Effects of Supplementation with a Microalgae Extract from Phaeodactylum tricornutum Containing Fucoxanthin on Cognition and Markers of Health in Older Individuals with Perceptions of Cognitive Decline
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Research Design
2.2. Study Participants
2.3. Testing Sequence
2.4. Participant Familiarization Session
2.5. Randomization
2.6. Supplementation Protocol
3. Procedures
3.1. Cognitive Screening
3.2. Diet Assessment
3.3. Anthropometrics and Hemodynamics
3.4. Cognitive Function Assessment
3.5. Light Reaction Test Assessment
3.6. Stress, Sleep, and Mood Assessment
3.7. Blood Collection and Analysis
3.8. Side Effects Questionnaire
3.9. Statistical Analysis
4. Results
4.1. Participant Demographics
4.2. Cognitive Function Parameter Assessment
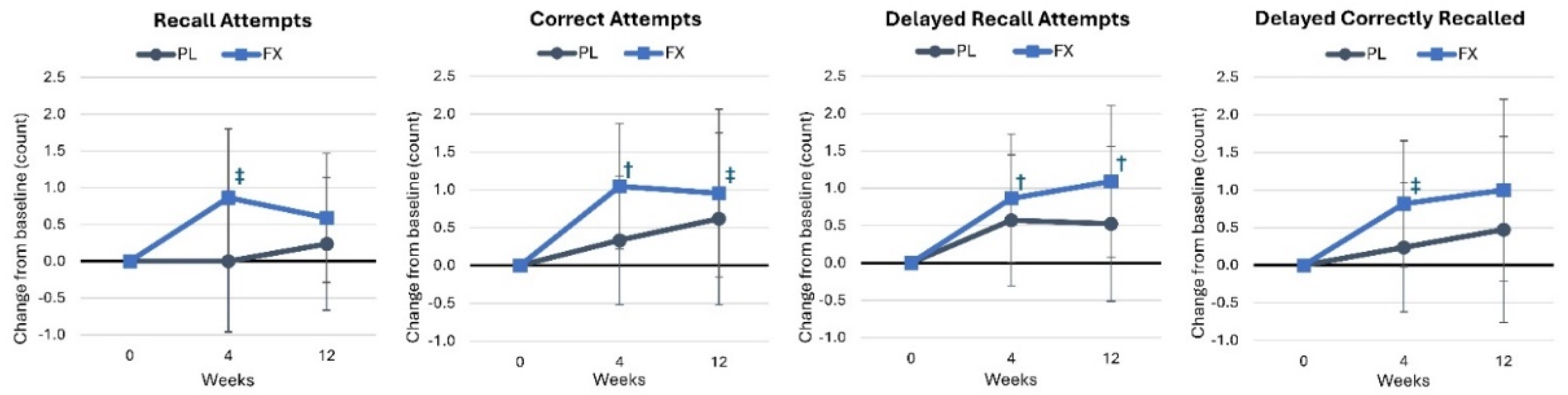
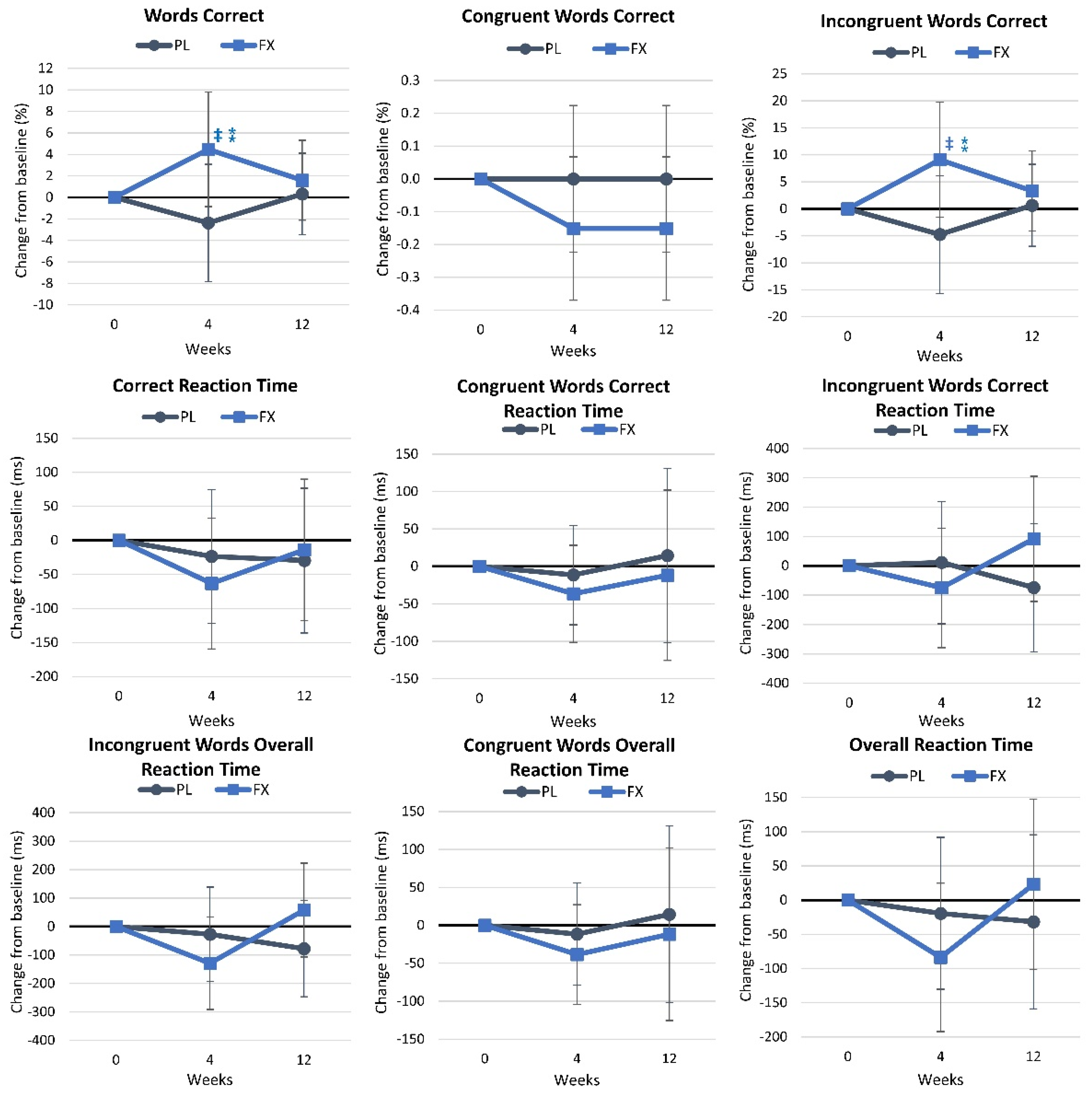
4.2.1. Word Recall
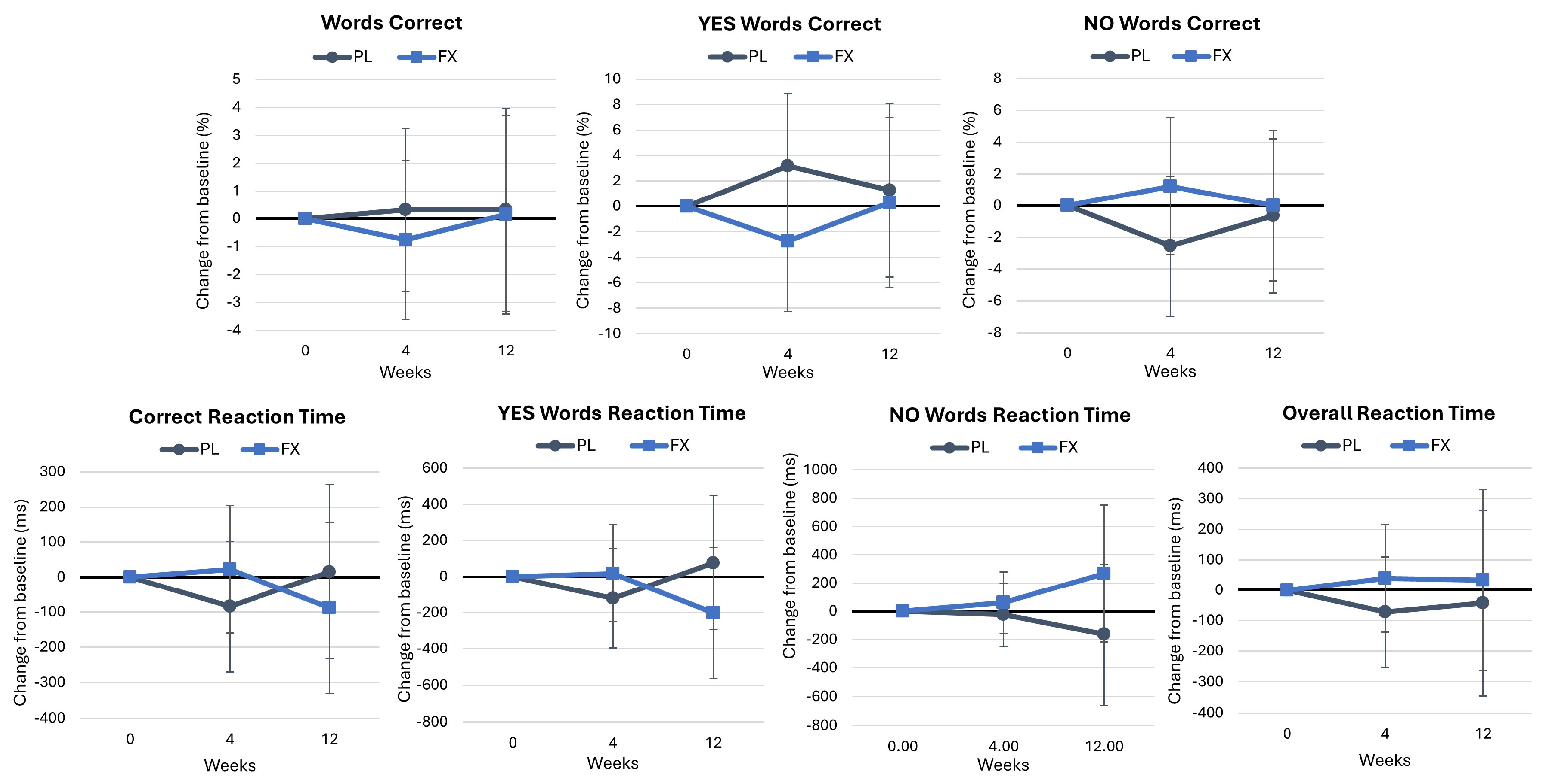
4.2.2. Word Recognition
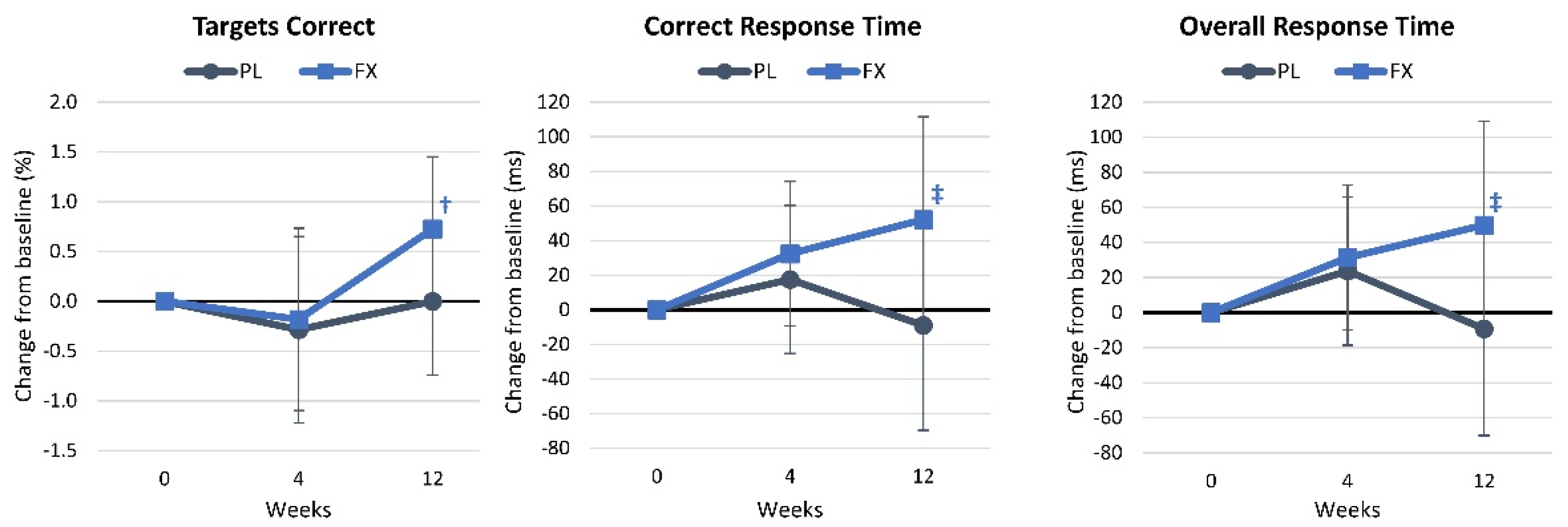
4.2.3. Choice Reaction Time
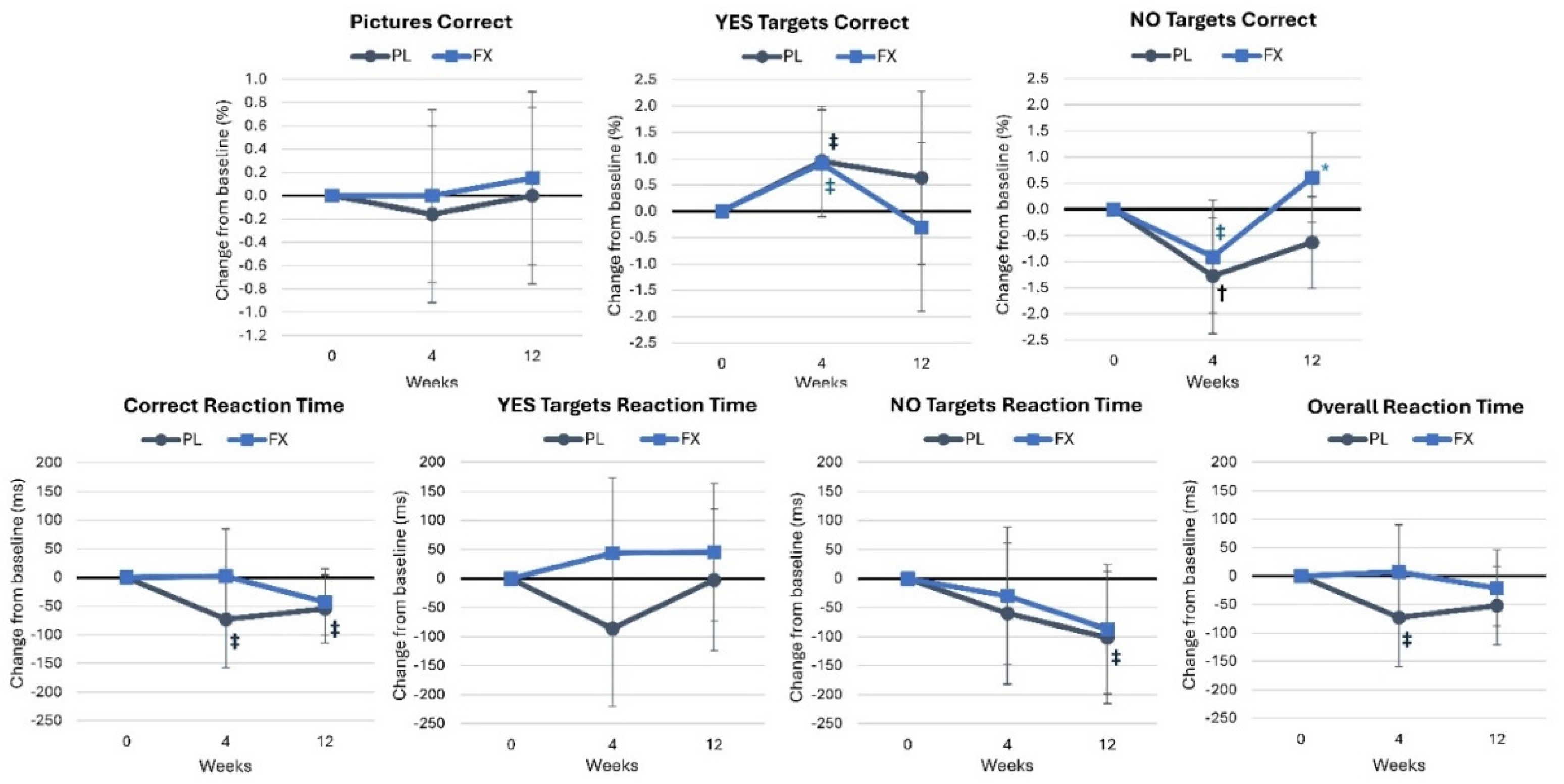
4.2.4. Picture Recognition Test
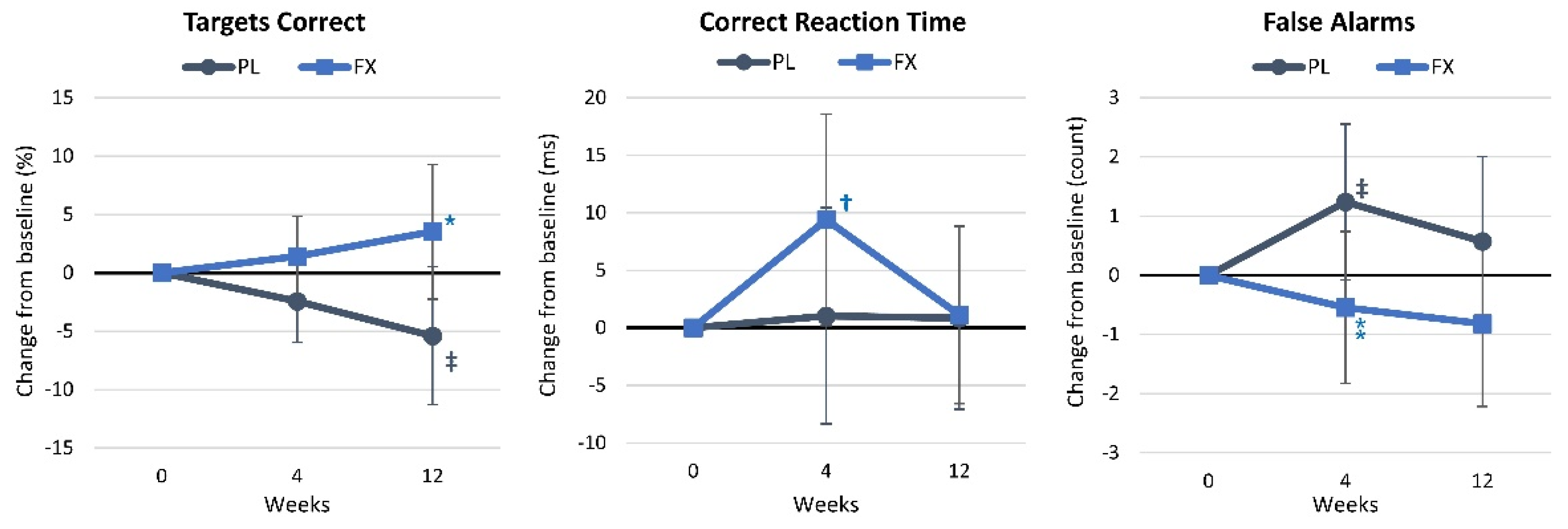
4.2.5. Digit Vigilance
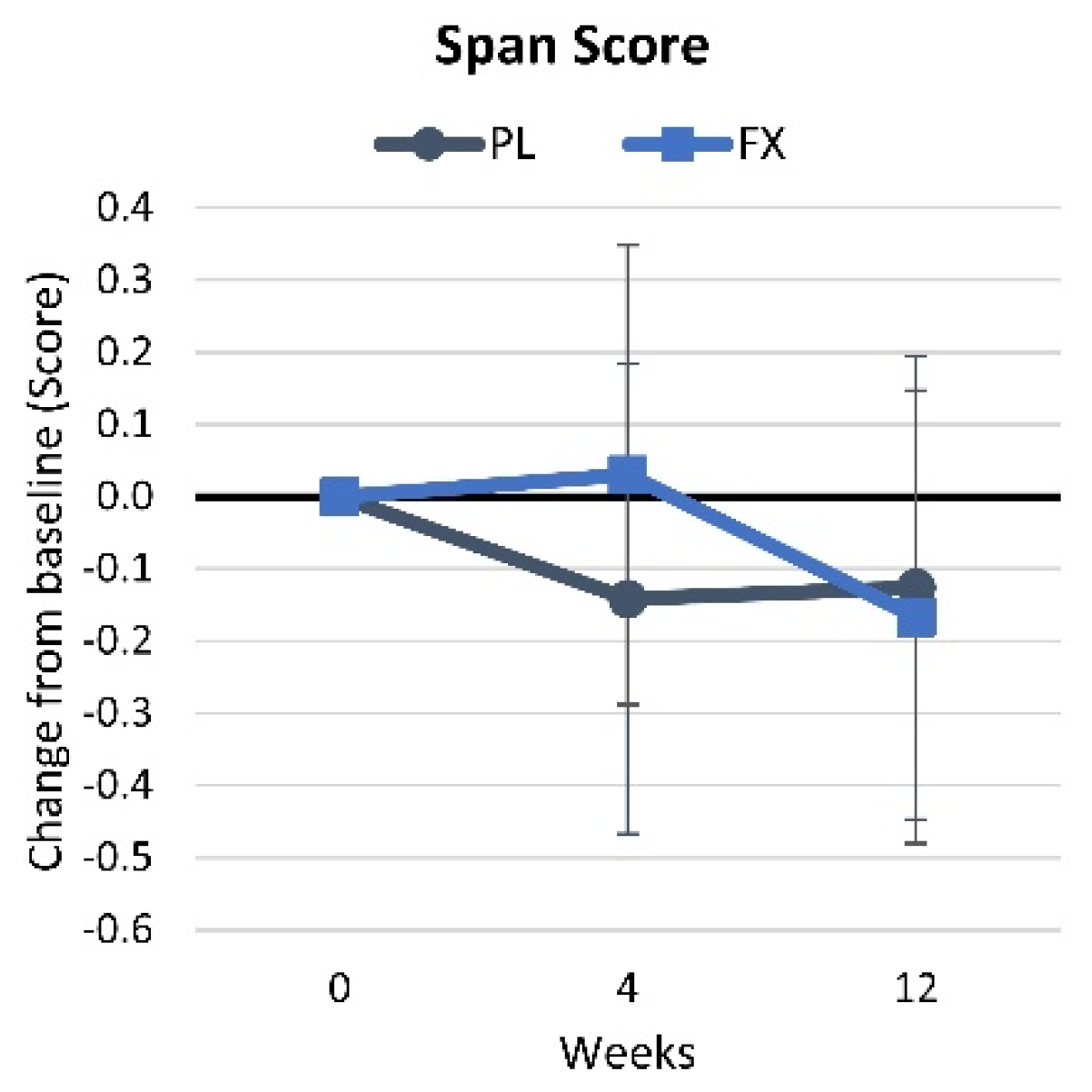
4.2.6. Corsi Block
4.2.7. Stroop Test
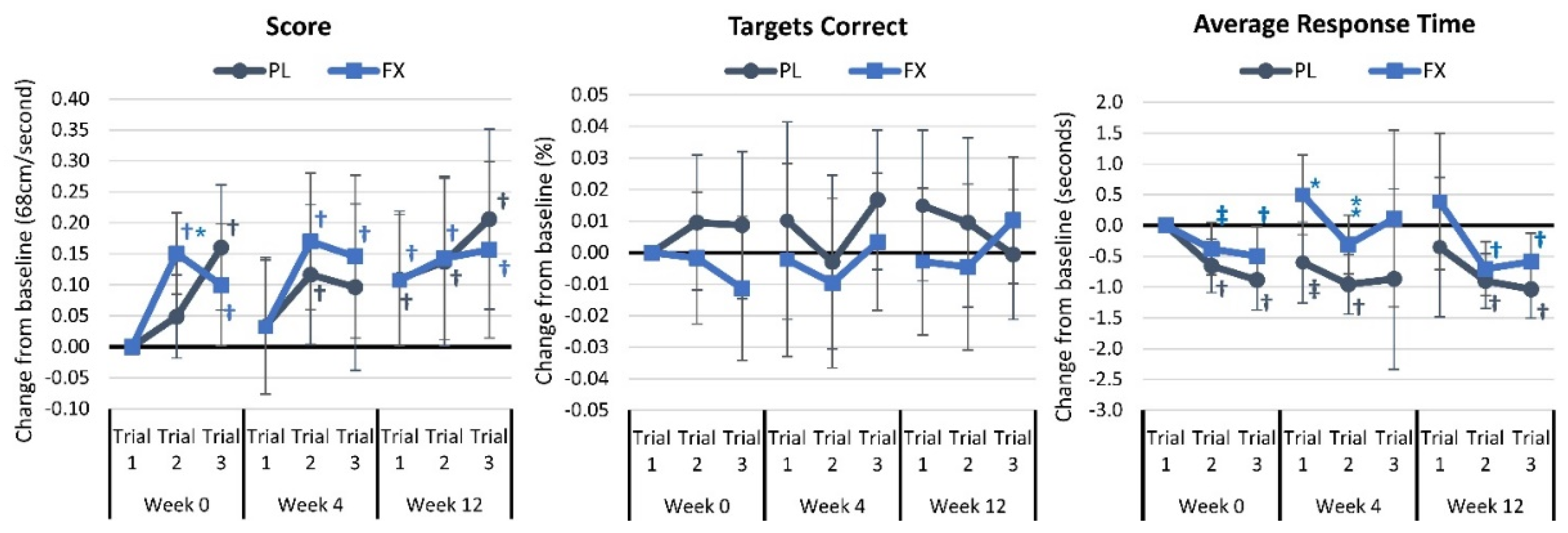
4.3. Light Reaction Test Results
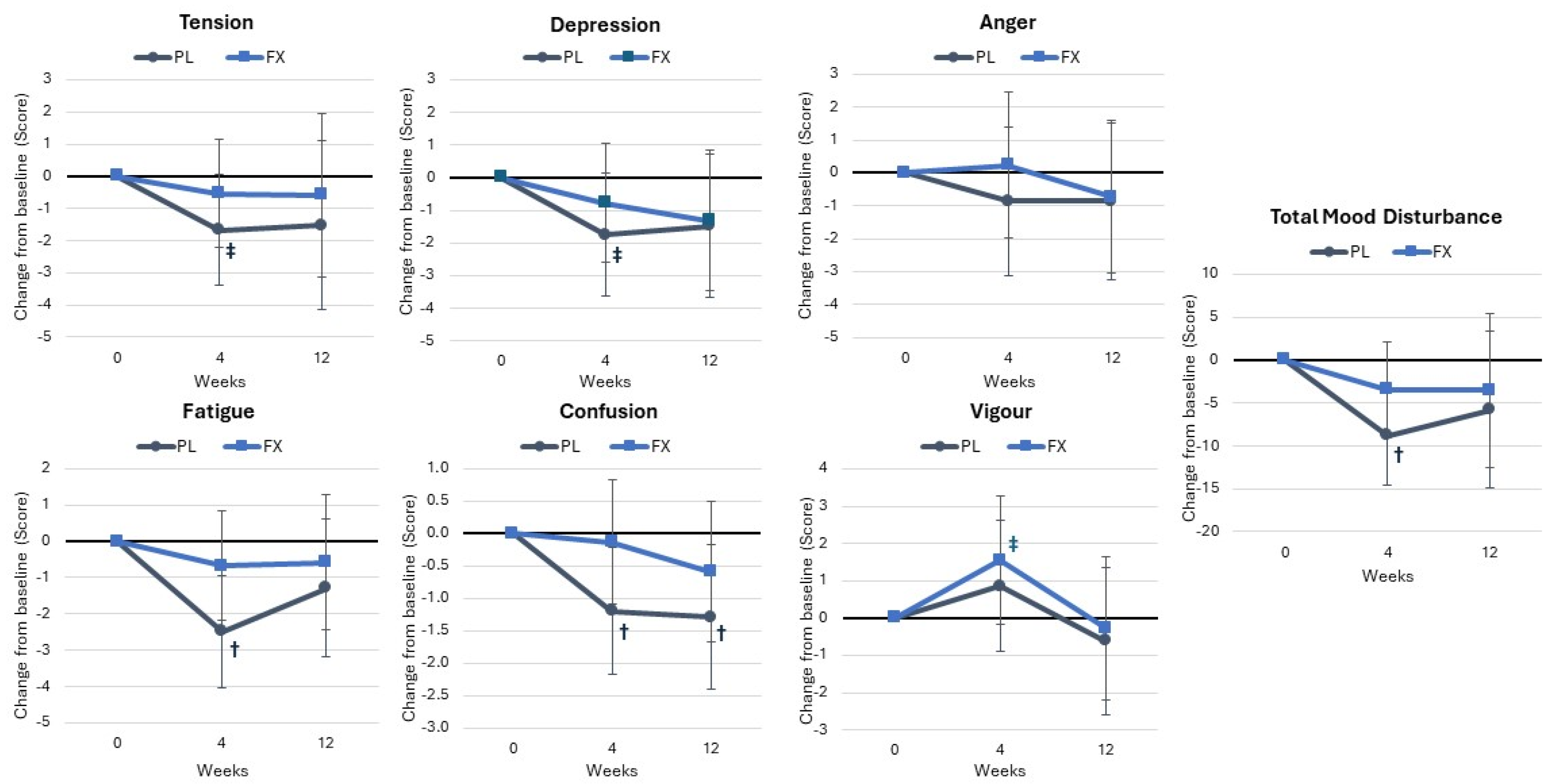
4.4. Psychological Assessment
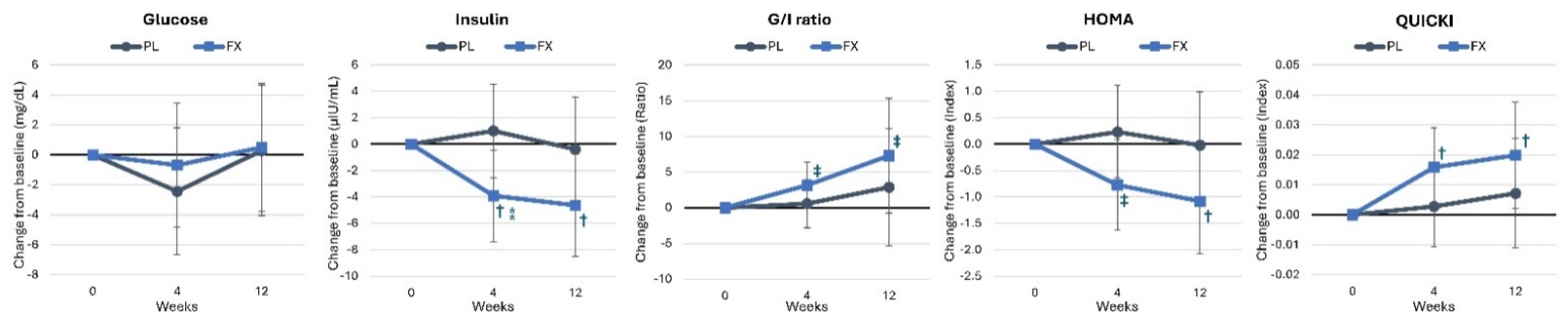
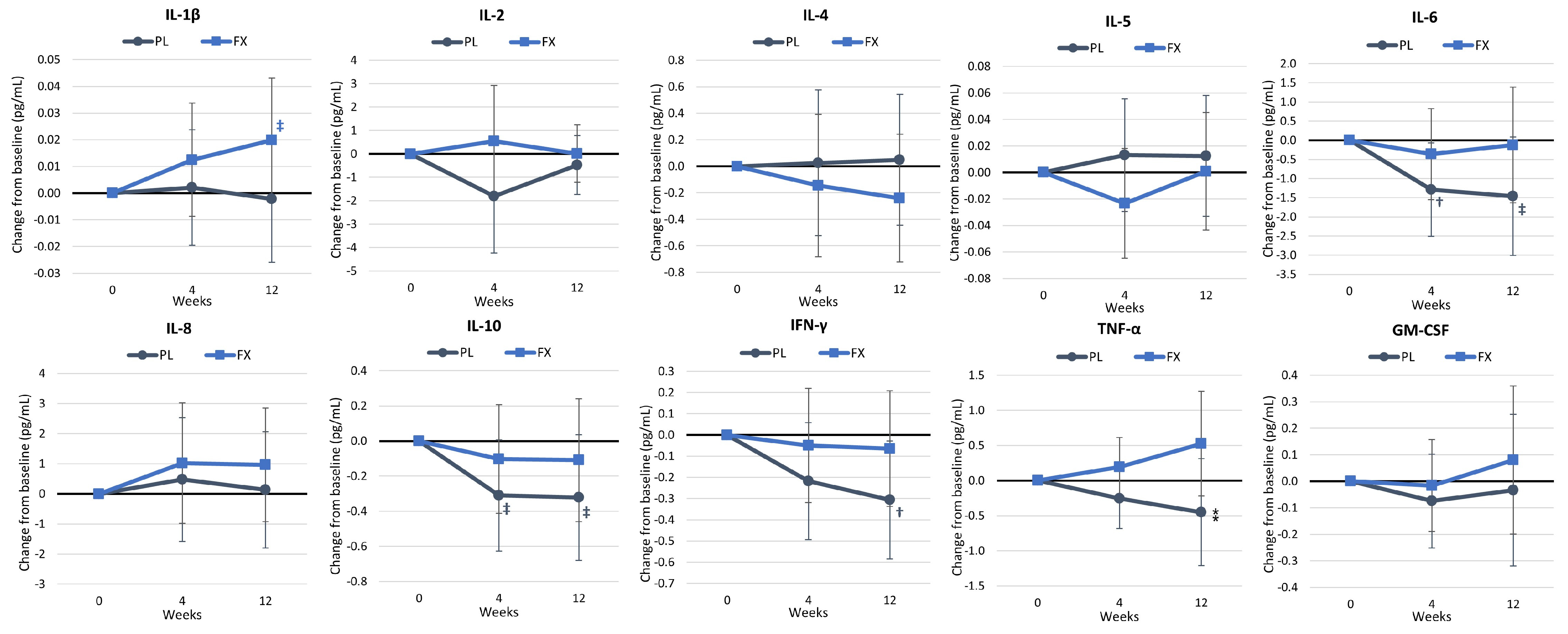
4.5. Health Biomarkers
4.6. Safety and Side Effects
5. Discussion
5.1. Primary Outcome
5.2. Secondary Outcomes
5.3. Limitations and Future Directions
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Glisky, E.L. Changes in cognitive function in human aging. Brain Aging Models Methods Mech. 2007, 1, 3–20. [Google Scholar]
- Salthouse, T. Consequences of age-related cognitive declines. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2012, 63, 201–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idowu, M.I.; Szameitat, A.J.; Parton, A. The assessment of executive function abilities in healthy and neurodegenerative aging-A selective literature review. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2024, 16, 1334309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; He, H.; Chen, Y.; Guan, Q. Effects of engagement, persistence and adherence on cognitive training outcomes in older adults with and without cognitive impairment: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Age Ageing 2024, 53, afad247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juan, S.M.; Adlard, P.A. Ageing and cognition. In Biochemistry and Cell Biology of Ageing: Part II Clinical Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 107–122. [Google Scholar]
- Freemantle, E.; Vandal, M.; Tremblay-Mercier, J.; Tremblay, S.; Blachère, J.-C.; Bégin, M.E.; Brenna, J.T.; Windust, A.; Cunnane, S.C. Omega-3 fatty acids, energy substrates, and brain function during aging. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fat. Acids 2006, 75, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritter, A.; Pillai, J.A. Treatment of Vascular Cognitive Impairment. Curr. Treat. Options Neurol. 2015, 17, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Rodriguez, S.; Canet-Vintro, M.; Wee, S.O.; Rodriguez-Sanz, J.; Lopez-de-Celis, C.; Oviedo, G.R.; Labata-Lezaun, N.; Perez-Bellmunt, A. Cognitive Enhancement Strategies for Older Adults: An Evaluation of Different Training Modalities to Improve Executive Function-A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhou, C.; Chen, A. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the effects of physical exercise on white matter integrity and cognitive function in older adults. Geroscience 2024, 46, 2641–2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, P.J.; Whitson, H.E.; Merwin, R.M.; O’Hayer, C.V.; Strauman, T.J. Engineering Virtuous health habits using Emotion and Neurocognition: Flexibility for Lifestyle Optimization and Weight management (EVEN FLOW). Front. Aging Neurosci. 2023, 15, 1256430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andlin-Sobocki, P.; Jonsson, B.; Wittchen, H.-U.; Olesen, J. Costs of Disorders of the Brain in Europe; Blackwell Science: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Martinez-Lapiscina, E.H.; Clavero, P.; Toledo, E.; San Julian, B.; Sanchez-Tainta, A.; Corella, D.; Lamuela-Raventos, R.M.; Martinez, J.A.; Martinez-Gonzalez, M.A. Virgin olive oil supplementation and long-term cognition: The PREDIMED-NAVARRA randomized, trial. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2013, 17, 544–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardelo, M.P.; Corina, A.; Leon-Acuna, A.; Quintana-Navarro, G.M.; Alcala-Diaz, J.F.; Rangel-Zuniga, O.A.; Camargo, A.; Conde-Gavilan, C.; Carmona-Medialdea, C.; Vallejo-Casas, J.A.; et al. Effect of the Mediterranean diet and probiotic supplementation in the management of mild cognitive impairment: Rationale, methods, and baseline characteristics. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 1037842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontifex, M.G.; Connell, E.; Le Gall, G.; Lang, L.; Pourtau, L.; Gaudout, D.; Angeloni, C.; Zallocco, L.; Ronci, M.; Giusti, L.; et al. A novel Mediterranean diet-inspired supplement ameliorates cognitive, microbial, and metabolic deficits in a mouse model of low-grade inflammation. Gut Microbes 2024, 16, 2363011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhn, L.; MacIntyre, U.E.; Kotze, C.; Becker, P.J.; Wenhold, F.A.M. Twelve Weeks of Additional Fish Intake Improves the Cognition of Cognitively Intact, Resource-Limited Elderly People: A Randomized Control Trial. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2022, 26, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fekete, M.; Lehoczki, A.; Tarantini, S.; Fazekas-Pongor, V.; Csipo, T.; Csizmadia, Z.; Varga, J.T. Improving Cognitive Function with Nutritional Supplements in Aging: A Comprehensive Narrative Review of Clinical Studies Investigating the Effects of Vitamins, Minerals, Antioxidants, and Other Dietary Supplements. Nutrients 2023, 15, 5116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobe, T.; Witte, A.V.; Schnelle, A.; Lesemann, A.; Fabian, S.; Tesky, V.A.; Pantel, J.; Floel, A. Combined omega-3 fatty acids, aerobic exercise and cognitive stimulation prevents decline in gray matter volume of the frontal, parietal and cingulate cortex in patients with mild cognitive impairment. Neuroimage 2016, 131, 226–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuszewski, J.C.; Wong, R.H.X.; Howe, P.R.C. Effects of Long-Chain Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids on Endothelial Vasodilator Function and Cognition-Are They Interrelated? Nutrients 2017, 9, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, C.S.; Vidoni, E.D.; Burns, J.M.; Alwatban, M.R.; Billinger, S.A. Self-Reported Omega-3 Supplement Use Moderates the Association between Age and Exercising Cerebral Blood Flow Velocity in Older Adults. Nutrients 2020, 12, 697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puga, A.M.; Ruperto, M.; Samaniego-Vaesken, M.L.; Montero-Bravo, A.; Partearroyo, T.; Varela-Moreiras, G. Effects of Supplementation with Folic Acid and Its Combinations with Other Nutrients on Cognitive Impairment and Alzheimer’s Disease: A Narrative Review. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, J.; Li, J.; Qin, J.; Fan, Y.; Ren, P.; Hu, H.; Wu, W. Effects of folic acid supplementation on cognitive impairment: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J. Evid. Based Med. 2024, 17, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Li, Y.; Meng, X. Vitamin D and neurodegenerative diseases. Heliyon 2023, 9, e12877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocaturk, R.R.; Temizyurek, A.; Ozcan, O.O.; Erguzel, T.T.; Karahan, M.; Konuk, M.; Tarhan, N. Effect of nutritional supports on malnutrition, cognition, function and biomarkers of Alzheimer’s disease: A systematic review. Int. J. Neurosci. 2023, 133, 1355–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheltens, P.; Kamphuis, P.J.; Verhey, F.R.; Olde Rikkert, M.G.; Wurtman, R.J.; Wilkinson, D.; Twisk, J.W.; Kurz, A. Efficacy of a medical food in mild Alzheimer’s disease: A randomized, controlled trial. Alzheimers Dement. 2010, 6, 1–10.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onakpoya, I.J.; Heneghan, C.J. The efficacy of supplementation with the novel medical food, Souvenaid, in patients with Alzheimer’s disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Nutr. Neurosci. 2017, 20, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, J.J.; Caldwell, H.G.; Neudorf, H.; Ainslie, P.N.; Little, J.P. Short-term ketone monoester supplementation improves cerebral blood flow and cognition in obesity: A randomized cross-over trial. J. Physiol. 2021, 599, 4763–4778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pujol, A.; Sanchis, P.; Tamayo, M.I.; Nicolau, J.; Grases, F.; Espino, A.; Estremera, A.; Rigo, E.; Amengual, G.J.; Rodriguez, M.; et al. Oral phytate supplementation on the progression of mild cognitive impairment, brain iron deposition and diabetic retinopathy in patients with type 2 diabetes: A concept paper for a randomized double blind placebo controlled trial (the PHYND trial). Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1332237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solfrizzi, V.; Agosti, P.; Lozupone, M.; Custodero, C.; Schilardi, A.; Valiani, V.; Sardone, R.; Dibello, V.; Di Lena, L.; Lamanna, A.; et al. Nutritional Intervention as a Preventive Approach for Cognitive-Related Outcomes in Cognitively Healthy Older Adults: A Systematic Review. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2018, 64, S229–S254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, V.E.; Herrera, P.F.; Laura, R. Effect of nutrition on neurodegenerative diseases. A systematic review. Nutr. Neurosci. 2021, 24, 810–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGrattan, A.M.; McGuinness, B.; McKinley, M.C.; Kee, F.; Passmore, P.; Woodside, J.V.; McEvoy, C.T. Diet and inflammation in cognitive ageing and Alzheimer’s disease. Curr. Nutr. Rep. 2019, 8, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersson, S.D.; Philippou, E. Mediterranean Diet, Cognitive Function, and Dementia: A Systematic Review of the Evidence. Adv. Nutr. 2016, 7, 889–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, T.Y.; Dong, Q.; Cui, M. Emerging Links between Cerebral Blood Flow Regulation and Cognitive Decline: A Role for Brain Microvascular Pericytes. Aging Dis. 2023, 14, 1276–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartman, S.; Coppotelli, G.; Ross, J.M. Mitochondrial Dysfunction: A Key Player in Brain Aging and Diseases. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2024, 46, 1987–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, R.; Chan, A.K.Y.; Wu, J.; Lee, T.M.C. Relationships between Inflammation and Age-Related Neurocognitive Changes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tönnies, E.; Trushina, E. Oxidative stress, synaptic dysfunction, and Alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2017, 57, 1105–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Vorburger, R.; Scarmeas, N.; Luchsinger, J.A.; Manly, J.J.; Schupf, N.; Mayeux, R.; Brickman, A.M. Circulating inflammatory biomarkers in relation to brain structural measurements in a non-demented elderly population. Brain Behav. Immun. 2017, 65, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, H.; Fan, Y.; Gao, Y.; Li, X.; Hu, Z.; Ding, K.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X. Fucoxanthin provides neuroprotection in models of traumatic brain injury via the Nrf2-ARE and Nrf2-autophagy pathways. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 46763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, M.; Kim, M.B.; Park, Y.K.; Lee, J.Y. Health benefits of fucoxanthin in the prevention of chronic diseases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2020, 1865, 158618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Dong, J.; Gong, L.; Hong, Y.; Hu, C.; Bao, Y.; Chen, H.; Liu, L.; Huang, L.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Fucoxanthin, a marine derived carotenoid, attenuates surgery-induced cognitive impairments via activating Akt and ERK pathways in aged mice. Phytomedicine 2023, 120, 155043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maury, J.; Delbrut, A.; Villard, V.; Pradelles, R. A Standardized Extract of Microalgae Phaeodactylum tricornutum (Mi136) Inhibit D-Gal Induced Cognitive Dysfunction in Mice. Mar. Drugs 2024, 22, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, H.; Kanno, S.; Kodate, M.; Hosokawa, M.; Miyashita, K. Fucoxanthinol, metabolite of fucoxanthin, improves obesity-induced inflammation in adipocyte cells. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 4799–4813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.S.; Zheng, J.W.; Manabe, Y.; Hirata, T.; Sugawara, T. Anti-Obesity Properties of the Dietary Green Alga, Codium cylindricum, in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Mice. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 2018, 64, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, M.; Dordevic, A.L.; Cox, K.H.M.; Scholey, A.; Ryan, L.; Bonham, M.P. Study protocol for a double-blind randomised controlled trial investigating the impact of 12 weeks supplementation with a Fucus vesiculosus extract on cholesterol levels in adults with elevated fasting LDL cholesterol who are overweight or have obesity. BMJ Open 2018, 8, e022195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bermano, G.; Stoyanova, T.; Hennequart, F.; Wainwright, C.L. Seaweed-derived bioactives as potential energy regulators in obesity and type 2 diabetes. Adv. Pharmacol. 2020, 87, 205–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonard, M.; Maury, J.; Dickerson, B.; Gonzalez, D.E.; Kendra, J.; Jenkins, V.; Nottingham, K.; Yoo, C.; Xing, D.; Ko, J.; et al. Effects of Dietary Supplementation of a Microalgae Extract Containing Fucoxanthin Combined with Guarana on Cognitive Function and Gaming Performance. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickerson, B.; Maury, J.; Jenkins, V.; Nottingham, K.; Xing, D.; Gonzalez, D.E.; Leonard, M.; Kendra, J.; Ko, J.; Yoo, C.; et al. Effects of Supplementation with Microalgae Extract from Phaeodactylum tricornutum (Mi136) to Support Benefits from a Weight Management Intervention in Overweight Women. Nutrients 2024, 16, 990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, M.; Parkinson, L.; Gibson, R.; Schofield, P.; D’Este, C.; Attia, J.; Tavener, M.; Byles, J. Memory complaint questionnaire performed poorly as screening tool: Validation against psychometric tests and affective measures. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2012, 65, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, V.; Voci, S.M.; Mendes-Netto, R.S.; da Silva, D.G. The relative validity of a food record using the smartphone application MyFitnessPal. Nutr. Diet. 2018, 75, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, A.W.; Morgan, N.; Ward, D.; Tangney, C.; Alshurafa, N.; Van Horn, L.; Spring, B. Comparative Validity of Mostly Unprocessed and Minimally Processed Food Items Differs among Popular Commercial Nutrition Apps Compared with a Research Food Database. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2022, 122, 825–832.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, C.; Xing, D.; Gonzalez, D.E.; Jenkins, V.; Nottingham, K.; Dickerson, B.; Leonard, M.; Ko, J.; Lewis, M.H.; Faries, M.; et al. Paraxanthine provides greater improvement in cognitive function than caffeine after performing a 10-km run. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2024, 21, 2352779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoi, K.K.F.; Chan, J.Y.C.; Hirai, H.W.; Wong, A.; Mok, V.C.T.; Lam, L.C.W.; Kwok, T.C.Y.; Wong, S.Y.S. Recall Tests Are Effective to Detect Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of 108 Diagnostic Studies. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2017, 18, 807.e17–807.e29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levie, W.H.; Hathaway, S.N. Picture recognition memory: A review of research and theory. J. Vis. Verbal Languaging 1988, 8, 6–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, B.; Hunfalvay, M.; Murray, N.; Roberts, C.-M.; Bolte, T. Reliability of computerized eye-tracking reaction time tests in non-athletes, athletes, and individuals with traumatic brain injury. Optom. Vis. Perform. 2018, 6, 119–129. [Google Scholar]
- Wesnes, K.A.; Brooker, H.; Ballard, C.; McCambridge, L.; Stenton, R.; Corbett, A. Utility, reliability, sensitivity and validity of an online test system designed to monitor changes in cognitive function in clinical trials. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2017, 32, e83–e92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Paula, J.J.; Malloy-Diniz, L.F.; Romano-Silva, M.A. Reliability of working memory assessment in neurocognitive disorders: A study of the Digit Span and Corsi Block-Tapping tasks. Braz. J. Psychiatry 2016, 38, 262–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegrist, M. Test-Retest Reliability of Different Versions of the Stroop Test. J. Psychol. 1997, 131, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mumme, K.D.; Conlon, C.A.; von Hurst, P.R.; Jones, B.; Haskell-Ramsay, C.F.; de Seymour, J.V.; Stonehouse, W.; Heath, A.-L.M.; Coad, J.; Mugridge, O.; et al. Dietary patterns and cognitive function in older New Zealand adults: The REACH study. Eur. J. Nutr. 2022, 61, 1943–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wightman, E.L.; Jackson, P.A.; Spittlehouse, B.; Heffernan, T.; Guillemet, D.; Kennedy, D.O. The Acute and Chronic Cognitive Effects of a Sage Extract: A Randomized, Placebo Controlled Study in Healthy Humans. Nutrients 2021, 13, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sowinski, R.; Gonzalez, D.; Xing, D.; Yoo, C.; Jenkins, V.; Nottingham, K.; Dickerson, B.; Humphries, M.; Leonard, M.; Ko, J. Effects of inositol-enhanced bonded arginine silicate ingestion on cognitive and executive function in gamers. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.-H. Review of the psychometric evidence of the perceived stress scale. Asian Nurs. Res. 2012, 6, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrott, A.C.; Hindmarch, I. The Leeds Sleep Evaluation Questionnaire in psychopharmacological investigations—A review. Psychopharmacology 1980, 71, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.; Kim, S.; Kim, B.; Kim, I. Psychometric properties of the Korean versions of three sleep evaluation questionnaires. Clin. Nurs. Res. 2015, 24, 526–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.