Long-Term Impact of Nutritional Intervention with Increased Polyphenol Intake and Physical Activity Promotion on Oxidative and Inflammatory Profiles in Patients with Metabolic Syndrome
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Anthropometric Measurements
2.3. Blood Collection and Analysis
2.4. Dietary Assessment, Physical Activity and Sedentarism
2.5. Enzymatic Activities Determination
2.6. Malondialdehyde Assay
2.7. Polyphenols Assay
2.8. Stimulated Neutrophils ROS Production
2.9. Immunoassay Kits
2.10. Statistics
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rochlani, Y.; Pothineni, N.V.; Kovelamudi, S.; Mehta, J.L. Metabolic syndrome: Pathophysiology, management, and modulation by natural compounds. Ther. Adv. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2017, 11, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masenga, S.K.; Kabwe, L.S.; Chakulya, M.; Kirabo, A. Mechanisms of Oxidative Stress in Metabolic Syndrome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saklayen, M.G. The Global Epidemic of the Metabolic Syndrome. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2018, 20, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, J.; Lee, J.; Lim, S.; Ha, H.; Kwon, H.; Park, Y.; Lee, W.; Kang, M.; Yim, H.; Yoon, K.; et al. Metabolic syndrome as a predictor of type 2 diabetes, and its clinical interpretations and usefulness. J. Diabetes Investig. 2013, 4, 334–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abagre, T.A.; Bandoh, D.A.; Addo-Lartey, A.A. Determinants of metabolic syndrome among patients attending diabetes clinics in two sub-urban hospitals: Bono Region, Ghana. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2022, 22, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boudreau, D.M.; Malone, D.C.; Raebel, M.A.; Fishman, P.A.; Nichols, G.A.; Feldstein, A.C.; Boscoe, A.N.; Ben-Joseph, R.H.; Magid, D.J.; Okamoto, L.J. Health Care Utilization and Costs by Metabolic Syndrome Risk Factors. Metab. Syndr. Relat. Disord. 2009, 7, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monserrat-Mesquida, M.; Quetglas-Llabrés, M.; Capó, X.; Bouzas, C.; Mateos, D.; Pons, A.; Tur, J.A.; Sureda, A. Metabolic Syndrome Is Associated with Oxidative Stress and Proinflammatory State. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vona, R.; Gambardella, L.; Cittadini, C.; Straface, E.; Pietraforte, D. Biomarkers of Oxidative Stress in Metabolic Syndrome and Associated Diseases. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 8267234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sies, H. Oxidative stress: A concept in redox biology and medicine. Redox Biol. 2015, 4, 180–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieur, X.; Rőszer, T.; Ricote, M. Lipotoxicity in macrophages: Evidence from diseases associated with the metabolic syndrome. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2010, 1801, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Fontana, B.; Morales-Santana, S.; Longobardo, V.; Reyes-García, R.; Rozas-Moreno, P.; García-Salcedo, J.; Muñoz-Torres, M. Relationship between Proinflammatory and Antioxidant Proteins with the Severity of Cardiovascular Disease in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 9469–9483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lastra, G.; Sowers, J.R. Obesity and cardiovascular disease: Role of adipose tissue, inflammation, and the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system. Horm. Mol. Biol. Clin. Investig. 