Irruption of Network Analysis to Explain Dietary, Psychological and Nutritional Patterns and Metabolic Health Status in Metabolically Healthy and Unhealthy Overweight and Obese University Students: Ecuadorian Case
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design and Participants
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Data Acquisition
2.3.1. Anthropometry
2.3.2. Socioeconomic Variables
2.3.3. Assessment of Dietary Intake
2.3.4. Cardiometabolic Risk Factors
2.3.5. Psychological Pattern
2.3.6. Level of Physical Activity
2.4. Data Analysis
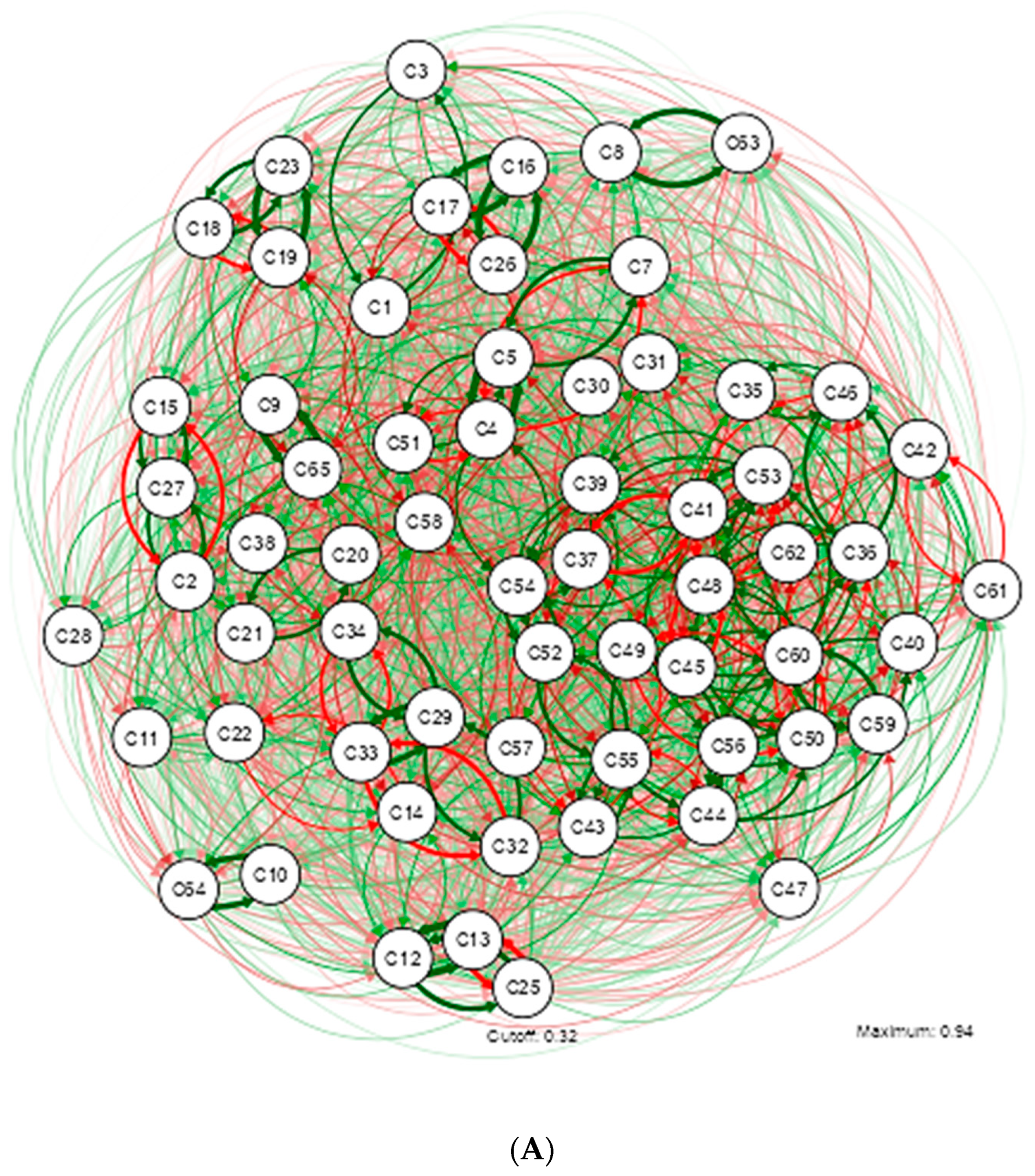
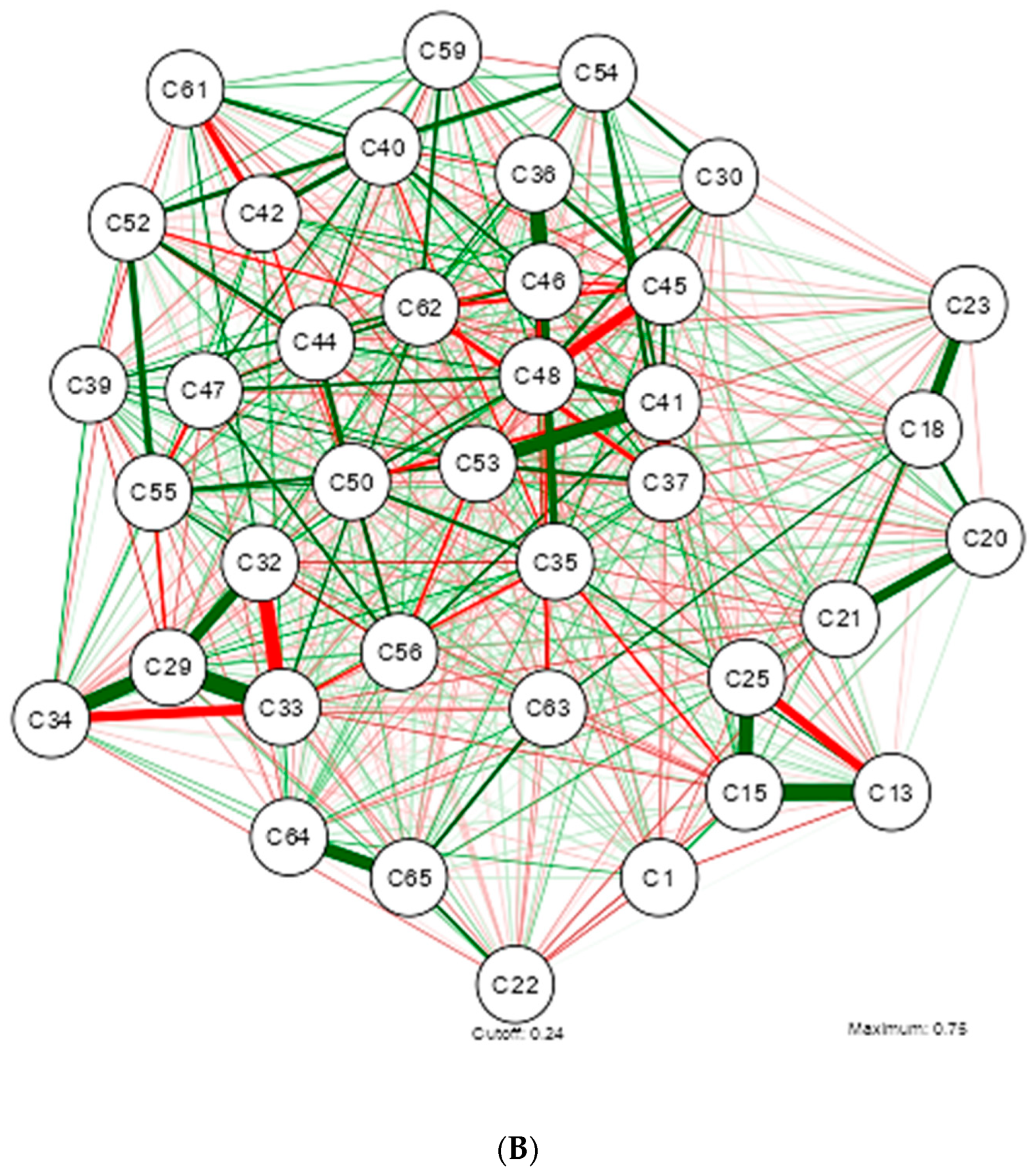
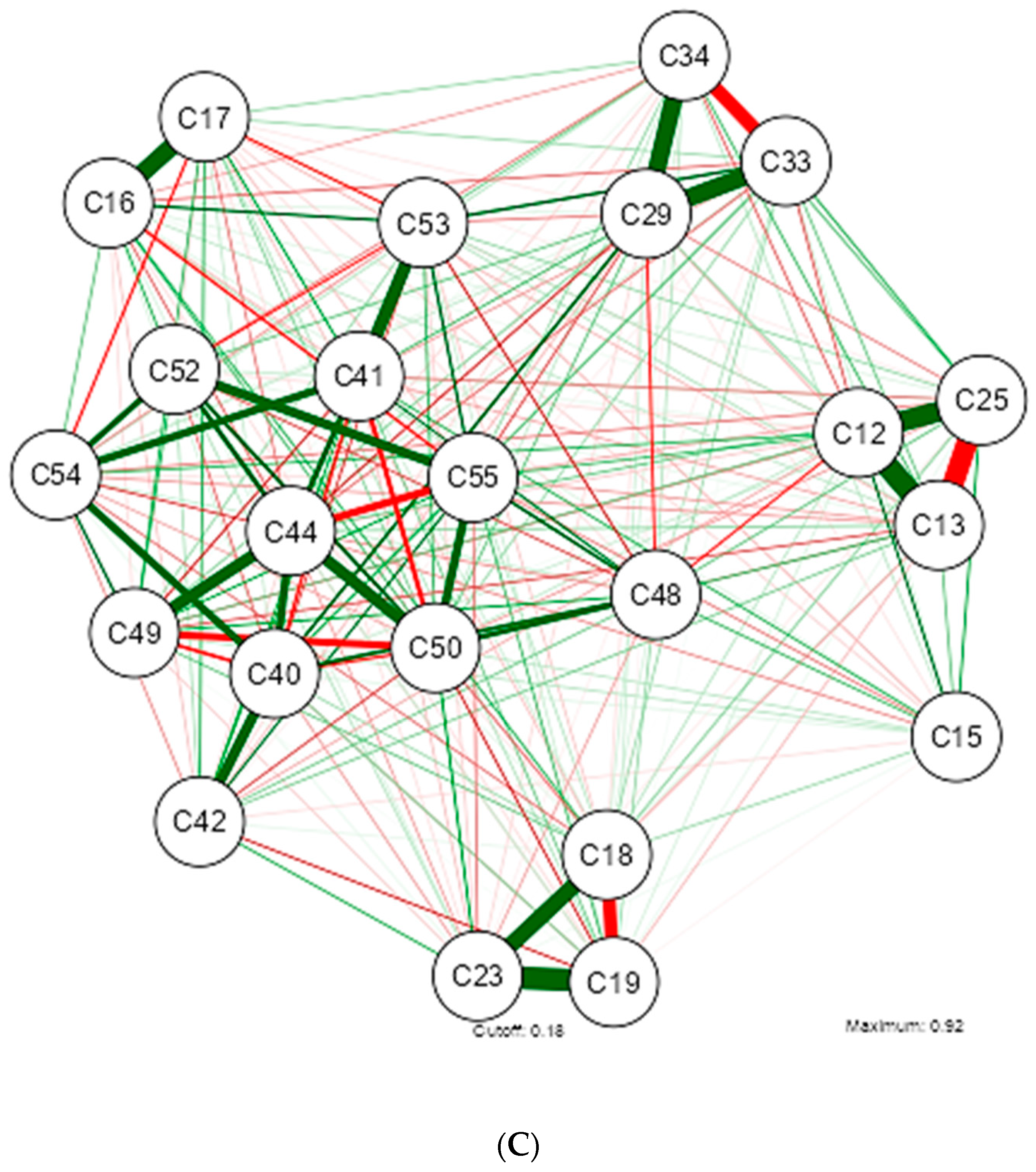
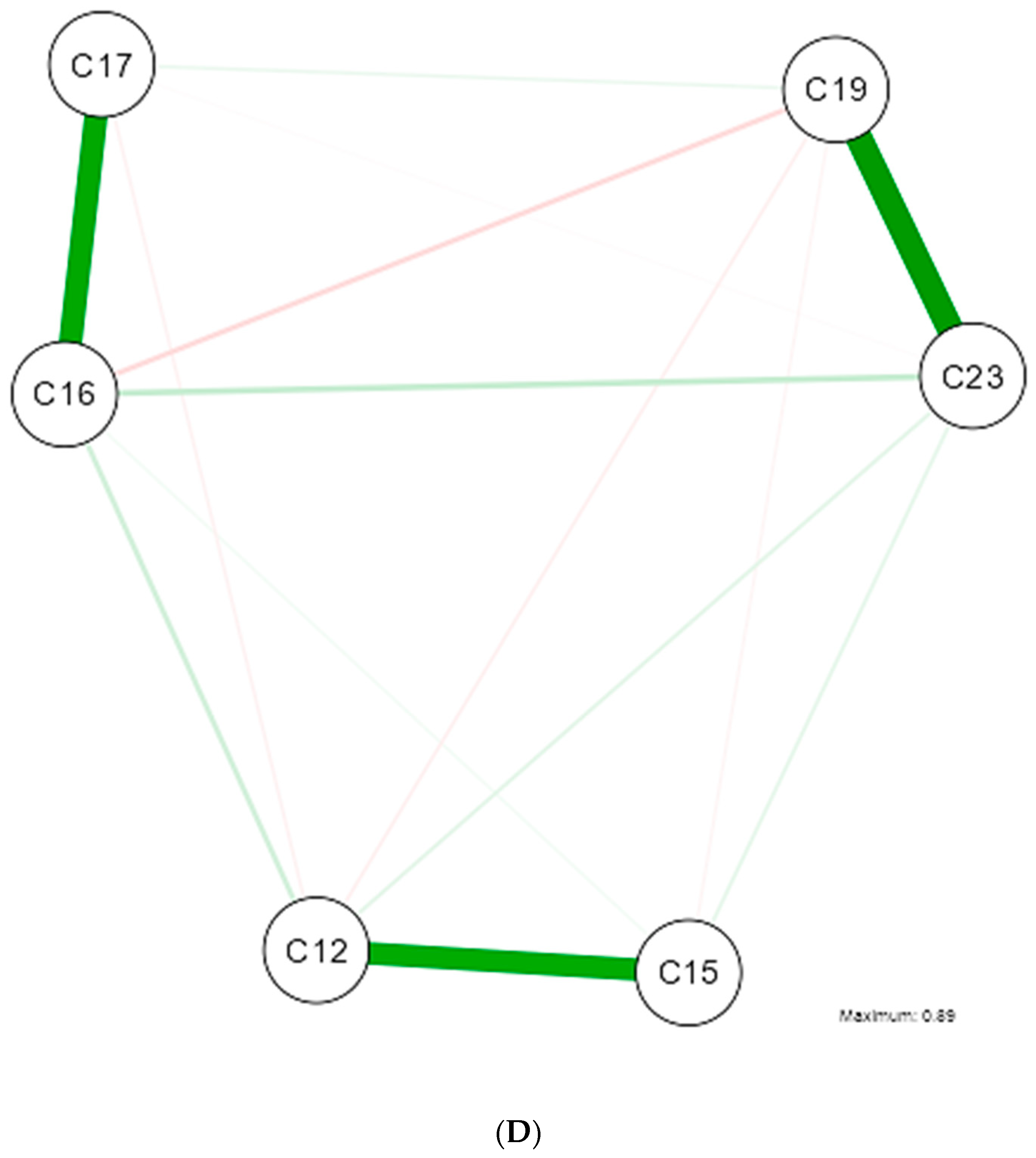
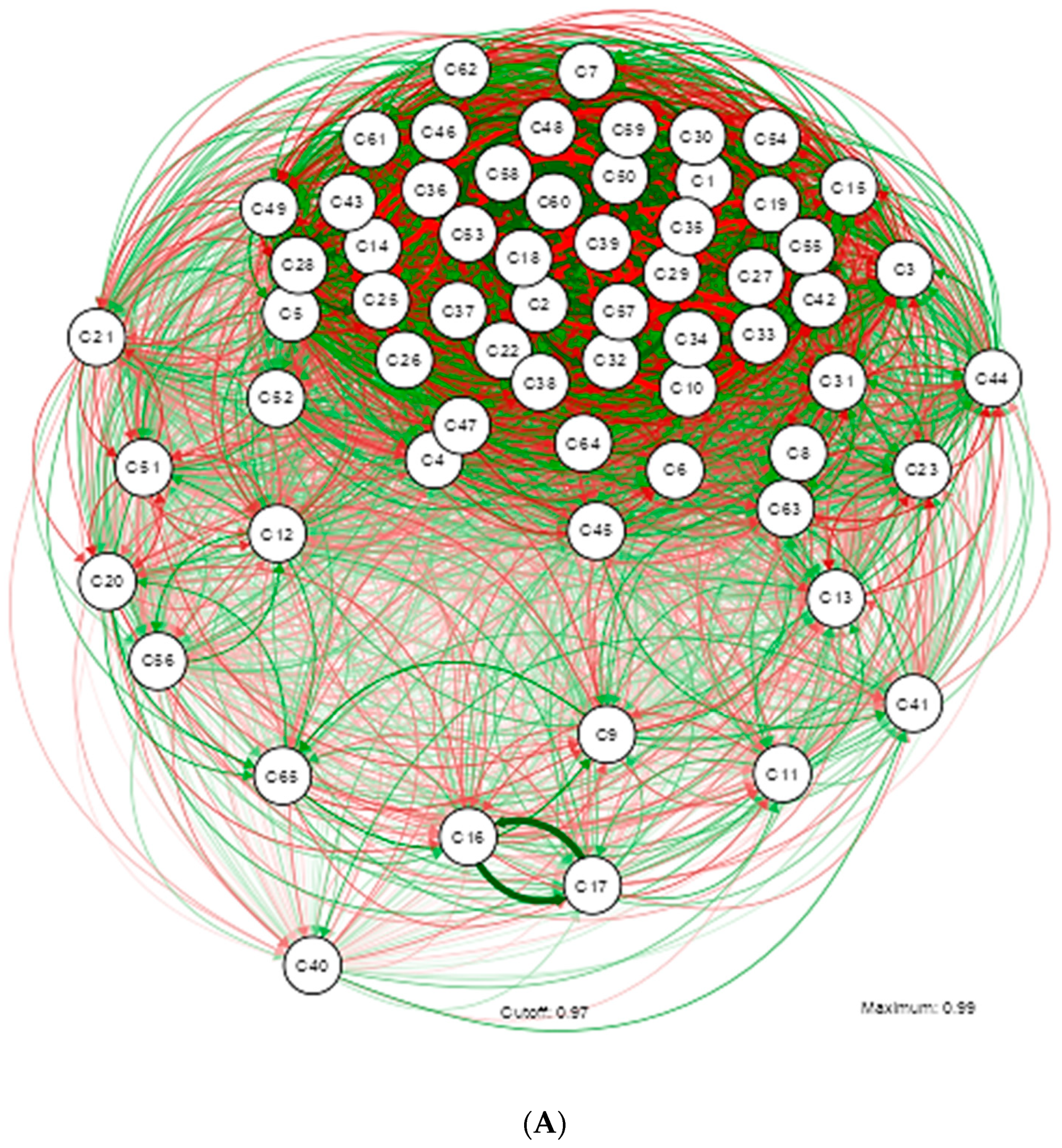
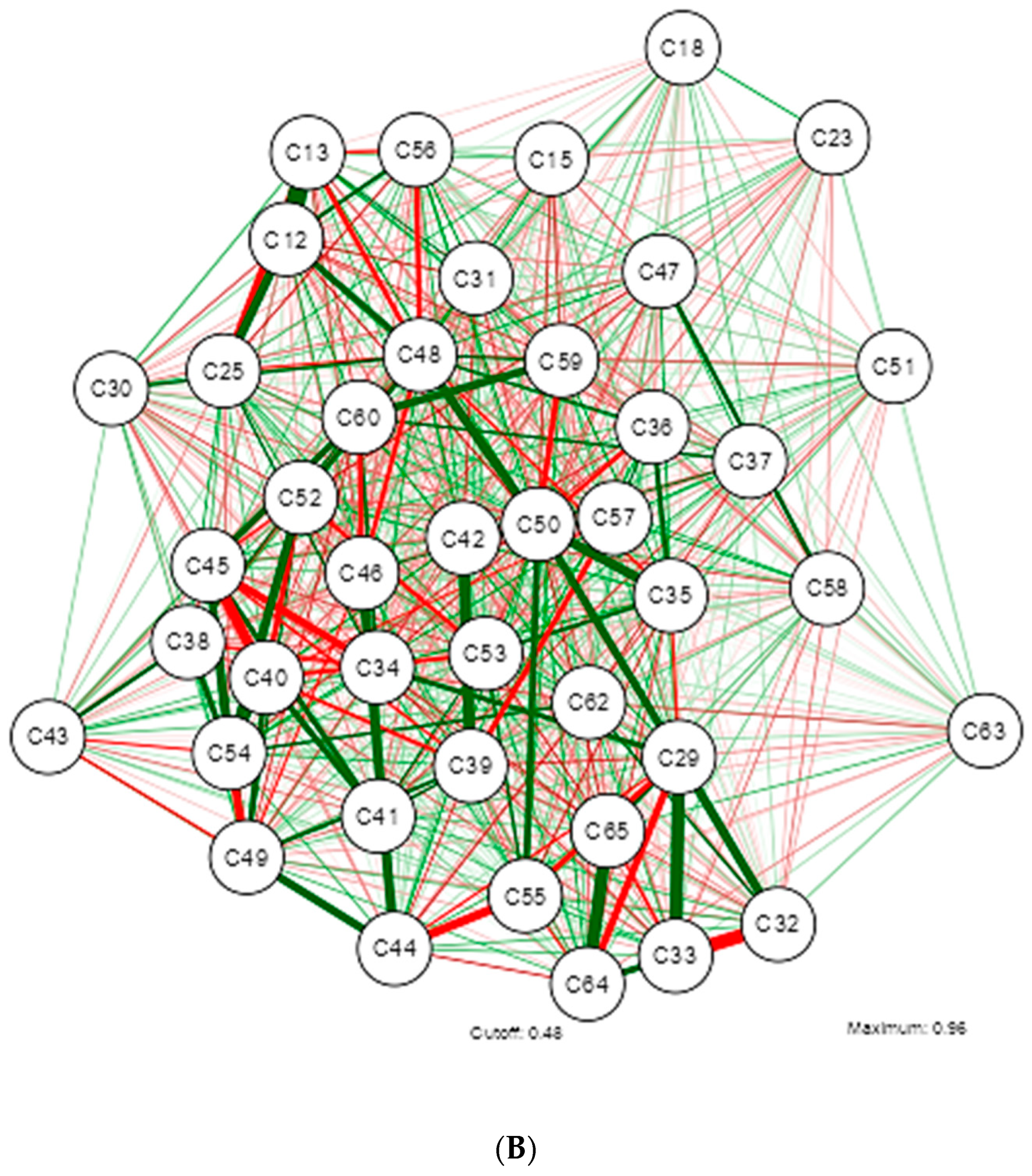
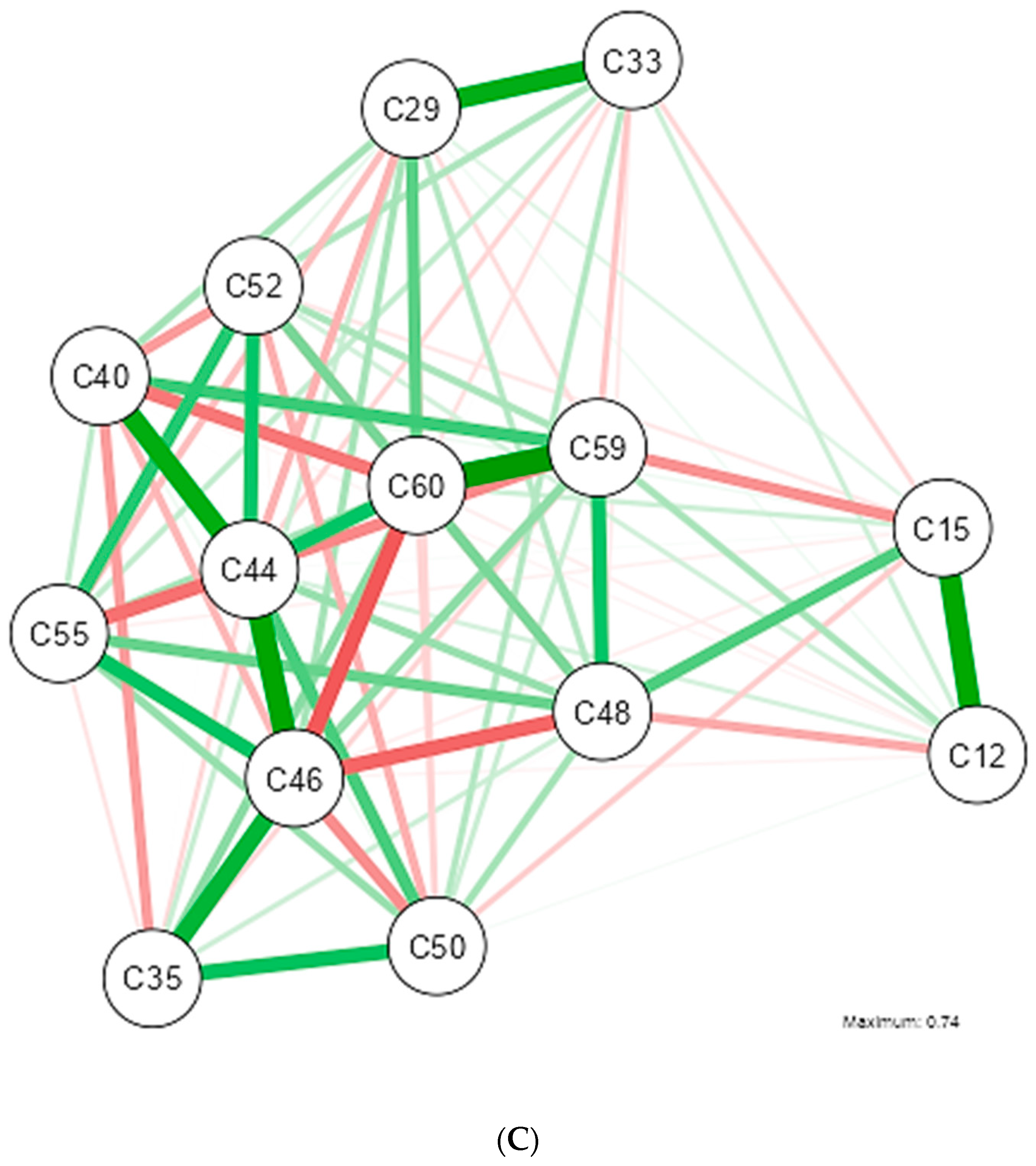
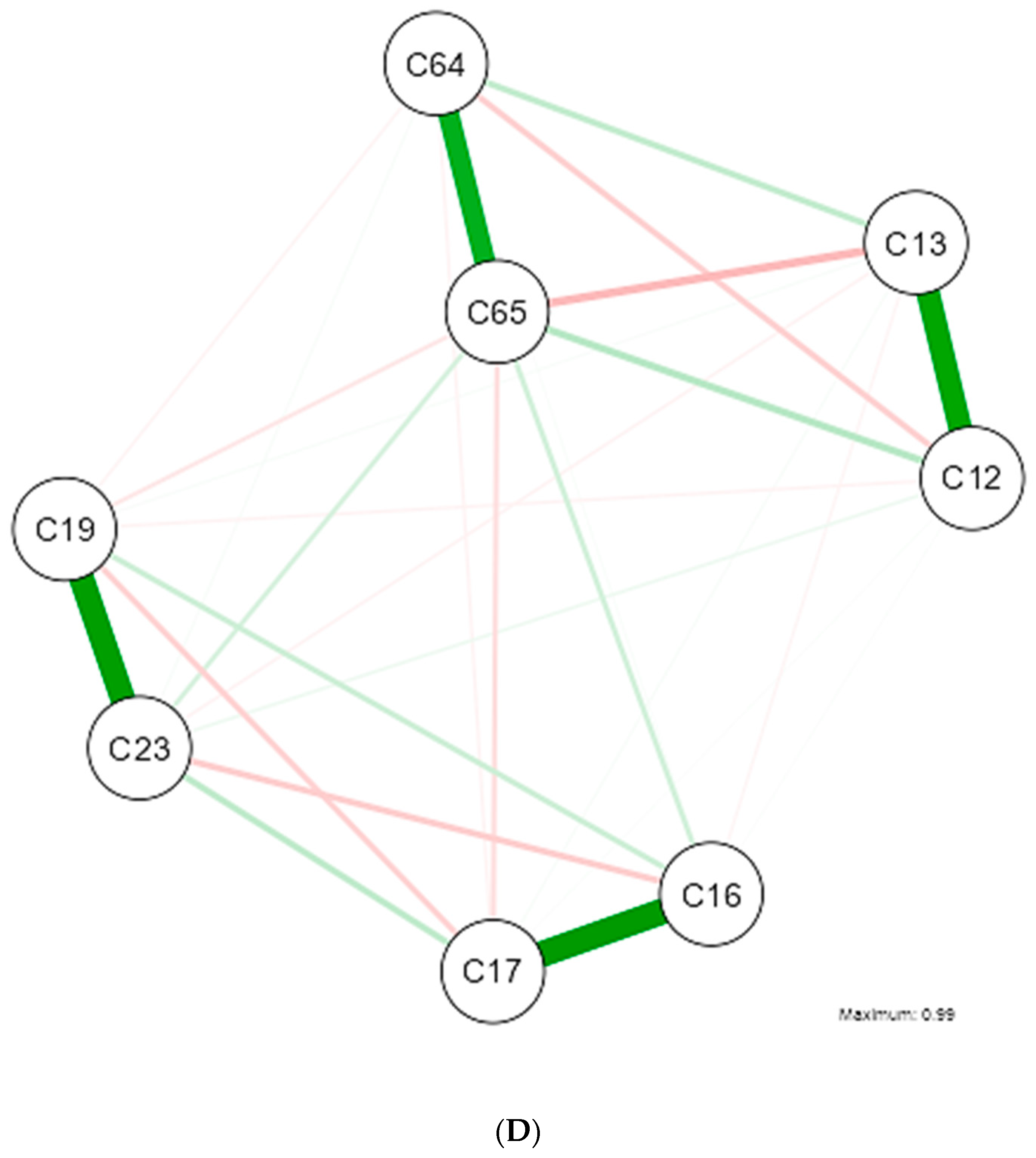
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Variable | Code |
|---|---|
| Age | C1 |
| Sex at Birth | C2 |
| Marital Status | C3 |
| Academic Unit | C4 |
| Mayor | C5 |
| Study Schedule | C6 |
| Socioeconomic Status | C7 |
| Depression Level Categorization | C8 |
| Anxiety Level Categorization | C9 |
| Stress Level Categorization | C10 |
| Physical Activity Level | C11 |
| Weight | C12 |
| Height | C13 |
| Nutritional Status | C14 |
| Waist Circumference | C15 |
| Systolic Blood Pressure | C16 |
| Diastolic Blood Pressure | C17 |
| Glucose | C18 |
| Insulin | C19 |
| Cholesterol | C20 |
| Triglycerides | C21 |
| HDL | C22 |
| HOMA | C23 |
| MUO and MHO Categorization | C24 |
| BMI (Body Mass Index) | C25 |
| Blood Pressure Categorization | C26 |
| Waist Circumference Categorization | C27 |
| MUO and MHO Categorization 2 by HOMA | C28 |
| Kcal/day | C29 |
| Cholesterol | C30 |
| Fiber | C31 |
| Proteins | C32 |
| Carbohydrates | C33 |
| Fats | C34 |
| Monounsaturated Fatty Acids | C35 |
| Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids | C36 |
| Saturated Fatty Acids | C37 |
| Water | C38 |
| Vitamin A | C39 |
| Vitamin D | C45 |
| Vitamin E | C46 |
| Thiamine (Vitamin B1) | C40 |
| Riboflavin (Vitamin B2) | C41 |
| Niacin (Vitamin B3) | C47 |
| Pantothenic Acid (Vitamin B5) | C48 |
| Pyridoxine (Vitamin B6) | C42 |
| Biotin (Vitamin B8) | C49 |
| Folic Acid (Vitamin B9) | C50 |
| Cobalamin (Vitamin B12) | C43 |
