Development and Management of Avoidant/Restrictive Food Intake Disorder and Food Neophobia in Pediatric Patients with Food Allergy: A Comprehensive Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Objectives
2.2. Search Strategy
- (food allergy OR food allergies) AND (ARFID OR avoidant restrictive food intake disorder OR selective eating disorder OR selective food intake disorder OR neophobia) AND (children OR adolescents OR youth OR child OR teenager) AND (nurse OR nurses OR nursing)
- (food allergy OR food allergies) AND (ARFID OR avoidant restrictive food intake disorder OR selective eating disorder OR selective food intake disorder OR neophobia) AND (children OR adolescents OR youth OR child OR teenager)
2.3. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.3.1. Inclusion Criteria
- (a)
- Type of Studies: All types of studies, including systematic reviews, randomized controlled trials (RCTs), observational studies, and case reports.
- (b)
- Language: Articles published in English or Italian.
- (c)
- Participants: Studies involving participants diagnosed with FA and the subsequent development of ARFID or food neophobia.
2.3.2. Exclusion Criteria
- (a)
- Non-peer-reviewed articles, conference abstracts, and letters to the editor.
- (b)
- Articles published in languages other than English or Italian.
- (c)
- Studies published outside the 15-year period.
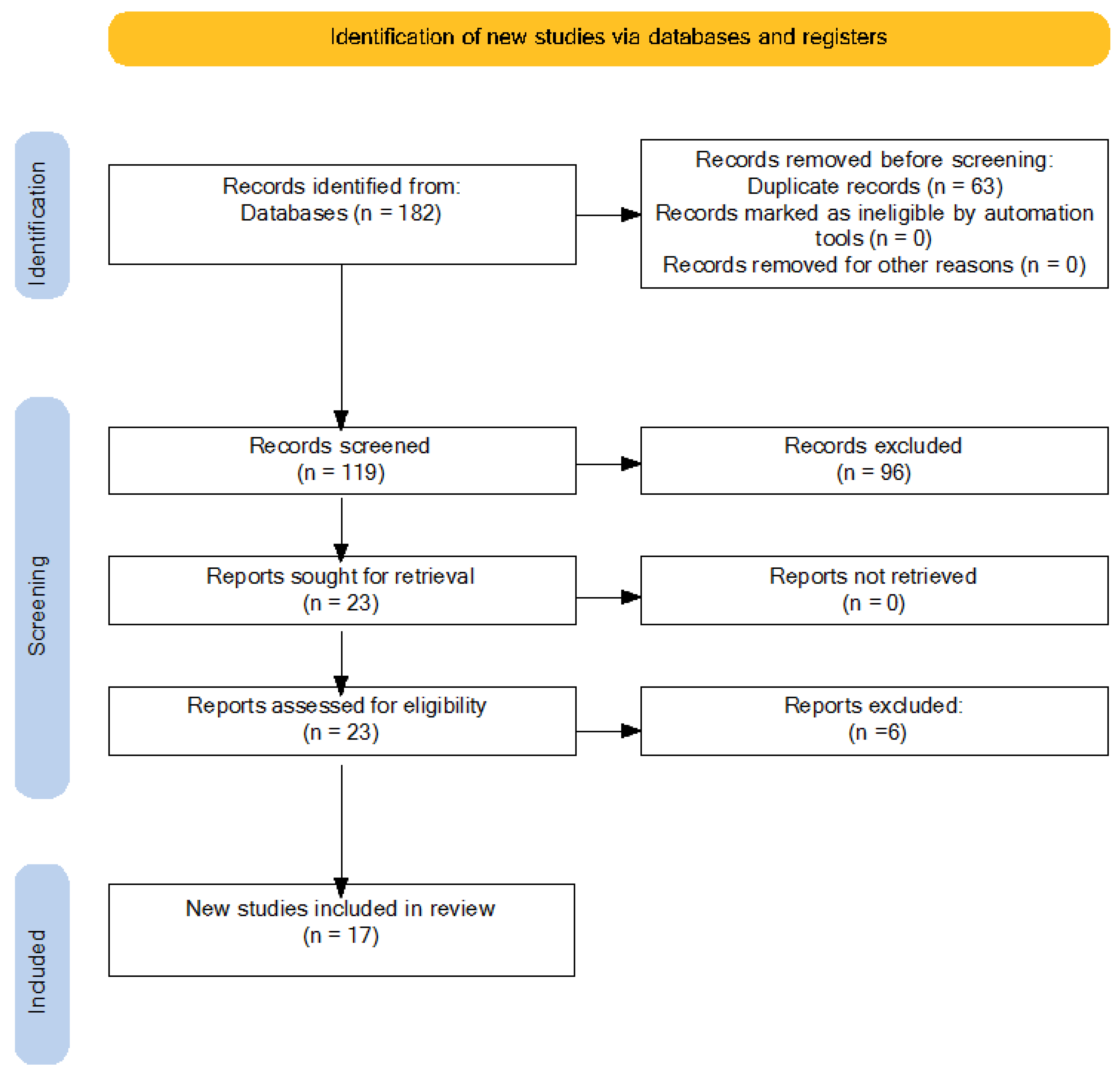
2.3.3. Selection Process
2.3.4. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
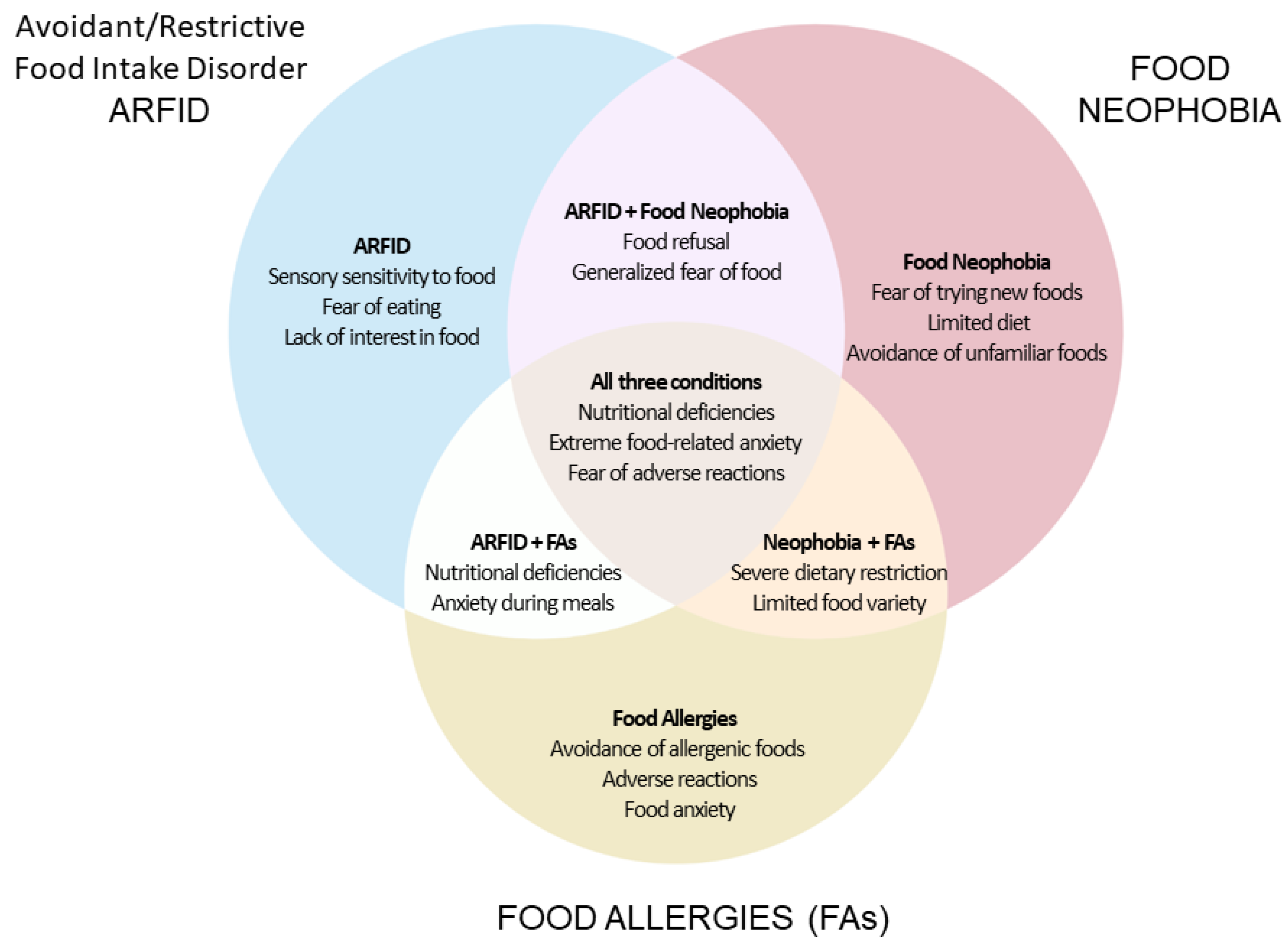
3.1. Food Allergy, ARFID, and Neophobia: Definitions, Etiology, and Clinical Aspects
3.2. ARFID and Food Neophobia in the Context of Food Allergy
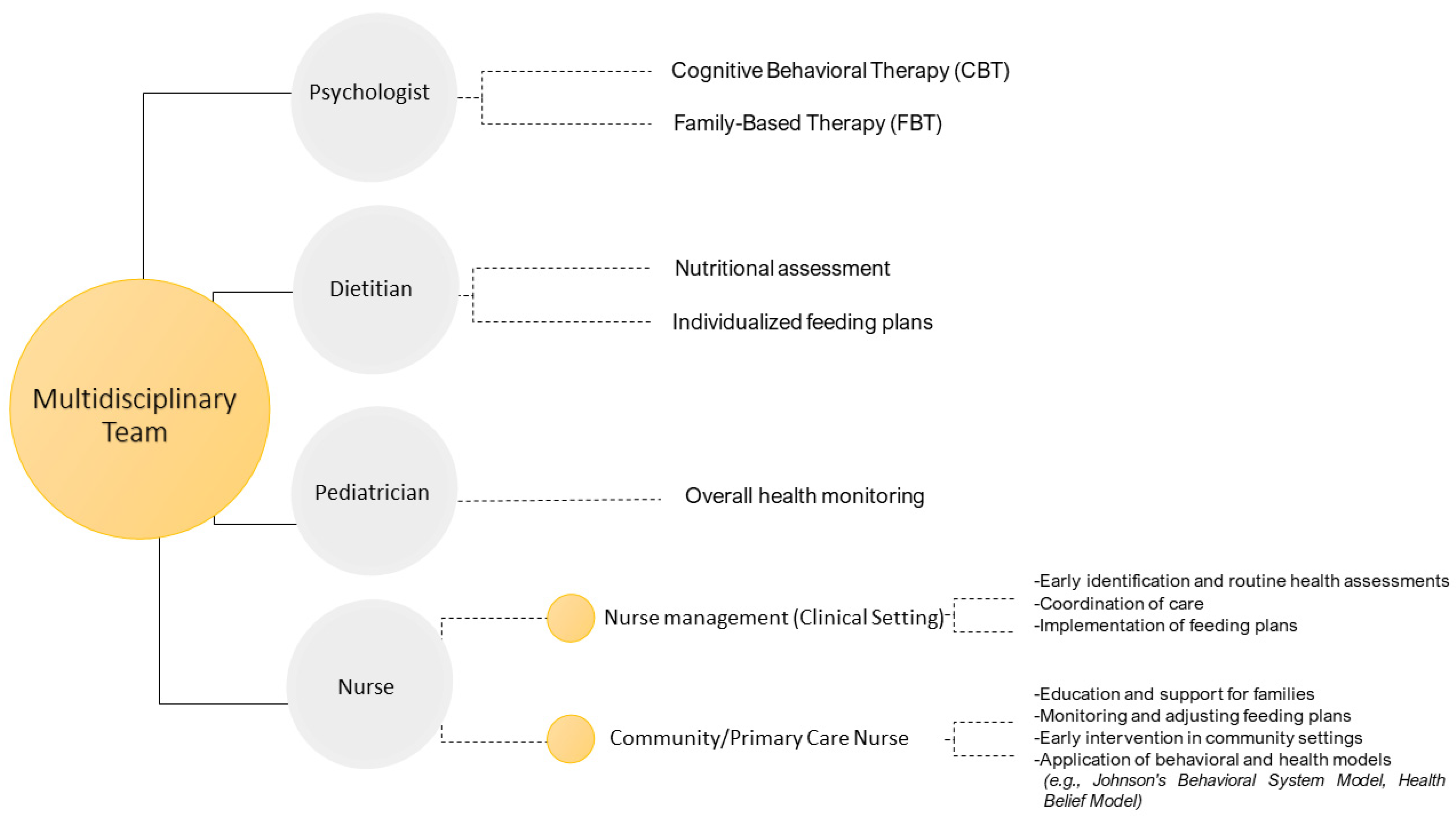
3.3. Interventions and Treatments: Comprehensive Approach
3.4. Role of Nurses in Managing ARFID and Food Neophobia
4. Strengths and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sanchez-Cerezo, J.; Nagularaj, L.; Gledhill, J.; Nicholls, D. What Do We Know about the Epidemiology of Avoidant/Restrictive Food Intake Disorder in Children and Adolescents? A Systematic Review of the Literature. Eur. Eat. Disord. Rev. 2023, 31, 226–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jafri, S.; Frykas, T.L.; Bingemann, T.; Phipatanakul, W.; Bartnikas, L.M.; Protudjer, J.L.P. Food Allergy, Eating Disorders and Body Image. J. Affect. Disord. Rep. 2021, 6, 100197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polloni, L.; Muraro, A. Anxiety and Food Allergy: A Review of the Last Two Decades. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2020, 50, 420–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singer, A.G.; Kosowan, L.; Soller, L.; Chan, E.S.; Nankissoor, N.N.; Phung, R.R.; Abrams, E.M. Prevalence of Physician-Reported Food Allergy in Canadian Children. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2021, 9, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerna, N.A.; Pruitt, K.D.; Jomsky, B.M.; Rodriguez, D.; Azi, C.I.; Carsrud, N.D.V.; Ngwu, D.C.; Holets, H.M.; Flores, J.V.; Chawla, S.; et al. Psychological and Sociological Influences Contributing to Avoidant Restrictive Food Intake Disorder (ARFID) Across Age Groups and Gender. Eur. J. Arts Humanit. Soc. Sci. 2024, 1, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwata, B.; Riordan, M.; Wohl, M.; Finney, J. Pediatric Feeding Disorders: Behavioral Analysis and Treatment. In Failure to Thrive in Infancy and Early Childhood: A Multidisciplinary Team Approach; University Park Press: University Park, PA, USA, 1982; pp. 297–329. [Google Scholar]
- Haas, A.M. Feeding Disorders in Food Allergic Children. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2010, 10, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, C.; Kuang, X.; Liu, Y.; Xiang, C.; Xi, Y.; Huo, J.; Liang, J.; Zou, H.; Lin, Q. Parental Food Neophobia, Feeding Practices, and Preschooler’s Food Neophobia: A Cross-Sectional Study in China. Appetite 2023, 185, 106547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Auria, E.; Cattaneo, C.; Panelli, S.; Pozzi, C.; Acunzo, M.; Papaleo, S.; Comandatore, F.; Mameli, C.; Bandi, C.; Zuccotti, G.; et al. Alteration of Taste Perception, Food Neophobia and Oral Microbiota Composition in Children with Food Allergy. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 7010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, M.M.; Rosen, D.S.; Ornstein, R.M.; Mammel, K.A.; Katzman, D.K.; Rome, E.S.; Callahan, S.T.; Malizio, J.; Kearney, S.; Walsh, B.T. Characteristics of Avoidant/Restrictive Food Intake Disorder in Children and Adolescents: A “New Disorder” in DSM-5. J. Adolesc. Health 2014, 55, 49–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, N.K.O.; Curtarelli, V.D.; Bertoletti, J.; Azevedo, K.; Cardinal, T.M.; Moreira, J.D.; Antunes, L.C. Avoidant Restrictive Food Intake Disorder: Recent Advances in Neurobiology and Treatment. J. Eat. Disord. 2024, 12, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feillet, F.; Bocquet, A.; Briend, A.; Chouraqui, J.-P.; Darmaun, D.; Frelut, M.-L.; Girardet, J.-P.; Guimber, D.; Hankard, R.; Lapillonne, A.; et al. Nutritional Risks of ARFID (Avoidant Restrictive Food Intake Disorders) and Related Behavior. Arch. Pédiatrie 2019, 26, 437–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, G.K.; Karim, A.A.; Khedr, E.M.; Elbeh, K.; Moheb, A.; Abokresha, M.; Haridy, N.A. Case Report: Avoidant/Restrictive Food Intake Disorder after Tonsillectomy. Front. Psychiatry 2024, 15, 1351056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sader, M.; Harris, H.A.; Waiter, G.D.; Jackson, M.C.; Voortman, T.; Jansen, P.W.; Williams, J.H.G. Prevalence and Characterization of Avoidant Restrictive Food Intake Disorder in a Pediatric Population. JAACAP Open 2023, 1, 116–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proctor, K.B.; Rodrick, E.; Belcher, S.; Sharp, W.G.; Kindler, J.M. Bone Health in Avoidant/Restrictive Food Intake Disorder: A Narrative Review. J. Eat. Disord. 