-M.; Snyder, M.; Krichbaum, K. Translation and equivalence: The Profile of Mood States Short Form in English and Chinese. Int. J. Nurs. Stud. 2002, 39, 619–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shacham, S. A Shortened Version of the Profile of Mood States. J. Personal. Assess. 1983, 47, 305–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grubic, T.J.; Sowinski, R.J.; Nevares, B.E.; Jenkins, V.M.; Williamson, S.L.; Reyes, A.G.; Rasmussen, C.; Greenwood, M.; Murano, P.S.; Earnest, C.P. Comparison of ingesting a food bar containing whey protein and isomalto-oligosaccharides to carbohydrate on performance and recovery from an acute bout of resistance-exercise and sprint conditioning: An open label, randomized, counterbalanced, crossover pilot study. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2019, 16, 34. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Collins, P.B.; Earnest, C.P.; Dalton, R.L.; Sowinski, R.J.; Grubic, T.J.; Favot, C.J.; Coletta, A.M.; Rasmussen, C.; Greenwood, M.; Kreider, R.B. Short-Term Effects of a Ready-to-Drink Pre-Workout Beverage on Exercise Performance and Recovery. Nutrients 2017, 9, 823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, Y.P.; Earnest, C.P.; Koozehchian, M.; Cho, M.; Barringer, N.; Walker, D.; Rasmussen, C.; Greenwood, M.; Murano, P.S.; Kreider, R.B. Effects of ingesting a pre-workout dietary supplement with and without synephrine for 8 weeks on training adaptations in resistance-trained males. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2017, 14, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, Y.P.; Earnest, C.P.; Koozehchian, M.; Galvan, E.; Dalton, R.; Walker, D.; Rasmussen, C.; Murano, P.S.; Greenwood, M.; Kreider, R.B. Effects of acute ingestion of a pre-workout dietary supplement with and without p-synephrine on resting energy expenditure, cognitive function and exercise performance. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2017, 14, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, E.R.; Ziegenfuss, T.; Kalman, D.; Kreider, R.; Campbell, B.; Wilborn, C.; Taylor, L.; Willoughby, D.; Stout, J.; Graves, B.S.; et al. International society of sports nutrition position stand: Caffeine and performance. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2010, 7, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagim, A.R.; Harty, P.S.; Tinsley, G.M.; Kerksick, C.M.; Gonzalez, A.M.; Kreider, R.B.; Arent, S.M.; Jager, R.; Smith-Ryan, A.E.; Stout, J.R.; et al. International society of sports nutrition position stand: Energy drinks and energy shots. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2023, 20, 2171314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minaei, S.; Rahimi, M.R.; Mohammadi, H.; Jourkesh, M.; Kreider, R.B.; Forbes, S.C.; Souza-Junior, T.P.; McAnulty, S.R.; Kalman, D. CYP1A2 Genotype Polymorphism Influences the Effect of Caffeine on Anaerobic Performance in Trained Males. Int. J. Sport. Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2022, 32, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, M.D.; Taylor, L.W.; Wismann, J.A.; Wilborn, C.D.; Kreider, R.B.; Willoughby, D.S. Effects of ingesting JavaFit Energy Extreme functional coffee on aerobic and anaerobic fitness markers in recreationally-active coffee consumers. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2007, 4, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowinski, R.J.; Grubic, T.J.; Dalton, R.L.; Schlaffer, J.; Reyes-Elrod, A.G.; Jenkins, V.M.; Williamson, S.; Rasmussen, C.; Murano, P.S.; Earnest, C.P.; et al. An Examination of a Novel Weight Loss Supplement on Anthropometry and Indices of Cardiovascular Disease Risk. J. Diet. Suppl. 2021, 18, 478–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, D.; Yoo, C.; Gonzalez, D.; Jenkins, V.; Nottingham, K.; Dickerson, B.; Leonard, M.; Ko, J.; Faries, M.; Kephart, W.; et al. Dose-Response of Paraxanthine on Cognitive Function: A Double Blind, Placebo Controlled, Crossover Trial. Nutrients 2021, 13, 4478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, C.; Xing, D.; Gonzalez, D.; Jenkins, V.; Nottingham, K.; Dickerson, B.; Leonard, M.; Ko, J.; Faries, M.; Kephart, W.; et al. Acute Paraxanthine Ingestion Improves Cognition and Short-Term Memory and Helps Sustain Attention in a Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Crossover Trial. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonard, M.; Dickerson, B.; Estes, L.; Gonzalez, D.E.; Jenkins, V.; Johnson, S.; Xing, D.; Yoo, C.; Ko, J.; Purpura, M.; et al. Acute and Repeated Ashwagandha Supplementation Improves Markers of Cognitive Function and Mood. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, D.; Yoo, C.; Gonzalez, D.; Jenkins, V.; Nottingham, K.; Dickerson, B.; Leonard, M.; Ko, J.; Faries, M.; Kephart, W.; et al. Effects of Acute Ashwagandha Ingestion on Cognitive Function. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 11852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Earnest, C.P.; Roberts, B.M.; Harnish, C.R.; Kutz, J.L.; Cholewa, J.M.; Johannsen, N.M. Reporting Characteristics in Sports Nutrition. Sports 2018, 6, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hopkins, W.G.; Marshall, S.W.; Batterham, A.M.; Hanin, J. Progressive statistics for studies in sports medicine and exercise science. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2009, 41, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, P. Beyond statistical significance: Clinical interpretation of rehabilitation research literature. Int. J. Sports Phys. Ther. 2014, 9, 726. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, H. Statistical significance or clinical significance? A researcher’s dilemma for appropriate interpretation of research results. Saudi J. Anaesth. 2021, 15, 431–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H. The prevention and handling of the missing data. Korean J. Anesthesiol. 2013, 64, 402–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintero, M.; Aera, L. Missing Data Imputation for Ordinal Data. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2018, 181, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, M.J.; Kim, K.; Park, Y.H.; Kim, S. The validity and reliability of the mini-mental state examination-2 for detecting mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease in a Korean population. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0163792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albert, M.S.; DeKosky, S.T.; Dickson, D.; Dubois, B.; Feldman, H.H.; Fox, N.C.; Gamst, A.; Holtzman, D.M.; Jagust, W.J.; Petersen, R.C. The diagnosis of mild cognitive impairment due to Alzheimer’s disease: Recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease. Focus 2013, 11, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royall, D.R.; Lauterbach, E.C.; Cummings, J.L.; Reeve, A.; Rummans, T.A.; Kaufer, D.I.; LaFrance, W.C., Jr.; Coffey, C.E. Executive control function: A review of its promise and challenges for clinical research. A report from the Committee on Research of the American Neuropsychiatric Association. J. Neuropsychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2002, 14, 377–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puri, S.; Shaheen, M.; Grover, B. Nutrition and cognitive health: A life course approach. Front. Public Health 2023, 11, 1023907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastasiou, C.A.; Yannakoulia, M.; Kosmidis, M.H.; Dardiotis, E.; Hadjigeorgiou, G.M.; Sakka, P.; Arampatzi, X.; Bougea, A.; Labropoulos, I.; Scarmeas, N. Mediterranean diet and cognitive health: Initial results from the Hellenic Longitudinal Investigation of Ageing and Diet. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0182048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, B.; Adair, L.S.; Plassman, B.L.; Batis, C.; Edwards, L.J.; Popkin, B.M.; Mendez, M.A. Dietary Patterns and Cognitive Decline Among Chinese Older Adults. Epidemiology 2015, 26, 758–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zbeida, M.; Goldsmith, R.; Shimony, T.; Vardi, H.; Naggan, L.; Shahar, D.R. Mediterranean diet and functional indicators among older adults in non-Mediterranean and Mediterranean countries. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2014, 18, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Lapiscina, E.H.; Clavero, P.; Toledo, E.; Estruch, R.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; San Julián, B.; Sanchez-Tainta, A.; Ros, E.; Valls-Pedret, C.; Martinez-Gonzalez, M. Mediterranean diet improves cognition: The PREDIMED-NAVARRA randomised trial. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2013, 84, 1318–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Scott, T.; Gao, X.; Maras, J.E.; Bakun, P.J.; Tucker, K.L. Mediterranean Diet, Healthy Eating Index 2005, and Cognitive Function in Middle-Aged and Older Puerto Rican Adults. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2013, 113, 276–281.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wengreen, H.; Munger, R.G.; Cutler, A.; Quach, A.; Bowles, A.; Corcoran, C.; Tschanz, J.T.; Norton, M.C.; Welsh-Bohmer, K.A. Prospective study of Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension– and Mediterranean-style dietary patterns and age-related cognitive change: The Cache County Study on Memory, Health and Aging123. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 98, 1263–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsivgoulis, G.; Judd, S.; Letter, A.J.; Alexandrov, A.V.; Howard, G.; Nahab, F.; Unverzagt, F.W.; Moy, C.; Howard, V.J.; Kissela, B.; et al. Adherence to a Mediterranean diet and risk of incident cognitive impairment. Neurology 2013, 80, 1684–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scarmeas, N.; Stern, Y.; Mayeux, R.; Manly, J.J.; Schupf, N.; Luchsinger, J.A. Mediterranean Diet and Mild Cognitive Impairment. Arch. Neurol. 2009, 66, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Y.; Brickman, A.M.; Stern, Y.; Habeck, C.G.; Razlighi, Q.R.; Luchsinger, J.A.; Manly, J.J.; Schupf, N.; Mayeux, R.; Scarmeas, N. Mediterranean diet and brain structure in a multiethnic elderly cohort. Neurology 2015, 85, 1744–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.; Wu, T.; Zhao, J.; Han, F.; Marseglia, A.; Liu, H.; Huang, G. Effects of 6-Month Folic Acid Supplementation on Cognitive Function and Blood Biomarkers in Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Randomized Controlled Trial in China. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2016, 71, 1376–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.; Hu, J.; Huo, X.; Miao, R.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, F. Effects of vitamin D supplementation on cognitive function and blood Abeta-related biomarkers in older adults with Alzheimer’s disease: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2019, 90, 1347–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thaung Zaw, J.J.; Howe, P.R.; Wong, R.H. Long-term effects of resveratrol on cognition, cerebrovascular function and cardio-metabolic markers in postmenopausal women: A 24-month randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover study. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 820–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foroumandi, E.; Javan, R.; Moayed, L.; Fahimi, H.; Kheirabadi, F.; Neamatshahi, M.; Shogofteh, F.; Zarghi, A. The effects of fenugreek seed extract supplementation in patients with Alzheimer’s disease: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Phytother. Res. 2023, 37, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahar-Fuchs, A.; Clare, L.; Woods, B. Cognitive training and cognitive rehabilitation for mild to moderate Alzheimer’s disease and vascular dementia. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2013, 2013, CD003260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima-Silva, T.B.; Fabrício, A.T.; Silva, L.; de Oliveira, G.M.; da Silva, W.T.; Kissaki, P.T.; da Silva, A.P.F.; Sasahara, T.F.; Ordonez, T.N.; de Oliveira, T.B.; et al. Training of executive functions in healthy elderly: Results of a pilot study. Dement. Neuropsychol. 2012, 6, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Craik, F.I.; Bialystok, E. Brain changes in development and aging. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2006, 3, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenwood, P.M. Functional plasticity in cognitive aging: Review and hypothesis. Neuropsychology 2007, 21, 657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, B.; O’Neill, G.; Abu-Ghannam, N. Potential Psychoactive Effects of Microalgal Bioactive Compounds for the Case of Sleep and Mood Regulation: Opportunities and Challenges. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chartier-Kastler, E.; Davidson, K. Evaluation of quality of life and quality of sleep in clinical practice. Eur. Urol. Suppl. 2007, 6, 576–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrov, K.K.; Hayley, A.; Catchlove, S.; Savage, K.; Stough, C. Is poor self-rated sleep quality associated with elevated systemic inflammation in healthy older adults? Mech. Ageing Dev. 2020, 192, 111388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackwell, T.; Yaffe, K.; Ancoli-Israel, S.; Schneider, J.L.; Cauley, J.A.; Hillier, T.A.; Fink, H.A.; Stone, K.L. Poor sleep is associated with impaired cognitive function in older women: The study of osteoporotic fractures. J. Gerontol. Ser. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2006, 61, 405–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.Q.; Jiang, C.Q.; Xu, L.; Zhang, W.S.; Zhu, F.; Jin, Y.L.; Thomas, G.N.; Lam, T.H. Sleep quality and cognitive impairment in older Chinese: Guangzhou Biobank Cohort Study. Age Ageing 2020, 49, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hita-Yanez, E.; Atienza, M.; Cantero, J.L. Polysomnographic and subjective sleep markers of mild cognitive impairment. Sleep. 