| Vitamin C | C44 |
| Sodium | C51 |
| Potassium | C52 |
| Calcium | C53 |
| Phosphorus | C54 |
| Magnesium | C55 |
| Iron | C56 |
| Zinc | C57 |
| Iodine | C58 |
| Copper | C59 |
| Chlorine | C60 |
| Manganese | C61 |
| Selenium | C62 |
| Depression score | C63 |
| Stress score | C64 |
| Anxiety score | C65 |
References
- Obesity Prevention—OPS/OMS PAHO. Available online: https://www.paho.org/es/temas/prevencion-obesidad (accessed on 16 July 2024).
- Aghili, S.M.M.; Ebrahimpur, M.; Arjmand, B.; Shadman, Z.; Sani, M.P.; Qorbani, M.; Larijani, B.; Payab, M. Obesity in COVID-19 era, implications for mechanisms, comorbidities, and prognosis: A review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Obes. 2021, 45, 998–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Obesity Federation. World Obesity Atlas. 2023. Available online: https://data.worldobesity.org/publications/?cat=19 (accessed on 20 June 2024).
- Pérez, M.A.A.; Blasco, E.F. Los costes económicos de la obesidad y el sobrepeso. HAL 2011, 1, 1–15. Available online: https://shs.hal.science/halshs-01764899/document (accessed on 2 June 2024).
- Josloff, K.; Beiriger, J.; Khan, A.; Gawel, R.J.; Kirby, R.S.; Kendrick, A.D.; Rao, A.K.; Wang, R.X.; Schafer, M.M.; Pearce, M.E.; et al. Comprehensive Review of Cardiovascular Disease Risk in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2022, 9, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.A.; Hashim, M.J.; Mustafa, H.; Baniyas, M.Y.; Al Suwaidi, S.K.B.M.; AlKatheeri, R.; Alblooshi, F.M.K.; Almatrooshi, M.E.A.H.; Alzaabi, M.E.H.; Al Darmaki, R.S.; et al. Global Epidemiology of Ischemic Heart Disease: Results from the Global Burden of Disease Study. Cureus 2020, 12, e9349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Noncommunicable Diseases: Mortality; Report of a WHO Scientific Group; Technical Report Series: 641; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. Noncommunicable Diseases. Available online: https://www.who.int/es/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/noncommunicable-diseases (accessed on 16 July 2024).
