Hunger, Satiety, and Their Vulnerabilities
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Hunger and Satiety, Learning and Memory, and the Medial Temporal Lobes (MTL)
3. Vulnerabilities of Hunger and Satiety
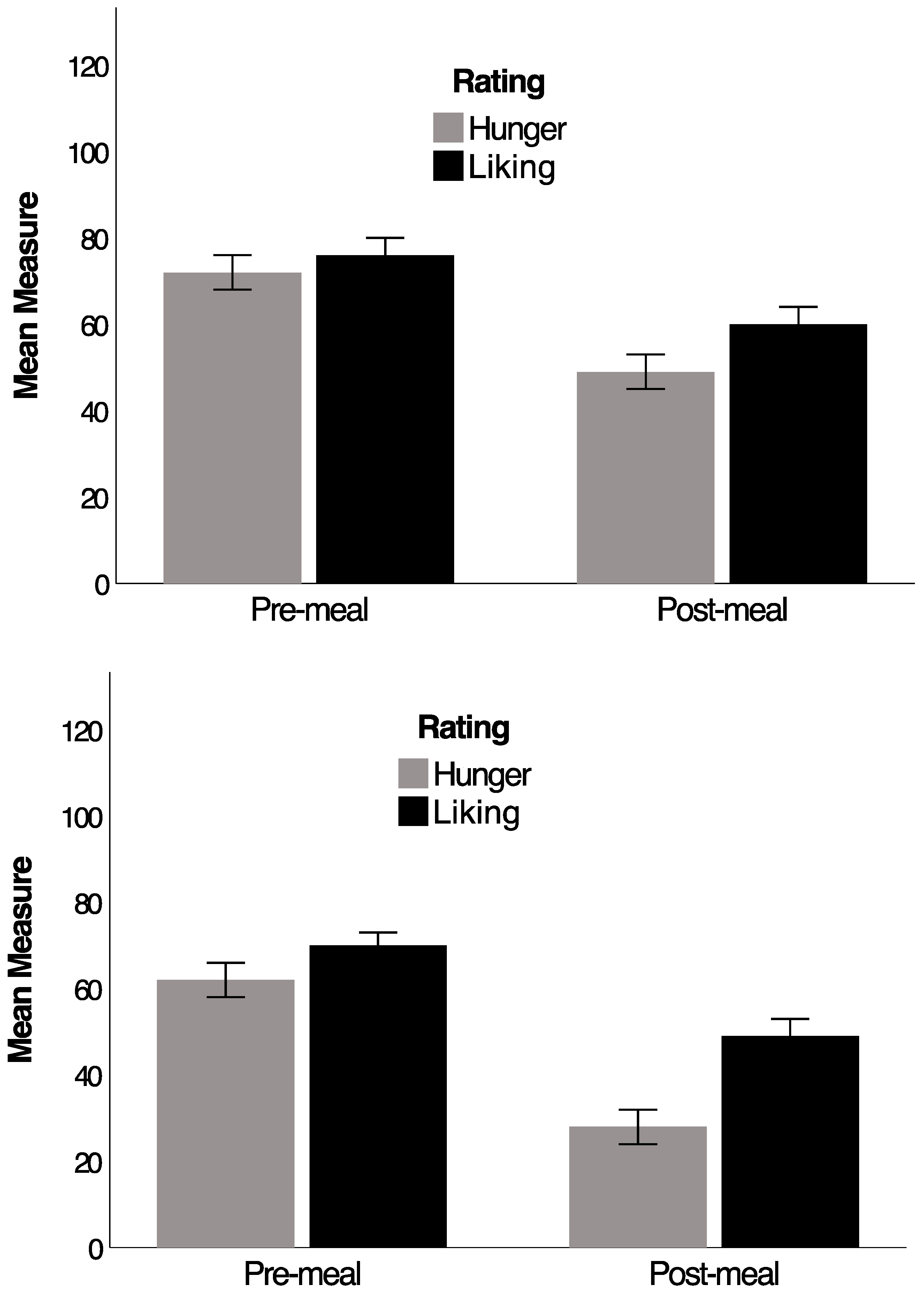
4. Western-Style Diet
5. Obesity
6. Anorexia Nervosa (AN)
7. MTL Epilepsy
8. Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
9. Implications for Intervention
10. Mechanism
11. Future Research Directions
12. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- de Castro, J.M.; Elmore, D.K. Subjective hunger relationships with meal patterns in the spontaneous feeding behavior of humans: Evidence for a causal connection. Physiol. Behav. 1988, 43, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drapeau, V.; Blundell, J.; Therrien, F.; Lawton, C.; Richard, D.; Tremblay, A. Appetite sensations as a marker of overall intake. Br. J. Nutr. 2005, 93, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drapeau, V.; King, N.; Hetherington, M.; Doucet, E.; Blundell, J.; Tremblay, A. Appetite sensations and satiety quotient: Predictors of energy intake and weight loss. Appetite 2007, 48, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibbons, C.; Hopkins, M.; Beaulieu, K.; Oustric, P.; Blundell, J.E. Issues in Measuring and Interpreting Human Appetite (Satiety/Satiation) and Its Contribution to Obesity. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2019, 8, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wardle, J.; Carnell, S. Appetite is a heritable phenotype associated with adiposity. Ann. Behav. Med. 2009, 38 (Suppl. S1), S25–S30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, T.L.; Jones, S.; Roy, M.; Stevenson, R.J. The Cognitive Control of Eating and Body Weight: It’s More Than What You “Think”. Front. Psychol. 2019, 10, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevenson, R.J.; Yeomans, M.R.; Francis, H.M. Human hunger as a memory process. Psychol. Rev. 2024, 131, 174–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, R.J. The psychological basis of hunger and its dysfunctions. Nutr. Rev. 2023, in press. [CrossRef]
- Strubbe, J.H.; Woods, S.C. The timing of meals. Psychol. Rev. 2004, 111, 128–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weingarten, H.P. Stimulus control of eating: Implications for a two-factor theory of theory. Appetite 1985, 6, 387–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woods, S.C.; May-Zhang, A.A.; Begg, D.P. How and why do gastrointestinal peptides influence food intake? Physiol. Behav. 2018, 193, 218–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schacter, D.L.; Wagner, A.D.; Buckner, R.L. Memory systems of 1999. In The Oxford Handbook of Memory; Tulving, E., Craik, F.I.M., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2000; pp. 627–643. [Google Scholar]
- Squire, L.R.; Dede, A.J. Conscious and unconscious memory systems. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2015, 7, a021667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tulving, E. How many memory systems are there? Am. Psychol. 1985, 40, 385–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tulving, E. Episodic and semantic memory. In Organisation of Memory; Tulving, E., Donaldson, W., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1972; pp. 381–402. [Google Scholar]
- Tulving, E. Episodic memory: From mind to brain. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2002, 53, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eichenbaum, H. A cortical–hippocampal system for declarative memory. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2000, 1, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Squire, L.R.; Zola, S.M. Episodic memory, semantic memory, and amnesia. Hippocampus 1998, 8, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tulving, E.; Markowitsch, H.J. Episodic and declarative memory: Role of the hippocampus. Hippocampus 1998, 8, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, R.R.; Halliday, G.M.; Xuereb, J.H.; Kril, J.J.; Hodges, J.R. The neural basis of semantic memory: Evidence from semantic dementia. Neurobiol. Aging 2009, 30, 2043–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodges, J.R.; Patterson, K. Semantic dementia: A unique clinicopathological syndrome. Lancet Neurol. 