Serum Adipocytokines Profile in Children Born Small and Appropriate for Gestational Age—A Comparative Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Source of Data
2.2. Survey
2.3. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- NCD Risk Factor Collaboration. Available online: http://www.cuore.iss.it/eng/collaboration/ncd (accessed on 14 January 2023).
- Bhattacharya, S.; Aggarwal, P.; Bera, O.P.; Saleem, S.M.; Shikha, D.; Vallabh, V.; Juyal, R.; Singh, A. Covid-19 and Childhood Obesity (Co-Besity) in the Era of New Normal Life: A Need for a Policy Research. J. Public Health Res. 2021, 10 (Suppl. S2), 2673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loos, R.J.F. Genetic Determinants of Common Obesity and Their Value in Prediction. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 26, 211–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sam, S.; Mazzone, T. Adipose Tissue Changes in Obesity and the Impact on Metabolic Function. Transl. Res. 2014, 164, 284–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nam, H.-K.; Lee, K.-H. Small for Gestational Age and Obesity: Epidemiology and General Risks. Ann. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 23, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matoss, S.S.; Mourano, F.A. Diet, Nutrition, and Fetal Programming; Humana Press: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 432–444. [Google Scholar]
- Giussani, D.A.; Davidge, S.T. Developmental Programming of Cardiovascular Disease by Prenatal Hypoxia. J. Dev. Orig. Health Dis. 2013, 4, 328–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelishadi, R.; Haghdoost, A.A.; Jamshidi, F.; Aliramezany, M.; Moosazadeh, M. Low Birthweight or Rapid Catch-up Growth: Which Is More Associated with Cardiovascular Disease and Its Risk Factors in Later Life? A Systematic Review and Cryptanalysis. Paediatr. Int. Child Health 2014, 35, 110–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinar, N.; Gurlek, A. Association between Novel Adipocytokines Adiponectin, Vaspin, Visfatin, and Thyroid: An Experimental and Clinical Update. Endocr. Connect. 2013, 2, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visentin, S.; Lapolla, A.; Londero, A.P.; Cosma, C.; Dalfrà, M.; Camerin, M.; Faggian, D.; Plebani, M.; Cosmi, E. Adiponectin Levels Are Reduced While Markers of Systemic Inflammation and Aortic Remodelling Are Increased in Intrauterine Growth Restricted Mother-Child Couple. Biomed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 401595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasshauer, M.; Blüher, M. Adipokines in health and disease. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2015, 36, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehzad, A.; Iqbal, W.; Shehzad, O.; Lee, Y.S. Adiponectin: Regulation of Its Production and Its Role in Human Diseases. Hormones 2012, 11, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahl, S.; Guenther, M.; Zhao, S.; James, R.; Marks, J.; Szabo, A.; Kidambi, S. Adiponectin Levels Differentiate Metabolically Healthy vs Unhealthy among Obese and Nonobese White Individuals. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 100, 4172–4180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwiat, V.R.; Reis, G.; Valera, I.C.; Parvatiyar, K.; Parvatiyar, M.S. Autoimmunity as a Sequela to Obesity and Systemic Inflammation. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadge, A.A.; Khaire, A.A. Leptin as a Predictive Marker for Metabolic Syndrome. Cytokine 2019, 121, 154735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zachariah, J.P.; Hwang, S.; Hamburg, N.M.; Benjamin, E.J.; Larson, M.G.; Levy, D.; Vita, J.A.; Sullivan, L.M.; Mitchell, G.F.; Vasan, R.S. Circulating Adipokines and Vascular Function. Hypertension 2016, 67, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, L.E.; Sullivan, J.C. Sex Differences in Obesity-Induced Hypertension and Vascular Dysfunction: A Protective Role for Estrogen in Adipose Tissue Inflammation? Am. J. Physiol.-Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2016, 311, R714–R720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, H.; Bhat, J.A.; Bhat, M.H.; Rashid, M.; Jan, R.; Afroze, D. Leptin in Obesity and Hypertension. Arter. Hypertens. 2022, 26, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Liu, Q. Relationship between 11β-HSD2 mRNA and insulin sensitivity in term small-for-gestational age neonates after birth. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2016, 8, 928–932. [Google Scholar]
- Farid, S.D.; Najati, N.; Gharebaghi, M.M.; Haghjo, A.G.; Ghojazadeh, M. Resistin in cord blood of small for gestation age and appropriate for gestation age term neonates. Iran. J. Pediatr. 2013, 23, 659–663. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Xu, L.; Zhu, W.; Wu, Y.; Xu, M.; Wang, Z. Impact of cord blood adiponectin and leptin levels and maternal obesity on birth weight of infants born to women with gestational diabetes mellitus. J. Reprod. Med. 2017, 62, 179–183. [Google Scholar]
- Orlando, A.; Nava, E.; Giussani, M.; Genovesi, S. Adiponectin and cardiovascular risk. From pathophysiology to clinic: Focus on children and adolescents. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3228. [Google Scholar]