- Barrea, L.; Muscogiuri, G.; Pugliese, G.; De Alteriis, G.; Colao, A.; Savastano, S. Metabolically Healthy Obesity (MHO) vs. Metabolically Unhealthy Obesity (MUO) Phenotypes in PCOS: Association with Endocrine-Metabolic Profile, Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet, and Body Composition. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ecuador—National Health and Nutrition Survey 2018—General Information. Available online: https://anda.inec.gob.ec/anda/index.php/catalog/891 (accessed on 16 July 2024).
- CES. Statistics on Higher Education, Science, Technology and Innovation—Services. SENESCYT. Available online: https://siau.senescyt.gob.ec/estadisticas-de-educacion-superior-ciencia-tecnologia-e-innovacion/ (accessed on 16 July 2024).
- Hernández Rodríguez, J.; Domínguez, Y.A.; Moncada Espinal, O.M. Prevalence and current trend of overweight and obesity in adults worldwide. Rev. Cub Endocr. 2019, 30, e193. [Google Scholar]
- Cruz, Z.G.; Ramírez, P.L.; Velarde, E.R.; Sanromán, R.T. Lifestyles and health risks in a university population. Rev. Sal. Public Nutr. 2016, 15, 15–21. [Google Scholar]
- Lazarevich, I.; Irigoyen Camacho, M.E.; Velázquez-Alva, M.D.C.; Zepeda Zepeda, M. Relationship among obesity, depression, and emotional eating in young adults. Appetite 2016, 107, 639–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, R.; Olivos, C. The relationship between obesity and depressive states. Rev. Méd. Clın. Condes 2020, 31, 130–138. [Google Scholar]
- Carmichael, I.; Marron, J.S. Data science vs. statistics: Two cultures? Jpn. J. Stat. Data Sci. 2018, 1, 117–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhushan, N.; Mohnert, F.; Sloot, D.; Jans, L.; Albers, C.; Steg, L. Using a Gaussian graphical model to explore relationships between items and variables in environmental psychology research. Front. Psych. 2019, 10, 1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajri, T.; Angamarca-Armijos, V.; Caceres, L. Prevalence of stunting and obesity in Ecuador: A systematic review. Public Health Nutr. 2021, 24, 2259–2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parra, M. Profile of the Latin American University Student—UNESCO Digital Library. Available online: https://unesdoc.unesco.org/ark:/48223/pf0000378123?posInSet=1&queryId=ad98780e-8fb0-499e-b2e5-5bf7429c74fa (accessed on 2 July 2024).
- WHO. Ginebra: OMS. Overweight and Obesity. Available online: https://www.who.int/es/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight (accessed on 10 January 2024).
