Weight-Control Behaviors and Dietary Intake in Chinese Adults: An Analysis of Three National Surveys (2002–2015)
Abstract
1. Introduction
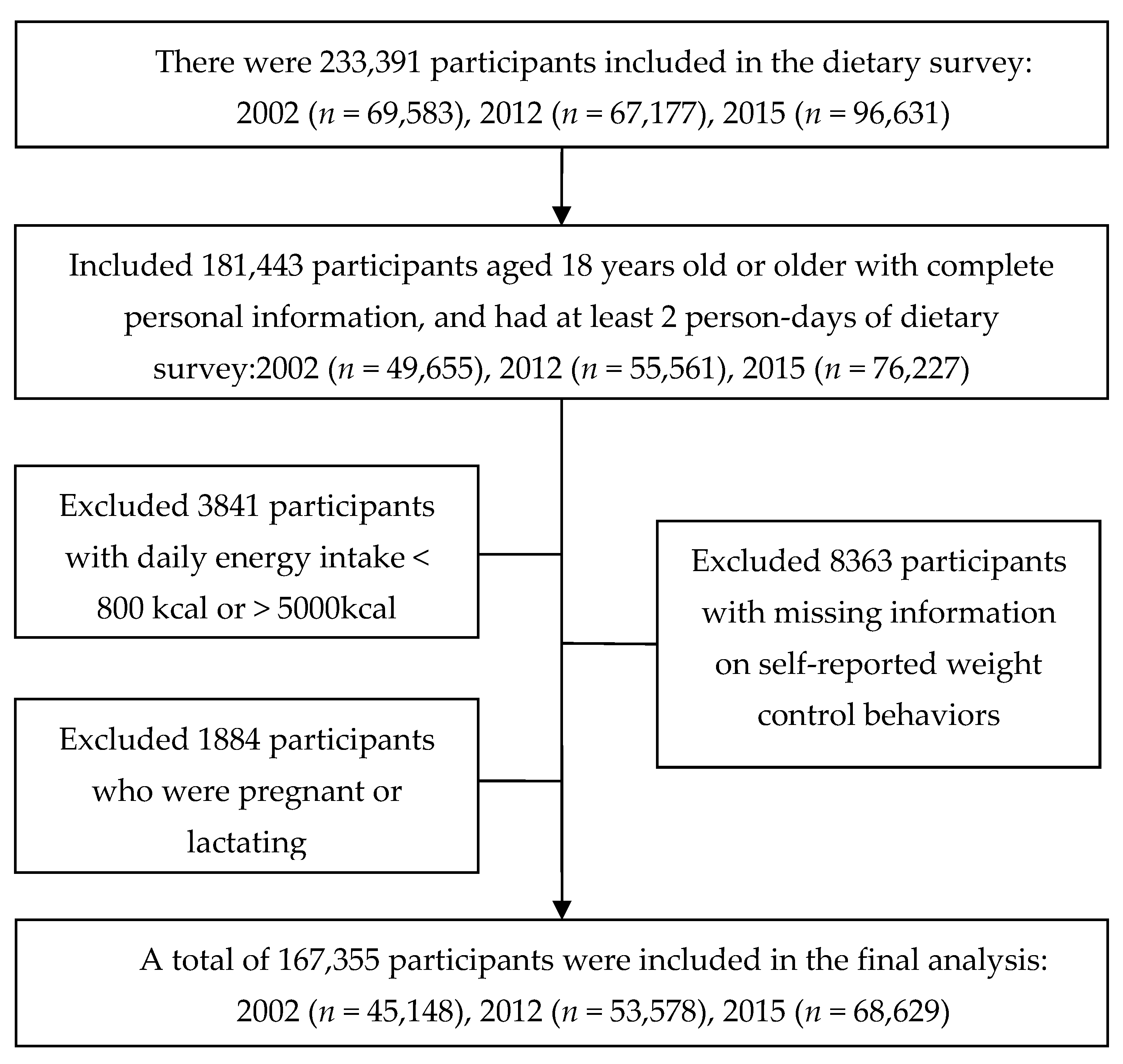
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Data Collection and Dietary Assessment
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Participant Characteristics
3.2. Comparison of Dietary Intake in Participants with and without Weight-Control Behavior
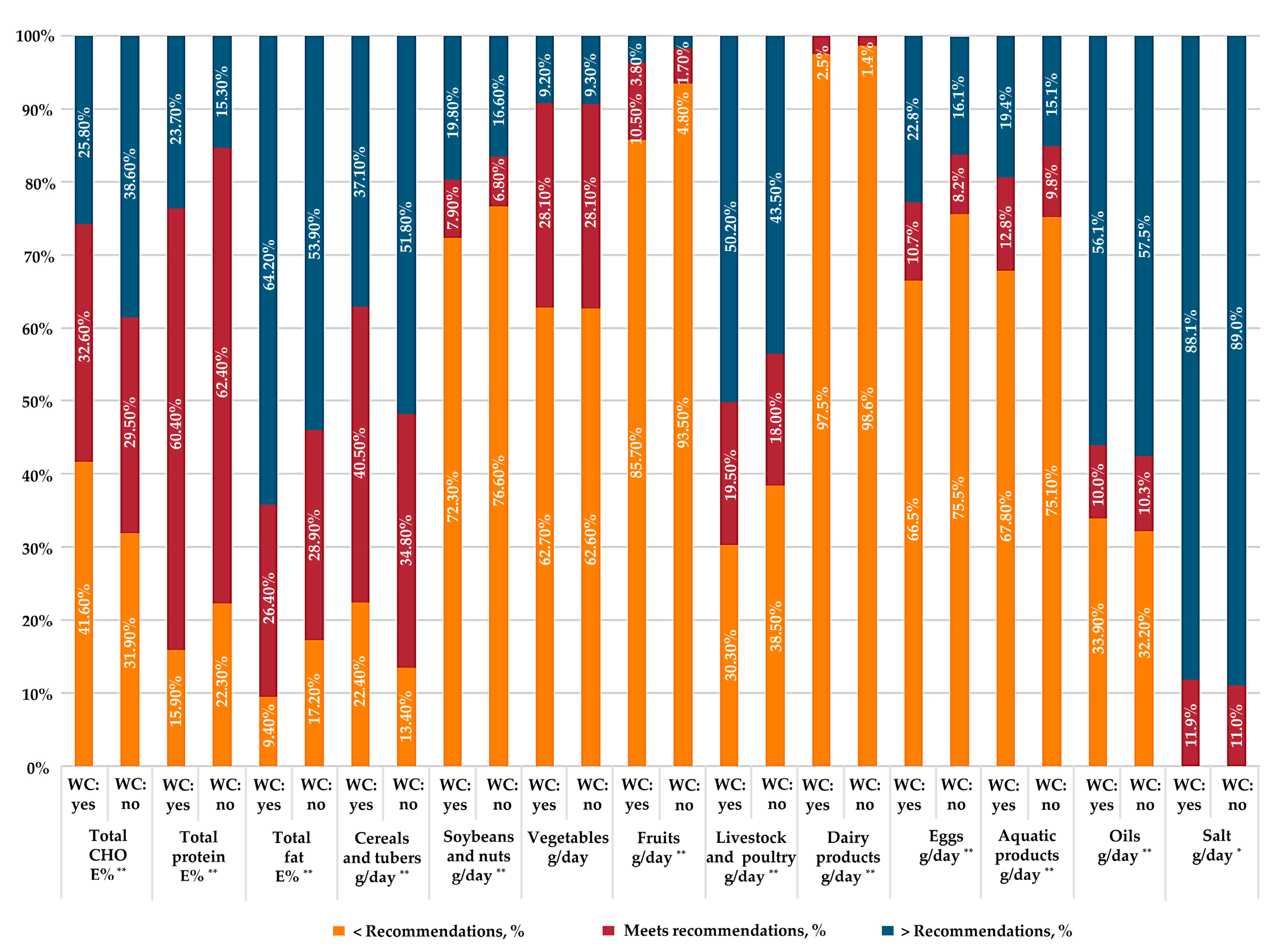
3.3. Adherence to Dietary Recommendations in Participants with and without Weight-Control Behavior
3.4. Comparison of Diet Quality in Participants with and without Weight-Control Behavior
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- GBD 2015 Obesity Collaborators; Afshin, A.; Forouzanfar, M.H.; Reitsma, M.B.; Sur, P.; Estep, K.; Lee, A.; Marczak, L.; Mokdad, A.H.; Moradi-Lakeh, M.; et al. Health Effects of Overweight and Obesity in 195 Countries over 25 Years. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisanu, S.; Palmas, V.; Madau, V.; Casula, E.; Deledda, A.; Cusano, R.; Uva, P.; Vascellari, S.; Boi, F.; Loviselli, A.; et al. Impact of a Moderately Hypocaloric Mediterranean Diet on the Gut Microbiota Composition of Italian Obese Patients. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deledda, A.; Annunziata, G.; Tenore, G.; Palmas, V.; Manzin, A.; Velluzzi, F. Diet-Derived Antioxidants and Their Role in Inflammation, Obesity and Gut Microbiota Modulation. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Wu, F.; Lv, G.; Zhuang, X.; Ma, G. Development and Validity of a General Nutrition Knowledge Questionnaire (GNKQ) for Chinese Adults. Nutrients 2021, 13, 4353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paquette, M.C. Perceptions of healthy eating: State of knowledge and research gaps. Can. J. Public Health 