Assessment of Protein Nutritional Quality of Novel Hairless Canary Seed in Comparison to Wheat and Oat Using In Vitro Static Digestion Models
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation and Determination of Protein Content of Canary Seed, Oat and Wheat Flours
2.3. Determination of Anti-Nutritional Components of Canary Seed, Oat, and Wheat Flours
2.3.1. Trypsin Inhibitor Activity (TIA)
2.3.2. Phytate Content
2.3.3. Total Polyphenol Content (TPC)
2.4. Determination of Amino Acid Content of Canary Seed Flours and In Vitro Digestates
2.5. Determination of Total In Vitro Protein Digestibility by the pH-Drop In Vitro Digestion Model
2.6. Determination of In Vitro Ileal Protein and Amino Acid Digestibility of Canary Seed, Oat, and Wheat Flours by the Harmonized INFOGEST Digestion Model
2.7. Determination of Protein Degree of Hydrolysis (DH)
2.8. Calculations of the In Vitro PDCAAS and DIAAS for Protein Quality Evaluation
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of Dehulled Canary Seed, Oat and Wheat Flours
3.2. Nutritional Quality of Canary Seed, Oat and Wheat Protein
3.2.1. Amino Acid Composition
3.2.2. In Vitro Protein and Amino Acid Digestibility
3.2.3. Calculation of PDCAAS and DIAAS Scores
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration (US-FDA). Agency Response Letter GRAS Notice No. GRN 000529. Available online: https://www.cfsanappsexternal.fda.gov/scripts/fdcc/index.cfm?set=GRASNotices&id=529 (accessed on 19 February 2023).
- Health Canada. Novel Food Information—Glabrous Canary Seed (Phalaris canariensis L.). Available online: http://www.hc-sc.gc.ca/fn-an/gmf-agm/appro/canary-seed-lang-graine-alpiste-decision-eng.php#share (accessed on 19 February 2023).
- Abdel-Aal, E.-S.M.; Hucl, P.J.; Sosulski, F.W. Structural and Compositional Characteristics of Canaryseed (Phalaris canariensis L.). J. Agric. Food Chem. 1997, 45, 3049–3055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Agriculture Organization/World Health Organization. Protein Quality Evaluation; Report of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Consultation; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Stein, H.H.; Sève, B.; Fuller, M.F.; Moughan, P.J.; de Lange, C.F. Invited review: Amino acid bioavailability and digestibility in pig feed ingredients: Terminology and application. J. Anim. Sci. 2007, 85, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sá, A.G.A.; Moreno, Y.M.F.; Carciofi, B.A.M. Food processing for the improvement of plant proteins digestibility. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 3367–3386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, G.J.; Ryan, D.J.; Mukherjea, R.; Schasteen, C.S. Protein Digestibility-Corrected Amino Acid Scores (PDCAAS) for Soy Protein Isolates and Concentrate: Criteria for Evaluation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 12707–12712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Food and Agriculture Organization. Dietary Protein Quality Evaluation in Human Nutrition: Report of an FAO Expert Consultation, 31 March–2 April, 2011, Auckland, New Zealand; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Rutherfurd, S.M.; Fanning, A.C.; Miller, B.J.; Moughan, P.J. Protein digestibility-corrected amino acid scores and digestible indispensable amino acid scores differentially describe protein quality in growing male rats. J. Nutr. 2015, 145, 372–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathai, J.K.; Liu, Y.; Stein, H.H. Values for digestible indispensable amino acid scores (DIAAS) for some dairy and plant proteins may better describe protein quality than values calculated using the concept for protein digestibility-corrected amino acid scores (PDCAAS). Br. J. Nutr. 2017, 117, 490–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deglaire, A.; Bos, C.; Tomé, D.; Moughan, P.J. Ileal digestibility of dietary protein in the growing pig and adult human. Br. J. Nutr. 2009, 102, 1752–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowan, A.M.; Moughan, P.J.; Wilson, M.N.; Maher, K.; Tasman-Jones, C. Comparison of the ileal and faecal digestibility of dietary amino acids in adult humans and evaluation of the pig as a model animal for digestion studies in man. Br. J. Nutr. 1994, 71, 29–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansilla, W.D.; Marinangeli, C.P.F.; Cargo-Froom, C.; Franczyk, A.; House, J.D.; Elango, R.; Columbus, D.A.; Kiarie, E.; Rogers, M.; Shoveller, A.K. Comparison of methodologies used to define the protein quality of human foods and support regulatory claims. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2020, 45, 917–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-García, E.; Carvajal-Lérida, I.; Pérez-Gálvez, A. In vitro bioaccessibility assessment as a prediction tool of nutritional efficiency. Nutr. Res. 2009, 29, 751–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubrecht, R.C.; Carter, E. The 3Rs and Humane Experimental Technique: Implementing Change. Animals 2019, 9, 754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinus, T.; Damour, M.; Van Riel, V.; Sopade, P.A. Particle size-starch–protein digestibility relationships in cowpea (Vigna unguiculata). J. Food Eng. 2012, 113, 254–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minekus, M.; Alminger, M.; Alvito, P.; Ballance, S.; Bohn, T.; Bourlieu, C.; Carriere, F.; Boutrou, R.; Corredig, M.; Dupont, D.; et al. A standardised static in vitro digestion method suitable for food—An international consensus. Food Funct. 