Alleviation of Porphyromonas gingivalis or Its Extracellular Vesicles Provoked Periodontitis and Cognitive Impairment by Lactobacillus pentosus NK357 and Bifidobacterium bifidum NK391
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Culture of PG
2.3. Preparation of pEVs
2.4. Culture of NK357 and NK391
2.5. Culture of SH-SY5Y Cells and BV2 Cells
2.6. Animals
2.7. Determination of Biomarkers
2.8. Immunofluorescence Assay
2.9. Microbiota 16S rRNA Sequencing
2.10. Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (qPCR)
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
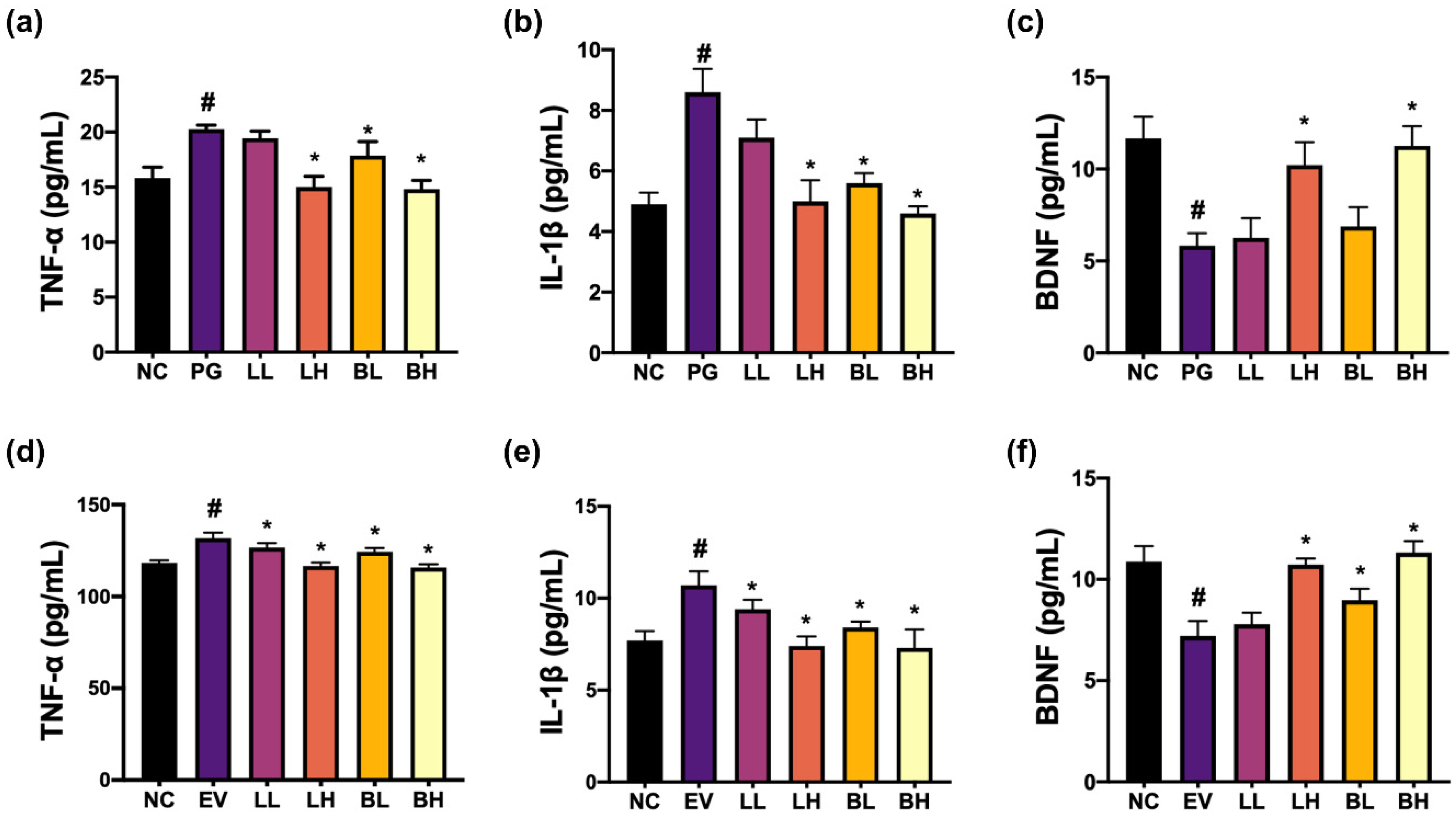
3.1. NK357 and NK391 Decreased PG- or pEVs-Induced TNF-α Expression in BV2 Cells and Increased PG- or pEVs-Suppressed BDNF Expression in SH-SY5Y Cells
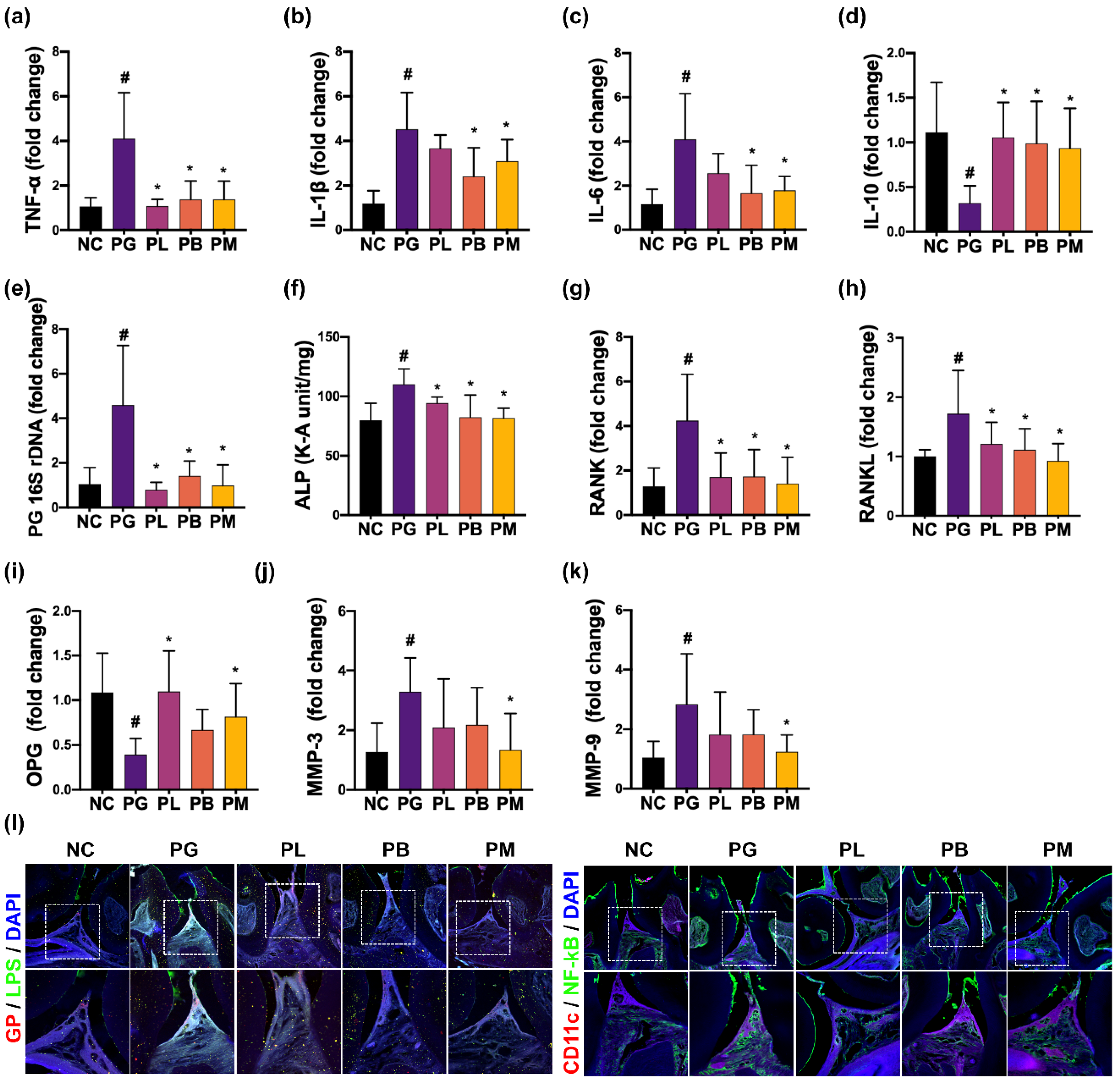
3.2. NK357 and NK391 Alleviated PG-Induced Periodontitis in Mice
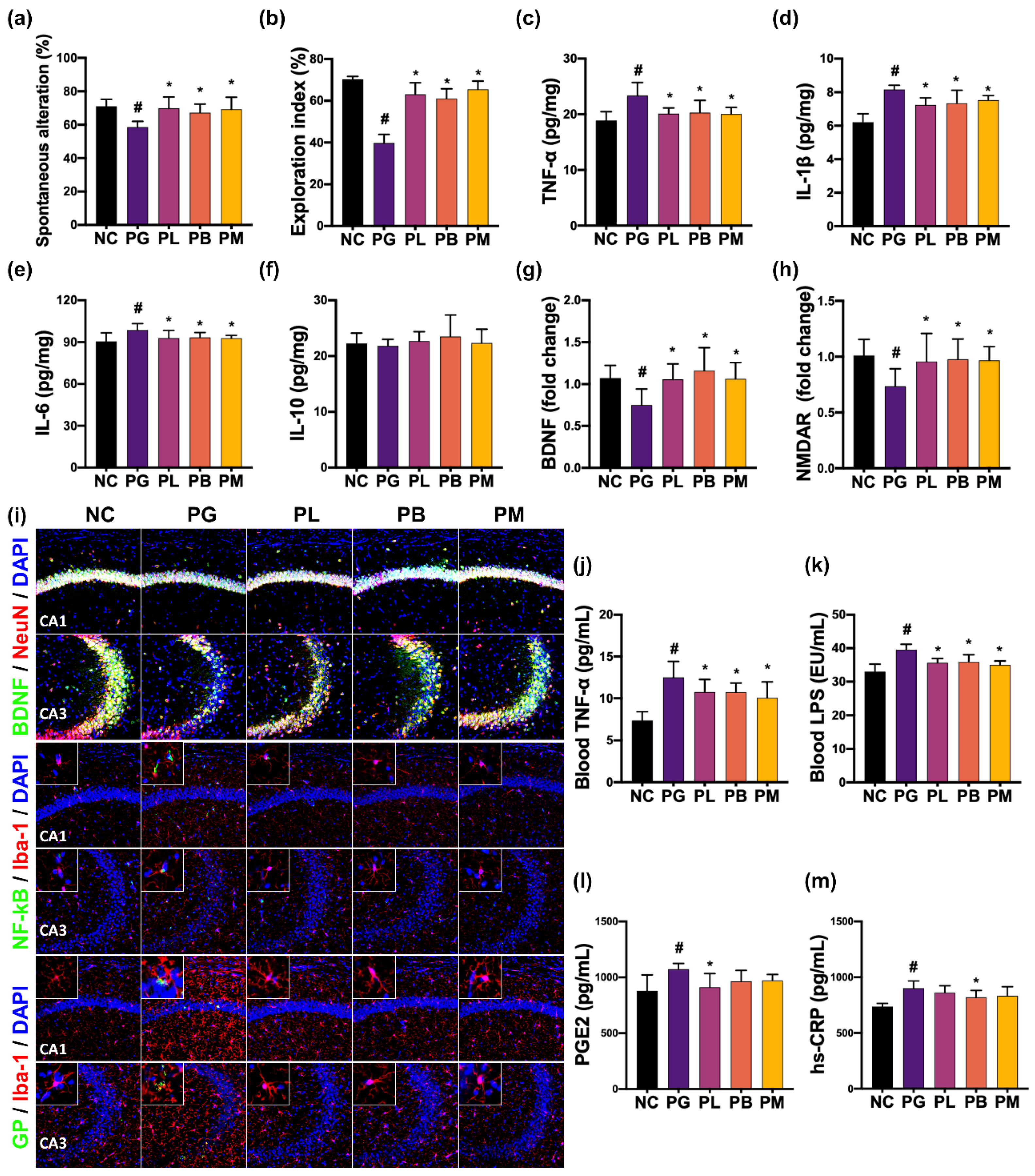
3.3. NK357 and NK391 Alleviated PG-Induced CI in Mice
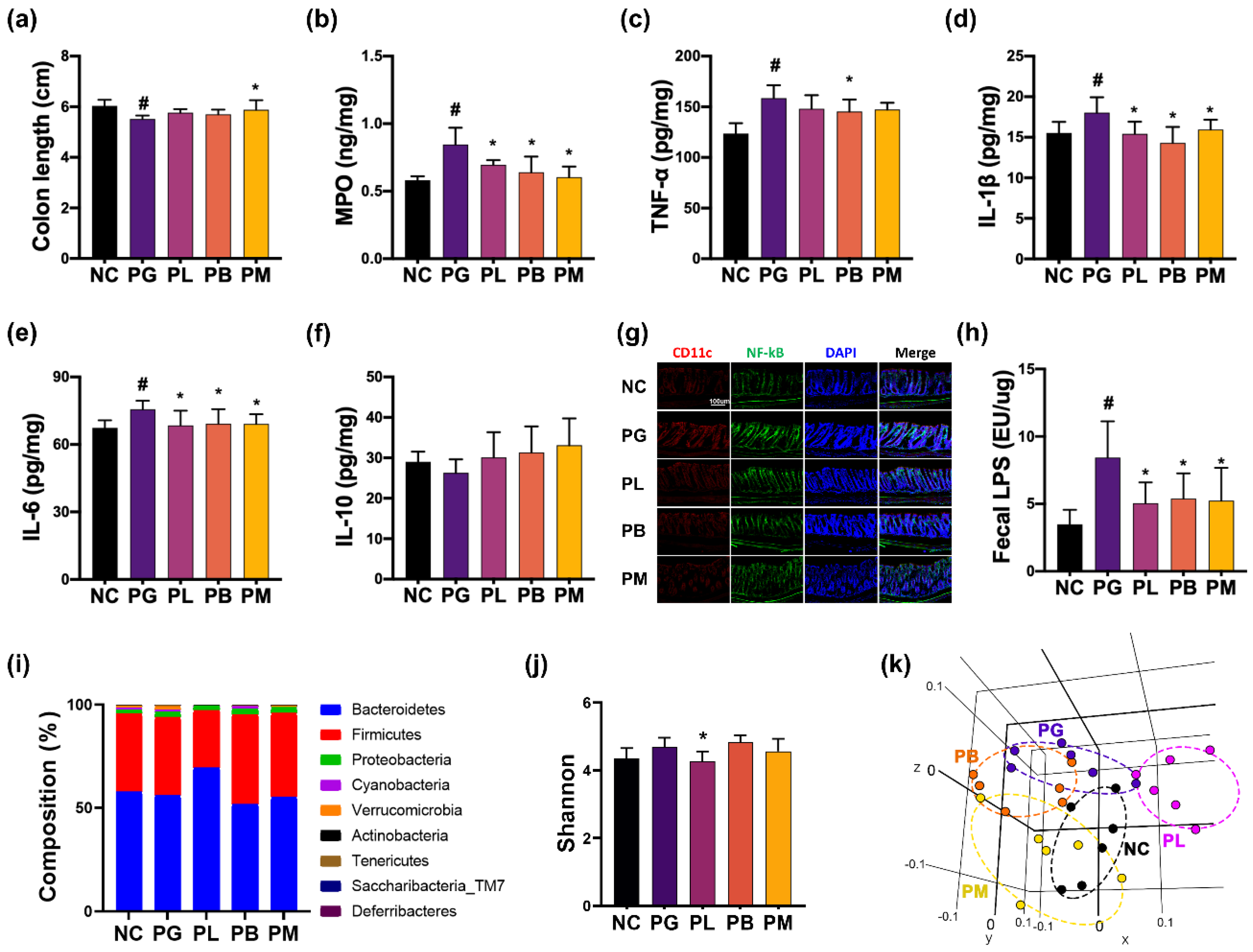
3.4. NK357 and NK391 Alleviated PG-Induced Colitis and Gut Dysbiosis in Mice
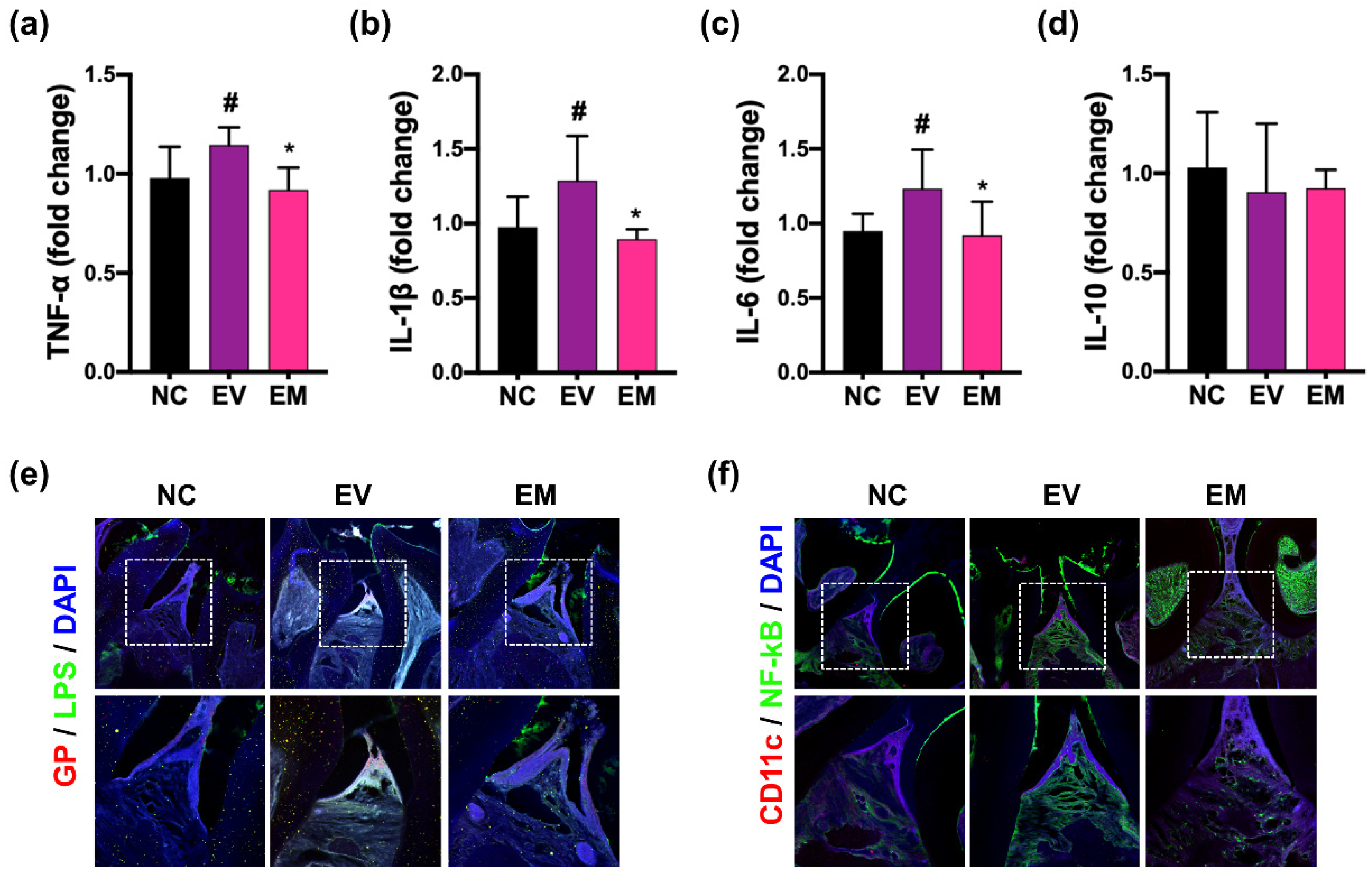
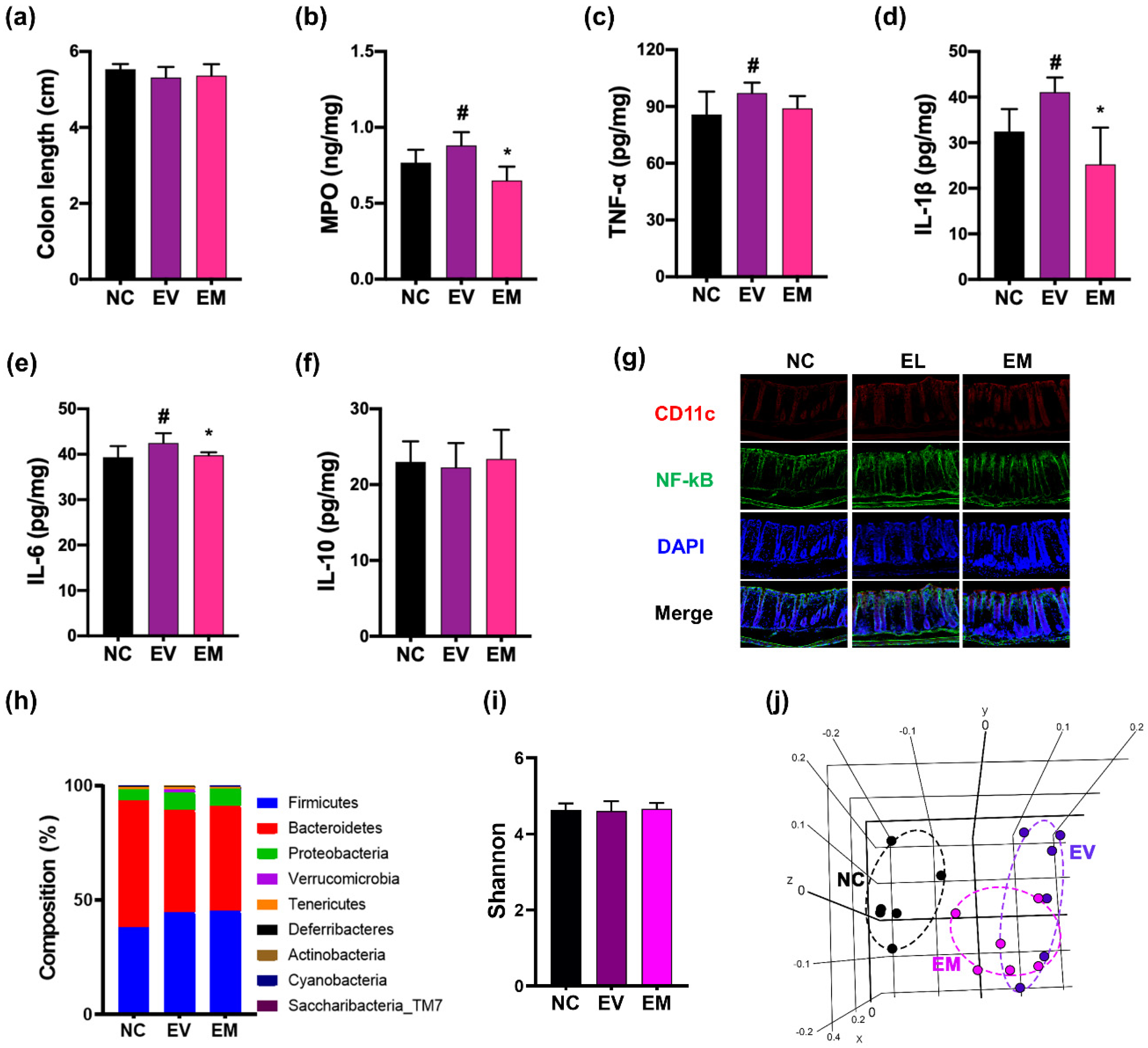
3.5. NKc Alleviated pEVs-Induced Periodontitis, CI, and Colitis in Mice
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- How, K.Y.; Song, K.P.; Chan, K.G. Porphyromonas gingivalis: An overview of periodontopathic pathogen below the gum line. Front Microbiol. 