2023, 11, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wronski, M.-L.; Kuja-Halkola, R.; Hedlund, E.; Martini, M.I.; Lichtenstein, P.; Lundström, S.; Larsson, H.; Taylor, M.J.; Micali, N.; Bulik, C.M.; et al. Co-Existing Mental and Somatic Conditions in Swedish Children with the Avoidant Restrictive Food Intake Disorder Phenotype. medRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. Text Revision. 2000. Available online: https://psychiatryonline.org/doi/book/10.1176/appi.books.9780890425596 (accessed on 24 June 2024).
- Tamura, A.; Minami, K.; Tsuda, Y.; Tsujimoto, H.; Ichikawa, T.; Mizumoto, K.; Suzuki, H. Characteristics and Outcomes of Avoidant/Restrictive Food Intake Disorder in Japanese Elementary-School Students on Total Parenteral Nutrition. Pediatr. Investig. 2021, 5, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciurez, B.-T.; Cobilinschi, O.-C.; Luca, A.-R.; Țincu, I.; Pleșca, D. Risk Factors Related to Eating Disorders in a Romanian Children Population. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pliner, P.; Hobden, K. Development of a Scale to Measure the Trait of Food Neophobia in Humans. Appetite 1992, 19, 105–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajaz, M.; Ajaz, S.; Furqan, Z.; Chikoto, L. Association between maternal use of pressure feeding and food neo-phobia in pre- school children of karachi. J. Popul. Ther. Clin. Pharmacol. 2023, 30, 2023–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iron-Segev, S.; Best, D.; Arad-Rubinstein, S.; Efron, M.; Serur, Y.; Dickstein, H.; Stein, D. Feeding, Eating, and Emotional Disturbances in Children with Avoidant/Restrictive Food Intake Disorder (ARFID). Nutrients 2020, 12, 3385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krom, H.; Van Oers, H.A.; Van Der Sluijs Veer, L.; Van Zundert, S.M.C.; Otten, M.G.M.; Haverman, L.; Benninga, M.A.; Kindermann, A. Health-Related Quality of Life and Distress of Parents of Children With Avoidant Restrictive Food Intake Disorder. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2021, 73, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dovey, T.M.; Staples, P.A.; Gibson, E.L.; Halford, J.C.G. Food Neophobia and ‘Picky/Fussy’ Eating in Children: A Review. Appetite 2008, 50, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pliner, P. Development of Measures of Food Neophobia in Children. Appetite 1994, 23, 147–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lafraire, J.; Rioux, C.; Giboreau, A.; Picard, D. Food Rejections in Children: Cognitive and Social/Environmental Factors Involved in Food Neophobia and Picky/Fussy Eating Behavior. Appetite 2016, 96, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Białek-Dratwa, A.; Szymańska, D.; Grajek, M.; Krupa-Kotara, K.; Szczepańska, E.; Kowalski, O. ARFID—Strategies for Dietary Management in Children. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zickgraf, H.F.; Murray, H.B.; Kratz, H.E.; Franklin, M.E. Characteristics of Outpatients Diagnosed with the Selective/Neophobic Presentation of Avoidant/Restrictive Food Intake Disorder. Int. J Eat. Disord. 