2007, 6, 1004–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebben, N.; Corkin, S.; Eichenbaum, H.; Shedlack, K. Diminished ability to interpret and report internal states after bilateral medial temporal resection: Case H.M. Behav. Neurosci. 1985, 99, 1031–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozin, P.; Dow, S.; Moscovitch, M.; Rajaram, S. What causes humans to begin and end a meal? A role for memory for what has been eaten, as evidenced by a study of multiple meal eating in amnesic patients. Psychol. Sci. 1998, 9, 392–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartsch, T.; Wulff, P. The hippocampus in aging and disease: From plasticity to vulnerability. Neuroscience 2015, 309, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, T.L.; Stevenson, R.J. Vulnerability of the Hippocampus to Insults: Links to Blood-Brain Barrier Dysfunction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harry, G.J.; Lefebvre d’Hellencourt, C. Dentate gyrus: Alterations that occur with hippocampal injury. Neurotoxicology 2003, 24, 343–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McEwen, B.S.; Gould, E.A.; Sakai, R.R. The vulnerability of the hippocampus to protective and destructive effects of glucocorticoids in relation to stress. Br. J. Psychiatry 1992, 160 (Suppl. S15), 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, L.L.; Bilbo, S.D. Chemokines and the hippocampus: A new perspective on hippocampal plasticity and vulnerability. Brain Behav. Immun. 2013, 30, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corkin, S. Permanent Present Tense; Penguin: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Higgs, S.; Williamson, A.; Rothstein, P.; Humphreys, G.W. Sensory-specific satiety is intact in amnesics who eat multiple meals. Psychol. Sci. 2008, 19, 623–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berriman, J.; Stevenson, R.J.; Thayer, Z.C.; Thompson, E.; Mohamed, A.; Watson, J.; Miller, L. Testing the importance of the Medial Temporal Lobes in human interoception: Does it matter if these is a memory component to the task? Neuropsychologia 2016, 91, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuniga, A.; Stevenson, R.J.; Thayer, Z.C.; Miller, L.; Francis, H.M.; Saluja, S.; Nikpour, A. The impact of hippocampal damage on appetitive control. Neurocase 2020, 26, 657–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannon, W.B.; Washburn, A.L. An explanation of hunger. Am. J. Physiol. 1912, 29, 441–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espel-Huynh, H.M.; Muratore, A.F.; Lowe, M.R. A narrative review of the construct of hedonic hunger and its measurement by the Power of Food Scale. Obes. Sci. Pract. 2018, 4, 238–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- May, J.; Andrade, J.; Kavanagh, D.J.; Hetherington, M. Elaborated intrusion theory: A cognitive-emotional theory of food craving. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2012, 1, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papies, E.K.; Barsalou, L.W.; Rusz, D. Understanding desire for food and drink: A grounded-cognition approach. Curr. Dir. Psychol. Sci. 2020, 29, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckner, R.L. The role of the hippocampus in prediction and imagination. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2010, 61, 27–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilboa, A.; Winocur, G.; Rosenbaum, R.; Poreh, A.; Gao, F.; Black, S.; Westmacott, R.; Moscovitch, M. Hippocampal contributions to recollection in retrograde and anterograde amnesia. Hippocampus 2006, 16, 966–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liljeholm, M.; O’Doherty, J.P. Contributions of the striatum to learning, motivation, and performance: An associative account. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2012, 16, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowe, M.R.; Butryn, M.L. Hedonic hunger: A new dimension of appetite? Physiol. Behav. 2007, 91, 432–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, J. Glucostatic mechanism of regulation of food intake. N. Engl. J. Med. 1953, 249, 13–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, A.; Wardle, J. The feeling of hunger. Br. J. Clin. Psychol. 1987, 26, 153–154. [Google Scholar]