2013, 15, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nani, A.; Murtaza, B.; Sayed Khan, A.; Khan, N.A.; Hichami, A. Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Potential of Polyphenols Contained in Mediterranean Diet in Obesity: Molecular Mechanisms. Molecules 2021, 26, 985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasmi, A.; Mujawdiya, P.K.; Noor, S.; Lysiuk, R.; Darmohray, R.; Piscopo, S.; Lenchyk, L.; Antonyak, H.; Dehtiarova, K.; Shanaida, M.; et al. Polyphenols in Metabolic Diseases. Molecules 2022, 27, 6280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de la Rosa, L.A.; Moreno-Escamilla, J.O.; Rodrigo-García, J.; Alvarez-Parrilla, E. Phenolic Compounds. In Postharvest Physiology and Biochemistry of Fruits and Vegetables; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 253–271. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, J.; Zang, H.; Yin, Z.; Guan, P.; Yu, C.; Shan, A.; Feng, X. Dietary pterostilbene exerts potential protective effects by regulating lipid metabolism and enhancing antioxidant capacity on liver in broilers. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, P.; Yu, H.; Wang, S.; Sun, J.; Chai, X.; Sun, X.; Qi, X.; Zhang, R.; Jiao, Y.; Li, Z.; et al. Dietary rutin alleviated the damage by cold stress on inflammation reaction, tight junction protein and intestinal microbial flora in the mice intestine. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2024, 130, 109658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberti, K.G.M.M.; Eckel, R.H.; Grundy, S.M.; Zimmet, P.Z.; Cleeman, J.I.; Donato, K.A.; Fruchart, J.-C.; James, W.P.T.; Loria, C.M.; Jr, S.C.S.; et al. Harmonizing the metabolic syndrome: A joint interim statement of the International Diabetes Federation Task Force on Epidemiology and Prevention; National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; American Heart Association; World Heart Federation; International. Circulation 2009, 120, 1640–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capó, X.; Ferrer, M.D.; Olek, R.A.; Salaberry, E.; Gomila, R.M.; Martorell, G.; Sureda, A.; Tur, J.A.; Pons, A. Simultaneous analysis of saturated and unsaturated oxylipins in ‘ex vivo’ cultured peripheral blood mononuclear cells and neutrophils. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2020, 186, 113258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Ballart, J.D.; Piñol, J.L.; Zazpe, I.; Corella, D.; Carrasco, P.; Toledo, E.; Perez-Bauer, M.; Martínez-González, M.Á.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; Martn-Moreno, J.M. Relative validity of a semi-quantitative food-frequency questionnaire in an elderly Mediterranean population of Spain. Br. J. Nutr. 2010, 103, 1808–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreiras, O.; Carbajal, A.; Cabrera, L.; Cuadrado, C. Tablas de Composicion de Alimentos (Ciencia Y Tecnica). Guía de Prácticas, 19th ed.; Pirámide: Madrid, Spain, 2018; pp. 37–46. [Google Scholar]
