Sex Differences in the Ergogenic Response of Acute Caffeine Intake on Muscular Strength, Power and Endurance Performance in Resistance-Trained Individuals: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Experimental Protocol
2.3.1. Body Composition, Dietary and Physical Activity Habits
2.3.2. Supplementation Protocol
2.3.3. One-Repetition Maximum (1RM)
2.3.4. Muscular Strength and Power Test
2.3.5. Muscular Endurance Test
2.3.6. Isometric Strength and Vertical Jump
2.3.7. Questionnaires and Scales
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
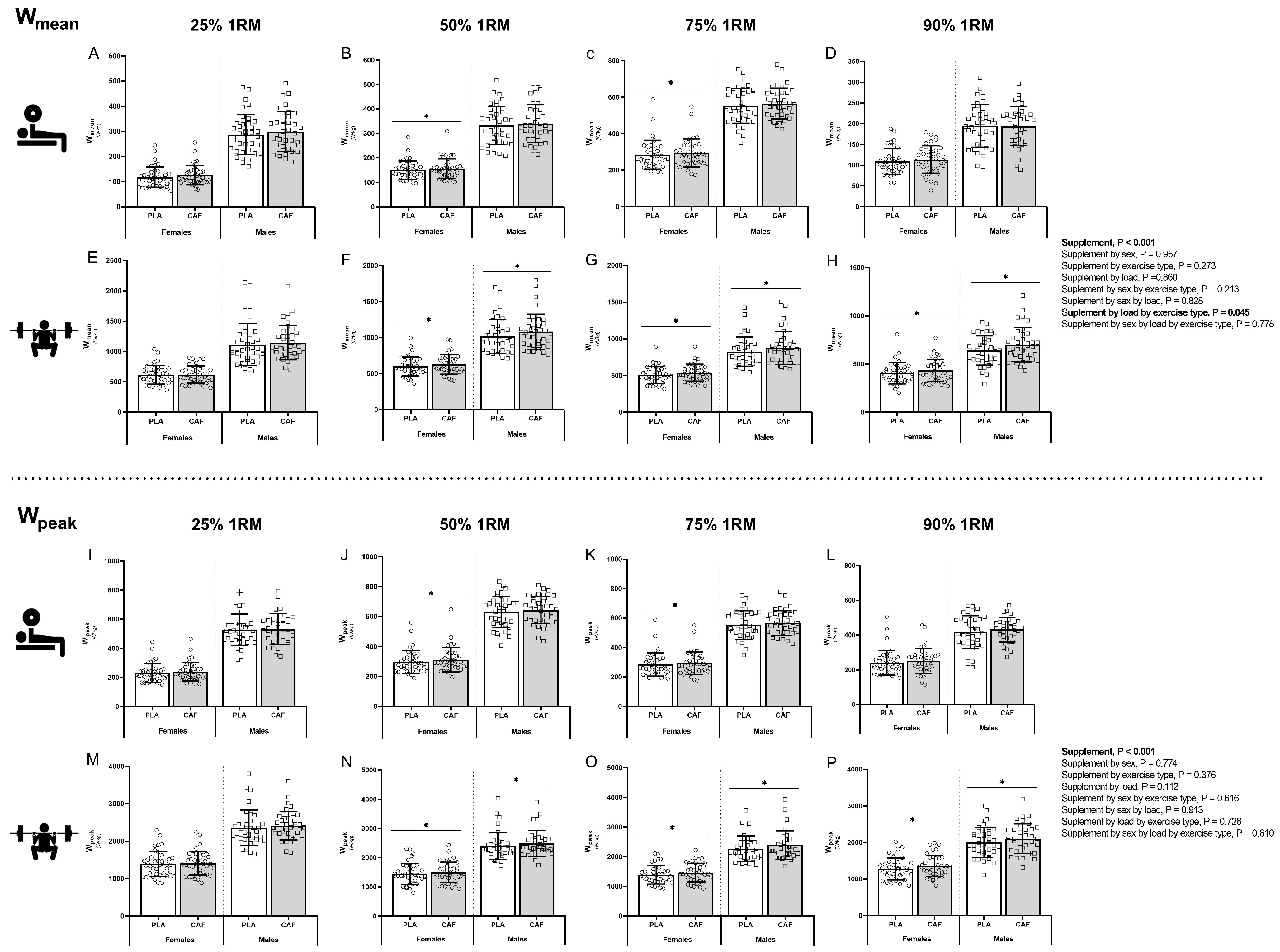
3.1. Muscular Strength and Power
3.2. Muscular Endurance
3.3. Isometric Strength and Vertical Jump
3.4. Questionnaires and Scales
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guest, N.S.; VanDusseldorp, T.A.; Nelson, M.T.; Grgic, J.; Schoenfeld, B.J.; Jenkins, N.D.M.; Arent, S.M.; Antonio, J.; Stout, J.R.; Trexler, E.T.; et al. International society of sports nutrition position stand: Caffeine and exercise performance. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2021, 18, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Fernandez, I.; Valades, D.; Dominguez, R.; Ferragut, C.; Perez-Lopez, A. Load and muscle group size influence the ergogenic effect of acute caffeine intake in muscular strength, power and endurance. Eur. J. Nutr. 2023, 62, 1783–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sims, S.T.; Kerksick, C.M.; Smith-Ryan, A.E.; Janse de Jonge, X.A.K.; Hirsch, K.R.; Arent, S.M.; Hewlings, S.J.; Kleiner, S.M.; Bustillo, E.; Tartar, J.L.; et al. International society of sports nutrition position stand: Nutritional concerns of the female athlete. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2023, 20, 2204066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mielgo-Ayuso, J.; Marques-Jimenez, D.; Refoyo, I.; Del Coso, J.; Leon-Guereno, P.; Calleja-Gonzalez, J. Effect of Caffeine Supplementation on Sports Performance Based on Differences between Sexes: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, C.L.; Chia, M.; Inbar, O. Gender differences in anaerobic power of the arms and legs—A scaling issue. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2006, 38, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bishop, P.; Cureton, K.; Collins, M. Sex difference in muscular strength in equally-trained men and women. Ergonomics 1987, 30, 675–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, B.M.; Nuckols, G.; Krieger, J.W. Sex Differences in Resistance Training: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2020, 34, 1448–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gentil, P.; Steele, J.; Pereira, M.C.; Castanheira, R.P.; Paoli, A.; Bottaro, M. Comparison of upper body strength gains between men and women after 10 weeks of resistance training. PeerJ 2016, 4, e1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, T.; DeHoyos, D.V.; Pollock, M.L.; Garzarella, L. Time course for strength and muscle thickness changes following upper and lower body resistance training in men and women. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2000, 81, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, A.E.; MacDougall, J.D.; Tarnopolsky, M.A.; Sale, D.G. Gender differences in strength and muscle fiber characteristics. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. Occup. Physiol. 1993, 66, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannah, R.; Minshull, C.; Buckthorpe, M.W.; Folland, J.P. Explosive neuromuscular performance of males versus females. Exp. Physiol. 2012, 97, 618–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trevino, M.A.; Sterczala, A.J.; Miller, J.D.; Wray, M.E.; Dimmick, H.L.; Ciccone, A.B.; Weir, J.P.; Gallagher, P.M.; Fry, A.C.; Herda, T.J. Sex-related differences in muscle size explained by amplitudes of higher-threshold motor unit action potentials and muscle fibre typing. Acta Physiol. 