Annual and Seasonal Patterns of Dietary Intake in Australian Adults: A Prospective Cohort Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
- To describe the patterns in diet (total energy intake, macronutrient intake, healthy food groups, and discretionary foods and beverages) across the year;
- To determine whether dietary intake varies by season.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Setting and Participants
2.3. Variables
2.3.1. Dietary Intake
2.3.2. Participant Descriptive Characteristics
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Participants
3.2. Dietary Patterns across the Year
3.3. Seasonal Differences in Dietary Patterns
4. Discussion
Implications
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boeing, H.; Bechthold, A.; Bub, A.; Ellinger, S.; Haller, D.; Kroke, A.; Leschik-Bonnet, E.; Müller, M.J.; Oberritter, H.; Schulze, M.; et al. Critical review: Vegetables and fruit in the prevention of chronic diseases. Eur. J. Nutr. 2012, 51, 637–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afshin, A.; Sur, P.J.; Fay, K.A.; Cornaby, L.; Ferrara, G.; Salama, J.S.; Mullany, E.C.; Abate, K.H.; Abbafati, C.; Abebe, Z.; et al. Health effects of dietary risks in 195 countries, 1990–2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet 2019, 393, 1958–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Micha, R.; Shulkin, M.L.; Peñalvo, J.L.; Khatibzadeh, S.; Singh, G.M.; Rao, M.; Fahimi, S.; Powles, J.; Mozaffarian, D. Etiologic effects and optimal intakes of foods and nutrients for risk of cardiovascular diseases and diabetes: Systematic reviews and meta-analyses from the Nutrition and Chronic Diseases Expert Group (NutriCoDE). PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0175149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Food-Based Dietary Guidelines. Available online: https://www.fao.org/nutrition/education/food-based-dietary-guidelines (accessed on 1 February 2024).
- World Health Organization. Global Nutrition Policy Review 2016-2017: Country Progress in Creating Enabling Policy Environments for Promoting Healthy Diets and Nutrition. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241514873 (accessed on 13 June 2024).
- Miller, V.; Webb, P.; Cudhea, F.; Shi, P.; Zhang, J.; Reedy, J.; Erndt-Marino, J.; Coates, J.; Mozaffarian, D.; Bas, M.; et al. Global dietary quality in 185 countries from 1990 to 2018 show wide differences by nation, age, education, and urbanicity. Nat. Food 2022, 3, 694–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendrie, G.A.; Rebuli, M.A.; James-Martin, G.; Baird, D.L.; Bogard, J.R.; Lawrence, A.S.; Ridoutt, B. Towards healthier and more sustainable diets in the Australian context: Comparison of current diets with the Australian Dietary Guidelines and the EAT-Lancet Planetary Health Diet. BMC Public Health 2022, 22, 1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Australian Institute of Health and Welfare. Nutrition Across the Life Stages; Cat. No. PHE 227; Australian Institute of Health and Welfare: Canberra, Australia, 2018.
- Chen, P.J.; Antonelli, M. Conceptual models of food choice: Influential factors related to foods, individual differences, and society. Foods 2020, 9, 1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helander, E.E.; Wansink, B.; Chieh, A. Weight gain over the holidays in three countries. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1200–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maher, C.; Ferguson, T.; Curtis, R.; Brown, W.; Dumuid, D.; Fraysse, F.; Hendrie, G.A.; Singh, B.; Esterman, A.; Olds, T. Weekly, seasonal, and festive period weight gain among Australian adults. JAMA Netw. Open 2023, 6, e2326038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadhim, N.; Amiot, C.E.; Louis, W.R. The buffering role of social norms for unhealthy eating before, during, and after the Christmas holidays: A longitudinal study. Group Dyn. Theory Res. Pract. 2023, 27, 133–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahns, L.; Johnson, L.K.; Scheett, A.J.; Stote, K.S.; Raatz, S.K.; Subar, A.F.; Tande, D. Measures of diet quality across calendar and winter holiday seasons among midlife women: A 1-year longitudinal study using the automated self-administered 24-hour recall. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2016, 116, 1961–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamri-Senhadji, M.Y.; El Kebir, B.; Belleville, J.; Bouchenak, M. Assessment of dietary consumption and time-course of changes in serum lipids and lipoproteins before, during and after Ramadan in young Algerian adults. Singap. Med. J. 2009, 50, 288–294. [Google Scholar]
