Acute Insulin Secretory Effects of a Classic Ketogenic Meal in Healthy Subjects: A Randomized Cross-Over Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Experimental Protocol
2.3. Laboratory Analyses
2.4. Analysis and Modelling of Meal
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
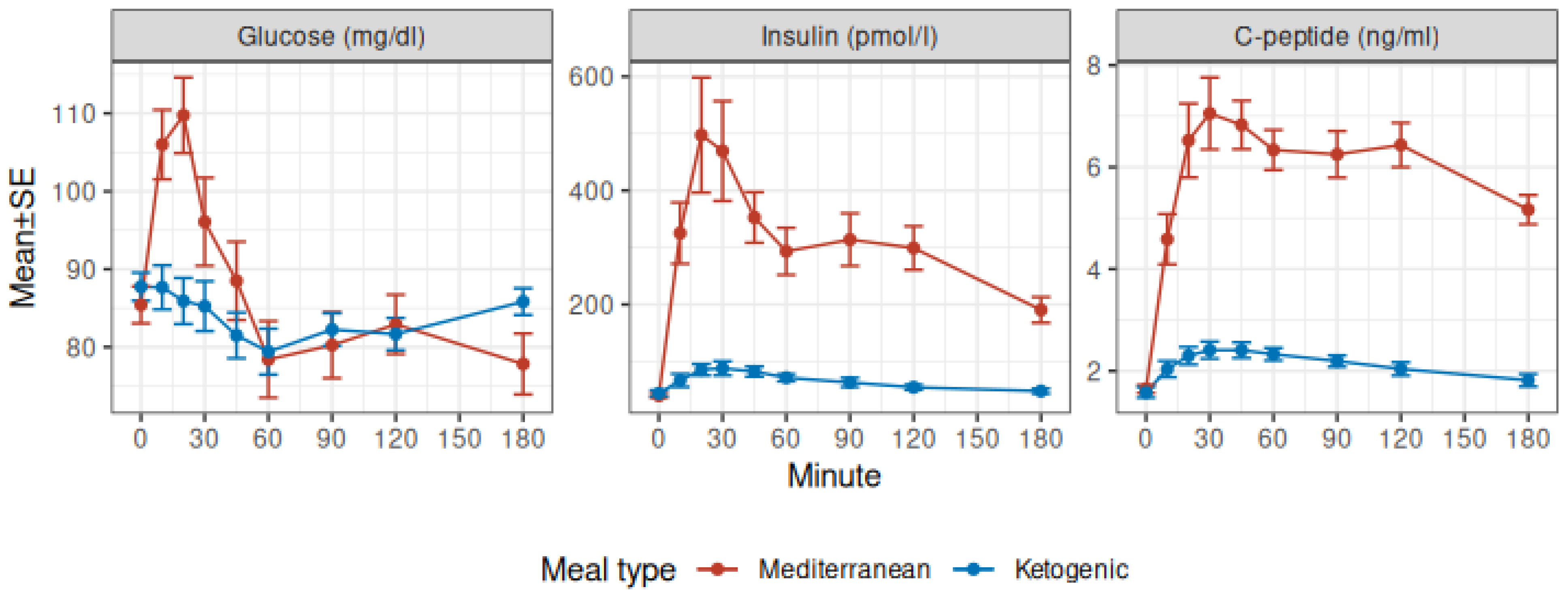
3.1. Glucose, Insulin, and C-Peptide
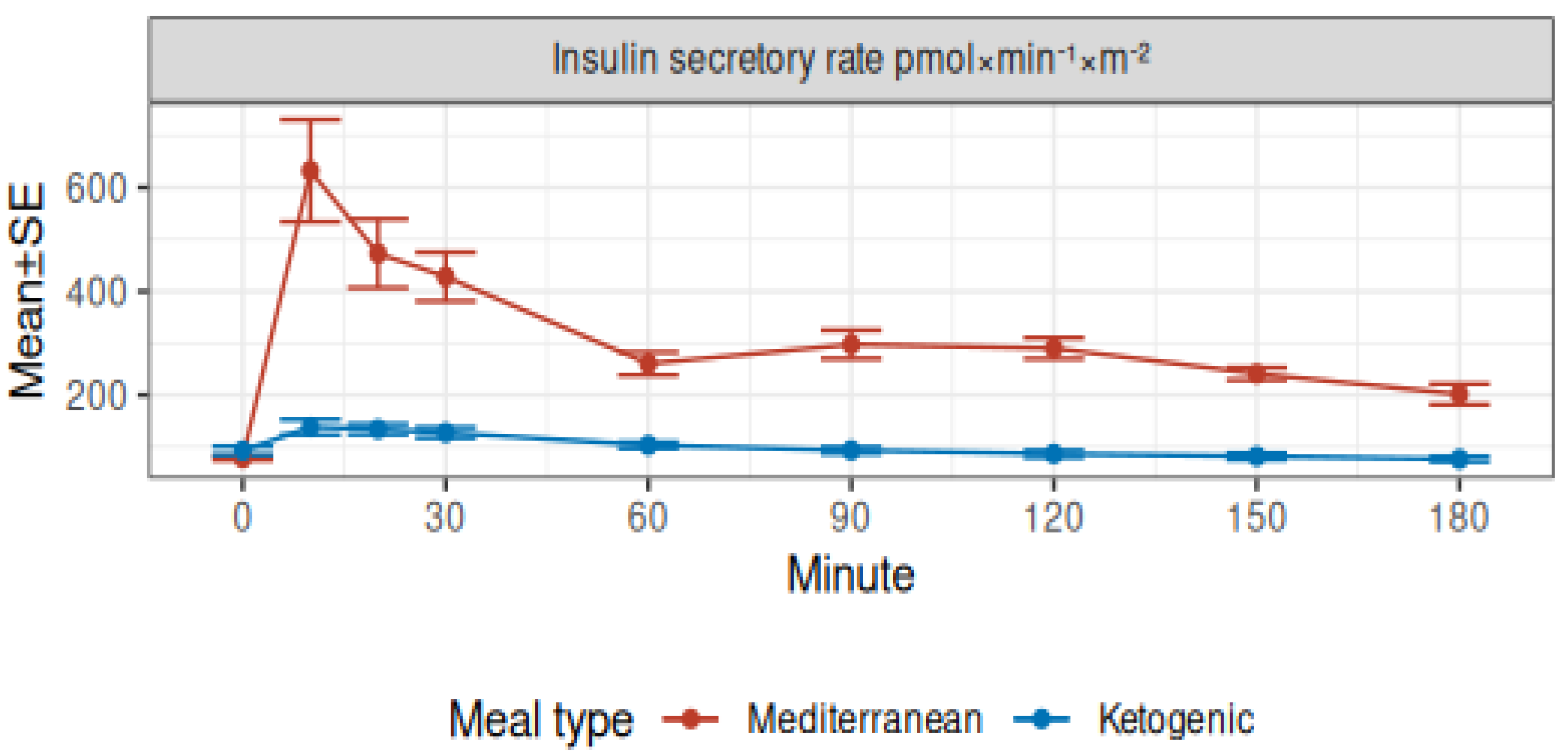
3.2. Modeled Insulin Secretion and Insulin Clearance
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Desli, E.; Spilioti, M.; Evangeliou, A.; Styllas, F.; Magkos, F.; Dalamaga, M. The efficacy and safety of ketogenic diets in drug-resistant epilepsy in children and adolescents: A systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Curr. Nutr. Rep. 2022, 11, 102–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koch, H.; Weber, Y.G. The glucose transporter type 1 (Glut1) syndromes. Epilepsy Behav. 2019, 91, 90–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Amicis, R.; Leone, A.; Lessa, C.; Foppiani, A.; Ravella, S.; Ravasenghi, S.; Trentani, C.; Ferraris, C.; Veggiotti, P.; De Giorgis, V.; et al. Long-term effects of a classic ketogenic diet on ghrelin and leptin concentration: A 12-month prospective study in a cohort of Italian children and adults with glut1-deficiency syndrome and drug resistant epilepsy. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varesio, C.; Pasca, L.; Parravicini, S.; Zanaboni, M.P.; Ballante, E.; Masnada, S.; Ferraris, C.; Bertoli, S.; Tagliabue, A.; Veggiotti, P.; et al. Quality of life in chronic ketogenic diet treatment: The glut1ds population perspective. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertoli, S.; Masnada, S.; De Amicis, R.; Sangiorgio, A.; Leone, A.; Gambino, M.; Lessa, C.; Tagliabue, A.; Ferraris, C.; De Giorgis, V.; et al. Glucose transporter 1 deficiency syndrome: Nutritional and growth pattern phenotypes at diagnosis. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 74, 1290–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietrzak, D.; Kasperek, K.; Rękawek, P.; Piątkowska-Chmiel, I. The therapeutic role of ketogenic diet in neurological disorders. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferraris, C.; Guglielmetti, M.; Pasca, L.; De Giorgis, V.; Ferraro, O.E.; Brambilla, I.; Leone, A.; De Amicis, R.; Bertoli, S.; Veggiotti, P.; et al. Impact of the ketogenic diet on linear growth in children: A single-center retrospective analysis of 34 cases. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wibisono, C.; Rowe, N.; Beavis, E.; Kepreotes, H.; Mackie, F.E.; Lawson, J.A.; Cardamone, M. Ten-year single-center experience of the ketogenic diet: Factors influencing efficacy, tolerability, and compliance. J. Pediatr. 2015, 166, 1030–1036.