Abstract
We aimed to assess dietary iodine intake and sources in Zhejiang Province a decade after a reduction in iodine concentration in iodized salt. Three-day 24 h dietary recall and household weighing were used, complemented by “Chinese Food Composition” data. Household water and salt samples were collected from 5890 residents and analyzed. Differences in iodized salt consumption rates were observed across the following regions: inland (84.20%), subcoastal (67.80%), and coastal (37.00%) areas. The median (P25, P75) iodine concentration in water and diet were 2.2 (0.9, 4.0) μg/L and 142.05 (58.94, 237.11) μg/d, respectively, with significant regional differences in dietary concentration (inland [185.61 μg/d], subcoastal [153.42 μg/d], and coastal [75.66 μg/d]). Males (149.99 μg/d) and iodized salt consumers (191.98 μg/d) had a significantly higher dietary iodine intake than their counterparts. Regions were ranked as follows based on the proportions of individuals meeting the recommended dietary iodine intake: inland (69.40%), subcoastal (56.50%), and coastal (34.10%) areas. Dietary sources included salt (48.54%), other foods (32.06%), drinking water (8.84%), laver (4.82%), kelp (3.02%), and other seafood (2.32%). The qualified iodized salt consumption rate was significantly lower than the national standard. Zhejiang Province should continue implementing measures to control iodine deficiency through salt iodization, education efforts, and increasing the qualified iodized salt consumption rate.
1. Introduction
Iodine is an essential trace element, and its intake is intricately linked to human health. As an essential micronutrient required for synthesizing thyroid hormones, iodine plays a pivotal role in regulating metabolism and facilitating growth and development in the body [1,2]. Both the deficiency and excessive levels of iodine can precipitate various diseases [3]. Prolonged excessive intake disrupts self-regulatory mechanisms and leads to functional imbalances, resulting in a range of conditions, such as hyperthyroidism and autoimmune thyroiditis [4]. Iodine deficiency can lead to disorders, such as stillbirths, congenital abnormalities, cretinism, and increased infant mortality, as well as impaired cognitive function and stunted growth in children and adolescents. In adults, iodine deficiency may induce hyperthyroidism, while pregnant women face a heightened risk of spontaneous abortion [5]. In China, combating iodine deficiency disorders (IDDs) has long been a pressing public health challenge.
Since China initiated the Universal Salt Iodization (USI) program in 1995, significant strides have been made toward improving iodine nutrition nationwide [6,7], with Zhejiang Province also achieving notable success in preventing and controlling IDDs [8]. Nevertheless, with its economic development in recent years, there have been substantial shifts in the dietary patterns and habits of urban and rural residents in Zhejiang Province, posing new challenges to IDD prevention and control efforts. On one hand, with the effective implementation of salt iodization, severe iodine deficiency-related conditions, such as cretinism, have become rare. However, thyroid-related diseases associated with mild iodine deficiency have become less recognized [9]. Consequently, residents’ awareness of the hazards of iodine deficiency is gradually diminishing, leading to a waning sense of urgency in implementing prevention and control efforts. This has led to some residents discontinuing the use of iodized salt, thereby heightening the risk of IDDs. On the other hand, in line with the “National Food Safety Standards—Iodine Content of Salt” (GB 26878-2011) [10], the iodine concentration in salt has gradually decreased since 2012 in China. Correspondingly, the concentration in Zhejiang Province dropped from 35 ± 30 mg/kg to 18–33 mg/kg over a 10-year period until 2022. Additionally, the introduction of the “Reform Plan for the Salt Industry System” [11] has expanded the variety of salt products available in the market, leading to the infiltration of non-iodized salt. Consequently, there has been a noticeable decline in the consumption rate of qualified iodized salt among residents in Zhejiang Province in recent years, prompting changes in the population’s iodine nutrition status.