- Ezzat, S.; Amin, M. Energy intake, dietary pattern and physical activity during Ramadan. Int. J. Food Nutr. Public Health 2013, 6, 291–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shatila, H.; Baroudi, M.; El Sayed Ahmad, R.; Chehab, R.; Forman, M.R.; Abbas, N.; Faris, M.; Naja, F. Impact of Ramadan fasting on dietary intakes among healthy adults: A year-round comparative study. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 689788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Husain, R.; Duncan, M.T.; Cheah, S.H.; Ch’ng, S.L. Effects of fasting in Ramadan on tropical Asiatic Moslems. Br. J. Nutr. 1987, 58, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capita, R.; Alonso-Calleja, C. Differences in reported winter and summer dietary intakes in young adults in Spain. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2005, 56, 431–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, N.; Okuda, T.; Shinohara, H.; Yamasaki, R.S.; Hirano, N.; Kang, J.; Ogawa, M.; Nishi, N.N. Relationship between seasonal changes in food intake and energy metabolism, physical activity, and body composition in young Japanese women. Nutrients 2022, 14, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.J.; Lawler, G.S.; Panemangalore, M.; Street, D. Nutritional status of middle-aged and elderly females in Kentucky in two seasons: Part 1. Body weight and related factors. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 1987, 6, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahar, D.R.; Yerushalmi, N.; Lubin, F.; Froom, P.; Shahar, A.; Kristal-Boneh, E. Seasonal variations in dietary intake affect the consistency of dietary assessment. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2001, 17, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Staveren, W.A.; Deurenberg, P.; Burema, J.; De Groot, L.C.; Hautvast, J.G. Seasonal variation in food intake, pattern of physical activity and change in body weight in a group of young adult Dutch women consuming self-selected diets. Int. J. Obes. 1986, 10, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Costa, A.F.; Yokoo, E.M.; Anjos, L.A.d.; Wahrlich, V.; Olinto, M.T.A.; Henn, R.L.; Waissmann, W. Seasonal variation of food intake of adults from Niteroi, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Rev. Bras. Epidemiol. 2013, 16, 513–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernstein, S.; Zambell, K.; Amar, M.J.; Arango, C.; Kelley, R.C.; Miszewski, S.G.; Tryon, S.; Courville, A.B. Dietary intake patterns are consistent across seasons in a cohort of healthy adults in a metropolitan population. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2016, 116, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Olendzki, B.C.; Li, W.; Hafner, A.R.; Chiriboga, D.; Hebert, J.R.; Campbell, M.; Sarnie, M.; Ockene, I.S. Seasonal variation in food intake, physical activity, and body weight in a predominantly overweight population. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 60, 519–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coogan, S.; Sui, Z.; Raubenheimer, D. Gluttony and guilt: Monthly trends in internet search query data are comparable with national-level energy intake and dieting behavior. Palgrave Commun. 2018, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutishauser, I.H.E.; Wheeler, C.E.; Conn, J.A.; O’Dea, K. Food and nutrient intake in a randomly selected sample of adults: Demographic and temporal influences on energy and nutrient intake. Aust. J. Nutr. Diet. 1995, 51, 157–166. [Google Scholar]
- Curtis, R.G.; Olds, T.; Fraysse, F.; Dumuid, D.; Hendrie, G.A.; Esterman, A.; Brown, W.J.; Ferguson, T.; Lagiseti, R.; Maher, C.A. Annual rhythms in adults’ lifestyle and health (ARIA): Protocol for a 12-month longitudinal study examining temporal patterns in weight, activity, diet, and wellbeing in Australian adults. BMC Public Health 2021, 21, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, A.; Maher, C.; Tomkinson, G.R.; Golley, R.; Fraysse, F.; Dumuid, D.; Lewthwaite, H.; Olds, T. Life on holidays: Study protocol for a 3-year longitudinal study tracking changes in children’s fitness and fatness during the in-school versus summer holiday period. BMC Public Health 2019, 19, 1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassett, J.K.; English, D.R.; Fahey, M.T.; Forbes, A.B.; Gurrin, L.C.; Simpson, J.A.; Brinkman, M.T.; Giles, G.G.; Hodge, A.M. Validity and calibration of the FFQ used in the Melbourne Collaborative Cohort Study. Public Health Nutr. 2016, 19, 2357–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giles, G.G.; Ireland, P.D. Dietary Questionnaire for Epidemiological Studies (Version 3.2); Cancer Council Victoria: Melbourne, Australia, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- NUTTAB 2010; Australian Food Composition Tables. Food Standards Australia New Zealand: Canberra, Australia, 2013.