2019, 225, e13151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieto-Acevedo, R.; Romero-Moraleda, B.; Diaz-Lara, F.J.; Rubia, A.; Gonzalez-Garcia, J.; Mon-Lopez, D. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Differences in Mean Propulsive Velocity between Men and Women in Different Exercises. Sports 2023, 11, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Askow, A.T.; Merrigan, J.J.; Neddo, J.M.; Oliver, J.M.; Stone, J.D.; Jagim, A.R.; Jones, M.T. Effect of Strength on Velocity and Power During Back Squat Exercise in Resistance-Trained Men and Women. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2019, 33, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilk, M.; Filip, A.; Krzysztofik, M.; Gepfert, M.; Zajac, A.; Del Coso, J. Acute Caffeine Intake Enhances Mean Power Output and Bar Velocity during the Bench Press Throw in Athletes Habituated to Caffeine. Nutrients 2020, 12, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pallares, J.G.; Fernandez-Elias, V.E.; Ortega, J.F.; Munoz, G.; Munoz-Guerra, J.; Mora-Rodriguez, R. Neuromuscular responses to incremental caffeine doses: Performance and side effects. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2013, 45, 2184–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora-Rodriguez, R.; Pallares, J.G.; Lopez-Gullon, J.M.; Lopez-Samanes, A.; Fernandez-Elias, V.E.; Ortega, J.F. Improvements on neuromuscular performance with caffeine ingestion depend on the time-of-day. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2015, 18, 338–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warren, G.L.; Park, N.D.; Maresca, R.D.; McKibans, K.I.; Millard-Stafford, M.L. Effect of caffeine ingestion on muscular strength and endurance: A meta-analysis. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2010, 42, 1375–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, M.J.; Stanley, M.; Parkhouse, N.; Cook, K.; Smith, M. Acute caffeine ingestion enhances strength performance and reduces perceived exertion and muscle pain perception during resistance exercise. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2013, 13, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazzucchi, I.; Felici, F.; Montini, M.; Figura, F.; Sacchetti, M. Caffeine improves neuromuscular function during maximal dynamic exercise. Muscle Nerve 2011, 43, 839–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, C.D.; Waddell, D.E.; Gonglach, A.R. Caffeine’s Ergogenic Effects on Cycling: Neuromuscular and Perceptual Factors. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2015, 47, 1145–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behrens, M.; Mau-Moeller, A.; Weippert, M.; Fuhrmann, J.; Wegner, K.; Skripitz, R.; Bader, R.; Bruhn, S. Caffeine-induced increase in voluntary activation and strength of the quadriceps muscle during isometric, concentric and eccentric contractions. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norum, M.; Risvang, L.C.; Bjornsen, T.; Dimitriou, L.; Ronning, P.O.; Bjorgen, M.; Raastad, T. Caffeine increases strength and power performance in resistance-trained females during early follicular phase. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2020, 30, 2116–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shield, A.; Zhou, S. Assessing voluntary muscle activation with the twitch interpolation technique. Sports Med. 2004, 34, 253–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timmins, T.D.; Saunders, D.H. Effect of caffeine ingestion on maximal voluntary contraction strength in upper- and lower-body muscle groups. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2014, 28, 3239–3244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, J.K.; Green, J.M. Caffeine and anaerobic performance: Ergogenic value and mechanisms of action. Sports Med. 2009, 39, 813–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filip, A.; Wilk, M.; Krzysztofik, M.; Del Coso, J. Inconsistency in the Ergogenic Effect of Caffeine in Athletes Who Regularly Consume Caffeine: Is It Due to the Disparity in the Criteria That Defines Habitual Caffeine Intake? Nutrients 2020, 12, 1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raya-Gonzalez, J.; Rendo-Urteaga, T.; Dominguez, R.; Castillo, D.; Rodriguez-Fernandez, A.; Grgic, J. Acute Effects of Caffeine Supplementation on Movement Velocity in Resistance Exercise: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Sports Med. 2020, 50, 717–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craig, C.L.; Marshall, A.L.; Sjostrom, M.; Bauman, A.E.; Booth, M.L.; Ainsworth, B.E.; Pratt, M.; Ekelund, U.; Yngve, A.; Sallis, J.F.; et al. International physical activity questionnaire: 12-country reliability and validity. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2003, 35, 1381–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benowitz, N.L. Clinical pharmacology of caffeine. Annu. Rev. Med. 1990, 41, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Villanueva, A.; Pino-Ortega, J.; Rico-Gonzalez, M. Validity and reliability of linear position transducers and linear velocity transducers: A systematic review. Sports Biomech. 2021, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Castilla, A.; Piepoli, A.; Delgado-Garcia, G.; Garrido-Blanca, G.; Garcia-Ramos, A. Reliability and Concurrent Validity of Seven Commercially Available Devices for the Assessment of Movement Velocity at Different Intensities during the Bench Press. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2019, 33, 1258–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadenas-Sanchez, C.; Sanchez-Delgado, G.; Martinez-Tellez, B.; Mora-Gonzalez, J.; Lof, M.; Espana-Romero, V.; Ruiz, J.R.; Ortega, F.B. Reliability and Validity of Different Models of TKK Hand Dynamometers. Am. J. Occup. Ther. 2016, 70, 7004300010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Hoffman, J.R.; Tanigawa, S.; Miramonti, A.A.; La Monica, M.B.; Beyer, K.S.; Church, D.D.; Fukuda, D.H.; Stout, J.R. Isometric Mid-Thigh Pull Correlates with Strength, Sprint, and Agility Performance in Collegiate Rugby Union Players. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2016, 30, 3051–3056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khamoui, A.V.; Brown, L.E.; Nguyen, D.; Uribe, B.P.; Coburn, J.W.; Noffal, G.J.; Tran, T. Relationship between force-time and velocity-time characteristics of dynamic and isometric muscle actions. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2011, 25, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Lopez, A.; Salinero, J.J.; Abian-Vicen, J.; Valades, D.; Lara, B.; Hernandez, C.; Areces, F.; Gonzalez, C.; Del Coso, J. Caffeinated energy drinks improve volleyball performance in elite female players. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2015, 47, 850–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jodra, P.; Lago-Rodriguez, A.; Sanchez-Oliver, A.J.; Lopez-Samanes, A.; Perez-Lopez, A.; Veiga-Herreros, P.; San Juan, A.F.; Dominguez, R. Effects of caffeine supplementation on physical performance and mood dimensions in elite and trained-recreational athletes. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2020, 17, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, E.; Arce, C.; De Francisco, C.; Torrado, J.; Garrido, J. Abbreviated version in spanish of the POMS questionnaire for adult athletes and general population. Rev. Psicol. Dep. 2016, 22, 95–102. [Google Scholar]