Approximately 80% of iodine intake in the human body is derived from food, 10–20% from drinking water, and <5% from the air [12]. Dietary iodine intake serves as a pivotal measure for assessing both the individual- and population-level iodine nutrition status, as well as for investigating the prevalence of thyroid diseases [13]. It is considered the most direct biological marker of iodine nutrition status in both populations and individuals [14,15]. The adequacy of iodine intake hinges on the consumption of iodine-rich foods and their iodine content. A deficiency of iodine in the diet directly results in iodine deficiency in the body [16].
Therefore, to further understand the dietary iodine status among residents in Zhejiang Province, a comprehensive survey on province-wide dietary iodine intake was conducted in 2022. This endeavor was aimed at evaluating the dietary iodine status among residents and to compare the contributions of iodized salt, drinking water, laver, kelp, and other foods to dietary iodine intake. The initiative sought to provide the public with a thorough and accurate understanding of the current state of iodine supplementation and the significance of various foods. It also endeavored to create a foundation for the effective implementation of a strategy involving “tailored measures, targeted guidance, and scientific iodine supplementation”, ensuring the eradication of IDDs while preventing the harms related to excessive iodine intake, thereby safeguarding the health of residents. In this study, we aimed to assess dietary iodine intake and sources among the residents of Zhejiang Province a decade after a reduction in iodine concentration in iodized salt using data from the 2022 survey.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
This cross-sectional analysis was based on data from the 2022 nutritional survey conducted in Zhejiang Province. By employing a stratified, multi-stage, systematic, random sampling approach, a representative sample reflecting Zhejiang Province’s demographic composition was established, spanning 16 surveyed counties (districts, cities). First, the province was categorized into three groups based on distinct geographical locations: coastal, subcoastal, and inland areas. Subsequently, leveraging the population composition ratio of selected monitoring points, six committees of residents (villagers) were chosen from each monitoring point, with 30 households selected from each committee through systematic sampling for dietary assessments.
2.2. Estimation of Dietary Iodine Intake
The questionnaire was primarily used to collect information on sociodemographic factors (age, ethnicity, marital status, education, occupation, etc.), dietary patterns, health status, and lifestyle choices. Trained surveyors, who underwent standardized technical training, conducted a 24 h dietary recall survey over 3 consecutive days; all permanent members of the surveyed households participated. During the survey, all foods consumed at home (or in school cafeterias) and in outside establishments were documented over 3 consecutive days, 24 h a day. Additionally, a household food weighing method was employed to assess the consumption of various cooking oils and condiments (such as monosodium glutamate, table salt, and soy sauce) over 3 consecutive days. By combining these data with the “Chinese Food Composition” data [17], the iodine content in each food item was determined in order to calculate individual dietary iodine intake. Meanwhile, samples of household drinking water and edible salt were collected, and their iodine contents were measured using cerium sulfate catalytic spectrophotometry and the direct titration method, respectively.
As shown in Table 1, references for the estimated average requirement (EAR), recommended nutrient intake (RNI), and tolerable upper intake level (UL) for iodine were obtained from the “Dietary Reference Intakes for Chinese Residents” [18] based on different age groups and physiological conditions.

Table 1.
Reference dietary iodine intake standards for Chinese residents.
Household edible salt was categorized into three groups according to the “National Food Safety Standards—Iodine Content of Salt” [10]: non-iodized salt (iodine content < 5 mg/kg), non-compliant iodized salt (iodine content < 18 mg/kg or > 33 mg/kg), and qualified iodized salt (iodine content 18–33 mg/kg). The coverage rate of iodized salt was calculated as the proportion of household salt samples with iodine content ≥ 5 mg/kg out of the total number of tested samples. Iodine-deficient areas (median water iodine < 40 μg/L) and iodine-adequate areas (40–100 μg/L) (based on administrative villages) were classified according to the “Definition and Demarcation of Iodine Deficient Areas and Iodine Adequate Areas” [19].