- Morejón, Y.; Manzano, A.; Betancourt, S.; Ulloa, V. Construction of a Food Consumption Frequency Questionnaire for Ecuadorian Adults, cross-sectional study. Rev. Esp. Nut Hum. Diet. 2021, 25, 394–402. [Google Scholar]
- Nutrimind. Software de Nutrición. Available online: https://www.nutrimind.net/ (accessed on 18 July 2024).
- Bauce, G.; Moya-Sifontes, M.Z. Waist circumference weight index as a complementary indicator of overweight and obesity in different groups of subjects. Rev. Dig. Postg 2020, 9, e195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-León Mandujano, A.; Morales López, S.; Álvarez Díaz CD, J. Technique for a correct blood pressure measurement in the ambulatory patient. Rev. Fac. Med. 2016, 59, 49–55. [Google Scholar]
- Gordon, A.; Benson, S. Resistance training improves metabolic health in type 2 diabetes: A systematic review. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2009, 83, 157–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garmendia, M.; Lera, L.; Sánchez, H.; Uauy, R. Valores normativos de resistencia a la insulina mediante HOMA-IR en adultos mayores de Santiago de Chile. Rev. Méd. Chil. 2009, 137, 1409–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buccini, G.; Wolfthal, D. Cut-off values for insulin resistance, insulin sensitivity and insulin secretion indices derived from the HOMA formula and the HOMAZ program, Interpretation of the data. Argent. J. Endocr. Metab. 2008, 45, 3–21. [Google Scholar]
- Nieto, O.; Cardona, E.; Ramírez, D.; González, M.; Castaño, J. Obesity and inflammation in students of a Colombian public university. Rev. Public Health 2020, 22, 582–588. [Google Scholar]
- Román, F.; Santibáñez, P.; Vinet, E.V. Use of the Depression Anxiety Stress Scales (DASS-21) as a Screening Instrument in Young People with Clinical Problems. Act. Investig. Psicol. 2016, 6, 2325–2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma-Leal, X.; Costa-Rodríguez, C.; Barranco-Ruiz, Y.; Hernández-Jaña, S.; Rodríguez-Rodríguez, F. Reliability of the International Physical Activity Questionnaire (IPAQ)-short version and the Physical Fitness Self-Assessment Questionnaire (IFIS) in Chilean university students. J. M. Health. 2022, 19, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Jamovi. Available online: https://www.jamovi.org/about.html (accessed on 18 July 2024).