- Deibert, C.; Ferrari, N.; Flöck, A.; Merz, W.M.; Gembruch, U.; Lehmacher, W.; Ehrhardt, C.; Graf, C. Adipokine-Myokine-Hepatokine Compartment-System in Mothers and Children: An Explorative Study. Contemp. Clin. Trials Commun. 2016, 3, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Simpson, J.; Smith, A.D.A.C.; Fraser, A.; Sattar, N.; Lindsay, R.S.; Ring, S.M.; Tilling, K.; Davey Smith, G.; Lawlor, D.A.; Nelson, S.M. Programming of Adiposity in Childhood and Adolescence: Associations with Birth Weight and Cord Blood Adipokines. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 102, 499–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volberg, V.; Heggeseth, B.; Harley, K.; Huen, K.; Yousefi, P.; Davé, V.; Tyler, K.; Vedar, M.; Eskenazi, B.; Holland, N. Adiponectin and Leptin Trajectories in Mexican-American Children from Birth to 9 Years of Age. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e77964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindström, L.; Ahlsson, F.; Lundgren, M.; Bergman, E.; Lampa, E.; Wikström, A.-K. Growth Patterns during Early Childhood in Children Born Small for Gestational Age and Moderate Preterm. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 11578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cianfarani, S.; Martinez, C.; Maiorana, A.; Scirè, G.; Spadoni, G.L.; Boemi, S. Adiponectin Levels Are Reduced in Children Born Small for Gestational Age and Are Inversely Related to Postnatal Catch-up Growth. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2004, 89, 1346–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Li, Y.; Chen, Q.; Chen, H.; Ma, H.; Su, Z.; Du, M. Low Serum Adiponectin Levels Are Associated with Reduced Insulin Sensitivity and Lipid Disturbances in Short Children Born Small for Gestational Age. Clin. Endocrinol. 2014, 83, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-J. Metabolic Syndrome in Children and Adolescents Born Premature and Small-for-Gestational Age: A Scenario of Developmental Origins of Health and Disease (Dohad). Pediatr. Neonatol. 2018, 59, 109–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boöttner, A.; Kratzsch, J.; Muöller, G.; Kapellen, T.M.; Bluöher, S.; Keller, E.; Bluöher, M.; Kiess, W. Gender Differences of Adiponectin Levels Develop during the Progression of Puberty and Are Related to Serum Androgen Levels. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2004, 89, 4053–4061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.-K.; Ahima, R.S. Physiology of Leptin: Energy Homeostasis, Neuroendocrine Function and Metabolism. Metabolism 2015, 64, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grajda, A.; Kułaga, Z.; Gurzkowska, B.; Wojtyło, M.; Góźdź, M.; Litwin, M. Preschool Children Blood Pressure Percentiles by Age and Height. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2016, 31, 400–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jornayvaz, F.R.; Vollenweider, P.; Bochud, M.; Mooser, V.; Waeber, G.; Marques-Vidal, P. Low Birth Weight Leads to Obesity, Diabetes and Increased Leptin Levels in Adults: The Colaus Study. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2016, 15, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazaki-Tovi, S.; Kasher-Meron, M.; Hemi, R.; Haas, J.; Gat, I.; Lantsberg, D.; Hendler, I.; Kanety, H. Chemerin Is Present in Human Cord Blood and Is Positively Correlated with Birthweight. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2012, 207, 412-e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Melo, A.S.; Bettiol, H.; da Silva, A.A.; Rosa-e-Silva, A.C.; Cardoso, V.C.; dos Reis, R.M.; Ferriani, R.A.; Barbieri, M.A.; Vieira, C.S. Small for Gestational Age Babies Are Not Related to Changes in Markers of Adipose Tissue Dysfunction during Reproductive Age. Early Hum. Dev. 2014, 90, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Challa, A.S.; Evagelidou, E.N.; Cholevas, V.I.; Kiortsis, D.N.; Giapros, V.I.; Drougia, A.A.; Andronikou, S.K. Growth Factors and Adipocytokines in Prepubertal Children Born Small for Gestational Age. Diabetes Care 2009, 32, 714–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evagelidou, E.N.; Giapros, V.I.; Challa, A.S.; Kiortsis, D.N.; Tsatsoulis, A.A.; Andronikou, S.K. Serum Adiponectin Levels, Insulin Resistance, and Lipid Profile in Children Born Small for Gestational Age Are Affected by the Severity of Growth Retardation at Birth. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2007, 156, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kistner, A.; Vanpée, M.; Hall, K. Leptin May Enhance Hepatic Insulin Sensitivity in Children and Women Born Small for Gestational Age. Early Hum. Dev. 2013, 2, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giapros, V.; Vavva, E.; Siomou, E.; Kolios, G.; Tsabouri, S.; Cholevas, V.; Bairaktari, E.; Tzoufi, M.; Challa, A. Low-birth-weight, but not catch-up growth, correlates with insulin resistance and resistin level in SGA infants at 12 months. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2017, 30, 1771–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima-Ishii, K.; Toda, N.; Okubo, K.; Tocan, V.; Ohyama, N.; Makimura, M.; Matsuo, T.; Ochiai, M.; Ohga, S.; Ihara, K. Metabolic and immunological assessment of small-for-gestational-age children during one-year treatment with growth hormone: The clinical impact of apolipoproteins. Endocr. J. 2018, 65, 449–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.-Z.; Deng, H.; Su, Z.; Li, Y.-H.; Ma, H.-M.; Chen, H.-S.; Du, M.