2.3. Statistical Analysis
Data analysis was conducted using SPSS 21.0 statistical software (IBM Corporation, Armonk, NY, USA). Normality was assessed using the Kolmogorov–Smirnov (KS) test. Dietary iodine intake and salt iodine content were expressed as the median and quartile range (P25, P75). Regional differences were examined using the Kruskal–Wallis H test for multiple independent samples, while demographic comparisons, such as those between urban and rural areas and between sexes, were performed using the Mann–Whitney U test for two independent samples. Pairwise comparisons were executed using the Nemenyi test. Count data were presented as rates/composition ratios, with inter-group differences evaluated via the χ2 test. A trend analysis was performed using the χ2 trend test. All tests were two-tailed, and the significance level was set at p < 0.05.
3. Results
3.1. Iodine Contents in Water and Salt in Zhejiang Province
As shown in Table 2, all 16 surveyed points relied on centralized water supply systems. A total of 251 samples of drinking water were collected, with a median (P25, P75) water iodine content of 2.2 (0.9, 4.0) μg/L.

Table 2.
Water iodine, salt iodine situation.
Furthermore, 3047 samples of household salt were collected, comprising 966 samples of non-iodized salt, 125 samples of non-compliant iodized salt, and 1956 samples of qualified iodized salt. The coverage rate of iodized salt was 68.30%, and the consumption rate of qualified iodized salt was 64.20%. The median (P25, P75) iodine content in the household salt of residents in Zhejiang Province was 22.08 (0.00, 24.51) mg/kg, with iodized salt having a median iodine content of 23.70 mg/kg.
Significant regional variations were observed in household iodized salt content (all p < 0.001), with the trend analysis demonstrating statistical significance. The proportions of households using qualified iodized salt by region, from the largest to the smallest, were as follows: inland (84.20%), subcoastal (67.80%), and coastal (37.00%) areas (χ2 trend = 504.765, p for trend < 0.001). Conversely, the proportions of households using non-iodized salt by region were as follows: coastal (58.40%), subcoastal (28.40%), and inland (11.90%) areas (χ2 trend = 519.281, p for trend < 0.001).
3.2. Demographic Characteristics of the Study Population
As shown in Table 3, 5890 residents with complete dietary intake data were enrolled in this study. Among them, 2106 were from coastal areas, 2031 from subcoastal areas, and 1753 from inland areas. Of these participants, 2734 were male, and 3156 were female. The age distribution included 868 individuals under 18 years old, 1713 aged between 18 and 44 years, 1636 aged between 45 and 59 years, and 1673 over 60 years old. Regarding urban-rural distribution, 3128 participants resided in urban areas, while 2762 were from rural areas. Among all participants, 3638 individuals (61.8%) reported consuming iodized salt, while 2252 (38.2%) reported not consuming iodized salt.

Table 3.
Demographic characteristics of the 5890 residents.
3.3. Dietary Iodine Intake among Residents in Zhejiang Province
As shown in Table 4, the median (P25, P75) dietary iodine intake among residents in Zhejiang Province was 142.05 (58.94, 237.11) μg/d. The dietary intakes in coastal, subcoastal, and inland areas were 75.66 (36.94, 172.02) μg/d, 153.42 (81.35, 251.47) μg/d, and 185.61 (118.13, 282.17) μg/day, respectively, with significant differences among the regions (χ2 = 588.592, p < 0.001).

Table 4.
Dietary iodine intake among residents in Zhejiang Province and its relationship with reference intake levels.
Regarding regional differences, the median (P25, P75) dietary iodine intakes in urban and rural areas were 136.00 (55.14, 244.50) μg/d and 145.89 (63.58, 230.63) μg/d, respectively. No significant difference was found between the areas (Z = −1.249, p = 0.211).
Regarding sex differences, the median (P25, P75) dietary iodine intakes in males and females were 149.99 (62.13, 250.26) μg/d and 136.05 (56.03, 227.92) μg/d, respectively. Males had a significantly higher dietary iodine intake than females (Z = −3.957, p < 0.001).