- Monello, L.F.; Mayer, J. Hunger and satiety sensations in men, women, boys, and girls. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1967, 20, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, R.J.; Hill, B.J.; Hughes, A.; Wright, M.; Bartlett, J.; Saluja, S.; Francis, H.M. Interoceptive hunger, eating attitudes and beliefs. Front. Psychol. 2023, 14, 1148413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Akker, K.; Havermans, R.C.; Jansen, A. Appetitive conditioning to specific times of day. Appetite 2017, 116, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harshaw, C. Alimentary epigenetics: A developmental psychobiological systems view of the perception of hunger, thirst and satiety. Dev. Rev. 2008, 28, 541–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevenson, R.J.; Bartlett, J.; Wright, M.; Hughes, A.; Hill, B.J.; Saluja, S.; Francis, H.M. The development of interoceptive hunger signals. Dev. Psychobiol. 2023, 65, e22374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevenson, R.J.; Martin-Rivera, D.; Dixon, G.; Francis, H.M. Parent-offspring similarity in hunger and thirst sensations. Appetite 2024, 195, 107208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantor, J.R.; Zillmann, D.; Bryant, J. Enhancement of experienced sexual arousal in response to erotic stimuli through misattribution of unrelated residual excitation. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 1975, 32, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tannenbaum, P.H.; Zillmann, D. Emotional arousal in the facilitation of aggression through communication. Adv. Exp. Soc. Psychol. 1975, 8, 149–192. [Google Scholar]
- Burianova, H.; McIntosh, A.R.; Grady, C.L. A common functional brain network for autobiographical, episodic, and semantic memory retrieval. NeuroImage 2010, 49, 865–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, K.M.; Holland, P.C. Occasion setting. Behav. Neurosci. 2019, 133, 145–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klooster, N.B.; Duff, M.C. Remote semantic memory is impoverished in hippocampal amnesia. Neuropsychologia 2015, 79 Pt A, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmajuk, N.A.; Buhusi, C.V. Stimulus configuration, occasion setting, and the hippocampus. Behav. Neurosci. 1997, 111, 235–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, T.; Graham, L.K.; Kim, J.J. Hippocampal lesion effects on occasion setting by contextual and discrete stimuli. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2011, 95, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, J.J.; Lin, A.; Samimi, M.S.; Mendez, M.F. Somatic symptom disorder in semantic dementia: The role of alexisomia. Psychosomatics 2016, 57, 598–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nonaka, A.; Toyoda, T.; Miura, Y.; Hitora-Imamura, N.; Naka, M.; Eguchi, M.; Yamaguchi, S.; Ikegaya, Y.; Matsuki, N.; Nomura, H. Synaptic Plasticity Associated with a Memory Engram in the Basolateral Amygdala. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 9305–9309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidson, T.L. Pavlovian occasion setting: A link between physiological change and appetitive behavior. Appetite 2000, 35, 271–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidson, T.L.; Kanoski, S.E.; Walls, E.K.; Jarrard, L.E. Memory inhibition and energy regulation. Physiol. Behav. 2005, 86, 731–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidson, T.L.; Kanoski, S.E.; Chan, K.; Clegg, D.J.; Benoit, S.C.; Jarrard, L.E. Hippocampal lesions impair retention of discriminative responding based on energy state cues. Behav. Neurosci. 2010, 124, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannapel, R.C.; Henderson, Y.H.; Nalloor, R.; Vazdarjanova, A.; Parent, M.B. Ventral hippocampal neurons inhibit postprandial energy intake. Hippocampus 2017, 27, 274–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, Y.O.; Smith, G.P.; Parent, M.B. Hippocampal neurons inhibit meal onset. Hippocampus 2013, 23, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parent, M.B. Cognitive control of meal onset and meal size: Role of dorsal hippocampal-dependent episodic memory. Physiol. Behav. 2016, 162, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, R.J.; Francis, H.M. The hippocampus and the regulation of human food intake. Psychol. Bull. 2017, 143, 1011–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, R.J.; Francis, H.M.; Attuquayefio, T.; Gupta, D.; Yeomans, M.R.; Oaten, M.J.; Davidson, T.L. Hippocampal-dependent appetitive control is impaired by experimental exposure to a Western-style diet. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2020, 7, 191338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attuquayefio, T.; Stevenson, R.J.; Boakes, R.A.; Oaten, M.J.; Yeomans, M.R.; Mahmut, M.; Francis, H.M. A high-fat high-sugar diet predicts poorer hippocampal-related memory and a reduced ability to suppress wanting under satiety. J. Exp. Psychol. Anim. Learn. Cogn. 2016, 42, 415–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanoski, S.E.; Grill, H.J. Hippocampus Contributions to Food Intake Control: Mnemonic, Neuroanatomical, and Endocrine Mechanisms. Biol. Psychiatry 2017, 81, 748–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanoski, S.E.; Davidson, T.L. Western diet consumption and cognitive impairment: Links to hippocampal dysfunction and obesity. Physiol. Behav. 2011, 103, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parent, M.B.; Darling, J.; Henderson, Y. Remembering to eat: Hippocampal regulation of meal onset. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2014, 306, R701–R713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, R.J.; Francis, H.M.; Hughes, A.; Wylie, F.; Yeomans, M.R. Predictors of state-based changes in wanting and liking. Appetite 2023, 188, 106640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, K.D.; Ayuketah, A.; Brychta, R.; Cai, H.; Cassimatis, T.; Chen, K.Y.; Chung, S.T.; Costa, E.; Courville, A.; Darcey, V.; et al. Ultra-Processed Diets Cause Excess Calorie Intake and Weight Gain: An Inpatient Randomized Controlled Trial of Ad Libitum Food Intake. Cell Metab. 2019, 30, 67–77.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, K.N.; Arnott, C.K.; Westbrook, R.F.; Tran, D.M.D. The effect of high fat, high sugar, and combined high fat-high sugar diets on spatial learning and memory in rodents: A meta-analysis. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2019, 107, 399–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, Z.B.; Stevenson, R.J.; Ehrenfeld, L.; Francis, H.M. The impact of saturated fat, added sugar and their combination on human hippocampal integrity and function: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2021, 130, 91–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attuquayefio, T.; Stevenson, R.J.; Oaten, M.J.; Francis, H.M. A four-day Western-style dietary intervention causes reductions in hippocampal-dependent learning and memory and interoceptive sensitivity. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0172645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francis, H.M.; Stevenson, R.J. Higher reported saturated fat and refined sugar intake is associated with reduced hippocampal-dependent memory and sensitivity to interoceptive signals. Behav. Neurosci. 2011, 125, 943–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, H.; Stevenson, R.J. Validity and test-retest reliability of a short dietary questionnaire to assess intake of saturated fat and free sugars: A preliminary study. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 2013, 26, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevenson, R.J.; Francis, H.M.; Wylie, F.; Hughes, A. The psychological basis of reductions in food desire during satiety. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2023, 10, 221404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benoit, S.C.; Davidson, T.L.; Chan, K.H.; Trigilio, T.; Jarrard, L.E. Pavlovian conditioning and extinction of context cues and punctate CSs in rats with ibotenate lesions of the hippocampus. Psychobiology 1999, 27, 26–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeomans, M.R.; Armitage, R.; Atkinson, R.; Francis, H.M.; Stevenson, R.J. Habitual intake of fat and sugar is associated with poorer memory and greater impulsivity. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0290308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Londerée, A.M.; Wagner, D.D. The orbitofrontal cortex spontaneously encodes food health and contains more distinct representations for foods highest in tastiness. Soc. Cogn. Affect. Neurosci. 2021, 16, 816–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riskey, D.R.; Parducci, A.; Beauchamp, G.K. Effects of context in judgments of sweetness and pleasantness. Percept. Psychophys. 