2005, 96 (Suppl. S3), S16–S21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, E.A.; Perez, W.J.; Phipps, B.; Ryan, A.S.; Prior, S.J.; Katzel, L.; Serra, M.C.; Addison, O. Dietary Quality and Perceived Barriers to Weight Loss among Older Overweight Veterans with Dysmobility. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 9153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neumark-Sztainer, D.; Rock, C.L.; Thornquist, M.D.; Cheskin, L.J.; Neuhouser, M.L.; Barnett, M.J. Weight-Control Behaviors among Adults and Adolescents: Associations with Dietary Intake. Prev. Med. 2000, 30, 381–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyrovolas, S.; Koyanagi, A.; Stickley, A.; Haro, J.M. Weight Perception, Satisfaction, Control, and Low Energy Dietary Reporting in the US Adult Population: Results from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2007–2012. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2016, 116, 579–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hjartaker, A.; Hiartaker, A.; Laake, P.; Lund, E. Body mass index and weight change attempts among adult women: The norwegian women and cancer study. Eur. J. Public Health 2001, 11, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wardle, J.; Griffith, J.; Johnson, F.; Rapoport, L. Intentional weight control and food choice habits in a national representative sample of adults in the UK. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 2000, 24, 534–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leme, A.C.B.; Haines, J.; Tang, L.; Fisberg, M.; Ferrari, G.; da Silva, V.A.; Fisberg, R.M. Association between weight control behaviors and diet quality among Brazilian adolescents and young adults: Health Survey of São Paulo with Focus on Nutrition, 2015. Eat. Weight. Disord. Stud. Anorex. Bulim. Obes. 2021, 27, 605–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.