2019, 52, 367–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, J.J.; Becker, K.R.; Kuhnle, M.C.; Jo, J.H.; Harshman, S.G.; Wons, O.B.; Keshishian, A.C.; Hauser, K.; Breithaupt, L.; Liebman, R.E.; et al. Cognitive-behavioral Therapy for Avoidant/Restrictive Food Intake Disorder: Feasibility, Acceptability, and Proof-of-concept for Children and Adolescents. Int. J Eat. Disord. 2020, 53, 1636–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berni Canani, R.; Leone, L.; D’Auria, E.; Riva, E.; Nocerino, R.; Ruotolo, S.; Terrin, G.; Cosenza, L.; Di Costanzo, M.; Passariello, A.; et al. The Effects of Dietary Counseling on Children with Food Allergy: A Prospective, Multicenter Intervention Study. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2014, 114, 1432–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrawala, M.M.; Vickery, B.P.; Proctor, K.B.; Scahill, L.; Stubbs, K.H.; Sharp, W.G. Avoidant-Restrictive Food Intake Disorder (ARFID): A Treatable Complication of Food Allergy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2022, 10, 326–328.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zickgraf, H.F.; Richard, E.; Zucker, N.L.; Wallace, G.L. Rigidity and Sensory Sensitivity: Independent Contributions to Selective Eating in Children, Adolescents, and Young Adults. J. Clin. Child Adolesc. Psychol. 2022, 51, 675–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Buuren, L.; Fleming, C.A.K.; Hay, P.; Bussey, K.; Trompeter, N.; Lonergan, A.; Mitchison, D. The Prevalence and Burden of Avoidant/Restrictive Food Intake Disorder (ARFID) in a General Adolescent Population. J. Eat. Disord. 2023, 11, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooney, M.; Lieberman, M.; Guimond, T.; Katzman, D.K. Clinical and Psychological Features of Children and Adolescents Diagnosed with Avoidant/Restrictive Food Intake Disorder in a Pediatric Tertiary Care Eating Disorder Program: A Descriptive Study. J. Eat. Disord. 2018, 6, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, L.; Goh, L.G.; Ramachandran, R. Evolution of Paediatric Eating Disorders in Singapore: A Historical Cohort Study. Arch. Dis. Child. 2022, 107, 1046–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norris, M.; Spettigue, W.; Katzman, D. Update on Eating Disorders: Current Perspectives on Avoidant/Restrictive Food Intake Disorder in Children and Youth. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2016, 12, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicely, T.A.; Lane-Loney, S.; Masciulli, E.; Hollenbeak, C.S.; Ornstein, R.M. Prevalence and Characteristics of Avoidant/Restrictive Food Intake Disorder in a Cohort of Young Patients in Day Treatment for Eating Disorders. J. Eat. Disord. 