Regarding differences based on the consumption of iodized salt, the median (P25, P75) dietary iodine intake was 191.98 (133.47, 283.93) μg/d in individuals consuming iodized salt, while it was 42.21 (26.33, 67.77) μg/d in those not consuming iodized salt. A significant difference in dietary iodine intake was observed between consumers and non-consumers (Z = −52.246, p < 0.001).
In the entire surveyed population, the proportions of individuals with dietary iodine levels falling below the EAR, between the EAR and RNI, between the RNI and UL, and exceeding the UL were 34.80%, 10.00%, 52.30%, and 2.90%, respectively, with significant difference among the regions (χ2 = 723.632, p < 0.001). The proportions of residents with a dietary iodine intake below the EAR by region, from the largest to the smallest, were as follows: coastal (54.80%), subcoastal (30.20%), and inland (16.00%) areas (χ2 trend = 647.777, p for trend < 0.001). The population of residents adhering to the RNI–UL range by region, from the largest to the smallest, were as follows: inland (69.40%), subcoastal (56.50%), and coastal (34.10%) areas (χ2 trend = 485.333, p for trend < 0.001). The proportions of residents exceeding the safe intake range by region were as follows: inland (5.10%), coastal (2.30%), and subcoastal (1.60%) areas (χ2 trend = 25.229, p for trend < 0.001).
3.4. Contribution of Food Sources, Salt, and Drinking Water to Dietary Iodine Intake
As shown in Figure 1, without considering cooking losses, the contributions of various food sources to dietary iodine intake among residents in Zhejiang Province, from the highest to the lowest, were as follows: salt (48.54%), other foods (32.46%), drinking water (8.84%), laver (4.82%), kelp (3.02%), and other seafood (2.32%).
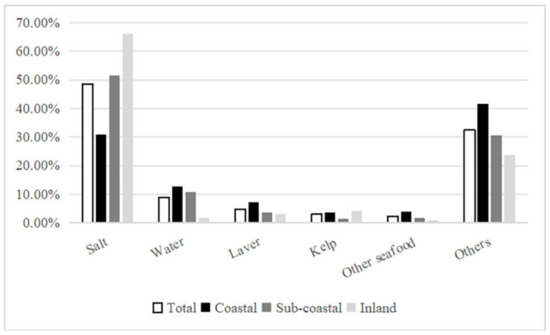
Figure 1.
Proportion of iodine intake from various sources.
As shown in Table 5, salt added during meal preparation stood out as the primary iodine source, comprising 48.54% of dietary intake. Notably, there was a significant regional variation in salt contribution as follows: inland areas (66.11%), subcoastal areas (51.61%), and coastal areas (30.95%) (χ2 = 853.271, p < 0.001). However, no significant sex-based difference in salt contribution was observed (Z = −0.679, p > 0.05). Furthermore, there was a significant difference in salt contribution between urban (46.23%) and rural (51.16%) areas (Z = −5.032, p < 0.001).

Table 5.
Contribution of different dietary sources to dietary iodine intake (%).
For individuals consuming iodized salt, the main contributors to dietary iodine, ranked from the highest to the lowest, were as follows: salt (73.34%), other foods (17.30%), drinking water (3.63%), laver (2.72%), kelp (2.10%), and other seafood (0.91%). Conversely, for individuals not consuming iodized salt, the main sources of dietary iodine were ranked in the following order: other foods (61.40%), drinking water (18.79%), laver (8.84%), other seafood (4.99%), and kelp (4.78%).
4. Discussion
The survey revealed that the median (P25, P75) dietary iodine intake among residents in Zhejiang Province was 142.05 (58.94, 237.11) μg/d, which is generally considered adequate. This value aligns closely with data reported in Fujian Province [20] and Xinjiang [21], China, as well as in Denmark [22], albeit it was significantly lower than the intake of 272.36 μg/d in 2010 in Zhejiang Province [23].