2016, 7, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elwishahy, A.; Antia, K.; Bhusari, S.; Ilechukwu, N.C.; Horstick, O.; Winkler, V. Porphyromonas gingivalis as a risk factor to Alzheimer’s disease: A systematic review. J. Alzheimers Dis. Rep. 2021, 5, 721–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsushita, K.; Yamada-Furukawa, M.; Kurosawa, M.; Shikama, Y. Periodontal disease and eriodontal disease-related bacteria involved in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Inflamm. Res. 2020, 13, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Chang, S.; Pi, X.; Hua, F.; Jiang, H.; Liu, C.; Du, M. The effect of periodontitis on dementia and cognitive impairment: A meta-analysis. Int. J. Environ Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 6823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imamura, T. The role of gingipains in the pathogenesis of periodontal disease. J. Periodontol. 2003, 74, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahar, B.; Singhrao, S.K. An evaluation of the molecular mode of action of trans-resveratrol in the Porphyromonas gingivalis lipopolysaccharide challenged neuronal cell model. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2021, 48, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Ren, J.; Yu, H.; Yu, W.; Zhou, Y. Porphyromonas gingivalis, a periodontitis causing bacterium, induces memory impairment and age-dependent neuroinflammation in mice. Immun. Ageing 2018, 15, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yu, C.; Zhang, X.; Chen, H.; Dong, J.; Lu, W.; Song, Z.; Zhou, W. Porphyromonas gingivalis lipopolysaccharide induces cognitive dysfunction, mediated by neuronal inflammation via activation of the TLR4 signaling pathway in C57BL/6 mice. J. Neuroinflammation 2018, 15, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominy, S.S.; Lynch, C.; Ermini, F.; Benedyk, M.; Marczyk, A.; Konradi, A.; Nguyen, M.; Haditsch, U.; Raha, D.; Griffin, C.; et al. Porphyromonas gingivalis in Alzheimer’s disease brains: Evidence for disease causation and treatment with small-molecule inhibitors. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaau3333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryder, M.I. Porphyromonas gingivalis and Alzheimer disease: Recent findings and potential therapies. J. Periodontol. 2020, 91 (Suppl. S1), S45–S49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, B.P.; Quigley, E.M.M. Probiotics in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterol. Clin. N. Am. 2017, 46, 769–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Xu, J.; Du, Y.; Wu, W.; Nie, W.; Zhang, D.; Luo, Y.; Lu, H.; Lei, M.; Xiao, S.; et al. Effects of gut microbiota and probiotics on Alzheimer’s disease. Transl. Neurosci. 2021, 12, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borchers, A.T.; Selmi, C.; Meyers, F.J.; Keen, C.L.; Gershwin, M.E. Probiotics and immunity. J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 44, 26–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikhi, A.; Giti, H.; Heibor, M.R.; Jafarzadeh, A.; Shakerian, M.; Baharifar, N.; Niruzad, F.; Moghaddam, A.S.; Kokhaei, P.; Baghaeifar, M. Lactobacilus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus modulates the secretion of Th1/Th2 and Treg cell-related cytokines by PBMCs from patients with atopic dermatitis. Drug Res. (Stuttg.) 2017, 67, 724–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mantegazza, C.; Molinari, P.; D’Auria, E.; Sonnino, M.; Morelli, L.; Zuccotti, G.V. Probiotics and antibiotic-associated diarrhea in children: A review and new evidence on Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG during and after antibiotic treatment. Pharmacol. Res. 2018, 128, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.K.; Lee, K.E.; Lee, S.A.; Jang, H.M.; Kim, D.H. Interplay between human gut bacteria Escherichia coli and Lactobacillus mucosae in the occurrence of neuropsychiatric disorders in mice. Front Immunol. 2020, 11, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.Y.; Son, Y.H.; Yoo, J.W.; Joo, M.K.; Kim, D.H. Tight junction protein expression-inducing probiotics alleviate TNBS-induced cognitive impairment with colitis in mice. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Lee, K.E.; Kim, J.K.; Kim, D.H. Suppression of gut dysbiosis by Bifidobacterium longum alleviates cognitive decline in 5XFAD transgenic and aged mice. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 11814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatej, S.M.; Marino, V.; Bright, R.; Fitzsimmons, T.R.; Gully, N.; Zilm, P.; Gibson, R.J.; Edwards, S.; Bartold, P.M. Probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG prevents alveolar bone loss in a mouse model of experimental periodontitis. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2018, 45, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales, A.; Carvajal, P.; Silva, N.; Hernandez, M.; Godoy, C.; Rodriguez, G.; Cabello, R.; Garcia-Sesnich, J.; Hoare, A.; Diaz, P.I.; et al. Clinical effects of Lactobacillus rhamnosus in non-surgical treatment of chronic periodontitis: A randomized placebo-controlled trial with 1-year follow-up. J. Periodontol. 