Association between Systemic Immunity-Inflammation Index and Hyperlipidemia: A Population-Based Study from the NHANES (2015–2020)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
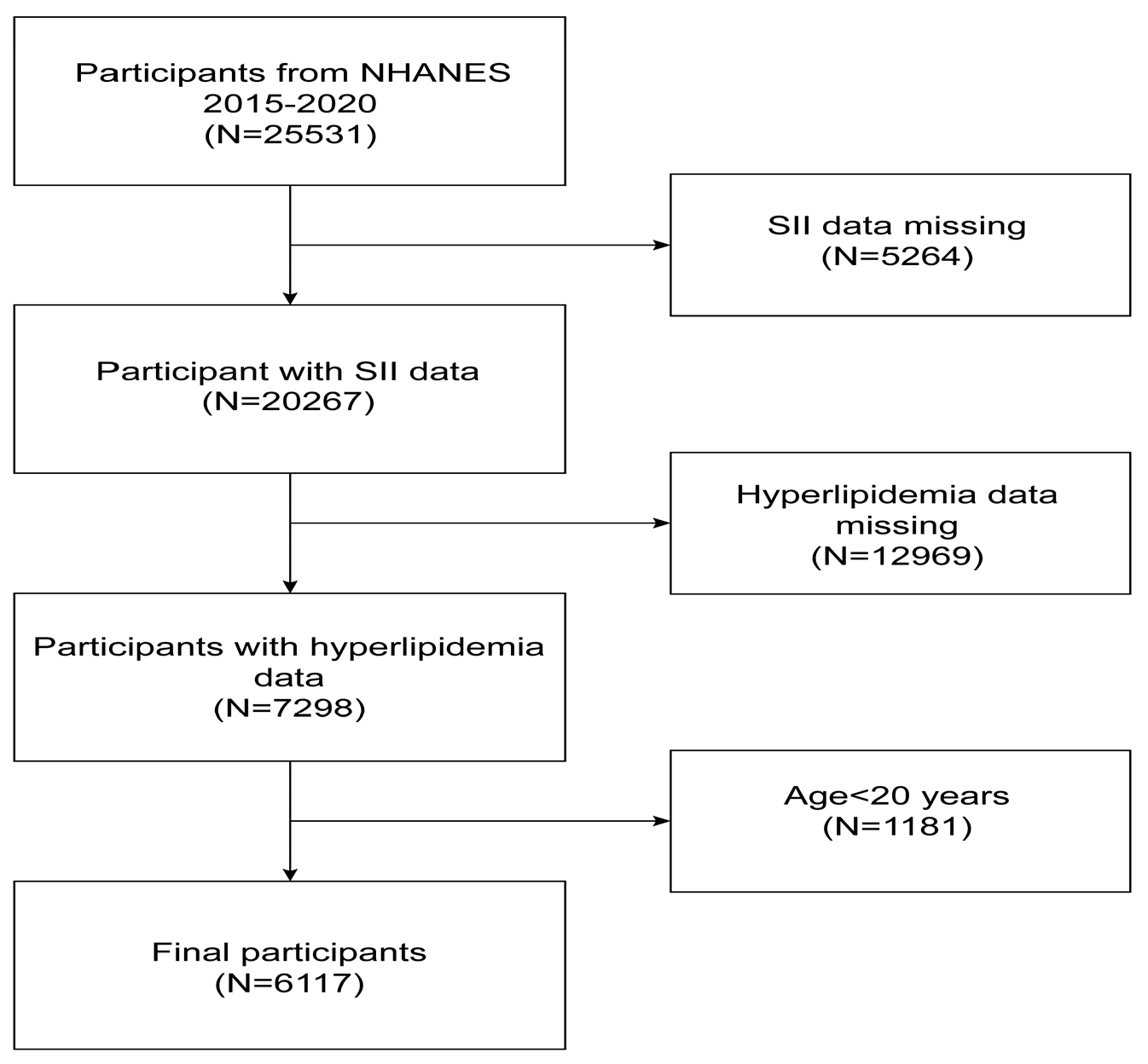
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Assessment of Hyperlipidemia
2.3. SII and Covariates
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics of Participants
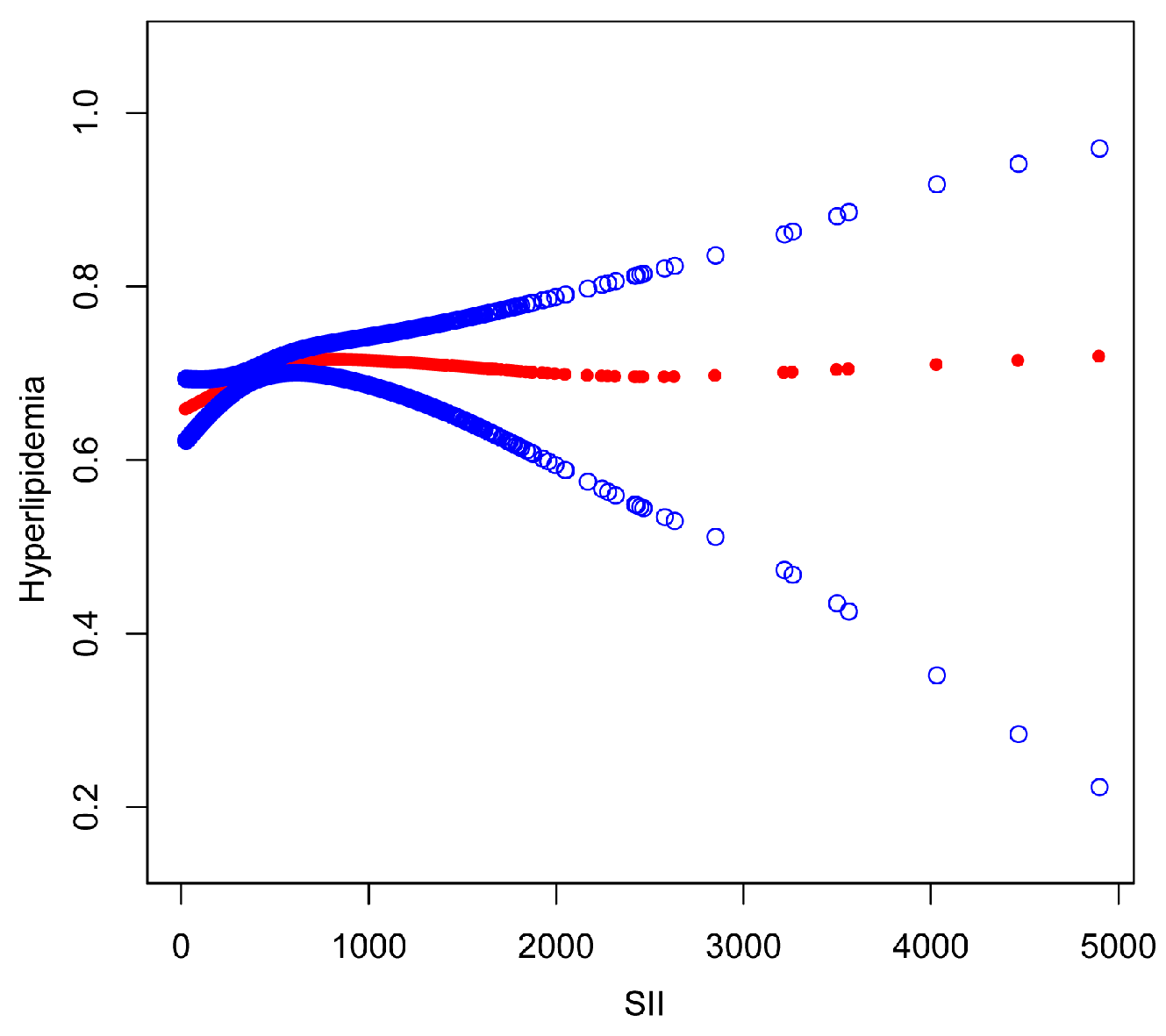
3.2. Association between SII and Hyperlipidemia
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Su, X.; Peng, H.; Chen, X.; Wu, X.; Wang, B. Hyperlipidemia and hypothyroidism. Clin. Chim. Acta 2022, 527, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.-Q.; Zhao, S.-P.; Zhao, Y.-H. Efficacy and tolerability of coenzyme A vs pantethine for the treatment of patients with hyperlipidemia: A randomized, double-blind, multicenter study. J. Clin. Lipidol. 2015, 9, 692–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yusuf, S.; Hawken, S.; Ôunpuu, S.; Dans, T.; Avezum, A.; Lanas, F.; McQueen, M.; Budaj, A.; Pais, P.; Varigos, J.; et al. Effect of potentially modifiable risk factors associated with myocardial infarction in 52 countries (the INTERHEART study): Case-control study. Lancet 2004, 364, 937–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsao, C.W.; Aday, A.W.; Almarzooq, Z.I.; Alonso, A.; Beaton, A.Z.; Bittencourt, M.S.; Boehme, A.K.; Buxton, A.E.; Carson, A.P.; Commodore-Mensah, Y.; et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics—2022 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2022, 145, e153–e639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozaffarian, D.; Benjamin, E.J.; Go, A.S.; Arnett, D.K.; Blaha, M.J.; Cushman, M.; de Ferranti, S.; Després, J.-P.; Fullerton, H.J.; Howard, V.J.; et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics—2015 update: A report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2015, 131, e29–e322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sylman, J.L.; Mitrugno, A.; Atallah, M.; Tormoen, G.W.; Shatzel, J.J.; Yunga, S.T.; Wagner, T.; Leppert, J.T.; Mallick, P.; Mccarty, O.J.T. The Predictive Value of Inflammation-Related Peripheral Blood Measurements in Cancer Staging and Prognosis. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Yang, X.-R.; Xu, Y.; Sun, Y.-F.; Sun, C.; Guo, W.; Zhang, X.; Wang, W.-M.; Qiu, S.-J.; Zhou, J.; et al. Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index Predicts Prognosis of Patients after Curative Resection for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 6212–6222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Y.-S.; Tan, J.; Zhou, X.-L.; Song, Y.-Q.; Song, Y.-J. Systemic immune-inflammation index predicting chemoradiation resistance and poor outcome in patients with stage III non-small cell lung cancer. J. Transl. Med. 2017, 15, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Niu, M.