The Effects of Long-Term High Fat and/or High Sugar Feeding on Sources of Postprandial Hepatic Glycogen and Triglyceride Synthesis in Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Animal Studies
2.2. Hepatic Triglyceride and Glycogen Extraction, Derivatization and Purification to Monoacetone Glucose (MAG)
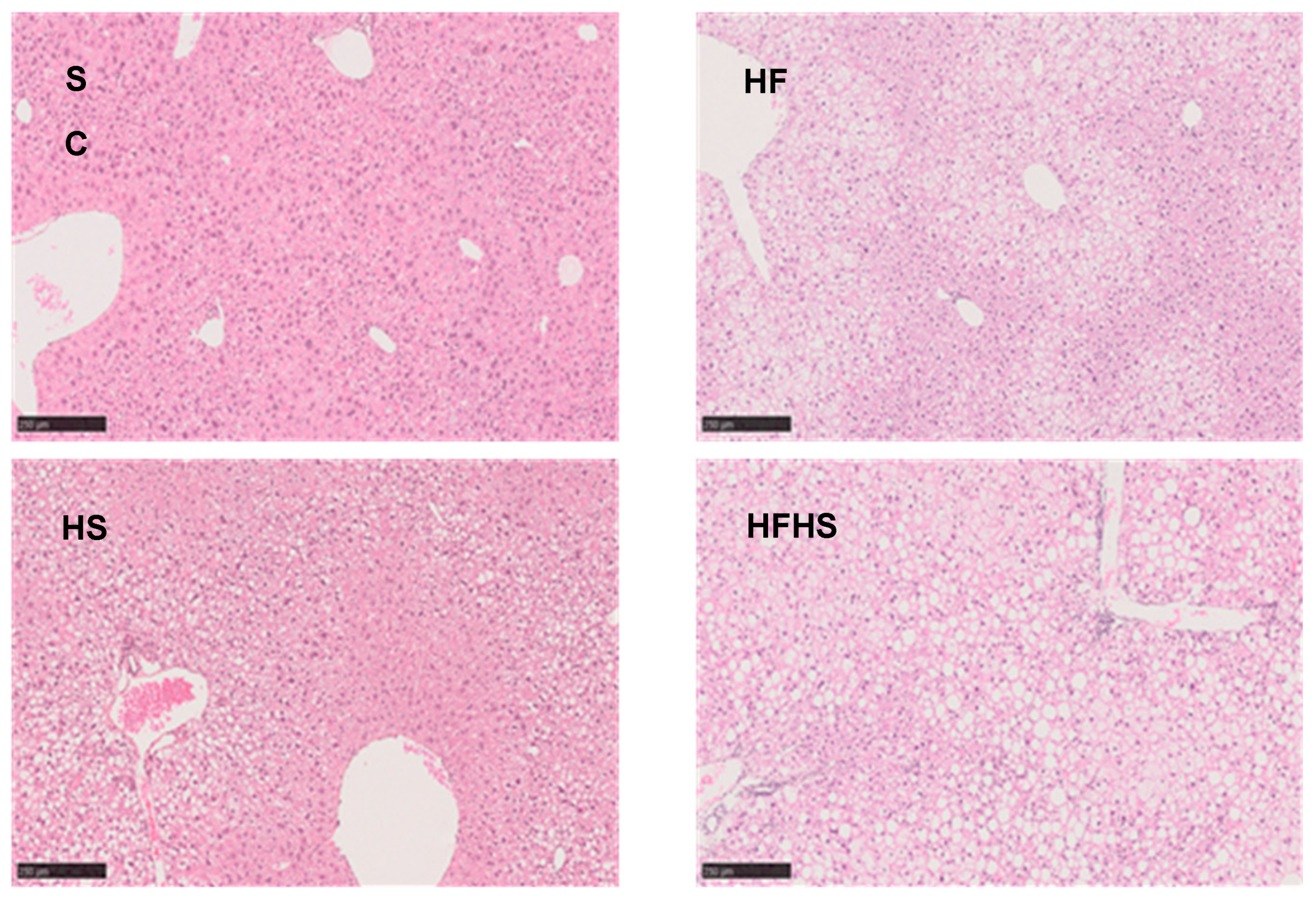
2.3. Liver Histology
2.4. NMR Spectroscopy
2.5. Metabolic Flux Calculations
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
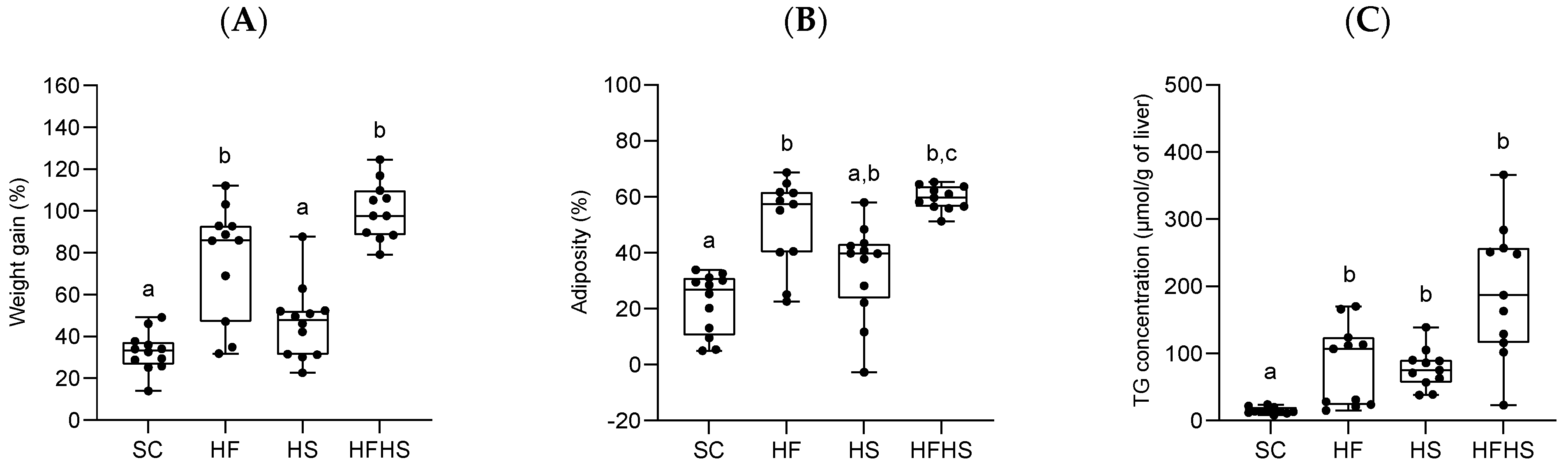
3.1. Effects of the Diets on Body Weight, Adiposity and Liver Triglyceride (TG)
3.2. Effects of the Diets on Hepatic Triglyceride Synthesis
3.3. Effects of the Diets on Hepatic Glycogen Synthesis
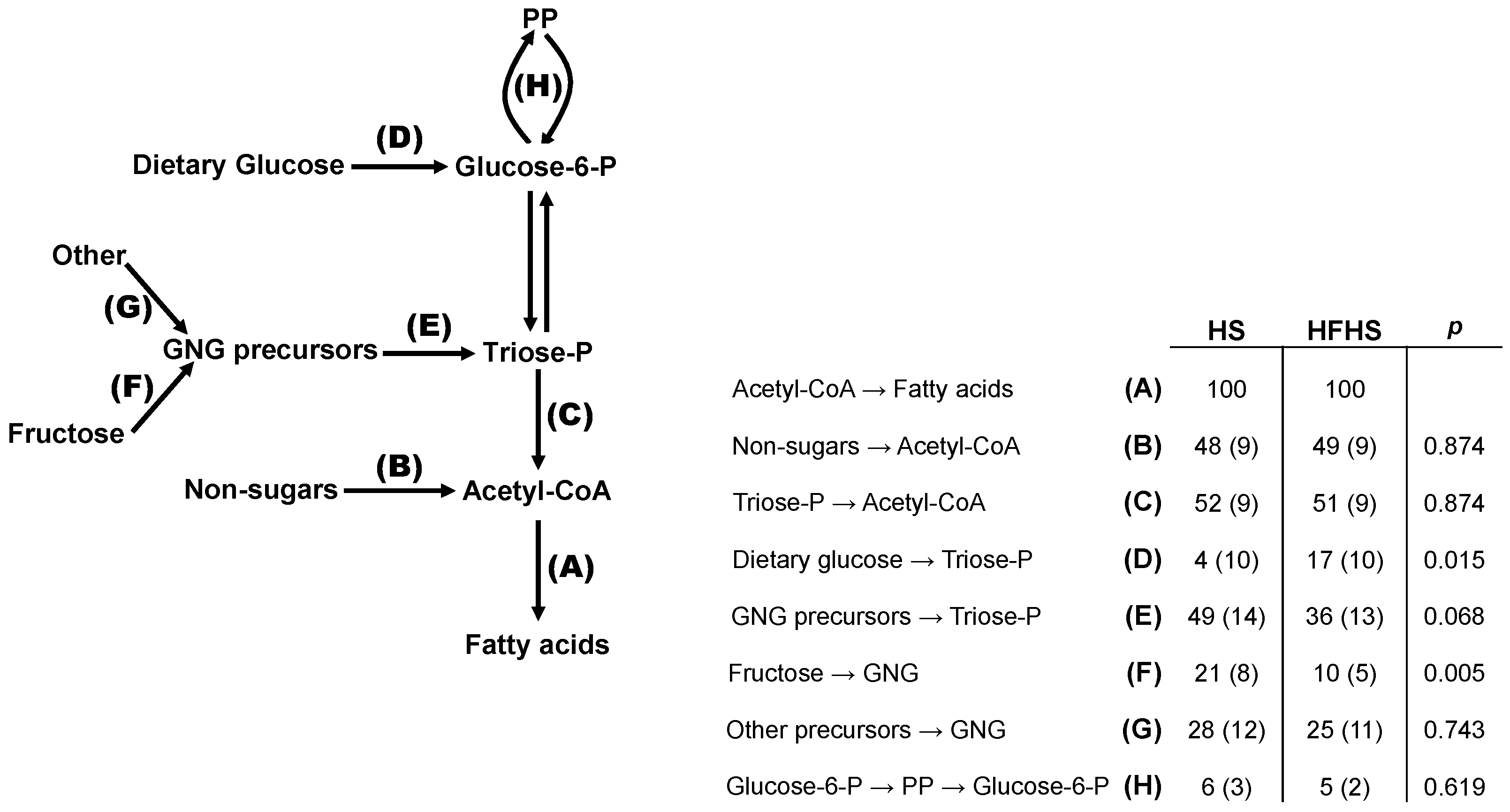
3.4. Integrated Analysis of Substrate Fluxes into De Novo Lipogenesis
4. Discussion
4.1. NAFLD Profiles of Our Mice Models
4.2. Interactions of Dietary Sugar and Lipid in Promoting Steatosis
4.3. Effects of Diet on Sources of Hepatic Glycogen Synthesis
4.4. Effects of Diets on the Sources of Hepatic Triglyceride Synthesis
4.5. Stoichiometry of PP and DNL Fluxes
4.6. Study Limitations
4.7. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Riazi, K.; Azhari, H.; Charette, J.H.; E Underwood, F.; A King, J.; Afshar, E.E.; Swain, M.G.; E Congly, S.; Kaplan, G.G.; Shaheen, A.-A. The prevalence and incidence of NAFLD worldwide: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 7, 851–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinella, M.E.; Lazarus, J.V.; Ratziu, V.; Francque, S.M.; Sanyal, A.J.; Kanwal, F.; Romero, D.; Abdelmalek, M.F.; Anstee, Q.M.; Arab, J.P.; et al. A multisociety Delphi consensus statement on new fatty liver disease nomenclature. Hepatology 2023, 78, 1966–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vacca, M.; Kamzolas, I.; Harder, L.M.; Oakley, F.; Trautwein, C.; Hatting, M.; Ross, T.; Bernardo, B.; Oldenburger, A.; Hjuler, S.T.; et al. An unbiased ranking of murine dietary models based on their proximity to human metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD). Nat. Metab. 2024, 6, 1178–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Golabi, P.; Paik, J.M.; Henry, A.; Van Dongen, C.; Henry, L. The global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH): A systematic review. Hepatology 2023, 77, 1335–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trépo, E.; Valenti, L. Update on NAFLD genetics: From new variants to the clinic. J. Hepatol. 2020, 72, 1196–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lonardo, A.; Nascimbeni, F.; Ballestri, S.; Fairweather, D.; Win, S.; Than, T.A.; Abdelmalek, M.F.; Suzuki, A. Sex Differences in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: State of the Art and Identification of Research Gaps. Hepatology 2019, 70, 1457–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luukkonen, P.K.; Qadri, S.; Ahlholm, N.; Porthan, K.; Männistö, V.; Sammalkorpi, H.; Penttilä, A.K.; Hakkarainen, A.; Lehtimäki, T.E.; Gaggini, M.; et al. Distinct contributions of metabolic dysfunction and genetic risk factors in the pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2021, 76, 526–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chhimwal, J.; Patial, V.; Padwad, Y. Beverages and Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): Think before you drink. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 2508–2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polyzos, S.A.; Kountouras, J.; Mantzoros, C.S. Obesity and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: From pathophysiology to therapeutics. Metabolism 2018, 92, 82–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alferink, L.J.; Jong, J.C.K.-D.; Erler, N.S.; Veldt, B.J.; Schoufour, J.D.; de Knegt, R.J.; Ikram, M.A.; Metselaar, H.J.; LA Janssen, H.; Franco, O.H.; et al. Association of dietary macronutrient composition and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in an ageing population: The Rotterdam Study. Gut 2018, 68, 1088–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anstee, Q.M.; Goldin, R.D. Mouse models in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and steatohepatitis research. Int. J. Exp. Pathol. 2006, 87, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parry, S.A.; Rosqvist, F.; Mozes, F.E.; Cornfield, T.; Hutchinson, M.; Piche, M.-E.; Hülsmeier, A.J.; Hornemann, T.; Dyson, P.; Hodson, L. Intrahepatic Fat and Postprandial Glycemia Increase After Consumption of a Diet Enriched in Saturated Fat Compared with Free Sugars. Diabetes Care 2020, 43, 1134–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Softic, S.; Cohen, D.E.; Kahn, C.R. Role of Dietary Fructose and Hepatic De Novo Lipogenesis in Fatty Liver Disease. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2016, 61, 1282–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eng, J.M.; Estall, J.L. Diet-Induced Models of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Food for Thought on Sugar, Fat, and Cholesterol. Cells 2021, 10, 1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Burrington, C.M.; Graff, E.C.; Zhang, J.; Judd, R.L.; Suksaranjit, P.; Kaewpoowat, Q.; Davenport, S.K.; O’Neill, A.M.; Greene, M.W. Metabolic phenotype and adipose and liver features in a high-fat western diet-induced mouse model of obesity-linked NAFLD. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 310, E418–E439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duarte, J.A.G.; Carvalho, F.; Pearson, M.; Horton, J.D.; Browning, J.D.; Jones, J.G.; Burgess, S.C. A high-fat diet suppresses de novo lipogenesis and desaturation but not elongation and triglyceride synthesis in mice. J. Lipid Res. 2014, 55, 2541–2553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Randle, P.J. Regulatory interactions between lipids and carbohydrates: The glucose fatty acid cycle after 35 years. Diabetes Metab. Rev. 1998, 14, 