Furthermore, the analysis revealed a descending trend in the dietary iodine intake across different regions of Zhejiang Province, with inland areas having higher levels, followed by subcoastal areas and coastal areas. While residents in subcoastal and inland regions maintained sufficient and safe iodine intake levels, attention should be directed towards addressing the inadequate iodine intake among coastal area residents.
The survey also indicated significant sex-based differences in dietary iodine intake, with female residents consuming lower levels of iodine than male residents. Similar trends were observed in recent studies conducted in Denmark and Norway [22,24,25], possibly due to substantial variations in dietary habits and intake between the sexes. The higher food intake among males could be a contributing factor to their elevated dietary iodine levels.
Regarding water iodine levels, the median iodine concentration at each surveyed site in this study was below 40 μg/L. According to the “Definition and Demarcation of Iodine Deficient Areas and Iodine Adequate Areas” (WS/T669-2020) standard [19], all counties (districts, cities) in Zhejiang Province were categorized as environmental iodine-deficient areas. Most areas had low iodine content in their drinking water, consistent with the 2015 external environment water iodine monitoring results [26]. This suggests that the daily drinking water of residents in Zhejiang Province fails to meet the human body’s iodine requirements, necessitating additional iodine supplementation.
The median iodine concentration in salt across Zhejiang Province was 22.08 mg/kg, reflecting a decline of 6.72 mg/kg compared with the levels recorded in 2010 [27]. Inland areas and subcoastal regions had median household salt iodine concentrations of 23.42 mg/kg and 22.27 mg/kg, respectively, meeting the national standard range of 18–33 mg/kg. However, the median iodine concentration in salt in coastal regions was only 0.42 mg/kg, which is significantly lower than the national standard. The following were the consumption rates of qualified iodized salt by region, from the highest to the lowest: inland (84.2%), subcoastal (67.8%), and coastal (37.00%) areas; all values fell below the standards established by the National Criteria for Elimination of IDDs. Additionally, notable regional variations were observed. The iodine intake and rate of consumption of qualified iodized salt among residents in different regions were positively correlated, and the regions were ranked as follows based on both these factors: inland, subcoastal, and coastal areas. This corresponds to the differences observed in the consumption rates of qualified iodized salt across different regions in the 2010 iodine nutrition survey in Zhejiang Province [28], suggesting that the decline in residents’ dietary iodine intake may be associated with the reduction in salt iodine concentration and the decrease in the iodized salt consumption rate [20].
Residents in Zhejiang Province obtain iodine from various dietary sources, with the primary contributors ranked in the following order: salt (48.54%), other foods (32.46%), drinking water (8.84%), laver (4.82%), kelp (3.02%), and other seafood (2.32%). This suggests that salt remains the main source of dietary iodine for Zhejiang residents, although its contribution has decreased compared with the ratio of 74.92% reported in the 2010 iodine nutrition survey [23]. Furthermore, there are significant regional differences in salt contribution, which were ranked in the following order by region: inland (66.11%), subcoastal (51.61%), and coastal (30.95%) areas. These differences positively correlated with variations in the consumption of qualified iodized salt and iodine concentrations in salt across regions. Additionally, residents’ dietary iodine intake positively correlated with salt contribution, showing a similar pattern by region: inland areas > subcoastal areas > coastal areas. This further underscores the view that iodized salt remains the primary source of dietary iodine intake, aligning with the findings of recent studies in other regions of China [21,29].
Significant sex differences were observed in dietary iodine intake. The contribution rates of various foods did not differ between sexes. This observation may be attributed to family-based dietary habits in China, suggesting that sex differences in iodine intake are more related to the total amount of food consumed rather than specific food preferences. Additionally, the contribution rate of salt intake among urban residents was lower than that of rural residents. This phenomenon may be because rural areas still retain more traditional Chinese dietary habits, such as a preference for saltier pickled foods. Moreover, rural residents, who are often engaged in physical labor such as agricultural work, may believe that consuming more salt can replenish electrolytes lost through sweating and aid in maintaining physical strength, leading them to add more salt to their food.