2014, 2, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forman, S.F.; McKenzie, N.; Hehn, R.; Monge, M.C.; Kapphahn, C.J.; Mammel, K.A.; Callahan, S.T.; Sigel, E.J.; Bravender, T.; Romano, M.; et al. Predictors of Outcome at 1 Year in Adolescents With DSM-5 Restrictive Eating Disorders: Report of the National Eating Disorders Quality Improvement Collaborative. J. Adolesc. Health 2014, 55, 750–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ornstein, R.M.; Rosen, D.S.; Mammel, K.A.; Callahan, S.T.; Forman, S.; Jay, M.S.; Fisher, M.; Rome, E.; Walsh, B.T. Distribution of Eating Disorders in Children and Adolescents Using the Proposed DSM-5 Criteria for Feeding and Eating Disorders. J. Adolesc. Health 2013, 53, 303–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dovey, T.M. 16—Avoidant/Restrictive Food Intake Disorder: An Eating Disorder on a Spectrum with Food Neophobia. In Food Neophobia; Reilly, S., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing Series in Food Science, Technology and Nutrition; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2018; pp. 329–349. ISBN 978-0-08-101931-3. [Google Scholar]
- Schmid, G.; Schreier, A.; Meyer, R.; Wolke, D. A Prospective Study on the Persistence of Infant Crying, Sleeping and Feeding Problems and Preschool Behaviour. Acta Paediatr. 2010, 99, 286–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolke, D.; Schmid, G.; Schreier, A.; Meyer, R. Crying and Feeding Problems in Infancy and Cognitive Outcome in Preschool Children Born at Risk: A Prospective Population Study. J. Dev. Behav. Pediatr. 2009, 30, 226–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guest, G.; MacQueen, K.M.; Namey, E.E. Applied Thematic Analysis; SAGE Publications: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2012; ISBN 978-1-4833-8443-6. [Google Scholar]
- Berni Canani, R.; Paparo, L.; Nocerino, R.; Di Scala, C.; Della Gatta, G.; Maddalena, Y.; Buono, A.; Bruno, C.; Voto, L.; Ercolini, D. Gut Microbiome as Target for Innovative Strategies Against Food Allergy. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nocerino, R.; Carucci, L.; Coppola, S.; Cecere, G.; Micillo, M.; Castaldo, T.; Russo, S.; Sandomenico, M.; Marino, A.; Gualano, R.; et al. Epidemiology of Paediatric Italian Food Allergy: Results of the EPIFA Study. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Glob. 2024, 3, 100246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, N.; Herbert, L.; Green, T.D. The Emotional, Social, and Financial Burden of Food Allergies on Children and Their Families. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2017, 38, 88–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryant-Waugh, R.; Higgins, C. Avoidant Restrictive Food Intake Disorder in Childhood and Adolescence: A Clinical Guide; Routledge: London, UK, 2020; ISBN 1-00-003281-7. [Google Scholar]
- Demattè, M.L.; Endrizzi, I.; Gasperi, F. Food Neophobia and Its Relation with Olfaction. Front. Psychol. 2014, 5, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders: DSM-5TM, 5th ed.; American Psychiatric Publishing, Inc.: Arlington, VA, USA, 2013; pp. xliv, 947. ISBN 978-0-89042-554-1.