2014, 5, 1113–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ariëns, R.M.C.; Bastiaan-Net, S.; van de Berg-Somhorst, D.B.P.M.; El Bachrioui, K.; Boudewijn, A.; van den Dool, R.T.M.; de Jong, G.A.H.; Wichers, H.J.; Mes, J.J. Comparing nutritional and digestibility aspects of sustainable proteins using the INFOGEST digestion protocol. J. Funct. Foods 2021, 87, 104748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, R.; Recio, I.; Heimo, D.; Dubois, S.; Moughan, P.J.; Hodgkinson, S.M.; Portmann, R.; Egger, L. In vitro digestibility of dietary proteins and in vitro DIAAS analytical workflow based on the INFOGEST static protocol and its validation with in vivo data. Food Chem. 2023, 404, 134720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hucl, P.; Matus-Cadiz, M.; Vandenberg, A.; Sosulski, F.W.; Abdel-Aal, E.S.M.; Hughes, G.R.; Slinkard, A.E. Cdc maria annual canarygrass. Can. J. Plant Sci. 2001, 81, 115–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC International; Latimer, G.W. Official Method 992.15. In Official Methods of Analysis of Aoac International, 19th ed.; AOAC International: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Makkar, H.P.S.; Siddhuraju, P.; Becker, K. Trypsin Inhibitor. In Plant Secondary Metabolites; Makkar, H.P.S., Siddhuraju, P., Becker, K., Eds.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2007; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKie, V.A.; McCleary, B.V. A Novel and Rapid Colorimetric Method for Measuring Total Phosphorus and Phytic Acid in Foods and Animal Feeds. J. AOAC Int. 2016, 99, 738–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singleton, V.L.; Rossi, J.A. Colorimetry of Total Phenolics with Phosphomolybdic-Phosphotungstic Acid Reagents. Am. J. Enol. Viticult. 1965, 16, 144–158. [Google Scholar]
- Long, W. Automated Amino Acid Analysis Using an Agilent Poroshell HPH-C18 Column; Agilent Technologies, Inc.: Santa Clara, CA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Yust, M.a.M.; Pedroche, J.; Girón-Calle, J.; Vioque, J.; Millán, F.; Alaiz, M. Determination of tryptophan by high-performance liquid chromatography of alkaline hydrolysates with spectrophotometric detection. Food Chem. 2004, 85, 317–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler-Nissen, J. Determination of the degree of hydrolysis of food protein hydrolysates by trinitrobenzenesulfonic acid. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1979, 27, 1256–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spellman, D.; McEvoy, E.; O’Cuinn, G.; FitzGerald, R.J. Proteinase and exopeptidase hydrolysis of whey protein: Comparison of the TNBS, OPA and pH stat methods for quantification of degree of hydrolysis. Int. Dairy J. 2003, 13, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havenaar, R.; Maathuis, A.; de Jong, A.; Mancinelli, D.; Berger, A.; Bellmann, S. Herring roe protein has a high digestible indispensable amino acid score (DIAAS) using a dynamic in vitro gastrointestinal model. Nutr. Res. 2016, 36, 798–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavazos, A.; Gonzalez de Mejia, E. Identification of Bioactive Peptides from Cereal Storage Proteins and Their Potential Role in Prevention of Chronic Diseases. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2013, 12, 364–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarwar Gilani, G.; Wu Xiao, C.; Cockell, K.A. Impact of Antinutritional Factors in Food Proteins on the Digestibility of Protein and the Bioavailability of Amino Acids and on Protein Quality. Br. J. Nutr. 2012, 108, S315–S332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Aal, E.-S.M.; Hucl, P.; Patterson, C.A.; Gray, D. Phytochemicals and heavy metals content of hairless canary seed: A variety developed for food use. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 44, 904–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greiner, R.; Konietzny, U. Phytase for Food Application. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2005, 44, 125–140. [Google Scholar]
- Hidvégi, M.; Lásztity, R. Phytic acid content of cereals and legumes and interaction with proteins. Period. Polytech. Chem. Eng. 2002, 46, 59–64. [Google Scholar]
- Lasztity, R. Phytic Acid in Cereal Technology. Adv. Cereal Sci. Technol. 1990, 10, 309–371. [Google Scholar]
- Reddy, N.R.; Sathe, S.K. Food Phytates; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Tian, J.-C.; Walker, C.E.; Wang, F.-C. Determination of phytic acid in cereals—A brief review. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2009, 44, 1671–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, K.B.; Rizvi, S.I. Plant polyphenols as dietary antioxidants in human health and disease. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2009, 2, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gemede, H.F.; Ratta, N. Antinutritional Factors in Plant Foods: Potential Health Benefits and Adverse Effects. Int. J. Nutr. Food Sci. 2014, 3, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfieri, M.; Redaelli, R. Oat phenolic content and total antioxidant capacity during grain development. J. Cereal Sci. 2015, 65, 39–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adom, K.K.; Liu, R.H. Antioxidant Activity of Grains. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 6182–6187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menga, V.; Fares, C.; Troccoli, A.; Cattivelli, L.; Baiano, A. Effects of genotype, location and baking on the phenolic content and some antioxidant properties of cereal species. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 45, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Qiu, Y.; Patterson, C.A.; Beta, T. The analysis of phenolic constituents in glabrous canaryseed groats. Food Chem. 2011, 127, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Yu, L.; Wang, X.; Gu, Z.; Beta, T. Changes of phenolic profiles and antioxidant activity in canaryseed (Phalaris canariensis L.) during germination. Food Chem. 2016, 194, 608–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canaryseed Development Comission of Saskatchewan. About Canaryseed. Available online: https://www.canaryseed.ca/about.html (accessed on 15 March 2016).