- AUSNUT 2007; Australian Food, Supplement and Nutrient Database for Estimation of Population Nutrient Intakes. Food Standards Australia New Zealand: Canberra, Australia, 2007. Available online: https://www.foodstandards.gov.au/science-data/monitoringnutrients/ausnut/ausnut2007 (accessed on 13 June 2024).
- Xinying, P.X.; Noakes, M.; Keogh, J. Can a food frequency questionnaire be used to capture dietary intake data in a 4 week clinical intervention trial? Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 13, 318–323. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hebden, L.; Kostan, E.; O’Leary, F.; Hodge, A.; Allman-Farinelli, M. Validity and reproducibility of a food frequency questionnaire as a measure of recent dietary intake in young adults. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e75156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodge, A.; Patterson, A.J.; Brown, W.J.; Ireland, P.; Giles, G. The Anti Cancer Council of Victoria FFQ: Relative validity of nutrient intakes compared with weighed food records in young to middle-aged women in a study of iron supplementation. Aust. N. Z. J. Public Health 2000, 24, 576–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. FAO Food and Nutrition Paper 77. Food Energy-Methods of Analysis and Conversion Factors; Report of a Technical Workshop; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Merrill, A.L.; Watt, B.K. Energy Value of Foods: Basis and Derivation; Human Nutrition Research Branch, Agricultural Research Service, US Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1973.
- Marfell-Jones, M.J.; Stewart, A.; De Ridder, J. International Standards for Anthropometric Assessment; International Society for the Advancement of Kinanthropometry: Wellington, New Zealand, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Holm, S. A simple sequentially rejective multiple test procedure. Scand. J. Stat. 1979, 6, 65–70. [Google Scholar]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Human Energy Requirements; Report of a Joint FAO/WHO/UNU Expert Consultation; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Australian Bureau of Statistics. Regional Population by Age and Sex. Available online: https://www.abs.gov.au/statistics/people/population/regional-population-age-and-sex/latest-release (accessed on 10 July 2024).
- Australian Institute of Health and Welfare. Australia’s Health 2018; Australia’s health series no. 16. AUS 221; Australian Institute of Health and Welfare: Canberra, Australia, 2018.
- Australian Bureau of Statistics. Pandemic Insights into Australian Smokers, 2020–2021. Available online: https://www.abs.gov.au/articles/pandemic-insights-australian-smokers-2020-21 (accessed on 10 July 2024).
- Australian Bureau of Statistics. Census of Population and Housing: General Community Profile, Australia, 2016; Cat. No. 2001.0; Commonwealth of Australia: Canberra, Australia, 2017.
- Berge, J.M.; Larson, N.; Bauer, K.W.; Neumark-Sztainer, D. Are parents of young children practicing healthy nutrition and physical activity behaviors? Pediatrics 2011, 27, 881–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winpenny, E.M.; Winkler, M.R.; Stochl, J.; van Sluijs, E.M.F.; Larson, N.; Neumark-Sztainer, D. Associations of early adulthood life transitions with changes in fast food intake: A latent trajectory analysis. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2020, 17, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millet, J.; Siracusa, J.; Tardo-Dino, P.-E.; Thivel, D.; Koulmann, N.; Malgoyre, A.; Charlot, K. Effects of acute heat and cold exposures at rest or during exercise on subsequent energy intake: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruddock, H.K.; Brunstrom, J.M.; Higgs, S. The social facilitation of eating: Why does the mere presence of others cause an increase in energy intake? Physiol. Behav. 2021, 240, 113539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verhoeven, A.A.C.; Adriaanse, M.A.; de Vet, E.; Fennis, B.M.; de Ridder, D.T.D. It’s my party and I eat if I want to. Reasons for unhealthy snacking. Appetite 2015, 84, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagström, H.; Widman, L.; von Seth, E. Association between temperature, sunlight hours and alcohol consumption. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0223312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uitenbroek, D.G. Seasonal variation in alcohol use. J. Stud. Alcohol 1996, 57, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malisova, O.; Bountziouka, V.; Zampelas, A.; Kapsokefalou, M. Evaluation of drinks contribution to energy intake in summer and winter. Nutrients 2015, 7, 3724–3738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seasonal Food Guide Australia. Available online: http://seasonalfoodguide.com/ (accessed on 23 May 2024).