263–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luukkonen, P.K.; Sädevirta, S.; Zhou, Y.; Kayser, B.; Ali, A.; Ahonen, L.; Lallukka, S.; Pelloux, V.; Gaggini, M.; Jian, C.; et al. Saturated Fat Is More Metabolically Harmful for the Human Liver Than Unsaturated Fat or Simple Sugars. Diabetes Care 2018, 41, 1732–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevastianova, K.; Santos, A.; Kotronen, A.; Hakkarainen, A.; Makkonen, J.; Silander, K.; Peltonen, M.; Romeo, S.; Lundbom, J.; Lundbom, N.; et al. Effect of short-term carbohydrate overfeeding and long-term weight loss on liver fat in overweight humans. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 96, 727–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGarry, J.; Takabayashi, Y.; Foster, D. The role of malonyl-coa in the coordination of fatty acid synthesis and oxidation in isolated rat hepatocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 1978, 253, 8294–8300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, H.R.; Landau, B.R. Pathways of fructose conversion to glucose and glycogen in liver. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1972, 150, 708–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, G.A.; Popkin, B.M. Dietary sugar and body weight: Have we reached a crisis in the epidemic of obesity and diabetes? Health be damned! Pour on the sugar. Diabetes Care 2014, 37, 950–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanhope, K.L. Sugar consumption, metabolic disease and obesity: The state of the controversy. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2015, 53, 52–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, R.W.; Dumke, K.A.; Goran, M.I. Fructose content in popular beverages made with and without high-fructose corn syrup. Nutrition 2014, 30, 928–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tappy, L.; Lê, K.-A. Metabolic effects of fructose and the worldwide increase in obesity. Physiol. Rev. 2010, 90, 23–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huneault, H.E.; Tovar, A.R.; Sanchez-Torres, C.; Welsh, J.A.; Vos, M.B. The Impact and Burden of Dietary Sugars on the Liver. Hepatol. Commun. 2023, 7, e0297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iizuka, K. Recent Progress on Fructose Metabolism—Chrebp, Fructolysis, and Polyol Pathway. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakim, D.; Herman, R.H.; Gordon, W.C. The conversion of glucose and fructose to fatty acids in the human liver. Biochem. Med. 1969, 2, 427–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geidl-Flueck, B.; Hochuli, M.; Németh, Á.; Eberl, A.; Derron, N.; Köfeler, H.C.; Tappy, L.; Berneis, K.; Spinas, G.A.; Gerber, P.A. Fructose- and sucrose- but not glucose-sweetened beverages promote hepatic de novo lipogenesis: A randomized controlled trial. J. Hepatol. 2021, 75, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smajis, S.; Gajdošík, M.; Pfleger, L.; Traussnigg, S.; Kienbacher, C.; Halilbasic, E.; Ranzenberger-Haider, T.; Stangl, A.; Beiglböck, H.; Wolf, P.; et al. Metabolic effects of a prolonged, very-high-dose dietary fructose challenge in healthy subjects. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 111, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, J.S.; Le, M.T.; Pan, Z.; Rivard, C.; Love-Osborne, K.; Robbins, K.; Johnson, R.J.; Sokol, R.J.; Sundaram, S.S. Oral fructose absorption in obese children with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Pediatr. Obes. 2014, 10, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Soldado, I.; Zafra, D.; Duran, J.; Adrover, A.; Calbó, J.; Guinovart, J.J. Liver glycogen reduces food intake and attenuates obesity in a high-fat diet–fed mouse model. Diabetes 2014, 64, 796–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Soldado, I.; Fuentes-Romero, R.; Duran, J.; Guinovart, J.J. Effects of hepatic glycogen on food intake and glucose homeostasis are mediated by the vagus nerve in mice. Diabetologia 2017, 60, 1076–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, K.F.; Laurent, D.; Yu, C.; Cline, G.W.; Shulman, G.I. Stimulating effects of low-dose fructose on insulin-stimulated hepatic glycogen synthesis in humans. Diabetes 2001, 50, 1263–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, J.C.; Marques, C.; Martins, F.O.; Viegas, I.; Tavares, L.; Macedo, M.P.; Jones, J.G. Determining contributions of exogenous glucose and fructose to de novo fatty acid and glycerol synthesis in liver and adipose tissue. Metab. Eng. 2019, 56, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiNunzio, G.; Belew, G.D.; Torres, A.N.; Silva, J.G.; Silva, L.P.; Barosa, C.; Tavares, L.; Jones, J.G. Determining the contribution of a high-fructose corn syrup formulation to hepatic glycogen synthesis during ad-libitum feeding in mice. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 12852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viegas, I.; Di Nunzio, G.; Belew, G.D.; Torres, A.N.; Silva, J.G.; Perpétuo, L.; Barosa, C.; Tavares, L.C.; Jones, J.G. Integration of Liver Glycogen and Triglyceride NMR Isotopomer Analyses Provides a Comprehensive Coverage of Hepatic Glucose and Fructose Metabolism. Metabolites 2022, 12, 1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belew, G.D.; Silva, J.; Rito, J.; Tavares, L.; Viegas, I.; Teixeira, J.; Oliveira, P.J.; Macedo, M.P.; Jones, J.G. Transfer of glucose hydrogens via acetyl-CoA, malonyl-CoA, and NADPH to fatty acids during de novo lipogenesis. J. Lipid Res. 2019, 60, 2050–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keppler, D.; Decker, K. Determination with amyloglucosidase. In Methods of Enzymatic Analysis; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1974; Volume 3, pp. 1127–1131. [Google Scholar]
