The Efficacy of Panax ginseng for the Treatment of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Preclinical Studies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Data Extraction
2.4. Quality Assessment
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
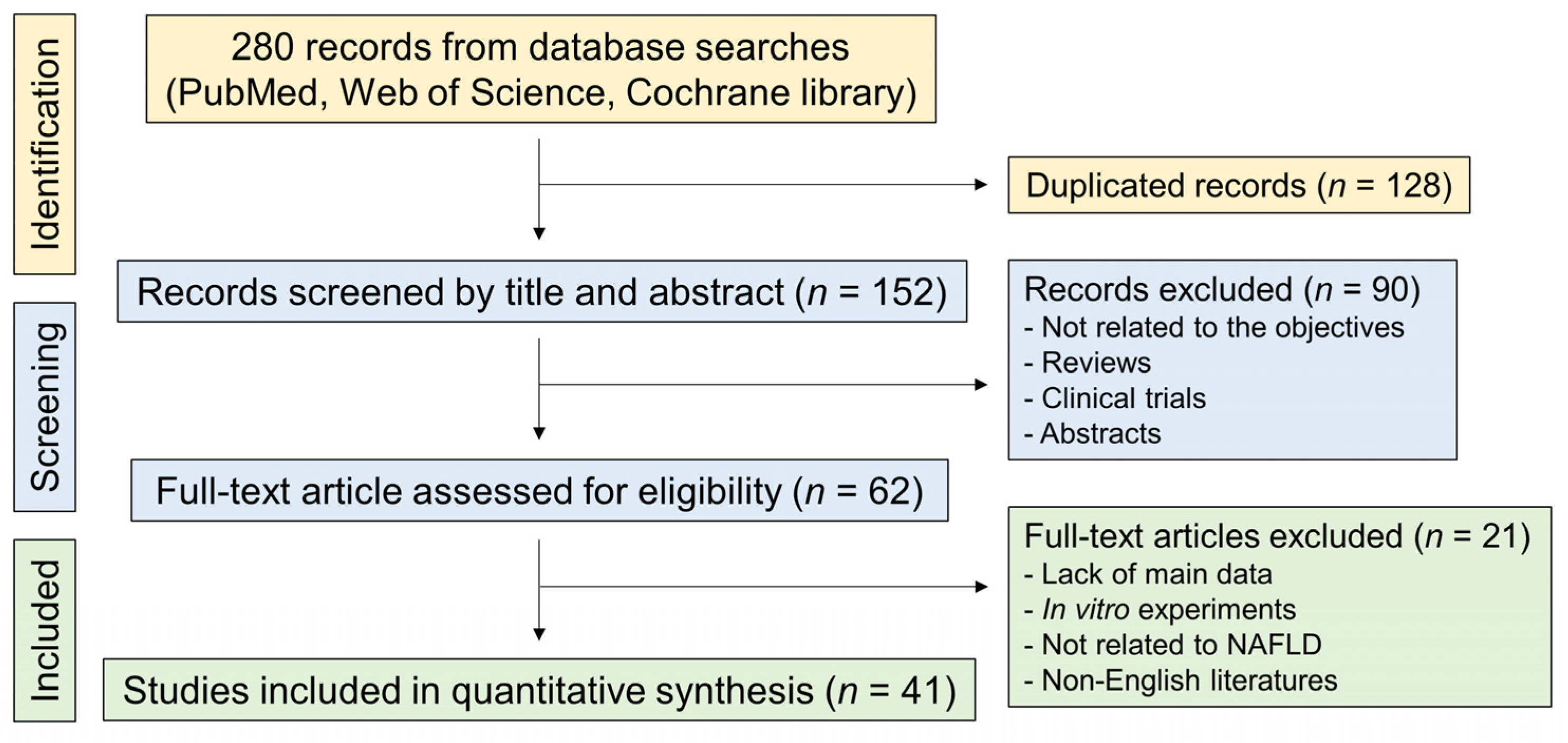
3.1. Study Identification and Selection
3.2. Study Characteristics
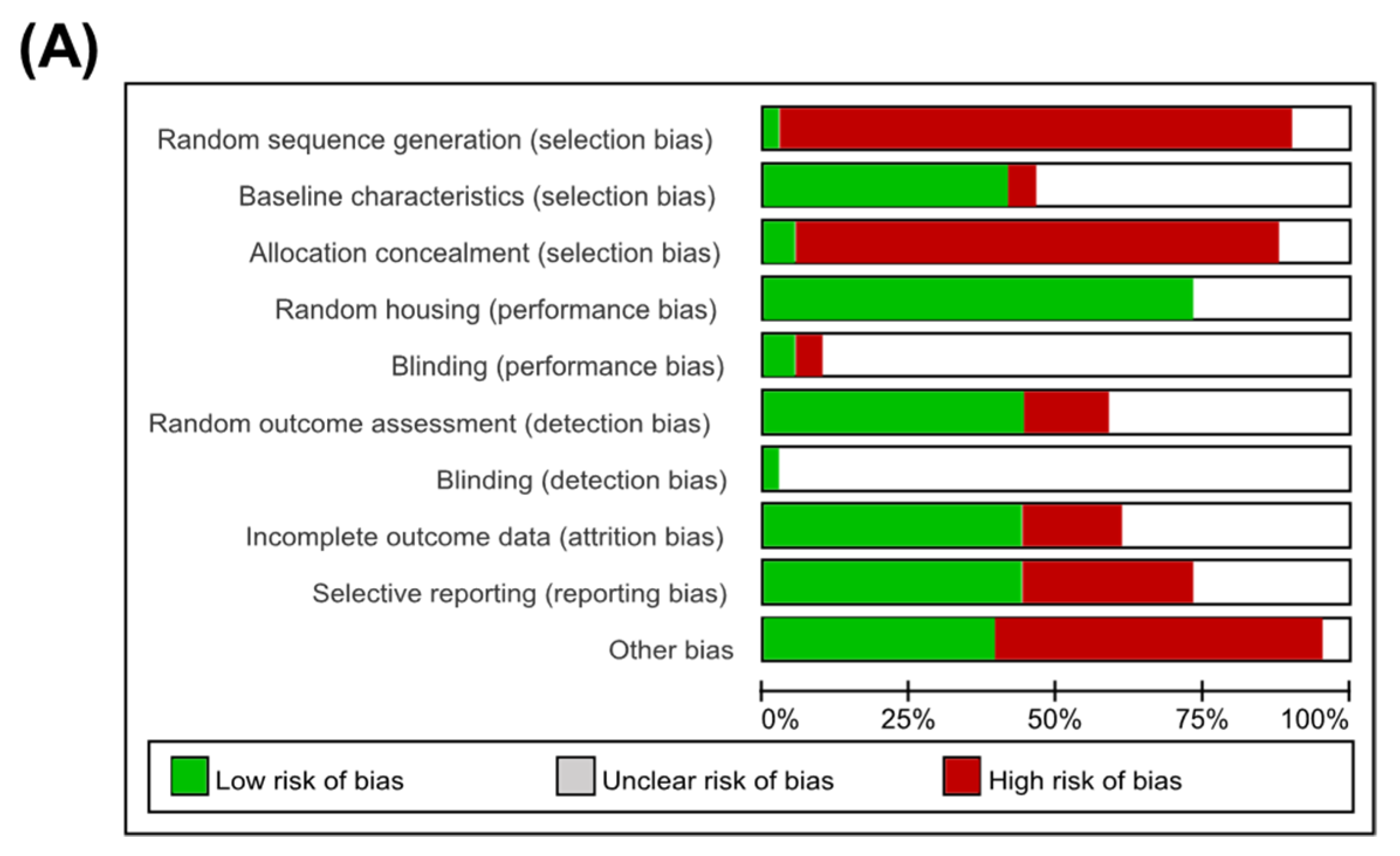
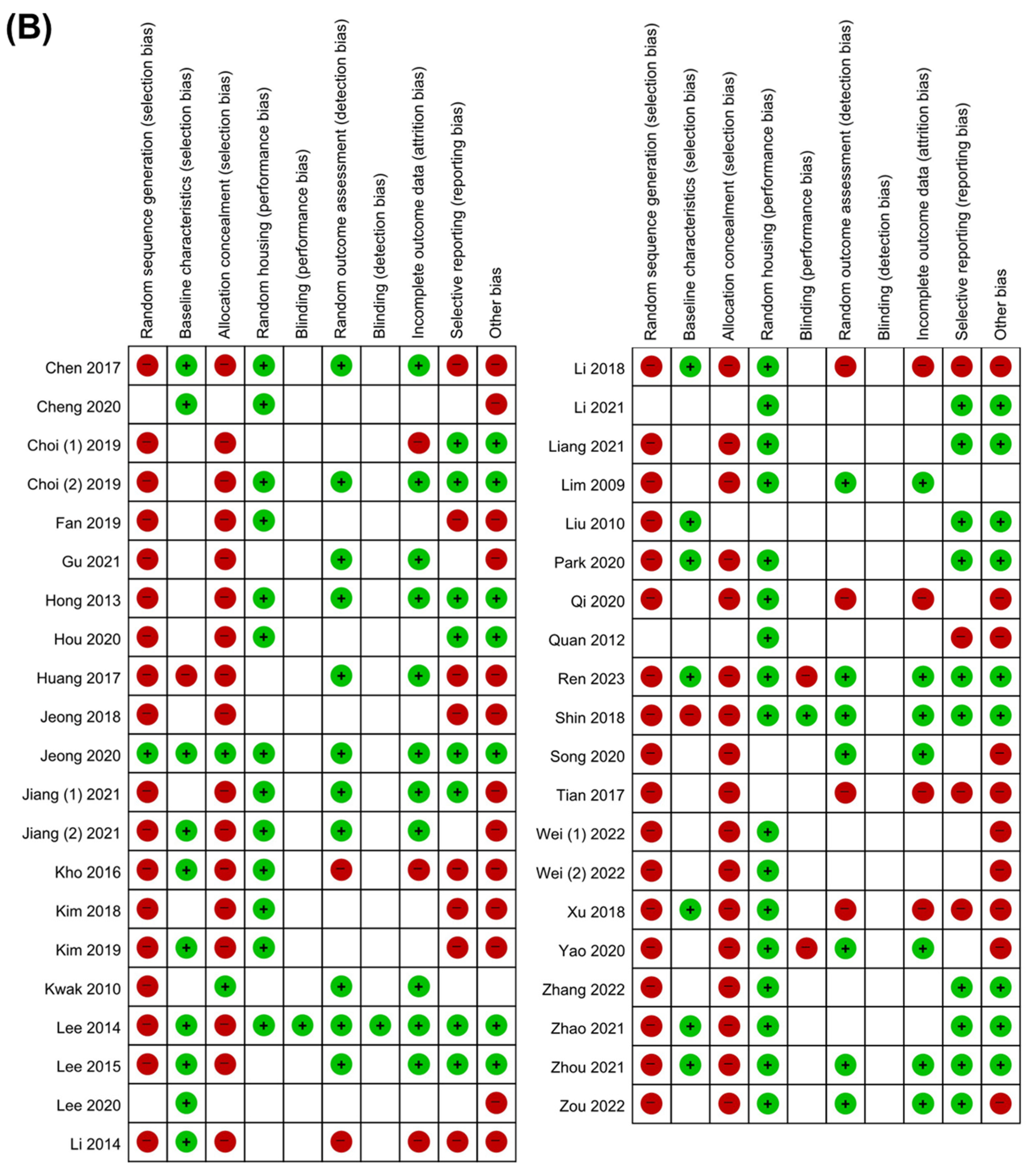
3.3. Quality Assessment
