Dietary Quality Indices in Early Pregnancy and Rate of Gestational Weight Gain among a Prospective Multi-Racial and Ethnic Cohort
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
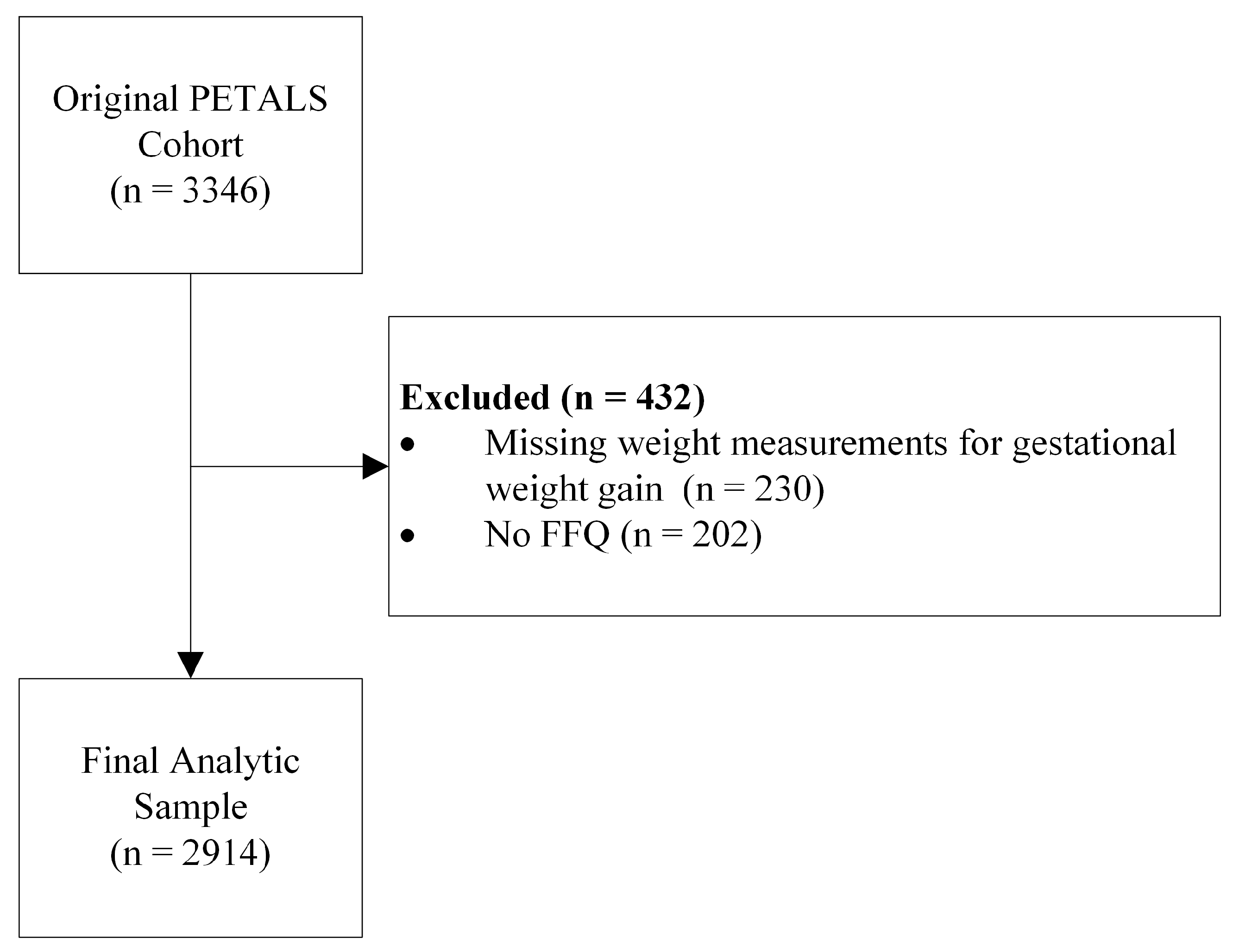
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Study Variables
2.2.1. Diet Quality Indices
2.2.2. Rate of Gestational Weight Gain
2.2.3. Covariates
2.3. Statistical Analysis
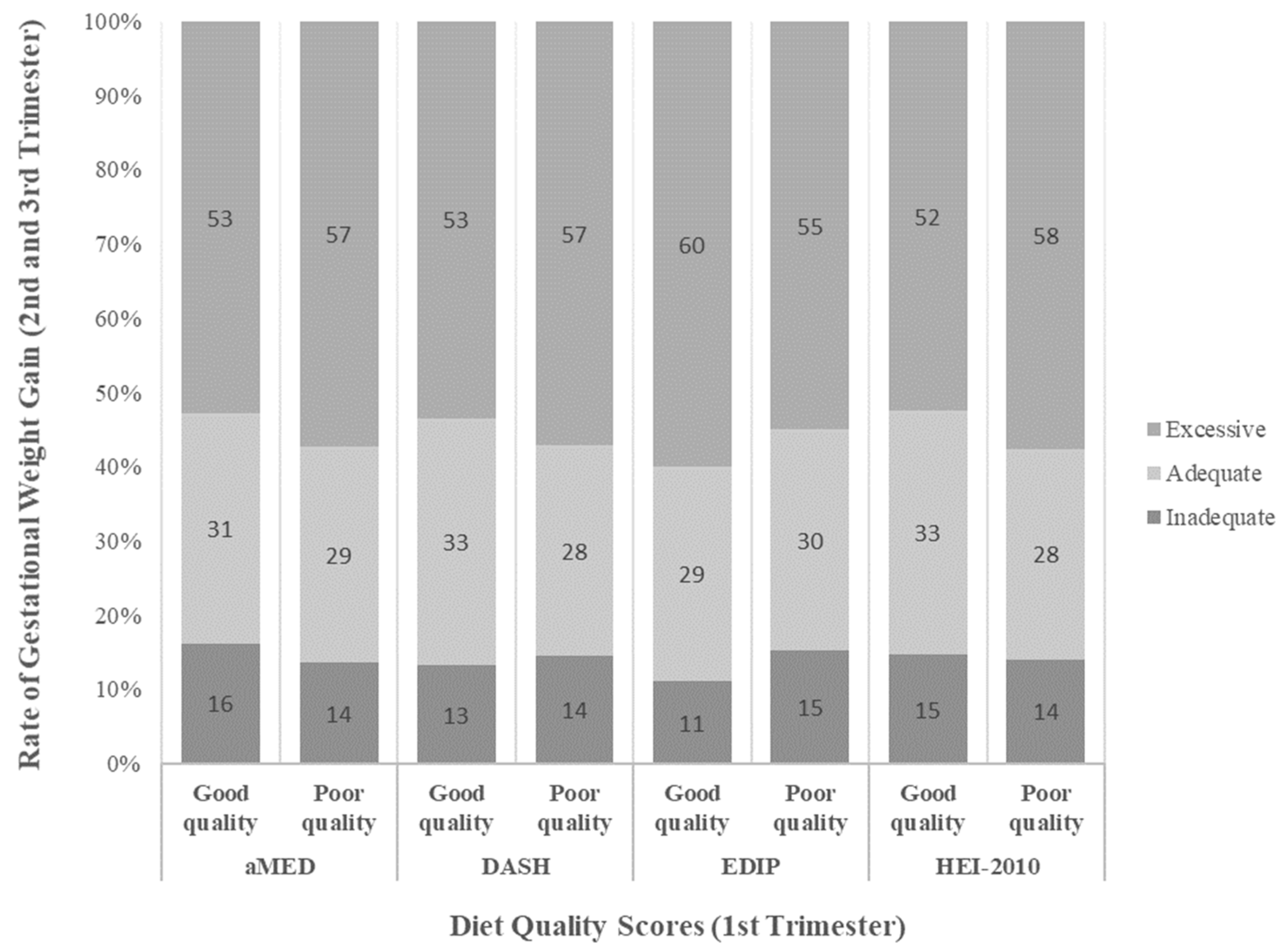
3. Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| aMED | Alternate Mediterranean Diet |
| DASH | Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension |
| EDIP | Empirical Dietary Inflammatory Pattern |
| EHR | Electronic health records |
| GWG | Gestational weight gain |
| HEI | Healthy Eating Index |
| IOM | Institute of Medicine |
References
- Rasmussen, K.M.; Catalano, P.M.; Yaktine, A.L. New guidelines for weight gain during pregnancy: What obstetrician/gynecologists should know. Curr. Opin. Obstet. Gynecol. 2009, 21, 521–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zilko, C.E.M.; Rehkopf, D.; Abrams, B. Association of maternal gestational weight gain with short- and long-term maternal and child health outcomes. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2010, 202, e571–e578. [Google Scholar]
- Mamun, A.A.; Kinarivala, M.; O’Callaghan, M.J.; Williams, G.M.; Najman, J.M.; Callaway, L.K. Associations of excess weight gain during pregnancy with long-term maternal overweight and obesity: Evidence from 21 y postpartum follow-up. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 91, 1336–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridhar, S.B.; Darbinian, J.; Ehrlich, S.F.; Markman, M.A.; Gunderson, E.P.; Ferrara, A.; Hedderson, M.M. Maternal gestational weight gain and offspring risk for childhood overweight or obesity. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2014, 211, 259.e1–259.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oken, E.; Rifas-Shiman, S.L.; Field, A.E.; Frazier, A.L.; Gillman, M.W. Maternal gestational weight gain and offspring weight in adolescence. Obstet. Gynecol. 2008, 112, 999–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oken, E.; Taveras, E.M.; Kleinman, K.P.; Rich-Edwards, J.W.; Gillman, M.W. Gestational weight gain and child adiposity at age 3 years. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2007, 196, 322.e1–322.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kominiarek, M.A.; Peaceman, A.M. Gestational weight gain. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2017, 217, 642–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudenhausen, J.W.; Grünebaum, A.; Kirschner, W. Prepregnancy body weight and gestational weight gain—Recommendations and reality in the USA and in Germany. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2015, 213, 591–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tielemans, M.J.; Garcia, A.H.; Peralta Santos, A.; Bramer, W.M.; Luksa, N.; Luvizotto, M.J.; Moreira, E.; Topi, G.; de Jonge, E.A.; Visser, T.L.; et al. Macronutrient composition and gestational weight gain: A systematic review. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 103, 83–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, M.; Boushey, C.J.; Shvetsov, Y.B.; Setiawan, V.W.; Paik, H.Y.; Wilkens, L.R.; Le Marchand, L.; Park, S.Y. Changes in diet quality and body weight over 10 years: The Multiethnic Cohort Study. Br. J. Nutr. 2021, 126, 1389–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoody, E.E.; Spahn, J.M.; Casavale, K.O. The Pregnancy and Birth to 24 Months Project: A series of systematic reviews on diet and health. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 109 (Suppl. 7), 685S–697S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, D.; Bianchi, L.; Chung, H.; Weatherspoon, L.; Song, W.O. Is gestational weight gain associated with diet quality during pregnancy? Matern. Child Health J. 2014, 18, 1433–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlaff, R.A.; Baruth, M.; Deere, S.J.; Boggs, A.; Odabasic, A. Associations between prenatal diet quality and gestational weight gain. Nutr. Health 2020, 26, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabung, F.K.; Smith-Warner, S.A.; Chavarro, J.E.; Wu, K.; Fuchs, C.S.; Hu, F.B.; Chan, A.T.; Willett, W.C.; Giovannucci, E.L. Development and Validation of an Empirical Dietary Inflammatory Index. J. Nutr. 2016, 146, 1560–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabung, F.K.; Satija, A.; Fung, T.T.; Clinton, S.K.; Giovannucci, E.L. Long-Term Change in both Dietary Insulinemic and Inflammatory Potential Is Associated with Weight Gain in Adult Women and Men. J. Nutr. 2019, 149, 804–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Hedderson, M.M.; Feng, J.; Mevi, A.A.; Ferrara, A. The Pregnancy Environment and Lifestyle Study (PETALS): A population-based longitudinal multi-racial birth cohort. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2017, 17, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Block, G.; Hartman, A.M.; Dresser, C.M.; Carroll, M.D.; Gannon, J.; Gardner, L. A data-based approach to diet questionnaire design and testing. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1986, 124, 453–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Block, G.; Woods, M.; Potosky, A.; Clifford, C. Validation of a self-administered diet history questionnaire using multiple diet records. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 1990, 43, 1327–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willett, W.C.; Howe, G.R.; Kushi, L.H. Adjustment for total energy intake in epidemiologic studies. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1997, 65 (Suppl. S4), 1220S–1228S; discussion 1229S–1231S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denny, C.H.; Acero, C.S.; Naimi, T.S.; SY, K. Consumption of Alcohol Beverages and Binge Drinking Among Pregnant Women Aged 18–44 Years—United States, 2015–2017. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2019, 68, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Hedderson, M.M.; Sridhar, S.; Xu, F.; Feng, J.; Ferrara, A. Poor diet quality in pregnancy is associated with increased risk of excess fetal growth: A prospective multi-racial/ethnic cohort study. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2019, 48, 423–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guenther, P.M.; Casavale, K.O.; Reedy, J.; Kirkpatrick, S.I.; Hiza, H.A.; Kuczynski, K.J.; Kahle, L.L.; Krebs-Smith, S.M. Update of the Healthy Eating Index: HEI-2010. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2013, 113, 569–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fung, T.T.; Chiuve, S.E.; McCullough, M.L.; Rexrode, K.M.; Logroscino, G.; Hu, F.B. Adherence to a DASH-style diet and risk of coronary heart disease and stroke in women. Arch. Intern. Med. 2008, 168, 713–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fung, T.T.; Rexrode, K.M.; Mantzoros, C.S.; Manson, J.E.; Willett, W.C.; Hu, F.B. Mediterranean diet and incidence of and mortality from coronary heart disease and stroke in women. Circulation 2009, 119, 1093–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehrhardt, C.; Deibert, C.; Flöck, A.; Merz, W.M.; Gembruch, U.; Bockler, A.; Dötsch, J.; Joisten, C.; Ferrari, N. Impact of Diet Quality during Pregnancy on Gestational Weight Gain and Selected Adipokines-Results of a German Cross-Sectional Study. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graziano, C.; Hansen, J.; Horgan, A.; Moe, E.; McLain, M.; Goldberg, L.; Stadler, D. Use of automated self-administered 24-hour recalls (ASA24-2011) and diet quality scores to characterize women who met or Exceeded Weight Gain Recommendations during Pregnancy. Procedia Food Sci. 2015, 4, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagiou, P.; Tamimi, R.M.; Mucci, L.A.; Adami, H.O.; Hsieh, C.C.; Trichopoulos, D. Diet during pregnancy in relation to maternal weight gain and birth size. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 58, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, H.W.; Tovar, A.; McCurdy, K.; Vadiveloo, M. Associations between pre-pregnancy BMI, gestational weight gain, and prenatal diet quality in a national sample. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0224034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augustin, H.; Winkvist, A.; Bärebring, L. Poor Dietary Quality is Associated with Low Adherence to Gestational Weight Gain Recommendations among Women in Sweden. Nutrients 2020, 12, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Institute of Medicine (US); National Research Council (US); Committee to Reexamine IOM Pregnancy Weight Guidelines. Weight Gain During Pregnancy: Reexamining the Guidelines; Rasmussen, K.M., Yaktine, A.L., Eds.; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2009.