-T.J.; Gao, Z.; Lee, J.-Y. Associations between self-reported weight management methods with diet quality as measured by the Healthy Eating Index–2005. Prev. Med. 2013, 57, 238–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raffoul, A.; Goodman, S.; Hammond, D.; Kirkpatrick, S.I. Weight Management Efforts, But Not Weight Perceptions, Are Associated with Dietary Quality among Youth and Young Adults in Canada. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2021, 121, 942–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, T.; Overcash, F.; Reicks, M. Frequency of Trying to Lose Weight and Its Association with Children’s Weight Perception and Dietary Intake (NHANES 2011–2012). Nutrients 2019, 11, 2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timperio, A.; Cameron-Smith, D.; Burns, C.; Crawford, D. The public’s response to the obesity epidemic in Australia: Weight concerns and weight control practices of men and women. Public Health Nutr. 2000, 3, 417–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, L.; Yang, Z.; Huo, J.; Yang, L.; Wang, J.; He, L.; Sun, J.; et al. Data Resource Profile: China National Nutrition Surveys. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2019, 48, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y. China Food Composition Tables, 2002 ed.; Peking University Medical Press: Beijing, China, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y. China Food Composition Tables, 2nd ed.; Peking University Medical Press: Beijing, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- National Health Commission of China. Chinese Dietary Reference Intakes-Part 1: Macronutrient (WS/T578.1-2017). Available online: http://www.nhc.gov.cn/wjw/yingyang/201710/fdade20feb8144ba921b412944ffb779.shtml (accessed on 3 November 2022).