While laver and kelp are known for their high iodine content, their consumption frequency and quantity among the surveyed individuals were relatively low [30], resulting in a limited contribution to dietary iodine. Despite other forms of seafood being consumed more frequently, their iodine content is not substantial, thus limiting their contribution to dietary iodine. Although residents in coastal areas consumed more seafood than those in subcoastal and inland areas, the dietary iodine intake in coastal regions was lower than that in subcoastal and inland areas, suggesting that seafood is not the primary source of dietary iodine. Furthermore, an analysis of the entire population, iodized salt consumers, and non-iodized salt consumers indicated that laver, kelp, and other seafood were not the main contributors to dietary iodine. This finding is consistent with that of research in Xinjiang [21], Tianjin [29], and other regions, confirming that laver, kelp, and other seafood are not the primary sources of dietary iodine.
Therefore, relying solely on regular dietary intake for iodine cannot fulfill the body’s daily iodine requirements. Dietary iodine intake is primarily influenced by the consumption of iodized salt, which in turn is affected by the qualified iodized salt consumption rate. In coastal regions, some residents choose not to use iodized salt and instead opt for non-iodized alternatives that are more readily available, thereby reducing their dietary iodine intake and the contribution of salt to iodine intake. Without the consumption of iodized salt, most residents will likely fail to meet the RNI for iodine, putting them at risk of iodine deficiency.
It is worth noting that 34.80% of the residents had a daily dietary iodine intake below the EAR, while only 2.90% had an iodine intake exceeding the UL. Specifically, in coastal areas, the dietary iodine intake of 54.80% fell below the EAR, attributed partly to less enthusiasm for iodized salt and reduced consumption of qualified iodized salt, leading to decreased iodine intake from salt. Furthermore, across coastal, subcoastal, and inland areas, the proportion of residents with dietary iodine intake exceeding the UL was generally small, suggesting that the health risks associated with iodine deficiency in Zhejiang Province far outweigh those of excessive iodine intake. Hence, without iodized salt consumption, the iodine obtained from current dietary and water sources in coastal regions fails to meet the recommended intake levels, highlighting the inadequacy of relying solely on iodine intake from water and food to satisfy the body’s demand.
This study had two limitations. First, the iodine content in foods was estimated based on the “Chinese Food Composition” data. However, due to the absence of data for certain processed food categories and potential variations in food composition across different brands, the iodine content of certain food items had to be estimated based on that of similar items, which may not accurately reflect the iodine intake derived from the diet. Second, a substantial number of residents were recruited for participation in this study, and their total iodine intake was estimated based on their dietary intake over 3 consecutive days. However, we only recorded the amount of food consumed, without considering the actual food intake, as meals prepared from food items may not have been entirely consumed. Moreover, the employed method did not accurately capture iodine loss during the cooking process. Consequently, the actual dietary iodine intake may be lower than the values derived from the survey, potentially resulting in an overestimation of iodine intake.
The human body has limited storage capacity for iodine, so iodine supplementation should follow the principles of long-term, daily, and lifelong. Based on the results of this survey, we propose several suggestions. First, iodized salt is still the most important source of dietary iodine. Government departments should strengthen the production and sale management of non-iodized salt to make it less readily available than iodized salt. Second, health education should be strengthened to inform residents, especially those in coastal areas, of the current status of iodine nutritional sources in Zhejiang Province (it is generally believed that seafood is not the main source of dietary iodine) and raise residents’ awareness of the importance of eating iodized salt. In addition, pregnant women and lactating mothers should increase their consumption of iodine-rich seafood such as kelp and laver, and supplement iodine-containing preparations according to medical advice.
