levels of C-reactive protein in the Seasonal Variation of Blood Cholesterol Study (SEASONS). Public Health Nutr. 2014, 17, 1825–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canto-Osorio, F.; Denova-Gutierrez, E.; Sanchez-Romero, L.M.; Salmeron, J.; Barrientos-Gutierrez, T. Dietary Inflammatory Index and metabolic syndrome in Mexican adult population. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 112, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characterisitics | Baseline Mean (SD) | Changes β | (95% CI) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 45.6 (12.9) | 4.70 | (4.65, 4.75) | <0.001 |
| Systolic Blood pressure (mm Hg) | 116.3 (13.1) | 2.37 | (1.94, 2.80) | <0.001 |
| Diastolic Blood pressure (mm Hg) | 71.7 (9.9) | 2.21 | (1.74, 2.68) | <0.001 |
| Sleep time (hours/d) | 7.3 (1.3) | −0.09 | (−0.13, −0.05) | <0.001 |
| Physical activity (MET-hour/week) | 14.3 (20.9) | −1.41 | (−1.98, −0.84) | <0.001 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 26.5 (4.4) | 0.46 | (0.34, 0.58) | <0.001 |
| Dietary variables | ||||
| Total energy (kcal/d) | 2129 (878) | −180.82 | (−205.68, −155.96) | <0.001 |
| Total carbohydrates (g/d) | 327.6 (146.6) | −23.64 | (−27.96, −19.32) | <0.001 |
| Total Proteins (g/d) | 41.2 (26.0) | 7.64 | (6.78, 8.50) | <0.001 |
| Total fats (g/d) | 55.5 (27.4) | −6.10 | (−6.86, −5.33) | <0.001 |
| Saturated fats (g/d) | 20.3 (10.8) | −2.77 | (−3.06, −2.47) | <0.001 |
| Sodium (mg/d) | 1939.7 (929.5) | −174.43 | (−202.06, −146.81) | <0.001 |
| Alcohol (g/d) | 4.5 (10.7) | −0.48 | (−0.92, −0.03) | 0.035 |
| Fiber (g/d) | 29.2 (16.0) | −1.25 | (−1.72, −0.78) | <0.001 |
| Dietary inflammatory index | 0.58 (2.07) | 0.28 | (0.23, 0.34) | <0.001 |
| Dietary Inflammatory Index | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Change T1 to T2 | Change T1 to T3 | ||||
| SBP | β | [95% CI] | β | [95% CI] | p-Trend |
| M1 | 1.55 | [−0.11; 3.20] | 2.98 | [0.92; 5.05] | 0.005 |
| M2 | 1.53 | [−0.17; 3.23] | 3.10 | [0.99; 5.20] | 0.004 |
| M3 | 1.93 | [0.05; 3.81] | 3.55 | [1.20; 5.91] | 0.003 |
| M4 | 1.60 | [−0.10; 3.30] | 3.23 | [1.11; 5.34] | 0.003 |
| DBP | |||||
| M1 | 0.39 | [−0.72; 1.50] | 1.00 | [−0.38; 2.39] | 0.148 |
| M2 | 0.25 | [−0.90; 1.40] | 0.96 | [−0.47; 2.39] | 0.173 |
| M3 | 0.27 | [−0.99; 1.54] | 0.94 | [−0.64; 2.53] | 0.228 |
| M4 | 0.28 | [−0.88; 1.43] | 1.01 | [−0.43; 2.44] | 0.156 |
| Quartiles of DII | Q1 (<−1.48) | Q2 (−1.48; −0.03) | Q3 (−0.02; 1.73) | Q4 (>1.73) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR [95% CI] | HR [95% CI] | HR [95% CI] | HR [95% CI] | p-Trend | |
| Cases | 82 | 94 | 85 | 80 | |
| Person years | 9.02 | 8.44 | 8.34 | 8.35 | |
| n | 301 | 301 | 301 | 300 | |
| M1 | Reference | 1.26 [0.89; 1.78] | 1.17 [0.80; 1.73] | 1.22 [0.77; 1.91] | 0.62 |
| M2 | Reference | 1.25 [0.88; 1.76] | 1.16 [0.79; 1.71] | 1.21 [0.77; 1.90] | 0.66 |
| M3 | Reference | 1.20 [0.85; 1.70] | 1.14 [0.77; 1.69] | 1.18 [0.74; 1.86] | 0.79 |
| M4 | Reference | 1.25 [0.88; 1.76] | 1.17 [0.79; 1.73] | 1.21 [0.77; 1.90] | 0.66 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Villaverde, P.; Rivera-Paredez, B.; Argoty-Pantoja, A.D.; Velázquez Cruz, R.; Salmerón, J. Dietary Inflammatory Index and Blood Pressure Levels in Mexican Adults. Nutrients 2024, 16, 3052. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16183052
Villaverde P, Rivera-Paredez B, Argoty-Pantoja AD, Velázquez Cruz R, Salmerón J. Dietary Inflammatory Index and Blood Pressure Levels in Mexican Adults. Nutrients. 2024; 16(18):3052. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16183052
Chicago/Turabian StyleVillaverde, Paola, Berenice Rivera-Paredez, Anna D. Argoty-Pantoja, Rafael Velázquez Cruz, and Jorge Salmerón. 2024. "Dietary Inflammatory Index and Blood Pressure Levels in Mexican Adults" Nutrients 16, no. 18: 3052. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16183052
APA StyleVillaverde, P., Rivera-Paredez, B., Argoty-Pantoja, A. D., Velázquez Cruz, R., & Salmerón, J. (2024). Dietary Inflammatory Index and Blood Pressure Levels in Mexican Adults. Nutrients, 16(18), 3052. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16183052