- Kleiner, D.E.; Brunt, E.M.; Van Natta, M.; Behling, C.; Contos, M.J.; Cummings, O.W.; Ferrell, L.D.; Liu, Y.-C.; Torbenson, M.S.; Unalp-Arida, A.; et al. Design and validation of a histological scoring system for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2005, 41, 1313–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.G.; Merritt, M.; Malloy, C. Quantifying tracer levels of 2H2O enrichment from microliter amounts of plasma and urine by 2H NMR. Magn. Reason. Med. 2001, 45, 156–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCabe, B.J.; Bederman, I.R.; Croniger, C.; Millward, C.; Norment, C.; Previs, S.F. Reproducibility of gas chromatography–mass spectrometry measurements of 2H labeling of water: Application for measuring body composition in mice. Anal. Biochem. 2006, 350, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belew, G.D.; Di Nunzio, G.; Tavares, L.; Silva, J.G.; Torres, A.N.; Jones, J.G. Estimating pentose phosphate pathway activity from the analysis of hepatic glycogen 13C-isotopomers derived from [U-13C]fructose and [U-13C]glucose. Magn. Reason. Med. 2020, 84, 2765–2771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, A.N.; Tavares, L.; Pereira, M.J.; Eriksson, J.W.; Jones, J.G. Positional and compositional analysis of saturated, monounsaturated, and polyunsaturated fatty acids in human adipose tissue triglyceride by 13C nuclear magnetic resonance. NMR Biomed. 2023, 36, e4632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Fleishman, J.S.; Li, T.; Li, Y.; Ren, Z.; Chen, J.; Ding, M. Pharmacological therapy of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease-driven hepatocellular carcinoma. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 14, 1336216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakurai, Y.; Zhang, X.J.; Wolfe, R.R. Effect of tumor necrosis factor on substrate and amino acid kinetics in conscious dogs. Am. J. Physiol. Metab. 1994, 266, E936–E945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanuri, G.; Spruss, A.; Wagnerberger, S.; Bischoff, S.C.; Bergheim, I. Role of tumor necrosis factor α (TNFα) in the onset of fructose-induced nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in mice. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2010, 22, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchida, T.; Lee, Y.A.; Fujiwara, N.; Ybanez, M.; Allen, B.; Martins, S.; Fiel, M.I.; Goossens, N.; Chou, H.-I.; Hoshida, Y.; et al. A simple diet- and chemical-induced murine NASH model with rapid progression of steatohepatitis, fibrosis and liver cancer. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 385–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetri, L.H.; Basaranoglu, M.; Brunt, E.M.; Yerian, L.M.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A. Severe NAFLD with hepatic necroinflammatory changes in mice fed trans fats and a high-fructose corn syrup equivalent. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2008, 295, G987–G995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asgharpour, A.; Cazanave, S.C.; Pacana, T.; Seneshaw, M.; Vincent, R.; Banini, B.A.; Kumar, D.P.; Daita, K.; Min, H.