- Shan, Z.; Rehm, C.D.; Rogers, G.; Ruan, M.; Wang, D.D.; Hu, F.B.; Mozaffarian, D.; Zhang, F.F.; Bhupathiraju, S.N. Trends in Dietary Carbohydrate, Protein, and Fat Intake and Diet Quality among US Adults, 1999–2016. JAMA J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2019, 322, 1178–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.-S.; Lay, S.; Yu, H.-N.; Shen, S.-R. Dietary Guidelines for Chinese Residents (2016): Comments and comparisons. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2016, 17, 649–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Fang, Y.; Yang, X. Establishment and application of China healthy diet index. Acta Nutr. Sin. 2017, 39, 436–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piernas, C.; Aveyard, P.; A Jebb, S. Recent trends in weight loss attempts: Repeated cross-sectional analyses from the health survey for England. Int. J. Obes. 2016, 40, 1754–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, I.; Sniehotta, F.F.; Marques, M.M.; Carraça, E.V.; Teixeira, P.J. Prevalence of personal weight control attempts in adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes. Rev. 2017, 18, 32–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.T.; Yan, H.M.; Wang, L.M.; Liu, S.B.; Xu, T.L.; Shen, T.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, X.; Li, C.; Huang, Z.J.; et al. A study regarding the control attempts on body weight and related factors among overweight and obese adults in China, 2013. Chin. J. Epidemiol. 2019, 40, 621–626. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, D.; Dong, J.; Wang, Z.; Wang, L.; Liu, W.; Zhang, H. Weight Control Measures and Influencing Factors for Overweight and Obese People in Qinhuangdao City in 2019. J. Prev. Med. Inf. 2021, 37, 89–95. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, L.; Zhao, W. Investigation on self-measurement and awareness of body weight among Chinese adults in 2010. Chin. J. Health Educ. 2013, 29, 485–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhanji, S.; Khuwaja, A.K.; Siddiqui, F.; Azam, I.; Kazmi, K. Underestimation of weight and its associated factors among overweight and obese adults in Pakistan: A cross sectional study. BMC Public Health 2011, 11, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, D.T.; Wolin, K.Y.; Scharoun-Lee, M.; Ding, E.L.; Warner, E.T.; Bennett, G.G. Does perception equal reality? Weight misperception in relation to weight-related attitudes and behaviors among overweight and obese US adults. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2011, 8, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kant, A. Weight-loss attempts and reporting of foods and nutrients, and biomarkers in a national cohort. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 2002, 26, 1194–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jebb, S.A.; Kopelman, P.; Butland, B. Executive Summary: Foresight ‘Tackling Obesities: Future Choices’ project. Obes. Rev. 2007, 8 (Suppl. S1), vi–ix. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margetts, B.M.; A Martinez, J.; Saba, A.; Holm, L.; Kearney, M.; Moles, A. Definitions of ‘healthy’ eating: A pan-EU survey of consumer attitudes to food, nutrition and health. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 1997, 51 (Suppl. S2), S23–S29. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, Y.; Wang, F.; Yuan, J.; Li, J.; Jiang, D.; Zhang, J.; Huang, T.; Zheng, J.; Mann, J.; Li, D. Effects of Macronutrient Distribution on Weight and Related Cardiometabolic Profile in Healthy Non-Obese Chinese: A 6-month, Randomized Controlled-Feeding Trial. Ebiomedicine 2017, 22, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Hattori, M.; Wada, S.; Iwase, H.; Kadono, M.; Tatsumi, H.; Kuwahata, M.; Fukui, M.; Hasegawa, G.; Nakamura, N.; et al. Assessment of Daily Food and Nutrient Intake in Japanese Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients Using Dietary Reference Intakes. Nutrients 2013, 5, 2276–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, S.; Bing, Z.; HuiJun, W.; ZhiHong, W.; JiGuo, Z.; WenWen, D. Analysis of the status of dietary fat intake among Chinese adults aged 18 to 64 years in fifteen provinces in 2015. Acta Nutr. Sin. 2019, 41, 118–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tognocchi, M.; Conte, M.; Testai, L.; Martucci, M.; Serra, A.; Salvioli, S.; Calderone, V.; Mele, M.; Conte, G. Supplementation of Enriched Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids and CLA Cheese on High Fat Diet: Effects on Lipid Metabolism and Fat Profile. Foods 2022, 11, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahnen, R.T.; Jonnalagadda, S.S.; Slavin, J.L. Role of plant protein in nutrition, wellness, and health. Nutr. Rev. 2019, 77, 735–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satija, A.; Malik, V.; Rimm, E.B.; Sacks, F.; Willett, W.; Hu, F.B. Changes in intake of plant-based diets and weight change: Results from 3 prospective cohort studies. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 110, 574–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, F.; Wang, Z.; Wang, L.; Wang, H.; Zhang, J.; Du, W.; Su, C.; Jia, X.; Ouyang, Y.; Wang, Y.; et al. Evaluating adherence to recommended diets in adults 1991–2015: Revised China dietary guidelines index. Nutr. J. 2019, 18, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Li, Y.; Yang, X.; Hemler, E.C.; Fang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Z.; Wang, Z.; He, L.; et al. The dietary transition and its association with cardiometabolic mortality among Chinese adults, 1982–2012: A cross-sectional population-based study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019, 7, 540–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.-N.; Zhai, F.-Y. Relative factors effecting dietary quality of Chinese adults. J. Hyg. Res. 2005, 34, 611–612. [Google Scholar]
| Variable | Overall n = 167,355 | Weight Control: Yes n = 11,906 | Weight Control: No n = 155,449 | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | <0.001 | |||
| Male | 79,531 (50.6) | 4731 (42.6) | 74,800 (51.2) | |
| Female | 87,824 (49.4) | 7175 (57.4) | 80,649 (48.8) | |
| Age group (years) | <0.001 | |||