- Catalano, P.; Demouzon, S.H. Maternal obesity and metabolic risk to the offspring: Why lifestyle interventions may have not achieved the desired outcomes. Int. J. Obes. 2015, 39, 642–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Gallagher, A.E.; Carta, C.M.; Torres, M.E.; Moran, R.; Wilcox, S. Racial differences in gestational weight gain and pregnancy-related hypertension. Ann. Epidemiol. 2014, 24, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caulfield, L.E.; Witter, F.R.; Stoltzfus, R.J. Determinants of gestational weight gain outside the recommended ranges among black and white women. Obstet. Gynecol. 1996, 87, 760–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunst, K.J.; Wright, R.O.; DiGioia, K.; Enlow, M.B.; Fernandez, H.; Wright, R.J.; Kannan, S. Racial/ethnic and sociodemographic factors associated with micronutrient intakes and inadequacies among pregnant women in an urban US population. Public Health Nutr. 2014, 17, 1960–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siega-Riz, A.M.; Bodnar, L.M.; Savitz, D.A. What are pregnant women eating? Nutrient and food group differences by race. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2002, 186, 480–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodnar, L.M.; Simhan, H.N.; Parker, C.B.; Meier, H.; Mercer, B.M.; Grobman, W.A.; Haas, D.M.; Wing, D.A.; Hoffman, M.K.; Parry, S.; et al. Racial or Ethnic and Socioeconomic Inequalities in Adherence to National Dietary Guidance in a Large Cohort of US Pregnant Women. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2017, 117, 867–877.e863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howarth, N.C.; Saltzman, E.; Roberts, S.B. Dietary fiber and weight regulation. Nutr. Rev. 2001, 59, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rolls, B.J. Dietary energy density: Applying behavioural science to weight management. Nutr. Bull. 2017, 42, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludwig, D.S. Dietary glycemic index and obesity. J. Nutr. 2000, 130 (Suppl. 2S ), 280S–283S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rifas-Shiman, S.L.; Rich-Edwards, J.W.; Willett, W.C.; Kleinman, K.P.; Oken, E.; Gillman, M.W. Changes in dietary intake from the first to the second trimester of pregnancy. Paediatr. Perinat. Epidemiol. 2006, 20, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crozier, S.R.; Robinson, S.M.; Godfrey, K.M.; Cooper, C.; Inskip, H.M. Women’s dietary patterns change little from before to during pregnancy. J. Nutr. 2009, 139, 1956–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, M.M.; Reedy, J.; Krebs-Smith, S.M. American Diet Quality: Where It Is, Where It Is Heading, and What It Could Be. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2016, 116, 302–310.e301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Characteristic | n = 2914 |
|---|---|
| Age at delivery, years | |
| 18–24 | 444 (15.2%) |
| 25–29 | 754 (25.9%) |
| 30–34 | 1072 (36.8%) |
| 35 and older | 644 (22.1%) |
| Nulliparous, n (%) | 1339 (46%) |
| Pre-pregnancy BMI, kg/m2 | 27.0 (6.0) |
| Race and ethnicity, n (%) | |
| Asian/Pacific Islander | 690 (24%) |
| Black | 280 (9.6%) |
| Hispanic | 1175 (40%) |
| Other/Unknown | 94 (3.2%) |
| White | 675 (23%) |
| Education level, n (%) | |
| Less than high school | 79 (2.7%) |
| High school graduate or GED | 324 (11%) |