3.4. Primary Outcomes
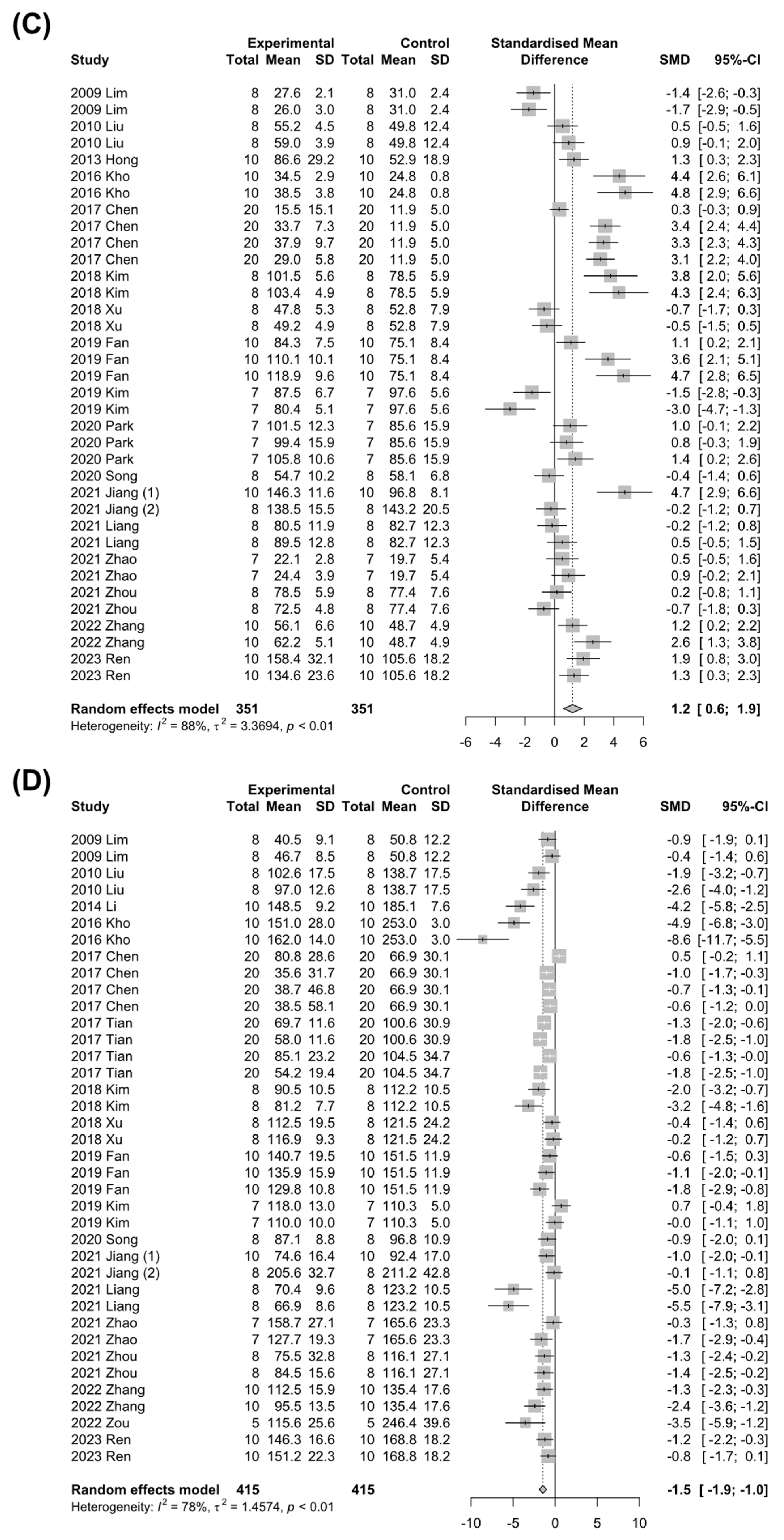
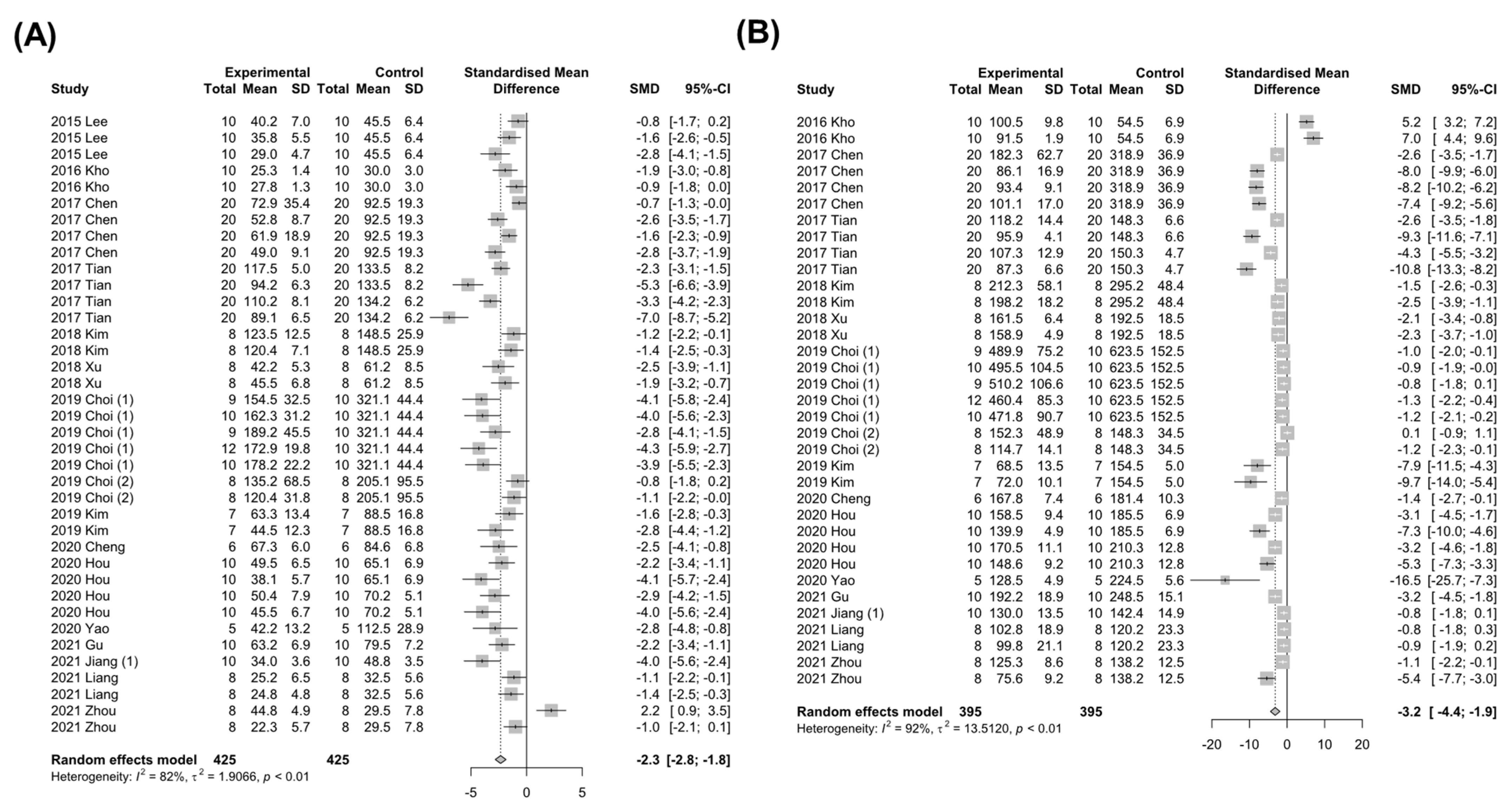
3.4.1. Markers for Liver Injury
3.4.2. Markers for Hepatic Lipid Metabolism
3.5. Subgroup Analysis
3.5.1. Subgroup Analysis in HFD-Induced NAFLD
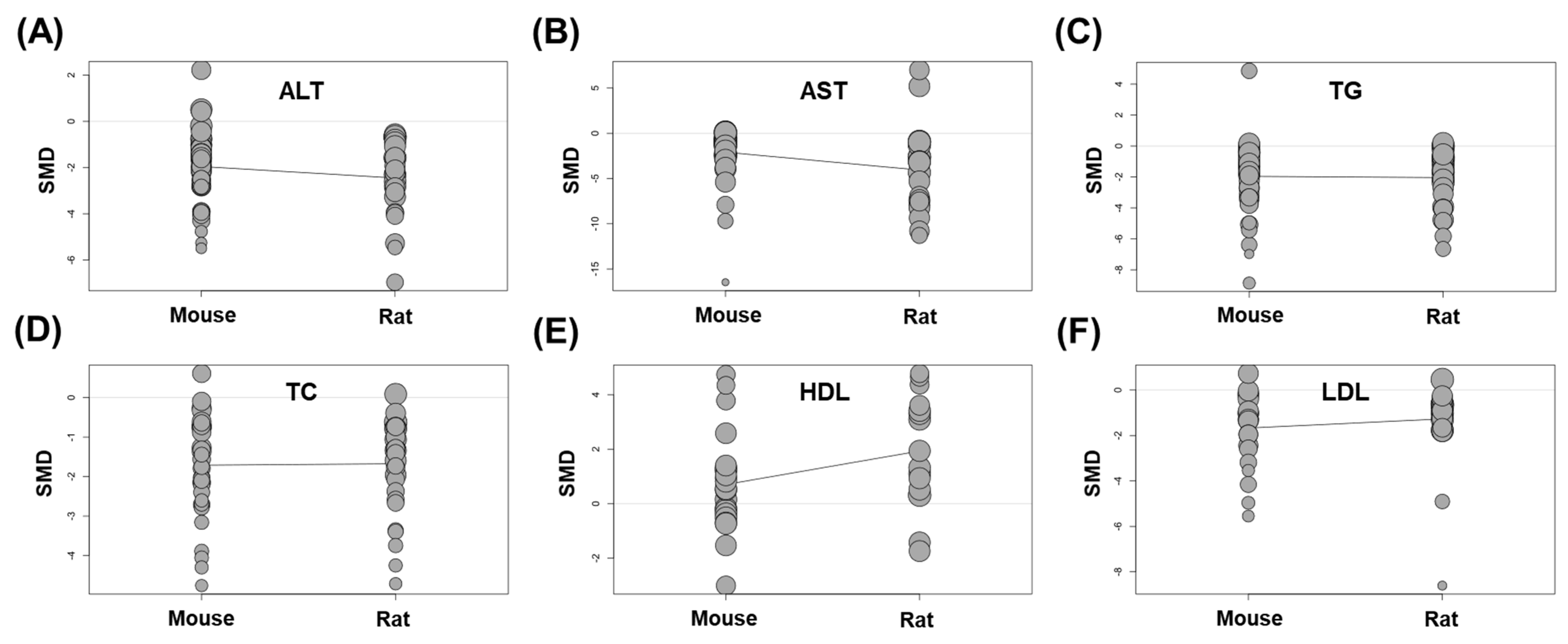
3.5.2. Subgroup Analysis According to the Animal Species
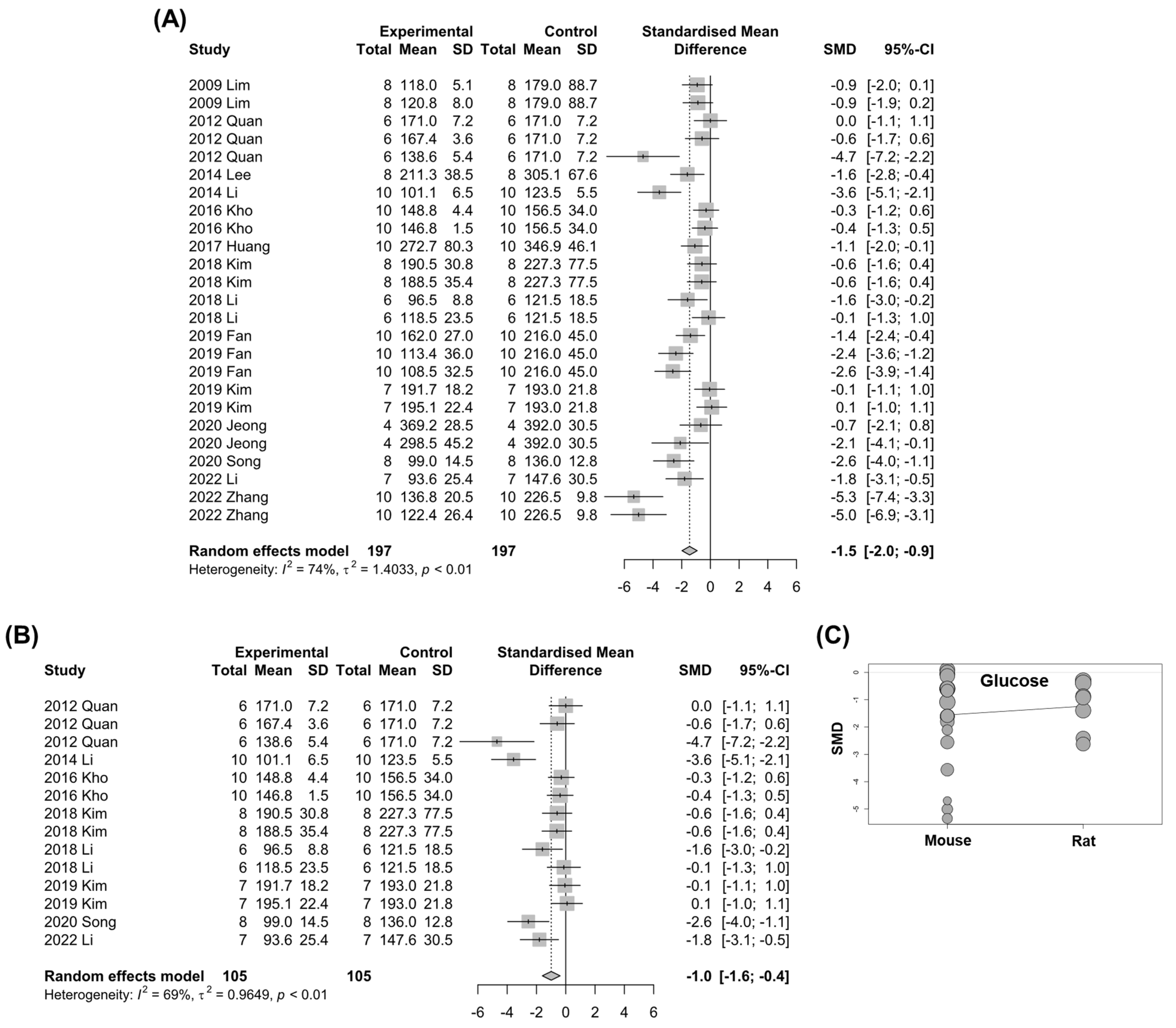
3.6. Fasting Blood Glucose
3.7. Publication Bias