- Ejeta, G.; Hassen, M.M.; Mertz, E.T. In vitro Digestibility and Amino Acid Composition of Pearl Millet (Pennisetum typhoides) and Other Cereals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1987, 84, 6016–6019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biel, W.; Bobko, K.; Maciorowski, R. Chemical composition and nutritive value of husked and naked oats grain. J. Cereal Sci. 2009, 49, 413–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, Z.; Belli, L.; Toniolo, S.; Sancesario, G.; Bianconi, C.; Martorana, A. Amyloid β, glutamate, excitotoxicity in Alzheimer’s disease: Are we on the right track? CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2013, 19, 549–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Xiang, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, X.; Evers, J.; van der Werf, W.; Duan, L. Optimizing soaking and germination conditions to improve gamma-aminobutyric acid content in japonica and indica germinated brown rice. J. Funct. Foods. 2014, 10, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millward, D.J.; Tomé, D.; Schaafsma, G.; Layman, D.K. Protein quality assessment: Impact of expanding understanding of protein and amino acid needs for optimal health. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 87, 1576S–1581S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afify, A.E.-M.M.R.; El-Beltagi, H.S.; Abd El-Salam, S.M.; Omran, A.A. Protein Solubility, Digestibility and Fractionation after Germination of Sorghum Varieties. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e31154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, C.-H. Functional properties and in vitro digestibility of buckwheat protein products: Influence of processing. J. Food Eng. 2007, 82, 568–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aryee, A.; Boye, J. Improving the Digestibility of Lentil Flours and Protein Isolate and Characterization of Their Enzymatically Prepared Hydrolysates. Int. J. Food Prop. 2016, 19, 2649–2665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nosworthy, M.G.; Franczyk, A.; Zimoch-Korzycka, A.; Appah, P.; Utioh, A.; Neufeld, J.; House, J.D. Impact of Processing on the Protein Quality of Pinto Bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) and Buckwheat (Fagopyrum esculentum Moench) Flours and Blends, As Determined by in vitro and in Vivo Methodologies. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 3919–3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Çabuk, B.; Nosworthy, M.G.; Stone, A.K.; Korber, D.R.; Tanaka, T.; House, J.D.; Nickerson, M.T. Effect of Fermentation on the Protein Digestibility and Levels of Non-Nutritive Compounds of Pea Protein Concentrate. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2018, 56, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abelilla, J.J.; Liu, Y.; Stein, H.H. Digestible indispensable amino acid score (DIAAS) and protein digestibility corrected amino acid score (PDCAAS) in oat protein concentrate measured in 20- to 30-kilogram pigs. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 98, 410–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervantes-Pahm, S.K.; Liu, Y.; Stein, H.H. Digestible indispensable amino acid score and digestible amino acids in eight cereal grains. Br. J. Nutr. 2014, 111, 1663–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darragh, A.J.; Garrick, D.J.; Moughan, P.J.; Hendriks, W.H. Correction for amino acid loss during acid hydrolysis of a purified protein. Anal. Biochem. 1996, 236, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darragh, A.J.; Moughan, P.J. The effect of hydrolysis time on amino acid analysis. J. AOAC Int. 2005, 88, 888–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, F.; Han, F.; Wang, Y.; Fan, L.; Song, G.; Chen, X.; Jiang, P.; Miao, H.; Han, Y. Digestible indispensable amino acid scores of nine cooked cereal grains. Br. J. Nutr. 2019, 121, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Guo, S. Phytic acid and its interactions: Contributions to protein functionality, food processing, and safety. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2021, 20, 2081–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
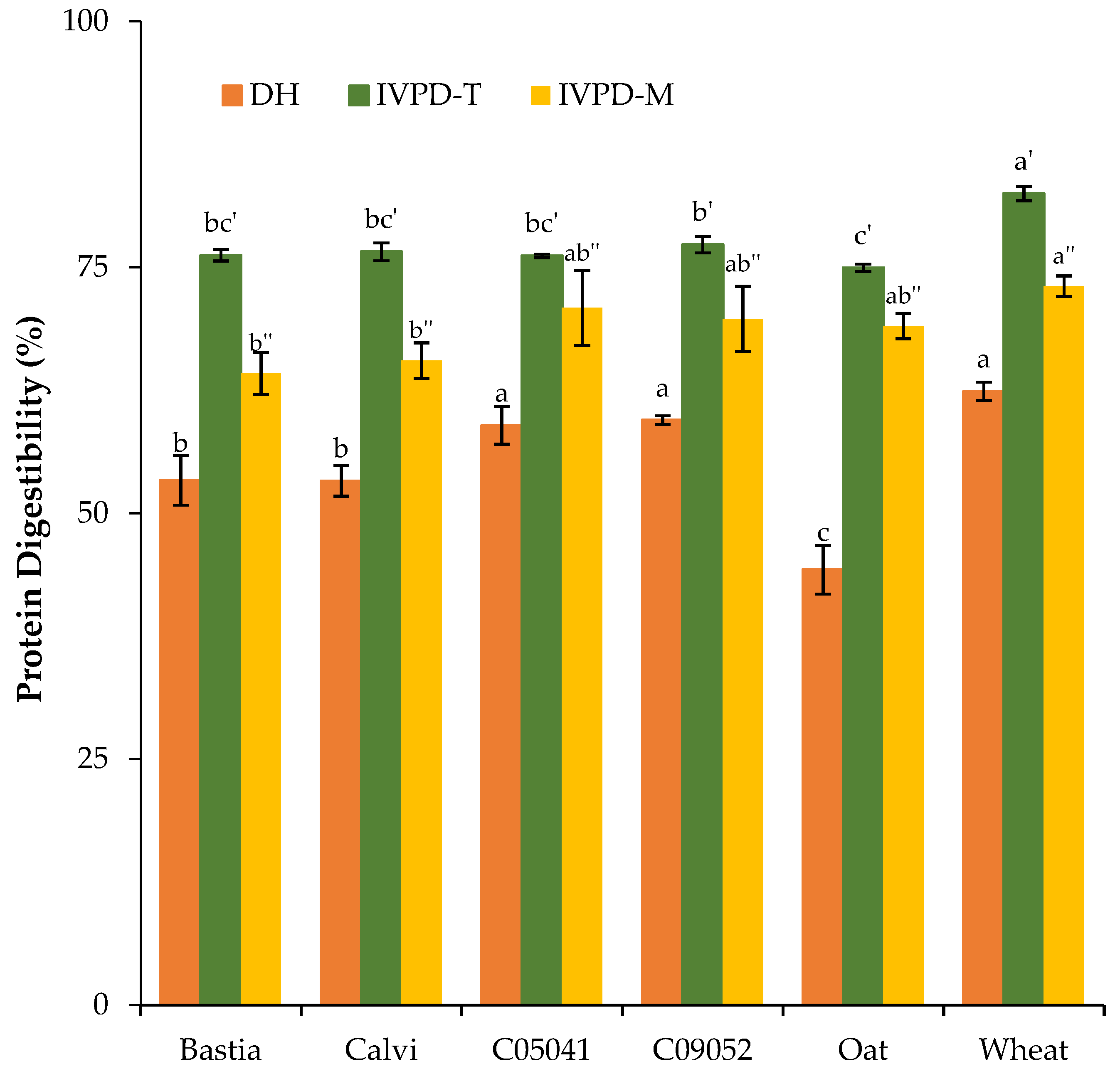

| Age Group | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Essential amino acid | Infant (0–6 months) | Child (6 months–3 years) | Older child/ adolescent/adult |
| Reference Pattern (mg/g protein) | |||
| His | 21 | 20 | 16 |
| Ile | 55 | 32 | 30 |
| Leu | 96 | 66 | 61 |
| Lys | 69 | 57 | 48 |
| SAA (Cys + Met) | 33 | 27 | 23 |
| AAA (Phe + Tyr) | 94 | 52 | 41 |
| Thr | 44 | 31 | 25 |
| Trp | 17 | 8.5 | 6.6 |
| Val | 55 | 43 | 40 |
| Cereal Variety | Brown Canary Seeds | Yellow Canary Seeds | Oat | Wheat | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bastia | Calvi | C05041 | C09052 | |||
| Protein (%) | 22.33 ± 0.26 a | 21.55 ± 0.10 a | 21.53 ± 0.25 a | 21.97 ± 0.56 a | 14.30 ± 0.12 c | 16.35 ± 0.07 b |
| TIA (mg/g) | 0.15 ± 0.001 ab | 0.16 ± 0.005 a | 0.12 ± 0.005 ab | 0.13 ± 0.003 ab | 0.14 ± 0.01 ab | 0.11 ± 0.035 b |
| Phytate (mg/g) | 12.36 ± 0.63 a | 12.12 ± 1.32 a | 11.96 ± 0.42 a | 12.17 ± 0.45 a | 5.94 ± 0.20 b | 3.14 ± 0.07 c |
| TPC (mg FAE/g) | 1.44 ± 0.03 b | 1.42 ± 0.01 b | 1.34 ± 0.06 b | 1.47 ± 0.01 b | 2.04 ± 0.15 a | 0.65 ± 0.05 c |
| Amino Acid | Cereal Variety | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brown Canary Seeds | Yellow Canary Seeds | Oat | Wheat | |||
| Bastia | Calvi | C05041 | C09052 | |||
| Asp | 4.47 ± 0.07 b | 4.47 ± 0.02 b | 4.52 ± 0.18 b | 4.39 ± 0.25 b | 9.04 ± 0.16 a | 4.09 ± 0.3 b |
| Glu | 26.56 ± 0.80 c | 28.63 ± 0.96 bc | 28.60 ± 0.2 bc | 28.84 ± 0.79 b | 22.18 ± 0.37 d | 35.04 ± 1.15 a |
| Ser | 3.28 ± 0.13 b | 4.45 ± 0.12 b | 3.25 ± 0.0 b | 3.40 ± 0.12 b | 5.01 ± 0.06 a | 4.64 ± 0.31 a |
| His * | 2.64 ± 0.24 a | 2.69 ± 0.22 a | 2.65 ± 0.23 a | 2.63 ± 0.23 a | 2.41 ± 0.03 a | 2.56 ± 0.12 a |
| Gly | 2.98 ± 0.19 b | 2.82 ± 0.23 bc | 2.71 ± 0.18 bc | 2.52 ± 0.03 c | 4.28 ± 3.27 a | 2.73 ± 0.17 bc |