-L. Insulin Resistance and Adiponectin Levels Are Associated with Height Catch-up Growth in Pre-Pubertal Chinese Individuals Born Small for Gestational Age. Nutr. Meta. 2012, 9, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, J.M.; Park, H.K.; Yang, S.; Hwang, I.T. Influence of Catch-up Growth on IGFBP-2 Levels and Association between IGFBP-2 and Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Korean Children Born SGA. Endocr. J. 2012, 59, 725–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stawerska, R.; Szałapska, M.; Hilczer, M.; Lewiński, A. Ghrelin, Insulin-like Growth Factor I and Adipocytokines Concentrations in Born Small for Gestational Age Prepubertal Children after the Catch-up Growth. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 29, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martos-Moreno, G.Á.; Barrios, V.; Sáenz de Pipaón, M.; Pozo, J.; Dorronsoro, I.; Martínez-Biarge, M.; Quero, J.; Argente, J. Influence of Prematurity and Growth Restriction on the Adipokine Profile, IGF1, and Ghrelin Levels in Cord Blood: Relationship with Glucose Metabolism. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2009, 161, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, S. Adiponectin and Resistin Levels in Umbilical Serum of Term Neonates and Relation to Birth Weight. Neonat. Pediatr. Med. 2017, 03, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozzola, E.; Meazza, C.; Arvigo, M.; Travaglino, P.; Pagani, S.; Stronati, M.; Gasparoni, A.; Bianco, C.; Bozzola, M. Role of Adiponectin and Leptin on Body Development in Infants during the First Year of Life. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2010, 36, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buck, C.O.; Eliot, M.N.; Kelsey, K.T.; Chen, A.; Kalkwarf, H.; Lanphear, B.P.; Braun, J.M. Neonatal Adipocytokines and Longitudinal Patterns of Childhood Growth. Obesity 2019, 27, 1323–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theodore, R.F.; Broadbent, J.; Nagin, D.; Ambler, A.; Hogan, S.; Ramrakha, S.; Cutfield, W.; Williams, M.J.A.; Harrington, H.L.; Moffitt, T.E.; et al. Childhood to Early-Midlife Systolic Blood Pressure Trajectories. Hypertension 2015, 66, 1108–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huxley, R.R.; Shiell, A.W.; Law, C.M. The Role of Size at Birth and Postnatal Catch-up Growth in Determining Systolic Blood Pressure. J. Hypertens. 2000, 18, 815–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Yu, L.; Zhou, L. Association between Serum Resistin Concentration and Hypertension: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 41529–41537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, A.F.; Frankfurt, J.A.; Heyne, R.J.; Rosenfeld, C.R. Biomarkers of Adiposity Are Elevated in Preterm Very-Low-Birth-Weight Infants at 1, 2, and 3 y of Age. Pediatr. Res. 2017, 81, 780–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Karakosta, P.; Roumeliotaki, T.; Chalkiadaki, G.; Sarri, K.; Vassilaki, M.; Venihaki, M.; Malliaraki, N.; Kampa, M.; Castanas, E.; Kogevinas, M.; et al. Cord Blood Leptin Levels in Relation to Child Growth Trajectories. Metabolism 2016, 65, 874–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