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heussinger, N.; Della Marina, A.; Beyerlein, A.; Leiendecker, B.; Hermann-Alves, S.; Dalla Pozza, R.; Klepper, J. 10 patients, 10 years long term follow-up of cardiovascular risk factors in Glut1 deficiency treated with ketogenic diet therapies: A prospective, multicenter case series. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 37, 2246–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gershuni, V.M.; Yan, S.L.; Medici, V. Nutritional Ketosis for Weight Management and Reversal of Metabolic Syndrome. Curr. Nutr. Rep. 2018, 7, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosinski, C.; Jornayvaz, F.R. Effects of Ketogenic Diets on Cardiovascular Risk Factors: Evidence from Animal and Human Studies. Nutrients 2017, 9, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, X.; Wang, J.; Yang, S.; Gao, M.; Cao, L.; Li, X.; Hong, D.; Tian, S.; Sun, C. Effect of the ketogenic diet on glycemic control, insulin resistance, and lipid metabolism in patients with T2DM: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutr. Diabetes 2020, 10, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Neill, B.; Raggi, P. The ketogenic diet: Pros and cons. Atherosclerosis 2019, 292, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopp, W. How western diet and lifestyle drive the pandemic of obesity and civilization diseases. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. Targets Ther. 2019, 12, 2221–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehran, A.E.; Templeman, N.M.; Brigidi, G.S.; Lim, G.E.; Chu, K.-Y.; Hu, X.; Botezelli, J.D.; Asadi, A.; Hoffman, B.G.; Kieffer, T.J.; et al. Hyperinsulinemia drives diet-induced obesity independently of brain insulin production. Cell Metab. 2012, 16, 723–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopp, W. High-insulinogenic nutritionan etiologic factor for obesity and the metabolic syndrome? Metabolism 2003, 52, 840–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nolan, C.; Prentki, M. Insulin resistance and insulin hypersecretion in the metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes: Time for a conceptual framework shift. Diabetes Vasc. Dis. Res. 2019, 16, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erion, K.A.; Corkey, B.E. Hyperinsulinemia: A cause of obesity? Curr. Obes. Rep. 2017, 6, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Templeman, N.M.; Skovsø, S.; Page, M.M.; Lim, G.E.; Johnson, J.D. A causal role for hyperinsulinemia in obesity. J. Endocrinol. 