| Thr * | 2.95 ± 0.15 ab | 2.88 ± 0.18 ab | 2.99 ± 0.04 ab | 2.55 ± 0.27 bc | 3.27 ± 0.04 a | 2.33 ± 0.24 c |
| Arg | 6.02 ± 0.13 a | 6.13 ± 0.17 a | 5.78 ± 0.09 a | 5.66 ± 0.31 a | 6.17 ± 0.10 a | 3.81 ± 0.41 b |
| Ala | 4.10 ± 0.13 a | 4.28 ± 0.21 a | 4.07 ± 0.07 a | 4.09 ± 0.10 a | 4.45 ± 0.04 a | 2.88 ± 0.34 b |
| Tyr | 2.37 ± 0.11 b | 2.48 ± 0.18 b | 2.18 ± 0.17 b | 2.12 ± 0.19 b | 3.41 ± 0.06 a | 3.14 ± 0.17 a |
| Cys | 1.36± 0.29 abc | 1.59 ± 0.20 a | 1.15 ± 0.03 bc | 1.04 ± 0.11 c | 1.51 ± 0.04 ab | 0.56 ± 0.00 d |
| Val * | 5.19 ± 0.20 b | 5.15 ± 0.02 b | 5.91 ± 0.18 a | 5.93 ± 0.06 a | 3.43 ± 0.07 d | 4.08 ± 0.26 c |
| Met * | 0.97 ± 0.12 a | 1.04 ± 0.10 a | 1.06 ± 0.04 a | 0.95 ± 0.06 a | 0.89 ± 0.22 a | 0.97 ± 0.02 a |
| Trp * | 2.46 ± 0.07 bc | 2.56 ± 0.04 ab | 2.44 ± 0.01 c | 2.60 ± 0.02 a | 1.50 ± 0.05 d | 1.11 ± 0.04 e |
| Phe * | 6.19 ± 0.17 a | 6.23 ± 0.17 a | 6.02 ± 0.12 a | 5.68 ± 0.04 ab | 5.11 ± 0.08 b | 5.27 ± 0.24 b |
| Ile * | 4.83 ± 0.30 a | 4.85 ± 0.17 a | 4.31 ± 0.13 ab | 4.16 ± 0.28 b | 2.49 ± 0.01 c | 3.80 ± 0.20 b |
| Leu * | 7.69 ± 0.22 ab | 7.86 ± 0.37 a | 7.37 ± 0.08 ab | 7.43 ± 0.21 ab | 6.66 ± 0.09 c | 7.02 ± 0.37 bc |
| Lys * | 2.48 ± 0.12 b | 2.41 ± 0.06 b | 2.43 ± 0.19 b | 2.27 ± 0.04 b | 4.34 ± 0.24 a | 2.19 ± 0.11 b |
| Total AA | 86.54 ± 0.85 a | 89.53 ± 2.65 a | 87.44 ± 0.84 a | 86.27 ± 1.91 a | 86.15 ± 0.60 a | 86.24 ± 2.18 a |
| Total EAA | 35.40 ± 0.99 a | 35.67 ± 1.13 a | 35.18 ± 0.32 a | 34.22 ± 1.35 a | 30.10 ± 0.15 b | 29.34 ± 0.71 b |
| Canary Seeds | Oat | Wheat | p-Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bastia | Calvi | C05041 | C09052 | ||||
| Infant (0–6 months) | |||||||
| AA score | 0.36 b | 0.35 b | 0.35 b | 0.33 b | 0.63 a | 0.32 b | <0.0001 |
| Limiting AA | Lysine | Lysine | Lysine | Lysine | Lysine | Lysine | |
| PDCAAS-T | 27.3 b | 26.8 b | 26.8 b | 25.4 b | 47.2 a | 26.2 b | <0.0001 |
| PDCAAS-M | 23.0 b | 22.9 b | 25.0 b | 22.9 b | 43.5 a | 23.2 b | <0.0001 |
| Child (6 months–3 years) | |||||||
| AA score | 0.43 b | 0.42 b | 0.43 b | 0.40 b | 0.76 a | 0.39 b | <0.0001 |
| Limiting AA | Lysine | Lysine | Lysine | Lysine | Lysine | Lysine | |
| PDCAAS-T | 33.1 b | 32.4 b | 32.5 b | 30.8 b | 57.1 a | 31.8 b | <0.0001 |
| PDCAAS-M | 27.9 b | 27.7 b | 30.2 b | 27.8 b | 52.6 a | 28.1 b | <0.0001 |
| Older children, adolescents, adults | |||||||
| AA score | 0.52 b | 0.50 b | 0.51 b | 0.47 b | 0.91 a | 0.46 b | <0.0001 |
| Limiting AA | Lysine | Lysine | Lysine | Lysine | Lysine | Lysine | |
| PDCAAS-T | 39.3 b | 38.5 b | 38.6 b | 36.6 b | 67.8 a | 37.7 b | <0.0001 |
| PDCAAS-M | 33.1 b | 32.9 b | 35.9 b | 33.0 b | 62.5 b | 33.4 b | <0.0001 |
| Minimum IV-TID (%) = Free AAs in Digestate Supernatant | |||||||
| Amino Acid | Cereal Variety | ||||||
| Bastia | Calvi | C05041 | C09052 | Oat | Wheat | p-value | |
| Ala | 27.15 b | 28.78 b | 40.20 a | 32.45 ab | 29.70 b | 28.53 b | 0.0004 |
| Arg | 71.59 c | 85.22 b | 90.79 b | 85.00 b | 105.20 a | 116.00 a | 0.0000 |
| Asp | 0.90 b | 0.83 b | 1.19 b | 0.40 b | 6.29 a | 7.19 a | 0.0000 |
| Cys | 2.96 c | 2.61 c | 7.74 c | 7.97 c | 19.64 b | 51.13 a | 0.0000 |