| Some college | 1069 (37%) |
| Completed 4-year college or higher | 1439 (49%) |
| Household income, n (%) | |
| Less than USD 50,000 per year | 910 (32%) |
| USD 50,000 to USD 99,999 per year | 911 (32%) |
| USD 100,000 to USD 149,999 per year | 531 (18%) |
| USD 150,000 and greater per year | 520 (18%) |
| Total energy intake, kcal/day | 1567.7 (734.8) |
| Physical activity, METs/week | 10.9 (14.2) |
| Dietary quality index score, mean (SD) | |
| HEI-2010 | 71 (10) |
| DASH | 24.0 (4.4) |
| aMED | 4.01 (1.79) |
| EDIP | −0.05 (0.45) |
| Gestational weight gain rate, n (%) | |
| Inadequate | 414 (14%) |
| Met | 860 (30%) |
| Excessive | 1640 (56%) |
| Diet Quality Index | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HEI-2010 1 | DASH 2 | aMED 3 | EDIP 4 | |
| Excessive GWG | ||||
| Good quality | 1 (reference) | 1 (reference) | 1 (reference) | 1 (reference) |
| Poor quality | 1.03 (1.00, 1.06) | 1.02 (0.99, 1.05) | 1.01 (0.98, 1.04) | 1.00 (0.97, 1.03) |
| Inadequate GWG | ||||
| Good quality | 1 (reference) | 1 (reference) | 1 (reference) | 1 (reference) |
| Poor quality | 1.00 (0.92, 1.09) | 0.94 (0.86, 1.03) | 1.04 (0.94, 1.15) | 0.98 (0.89, 1.08) |
| Pre-Pregnancy BMI | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| BMI < 25.0 n = 1066 | 25.0 ≤ BMI ≤ 29.9 n = 763 | BMI ≥ 30.0 n = 671 | |
| Excessive GWG | |||
| Good quality | Ref | Ref | Ref |
| Poor quality | 1.05 (1.00, 1.10) | 1.04 (0.97, 1.06) | 1.01 (0.97, 1.06) |
| Race and Ethnicity | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Asian and Pacific Islander n = 567 | Black, n = 246 | Hispanic, n = 1001 | Other or Unknown, n = 86 | White, n = 600 | |
| Excessive GWG | |||||
| Good quality | Ref | Ref | Ref | Ref | Ref |
| Poor quality | 1.00 (0.94, 1.06) | 1.14 (1.02, 1.28) | 0.99 (0.95, 1.03) | 1.15 (0.99, 1.35) | 1.07 (1.01, 1.12) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, E.F.; Zhu, Y.; Ferrara, A.; Hedderson, M.M. Dietary Quality Indices in Early Pregnancy and Rate of Gestational Weight Gain among a Prospective Multi-Racial and Ethnic Cohort. Nutrients 2023, 15, 835. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15040835
Liu EF, Zhu Y, Ferrara A, Hedderson MM. Dietary Quality Indices in Early Pregnancy and Rate of Gestational Weight Gain among a Prospective Multi-Racial and Ethnic Cohort. Nutrients. 2023; 15(4):835. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15040835
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Emily F., Yeyi Zhu, Assiamira Ferrara, and Monique M. Hedderson. 2023. "Dietary Quality Indices in Early Pregnancy and Rate of Gestational Weight Gain among a Prospective Multi-Racial and Ethnic Cohort" Nutrients 15, no. 4: 835. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15040835
APA StyleLiu, E. F., Zhu, Y., Ferrara, A., & Hedderson, M. M. (2023). Dietary Quality Indices in Early Pregnancy and Rate of Gestational Weight Gain among a Prospective Multi-Racial and Ethnic Cohort. Nutrients, 15(4), 835. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15040835