- Fereidani, S.S.; Sedaghat, F.; Eini-Zinab, H.; Heidari, Z.; Jalali, S.; Mohammadi, E.; Naja, F.; Assadi, M.; Rashidkhani, B. Gaussian Graphical Models Identified Food Intake Networks among Iranian Women with and without Breast Cancer: A Case-Control Study. Nutr. Cancer 2021, 73, 1890–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalid, I.; Brian, B.; Janine, W. Gaussian Graphical Models Identify Networks of Dietary Intake in a German Adult Population123. J. Nutr. 2016, 146, 646–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, C.; Li, Z.; Chen, H.; Zhang, L.; Liang, Y.; Wu, Z. Evaluation of (2S,4S)-4-[18F] FEBGln as a Positron Emission Tomography Tracer for Tumor Imaging. Mol. Pharm. 2023, 20, 5195–5205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, B.R.; Beck, A.G.; Yeung, L.; Li, A.; Lee, D.H.; Bateman, K.P.; Chopra, G. Automated Bioanalytical Workflow for Ligand Binding-Based Pharmacokinetic Assay Development. Anal. Chem. 2023, 96, 488–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shutta, K.H.; De Vito, R.; Scholtens, D.M.; Balasubramanian, R. Gaussian graphical models with applications to omics analyses. Stat. Med. 2022, 41, 5150–5187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rydén, M.; Sjögren, A.; Önnerfjord, P.; Turkiewicz, A.; Tjörnstrand, J.; Englund, M.; Ali, N. Exploring the Early Molecular Pathogenesis of Osteoarthritis Using Differential Network Analysis of Human Synovial Fluid. Mol. Cell Proteom. 2024, 23, 100785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kean, T.; Witten, D. The cluster graphical lasso for improved estimation of Gaussian graphical models. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 2015, 85, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.X.; Quek, K.F.; Ramadas, A. Dietary and Lifestyle Risk Factors of Obesity Among Young Adults: A Scoping Review of Observational Studies. Curr. Nutr. Rep. 2023, 12, 733–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tazzeo, C.; Zucchelli, A.; Vetrano, D.L.; Demurtas, J.; Smith, L.; Schoene, D.; Sanchez-Rodriguez, D.; Onder, G.; Balci, C.; Bonetti, S.; et al. Risk factors for multimorbidity in adulthood: A systematic review. Ageing Res. Rev. 2023, 91, 102039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Gong, S.; Chen, Y.; Hou, X.; Sun, T.; Wen, J.; Wang, Z.; He, J.; Sun, X.; Wang, S.; et al. Lifestyle behaviors and stress are risk factors for overweight and obesity in healthcare workers: A cross-sectional survey. BMC Public Health 2023, 23, 1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Epskamp, S.; Cramer, A.O.J.; Waldorp, L.J.; Schmittmann, V.D.; Borsboom, D. Qgraph: Network visualizations of relationships in psychometric data. J. Stat. Softw. 2012, 48, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obirikorang, C.; Adu, E.A.; Anto, E.O.; Awuah, A.A.-A.; Fynn, A.N.B.; Osei-Somuah, G.; Ansong, P.N.; Boakye, A.O.; Ofori-Boadu, I.; Obirikorang, Y.; et al. Prevalence and risk factors of obesity among undergraduate student population in Ghana: An evaluation study of body composition indices. BMC Public Health 2024, 24, 877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talati, K.; Parmar, A.; Zalavadiya, D.; Shinde, M.; Madan-Patel, G. Epidemiological Insights into Anthropometric Indices and Their Correlates among College Students through a University-Level Screening Program in Western India. Indian. J. Community Med. 2022, 47, 445–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Lahole, S.; Rawekar, R.; Acharya, S.; Wanjari, A.; Gaidhane, S.; Agrawal, S. Anthropometric indices and its association with hypertension among young medical students: A 2 year cross-sectional study. J. Fam. Med. Prim. Care 2022, 11, 281–286. [Google Scholar]
- Spiegelman, B.M.; Flier, J.S. Obesity and the regulation of energy balance. Cell 2001, 104, 531–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engin, A. The Definition and Prevalence of Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2017, 960, 1–17. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28585193/ (accessed on 15 May 2024).