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; Shi, L.; Cao, J.; Mi, W.; Ma, Y.; Liu, J. Systemic-Immune-Inflammation Index as a Promising Biomarker for Predicting Perioperative Ischemic Stroke in Older Patients Who Underwent Non-cardiac Surgery. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2022, 14, 865244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhou, D.; Dai, Z.; Li, X. Association Between Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index and Diabetic Depression. Clin. Interv. Aging 2021, 16, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diakos, C.I.; Charles, K.A.; McMillan, D.C.; Clarke, S.J. Cancer-related inflammation and treatment effectiveness. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, e493–e503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crusz, S.M.; Balkwill, F.R. Inflammation and cancer: Advances and new agents. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 12, 584–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Liu, Q.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, X.; Wu, Y.; Liu, L. Prognostic Value of Preoperative Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index in Patients with Cervical Cancer. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, Y.; Shao, Y.; Zhu, D.; Zheng, X.; Zhou, Q.; Zhou, W.; Ni, X.; Wu, C.; Jiang, J. Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index Predicts Prognosis of Patients with Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Propensity Score-matched Analysis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 39482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Zheng, J.; Cai, J.; Zeng, K.; Yao, J.; Chen, L.; Li, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, H.; et al. Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index (SII) is Useful to Predict Survival Outcomes in Patients After Liver Transplantation for Hepatocellular Carcinoma within Hangzhou Criteria. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 47, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.-L.; Wu, C.-H.; Hsu, P.-F.; Chen, S.-C.; Huang, S.-S.; Chan, W.L.; Lin, S.-J.; Chou, C.-Y.; Chen, J.-W.; Pan, J.-P.; et al. Systemic immune-inflammation index (SII) predicted clinical outcome in patients with coronary artery disease. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 50, e13230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Xie, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, D.; Cao, L.; Zhou, M.; Wang, X.; Wang, B.; Chen, W. Urinary copper, systemic inflammation, and blood lipid profiles: Wuhan-Zhuhai cohort study. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 267, 115647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mena-Vázquez, N.; Redondo-Rodríguez, R.; Rioja, J.; Jimenez-Nuñez, F.G.; Manrique-Arija, S.; Lisbona-Montañez, J.M.; Cano-García, L.; Rojas-Gimenez, M.; Ureña, I.; Valdivielso, P.; et al. Postprandial Hyperlipidemia: Association with Inflammation and Subclinical Atherosclerosis in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasher, M.; Cherny, S.S.; Livshits, G. Exploring