2017, 232, R173–R183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battezzati, A.; Terruzzi, I.; Perseghin, G.; Bianchi, E.; Carlo, V.D.; Pozza, G.; Luzi, L. Defective insulin action on protein and glucose metabolism during chronic hyperinsulinemia in subjects with benign insulinoma. Diabetes 1995, 44, 837–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corkey, B.E. Banting lecture 2011. Diabetes 2011, 61, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanik, M.H.; Xu, Y.; Skrha, J.; Dankner, R.; Zick, Y.; Roth, J. Insulin resistance and hyperinsulinemia. Diabetes Care 2008, 31 (Suppl. S2), S262–S268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.S.; Gerber, J.N.; You, H.J. Association between fasting insulin and high-sensitivity C reactive protein in Korean adults. BMJ Open Sport Exerc. Med. 2017, 3, e000236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pyörälä, M.; Miettinen, H.; Laakso, M.; Pyörälä, K. Hyperinsulinemia predicts coronary heart disease risk in healthy middle-aged men. Circulation 1998, 98, 398–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, G.L.; Park, K.; Li, Q. Selective insulin resistance and the development of cardiovascular diseases in diabetes: The 2015 edwin bierman award lecture. Diabetes 2016, 65, 1462–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlot, A.; Zoll, J. Beneficial Effects of the Ketogenic Diet in Metabolic Syndrome: A Systematic Review. Diabetology 2022, 3, 292–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, T.L.; Sutherland, J.P.; Wolfe, P.; Allian-Sauer, M.; Capell, W.H.; Talley, N.D.; Wyatt, H.R.; Foster, G.D.; Hill, J.O.; Eckel, R.H. Lack of suppression of circulating free fatty acids and hypercholesterolemia during weight loss on a high-fat, low-carbohydrate diet. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 91, 578–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bojsen-Møller, K.N.; Lundsgaard, A.-M.; Madsbad, S.; Kiens, B.; Holst, J.J. Hepatic insulin clearance in regulation of systemic insulin concentrations—Role of carbohydrate and energy availability. Diabetes 2018, 67, 2129–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mari, A.; Tura, A.; Gastaldelli, A.; Ferrannini, E. Assessing insulin secretion by modeling in multiple-meal tests: Role of potentiation. Diabetes 2002, 51 (Suppl. S1), S221–S226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, J.A.; Benedict, F.G. A biometric study of human basal metabolism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1918, 4, 370–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Società Italiana di Nutrizione Umana. LARN: Livelli di Assunzione di Riferimento di Nutrienti ed Energia per la Popolazione Italiana; Società Italiana di Comunicazione Scientifica e Sanitaria: Milan, Italy, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Foppiani, A.; De Amicis, R.; Lessa, C.; Leone, A.; Ravella, S.; Ciusani, E.; Silvani, A.; Zuccoli, G.; Battezzati, A.; Lamperti, E.; et al. Isocaloric ketogenic diet in adults with high-grade gliomas: A prospective metabolic study. Nutr. Cancer 2020, 73, 1004–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2019; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 8 January 2023).