-K.; Mirshahi, F.; et al. A diet-induced animal model of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and hepatocellular cancer. J. Hepatol. 2016, 65, 579–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randle, P.J.; Priestman, D.A.; Mistry, S.C.; Halsall, A. Glucose fatty acid interactions and the regulation of glucose disposal. J. Cell. Biochem. 1994, 55, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randle, P.J. Metabolic fuel selection: General integration at the whole-body level. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 1995, 54, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenkins, C.M.; Yang, J.; Sims, H.F.; Gross, R.W. Reversible high affinity inhibition of phosphofructokinase-1 by acyl-CoA: A mechanism integrating glycolytic flux with lipid metabolism. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 11937–11950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hue, L.; Taegtmeyer, H. The Randle cycle revisited: A new head for an old hat. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 297, E578–E591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Soldado, I.; Bertini, A.; Adrover, A.; Duran, J.; Guinovart, J.J. Maintenance of liver glycogen during long-term fasting preserves energy state in mice. FEBS Lett. 2020, 594, 1698–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bisschop, P.H.; Arias, A.P.; Ackermans, M.T.; Endert, E.; Pijl, H.; Kuipers, F.; Meijer, A.J.; Sauerwein, H.P.; Romijn, J.A. The effects of carbohydrate variation in isocaloric diets on glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis in healthy men. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2000, 85, 1963–1967. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Davies, D.R.; Detheux, M.; VAN Schaftingen, E. Fructose 1-phosphate and the regulation of glucokinase activity in isolated hepatocytes. Eur. J. Biochem. 1990, 192, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarak, I.; Barosa, C.; Martins, F.O.; Silva, J.C.P.; Santos, C.; Belew, G.D.; Rito, J.; Viegas, I.; Teixeira, J.; Oliveira, P.J.; et al. Sources of hepatic glycogen synthesis in mice fed with glucose or fructose as the sole dietary carbohydrate. Magn. Reson. Med. 2018, 81, 639–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdul-Wahed, A.; Guilmeau, S.; Postic, C. Sweet Sixteenth for ChREBP: Established Roles and Future Goals. Cell Metab. 2017, 26, 324–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Softic, S.; Gupta, M.K.; Wang, G.-X.; Fujisaka, S.; O’neill, B.T.; Rao, T.N.; Willoughby, J.; Harbison, C.; Fitzgerald, K.; Ilkayeva, O.; et al. Divergent effects of glucose and fructose on hepatic lipogenesis and insulin signaling. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 4059–4074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ter Horst, K.W.; Vatner, D.F.; Zhang, D.; Cline, G.W.; Ackermans, M.T.; Nederveen, A.J.; Verheij, J.; Demirkiran, A.; van Wagensveld, B.A.; Dallinga-Thie, G.M.; et al. Hepatic Insulin Resistance Is Not Pathway Selective in Humans With Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Diabetes Care 2020, 44, 489–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, F.W.B.; Griffin, J.L. De novo lipogenesis in the liver in health and disease: More than just a shunting yard for glucose. Biol. Rev. Camb. Philos. Soc. 2016, 91, 452–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, J.S.; Mietus-Snyder, M.; Valente, A.; Schwarz, J.-M.; Lustig, R.H. The role of fructose in the pathogenesis of NAFLD and the metabolic syndrome. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2010, 7, 251–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruhama, Y. Conversion of ingested carbohydrate-14C into glycerol and fatty acids of serum triglyceride in patients with myocardial infarction. Metabolism 1970, 19, 1085–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Boca, J.; Flatt, J.P. Fatty acid synthesis from glucose and acetate and the control of lipogenesis in adipose tissue. Eur. J. Biochem. 1969, 11, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baquet, A.; Lavoinne, A.; Hue, L. Comparison of the effects of various amino acids on glycogen synthesis, lipogenesis and ketogenesis in isolated rat hepatocytes. Biochem. J. 1991, 273, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Jang, C.; Liu, J.; Uehara, K.; Gilbert, M.; Izzo, L.; Zeng, X.; Trefely, S.; Fernandez, S.; Carrer, A.; et al. Dietary fructose feeds hepatic lipogenesis via microbiota-derived acetate. Nature 2020, 579, 586–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.; Chassaing, B.; Zhang, L.; Yeoh, B.S.; Xiao, X.; Kumar, M.; Baker, M.T.; Cai, J.; Walker, R.; Borkowski, K.; et al. Microbiota-Dependent Hepatic Lipogenesis Mediated by Stearoyl CoA Desaturase 1 (SCD1) Promotes Metabolic Syndrome in TLR5-Deficient Mice. Cell Metab. 2015, 22, 983–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bederman, I.R.; Reszko, A.E.; Kasumov, T.; David, F.; Wasserman, D.H.; Kelleher, J.K.; Brunengraber, H. Zonation of labeling of lipogenic acetyl-CoA across the liver: Implications for studies of lipogenesis by mass isotopomer analysis. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 43207–43216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hijmans, B.S.; Grefhorst, A.; Oosterveer, M.H.; Groen, A.K. Zonation of glucose and fatty acid metabolism in the liver: Mechanism and metabolic consequences. Biochimie 2014, 96, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seubnooch, P.; Montani, M.; Tsouka, S.; Claude, E.; Rafiqi, U.; Perren, A.; Dufour, J.-F.; Masoodi, M. Characterisation of hepatic lipid signature distributed across the liver zonation using mass spectrometry imaging. JHEP Rep. 2023, 5, 100725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.Z.; Empie, M.W. Fructose metabolism in humans—What isotopic tracer studies tell us. Nutr. Metab. 2012, 9, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Diet | FSR (%) | FSR × [Lipid Species] (μmol/g Liver) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GLY | DNL | EL | DS | [TG]total | GLY | [FANE] | DNL | EL | [FAMU] | DS | |