5. Conclusions
Zhejiang Province is classified as an area with environmental iodine deficiency, indicating a persistent natural iodine deficiency. While overall dietary iodine intake is adequate, it is notably insufficient and declining in coastal regions. Iodized salt remains the primary source of dietary iodine for residents, with the contributions of laver, kelp, and other seafood being limited. Therefore, Zhejiang Province must continue to prioritize comprehensive prevention and control measures for IDDs, centered on iodized salt. Additionally, through various approaches such as health education, efforts should be made to reverse the declining trend in the consumption of iodized salt, thereby ensuring the health of residents and preventing the resurgence of IDDs.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.H. and G.M.; methodology, J.H.; software, J.H.; validation, J.H., G.M. and C.L.; formal analysis, L.H.; investigation, G.M., L.H. and Z.M.; resources, D.S.; data curation, J.H.; writing—original draft preparation, J.H.; writing—review and editing, J.H. and G.M.; visualization, S.G.; supervision, F.G. and Y.W.; project administration, Z.C. and X.W.; funding acquisition, R.Z. and X.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by Science Foundation of National Health Commission (WKJ-ZJ-2332) and Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (TGY23H24001).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Ethics Committee of the Zhejiang Provincial Center for Disease Control and Prevention (Approval No. 2022-018-01; Date: 10 May 2022).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to confidentiality concerns.
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge all subjects and staff at Zhejiang Nutrition and Health Surveillance and the support from the related departments of 16 counties, districts, and county-level cities.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- World Health Organization; International Council for Control of Iodine Deficiency Disorders; United Nations International Children’s Emergency Fund. Assessment of Iodine Deficiency Disorders and Monitoring Their Elimination: A Guide for Programme Managers; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Delange, F. The disorders induced by thyroid deficiency. Thyroid 1994, 4, 107–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farebrother, J.; Zimmermann, M.B.; Andersson, M. Excess iodine intake: Sources, assessment, and effects on thyroid function. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci 2019, 1446, 44–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, D.; Xu, H.; Li, P.; Liu, J.; Qian, Z. Potential role of iodine excess in papillary thyroid cancer and benign thyroid tumor: A case—Control study. Asia. Pac. J. Clin. Nutr 2020, 29, 603–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Endemic Diseases Branch of Chinese Medical Association; Chinese Nutrition Society; Endocrinology Branch of Chinese Medical Association. Guidelines for Chinese Residents of Iodine Supplementation; People’s Health Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.C.; Li, M.; Liu, X.B.; Wu, M.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, L.Y.; Ding, G.Q.; Yang, X.G. Evaluation of iodine nutritional status among pregnant women in China. Thyroid 2020, 30, 443–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, D.J.; Codling, K.; Chang, S.Y.; Zhang, S.B.; Shen, H.M.; Su, X.H.; Chen, Z.P.; Scherpbier, R.W.; Yan, J. Eliminating iodine deficiency in China: Achievements, challenges and global implications. Nutrients 2017, 9, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, W.M.; Zhou, J.S.; Mao, G.M.; Mo, Z. Analysis of iodine deficiency disorders surveillance of Zhejiang province in 2011. Zhejiang Prev. Med. 2012, 24, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, Z.Y. Interpretation of guidelines to iodine supplementation for Chinese residents. Chin. J. Pract. Intern. Med. 2019, 39, 347–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 26878-2011; National Food Safety Standard—Edible Iodized Salt Content. Ministry of Health: Beijing, China, 2011. Available online: https://www.foodtalks.cn/news/32623 (accessed on 1 June 2024).
- State Council of the PRC. Circular of the State Council on the Publication of the Salt Industry Reform Plan. Available online: https://www.gov.cn/gongbao/content/2016/content_5073711.htm (accessed on 1 June 2024).