- Battezzati, A.; Mari, A.; Zazzeron, L.; Alicandro, G.; Claut, L.; Battezzati, P.M.; Colombo, C. Identification of insulin secretory defects and insulin resistance during oral glucose tolerance test in a cohort of cystic fibrosis patients. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2011, 165, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilsbøll, T.; Krarup, T.; Sonne, J.; Madsbad, S.; Vølund, A.; Juul, A.G.; Holst, J.J. Incretin secretion in relation to meal size and body weight in healthy subjects and people with type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 88, 2706–2713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Behl, T.; Sachdeva, M.; Sehgal, A.; Kumari, S.; Kumar, A.; Kaur, G.; Yadav, H.N.; Bungau, S. Implicating the effect of ketogenic diet as a preventive measure to obesity and diabetes mellitus. Life Sci. 2020, 264, 118661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Società Italiana di Diabetologia. Terapia Insulinica. 2022. Available online: https://www.siditalia.it/divulgazione/insulina (accessed on 8 January 2023).
- Diakogiannaki, E.; Gribble, F.M.; Reimann, F. Nutrient detection by incretin hormone secreting cells. Physiol. Behav. 2012, 106, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Najjar, S.M.; Perdomo, G. Hepatic insulin clearance: Mechanism and physiology. Physiology 2019, 34, 198–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergman, R.N.; Kabir, M.; Ader, M. The physiology of insulin clearance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Characteristic | Overall, n = 12 1 | Female, n = 6 1 | Male, n = 6 1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 24.1 (23.1, 25.2) | 23.7 (23.3, 24.6) | 24.7 (23.2, 25.7) |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 21.5 (20.4, 23.4) | 21.8 (20.3, 23.0) | 21.5 (20.7, 23.7) |
| Waist circumference (cm) | 73.9 (72.7, 78.4) | 72.6 (72.4, 73.5) | 76.7 (74.3, 78.8) |
| Fat mass fraction (as %) | 20.7 (16.4, 30.0) | 30.1 (28.6, 33.9) | 15.9 (12.3, 17.4) |
| Total energy expenditure (kcal) | 2393 (2164, 2655) | 2156 (2139, 2215) | 2679 (2555, 2776) |
| OGTT Minutes | Two-Way ANOVA p-Values 2 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characteristic | Group | 0 1 | 10 1 | 20 1 | 30 1 | 60 1 | 90 1 | 120 1 | 180 1 | Minute | Meal | Interaction |
| Glucose (mg/dL) | <0.001 | 0.005 | <0.001 | |||||||||
| Mediterranean | 85 ± 2 | 106 ± 4 | 110 ± 5 | 96 ± 6 | 78 ± 5 | 80 ± 4 | 83 ± 4 | 78 ± 4 | ||||
| Ketogenic | 88 ± 2 | 88 ± 3 | 86 ± 3 | 85 ± 3 | 79 ± 3 | 82 ± 2 | 82 ± 2 | 86 ± 2 | ||||
| Insulin (pmol/L) | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||||||||
| Mediterranean | 40 ± 4 | 325 ± 54 | 497 ± 101 | 469 ± 88 | 293 ± 41 | 314 ± 46 | 299 ± 38 | 190 ± 23 | ||||
| Ketogenic | 44 ± 5 | 67 ± 11 | 86 ± 10 | 88 ± 12 | 71 ± 6 | 63 ± 8 | 55 ± 5 | 48 ± 4 | ||||