1979, 26, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, E. Relationships between expected, online and remembered enjoyment for food products. Appetite 2014, 74, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rode, E.; Rozin, P.; Durlach, P. Experienced and remembered pleasure for meals: Duration neglects but minimal peak, end (recency) or primacy effects. Appetite 2007, 49, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prickett, C.; Brennan, L.; Stolwyk, R. Examining the relationship between obesity and cognitive function: A systematic literature review. Obes. Res. Clin. Pract. 2015, 9, 93–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janowitz, D.; Wittfeld, K.; Terock, J.; Freyberger, H.J.; Hegenscheid, K.; Völzke, H.; Habes, M.; Hosten, N.; Friedrich, N.; Nauck, M.; et al. Association between waist circumference and gray matter volume in 2344 individuals from two adult community-based samples. Neuroimage 2015, 122, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nouwen, A.; Chambers, A.; Chechlacz, M.; Higgs, S.; Blissett, J.; Barrett, T.G.; Allen, H.A. Microstructural abnormalities in white and gray matter in obese adolescents with and without type 2 diabetes. Neuroimage Clin. 2017, 16, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hargrave, S.L.; Jones, S.; Davidson, T.L. The Outward Spiral: A vicious cycle model of obesity and cognitive dysfunction. Curr. Opin. Behav. Sci. 2016, 9, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakib, M.N.; Best, J.R.; Hall, P.A. Bidirectional Associations Between Adiposity and Cognitive Function and Mediation by Brain Morphology in the ABCD Study. JAMA Netw. Open 2023, 6, e2255631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schachter, S. Obesity and eating: Internal and external cues differentially affect the eating behavior of obese and normal subjects. Science 1968, 161, 751–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutelle, K.N.; Manzano, M.A.; Eichen, D.M. Appetitive traits as targets for weight loss: The role of food cue responsiveness and satiety responsiveness. Physiol. Behav. 2020, 224, 113018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llewellyn, C.H.; Fildes, A. Behavioural Susceptibility Theory: Professor Jane Wardle and the Role of Appetite in Genetic Risk of Obesity. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2017, 6, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llewellyn, C.; Wardle, J. Behavioral susceptibility to obesity: Gene-environment interplay in the development of weight. Physiol. Behav. 2015, 152 Pt B, 494–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman, C.P.; Polivy, J. External cues in the control of food intake in humans: The sensory-normative distinction. Physiol. Behav. 2008, 94, 722–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polivy, J.; Herman, C.P.; Coelho, J.S. Caloric restriction in the presence of attractive food cues: External cues, eating, and weight. Physiol. Behav. 2008, 94, 729–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanoski, S.E.; Boutelle, K.N. Food cue reactivity: Neurobiological and behavioral underpinnings. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2022, 23, 683–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morys, F.; García-García, I.; Dagher, A. Is obesity related to enhanced neural reactivity to visual food cues? A review and meta-analysis. Soc. Cogn. Affect. Neurosci. 2020, 18, nsaa113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boswell, R.G.; Kober, H. Food cue reactivity and craving predict eating and weight gain: A meta-analytic review. Obes. Rev. Off. J. Int. Assoc. Study Obes. 2016, 17, 159–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, R.J.; Mahmut, M.; Rooney, K. Individual differences in the interoceptive states of hunger, fullness and thirst. Appetite 2015, 95, 44–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, E.; Foote, G.; Smith, J.; Higgs, S.; Jones, A. Interoception and obesity: A systematic review and meta-analysis of the relationship between interoception and BMI. Int. J. Obes. 2021, 45, 2515–2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkeling, B.; King, N.A.; Näslund, E.; Blundell, J.E. Characterization of obese individuals who claim to detect no relationship between their eating pattern and sensations of hunger or fullness. Int. J. Obes. 2007, 31, 435–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodin, J. Causes and consequences of time perception differences in overweight and normal weight people. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 1975, 31, 898–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, T.L.; Ramirez, E.; Kwarteng, E.A.; Djan, K.G.; Faulkner, L.M.; Parker, M.N.; Yang, S.B.; Zenno, A.; Kelly, N.R.; Shank, L.M.; et al. Retrieval-induced forgetting in children and adolescents with and without obesity. Int. J. Obes. 2022, 46, 851–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, J.E.; Peterson, C.B. Anorexia Nervosa. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1343–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collantoni, E.; Tenconi, E.; Solmi, M.; Meneguzzo, P.; Marzola, E.; D’Agata, F.; Gotti, S.; Daga, G.A.; Manara, R.; Favaro, A. Hippocampal volumes in anorexia nervosa at different stages of the disorder. Eur. Eat. Disord. Rev. J. Eat. Disord. Assoc. 2021, 29, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cucarella, J.; Tortajada, R.; Moreno, L. Neuropsychology and anorexia nervosa. Cognitive and radiological findings. Neurologia 2012, 27, 504–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keeler, J.; Patsalos, O.; Thuret, S.; Ehrlich, S.; Tchanturia, K.; Himmerich, H.; Treasure, J. Hippocampal volume, function, and related molecular activity in anorexia nervosa: A scoping review. Expert Rev. Clin. Pharmacol. 2020, 13, 1367–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halmi, K.A.; Sunday, S.; Puglisi, A.; Marchi, P. Hunger and satiety in anorexia and bulimia nervosa. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1989, 575, 431–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halmi, K.A.; Sunday, S.R. Temporal patterns of hunger and fullness ratings and related cognitions in anorexia and bulimia. Appetite 1991, 16, 219–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herpertz, S.; Moll, A.; Gizewski, E.; Tagay, S.; Senf, W. Störung des Hunger- und Sättigungsempfindens bei restriktiver Anorexia nervosa [Distortion of hunger and satiation in patients with restrictive anorexia nervosa]. Psychother. Psychosom. Med. Psychol. 2008, 58, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klastrup, C.; Frølich, J.; Winkler, L.A.; Støving, R.K. Hunger and satiety perception in patients with severe anorexia nervosa. Eat. Weight. Disord. 2020, 25, 1347–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norris, M.L.; Harrison, M.E.; Isserlin, L.; Robinson, A.; Feder, S.; Sampson, M. Gastrointestinal complications associated with anorexia nervosa: A systematic review. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2016, 49, 216–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkinson, P.M.; Taylor, L.; Laws, K.R. Self-reported interoceptive deficits in eating disorders: A meta-analysis of studies using the eating disorder inventory. J. Psychosom. Res. 2018, 110, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garfinkel, P.E. Perception of hunger and satiety in anorexia nervosa. Psychol. Med. 1974, 4, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakai, Y.; Koh, T. Perception of hunger to insulin-induced hypoglycemia in anorexia nervosa. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2001, 29, 354–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silverstone, J.T.; Russell, G.F. Gastric “hunger” contractions in anorexia nervosa. Br. J. Psychiatry J. Ment. Sci. 1967, 113, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, M.C. Hippocampal Sclerosis: Causes and Prevention. Semin. Neurol. 2015, 35, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kramer, C.K.; Leitão, C.B.; Pinto, L.C.; Canani, L.H.; Azevedo, M.J.; Gross, J.L. Efficacy and safety of topiramate on weight loss: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Obes. Rev. 2011, 12, e338–e347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Wu, X.; Zhang, B.; Shen, S.; He, L.; Zhou, D. Associations of overweight and obesity with drug-resistant epilepsy. Seizure 2021, 92, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulton, J.J.; Calhoun, P.S.; Wagner, H.R.; Schry, A.R.; Hair, L.P.; Feeling, N.; Elbogen, E.; Beckham, J.C. The prevalence of posttraumatic stress disorder in Operation Enduring Freedom/Operation Iraqi Freedom (OEF/OIF) Veterans: A meta-analysis. J. Anxiety Disord. 2015, 31, 98–107. [Google Scholar]