- Bouzas, C.; Bibiloni, M.d.M.; Julibert, A.; Ruiz-Canela, M.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; Corella, D.; Zomeño, M.D.; Romaguera, D.; Vioque, J.; Alonso-Gómez, Á.M.; et al. Adherence to the Mediterranean Lifestyle and Desired Body Weight Loss in a Mediterranean Adult Population with Overweight: A PREDIMED-Plus Study. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neveu, V.; Perez-Jimenez, J.; Vos, F.; Crespy, V.; du Chaffaut, L.; Mennen, L.; Knox, C.; Eisner, R.; Cruz, J.; Wishart, D.; et al. Phenol-Explorer: An online comprehensive database on polyphenol contents in foods. Database 2010, 2010, bap024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balentine, D.A.; Dwyer, J.T.; Erdman, J.W.; Ferruzzi, M.G.; Gaine, P.C.; Harnly, J.M.; Kwik-Uribe, C.L. Recommendations on reporting requirements for flavonoids in research. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 101, 1113–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ainsworth, B.E.; Haskell, W.L.; Leon, A.S.; Jacobs, D.R., Jr.; Montoye, H.J.; Sallis, J.F.; Paffenbarger, R.S., Jr. Compendium of physical activities: Classification of energy costs of human physical activities. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 1993, 25, 71–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-González, M.A.; López-Fontana, C.; Varo, J.J.; Sánchez-Villegas, A.; Martinez, J.A. Validation of the Spanish version of the physical activity questionnaire used in the Nurses’ Health Study and the Health Professionals’ Follow-up Study. Public Health Nutr. 2005, 8, 920–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aebi, H. Catalase in Vitro. Methods Enzymol. Anal. 1984, 105, 121–126. [Google Scholar]
- Flohé, L.; Ötting, F. Superoxide Dismutase Assay. Methods Enzymol. 1984, 105, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Capeillère-Blandin, C. Oxidation of guaiacol by myeloperoxidase: A two-electron-oxidized guaiacol transient species as a mediator of NADPH oxidation. Biochem. J. 1998, 336, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kompaniyets, L.; Freedman, D.S.; Belay, B.; Pierce, S.L.; Kraus, E.M.; Blanck, H.M.; Goodman, A.B. Probability of 5% or Greater Weight Loss or BMI Reduction to Healthy Weight among Adults with Overweight or Obesity. JAMA Netw. Open 2023, 6, e2327358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, K.D.; Kahan, S. Maintenance of Lost Weight and Long-Term Management of Obesity. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2018, 102, 183–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothberg, A.E.; McEwen, L.N.; Kraftson, A.T.; Ajluni, N.; Fowler, C.E.; Nay, C.K.; Miller, N.M.; Burant, C.F.; Herman, W.H. Impact of weight loss on waist circumference and the components of the metabolic syndrome. BMJ Open Diabetes Res. Care 2017, 5, e000341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Gui, J.; Mei, Y.; Yang, X.; Liu, H.; Guo, L.; Li, J.; Lei, Y.; et al. Four-years change of BMI and waist circumference are associated with metabolic syndrome in middle-aged and elderly Chinese. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 10220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Zhou, Z.; Miao, H.; Zhang, Y. Effect of weight loss on blood pressure changes in overweight patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2023, 25, 404–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryder, E.; Diez-Ewald, M.; Mosquera, J.; Fernández, E.; Pedreañez, A.; Vargas, R.; Peña, C.; Fernández, N. Association of obesity with leukocyte count in obese individuals without metabolic syndrome. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Clin. Res. Rev. 2014, 8, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tussing-Humphreys, L.; Lamar, M.; McLeod, A.; Schiffer, L.; Blumstein, L.; Dakers, R.; Karstens, A.; Hemphill, N.O.N.; Strahan, D.; Siegel, L.; et al. Effect of Mediterranean diet and Mediterranean diet plus calorie restriction on cognition, lifestyle, and cardiometabolic health: A randomized clinical trial. Prev. Med. Rep. 2022, 29, 101955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lotfi, K.; Saneei, P.; Hajhashemy, Z.; Esmaillzadeh, A. Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet, Five-Year Weight Change, and Risk of Overweight and Obesity: A Systematic Review and Dose–Response Meta-Analysis of Prospective Cohort Studies. Adv. Nutr. 2022, 13, 152–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Baak, M.A. Dietary carbohydrates and weight loss maintenance. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2021, 24, 354–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardy, D.S.; Garvin, J.T.; Xu, H. Carbohydrate quality, glycemic index, glycemic load and cardiometabolic risks in the US, Europe and Asia: A dose–response meta-analysis. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2020, 30, 853–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velázquez-López, L.; Santiago-Díaz, G.; Nava-Hernández, J.; Muñoz-Torres, A.V.; Medina-Bravo, P.; Torres-Tamayo, M. Mediterranean-style diet reduces metabolic syndrome components in obese children and adolescents with obesity. BMC Pediatr. 2014, 14, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, S.K.; Chin, K.-Y.; Ima-Nirwana, S. Vitamin C: A Review on its Role in the Management of Metabolic Syndrome. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2020, 17, 1625–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramaiah, P.; Baljon, K.J.; Hjazi, A.; Qasim, M.T.; Salih Al-ani, O.A.; Imad, S.; Hussien, B.M.; Alsalamy, A.; Garousi, N. Dietary polyphenols and the risk of metabolic syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2024, 24, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Ma, D.; Shang, Q.; Xu, H. Association between dietary flavonoid intake and hypertension among U.S. adults. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1380493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gouveia, H.J.C.B.; Urquiza-Martínez, M.V.; Manhães-de-Castro, R.; Costa-de-Santana, B.J.R.; Villarreal, J.P.; Mercado-Camargo, R.; Torner, L.; de Souza Aquino, J.; Toscano, A.E.; Guzmán-Quevedo, O. Effects of the Treatment with Flavonoids on Metabolic Syndrome Components in Humans: A Systematic Review Focusing on Mechanisms of Action. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Tresserra-Rimbau, A.; Estruch, R.; Martínez-González, M.; Medina-Remón, A.; Fitó, M.; Corella, D.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; Portillo, M.; Moreno, J.; et al. Polyphenol Levels Are Inversely Correlated with Body Weight and Obesity in an Elderly Population after 5 Years of Follow Up (The Randomised PREDIMED Study). Nutrients 2017, 9, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esposito, K.; Kastorini, C.-M.; Panagiotakos, D.B.; Giugliano, D. Mediterranean Diet and Weight Loss: Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Metab. Syndr. Relat. Disord. 2011, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franz, M.J.; Boucher, J.L.; Rutten-Ramos, S.; VanWormer, J.J. Lifestyle Weight-Loss Intervention Outcomes in Overweight and Obese Adults with Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2015, 115, 1447–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myers, J.; Kokkinos, P.; Nyelin, E. Physical Activity, Cardiorespiratory Fitness, and the Metabolic Syndrome. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adenan, D.M.; Jaafar, Z.; Jayapalan, J.J.; Abdul Aziz, A. Plasma antioxidants and oxidative stress status in obese women: Correlation with cardiopulmonary response. PeerJ 2020, 8, e9230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tumova, E.; Sun, W.; Jones, P.H.; Vrablik, M.; Ballantyne, C.M.; Hoogeveen, R.C. The Impact of Rapid Weight Loss on Oxidative Stress Markers and the Expression of the Metabolic Syndrome in Obese Individuals. J. Obes. 2013, 2013, 729515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klebanoff, S.J. Myeloperoxidase: Friend and foe. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2005, 77, 598–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.-J.; Yen, C.-H.; Huang, Y.-C.; Lee, B.-J.; Hsia, S.; Lin, P.-T. Relationships between Inflammation, Adiponectin, and Oxidative Stress in Metabolic Syndrome. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e45693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monserrat-Mesquida, M.; Quetglas-Llabrés, M.; Bouzas, C.; García, S.; Mateos, D.; Gómez, C.; Gámez, J.M.; Poulsen, H.E.; Tur, J.A.; Sureda, A. Effects of 2-Year Nutritional and Lifestyle Intervention on Oxidative and Inflammatory Statuses in Individuals of 55 Years of Age and over at High Cardiovascular Risk. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crujeiras, A.B.; Parra, D.; Abete, I.; Martínez, J.A. A hypocaloric diet enriched in legumes specifically mitigates lipid peroxidation in obese subjects. Free Radic. Res. 2007, 41, 498–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furukawa, S.; Fujita, T.; Shimabukuro, M.; Iwaki, M.; Yamada, Y.; Nakajima, Y.; Nakayama, O.; Makishima, M.; Matsuda, M.; Shimomura, I. Increased oxidative stress in obesity and its impact on metabolic syndrome. J. Clin. Investig. 2004, 114, 1752–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraga, C.G.; Celep, G.S.; Galleano, M. Biochemical actions of plant phenolics compounds: Thermodynamic and kinetic aspects. Plant Phenolics Hum. Health Biochem. Nutr. Pharmacol. 2009, 3, 91–106. [Google Scholar]