potential shared genetic influences between rheumatoid arthritis and blood lipid levels. Atherosclerosis 2022, 363, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feingold, K.R.; Anawalt, B.; Blackman, M.R.; Boyce, A.; Chrousos, G.; Corpas, E.; de Herder, W.W.; Dhatariya, K.; Hofland, J.; Dungan, K.; et al. (Eds.) Endotext; MDText.com, Inc.: South Dartmouth, MA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Grundy, S.M. Third Report of the National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults (Adult Treatment Panel III) final report. Circulation 2002, 106, 3143–3421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albany, C. Systemic immune-inflammation index in germ-cell tumours: Search for a biological prognostic biomarker. Br. J. Cancer 2018, 118, 761–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, R.; Xiao, M.; Li, L.; Ma, N.; Liu, M.; Huang, X.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, Y. Association between SII and hepatic steatosis and liver fibrosis: A population-based study. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 925690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, W.; Zhang, W.; Cheng, R.; Tan, A.; Shen, S.; Xiong, Y.; Zhao, L.; Lei, X. Association between blood lead levels and hyperlipidemiais: Results from the NHANES (1999–2018). Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 981749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, H.H.; Niemann, D.; Munson-McGee, S.H. Association of albumin to creatinine ratio with urinary arsenic and metal exposure: Evidence from NHANES 2015–2016. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2021, 54, 1343–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, J.A. Dietary Guidelines for Americans, 2020–2025. Work. Health Saf. 2021, 69, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidell, J.C.; Deurenberg, P.; Hautvast, J.A. Obesity and Fat Distribution in Relation to Health—Current Insights and Recommendations. World Rev. Nutr. Diet. 1987, 50, 57–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Kong, X.; Chen, M.; Shi, S.; Cheang, I.; Zhu, Q.; Lu, X.; Yue, X.; Tang, Y.; Liao, S.; et al. Blood ethylene oxide, systemic inflammation, and serum lipid profiles: Results from NHANES 2013–2016. Chemosphere 2022, 299, 134336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Guo, X.; Zhou, Y.; Li, Z.; Yu, S.; Sun, Y.; Hua, Y. Monocyte-to-high-density lipoprotein ratio and systemic inflammation response index are associated with the risk of metabolic disorders and cardiovascular diseases in general rural population. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 944991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Wang, T.; Li, G.; Feng, J.; Deng, L.; Xu, H.; Yin, L.; Ma, J.; Chen, D.; Chen, J. Investigation of systemic immune-inflammation index, neutrophil/high-density lipoprotein ratio, lymphocyte/high-density lipoprotein ratio, and monocyte/high-density lipoprotein ratio as indicators of inflammation in patients with schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Front. Psychiatry 2022, 13, 941728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, N.; Lin, Y.; Ye, Z.; Yang, C.; Huang, Y.; Duan, Q.; Xie, S. The relationship between dyslipidemia and inflammation among adults in east coast China: A cross-sectional study. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 937201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piquer, B.R.; Nazih, H.; Bourreille, A.; Segain, J.P.; Huvelin, J.M.; Galmiche, J.-P.; Bard, J.-M. Altered lipid, apolipoprotein, and lipoprotein profiles in inflammatory bowel disease: Consequences on the cholesterol efflux capacity of serum using Fu5AH cell system. Metabolism 2006, 55, 980–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biyyani, R.S.R.S.; Putka, B.S.; Mullen, K.D. Dyslipidemia and lipoprotein profiles in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. J. Clin. Lipidol. 2010, 4, 478–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koutroumpakis, E.; Ramos-Rivers, C.; Regueiro, M.; Hashash, J.G.; Barrie, A.; Swoger, J.; Baidoo, L.; Schwartz, M.; Dunn, M.A.; Koutroubakis, I.E.; et al. Association Between Long-Term Lipid Profiles and Disease Severity in a Large Cohort of Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2015, 61, 865–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papagoras, C.; Markatseli, T.E.; Saougou, I.; Alamanos, Y.; Zikou, A.K.; Voulgari, P.V.; Kiortsis, D.N.; Drosos, A.A. Cardiovascular risk profile in patients with spondyloarthritis. Jt. Bone Spine 2014, 81, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Cai, Y.; Cai, L.; Hu, Y.; Chen, X.; Deng, J. Altered Lipid Levels in Untreated Patients with Early Polymyositis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e89827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, Z.; He, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Li, T.; Wen, S.; Ren, Z.; Cai, N.; Yang, J.; Li, M.; et al. Hyperlipidemia induces proinflammatory responses by activating STING pathway through IRE1α-XBP1 in retinal endothelial cells. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2023, 112, 109213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Jesus, A.A.; Marrero, B.; Yang, D.; Ramsey, S.E.; Montealegre Sanchez, G.A.; Tenbrock, K.; Wittkowski, H.; Jones, O.Y.; Kuehn, H.S.; et al. Activated STING in a Vascular and Pulmonary Syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 507–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witkowski, A.; Carta, S.; Lu, R.; Yokoyama, S.; Rubartelli, A.; Cavigiolio, G. Oxidation of methionine residues in human apolipoprotein A-I generates a potent pro-inflammatory molecule. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 3634–3646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazir, S.; Jankowski, V.; Bender, G.; Zewinger, S.; Rye, K.-A.; van der Vorst, E.P. Interaction between high-density lipoproteins and inflammation: Function matters more than concentration! Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2020, 159, 94–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalli, J.; Chiang, N.; Serhan, C.N. Elucidation of novel 13-series resolvins that increase with atorvastatin and clear infections. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 1071–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planagumà, A.; Pfeffer, M.A.; Rubin, G.; Croze, R.; Uddin, M.; Serhan, C.N.; Levy, B.D. Lovastatin decreases acute mucosal inflammation via 15-epi-lipoxin A4. Mucosal Immunol. 2010, 3, 270–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serhan, C.N.; Chiang, N.; Dalli, J.; Levy, B.D. Lipid Mediators in the Resolution of Inflammation. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2014, 7, a016311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serhan, C.N.; Levy, B.D. Resolvins in inflammation: Emergence of the pro-resolving superfamily of mediators. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 2657–2669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elabdeen, H.R.Z.; Mustafa, M.; Szklenar, M.; Rühl, R.; Ali, R.; Bolstad, A.I. Ratio of Pro-Resolving and Pro-Inflammatory Lipid Mediator Precursors as Potential Markers for Aggressive Periodontitis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e70838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.-W.; Colas, R.A.; Dalli, J.; Arnardottir, H.H.; Nguyen, D.; Hasturk, H.; Chiang, N.; Van Dyke, T.E.; Serhan, C.N. Maresin 1 Biosynthesis and Proresolving Anti-infective Functions with Human-Localized Aggressive Periodontitis Leukocytes. Infect. Immun. 2016, 84, 658–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tobón-Arroyave, S.I.; Isaza-Guzmán, D.M.; Gómez-Ortega, J.; Flórez-Alzate, A.A. Salivary levels of specialized pro-resolving lipid mediators as indicators of periodontal health/disease status. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2019, 46, 978–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flesher, R.P.; Herbert, C.; Kumar, R.K. Resolvin E1 promotes resolution of inflammation in a mouse model of an acute exacerbation of allergic asthma. Clin. Sci. 2014, 126, 805–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bharath, L.P.; Agrawal, M.; McCambridge, G.; Nicholas, D.A.; Hasturk, H.; Liu, J.; Jiang, K.; Liu, R.; Guo, Z.; Deeney, J.; et al. Metformin Enhances Autophagy and Normalizes Mitochondrial Function to Alleviate Aging-Associated Inflammation. Cell Metab. 2020, 32, 44–55.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bharath, L.P.; Nikolajczyk, B.S. The intersection of metformin and inflammation. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 2021, 320, C873–C879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Hyperlipidemia | Non-Hyperlipidemia | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| N = 4265 | N = 1852 | ||
| Age(years) | 52.04 ± 16.37 | 41.30 ± 16.40 | <0.001 |
| Sex (%) | 0.034 | ||
| Men | 47.14 | 51.17 | |