| 18–39 | 43,488 (43.2) | 4118 (54.7) | 39,370 (42.2) | |
| 40–64 | 94,051 (45.7) | 6513 (40.0) | 87,538 (46.2) | |
| ≥65 | 29,816 (11.1) | 1275 (5.3) | 28,541 (11.6) | |
| Education level | <0.001 | |||
| Elementary school and below | 75,197 (37.2) | 2449 (15.3) | 72,748 (39.2) | |
| Secondary school | 79,730 (52.6) | 6934 (57.3) | 72,796 (52.1) | |
| College and above | 12,361 (10.2) | 2521 (27.4) | 9840 (8.7) | |
| Occupation | <0.001 | |||
| Employed | 114,622 (72.2) | 7420 (68.9) | 107,202 (72.5) | |
| Unemployed | 52,655 (27.8) | 4482 (31.1) | 48,173 (27.5) | |
| Annual income per capita | <0.001 | |||
| Low | 84,758 (55.4) | 3558 (33.4) | 81,200 (57.3) | |
| High | 67,883 (44.6) | 7363 (66.6) | 60,520 (42.7) | |
| Area | <0.001 | |||
| Urban | 68,954 (40.6) | 8314 (67.9) | 60,640 (38.2) | |
| Rural | 98,401 (59.4) | 3592 (32.1) | 94,809 (61.8) | |
| Body mass index (kg/m²) | <0.001 | |||
| <18.5 | 7373 (5.7) | 98 (1.2) | 7275 (6.1) | |
| 18.5–23.9 | 78,492 (52.6) | 2705 (28.4) | 75,787 (54.7) | |
| 24.0–27.9 | 50,047 (30.1) | 4774 (40.4) | 45,273 (29.2) | |
| ≥28.0 | 19,024 (11.6) | 3506 (30.0) | 15,518 (10.0) |
| Variable | Recommendations 1 | Weighted Mean (95%CI) | p 2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weight Control: Yes | Weight Control: No | |||
| Energy and nutrients 3 | ||||
| Energy intake, kcal/day | 1958.4 | 2115.8 | <0.001 | |
| (1947.3–1969.6) | (2112.2–2119.4) | |||
| Carbohydrate intake, g/day | 253.9 | 296.3 | <0.001 | |
| (252.1–255.7) | (295.6–296.9) | |||
| Protein intake, g/day | 63.3 | 64.0 | <0.001 | |
| (62.8–63.7) | (63.8–64.1) | |||
| Fat intake, g/day | 76.6 | 75.0 | 0.003 | |
| (75.9–77.3) | (74.8–75.2) | |||
| Total carbohydrates, E% | 50–65 | 51.9 | 55.6 | <0.001 |
| (51.7–52.1) | (55.6–55.7) | |||
| High-quality carbohydrates, E% | 5.7 | 4.6 | <0.001 | |
| (5.6–5.8) | (4.5–4.6) | |||
| Low-quality carbohydrates, E% | 47.5 | 52.0 | <0.001 | |
| (47.3–47.7) | (51.9–52.1) | |||
| Total protein, E% | 10–15 | 13.0 | 12.2 | <0.001 |
| (13.0–13.1) | (12.2–12.3) | |||
| Animal protein, E% | 5.4 | 4.4 | <0.001 | |
| (5.3–5.4) | (4.3–4.4) | |||
| Plant protein, E% | 7.0 | 7.5 | <0.001 | |
| (6.9–7.0) | (7.5–7.5) | |||
| Total fat, E% | 20–30 | 35.1 | 32.1 | <0.001 |
| (34.9–35.3) | (32.1–32.2) | |||
| Saturated fatty acids, E% | 9.1 | 8.6 | 0.009 | |
| (9.1–9.2) | (8.6–8.7) | |||
| Monounsaturated fatty acids, E% | 14.8 | 9.4 | 0.001 | |
| (14.6–14.9) | (9.4–9.4) | |||
| Polyunsaturated fatty acids, E% | 10.8 | 13.9 | 0.064 | |
| (10.7–10.9) | (13.9–14.0) | |||
| Food groups | ||||
| Cereals and tubers, g/day | 250–400 | 359.1 | 430.6 | <0.001 |
| (356.1–361.8) | (429.3–431.4) | |||
| Soybeans and nuts, g/day | 25–35 | 19.7 | 17.3 | <0.001 |
| (19.1–20.2) | (17.2–17.5) | |||
| Vegetables, g/day | 300–500 | 269.2 | 272.2 | 0.003 |
| (266.3–272.0) | (271.4–273.1) | |||
| Fruits, g/day | 200–350 | 78.8 | 44.3 | <0.001 |
| (76.6–81.0) | (43.8–44.8) | |||
| Livestock and poultry meats, g/day | 40–75 | 101.6 | 91.3 | 0.045 |
| (100.0–103.2) | (90.8–91.8) | |||
| Dairy products, g/day | >300 | 41.7 | 23.4 | <0.001 |
| (39.7–43.8) | (22.9–23.9) | |||