- Blissett, J.; Fogel, A. Intrinsic and Extrinsic Influences on Children’s Acceptance of New Foods. Physiol. Behav. 2013, 121, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farag, F.; Sims, A.; Strudwick, K.; Carrasco, J.; Waters, A.; Ford, V.; Hopkins, J.; Whitlingum, G.; Absoud, M.; Kelly, V.B. Avoidant/Restrictive Food Intake Disorder and Autism Spectrum Disorder: Clinical Implications for Assessment and Management. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2022, 64, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sysko, R.; Glasofer, D.R.; Hildebrandt, T.; Klimek, P.; Mitchell, J.E.; Berg, K.C.; Peterson, C.B.; Wonderlich, S.A.; Walsh, B.T. The Eating Disorder Assessment for DSM-5 (EDA-5): Development and Validation of a Structured Interview for Feeding and Eating Disorders. Int. J Eat. Disord. 2015, 48, 452–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozak, A.; Czepczor-Bernat, K.; Modrzejewska, J.; Modrzejewska, A.; Matusik, E.; Matusik, P. Avoidant/Restrictive Food Disorder (ARFID), Food Neophobia, Other Eating-Related Behaviours and Feeding Practices among Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder and in Non-Clinical Sample: A Preliminary Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 5822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, R.; Archibald, T.; Hembry, P.; Howard, M.; Kelly, C.; Loomes, R.; Markham, L.; Moss, H.; Munuve, A.; Oros, A.; et al. The Clinical Presentation of Avoidant Restrictive Food Intake Disorder in Children and Adolescents Is Largely Independent of Sex, Autism Spectrum Disorder and Anxiety Traits. eClinicalMedicine 2023, 63, 102190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciciulla, D.; Soriano, V.X.; McWilliam, V.; Koplin, J.J.; Peters, R.L. Systematic Review of the Incidence and/or Prevalence of Eating Disorders in Individuals With Food Allergies. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2023, 11, 2196–2207.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitt, P.D.; Middleman, A.B. A Focus on Behavior Management of Avoidant/Restrictive Food Intake Disorder (ARFID): A Case Series. Clin. Pediatr. 2018, 57, 478–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiq, R.; Aziz, A.; Asif, G.; Hussain, M.I.; Hayee, A. Assessing Dietary Practices of Children with Avoidant Restrictive Food Intake Disorder (ARFID)—A Cross-Sectional Study. J. Liaquat Univ. Med. Health Sci. 2023, 22, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeBovidge, J.S.; Strauch, H.; Kalish, L.A.; Schneider, L.C. Assessment of Psychological Distress among Children and Adolescents with Food Allergy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2009, 124, 1282–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, S.; Rhodes, L.; Moreea, O.; McMillan, D.; Gilbody, S.; Leach, C.; Lucock, M.; Lutz, W.; Delgadillo, J. How Durable Is the Effect of Low Intensity CBT for Depression and Anxiety? Remission and Relapse in a Longitudinal Cohort Study. Behav. Res. Ther. 2017, 94, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanter, A.B.; Yasik, A.E.; Zaccario, M.L.; Saviano, J.C. Self-Reported Anxiety Ratings in Children With and Without Food Allergies and Teacher Knowledge of Food Allergies. J. Sch. Health 2022, 92, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto-Hanada, K.; Kobayashi, T.; Mikami, M.; Williams, H.C.; Saito, H.; Saito-Abe, M.; Sato, M.; Irahara, M.; Miyaji, Y.; Ishikawa, F.; et al. Enhanced Early Skin Treatment for Atopic Dermatitis in Infants Reduces Food Allergy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2023, 152, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caffarelli, C.; Santamaria, F.; Di Mauro, D.; Mastrorilli, C.; Montella, S.; Bernasconi, S. Advances in Paediatrics in 2016: Current Practices and Challenges in Allergy, Autoimmune Diseases, Cardiology, Endocrinology, Gastroenterology, Infectious Diseases, Neonatology, Nephrology, Neurology, Nutrition, Pulmonology. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2017, 43, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Loh, W.; Tang, M.L.K. The Epidemiology of Food Allergy in the Global Context. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, R.L.; Koplin, J.J.; Gurrin, L.C.; Dharmage, S.C.; Wake, M.; Ponsonby, A.-L.; Tang, M.L.K.; Lowe, A.J.; Matheson, M.; Dwyer, T.; et al. The Prevalence of Food Allergy and Other Allergic Diseases in Early Childhood in a Population-Based Study: HealthNuts Age 4-Year Follow-Up. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 140, 145–153.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fink, M.; Simons, M.; Tomasino, K.; Pandit, A.; Taft, T. When Is Patient Behavior Indicative of Avoidant Restrictive Food Intake Disorder (ARFID) Vs Reasonable Response to Digestive Disease? Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 20, 1241–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketchem, C.J.; Dellon, E.S. Avoidant Restrictive Food Intake Disorder in Adults With Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Gastro Hep Adv. 2022, 1, 52–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieberman, M.; Houser, M.E.; Voyer, A.; Grady, S.; Katzman, D.K. Children with Avoidant/Restrictive Food Intake Disorder and Anorexia Nervosa in a Tertiary Care Pediatric Eating Disorder Program: A Comparative Study. Int. J Eat. Disord. 2019, 52, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyholmer, M.; Wronski, M.-L.; Hog, L.; Kuja-Halkola, R.; Lichtenstein, P.; Lundström, S.; Larsson, H.; Taylor, M.J.; Bulik, C.M.; Dinkler, L. Neurodevelopmental and Psychiatric Conditions in 600 Swedish Children with the ARFID Phenotype. medRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharp, W.G.; Stubbs, K.H.; Adams, H.; Wells, B.M.; Lesack, R.S.; Criado, K.K.; Simon, E.L.; McCracken, C.E.; West, L.L.; Scahill, L.D. Intensive, Manual-based Intervention for Pediatric Feeding Disorders: Results From a Randomized Pilot Trial. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2016, 62, 658–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mairs, R.; Nicholls, D. Assessment and Treatment of Eating Disorders in Children and Adolescents. Arch. Dis. Child. 2016, 101, 1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howard, M.; Hembry, P.; Rhind, C.; Siddall, A.; Uddin, M.F.; Bryant-Waugh, R. Cognitive Behaviour Therapy (CBT) as a Psychological Intervention in the Treatment of ARFID for Children and Young People. Cogn. Behav. Ther. 2023, 16, e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willmott, E.; Dickinson, R.; Hall, C.; Sadikovic, K.; Wadhera, E.; Micali, N.; Trompeter, N.; Jewell, T. A Scoping Review of Psychological Interventions and Outcomes for Avoidant and Restrictive Food Intake Disorder (ARFID). Int. J Eat. Disord. 2024, 57, 27–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richmond, T.K.; Carmody, J.; Freizinger, M.; Milliren, C.E.; Crowley, P.M.; Jhe, G.B.; Bern, E. Assessment of Patients With ARFID Presenting to Multi-Disciplinary Tertiary Care Program. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2023, 76, 743–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- House, J.; Schmidt, U.; Craig, M.; Landau, S.; Simic, M.; Nicholls, D.; Hugo, P.; Berelowitz, M.; Eisler, I. Comparison of Specialist and Nonspecialist Care Pathways for Adolescents with Anorexia Nervosa and Related Eating Disorders. Int. J Eat. Disord. 2012, 45, 949–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Wye, E.; Matheson, B.; Citron, K.; Yang, H.-J.; Datta, N.; Bohon, C.; Lock, J.D. Protocol for a Randomized Clinical Trial for Avoidant Restrictive Food Intake Disorder (ARFID) in Low-Weight Youth. Contemp. Clin. Trials 2023, 124, 107036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiner, C.E.; Miller, M.L.; Hormes, J.M. ARFID Parent Training Protocol: A Randomized Pilot Trial Evaluating a Brief, Parent-training Program for Avoidant/Restrictive Food Intake Disorder. Int. J Eat. Disord. 2021, 54, 2229–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herpertz-Dahlmann, B. Treatment of Eating Disorders in Child and Adolescent Psychiatry. Curr. Opin. Psychiatry 2017, 30, 438–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noel, R.J. Avoidant Restrictive Food Intake Disorder and Pediatric Feeding Disorder: The Pediatric Gastroenterology Perspective. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 2023, 35, 566–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cucinotta, U.; Romano, C.; Dipasquale, V. A Systematic Review to Manage Avoidant/Restrictive Food Intake Disorders in Pediatric Gastroenterological Practice. Healthcare 2023, 11, 2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, J.; Zlomke, K.R. A Behavioral Parent-Training Intervention for a Child with Avoidant/Restrictive Food Intake Disorder. Clin. Pract. Pediatr. Psychol. 2016, 4, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenz, K.R.; Mitan, L.A.; Kleinhenz, S.R.; Matthews, A. When Outpatient Care Is Not Enough: Successful Use of an Inpatient Behavioral Intervention for a Child With ARFID. Clin. Case Stud. 2018, 17, 469–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spettigue, W.; Norris, M.L.; Santos, A.; Obeid, N. Treatment of Children and Adolescents with Avoidant/Restrictive Food Intake Disorder: A Case Series Examining the Feasibility of Family Therapy and Adjunctive Treatments. J. Eat. Disord. 2018, 6, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Treasure, J.; Livanou, M. Listening to Parents Caring for Individuals with Eating Disorders through the Lens of the Common-sense Model of Illness Perception. Int. J Eat. Disord. 2024, 57, 1119–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchetti, D.; Sawrikar, V. Parents’ Illness Representations of Their Child with Anorexia Nervosa: A Systematic Review of Qualitative Studies Using the Common-sense Model. Int. J Eat. Disord. 2024, 57, 1049–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fynn, G.; Porter, M.; Borchard, T.; Kazzi, C.; Zhong, Q.; Campbell, L. The Effectiveness of Cognitive Behavioural Therapy for Individuals with an Intellectual Disability and Anxiety: A Systematic Review. J. Intellect Disabil. Res. 2023, 67, 816–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niesen, C.R.; Olson, D.M.; Nowdesha, K.D.; Tynsky, D.A.; Loftus, C.G.; Meiers, S.J. Enhancing Self-Management for Adults With Functional Abdominal Pain: A Registered Nurse-Led Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy Approach. Gastroenterol. Nurs. 2018, 41, 321–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Lim, Y.; Yoo, M.-S.; Kim, Y. Effects of a Nurse-Led Cognitive-Behavior Therapy on Fatigue and Quality of Life of Patients With Breast Cancer Undergoing Radiotherapy: An Exploratory Study. Cancer Nurs. 2011, 34, E22–E30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brigham, K.S.; Manzo, L.D.; Eddy, K.T.; Thomas, J.J. Evaluation and Treatment of Avoidant/Restrictive Food Intake Disorder (ARFID) in Adolescents. Curr. Pediatr. Rep. 2018, 6, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mauldin, T.R. Pediatric Food Allergy Management. Nurs. Made Incred. Easy 2017, 15, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard-Ruben, J.; Doucette, J. Exploring Novel Approaches to Food Allergy Management. J. Am. Assoc. Nurse Pract. 2023, 35, 843–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oakley, T.J.; Dey, I.; Discombe, S.; Fitzpatrick, L.; Paul, S.P. Recognition and Management of Eating Disorders in Children and Young People. Nurs. Stand. 2017, 32, 52–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oktarina, M.; Asniar, A.; Maulina, M. Improving mothers’ ability to care for toddlers with avoidant restrictive food intake disorder (ARFID). J. Pengabdi. Masy. Dalam Kesehat. 