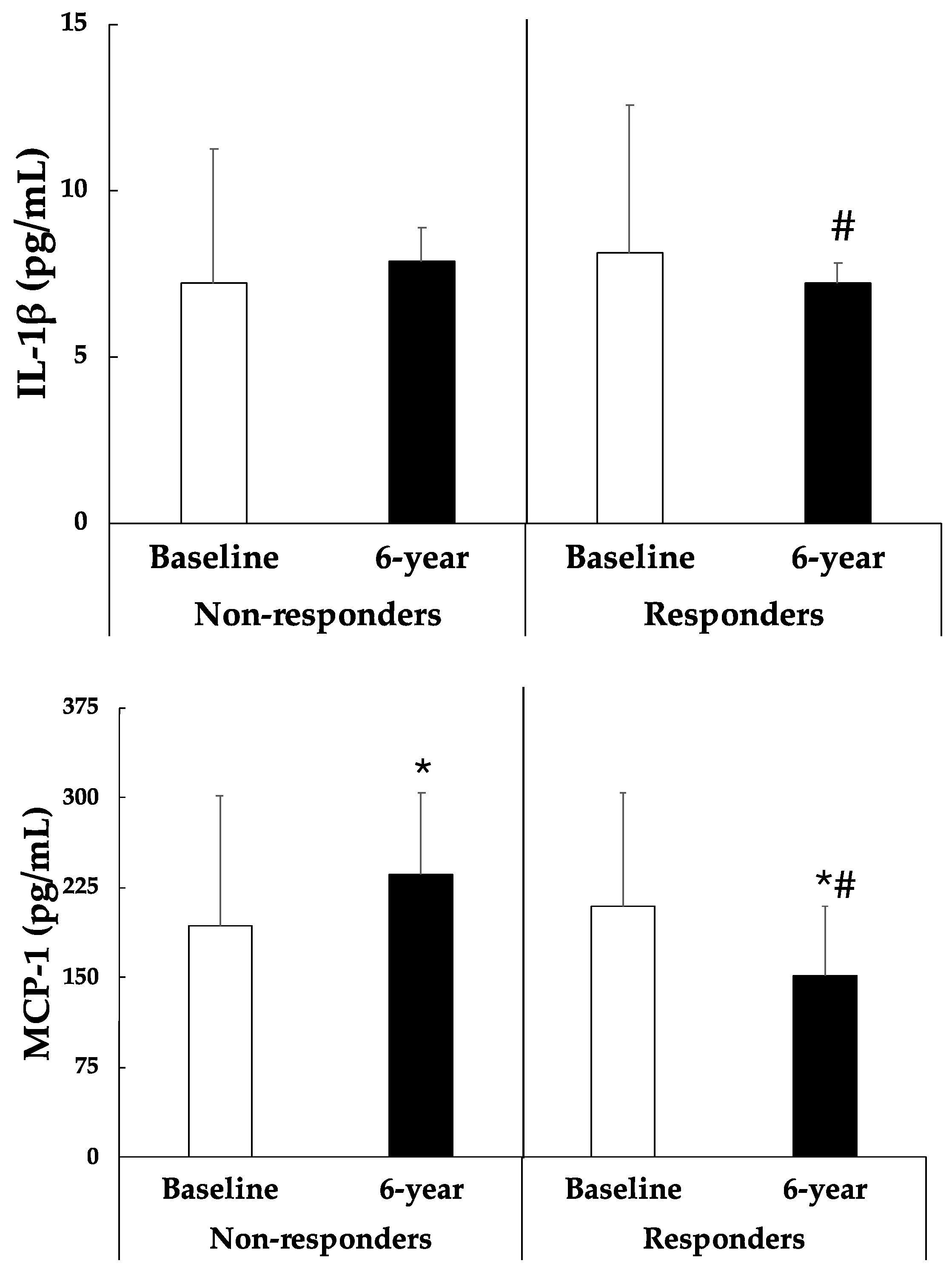
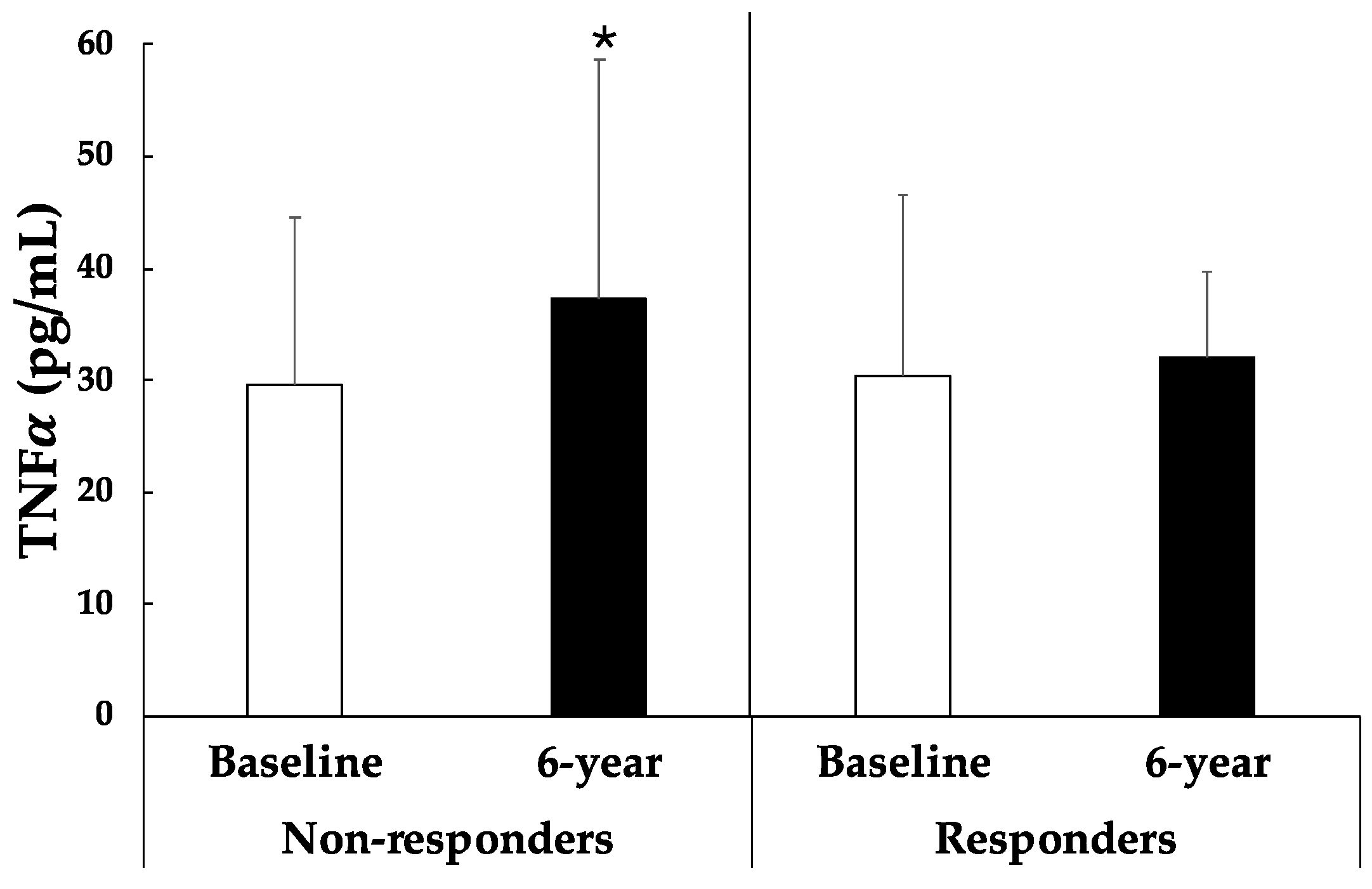
- Moschen, A.R.; Molnar, C.; Enrich, B.; Geiger, S.; Ebenbichler, C.F.; Tilg, H. Adipose and Liver Expression of Interleukin (IL)-1 Family Members in Morbid Obesity and Effects of Weight Loss. Mol. Med. 2011, 17, 840–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanda, H. MCP-1 contributes to macrophage infiltration into adipose tissue, insulin resistance, and hepatic steatosis in obesity. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 1494–1505. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fu, C.-P.; Sheu, W.H.-H.; Lee, I.-T.; Lee, W.-J.; Wang, J.-S.; Liang, K.-W.; Lee, W.-L.; Lin, S.-Y. Weight loss reduces serum monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 concentrations in association with improvements in renal injury in obese men with metabolic syndrome. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2015, 53, 623–629. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jung, S.H.; Park, H.S.; Kim, K.-S.; Choi, W.H.; Ahn, C.W.; Kim, B.T.; Kim, S.M.; Lee, S.Y.; Ahn, S.M.; Kim, Y.K.; et al. Effect of weight loss on some serum cytokines in human obesity: Increase in IL-10 after weight loss. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2008, 19, 371–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monserrat-Mesquida, M.; Quetglas-Llabrés, M.; Bouzas, C.; Capó, X.; Mateos, D.; Ugarriza, L.; Tur, J.A.; Sureda, A. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells oxidative stress and plasma inflammatory biomarkers in adults with normal weight, overweight and obesity. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
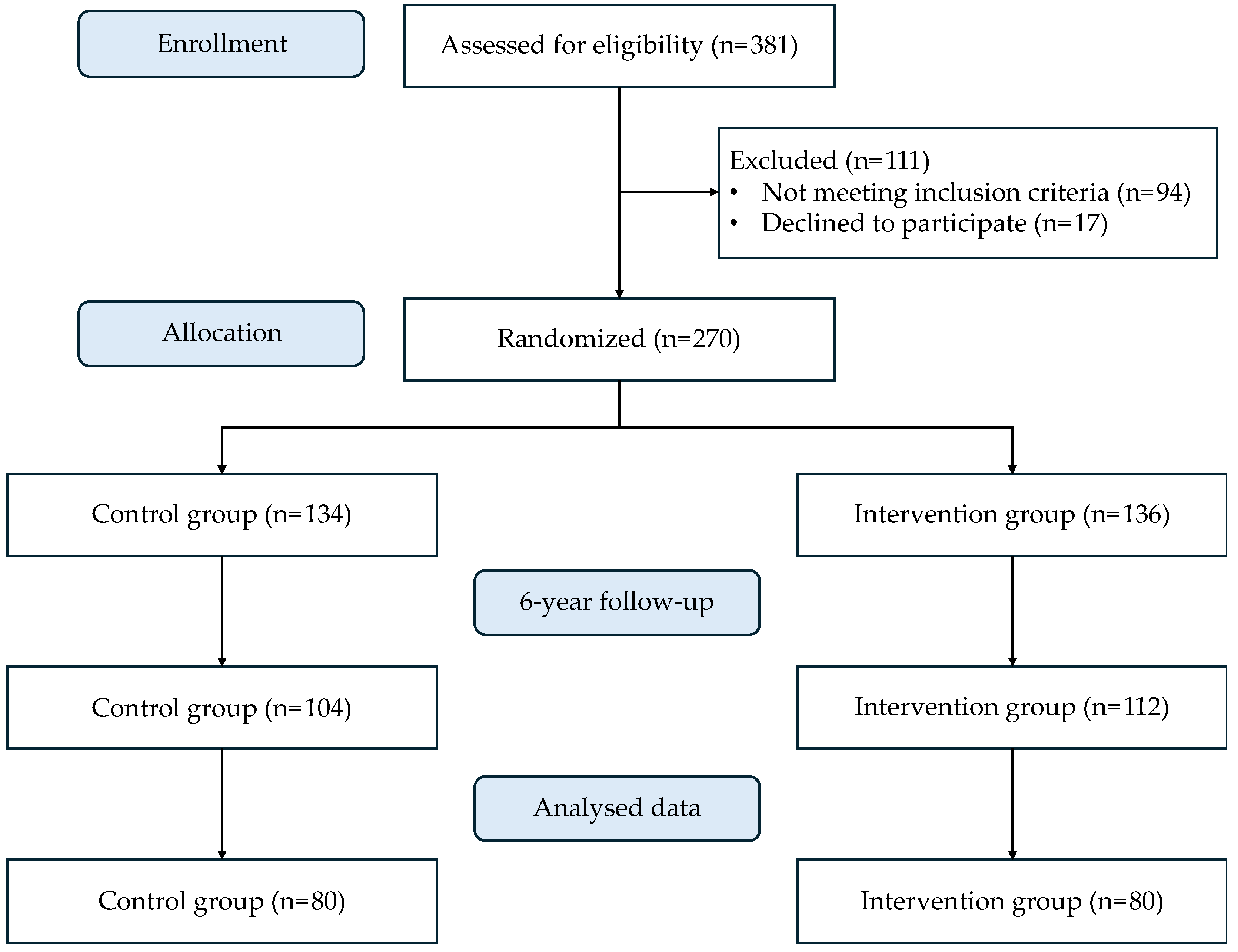
| Non-Responders (n = 40) | Responders (n = 40) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | 6-Year | Baseline | 6-Year | p-Value | |
| Anthropometry parameters | |||||
| Weight (kg) | 86.5 ± 12.0 | 87.7 ± 11.9 * | 90.4 ± 13.9 | 83.6 ± 13.9 * | <0.001 |
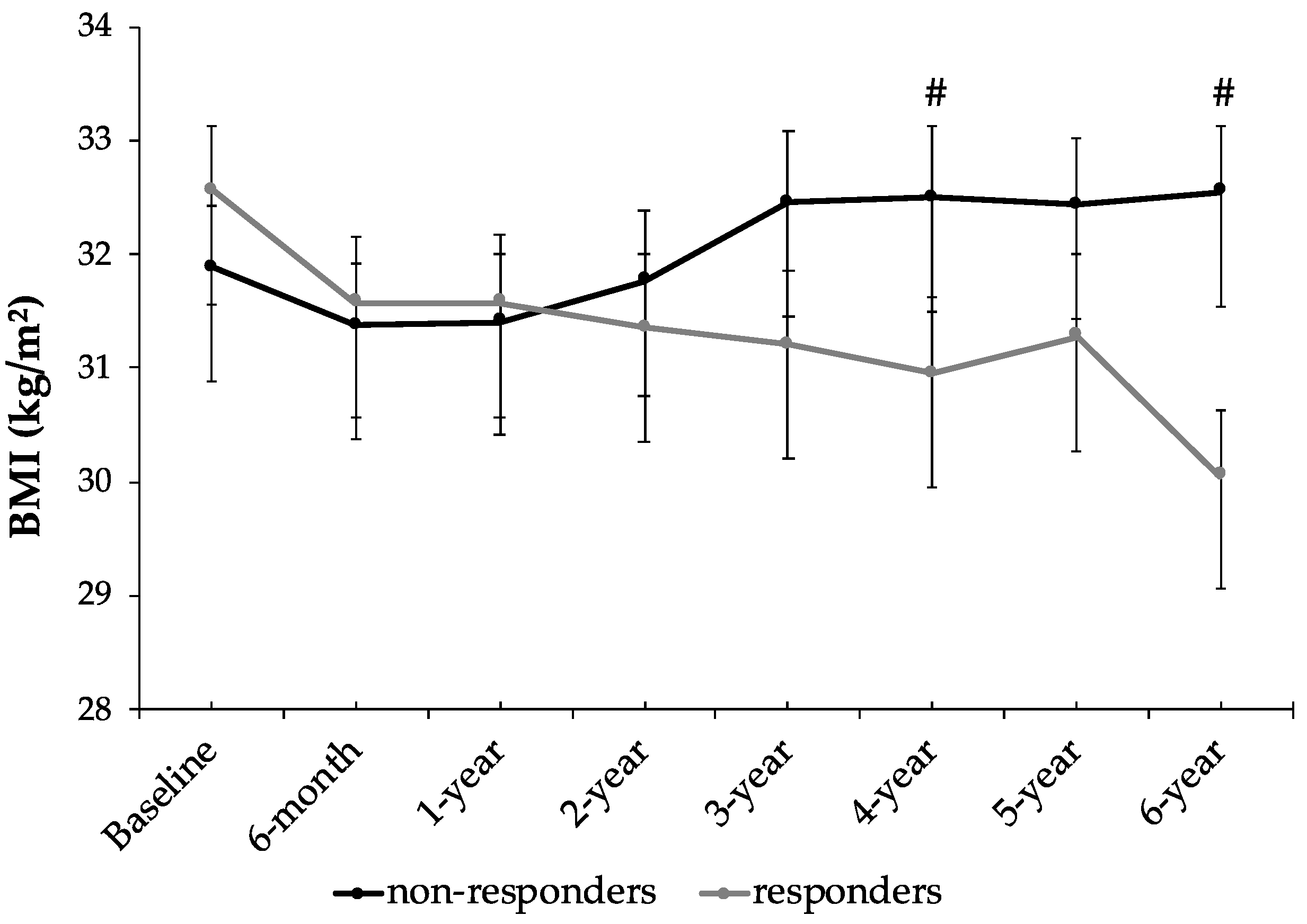
| BMI (kg/m2) | 31.9 ± 3.5 | 32.5 ± 3.6 * | 32.6 ± 3.5 | 30.1 ± 3.6 *# | <0.001 |
| WHtR | 0.650 ± 0.055 | 0.656 ± 0.057 | 0.669 ± 0.041 | 0.629 ± 0.039 *# | <0.001 |
| Abdominal obesity (cm) | 107.1 ± 9.8 | 107.8 ± 10.0 | 112.5 ± 7.1 # | 105.5 ± 8.0 * | <0.001 |
| Clinical parameters | |||||
| Systolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 139.2 ± 14.1 | 148.4 ± 16.4 * | 144.3 ± 17.5 | 146.8 ± 15.7 | 0.280 |
| Diastolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 82.9 ± 9.9 | 85.0 ± 10.3 | 83.5 ± 12.6 | 77.3 ± 9.4 *# | 0.010 |
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 109.8 ± 20.6 | 113.1 ± 31.0 | 124.9 ± 35.2 # | 116.0 ± 24.7 * | 0.037 |
| HbA1c (%) | 6.03 ± 0.77 | 6.28 ± 0.93 * | 6.37 ± 1.01 | 6.26 ± 0.79 | 0.013 |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL) | 136.9 ± 65.6 | 124.2 ± 47.1 | 160.1 ± 63.4 | 148.9 ± 90.6 | 0.884 |
| HDL-cholesterol (mg/dL) | 45.4 ± 9.2 | 47.3 ± 14.5 | 39.9 ± 9.0 # | 45.3 ± 11.9 * | 0.105 |
| LDL-cholesterol (mg/dL) | 115.5 ± 30.1 | 104.1 ± 33.6 | 101.1 ± 34.8 | 89.9 ± 29.4 | 0.888 |
| Cholesterol total (mg/dL) | 184.0 ± 33.0 | 175.9 ± 37.9 | 171.9 ± 37.0 | 163.8 ± 34.0 | 0.871 |
| Haematological parameters | |||||