- Lin, X.; Li, H. Obesity: Epidemiology, Pathophysiology, and Therapeutics. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 706978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vega, G.; Rico, M. Adipose tissue: Immune function and alterations induced by obesity. Rev. Allergy Mex. 2019, 66, 340–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, M.; Izurieta, R.; Nishio, A.; Horita, R.; Yamamoto, M. Nutritional intake and metabolic parameters of Japanese university students with and without obesity: Sex-specific differences. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0285088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebremeskel, G.; Haile, T.; Gebrewahd, G.; Tadesse, D. High Blood Pressure and Its Associated Factors Among Aksum University Students, Northern Ethiopia, 2019: A Cross-Sectional Study. Int. J. Public Health 2024, 69, 1607275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Dakanalis, A.; Mentzelou, M.; Papadopoulou, S.K.; Papandreou, D.; Spanoudaki, M.; Vasios, G.K.; Pavlidou, E.; Mantzorou, M.; Giaginis, C. The Association of Emotional Eating with Overweight/Obesity, Depression, Anxiety/Stress, and Dietary Patterns: A Review of the Current Clinical Evidence. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajan, T.; Menon, V. Psychiatric disorders and obesity: A review of association studies. J. Postgrad. Med. 2017, 63, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavallee, K.L.; Zhang, X.C.; Schneider, S.; Margraf, J. Obesity and Mental Health: A Longitudinal, Cross-Cultural Examination in Germany and China. Front. Psychol. 2021, 12, 712567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Juras, A.R.; Hsu, W.-C.; Hu, S.C. Prevalence and Determinants of the Co-Occurrence of Overweight or Obesity and Micronutrient Deficiencies among Adults in the Philippines: Results from a National Representative Survey. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Zhang, X.; Shen, Y.; Fang, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, F. Obesity and iron deficiency: A quantitative meta-analysis. Obes. Rev. 2015, 16, 1081–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, A.; Benton, D.; Gaylor, C.; Young, H. The role of interception in age-related obesity: A structural equation modelling study. Appetite 2023, 191, 107045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, J.A.; Hamer, M.; Batty, G.D.; Singh-Manoux, A.; Sabia, S.; Kivimäki, M. Incidence of Metabolic Risk Factors among Healthy Obese Adults. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2015, 66, 871–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, J.A.; Kivimaki, M.; Hamer, M. Metabolically healthy obesity and risk of incident type 2 diabetes: A meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Obes. Rev. 2014, 15, 504–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twig, G.; Afek, A.; Derazne, E.; Tzur, D.; Cukierman-Yaffe, T.; Gerstein, H.; Tirosh, A. Diabetes risk among overweight and obese metabolically healthy young adults. Diab Care 2014, 37, 2989–2995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wang, C.; Guan, S.; Liu, H.; Wu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Gu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Tse, L.A.; et al. The Prevalence of Metabolically Healthy and Unhealthy Obesity according to Different Criteria. Obes. Facts 2019, 12, 78–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, F.; Garvey, W.T. Cardiometabolic disease risk in metabolically healthy and unhealthy obesity: Stability of metabolic health status in adults. Obes. Silver Spring Md. 2016, 24, 516–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosseinpanah, F.; Tasdighi, E.; Barzin, M.; Mahdavi, M.; Ghanbarian, A.; Valizadeh, M.; Azizi, F. The association between transition from metabolically healthy obesity to metabolic syndrome, and incidence of cardiovascular disease: Tehran lipid and glucose study. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0239164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharooi Ahangar, O.; Javanrouh, N.; Daneshpour, M.S.; Barzin, M.; Valizadeh, M.; Azizi, F.; Hosseinpanah, F. Genetic markers and continuity of healthy metabolic status: Tehran cardio-metabolic genetic study (TCGS). Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 13600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonnie, M.; Wadolowska, L.; Morze, J.; Bandurska-Stankiewicz, E. Associations of Dietary-Lifestyle Patterns with Obesity and Metabolic Health: Two-Year Changes in MeDiSH® Study Cohort. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 13647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
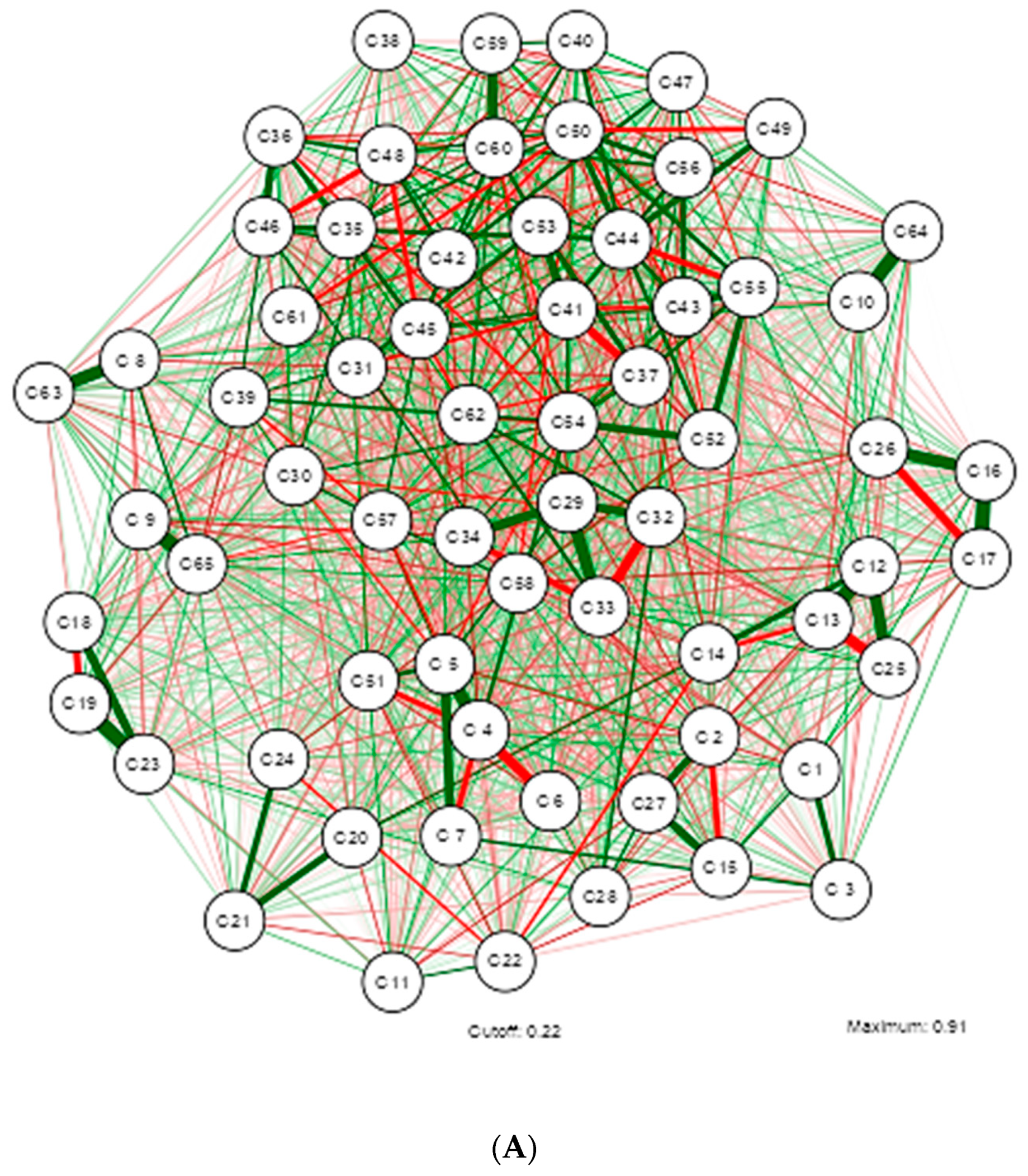
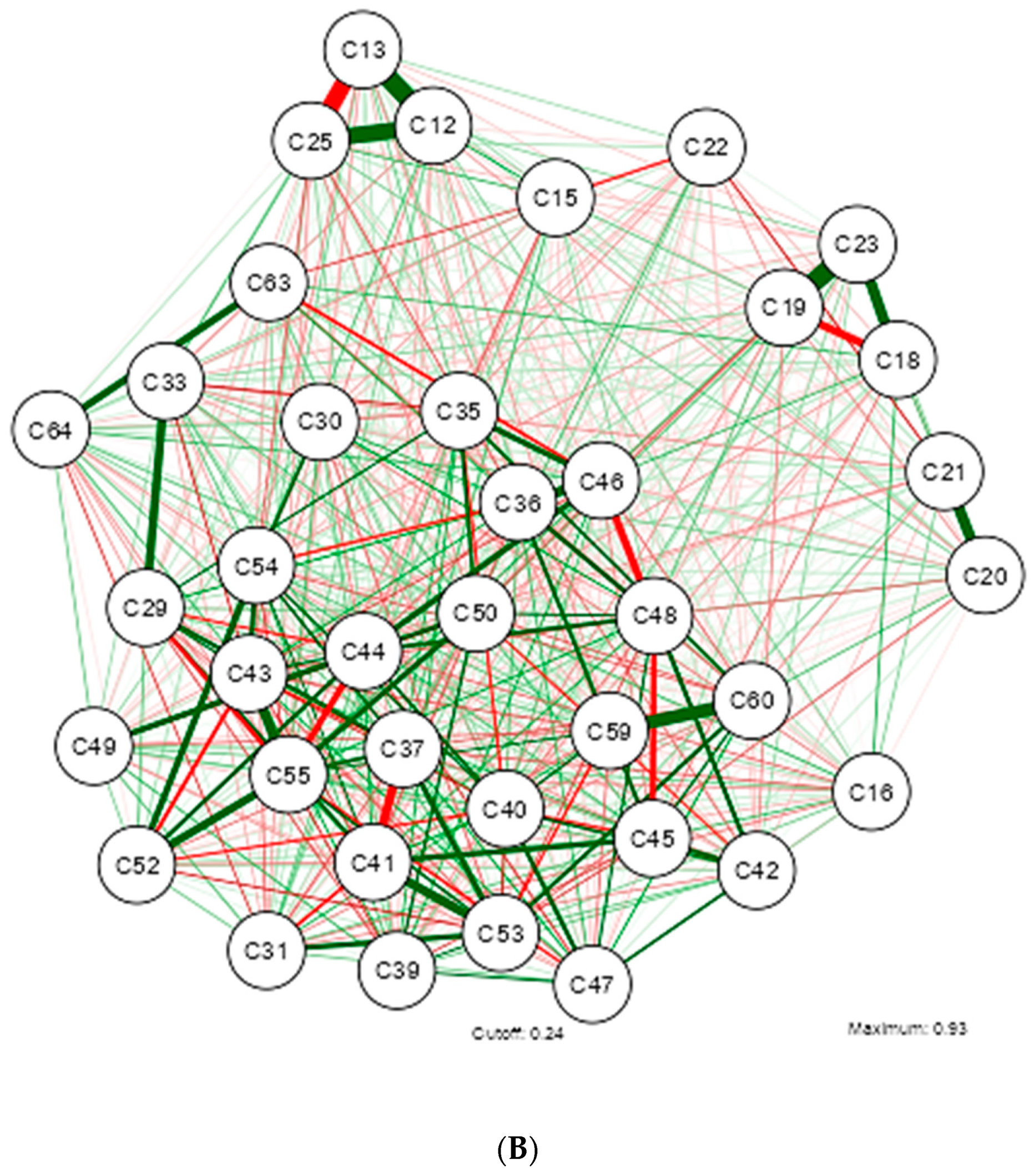
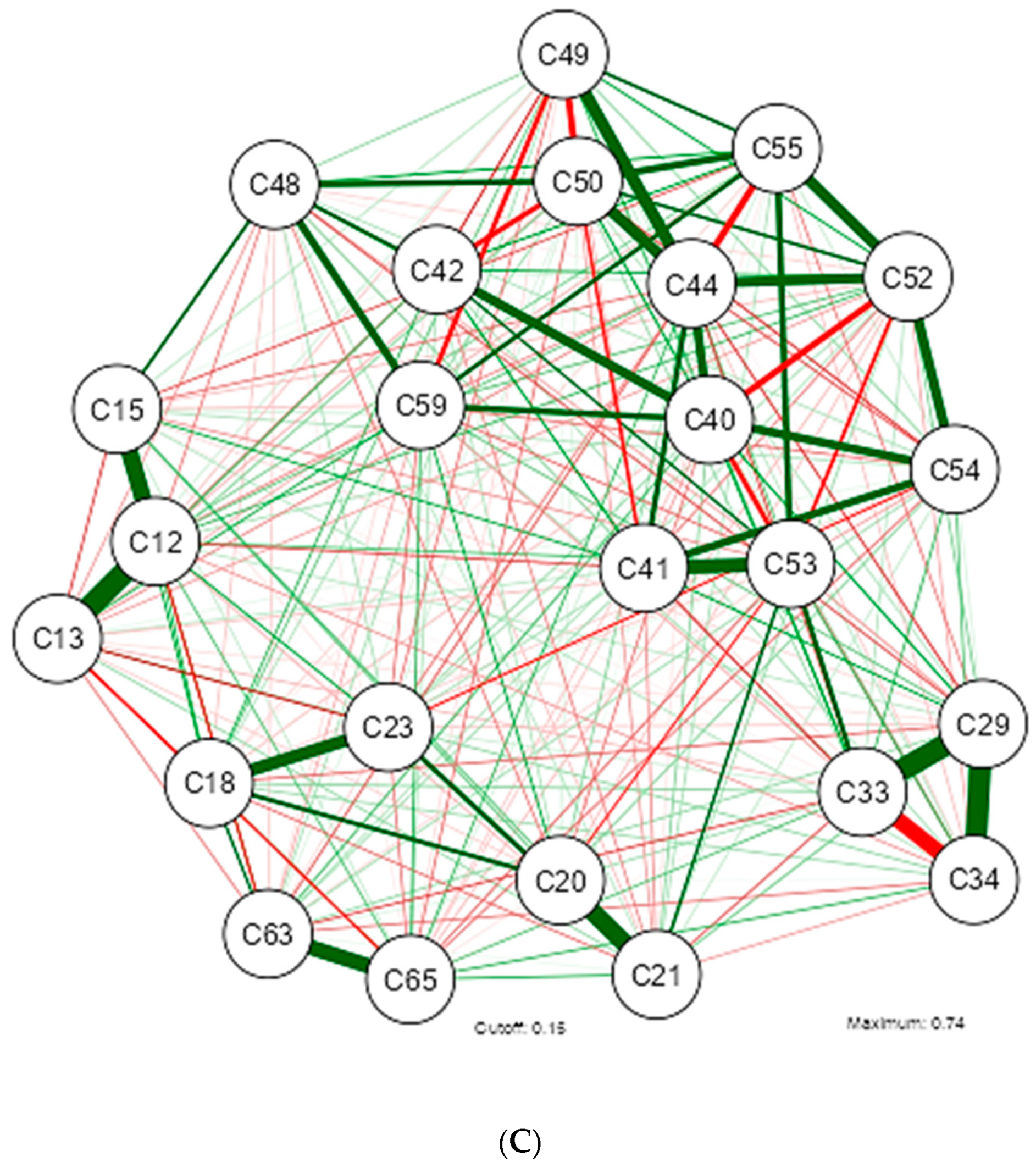
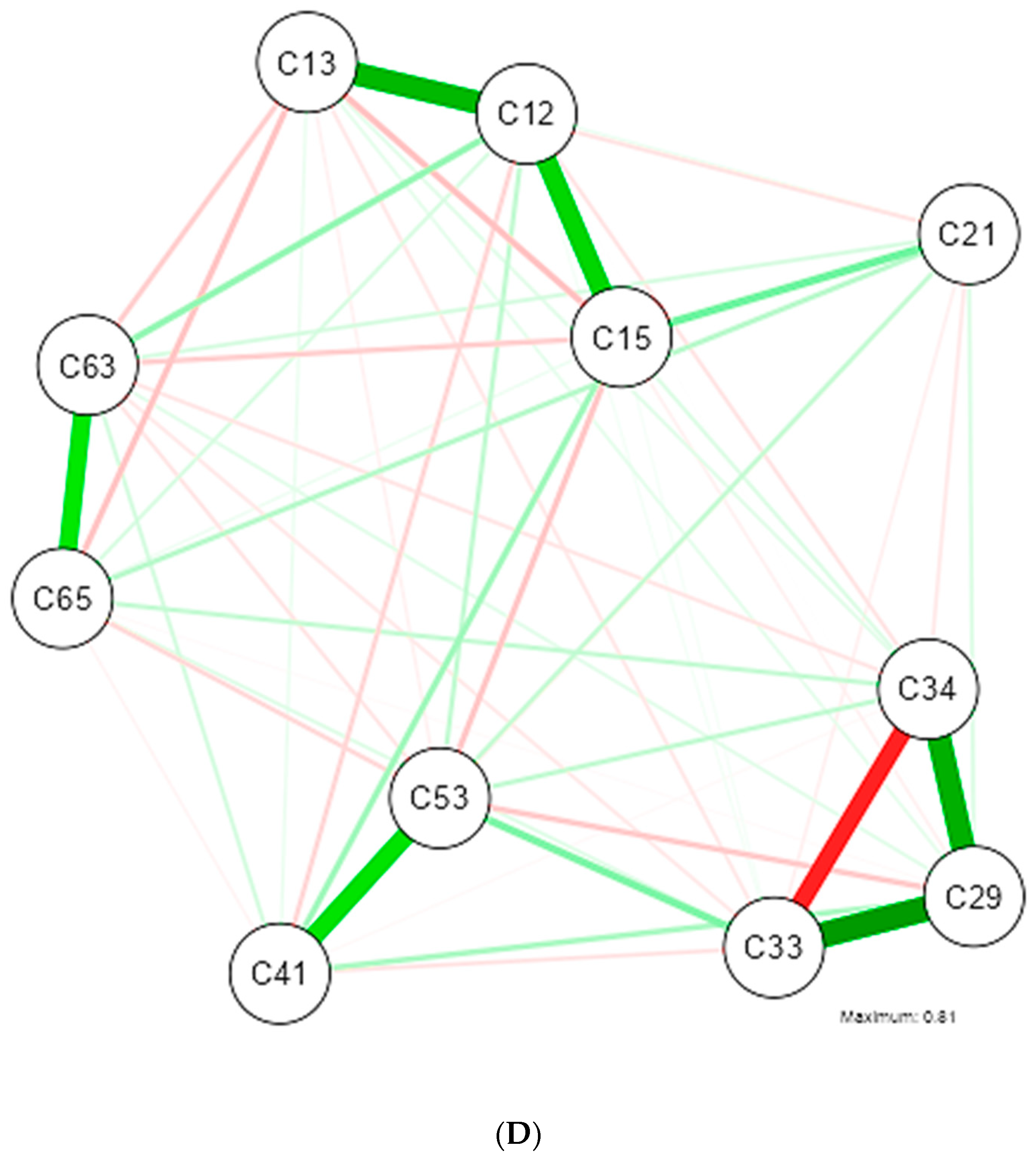
| Shapiro-Wilk | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | Median | DE | Minimum | Maximum | W | p |
| Age | 21.00 | 2.51 | 18 | 28 | 0.906 | <0.001 |
| Anthropometric | ||||||
| Weight (kg) | 74.80 | 11.14 | 52.5 | 113.50 | 0.967 | <0.001 |
| Height (m) | 1.63 | 0.09 | 1.41 | 1.88 | 0.991 | 0.194 |
| IMC | 27.60 | 2.76 | 25.1 | 42.30 | 0.852 | <0.001 |
| Cardiometabolic risk factors | ||||||
| Waist circumference (cm) | 90.00 | 7.53 | 76 | 112 | 0.967 | <0.001 |
| Systolic blood pressure (mm Hg) | 120.00 | 8.54 | 90 | 139 | 0.854 | <0.001 |