2016, 87, 944–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutaga, K.; van Winkelhoff, A.J.; Vandenbroucke-Grauls, C.M.; Savelkoul, P.H. Comparison of real-time PCR and culture for detection of Porphyromonas gingivalis in subgingival plaque samples. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 4950–4954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okamura, H.; Hirota, K.; Yoshida, K.; Weng, Y.; He, Y.; Shiotsu, N.; Ikegame, M.; Uchida-Fukuhara, Y.; Tanai, A.; Guo, J. Outer membrane vesicles of Porphyromonas gingivalis: Novel communication tool and strategy. Jpn. Dent. Sci. Rev. 2021, 57, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, H.M.; Lee, K.E.; Kim, D.H. The Preventive and curative effects of Lactobacillus reuteri NK33 and Bifidobacterium adolescentis NK98 on immobilization stress-induced anxiety/depression and colitis in mice. Nutrients 2019, 11, 819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.E.; Kim, J.K.; Han, S.K.; Lee, D.Y.; Lee, H.J.; Yim, S.V.; Kim, D.H. The extracellular vesicle of gut microbial Paenalcaligenes hominis is a risk factor for vagus nerve-mediated cognitive impairment. Microbiome 2020, 8, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, S.E.; Lim, S.M.; Jeong, J.J.; Jang, H.M.; Lee, H.J.; Han, M.J.; Kim, D.H. Gastrointestinal inflammation by gut microbiota disturbance induces memory impairment in mice. Mucosal. Immunol. 2018, 11, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarter, M.; Bodewitz, G.; Stephens, D.N. Attenuation of scopolamine-induced impairment of spontaneous alteration behaviour by antagonist but not inverse agonist and agonist beta-carbolines. Psychopharmacology (Berl.) 1988, 94, 