- Kamiya, K.; Abe, O. Imaging of Posttraumatic Stress Disorder. Neuroimaging Clin. N. Am. 2020, 30, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masodkar, K.; Johnson, J.; Peterson, M.J. A Review of Posttraumatic Stress Disorder and Obesity: Exploring the Link. Prim. Care Companion CNS Disord. 2016, 18, 22710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmisano, G.L.; Innamorati, M.; Vanderlinden, J. Life adverse experiences in relation with obesity and binge eating disorder: A systematic review. J. Behav. Addict. 2016, 5, 11–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessler, R.M.; Hutson, P.H.; Herman, B.K.; Potenza, M.N. The neurobiological basis of binge-eating disorder. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2016, 63, 223–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, S.L.; Holton, K.F. Post-traumatic stress disorder may set the neurobiological stage for eating disorders: A focus on glutamatergic dysfunction. Appetite 2021, 167, 105599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhikav, V.; Anand, K.S. Is hippocampal atrophy a future drug target? Med. Hypotheses 2007, 68, 1300–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, H.H.; Fabricius, K.; Barkholt, P.; Niehoff, M.L.; Morley, J.E.; Jelsing, J.; Pyke, C.; Knudsen, L.B.; Farr, S.A.; Vrang, N. The GLP-1 Receptor Agonist Liraglutide Improves Memory Function and Increases Hippocampal CA1 Neuronal Numbers in a Senescence-Accelerated Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2015, 46, 877–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verrotti, A.; D’Egidio, C.; Mohn, A.; Coppola, G.; Chiarelli, F. Weight gain following treatment with valproic acid: Pathogenetic mechanisms and clinical implications. Obes. Rev. Off. J. Int. Assoc. Study Obes. 2011, 12, e32–e43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, S.N.; Yan, Y.H.; Zhu, T.L.; Ma, B.K.; Fan, H.R.; Liu, Y.M.; Li, W.G.; Li, F. Long-Term NMDAR Antagonism Correlates Weight Loss with Less Eating. Front. Psychiatry 2019, 10, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michelson, D.; Amsterdam, J.D.; Quitkin, F.M.; Reimherr, F.W.; Rosenbaum, J.F.; Zajecka, J.; Sundell, K.L.; Kim, Y.; Beasley, C.M., Jr. Changes in weight during a 1-year trial of fluoxetine. Am. J. Psychiatry 1999, 156, 1170–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eren-Yazicioglu, C.Y.; Yigit, A.; Dogruoz, R.E.; Yapici-Eser, H. Can GLP-1 Be a Target for Reward System Related Disorders? A Qualitative Synthesis and Systematic Review Analysis of Studies on Palatable Food, Drugs of Abuse, and Alcohol. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2021, 14, 614884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, S.; Sample, C.H.; Davidson, T.L. The effects of a GLP-1 analog liraglutide on reward value and the learned inhibition of appetitive behavior in male and female rats. Int. J. Obes. 2019, 43, 1875–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, B.P.; Roberts, J.L.; Fogarty, K.V.; Reynolds, K.A.; Jonas, J.M.; Hudson, J.I. Memantine in the treatment of binge eating disorder: An open-label, prospective trial. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2008, 41, 520–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaefer, J.; Magnuson, A. A review of interventions that promote eating by internal cues. J. Am. Acad. Diet. 2014, 114, 734–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tribole, E.; Resch, E. Intuitive Eating: A Revolutionary Program that Works; St Martin’s Griffin: New York, NY, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Assanand, S.; Pinel, J.; Lehman, D. Personal theories of hunger and eating. J. Appl. Soc. Psychol. 1998, 28, 998–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutelle, K.N.; Zucker, N.L.; Peterson, C.B.; Rydell, S.A.; Cafri, G.; Harnack, L. Two novel treatments to reduce overeating in overweight children: A randomized controlled trial. J. Consult. Clin. Psychol. 2011, 79, 759–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arjmand, G.; Abbas-Zadeh, M.; Eftekhari, M.H. Effect of MIND diet intervention on cognitive performance and brain structure in healthy obese women: A randomized controlled trial. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 2871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dias, G.P.; Cavegn, N.; Nix, A.; do Nascimento Bevilaqua, M.C.; Stangl, D.; Zainuddin, M.S.; Nardi, A.E.; Gardino, P.F.; Thuret, S. The role of dietary polyphenols on adult hippocampal neurogenesis: Molecular mechanisms and behavioural effects on depression and anxiety. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2012, 2012, 541971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgs, S. Memory for recent eating and its influence on subsequent food intake. Appetite 2002, 39, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgs, S.; Williamson, A.C.; Attwood, A.S. Recall of recent lunch and its effect on subsequent snack intake. Physiol. Behav. 2008, 94, 454–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parent, M.B.; Higgs, S.; Cheke, L.G.; Kanoski, S.E. Memory and eating: A bidirectional relationship implicated in obesity. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2022, 132, 110–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, D.A.N.; Gattas, S.; Salgado, J.S.; Kuijper, F.M.; Wang, A.R.; Huang, Y.; Kakusa, B.; Leuze, C.; Luczak, A.; Rapp, P.; et al. An orexigenic subnetwork within the human hippocampus. Nature 2023, 621, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.-Q.; Chen, H.; Quon, M.J.; Alkon, D.L. Insulin and the insulin receptor in experimental models of learning and memory. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2004, 490, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lathe, R. Hormones and the hippocampus. J. Endocrinol. 2001, 169, 205–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knierim, J.J. The hippocampus. Curr. Biol. 2015, 25, R1116–R1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binicewicz, F.Z.M.; van Strien, N.M.; Wadman, W.J.; van den Heuvel, M.P.; Cappaert, N.L.M. Graph analysis of the anatomical network organization of the hippocampal formation and parahippocampal region in the rat. Brain Struct. Funct. 2016, 221, 1607–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zaidi, A.; Pal, R.; Garrett, A.S.; Braceras, R.; Chen, X.W.; Michaelis, M.L.; Michaelis, E.K. Genomic and biochemical approaches in the discovery of mechanisms for selective neuronal vulnerability to oxidative stress. BMC Neurosci. 2009, 10, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.T.; Lin, C.; Hsu, C.T.; Wang, T.F.; Ke, F.Y.; Kuo, Y.M. Differential distribution and activation of microglia in the brain of male C57BL/6J mice. Brain Struct. Funct. 2013, 218, 1051–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvajal, F.J.; Mattison, H.A.; Cerpa, W. Role of NMDA Receptor-Mediated Glutamatergic Signaling in Chronic and Acute Neuropathologies. Neural Plast. 2016, 2016, 2701526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sternson, S.M.; Eiselt, A.K. Three Pillars for the Neural Control of Appetite. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2017, 79, 401–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wynne, K.; Stanley, S.; McGowan, B.; Bloom, S. Appetite control. J. Endocrinol. 2005, 184, 291–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Hernandez-Sanchez, D.; Herzog, H. Regulation of feeding-related behaviors by arcuate neuropeptide Y neurons. Endocrinology 2019, 160, 1411–1420. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, S.; Chen, H.; Weingarth, D.; Trumbauer, M.E.; Novi, D.E.; Guan, X.; Yu, H.; Shen, Z.; Feng, Y.; Frazier, E.; et al. Neither agouti-related protein nor neuropeptide Y is critically required for the regulation of energy homeostasis in mice. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2002, 22, 5027–5035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgs, S. Memory and its role in appetite regulation. Physiol. Behav. 2005, 85, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stevenson, R.J.; Boutelle, K. Hunger, Satiety, and Their Vulnerabilities. Nutrients 2024, 16, 3013. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16173013
Stevenson RJ, Boutelle K. Hunger, Satiety, and Their Vulnerabilities. Nutrients. 2024; 16(17):3013. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16173013
Chicago/Turabian StyleStevenson, Richard J., and Kerri Boutelle. 2024. "Hunger, Satiety, and Their Vulnerabilities" Nutrients 16, no. 17: 3013. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16173013
APA StyleStevenson, R. J., & Boutelle, K. (2024). Hunger, Satiety, and Their Vulnerabilities. Nutrients, 16(17), 3013. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16173013