| Haematocrit (%) | 43.2 ± 4.1 | 43.1 ± 5.9 | 43.6 ± 3.9 | 43.0 ± 6.2 | 0.825 |
| Erythrocytes (106/mm3) | 4.84 ± 0.47 | 4.77 ± 0.56 | 4.91 ± 0.50 | 4.82 ± 0.54 | 0.989 |
| Leukocytes (106/mm3) | 7.07 ± 1.88 | 7.10 ± 1.48 | 7.04 ± 1.54 | 7.01 ± 1.68 | 0.814 |
| Neutrophils (106/mm3) | 5.09 ± 7.66 | 3.85 ± 1.16 | 4.71 ± 4.63 | 4.10 ± 1.43 | 0.723 |
| Lymphocytes (106/mm3) | 3.00 ± 4.11 | 2.28 ± 0.68 | 2.21 ± 0.61 | 2.03 ± 0.71 | 0.425 |
| Monocytes (106/mm3) | 0.602 ± 0.204 | 0.673 ± 0.184 * | 0.629 ± 0.157 | 0.636 ± 0.157 | 0.094 |
| Eosinophils (106/mm3) | 0.231 ± 0.146 | 0.254 ± 0.180 | 0.275 ± 0.397 | 0.196 ± 0.109 | 0.148 |
| Basophils (106/mm3) | 0.066 ± 0.143 | 0.170 ± 0.734 | 0.042 ± 0.022 | 0.055 ± 0.116 | 0.476 |
| Non-Responders (n = 40) | Responders (n = 40) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | 6-Year | Baseline | 6-Year | p-Value | |
| Dietary assessment | |||||
| Adherence erMedDiet (17-items) | 7.00 ± 1.88 | 10.7 ± 2.8 * | 7.95 ± 2.53 | 11.2 ± 3.1 * | 0.432 |
| Energy intake (kcal/day) | 2461 ± 810 | 2374 ± 496 | 2676 ± 811 | 2368 ± 491 * | 0.256 |
| Glycaemic load | 141.7 ± 61.6 | 122.3 ± 41.0 | 164.4 ± 71.3 | 127.4 ± 36.0 * | 0.398 |
| Glycaemic index | 56.8 ± 3.8 | 53.1 ± 5.0 * | 56.8 ± 5.5 | 53.8 ± 4.8 * | 0.716 |
| Macronutrients | |||||
| Carbohydrates (g/day) | 245.7 ± 96.0 | 226.8 ± 64.3 | 285.3 ± 109.8 | 234.7 ± 54.6 * | 0.322 |
| Proteins (g/day) | 97.1 ± 30.1 | 95.7 ± 15.6 | 100.7 ± 30.9 | 99.8 ± 21.6 | 0.856 |
| Lipids (g/day) | 110.9 ± 45.5 | 114.5 ± 27.8 | 114.0 ± 36.6 | 105.8 ± 25.0 | 0.346 |
| Micronutrients | |||||
| MUFAs (g/day) | 56.6 ± 23.8 | 63.9 ± 17.1 | 56.9 ± 17.2 | 60.9 ± 16.0 | 0.677 |
| PUFAs (g/day) | 18.2 ± 9.41 | 21.1 ± 5.36 | 20.5 ± 7.32 | 18.9 ± 3.8 | 0.095 |
| SFA (g/day) | 29.0 ± 12.7 | 26.0 ± 7.74 | 31.8 ± 15.1 | 25.4 ± 7.60 * | 0.505 |
| Trans FA (g/day) | 0.717 ± 0.473 | 0.563 ± 0.294 | 0.802 ± 0.692 | 0.578 ± 0.313 | 0.882 |
| ω-6 FA (g/day) | 13.9 ± 7.0 | 16.4 ± 4.83 | 14.9 ± 6.83 | 13.9 ± 3.70 # | 0.092 |
| ω-3 FA (g/day) | 1.96 ± 0.61 | 2.62 ± 0.80 * | 2.23 ± 0.92 | 2.56 ± 0.94 * | 0.196 |
| Cholesterol (mg/day) | 416.0 ± 137.9 | 351.6 ± 93.7 | 409.5 ± 217.0 | 382.8 ± 124.3 | 0.441 |
| Folic acid (µg/day) | 290.5 ± 76.2 | 399.6 ± 113.5 * | 353.6 ± 117.7 # | 419.4 ± 114.7 * | 0.267 |
| Fibre (g/day) | 24.5 ± 9.74 | 33.9 ± 9.39 * | 30.7 ± 11.0 # | 36.0 ± 10.5 * | 0.255 |
| Vitamin A (µg/day) | 1090 ± 484 | 1276 ± 475 | 1234 ± 692 | 1391 ± 679 | 0.998 |
| Vitamin C (mg/day) | 197.2 ± 89.1 | 217.2 ± 74.8 | 213.1 ± 92.2 | 266.6 ± 85.5 *# | 0.315 |
| Vitamin D (µg/day) | 4.48 ± 2.19 | 5.69 ± 2.70 | 5.91 ± 3.77 | 6.20 ± 4.03 | 0.300 |
| Vitamin E (mg/day) | 11.9 ± 5.4 | 13.3 ± 2.6 | 12.0 ± 4.3 | 13.4 ± 4.9 | 0.981 |
| Polyphenol intake | |||||
| Total polyphenol (mg/day) | 593.2 ± 177.4 | 659.1 ± 184.3 | 647.6 ± 220.6 | 735.6 ± 223.7 * | 0.571 |
| Flavonoids (mg/day) | 367.9 ± 140.1 | 347.4 ± 105.8 | 393.6 ± 162.4 | 447.6 ± 148.1 # | 0.131 |
| Phenolic acid (mg/day) | 120.7 ± 59.5 | 171.8 ± 80.6 * | 121.4 ± 59.8 | 163.1 ± 85.5 * | 0.852 |
| Lignans (mg/day) | 3.56 ± 2.73 | 15.1 ± 11.1 * | 6.08 ± 7.70 | 8.53 ± 7.60 # | 0.002 |