- Yanovski Jack, A.; Yanovski Susan, Z.; Sovik Kara, N.; Nguyen Tuc, T.; O’Neil Patrick, M.; Sebring Nancy, G. A prospective study of holiday weight gain. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 342, 861–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, K.D. What is the required energy deficit per unit weight loss? Int. J. Obes. 2008, 32, 573–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanamas, S.K.; Shaw, J.E.; Backholer, K.; Magliano, D.J.; Peeters, A. Twelve-year weight change, waist circumference change and incident obesity: The Australian diabetes, obesity and lifestyle study. Obesity 2014, 22, 1538–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, W.J.; Williams, L.; Ford, J.H.; Ball, K.; Dobson, A.J. Identifying the energy gap: Magnitude and determinants of 5-year weight gain in midage women. Obes. Res. 2005, 13, 1431–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Room, R.; Babor, T.; Rehm, J. Alcohol and public health. Lancet 2005, 365, 519–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Australian Guidelines to Reduce Health Risks from Drinking Alcohol. Available online: https://www.nhmrc.gov.au/about-us/publications/australian-guidelines-reduce-health-risks-drinking-alcohol (accessed on 13 June 2024).

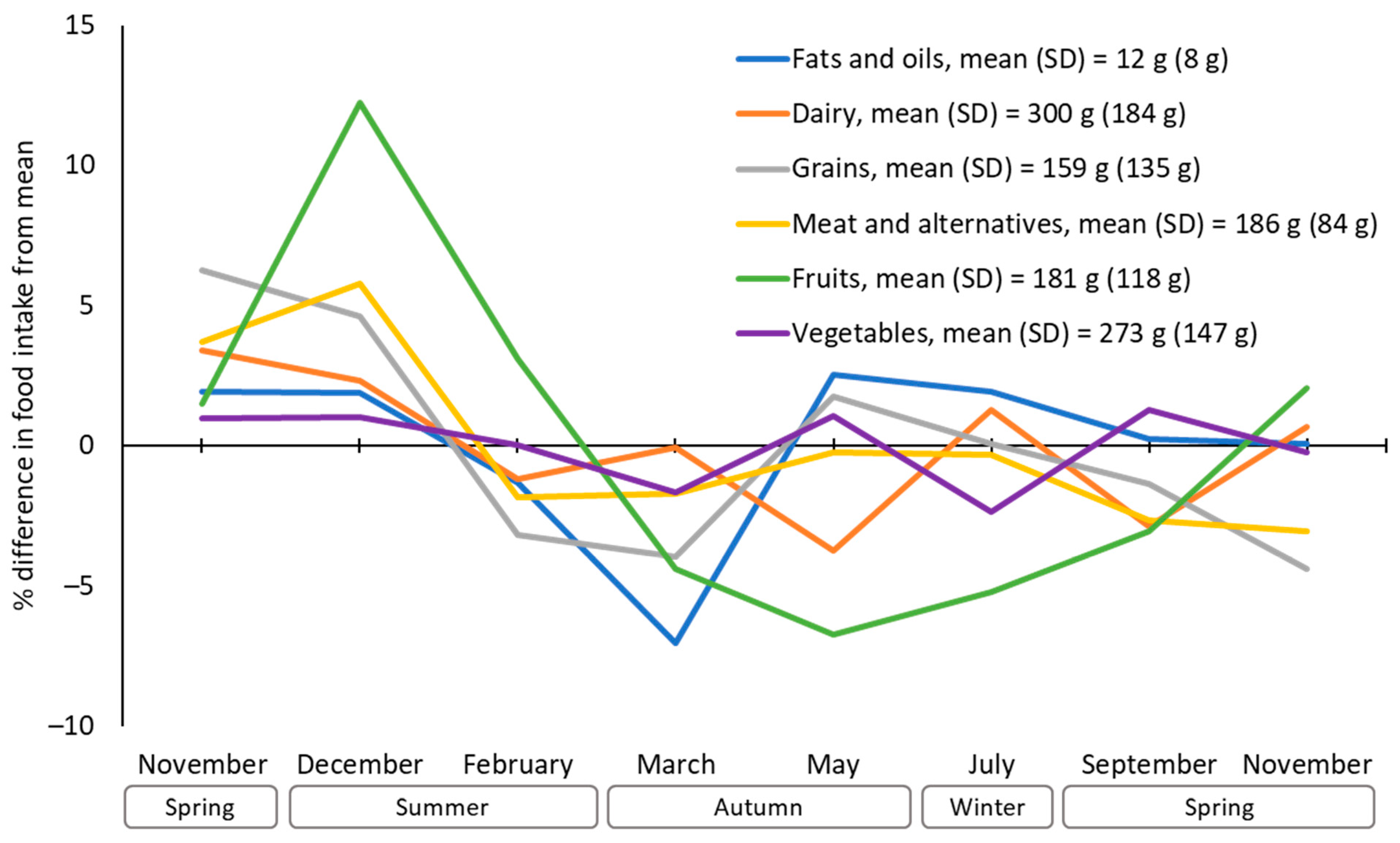
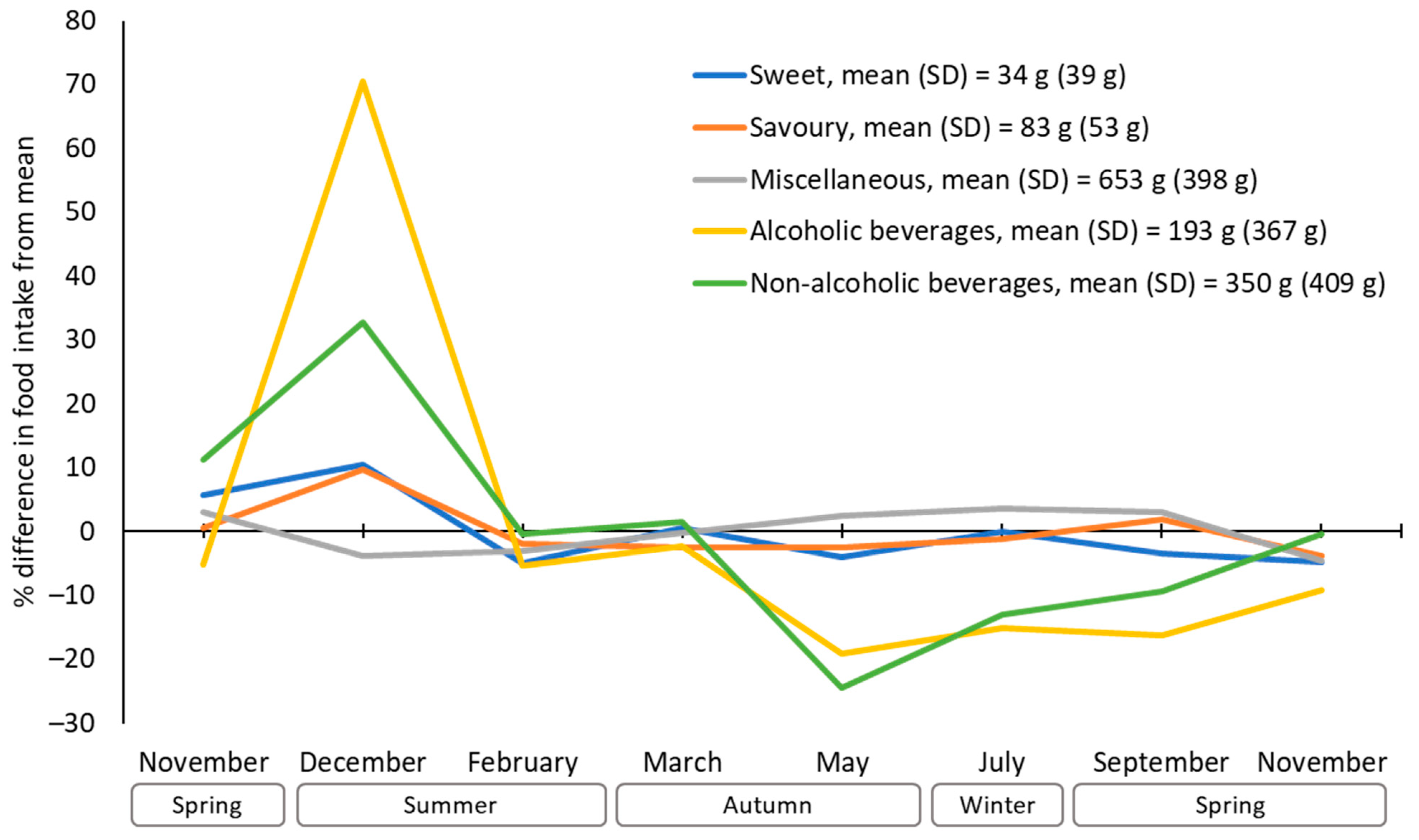
| Mean | (SD) | |
|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 40.2 | (5.9) |
| Weight at baseline (kg) | 83.7 | (20.2) |
| Height (cm) | 170.3 | (9.5) |
| Total energy intake (kJ/day) | 7683 | (3222) |
| Percentage of energy intake | ||
| Energy from protein (%) | 19.4 | (3.8) |
| Energy from fat (%) | 36.9 | (5.8) |
| Energy from carbohydrate (%) | 40.4 | (7.5) |
| Energy from alcohol (%) | 3.2 | (5.3) |
| n | (%) | |
| Sex | ||