| Glu | 0.04 b | 0.15 b | 0.52 b | 0.17 b | 3.70 b | 0.92 ab | 0.0000 |
| Gly | 5.24 b | 5.97 b | 9.39 ab | 9.08 ab | 5.66 b | 11.84 a | 0.0014 |
| His | 5.95 b | 5.14 b | 5.53 b | 5.57 b | 27.81 a | 19.04 a | 0.0004 |
| Ile | 38.78 c | 38.19 c | 44.55 b | 39.36 bc | 61.43 a | 38.14 c | 0.0000 |
| Leu | 55.75 b | 59.10 ab | 62.40 a | 57.26 b | 49.43 c | 36.83 d | 0.0000 |
| Lys | 23.21 b | 18.06 bc | 12.75 c | 17.35 bc | 32.28 a | 36.55 ab | 0.0002 |
| Met | 87.08 bc | 105.08 a | 73.31 cd | 90.24 b | 93.26 ab | 59.58 d | 0.0000 |
| Phe | 59.23 ab | 58.69 b | 66.36 a | 60.43 ab | 57.51 b | 35.05 c | 0.0000 |
| Ser | 9.11 b | 10.28 b | 16.05 a | 13.38 ab | 12.66 ab | 12.17 ab | 0.0038 |
| Thr | 17.99 de | 17.65 e | 27.51 bc | 22.75 cd | 45.22 ab | 41.55 a | 0.0000 |
| Tyr | 75.98 c | 70.04 c | 104.09 ab | 106.57 a | 93.31 b | 44.00 d | 0.0000 |
| Val | 37.19 b | 34.87 bc | 28.93 de | 27.22 e | 50.91 a | 31.36 cd | 0.0000 |
| SAA (Cys + Met) | 53.39 a | 57.36 a | 52.83 a | 57.63 a | 47.03 a | 56.49 a | 0.0560 |
| AAA (Phe + Tyr) | 63.86 b | 61.87 b | 76.93 a | 72.76 a | 71.83 a | 38.39 c | 0.0000 |
| ∑ Free AAs digestibility | 25.93 c | 26.45 bc | 29.78 ab | 27.96 bc | 32.42 a | 21.63 d | 0.0000 |
| Maximum IV-TID (%) = Total AAs in digestate supernatant | |||||||
| Amino Acid | Cereal Variety | ||||||
| Bastia | Calvi | C05041 | C09052 | Oat | Wheat | ||
| Ala | 73.28 d | 73.26 d | 88.93 b | 82.83 bc | 76.35 cd | 100.60 a | 0.0000 |
| Arg | 90.02 ab | 98.20 a | 100.94 a | 100.44 a | 66.27 c | 84.78 b | 0.0000 |
| Asp | 40.79 c | 48.00 bc | 49.13 bc | 44.50 bc | 58.77 b | 88.56 a | 0.0000 |
| Cys | 210.41 bc | 198.19 c | 249.11 b | 218.71 bc | 137.03 d | 298.13 a | 0.0000 |
| Glu | 61.14 b | 62.57 b | 65.42 ab | 67.17 ab | 66.19 ab | 68.80 a | 0.0113 |
| Gly | 96.13 bc | 108.31 ab | 131.97 ab | 146.12 a | 27.12 d | 56.41 cd | 0.0000 |
| His | 22.34 c | 19.88 c | 30.08 b | 25.69 bc | 90.57 a | 77.38 a | 0.0000 |
| Ile | 47.59 d | 47.70 d | 57.68 c | 52.17 d | 114.46 a | 72.41 b | 0.0000 |
| Leu | 88.50 b | 101.46 a | 102.65 a | 96.67 ab | 63.22 c | 60.14 c | 0.0000 |
| Lys | 23.99 b | 20.80 b | 23.21 b | 20.34 b | 53.60 a | 47.13 a | 0.0000 |
| Met | 87.64 b | 81.17 b | 90.97 b | 84.57 b | 149.89 a | 135.50 a | 0.0000 |
| Phe | 65.14 cd | 62.98 d | 76.59 b | 70.51 bc | 85.30 a | 77.29 b | 0.0000 |
| Ser | 102.24 ab | 92.08 b | 103.70 a | 111.32 a | 61.13 c | 65.78 c | 0.0000 |
| Thr | 16.60 c | 17.64 c | 21.70 c | 20.08 c | 77.01 b | 98.40 a | 0.0000 |
| Tyr | 24.08 d | 25.37 cd | 43.29 ab | 35.69 bc | 42.35 ab | 39.49 a | 0.0001 |
| Val | 50.42 c | 48.93 c | 40.20 d | 39.77 d | 100.09 a | 77.96 b | 0.0000 |
| SAA (Cys + Met) | 136.80 b | 135.67 b | 140.36 b | 137.74 b | 141.81 b | 195.11 a | 0.0000 |
| AAA (Phe + Tyr) | 53.80 bc | 52.45 b | 67.26 a | 61.21 ab | 53.24 c | 50.00 c | 0.0000 |
| ∑ Free AAs digestibility | 64.19 a | 65.54 a | 70.87 a | 69.75 a | 67.53 a | 71.78 a | 0.0343 |
| Indispensable Amino Acids (IAA) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cereal variety | His | Thr | Val | Ile | Leu | Lys | SAA | AAA | DIAAS, % |