| SC | 50 (14) a | 17 (7) a | 16 (2) a | 16 (6) a | 18 (10) a | 9 (6) a | 43 (25) a | 8 (7) a | 8 (4) a | 32 (19) a | 6 (5) a |
| HF | 35 (18) a,b | 5 (2) b | 8 (4) a,b | 3 (1) b | 82 (60) b | 21 (11) a,b | 162 (121) b | 6 (4) a | 9 (5) a | 99 (75) a,b | 3 (2) a |
| HS | 30 (7) b | 15 (6) a | 10 (3) b | 9 (4) a,c | 95 (66) b | 28 (17) b | 275 (207) b | 38 (26) b | 26 (15) b | 209 (152) b,c | 18 (12) b |
| HFHS | 26 (8) b | 9 (3) c | 6 (3) b | 6 (3) b,c | 193 (98) b | 45 (19) b | 467 (245) c | 38 (18) b | 27 (16) b | 311 (170) c | 17 (8) b |
| Diet | Triglyceride Component | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| SFA | OL | GLY | |
| HS | 27 (15) | 16 (10) * a | 40 (13) b |
| HFHS | 18 (9) | 7 (5) *** | 22 (11) |
| Diet | Direct Pathway | Indirect Pathways | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | KC | TP | FruKC | FruTP | Frutotal | ||
| SC | 71 (3) a | 29 (3) a | 19 (3) a | 10 (1) a | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. |
| HF | 52 (4) b | 47 (2) b | 34 (3) b | 12 (3) a,c | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. |
| HS | 64 (6) c | 36 (6) c | 12 (3) c | 24 (5) b | 1 (1) | 16 (8) ** | 17 (9) ** |
| HFHS | 60 (3) c | 40 (3) c | 21 (4) a | 20 (3) b,c | 1 (1) | 11 (5) | 11 (6) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Reis-Costa, A.; Belew, G.D.; Viegas, I.; Tavares, L.C.; Meneses, M.J.; Patrício, B.; Gastaldelli, A.; Macedo, M.P.; Jones, J.G. The Effects of Long-Term High Fat and/or High Sugar Feeding on Sources of Postprandial Hepatic Glycogen and Triglyceride Synthesis in Mice. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2186. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16142186
Reis-Costa A, Belew GD, Viegas I, Tavares LC, Meneses MJ, Patrício B, Gastaldelli A, Macedo MP, Jones JG. The Effects of Long-Term High Fat and/or High Sugar Feeding on Sources of Postprandial Hepatic Glycogen and Triglyceride Synthesis in Mice. Nutrients. 2024; 16(14):2186. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16142186
Chicago/Turabian StyleReis-Costa, Ana, Getachew D. Belew, Ivan Viegas, Ludgero C. Tavares, Maria João Meneses, Bárbara Patrício, Amalia Gastaldelli, Maria Paula Macedo, and John G. Jones. 2024. "The Effects of Long-Term High Fat and/or High Sugar Feeding on Sources of Postprandial Hepatic Glycogen and Triglyceride Synthesis in Mice" Nutrients 16, no. 14: 2186. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16142186
APA StyleReis-Costa, A., Belew, G. D., Viegas, I., Tavares, L. C., Meneses, M. J., Patrício, B., Gastaldelli, A., Macedo, M. P., & Jones, J. G. (2024). The Effects of Long-Term High Fat and/or High Sugar Feeding on Sources of Postprandial Hepatic Glycogen and Triglyceride Synthesis in Mice. Nutrients, 16(14), 2186. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16142186