| Female | 203 | (57) |
| Male | 155 | (43) |
| Weight status category | ||
| Underweight | 1 | (0.3) |
| Normal | 112 | (31.2) |
| Overweight | 121 | (33.7) |
| Obese | 124 | (34.5) |
| Smoker | 32 | (8.9) |
| Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander peoples | 4 | (1.1) |
| Born in Australia | 274 | (76.5) |
| Marital status | ||
| Married/de facto | 305 | (85.2) |
| Separated, divorced or widowed | 28 | (7.8) |
| Never married | 25 | (7.0) |
| Education | ||
| Year 10 or less | 17 | (4.8) |
| Year 11–12 | 48 | (13.4) |
| Certificate/Diploma | 120 | (33.6) |
| University degree | 173 | (48.3) |
| Chronic conditions | ||
| None | 156 | (43.6) |
| Single | 106 | (29.6) |
| Multiple | 96 | (26.9) |
| Season | Estimated Marginal Means | [95% CI] | Group | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total energy | Summer | 7582.8 | [7316.5, 7849.2] | A | |
| Autumn | 7238.2 | [6970.4, 7506.0] | B | ||
| Winter | 7332.8 | [7066.7, 7598.9] | B | ||
| Spring | 7225.4 | [6956.6, 7494.1] | B | ||
| Protein | Summer | 1456.7 | [1403.1, 1510.3] | A | |
| Autumn | 1395.4 | [1341.5, 1449.3] | B | ||
| Winter | 1406.3 | [1352.8, 1459.9] | B | ||
| Spring | 1389.5 | [1335.3, 1443.6] | B | ||
| Fat | Summer | 2746.5 | [2637.5, 2855.6] | A | |
| Autumn | 2636.0 | [2526.3, 2745.7] | B | ||
| Winter | 2700.6 | [2591.6, 2809.5] | A | B | |
| Spring | 2630.8 | [2520.7, 2740.9] | B | ||
| Carbohydrate | Summer | 3064.2 | [2945.4, 3182.9] | A | |
| Autumn | 2952.7 | [2833.2, 3072.1] | A | ||
| Winter | 2975.7 | [2857.1, 3094.2] | A | ||
| Spring | 2967.1 | [2849.1, 3087.1] | A | ||
| Alcohol | Summer | 308.7 | [259.0, 358.4] | A | |
| Autumn | 245.5 | [195.6, 295.5] | B | ||
| Winter | 243.2 | [193.5, 292.9] | B | ||
| Spring | 231.9 | [181.7, 282.0] | B | ||