| Infant DIAA reference ratio (0–6 months) | |||||||||
| Bastia | 0.08 b | 0.11 b | 0.34 ab | 0.33 a | 0.49 a | 0.08 b | 0.29 ab | 0.66 b | 8 (Lys) b |
| Calvi | 0.08 b | 0.12 b | 0.37 a | 0.36 a | 0.50 a | 0.08 bc | 0.35 a | 0.71 ab | 8 (Lys) bc |
| C05041 | 0.06 b | 0.13 b | 0.37 a | 0.35 a | 0.50 a | 0.05 c | 0.31 ab | 0.73 ab | 5 (Lys) c |
| C09052 | 0.07 b | 0.12 b | 0.35 ab | 0.33 a | 0.49 a | 0.07 bc | 0.32 ab | 0.72 a | 7 (Lys) bc |
| Oat | 0.32 a | 0.34 a | 0.32 b | 0.28 b | 0.34 b | 0.20 a | 0.34 a | 0.64 b | 20 (Lys) a |
| Wheat | 0.23 a | 0.22 a | 0.23 c | 0.26 b | 0.27 c | 0.12 b | 0.26 b | 0.34 c | 12 (Lys) b |
| p-value | 0.0006 | 0.0001 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.0001 | 0.0077 | 0 | 0.0001 |
| Child DIAA reference ratio (6 months–3 years) | |||||||||
| Bastia | 0.09 b | 0.15 b | 0.43 ab | 0.57 a | 0.71 a | 0.09 b | 0.35 ab | 1.20 a | 9 (Lys) b |
| Calvi | 0.09 b | 0.17 b | 0.48 a | 0.62 a | 0.73 a | 0.09 bc | 0.42 a | 1.29 a | 9 (Lys) bc |
| C05041 | 0.07 b | 0.18 b | 0.47 a | 0.60 a | 0.73 a | 0.06 c | 0.38 ab | 1.33 a | 6 (Lys) c |
| C09052 | 0.08 b | 0.17 b | 0.44 ab | 0.56 a | 0.71 a | 0.08 bc | 0.40 ab | 1.31 a | 8 (Lys) bc |
| Oat | 0.33 a | 0.48 a | 0.41 b | 0.48 b | 0.50 b | 0.25 a | 0.41 a | 1.16 a | 25 (Lys) a |
| Wheat | 0.24 a | 0.31 a | 0.30 c | 0.45 b | 0.39 c | 0.14 b | 0.32 b | 0.62 b | 14 (Lys) b |
| p-value | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.0077 | 0 | 0 |
| Older child, adolescent, adult DIAA reference ratio | |||||||||
| Bastia | 0.11 b | 0.19 b | 0.47 ab | 0.61 a | 0.77 a | 0.11 b | 0.41 ab | 1.52 a | 11 (Lys) b |
| Calvi | 0.09 b | 0.23 b | 0.51 a | 0.64 a | 0.79 a | 0.08 bc | 0.45 a | 1.68 a | 11 (Lys) bc |
| C05041 | 0.11 b | 0.21 b | 0.51 a | 0.67 a | 0.79 a | 0.11 c | 0.50 ab | 1.63 a | 8 (Lys) c |
| C09052 | 0.10 b | 0.21 b | 0.48 ab | 0.60 a | 0.77 a | 0.10 bc | 0.46 ab | 1.66 a | 10 (Lys) bc |
| Oat | 0.42 a | 0.59 a | 0.44 b | 0.51 b | 0.54 b | 0.29 a | 0.48 a | 1.48 a | 29 (Lys) a |
| Wheat | 0.30 a | 0.39 a | 0.32 c | 0.48 b | 0.42 c | 0.17 b | 0.37 b | 0.79 b | 17 (Lys) b |
| p-value | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.0077 | 0 | 0 |
| Indispensable Amino Acids (IAA) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cereal variety | His | Thr | Val | Ile | Leu | Lys | SAA | AAA | DIAAS, % |
| Infant DIAA reference ratio (0–6 months) | |||||||||
| Bastia | 0.31 b | 0.10 b | 0.46 c | 0.41 b | 0.77 b | 0.08 c | 0.73 c | 0.56 ab | 8 (Lys ) c |
| Calvi | 0.32 b | 0.12 b | 0.52 bc | 0.45 b | 0.86 a | 0.09 bc | 0.82 bc | 0.60 ab | 9 (Lys) bc |
| C05041 | 0.35 b | 0.10 b | 0.51 bc | 0.45 b | 0.83 ab | 0.10 bc | 0.83 bc | 0.64 a | 10 (Lys) bc |
| C09052 | 0.34 b | 0.10 b | 0.50 bc | 0.43 b | 0.82 ab | 0.08 c | 0.77 bc | 0.61 a | 8 (Lys) c |
| Oat | 1.04 a | 0.57 a | 0.63 a | 0.52 a | 0.44 c | 0.34 a | 1.03 a | 0.48 bc | 34 (Lys) a |
| Wheat | 0.94 a | 0.52 a | 0.58 ab | 0.50 a | 0.44 c | 0.15 b | 0.90 ab | 0.45 c | 15 (Lys) b |