- Li, Z.T.; Ren, J.S.; Hao, J.X. Detection and analysis of trace iodine in main food from different soil of the same village in different terrain. Henan J. Prev. Med. 1993, 4, 203–204. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, J.; Sang, Z.N.; Liu, J.Y.; Wu, Y.T.; Chen, Z.P.; Zhang, W.Q. Study on the relation between iodine intake and fasting urine iodine excretion. Acta Nutr. Sin. 2008, 30, 22–25. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.L.; Chen, W.; Shen, J.; Tan, L.; L’Abbe, M.R.; Pearce, E.N.; Wang, W.Q.; Tian, X.X.; Wang, W.; Zhang, W.Q. Reproducible and reliable general semiquantitative food frequency questionnaire for evaluating iodine intake in Chinese children. Nutr. Res. 2018, 55, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jooste, P.L.; Upson, N.; Charlton, K.E. Knowledge of iodine nutrition in the South African adult population. Public Health Nutr. 2005, 8, 382–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohner, F.; Zimmermann, M.; Jooste, P.; Pandav, C.; Caldwell, K.; Raghavan, R.; Raiten, D.J. Biomarkers of nutrition for development–iodine review. J Nutr. 2014, 144, 1322s–1342s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.X. China Food Composition Tables-Standard Edition, 6th ed.; Peking University Medical Press: Beijing, China, 2019; ISBN 978-7-56591-699-1. [Google Scholar]
- Chinese Nutrition Society. Dietary Reference Intakes for Chinese Residents (2023); Science Press: Beijing, China, 2023. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- WS/T669-2020; Definition and Demarcation of Iodine Deficient Areas and Iodine Adequate Areas. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2020. (In Chinese)
- Chen, D.Q.; Zhang, X.Z.; Lan, Y.; He, M.; Wu, X.Y.; Chen, Z.H. Effects of salt reduction on dietary iodine intake and iodine nutritional status among adults in Fujian province. Acta Nutr. Sin. 2023, 45, 431–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.M.; Wang, C.C.; Duan, Y.M.; Huang, J.; Lin, Q.; Zhang, L. Iodine nutritional status and intake levels in adult from different water iodine content areas of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region in 2017. J. Hyg. Res. 2020, 49, 36–40+50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Outzen, M.; Lund, C.E.; Christensen, T.; Trolle, E.; Ravn-Haren, G. Assessment of iodine fortification of salt in the Danish population. Eur. J. Nutr. 2022, 61, 2939–2951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, G.Q.; Mo, Z.; Huang, L.C.; Lou, X.M.; Zou, Y.; Mao, G.M. Assessment of dietary iodine intakes by 3-day dietary records in Zhejiang residents. Acta Nutr. Sin. 2014, 36, 553–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medin, A.C.; Carlsen, M.H.; Andersen, L.F. Iodine intake among children and adolescents in Norway: Estimates from the national dietary survey Ungkost 3 (2015–2016). J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2020, 58, 126427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henjum, S.; Brantsæter, A.L.; Kurniasari, A.; Dahl, L.; Aadland, E.K.; Gjengedal, E.L.F.; Birkeland, S.; Aakre, I. Suboptimal iodine status and low iodine knowledge in young Norwegian women. Nutrients 2018, 10, 941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.M.; Mo, Z.; Mao, G.M.; Wang, Y.Y.; Lou, X.M. A study on the iodine nutrition of children and pregnant woman after the iodine salt concentration adjustment in Zhejiang Province. Prev. Med. 2016, 28, 1087–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB16006-2008; Criteria for Elimination of Iodine Deficiency Disorders. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2008. (In Chinese)
- Mao, G.M.; Ding, G.Q.; Lou, X.M.; Zhu, W.M.; Wang, X.F.; Mo, Z.; Zhou, J.S. Analysis of urine iodine level and its influencing factors in Zhejiang from 2009 to 2011. Chin. J. Prev. Med. 2013, 47, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hou, C.C.; Liu, Z.H.; Cui, Y.S.; Wang, Y.; Fu, G.; Liu, H.L. An investigation of iodine intake and iodine nutritional status of adults in Tianjin City. Chin. J. Endem. 2016, 35, 138–142. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, C.; Tao, X.Y.; Xiao, Y. Dietary Iodine intake and related factors among secondary school students in Macao. Healthcare 2023, 11, 1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).