| Women | 52.86 | 48.83 | |
| Race/Ethnicity (%) | <0.001 | ||
| Mexican American | 8.51 | 8.64 | |
| Non-Hispanic White | 65.46 | 60.41 | |
| Non-Hispanic Black | 9.25 | 14.06 | |
| Other Hispanic | 6.92 | 6.92 | |
| Other Race | 9.86 | 9.97 | |
| Education (%) | 0.007 | ||
| Less than high school | 5.37 | 4.20 | |
| High school | 8.42 | 6.69 | |
| More than high school | 86.20 | 89.10 | |
| Marital status (%) | <0.001 | ||
| Married/Living with partner | 66.02 | 57.72 | |
| Widowed/Divorced/ Separated | 20.29 | 14.43 | |
| Never married | 13.68 | 27.85 | |
| Income to poverty ratio (%) | 0.231 | ||
| 0–1.5 | 20.42 | 21.97 | |
| 1.5–3.5 | 39.13 | 37.13 | |
| >3.5 | 40.45 | 40.90 | |
| BMI (kg/m2) (%) | <0.001 | ||
| 0–25 | 16.54 | 34.85 | |
| 25–30 | 47.37 | 42.34 | |
| >30 | 36.09 | 22.80 | |
| Drinking status (%) | <0.001 | ||
| Excessive alcohol consumption | 15.34 | 19.56 | |
| Moderate alcohol consumption | 16.34 | 20.39 | |
| Light alcohol consumption | 68.32 | 60.05 | |
| Smoking status (%) | <0.001 | ||
| Smoking now | 18.02 | 16.22 | |
| Smoking former | 29.10 | 22.60 | |
| Never | 52.87 | 61.18 | |
| Hypertension (%) | <0.001 | ||
| Yes | 40.61 | 21.10 | |
| No | 59.39 | 78.90 | |
| Diabetes (%) | <0.001 | ||
| Yes | 24.15 | 14.66 | |
| No | 75.85 | 85.34 | |
| SII | 467.67 ± 332.58 | 416.94 ± 264.87 | <0.001 |
| SII Quartiles | p-Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 | ||
| N = 1529 | N = 1529 | N = 1529 | N = 1530 | ||
| Age (years) | 48.99 ± 16.91 | 46.02 ± 17.13 | 49.18 ± 16.93 | 50.40 ± 17.21 | <0.001 |
| Sex (%) | <0.001 | ||||
| Men | 52.77 | 51.36 | 48.88 | 40.49 | |
| Women | 47.23 | 48.64 | 51.12 | 59.51 | |
| Race/Ethnicity (%) | <0.001 | ||||
| Mexican American | 7.10 | 10.51 | 9.23 | 7.54 | |
| Non-Hispanic White | 60.07 | 61.15 | 64.86 | 69.52 | |
| Non-Hispanic Black | 15.09 | 11.31 | 8.65 | 7.75 | |
| Other Hispanic | 6.71 | 6.88 | 6.92 | 7.17 | |
| Other Race | 11.03 | 10.15 | 10.33 | 8.02 | |
| Education (%) | 0.392 | ||||
| Less than high school | 5.60 | 5.30 | 4.32 | 4.78 | |
| High school | 8.00 | 7.88 | 7.00 | 8.66 | |
| More than high school | 86.40 | 86.82 | 88.68 | 86.56 | |
| Marital status (%) | 0.011 | ||||
| Married/Living with partner | 63.91 | 62.63 | 64.15 | 62.97 | |
| Widowed/Divorced/Separated | 17.03 | 17.05 | 19.90 | 19.88 | |
| Never married | 19.07 | 20.33 | 15.95 | 17.16 | |
| Income to poverty ratio (%) | 0.095 | ||||
| 0–1.5 | 20.55 | 21.71 | 19.25 | 22.18 | |
| 1.5–3.5 | 37.36 | 39.85 | 37.93 | 39.00 | |
| >3.5 | 42.09 | 38.44 | 42.82 | 38.82 | |
| BMI (kg/m2) (%) | <0.001 | ||||
| 0–25 | 15.08 | 27.14 | 23.79 | 23.67 | |
| 25–30 | 73.38 | 42.58 | 35.95 | 29.67 | |
| >30 | 11.55 | 30.29 | 40.25 | 46.65 | |
| Drinking status (%) | <0.001 | ||||
| Excessive alcohol consumption | 12.81 | 17.46 | 17.91 | 18.69 | |
| Moderate alcohol consumption | 17.22 | 18.63 | 17.05 | 17.61 | |
| Light alcohol consumption | 55.62 | 58.51 | 55.16 | 52.74 | |
| Smoking status (%) | 0.002 | ||||