| p-value | 0 | 0 | 0.0004 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.0004 | 0 | 0 |
| Child DIAA reference ratio (6 months–3 years) | |||||||||
| Bastia | 0.31 b | 0.14 b | 0.57 c | 0.68 c | 1.10 b | 0.09 c | 0.86 c | 0.93 abc | 9 (Lys) c |
| Calvi | 0.33 b | 0.17 b | 0.67 bc | 0.78 b | 1.25 a | 0.11 bc | 1.00 bc | 1.09 ab | 11 (Lys) bc |
| C05041 | 0.37 b | 0.14 b | 0.66 bc | 0.77 b | 1.20 ab | 0.12 bc | 1.02 bc | 1.16 a | 12 (Lys) bc |
| C09052 | 0.36 b | 0.15 b | 0.65 bc | 0.74 bc | 1.20 ab | 0.10 c | 0.94 bc | 1.10 b | 10 (Lys) c |
| Oat | 1.09 a | 0.81 a | 0.80 a | 0.89 a | 0.64 c | 0.41 a | 1.26 a | 0.87 bc | 41 (Lys) a |
| Wheat | 0.99 a | 0.74 a | 0.74 ab | 0.86 a | 0.64 c | 0.18 b | 1.10 ab | 0.81 c | 18 (Lys) b |
| p-value | 0 | 0 | 0.0001 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.0001 | 0 | 0 |
| Older child, adolescent, adult DIAA reference ratio | |||||||||
| Bastia | 0.39 b | 0.17 b | 0.61 c | 0.72 c | 1.19 b | 0.11 c | 1.01 c | 1.18 abc | 11 (Lys) c |
| Calvi | 0.42 b | 0.21 b | 0.72 bc | 0.83 b | 1.36 a | 0.13 bc | 1.17 bc | 1.39 ab | 13 (Lys) bc |
| C05041 | 0.46 b | 0.18 b | 0.70 bc | 0.83 b | 1.30 ab | 0.14 bc | 1.20 bc | 1.47 a | 14 (Lys) bc |
| C09052 | 0.45 b | 0.18 b | 0.69 bc | 0.79 bc | 1.30 ab | 0.12 c | 1.11 bc | 1.39 a | 12 (Lys) c |
| Oat | 1.36 a | 1.01 a | 0.86 a | 0.95 a | 0.69 c | 0.49 a | 1.48 a | 1.11 bc | 49 (Lys) a |
| Wheat | 1.24 a | 0.92 a | 0.80 ab | 0.92 a | 0.69 c | 0.22 b | 1.29 ab | 1.03 c | 22 (Lys) b |
| p-value | 0 | 0 | 0.0001 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.0001 | 0 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
L’Hocine, L.; Achouri, A.; Mason, E.; Pitre, M.; Martineau-Côté, D.; Sirois, S.; Karboune, S. Assessment of Protein Nutritional Quality of Novel Hairless Canary Seed in Comparison to Wheat and Oat Using In Vitro Static Digestion Models. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1347. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15061347
L’Hocine L, Achouri A, Mason E, Pitre M, Martineau-Côté D, Sirois S, Karboune S. Assessment of Protein Nutritional Quality of Novel Hairless Canary Seed in Comparison to Wheat and Oat Using In Vitro Static Digestion Models. Nutrients. 2023; 15(6):1347. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15061347
Chicago/Turabian StyleL’Hocine, Lamia, Allaoua Achouri, Emily Mason, Mélanie Pitre, Delphine Martineau-Côté, Stéphane Sirois, and Salwa Karboune. 2023. "Assessment of Protein Nutritional Quality of Novel Hairless Canary Seed in Comparison to Wheat and Oat Using In Vitro Static Digestion Models" Nutrients 15, no. 6: 1347. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15061347
APA StyleL’Hocine, L., Achouri, A., Mason, E., Pitre, M., Martineau-Côté, D., Sirois, S., & Karboune, S. (2023). Assessment of Protein Nutritional Quality of Novel Hairless Canary Seed in Comparison to Wheat and Oat Using In Vitro Static Digestion Models. Nutrients, 15(6), 1347. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15061347