| Stilbens (mg/day) | 4.36 ± 3.91 | 14.7 ± 10.9 * | 7.83 ± 7.98 | 9.00 ± 7.77 # | 0.002 |
| Others (mg/day) | 84.5 ± 43.0 | 100.8 ± 44.9 | 93.4 ± 59.3 | 92.2 ± 44.2 | 0.358 |
| Activity | |||||
| Sedentary time (hour/day) | 7.85 ± 2.13 | 8.29 ± 1.61 | 8.03 ± 1.75 | 7.60 ± 1.82 * | 0.082 |
| Total PA (MET·min/week) | 3190 ± 2757 | 3550 ± 2786 | 2697 ± 1951 | 3996 ± 3839 * | 0.292 |
| Light PA (MET·min/week) | 682.1 ± 1122 | 918.0 ± 878.0 | 703.4 ± 936.5 | 1105 ± 1578 | 0.625 |
| Moderate PA (MET·min/week) | 1695 ± 1820 | 2025 ± 2673 | 1027 ± 1224 | 1887 ± 2207 | 0.586 |
| Vigorous PA (MET·min/week) | 812.6 ± 1625 | 608.0 ± 684.7 | 910.0 ± 1471 | 904.3 ± 1827 | 0.565 |
| Non-Responders (n = 40) | Responders (n = 40) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | 6-Year | Baseline | 6-Year | p-Value | |
| Polyphenols plasma (mg/mL) | 0.056 ± 0.019 | 0.057 ± 0.013 | 0.057 ± 0.013 | 0.055 ± 0.008 | 0.740 |
| Oxidative activities | |||||
| CAT (K/L blood) | 50.6 ± 19.4 | 212.4 ± 238.3 * | 91.2 ± 156.3 | 166.4 ± 129.9 | 0.139 |
| SOD (pkat/L blood) | 101.1 ± 94.5 | 104.9 ± 64.5 | 103.1 ± 80.2 | 105.1 ± 58.6 | 0.906 |
| MPO (μkat/mL blood) | 62.1 ± 55.5 | 55.5 ± 31.4 | 52.2 ± 28.8 | 30.6 ± 12.7 *# | 0.246 |
| Oxidative damage | |||||
| ROS production by neutrophils(RLU/min·103 cells) | 2177 ± 1096 | 1367 ± 614 | 3151 ± 2014 | 1519 ± 807 * | 0.092 |
| MDA plasma (nM) | 1.60 ± 1.58 | 1.22 ± 0.89 | 1.28 ± 1.26 | 0.95 ± 0.79 * | 0.499 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Quetglas-Llabrés, M.M.; Monserrat-Mesquida, M.; Bouzas, C.; García, S.; Mateos, D.; Ugarriza, L.; Gómez, C.; Sureda, A.; Tur, J.A. Long-Term Impact of Nutritional Intervention with Increased Polyphenol Intake and Physical Activity Promotion on Oxidative and Inflammatory Profiles in Patients with Metabolic Syndrome. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2121. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16132121
Quetglas-Llabrés MM, Monserrat-Mesquida M, Bouzas C, García S, Mateos D, Ugarriza L, Gómez C, Sureda A, Tur JA. Long-Term Impact of Nutritional Intervention with Increased Polyphenol Intake and Physical Activity Promotion on Oxidative and Inflammatory Profiles in Patients with Metabolic Syndrome. Nutrients. 2024; 16(13):2121. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16132121
Chicago/Turabian StyleQuetglas-Llabrés, Maria Magdalena, Margalida Monserrat-Mesquida, Cristina Bouzas, Silvia García, David Mateos, Lucía Ugarriza, Cristina Gómez, Antoni Sureda, and Josep A. Tur. 2024. "Long-Term Impact of Nutritional Intervention with Increased Polyphenol Intake and Physical Activity Promotion on Oxidative and Inflammatory Profiles in Patients with Metabolic Syndrome" Nutrients 16, no. 13: 2121. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16132121
APA StyleQuetglas-Llabrés, M. M., Monserrat-Mesquida, M., Bouzas, C., García, S., Mateos, D., Ugarriza, L., Gómez, C., Sureda, A., & Tur, J. A. (2024). Long-Term Impact of Nutritional Intervention with Increased Polyphenol Intake and Physical Activity Promotion on Oxidative and Inflammatory Profiles in Patients with Metabolic Syndrome. Nutrients, 16(13), 2121. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16132121