| Eggs, g/day | 40–50 | 30.8 | 23.9 | 0.009 |
| (30.2–31.4) | (23.8–24.1) | |||
| Aquatic products, g/day | 40–75 | 39.7 | 30.9 | <0.001 |
| (38.6–40.9) | (30.6–31.3) | |||
| Oil, g/day | 25–30 | 40.4 | 41.7 | <0.001 |
| (39.8–40.9) | (41.5–41.8) | |||
| Salt, g/day | <6 | 12.1 | 13.2 | <0.001 |
| (12.0–12.3) | (13.1–13.2) | |||
| CHDI Component | Score Range | Standard for Maximum Score | Standard for Minimum Score of Zero | Weighted Mean (95%CI) | p 1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weight Control: Yes | Weight Control: No | |||||
| Food variety | 0–10 | ≥12 kind | ≤5 kind | 6.73 (6.68–6.78) | 5.01 (5.00–5.03) | <0.001 |
| Refined grains | 0–5 | ≥100 g/1000 kcal | 0 | 4.84 (4.83–4.85) | 4.93 (4.92–4.93) | <0.001 |
| Whole grain, dry bean, and tuber | 0–5 | ≥40 g/1000 kcal | 0 | 2.08 (2.04–2.11) | 2.09 (2.08–2.10) | 0.392 |
| Total vegetables | 0–5 | ≥180 g/1000 kcal | 0 | 3.43 (3.41–3.45) | 3.29 (3.28–3.30) | <0.001 |
| Dark green and orange vegetables | 0–5 | ≥90 g/1000 kcal | 0 | 2.16 (2.13–2.19) | 1.94 (1.93–1.95) | <0.001 |
| Fruit | 0–10 | ≥110 g/1000 kcal | 0 | 3.04 (2.98–3.11) | 1.69 (1.67–1.70) | <0.001 |
| Dairy | 0–10 | ≥100 g/1000 kcal | 0 | 1.63 (1.57–1.68) | 0.85 (0.84–0.86) | <0.001 |
| Soybean | 0–10 | ≥10 g/1000 kcal | 0 | 3.72 (3.65–3.79) | 3.20 (3.18–3.22) | <0.001 |
| Meat and egg | 0–5 | ≥50 g/1000 kcal | 0 | 4.08 (4.05–4.10) | 3.56 (3.55–3.56) | <0.001 |
| Fish, shellfish, and mollusk | 0–5 | ≥30 g/1000 kcal | 0 | 1.88 (1.85–1.92) | 1.43 (1.42–1.44) | <0.001 |
| Calories from SFAs | 0–10 | <10% | ≥15% | 8.52 (8.47–8.56) | 8.58 (8.56–8.59) | <0.001 |
| Sodium | 0–10 | ≤1 g/1000 kcal | ≥4 g/1000 kcal | 4.98 (4.92–5.04) | 5.03 (5.01–5.05) | 0.020 |
| Empty calories | 0–10 | ≤20% | ≥40% | 7.94 (7.88–7.99) | 8.05 (8.04–8.07) | 0.407 |
| Total | 0–100 | 53.40 (53.20–53.60) | 48.79 (48.73–48.85) | <0.001 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, M.; Liu, Y.; Ye, P.; Cai, S.; Yao, Z.; Zhao, L.; Luo, J.; Yu, D. Weight-Control Behaviors and Dietary Intake in Chinese Adults: An Analysis of Three National Surveys (2002–2015). Nutrients 2023, 15, 1395. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15061395
Luo M, Liu Y, Ye P, Cai S, Yao Z, Zhao L, Luo J, Yu D. Weight-Control Behaviors and Dietary Intake in Chinese Adults: An Analysis of Three National Surveys (2002–2015). Nutrients. 2023; 15(6):1395. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15061395
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Miyang, Yixu Liu, Ping Ye, Shuya Cai, Zhenzhen Yao, Liyun Zhao, Jiayou Luo, and Dongmei Yu. 2023. "Weight-Control Behaviors and Dietary Intake in Chinese Adults: An Analysis of Three National Surveys (2002–2015)" Nutrients 15, no. 6: 1395. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15061395
APA StyleLuo, M., Liu, Y., Ye, P., Cai, S., Yao, Z., Zhao, L., Luo, J., & Yu, D. (2023). Weight-Control Behaviors and Dietary Intake in Chinese Adults: An Analysis of Three National Surveys (2002–2015). Nutrients, 15(6), 1395. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15061395