| Smoking now | 17.03 | 14.79 | 17.12 | 20.78 | |
| Smoking former | 27.35 | 26.70 | 27.73 | 26.48 | |
| Never | 55.62 | 58.51 | 55.16 | 52.74 | |
| Hypertension (%) | <0.001 | ||||
| Yes | 25.09 | 32.06 | 39.02 | 42.25 | |
| No | 74.91 | 67.94 | 60.98 | 57.75 | |
| Diabetes (%) | <0.001 | ||||
| Yes | 37.39 | 15.90 | 14.98 | 15.35 | |
| No | 62.61 | 84.10 | 85.02 | 84.65 | |
| Hyperlipidemia (%) | <0.001 | ||||
| Yes | 63.99 | 65.01 | 73.68 | 72.37 | |
| No | 36.01 | 34.99 | 26.32 | 27.63 | |
| Crude Model (Model 1) | Partially Adjusted Model (Model 2) | Fully Adjusted Model (Model 3) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| OR (95% CI) p-Value | OR (95% CI) p-Value | OR (95% CI) p-Value | |
| SII/100 | 1.04 (1.02, 1.06) *** | 1.03 (1.01, 1.05) * | 1.02 (1.00, 1.04) |
| SII quartiles | |||
| Quartile 1 | Reference | Reference | Reference |
| Quartile 2 | 1.03 (0.88, 1.19) | 1.05 (0.90, 1.23) | 1.09 (0.92, 1.29) |
| Quartile 3 | 1.36 (1.17, 1.59) *** | 1.31 (1.12, 1.54) ** | 1.31 (1.10, 1.55) ** |
| Quartile 4 | 1.40 (1.20, 1.63) *** | 1.27 (1.08, 1.50) ** | 1.18 (0.99, 1.41) |
| p for trend | <0.0001 | 0.0009 | 0.0416 |
| Adjusted OR (95% CI), p Value | |
|---|---|
| SII | |
| Inflection point | 479.15 |
| SII < 479.15 | 1.0008 (1.0003, 1.0013) ** |
| SII ≥ 479.15 | 0.9999 (0.9996, 1.0002) |
| Log likelihood ratio | 0.008 |
| Men | |
| Inflection point | 112.35 |
| SII < 112.35 | 1.0056 (0.9965, 1.0147) |
| SII ≥112.35 | 1.0001 (0.9997, 1.0004) |
| Log likelihood ratio | 0.243 |
| Women | |
| Inflection point | 958.14 |
| SII < 958.14 | 1.0006 (1.0002, 1.1010) ** |
| SII ≥ 958.14 | 0.9997 (0.9992, 1.0002) |
| Log likelihood ratio | 0.013 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mahemuti, N.; Jing, X.; Zhang, N.; Liu, C.; Li, C.; Cui, Z.; Liu, Y.; Chen, J. Association between Systemic Immunity-Inflammation Index and Hyperlipidemia: A Population-Based Study from the NHANES (2015–2020). Nutrients 2023, 15, 1177. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15051177
Mahemuti N, Jing X, Zhang N, Liu C, Li C, Cui Z, Liu Y, Chen J. Association between Systemic Immunity-Inflammation Index and Hyperlipidemia: A Population-Based Study from the NHANES (2015–2020). Nutrients. 2023; 15(5):1177. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15051177
Chicago/Turabian StyleMahemuti, Nayili, Xiyue Jing, Naijian Zhang, Chuanlang Liu, Changping Li, Zhuang Cui, Yuanyuan Liu, and Jiageng Chen. 2023. "Association between Systemic Immunity-Inflammation Index and Hyperlipidemia: A Population-Based Study from the NHANES (2015–2020)" Nutrients 15, no. 5: 1177. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15051177
APA StyleMahemuti, N., Jing, X., Zhang, N., Liu, C., Li, C., Cui, Z., Liu, Y., & Chen, J. (2023). Association between Systemic Immunity-Inflammation Index and Hyperlipidemia: A Population-Based Study from the NHANES (2015–2020). Nutrients, 15(5), 1177. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15051177