- Petrowski, K.; Albani, C.; Zenger, M.; Brahler, E.; Schmalbach, B. Revised Short Screening Version of the Profile of Mood States (POMS) From the German General Population. Front. Psychol. 2021, 12, 631668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, I.; Tomas, I.; Balaguer, I. The Spanish-Version of the Subjective Vitality Scale: Psychometric Properties and Evidence of Validity. Span. J. Psychol. 2017, 20, E26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.Y.; Wang, H.S.; Tung, K.; Chao, H.H. Effects of Gender Difference and Caffeine Supplementation on Anaerobic Muscle Performance. Int. J. Sports Med. 2015, 36, 974–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lara, B.; Salinero, J.J.; Giraldez-Costas, V.; Del Coso, J. Similar ergogenic effect of caffeine on anaerobic performance in men and women athletes. Eur. J. Nutr. 2021, 60, 4107–4114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skinner, T.L.; Desbrow, B.; Arapova, J.; Schaumberg, M.A.; Osborne, J.; Grant, G.D.; Anoopkumar-Dukie, S.; Leveritt, M.D. Women Experience the Same Ergogenic Response to Caffeine as Men. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2019, 51, 1195–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arazi, H.; Hoseinihaji, M.; Eghbali, E.T. The effects of different doses of caffeine on performance, rating of perceived exertion and pain perception in teenagers female karate athletes. Braz. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 52, 685–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fett, C.A.; Aquino, N.M.; Schantz Junior, J.; Brandao, C.F.; de Araujo Cavalcanti, J.D.; Fett, W.C. Performance of muscle strength and fatigue tolerance in young trained women supplemented with caffeine. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fit. 2018, 58, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filip-Stachnik, A.; Wilk, M.; Krzysztofik, M.; Lulinska, E.; Tufano, J.J.; Zajac, A.; Stastny, P.; Del Coso, J. The effects of different doses of caffeine on maximal strength and strength-endurance in women habituated to caffeine. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2021, 18, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldstein, E.; Jacobs, P.L.; Whitehurst, M.; Penhollow, T.; Antonio, J. Caffeine enhances upper body strength in resistance-trained women. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2010, 7, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabblah, S.; Dixon, D.; Bottoms, L. Sex differences on the acute effects of caffeine on maximal strength and muscular endurance. Comp. Exerc. Physiol. 2015, 11, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filip-Stachnik, A.; Krzysztofik, M.; Del Coso, J.; Wilk, M. Acute effects of two caffeine doses on bar velocity during the bench press exercise among women habituated to caffeine: A randomized, crossover, double-blind study involving control and placebo conditions. Eur. J. Nutr. 2022, 61, 947–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Moraleda, B.; Del Coso, J.; Gutierrez-Hellin, J.; Lara, B. The Effect of Caffeine on the Velocity of Half-Squat Exercise during the Menstrual Cycle: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trevino, M.A.; Coburn, J.W.; Brown, L.E.; Judelson, D.A.; Malek, M.H. Acute effects of caffeine on strength and muscle activation of the elbow flexors. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2015, 29, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, T.T.; da Silva, J.V.F.; Bueno, N.B. Effects of caffeine supplementation on muscle endurance, maximum strength, and perceived exertion in adults submitted to strength training: A systematic review and meta-analyses. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 61, 2587–2600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grgic, J.; Pickering, C.; Bishop, D.J.; Schoenfeld, B.J.; Mikulic, P.; Pedisic, Z. CYP1A2 genotype and acute effects of caffeine on resistance exercise, jumping, and sprinting performance. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2020, 17, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staron, R.S.; Hagerman, F.C.; Hikida, R.S.; Murray, T.F.; Hostler, D.P.; Crill, M.T.; Ragg, K.E.; Toma, K. Fiber type composition of the vastus lateralis muscle of young men and women. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2000, 48, 623–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, M.; Santos, P.; Correia, P.; Pezarat-Correia, P.; Mendonca, G.V. Sex differences in muscle fatigue following isokinetic muscle contractions. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 8141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, S.K. Sex differences in fatigability of dynamic contractions. Exp. Physiol. 2016, 101, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| CAF (N = 76) | PLA (N = 76) | ANOVA Effects | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Females (N = 38) | Males (N = 38) | Females (N = 38) | Males (N = 38) | Sex (Partial η2) | Supplement (Partial η2) | Sex × Supplement (Partial η2) | |
| Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | ||||
| Body composition | |||||||
| Body mass (kg) | 59.9 ± 7.1 | 78.5 ± 11.7 | 60.0 ± 7.2 | 78.2 ± 11.9 | <0.001 (0.634) | 0.564 (0.009) | 0.955 (0.003) |
| Fat mass (kg) | 12.6 ± 3.4 | 9.9 ± 5.1 | 12.7 ± 3.2 | 9.8 ± 5.2 | 0.004 (0.213) | 0.882 (0.001) | 0.257 (0.035) |
| Fat-free mass (kg) | 47.3 ± 5.5 | 68.6 ± 7.9 | 47.3 ± 5.7 | 68.3 ± 7.9 | <0.001 (0.815) | 0.991 (<0.001) | 0.758 (0.003) |
| Dietary habits | |||||||
| Energy intake (kcal) | 1270 ± 336 | 1972 ± 847 | 1264 ± 354 | 1959 ± 846 | <0.001 (0.436) | 0.415 (0.019) | 0.929 (0.008) |
| Protein (g/kg) | 1.30 ± 0.50 | 1.59 ± 0.89 | 1.28 ± 0.50 | 1.56 ± 0.85 | 0.186 (0.048) | 0.306 (0.047) | 0.560 (0.010) |
| Carbohydrate (g/kg) | 2.28 ± 0.78 | 2.49 ± 1.50 | 2.27 ± 0.86 | 2.39 ± 1.28 | 0.761 (0.003) | 0.538 (0.011) | 0.818 (0.054) |
| Fat (g/kg) | 0.82 ± 0.33 | 1.24 ± 0.91 | 0.84 ± 0.39 | 1.25 ± 0.86 | 0.290 (0.126) | 0.989 (0.017) | 0.833 (0.045) |
| Physical Activity habits | |||||||
| METs-min/week | 5027 ± 757 | 6048 ± 899 | 4906 ± 557 | 6725 ± 924 | 0.916 (<0.001) | 0.775 (0.003) | 0.478 (0.018) |
| Sedentary time (h/day) | 7.40 ± 5.57 | 7.95 ± 7.78 | 7.38 ± 5.91 | 8.20 ± 6.42 | 0.379 (0.023) | 0.346 (0.039) | 0.349 (0.026) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Montalvo-Alonso, J.J.; Ferragut, C.; del Val-Manzano, M.; Valadés, D.; Roberts, J.; Pérez-López, A. Sex Differences in the Ergogenic Response of Acute Caffeine Intake on Muscular Strength, Power and Endurance Performance in Resistance-Trained Individuals: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1760. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16111760
Montalvo-Alonso JJ, Ferragut C, del Val-Manzano M, Valadés D, Roberts J, Pérez-López A. Sex Differences in the Ergogenic Response of Acute Caffeine Intake on Muscular Strength, Power and Endurance Performance in Resistance-Trained Individuals: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutrients. 2024; 16(11):1760. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16111760
Chicago/Turabian StyleMontalvo-Alonso, Juan Jesús, Carmen Ferragut, Marta del Val-Manzano, David Valadés, Justin Roberts, and Alberto Pérez-López. 2024. "Sex Differences in the Ergogenic Response of Acute Caffeine Intake on Muscular Strength, Power and Endurance Performance in Resistance-Trained Individuals: A Randomized Controlled Trial" Nutrients 16, no. 11: 1760. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16111760
APA StyleMontalvo-Alonso, J. J., Ferragut, C., del Val-Manzano, M., Valadés, D., Roberts, J., & Pérez-López, A. (2024). Sex Differences in the Ergogenic Response of Acute Caffeine Intake on Muscular Strength, Power and Endurance Performance in Resistance-Trained Individuals: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutrients, 16(11), 1760. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16111760