| Diastolic blood pressure (mm Hg) | 80.00 | 6.45 | 60 | 100 | 0.754 | <0.001 |
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 95.86 | 10.77 | 75.31 | 130.10 | 0.804 | <0.001 |
| Insulin (U/mL) | 10.41 | 2.76 | 2.4 | 22.62 | 0.999 | <0.001 |
| Cholesterol (mg/dL) | 195.73 | 55.41 | 93.87 | 456.24 | 0.888 | <0.001 |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL) | 157.24 | 50.72 | 52 | 385.44 | 0.882 | <0.001 |
| HDL (mg/dL) | 44.25 | 3.10 | 40 | 53.19 | 0.958 | <0.001 |
| HOMA | 2.46 | 0.74 | 0.57 | 5.20 | 0.971 | <0.001 |
| Intake pattern | ||||||
| Kcal/día | 2249.94 | 239.80 | 1687 | 2956.57 | 0.961 | <0.001 |
| Cholesterol (mg) | 355.99 | 101.63 | 139.62 | 733.81 | 0.945 | <0.001 |
| Fiber (g) | 21.24 | 6.25 | 7.58 | 35.36 | 0.989 | 0.067 |
| Proteins(g) | 72.41 | 19.48 | 25 | 139.20 | 0.986 | 0.021 |
| Carbohydrates (g) | 297.75 | 49.29 | 165.51 | 448.40 | 0.984 | 0.011 |
| Fats (g) | 87.05 | 12.53 | 60.07 | 131.64 | 0.972 | <0.001 |
| Monounsaturated fatty acids (g) | 40.99 | 12.01 | 9.46 | 78.38 | 0.935 | <0.001 |
| Polyunsaturated fatty acids (g) | 8.80 | 4.12 | 1.01 | 49.69 | 0.655 | <0.001 |
| Saturated fatty acids (g) | 29.75 | 9.57 | 12.85 | 54.61 | 0.963 | <0.001 |
| Water (mL) | 1493.89 | 262.60 | 857.88 | 1994.96 | 0.983 | 0.006 |
| Vitamin A (μg) | 633.29 | 367.14 | 222.56 | 3961.87 | 0.645 | <0.001 |
| Vitamin D (μg) | 2.15 | 0.73 | 0 | 529.50 | 0.069 | <0.001 |
| Vitamin E (mg) | 9.84 | 0.80 | 2.06 | 53.33 | 0.664 | <0.001 |
| Thiamine (Vitamin B1) (mg) | 1.19 | 0.90 | 0.45 | 6.01 | 0.702 | <0.001 |
| Riboflavin (Vitamin B2) (mg) | 1.87 | 8.02 | 0.64 | 8.02 | 0.591 | <0.001 |
| Niacin (Vitamin B3) (mg) | 18.27 | 94.89 | 5.88 | 39.61 | 0.964 | <0.001 |
| Pantothenic Acid (Vitamin B5) (mg) | 3.95 | 34.85 | 1.31 | 9.51 | 0.911 | <0.001 |
| Pyridoxine (Vitamin B6) (mg) | 1.58 | 5.98 | 0.71 | 8.41 | 0.604 | <0.001 |
| Biotin (Vitamin B8) (μg) | 3.57 | 6.74 | 0.05 | 9.69 | 0.987 | 0.030 |
| Folic Acid (Vitamin B9) (μg) | 302.54 | 1.69 | 78.69 | 670.29 | 0.959 | <0.001 |
| Cobalamin (Vitamin B12) (μg) | 13.08 | 1.67 | 1.73 | 42.05 | 0.900 | <0.001 |
| Vitamin C (mg) | 151.04 | 98.94 | 12.45 | 403.44 | 0.944 | <0.001 |
| Sodium (mg) | 7099.66 | 2332.11 | 861.56 | 14,663.46 | 0.978 | 0.001 |
| Potassium (mg) | 3362.47 | 1132.61 | 1285.65 | 8695.05 | 0.936 | <0.001 |
| Calcium (mg) | 1234.77 | 359.12 | 550.51 | 3872.18 | 0.897 | <0.001 |
| Phosphorus (mg) | 1451.23 | 376.28 | 546.80 | 2918.23 | 0.971 | <0.001 |
| Magnesium (mg) | 384.68 | 119.86 | 168.47 | 1115.64 | 0.931 | <0.001 |
| Iron (mg) | 15.40 | 6.54 | 4.45 | 103.20 | 0.381 | <0.001 |
| Zinc (mg) | 9.46 | 3.09 | 2.62 | 20.17 | 0.984 | 0.009 |
| Iodine (μg) | 144.19 | 1093.68 | 32.72 | 16,698 | 0.060 | <0.001 |
| Copper (mg) | 1.02 | 0.40 | 0.18 | 2.74 | 0.957 | <0.001 |
| Chlorine (mg) | 1810.66 | 1835.37 | 408.88 | 9127.22 | 0.648 | <0.001 |
| Manganese (mg) | 2.76 | 1.68 | 0.33 | 6.96 | 0.902 | <0.001 |
| Selenium (μg) | 55.78 | 517.56 | 29.90 | 5666 | 0.079 | <0.001 |
| Psychological Pattern | ||||||
| Depression score | 5.00 | 1.27 | 5 | 11 | 0.758 | <0.001 |
| Stress score | 11.00 | 2.87 | 8 | 17 | 0.872 | <0.001 |
| Anxiety score | 5.00 | 1.63 | 4 | 9 | 0.809 | <0.001 |
| Variable | MHO N = 66 (29%) | MUO N = 164 (71%) | p-Value | q-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 20.00 (19.00, 22.00) | 21.00 (19.00, 23.00) | 0.25 | 0.40 |
| Weight (kg) | 72 (63, 78) | 76 (68, 83) | 0.003 * | 0.012 |
| Height (m) | 1.64 (1.55, 1.68) | 1.62 (1.56, 1.69) | 0.91 | 0.93 |
| Waist circumference (cm) | 86 (82, 91) | 90 (86, 96) | <0.001 * | <0.001 |
| Systolic blood pressure (mm Hg) | <0.001 * | <0.001 | ||
| 4 (6.1%) | 0 (0%) | |||
| 1 (1.5%) | 0 (0%) | |||
| 26 (39%) | 60 (37%) | |||
| 35 (53%) | 50 (30%) | |||
| 0 (0%) | 7 (4.3%) | |||
| 0 (0%) | 46 (28%) | |||
| 0 (0%) | 1 (0.6%) | |||
| Diastolic blood pressure (mm Hg) | 0.004 * | 0.014 | ||
| 7 (11%) | 1 (0.6%) | |||
| 24 (36%) | 61 (37%) | |||
| 35 (53%) | 96 (59%) | |||
| 0 (0%) | 3 (1.8%) | |||
| 0 (0%) | 3 (1.8%) | |||
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 93 (90, 96) | 97 (93, 104) | <0.001 * | <0.001 |
| Insulin (U/mL) | 9.78 (8.70, 10.40) | 10.64 (10.21, 11.46) | <0.001 * | <0.001 |
| Cholesterol (mg/dL) | 155 (142, 172) | 208 (186, 230) | <0.001 * | <0.001 |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL) | 101 (90, 112) | 162 (156, 175) | <0.001 * | <0.001 |
| HDL (mg/dL) | 47.09 (44.78, 49.16) | 43.73 (40.93, 45.35) | <0.001 * | <0.001 |
| HOMA | 2.24 (1.94, 2.42) | 2.53 (2.30, 3.14) | <0.001 * | <0.001 |
| IMC | 26.65 (25.90, 27.58) | 28.20 (26.78, 30.47) | <0.001 * | <0.001 |
| Kcal/día | 2.258 (2.165, 2.318) | 2.238 (2.104, 2.447) | 0.81 | 0.90 |