491–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, G.B.; Keating, D.J.; Young, R.L.; Wong, M.L.; Licinio, J.; Wesselingh, S. From gut dysbiosis to altered brain function and mental illness: Mechanisms and pathways. Mol. Psychiatry 2016, 21, 738–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomaa, E.Z. Human gut microbiota/microbiome in health and diseases: A review. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2020, 113, 2019–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukui, H. Increased intestinal permeability and decreased barrier function: Does it really influence the risk of inflammation? Inflamm. Intest Dis. 2016, 1, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schietroma, M.; Pessia, B.; Carlei, F.; Mariani, P.; Sista, F.; Amicucci, G. Intestinal permeability and systemic endotoxemia in patients with acute pancreatitis. Ann. Ital. Chir. 2016, 87, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bischoff, S.C.; Barbara, G.; Buurman, W.; Ockhuizen, T.; Schulzke, J.D.; Serino, M.; Tilg, H.; Watson, A.; Wells, J.M. Intestinal permeability--a new target for disease prevention and therapy. BMC Gastroenterol. 2014, 14, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, H.M.; Lee, K.E.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, D.H. Immobilization stress-induced Escherichia coli causes anxiety by inducing NF-κB activation through gut microbiota disturbance. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.Y.; Shin, Y.J.; Kim, J.K.; Jang, H.M.; Joo, M.K.; Kim, D.H. Alleviation of cognitive impairment by gut microbiota lipopolysaccharide production-suppressing Lactobacillus plantarum and Bifidobacterium longum in mice. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 10750–10763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haditsch, U.; Roth, T.; Rodriguez, L.; Hancock, S.; Cecere, T.; Nguyen, M.; Arastu-Kapur, S.; Broce, S.; Raha, D.; Lynch, C.C.; et al. Alzheimer’s disease-like neurodegeneration in Porphyromonas gingivalis infected neurons with persistent expression of active gingipains. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2020, 75, 1361–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afonso, P.; De Luca, P.; Carvalho, R.S.; Cortes, L.; Pinheiro, P.; Oliveiros, B.; Almeida, R.D.; Mele, M.; Duarte, C.B. BDNF increases synaptic NMDA receptor abundance by enhancing the local translation of Pyk2 in cultured hippocampal neurons. Sci. Signal. 2019, 12, eaav3577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maqsood, R.; Stone, T.W. The gut-brain axis, BDNF, NMDA and CNS disorders. Neurochem. Res. 2016, 41, 2819–2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kairisalo, M.; Korhonen, L.; Sepp, M.; Pruunsild, P.; Kukkonen, J.P.; Kivinen, J.; Timmusk, T.; Blomgren, K.; Lindholm, D. NF-kappaB-dependent regulation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in hippocampal neurons by X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2009, 30, 958–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marini, A.M.; Jiang, X.; Wu, X.; Tian, F.; Zhu, D.; Okagaki, P.; Lipsky, R.H. Role of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and NF-kappaB in neuronal plasticity and survival: From genes to phenotype. Restor. Neurol. Neurosci. 2004, 22, 121–130. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.W.; Jung, B.H.; Lee, J.H.; Yoo, K.Y.; Lee, H.; Kang, M.S.; Lee, J.K. Effect of Weissella cibaria on the reduction of periodontal tissue destruction in mice. J. Periodontol. 2020, 91, 1367–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, X.; Yoo, J.-W.; Shin, Y.-J.; Park, H.-S.; Son, Y.-H.; Kim, D.-H. Alleviation of Porphyromonas gingivalis or Its Extracellular Vesicles Provoked Periodontitis and Cognitive Impairment by Lactobacillus pentosus NK357 and Bifidobacterium bifidum NK391. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1068. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15051068
Ma X, Yoo J-W, Shin Y-J, Park H-S, Son Y-H, Kim D-H. Alleviation of Porphyromonas gingivalis or Its Extracellular Vesicles Provoked Periodontitis and Cognitive Impairment by Lactobacillus pentosus NK357 and Bifidobacterium bifidum NK391. Nutrients. 2023; 15(5):1068. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15051068
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Xiaoyang, Jong-Wook Yoo, Yoon-Jung Shin, Hee-Seo Park, Young-Hoo Son, and Dong-Hyun Kim. 2023. "Alleviation of Porphyromonas gingivalis or Its Extracellular Vesicles Provoked Periodontitis and Cognitive Impairment by Lactobacillus pentosus NK357 and Bifidobacterium bifidum NK391" Nutrients 15, no. 5: 1068. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15051068
APA StyleMa, X., Yoo, J.-W., Shin, Y.-J., Park, H.-S., Son, Y.-H., & Kim, D.-H. (2023). Alleviation of Porphyromonas gingivalis or Its Extracellular Vesicles Provoked Periodontitis and Cognitive Impairment by Lactobacillus pentosus NK357 and Bifidobacterium bifidum NK391. Nutrients, 15(5), 1068. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15051068