| Season | Estimated Marginal Means | [95% CI] | Group | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fats and oils | Summer | 12.0 | [11.1, 12.9] | A | |
| Autumn | 11.8 | [10.9, 12.7] | A | ||
| Winter | 12.1 | [11.2, 13.0] | A | ||
| Spring | 11.9 | [11.00, 12.8] | A | ||
| Dairy | Summer | 299.8 | [277.7, 321.8] | A | |
| Autumn | 298.0 | [275.8, 320.1] | A | ||
| Winter | 299.8 | [277.8, 321.9] | A | ||
| Spring | 302.7 | [280.4, 325.0] | A | ||
| Grains | Summer | 154.9 | [143.8, 165.9] | A | |
| Autumn | 152.26 | [141.0, 163.3] | A | ||
| Winter | 151.2 | [140.2, 162.3] | A | ||
| Spring | 151.5 | [140.4, 162.7] | A | ||
| Meats | Summer | 189.8 | [179.6, 200.1] | A | |
| Autumn | 180.6 | [170.3, 190.8] | A | B | |
| Winter | 179.6 | [169.4, 189.8] | B | ||
| Spring | 177.0 | [166.7, 187.4] | B | ||
| Fruits | Summer | 187.8 | [173.4, 202.1] | A | |
| Autumn | 172.4 | [157.9, 186.9] | A | B | |
| Winter | 169.8 | [155.5, 184.1] | B | ||
| Spring | 182.5 | [167.9, 197.0] | A | B | |
| Vegetables | Summer | 273.5 | [255.2, 291.7] | A | |
| Autumn | 273.2 | [254.9, 291.6] | A | ||
| Winter | 270.8 | [252.6, 289.0] | A | ||
| Spring | 274.1 | [255.6, 292.5] | A | ||
| Season | Estimated Marginal Means | [95% CI] | Group | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sweet discretionary | Summer | 31.6 | [27.2, 36.1] | A | |
| Autumn | 31.5 | [27.1, 36.0] | A | ||
| Winter | 32.6 | [28.2, 37.0] | A | ||
| Spring | 31.9 | [27.4, 36.3] | A | ||
| Savoury discretionary | Summer | 84.7 | [79.1, 90.2] | A | |
| Autumn | 77.7 | [72.1, 83.3] | B | ||
| Winter | 82.1 | [76.5, 87.6] | A | B | |
| Spring | 79.7 | [74.1, 85.3] | A | B | |
| Alcoholic beverages | Summer | 218.0 | [179.5, 256.5] | A | |
| Autumn | 177.8 | [139.1, 216.5] | B | ||
| Winter | 167.0 | [128.5, 205.5] | B | ||