| Cholesterol (mg) | 336 (285, 399) | 369 (317, 432) | 0.014 | 0.038 |
| Fiber (g) | 23 (20, 29) | 21 (17, 25) | 0.006 | 0.017 |
| Proteins (g) | 69 (55, 82) | 74 (62, 85) | 0.078 | 0.17 |
| Carbohydrates (g) | 298 (270, 325) | 297 (265, 330) | 0.83 | 0.90 |
| Fats (g) | 88 (85, 94) | 86 (79, 96) | 0.17 | 0.30 |
| Monounsaturated fatty acids (g) | 42 (39, 47) | 40 (35, 45) | 0.035 | 0.091 |
| Polyunsaturated fatty acids (g) | 8.86 (7.20, 9.88) | 8.77 (7.49, 10.17) | 0.51 | 0.66 |
| Saturated fatty acids (g) | 27 (22, 37) | 30 (24, 39) | 0.15 | 0.29 |
| Water (mL) | 1.551 (1.299, 1.738) | 1.475 (1.267, 1.667) | 0.060 | 0.15 |
| Vitamin A (μg) | 657 (500, 870) | 612 (502, 881) | 0.45 | 0.61 |
| Thiamine (Vitamin B1) (mg) | 1.13 (0.99, 1.42) | 1.22 (1.02, 1.71) | 0.073 | 0.16 |
| Riboflavin (Vitamin B2) (mg) | 1.88 (1.66, 2.06) | 1.87 (1.65, 2.10) | 0.72 | 0.87 |
| Pyridoxine (VitaminaB6) (mg) | 1.56 (1.36, 1.76) | 1.60 (1.41, 2.02) | 0.36 | 0.51 |
| Cobalamin (Vitamin B12) (μg) | 15 (3, 20) | 13 (4, 19) | 0.78 | 0.90 |
| Vitamin C (mg) | 152 (80, 213) | 151 (94, 227) | 0.26 | 0.40 |
| Vitamin D (μg) | 2.24 (0.71, 2.82) | 2.02 (1.33, 2.67) | 0.86 | 0.91 |
| Vitamin E (mg) | 9.7 (6.4, 13.1) | 10.0 (8.0, 12.1) | 0.81 | 0.90 |
| Niacin (Vitamin B3) (mg) | 17.8 (15.6, 22.2) | 18.6 (13.8, 25.3) | 0.35 | 0.51 |
| Pantothenic Acid (Vitamin B5) | 3.63 (3.14, 4.93) | 4.00 (3.33, 5.01) | 0.26 | 0.40 |
| Biotin (Vitamin B8) | 3.33 (2.56, 4.49) | 3.77 (2.79, 4.87) | 0.071 | 0.16 |
| Folic Acid (Vitamin B9) (μg) | 311 (244, 366) | 300 (231, 347) | 0.29 | 0.44 |
| Sodium (mg) | 6.608 (5.590, 7.638) | 7.652 (5.852, 9.603) | 0.011 | 0.032 |
| Potassium (mg) | 3.500 (2.504, 3.782) | 3.316 (2.732, 4.003) | 0.99 | 0.99 |
| Calcium (mg) | 1.281 (1.140, 1.484) | 1.224 (1.093, 1.441) | 0.26 | 0.40 |
| Phosphorus (mg) | 1.429 (1.291, 1.541) | 1.465 (1.266, 1.702) | 0.22 | 0.38 |
| Magnesium (mg) | 383 (328, 434) | 385 (324, 455) | 0.61 | 0.75 |
| Iron (mg) | 15.4 (14.0, 16.1) | 15.4 (13.8, 17.1) | 0.48 | 0.63 |
| Zinc (mg) | 8.57 (6.37, 11.26) | 9.73 (7.39, 11.78) | 0.081 | 0.17 |
| Iodine (μg) | 99 (60, 156) | 155 (94, 179) | <0.001 * | <0.001 |
| Copper (mg) | 0.97 (0.69, 1.09) | 1.04 (0.83, 1.22) | 0.10 | 0.19 |
| Chlorine (mg) | 1.787 (1.511, 2.509) | 1.813 (1.496, 2.467) | 0.90 | 0.93 |
| Manganese (mg) | 1.37 (1.07, 2.90) | 2.88 (1.52, 3.76) | <0.001 * | <0.001 |
| Selenium (μg) | 56 (47, 61) | 56 (48, 67) | 0.53 | 0.66 |
| Depression score | 0.001 * | 0.004 | ||
| 48 (73%) | 71 (43%) | |||
| 9 (14%) | 25 (15%) | |||
| 8 (12%) | 45 (27%) | |||
| 1 (1.5%) | 15 (9.1%) | |||
| 0 (0%) | 4 (2.4%) | |||
| 0 (0%) | 4 (2.4%) | |||
| Stress score | 8.00 (8.00, 10.00) | 11.00 (10.00, 14.00) | <0.001 * | <0.001 |
| Anxiety score | ||||
| 48 (73%) | 47 (29%) | |||
| 7 (11%) | 40 (24%) | |||
| 0 (0%) | 14 (8.5%) | |||
| 5 (7.6%) | 24 (15%) | |||
| 5 (7.6%) | 34 (21%) | |||
| 0 (0%) | 4 (2.4%) | |||
| 0 (0%) | 4 (2.4%) | |||
| Stress score | 8.00 (8.00, 10.00) | 11.00 (10.00, 14.00) | <0.001 * | <0.001 |
| Anxiety score | ||||
| 48 (73%) | 47 (29%) | |||
| 7 (11%) | 40 (24%) | |||
| 0 (0%) | 14 (8.5%) | |||
| 5 (7.6%) | 24 (15%) | |||
| 5 (7.6%) | 34 (21%) | |||
| 1 (1.5%) | 5 (3.0%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aguirre-Quezada, M.A.; Aranda-Ramírez, M.P. Irruption of Network Analysis to Explain Dietary, Psychological and Nutritional Patterns and Metabolic Health Status in Metabolically Healthy and Unhealthy Overweight and Obese University Students: Ecuadorian Case. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2924. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16172924
Aguirre-Quezada MA, Aranda-Ramírez MP. Irruption of Network Analysis to Explain Dietary, Psychological and Nutritional Patterns and Metabolic Health Status in Metabolically Healthy and Unhealthy Overweight and Obese University Students: Ecuadorian Case. Nutrients. 2024; 16(17):2924. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16172924
Chicago/Turabian StyleAguirre-Quezada, María Alejandra, and María Pilar Aranda-Ramírez. 2024. "Irruption of Network Analysis to Explain Dietary, Psychological and Nutritional Patterns and Metabolic Health Status in Metabolically Healthy and Unhealthy Overweight and Obese University Students: Ecuadorian Case" Nutrients 16, no. 17: 2924. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16172924
APA StyleAguirre-Quezada, M. A., & Aranda-Ramírez, M. P. (2024). Irruption of Network Analysis to Explain Dietary, Psychological and Nutritional Patterns and Metabolic Health Status in Metabolically Healthy and Unhealthy Overweight and Obese University Students: Ecuadorian Case. Nutrients, 16(17), 2924. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16172924