| C-peptide (ng/mL) | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||||||||
| Mediterranean | 1.65 ± 0.08 | 4.58 ± 0.49 | 6.52 ± 0.72 | 7.05 ± 0.71 | 6.34 ± 0.39 | 6.25 ± 0.46 | 6.43 ± 0.43 | 5.16 ± 0.29 | ||||
| Ketogenic | 1.58 ± 0.10 | 2.04 ± 0.16 | 2.30 ± 0.17 | 2.41 ± 0.17 | 2.33 ± 0.12 | 2.19 ± 0.11 | 2.04 ± 0.13 | 1.82 ± 0.12 | ||||
| Insulin secretion rate (pmol × min−1 × m−2) | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||||||||
| Mediterranean | 78 ± 4 | 632 ± 98 | 473 ± 66 | 428 ± 47 | 261 ± 22 | 298 ± 27 | 290 ± 20 | 202 ± 20 | ||||
| Ketogenic | 93 ± 8 | 138 ± 15 | 134 ± 10 | 128 ± 10 | 103 ± 6 | 94 ± 6 | 87 ± 7 | 77 ± 5 | ||||
| Characteristic | Mediterranean, n = 12 1 | Ketogenic, n = 12 1 | Difference 2 | 95% CI 2,3 | p-Value 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Basal rate of insulin secretion (pmol × min−1 × m−2) | 78 ± 4 | 93 ± 8 | −14 | −32, 2.7 | 0.091 |
| Peak rate of insulin secretion (pmol × min−1 × m−2) | 697 ± 95 | 161 ± 14 | 535 | 308, 763 | <0.001 |
| Basal insulin concentration (pmol/L) | 40 ± 4 | 44 ± 5 | −3.8 | −12, 4.1 | 0.3 |
| Incremental insulin concentration (pmol/L) | 7929 ± 999 | 668 ± 110 | 7261 | 5040, 9482 | <0.001 |
| Total insulin concentration (pmol/L) | 54,764 ± 6378 | 9821 ± 1103 | 44,943 | 30,706, 59,181 | <0.001 |
| Basal insulin clearance (l × min−1 × m−2) | 2.12 ± 0.18 | 2.48 ± 0.39 | −0.36 | −0.95, 0.22 | 0.2 |
| Insulin clearance during the test (l × min−1 × m−2) | 1.10 ± 0.08 | 1.39 ± 0.18 | −0.30 | −0.74, 0.15 | 0.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Battezzati, A.; Foppiani, A.; Leone, A.; De Amicis, R.; Spadafranca, A.; Mari, A.; Bertoli, S. Acute Insulin Secretory Effects of a Classic Ketogenic Meal in Healthy Subjects: A Randomized Cross-Over Study. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1119. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15051119
Battezzati A, Foppiani A, Leone A, De Amicis R, Spadafranca A, Mari A, Bertoli S. Acute Insulin Secretory Effects of a Classic Ketogenic Meal in Healthy Subjects: A Randomized Cross-Over Study. Nutrients. 2023; 15(5):1119. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15051119
Chicago/Turabian StyleBattezzati, Alberto, Andrea Foppiani, Alessandro Leone, Ramona De Amicis, Angela Spadafranca, Andrea Mari, and Simona Bertoli. 2023. "Acute Insulin Secretory Effects of a Classic Ketogenic Meal in Healthy Subjects: A Randomized Cross-Over Study" Nutrients 15, no. 5: 1119. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15051119
APA StyleBattezzati, A., Foppiani, A., Leone, A., De Amicis, R., Spadafranca, A., Mari, A., & Bertoli, S. (2023). Acute Insulin Secretory Effects of a Classic Ketogenic Meal in Healthy Subjects: A Randomized Cross-Over Study. Nutrients, 15(5), 1119. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15051119