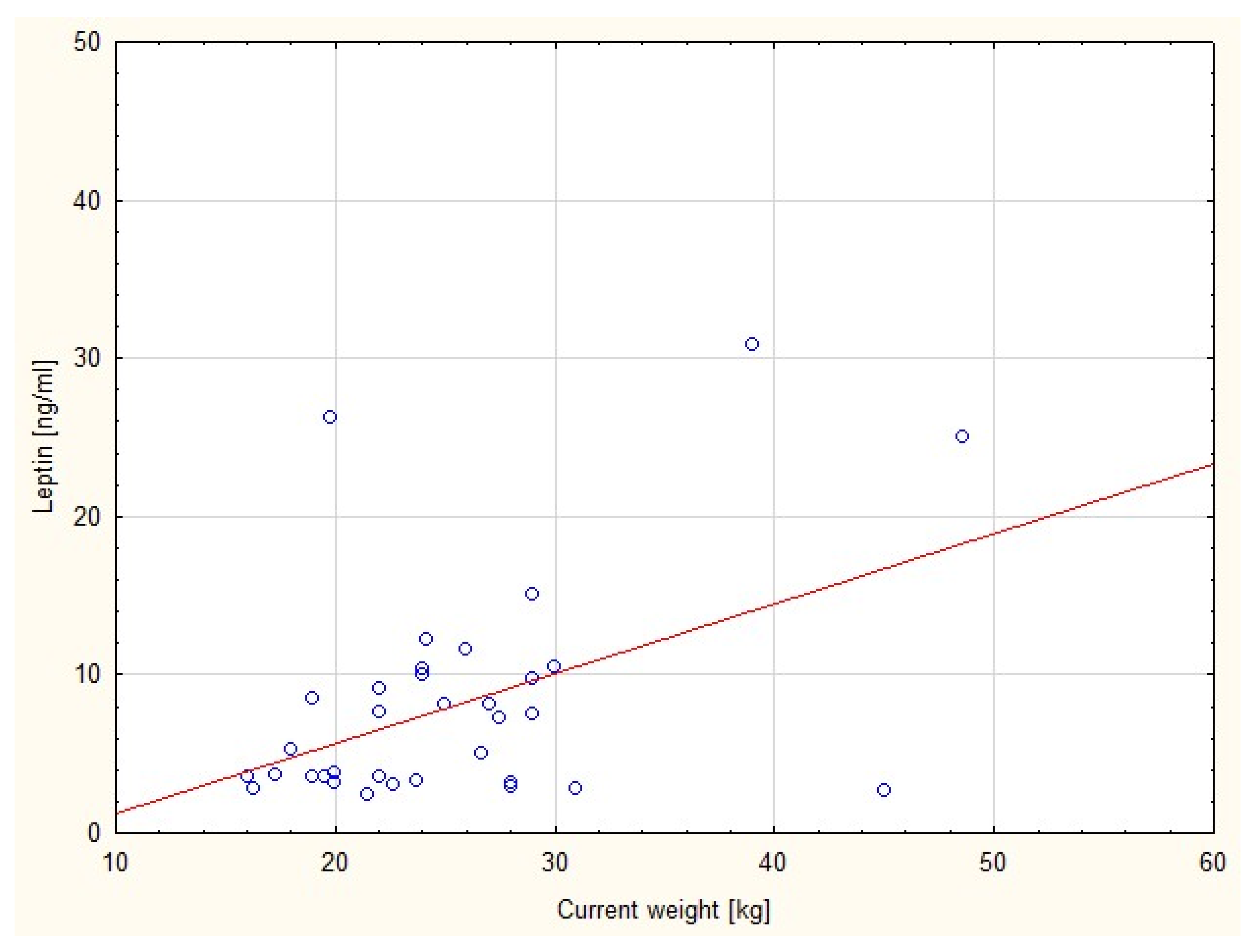
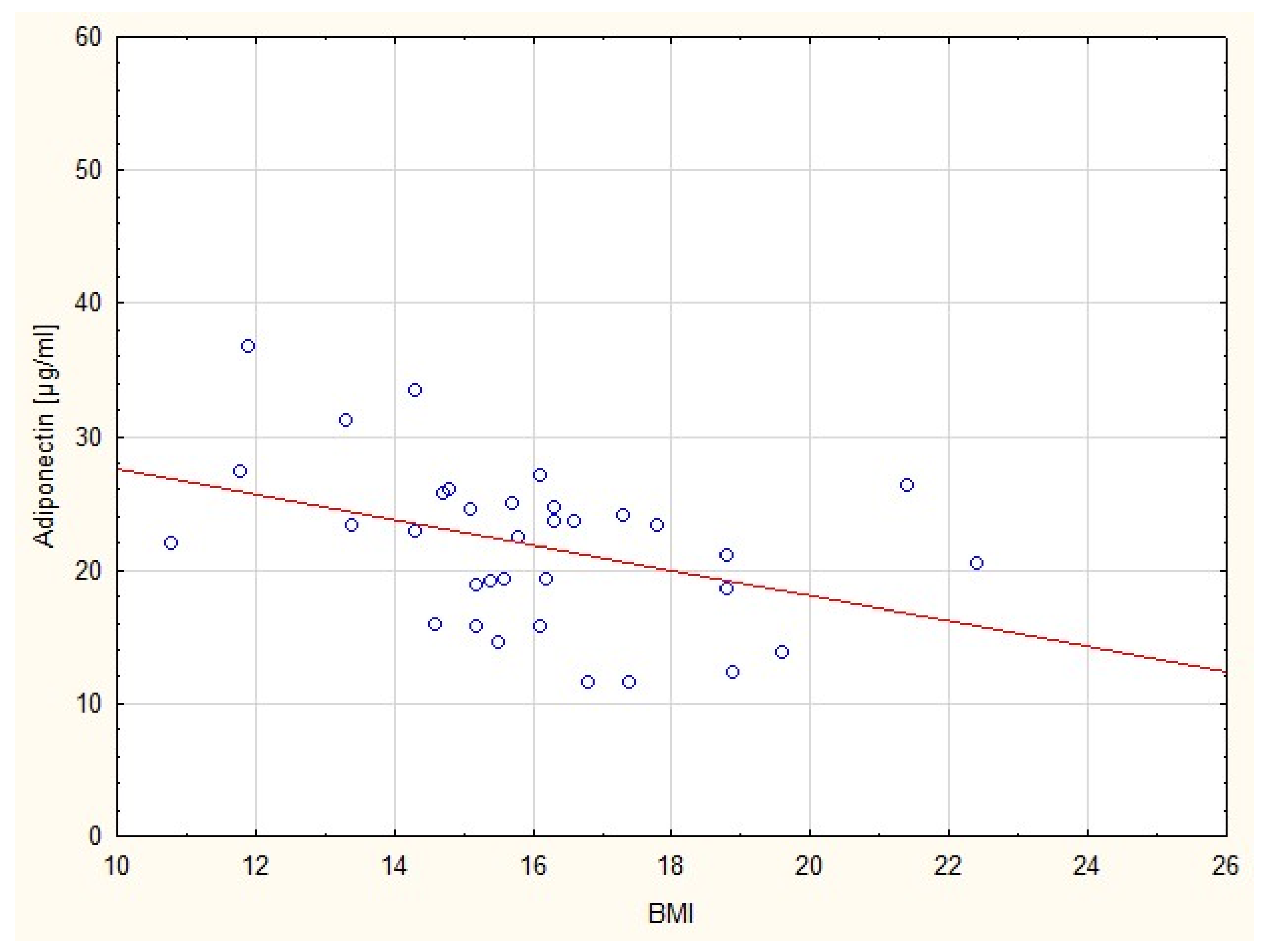
| Parameter | SGA a Group (N c = 35) Median (25th Percentile, 75th Percentile) | AGA b Group (N c = 25) Median (25th Percentile, 75th Percentile) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex (M e/F f) | 17/18 | 11/14 | NS d |
| Age on examination | 8 (7, 9) | 9 (8, 12) | NS d |
| Birthweight (g) | 2700 (2480, 2730) | 3100 (3000, 3550) | *** p < 0.001 |
| Gestational age (hbd g) | 39 (38, 40) | 39 (38, 40) | NS d |
| Current weight (kg) | 24 (20, 28) | 23.7 (21.2, 23.9) | NS d |
| BMI h (kg/m2) | 15.7 (14.7, 17.3) | 14.4 (13.7, 15.4) | *** p < 0.005 |
| Parameter | SGA a Group (N c = 35) Median (25th Percentile, 75th Percentile) | AGA b Group (N c = 25) Median (25th Percentile, 75th Percentile) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Adiponectin [µg/mL] | 22.84 (18.54, 24.96) | 18.85 (10.16, 21.93) | * p < 0.05 (p = 0.0134) |
| Leptin [ng/mL] | 5.33 (3.16, 9.98) | 4.20 (1.57, 6.50) | * p < 0.05 (p = 0.0415) |
| Resistin [ng/mL] | 2.07 (1.74, 2.74) | 1.94 (1.66, 2.69) | NS d (p = 0.8858) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zamojska, J.; Niewiadomska-Jarosik, K.; Wosiak, A.; Gruca, M.; Smolewska, E. Serum Adipocytokines Profile in Children Born Small and Appropriate for Gestational Age—A Comparative Study. Nutrients 2023, 15, 868. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15040868
Zamojska J, Niewiadomska-Jarosik K, Wosiak A, Gruca M, Smolewska E. Serum Adipocytokines Profile in Children Born Small and Appropriate for Gestational Age—A Comparative Study. Nutrients. 2023; 15(4):868. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15040868
Chicago/Turabian StyleZamojska, Justyna, Katarzyna Niewiadomska-Jarosik, Agnieszka Wosiak, Marta Gruca, and Elżbieta Smolewska. 2023. "Serum Adipocytokines Profile in Children Born Small and Appropriate for Gestational Age—A Comparative Study" Nutrients 15, no. 4: 868. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15040868
APA StyleZamojska, J., Niewiadomska-Jarosik, K., Wosiak, A., Gruca, M., & Smolewska, E. (2023). Serum Adipocytokines Profile in Children Born Small and Appropriate for Gestational Age—A Comparative Study. Nutrients, 15(4), 868. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15040868