| Spring | 161.1 | [122.2, 200.0] | B | ||
| Non-alcoholic beverages | Summer | 364.6 | [322.0, 407.2] | A | |
| Autumn | 285.0 | [242.0, 328.1] | B | ||
| Winter | 289.8 | [247.3, 332.4] | B | ||
| Spring | 322.3 | [278.9, 365.6] | A | B | |
| Miscellaneous | Summer | 625.5 | [581.6, 669.5] | A | |
| Autumn | 649.3 | [605.2, 693.5] | A | B | |
| Winter | 673.7 | [629.8, 717.6] | B | ||
| Spring | 646.8 | [602.5, 691.0] | A | B | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Curtis, R.G.; Hendrie, G.A.; Ferguson, T.; Olds, T.; Fraysse, F.; Dumuid, D.; Brown, W.J.; Esterman, A.; Maher, C.A. Annual and Seasonal Patterns of Dietary Intake in Australian Adults: A Prospective Cohort Study. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2718. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16162718
Curtis RG, Hendrie GA, Ferguson T, Olds T, Fraysse F, Dumuid D, Brown WJ, Esterman A, Maher CA. Annual and Seasonal Patterns of Dietary Intake in Australian Adults: A Prospective Cohort Study. Nutrients. 2024; 16(16):2718. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16162718
Chicago/Turabian StyleCurtis, Rachel G., Gilly A. Hendrie, Ty Ferguson, Timothy Olds, François Fraysse, Dorothea Dumuid, Wendy J. Brown, Adrian Esterman, and Carol A. Maher. 2024. "Annual and Seasonal Patterns of Dietary Intake in Australian Adults: A Prospective Cohort Study" Nutrients 16, no. 16: 2718. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16162718
APA StyleCurtis, R. G., Hendrie, G. A., Ferguson, T., Olds, T., Fraysse, F., Dumuid, D., Brown, W. J., Esterman, A., & Maher, C. A. (2024). Annual and Seasonal Patterns of Dietary Intake in Australian Adults: A Prospective Cohort Study. Nutrients, 16(16), 2718. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16162718