2013, 36, 1327–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavitsky, K.; Neargarder, S.; Bogdanova, Y.; McNamara, P.; Cronin-Golomb, A. The impact of sleep quality on cognitive functioning in Parkinson’s disease. J. Int. Neuropsychol. Soc. 2012, 18, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moskalev, A.; Shaposhnikov, M.; Zemskaya, N.; Belyi, A.; Dobrovolskaya, E.; Patova, A.; Guvatova, Z.; Lukyanova, E.; Snezhkina, A.; Kudryavtseva, A. Transcriptome analysis reveals mechanisms of geroprotective effects of fucoxanthin in Drosophila. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, H.; Hosokawa, M.; Sashima, T.; Funayama, K.; Miyashita, K. Fucoxanthin from edible seaweed, Undaria pinnatifida, shows antiobesity effect through UCP1 expression in white adipose tissues. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 332, 392–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishikawa, S.; Hosokawa, M.; Miyashita, K. Fucoxanthin promotes translocation and induction of glucose transporter 4 in skeletal muscles of diabetic/obese KK-Ay mice. Phytomedicine 2012, 19, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Ramos, A.; González-Ortiz, M.; Martínez-Abundis, E.; Pérez-Rubio, K.G. Effect of Fucoxanthin on Metabolic Syndrome, Insulin Sensitivity, and Insulin Secretion. J. Med. Food 2023, 26, 521–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullins, R.J.; Diehl, T.C.; Chia, C.W.; Kapogiannis, D. Insulin Resistance as a Link between Amyloid-Beta and Tau Pathologies in Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2017, 9, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, A.I.; Moreira, P.I.; Oliveira, C.R. Insulin in central nervous system: More than just a peripheral hormone. J. Aging Res. 2012, 2012, 384017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulshreshtha, A.; Piplani, P. Current pharmacotherapy and putative disease-modifying therapy for Alzheimer’s disease. Neurol. Sci. 2016, 37, 1403–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Huang, L.; Yu, J.; Xiang, S.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Yan, X.; Cui, W.; He, S.; Wang, Q. Fucoxanthin, a Marine Carotenoid, Reverses Scopolamine-Induced Cognitive Impairments in Mice and Inhibits Acetylcholinesterase in Vitro. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alecu, M.; Geleriu, L.; Coman, G.; Gălăţescu, L. The interleukin-1, interleukin-2, interleukin-6 and tumour necrosis factor alpha serological levels in localised and systemic sclerosis. Rom. J. Intern. Med. 1998, 36, 251–259. [Google Scholar]
- Hampel, H.; Cummings, J.; Blennow, K.; Gao, P.; Jack, C.R.; Vergallo, A. Developing the ATX(N) classification for use across the Alzheimer disease continuum. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2021, 17, 580–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yoo, C.; Maury, J.; Gonzalez, D.E.; Ko, J.; Xing, D.; Jenkins, V.; Dickerson, B.; Leonard, M.; Estes, L.; Johnson, S.; et al. Effects of Supplementation with a Microalgae Extract from Phaeodactylum tricornutum Containing Fucoxanthin on Cognition and Markers of Health in Older Individuals with Perceptions of Cognitive Decline. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2999. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16172999
Yoo C, Maury J, Gonzalez DE, Ko J, Xing D, Jenkins V, Dickerson B, Leonard M, Estes L, Johnson S, et al. Effects of Supplementation with a Microalgae Extract from Phaeodactylum tricornutum Containing Fucoxanthin on Cognition and Markers of Health in Older Individuals with Perceptions of Cognitive Decline. Nutrients. 2024; 16(17):2999. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16172999
Chicago/Turabian StyleYoo, Choongsung, Jonathan Maury, Drew E. Gonzalez, Joungbo Ko, Dante Xing, Victoria Jenkins, Broderick Dickerson, Megan Leonard, Landry Estes, Sarah Johnson, and et al. 2024. "Effects of Supplementation with a Microalgae Extract from Phaeodactylum tricornutum Containing Fucoxanthin on Cognition and Markers of Health in Older Individuals with Perceptions of Cognitive Decline" Nutrients 16, no. 17: 2999. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16172999
APA StyleYoo, C., Maury, J., Gonzalez, D. E., Ko, J., Xing, D., Jenkins, V., Dickerson, B., Leonard, M., Estes, L., Johnson, S., Chun, J., Broeckel, J., Pradelles, R., Sowinski, R., Rasmussen, C. J., & Kreider, R. B. (2024). Effects of Supplementation with a Microalgae Extract from Phaeodactylum tricornutum Containing Fucoxanthin on Cognition and Markers of Health in Older Individuals with Perceptions of Cognitive Decline. Nutrients, 16(17), 2999. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16172999