2023, 5, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasetyo, Y.; Wardojo, S.; Pratiwi, I. Role of Community Nurses in Improving Caregivers’ Ability in Caring Children with ARFID (Avoidant Restrictive Food Intake Disorder). In Proceedings of the Health Science International Conference (HSIC 2017), Malang, Indonesia, 4–5 October 2017; Atlantis Press: Malang, Indonesia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Garg, P.; Williams, J.A.; Satyavrat, V. A Pilot Study to Assess the Utility and Perceived Effectiveness of a Tool for Diagnosing Feeding Difficulties in Children. Asia Pac. Fam. Med. 2015, 14, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Væver, M.S.; Smith-Nielsen, J.; Lange, T. Copenhagen Infant Mental Health Project: Study Protocol for a Randomized Controlled Trial Comparing Circle of Security—Parenting and Care as Usual as Interventions Targeting Infant Mental Health Risks. BMC Psychol. 2016, 4, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Toro, V.; Aedo, K.; Urrejola, P. Trastorno de Evitación y Restricción de La Ingesta de Alimentos (ARFID): Lo Que El Pediatra Debe Saber. Andes Pediatr. 2021, 92, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, F.; Howard, A.G.; Herring, A.H.; Thompson, A.L.; Adair, L.S.; Popkin, B.M.; Aiello, A.E.; Zhang, B.; Gordon-Larsen, P. Parent–Child Associations for Changes in Diet, Screen Time, and Physical Activity across Two Decades in Modernizing China: China Health and Nutrition Survey 1991–2009. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2016, 13, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntosh, C.E.; Kandiah, J.; Boucher, N.R. Practical Considerations for School Nurses in Improving the Nutrition of Children With Autism Spectrum Disorder. NASN Sch. Nurse 2019, 34, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, R.L.T.; Wang, J.J. Effectiveness of an Adolescent Healthcare Training Programme for Enhancing Paediatric Nurses’ Competencies. J. Clin. Nurs. 2016, 25, 3300–3310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Intervention | Strategies | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Education and Empowerment | Providing Comprehensive Education: Nurses educate families about ARFID, explaining its symptoms, causes, and potential impacts. By covering both the psychological and physical aspects of the disorder, they help families understand the importance of addressing these issues together. | Lee & Wang, 2016 [99] |
| Teaching Anxiety Management Techniques: Nurses train parents and children in managing anxiety related to food intake, such as through deep breathing exercises, mindfulness, and relaxation techniques. These skills help reduce mealtime stress and foster a more positive eating environment. | Prasetyo et al., 2017 [93] | |
| Implementation of Structured Feeding Plans | Developing and Monitoring Individualized Feeding Plans: Nurses collaborate with dietitians to create tailored feeding plans that gradually introduce new foods while ensuring nutritional adequacy. Techniques like food chaining are used to introduce new foods in small, manageable steps. | Białek-Dratwa et al., 2022 [27] |
| Routine Monitoring and Adjustments: Regular follow-ups are essential to assess progress and adjust feeding plans as necessary. Nurses track the child’s growth, nutritional intake, and psychological well-being to provide comprehensive care. | Richmond et al., 2023 [73] | |
| Emotional and Social Support | Providing Emotional Support: Nurses offer emotional support by acknowledging the challenges families face and validating their experiences. They provide a listening ear and empathetic responses to alleviate feelings of isolation and frustration. | Oktarina et al., 2023 [92] |
| Facilitating Support Groups: Nurses can organize or recommend support groups where families share experiences and strategies with others facing similar challenges. These groups provide mutual support and practical advice. | Prasetyo et al., 2017 [93] | |
| Coordination of Multidisciplinary Care | Coordinating Multidisciplinary Care: Nurses coordinate care among various healthcare providers, including pediatricians, dietitians, psychologists, and gastroenterologists. This ensures comprehensive and integrated care addressing all aspects of ARFID. | Cucinotta et al., 2023 [79] |
| Utilizing Evidence-Based Interventions: Nurses implement evidence-based interventions and stay updated with the latest research and guidelines in ARFID management. This includes staying informed about new therapeutic techniques and best practices for managing food-related anxiety. | Lee & Wang, 2016 [99] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nocerino, R.; Mercuri, C.; Bosco, V.; Giordano, V.; Simeone, S.; Guillari, A.; Rea, T. Development and Management of Avoidant/Restrictive Food Intake Disorder and Food Neophobia in Pediatric Patients with Food Allergy: A Comprehensive Review. Nutrients 2024, 16, 3034. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16173034
Nocerino R, Mercuri C, Bosco V, Giordano V, Simeone S, Guillari A, Rea T. Development and Management of Avoidant/Restrictive Food Intake Disorder and Food Neophobia in Pediatric Patients with Food Allergy: A Comprehensive Review. Nutrients. 2024; 16(17):3034. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16173034
Chicago/Turabian StyleNocerino, Rita, Caterina Mercuri, Vincenzo Bosco, Vincenza Giordano, Silvio Simeone, Assunta Guillari, and Teresa Rea. 2024. "Development and Management of Avoidant/Restrictive Food Intake Disorder and Food Neophobia in Pediatric Patients with Food Allergy: A Comprehensive Review" Nutrients 16, no. 17: 3034. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16173034
APA StyleNocerino, R., Mercuri, C., Bosco, V., Giordano, V., Simeone, S., Guillari, A., & Rea, T. (2024). Development and Management of Avoidant/Restrictive Food Intake Disorder and Food Neophobia in Pediatric Patients with Food Allergy: A Comprehensive Review. Nutrients, 16(17), 3034. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16173034