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Friedman, S.L.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A.; Rinella, M.; Sanyal, A.J. Mechanisms of NAFLD development and therapeutic strategies. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 908–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, C.P.; James, O.F. Steatohepatitis: A tale of two “hits”? Gastroenterology 1998, 114, 842–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzzetti, E.; Pinzani, M.; Tsochatzis, E.A. The multiple-hit pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Metabolism 2016, 65, 1038–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arab, J.P.; Arrese, M.; Trauner, M. Recent Insights into the Pathogenesis of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2018, 13, 321–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockwell, S.; Trott, M.; Tully, M.; Shin, J.; Barnett, Y.; Butler, L.; McDermott, D.; Schuch, F.; Smith, L. Changes in physical activity and sedentary behaviours from before to during the COVID-19 pandemic lockdown: A systematic review. BMJ. Open. Sport. Exerc. Med. 2021, 7, e000960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannah, W.N., Jr.; Harrison, S.A. Lifestyle and Dietary Interventions in the Management of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2016, 61, 1365–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Zhou, K.; Jian, P.; Chang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Xiao, S.; Zhang, L. Ginsenosides Improve Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease via Integrated Regulation of Gut Microbiota, Inflammation and Energy Homeostasis. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 622841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H. Chemical Diversity of Panax ginseng, Panax quinquifolium, and Panax notoginseng. J. Ginseng. Res. 2012, 36, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratan, Z.A.; Haidere, M.F.; Hong, Y.H.; Park, S.H.; Lee, J.O.; Lee, J.; Cho, J.Y. Pharmacological potential of ginseng and its major component ginsenosides. J. Ginseng. Res. 2021, 45, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huu Tung, N.; Uto, T.; Morinaga, O.; Kim, Y.H.; Shoyama, Y. Pharmacological effects of ginseng on liver functions and diseases: A minireview. Evid. Based. Complement. Alternat. Med. 2012, 2012, 173297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.W.; Kim, H.N.; Shim, J.Y.; Yoo, B.Y.; Kim, D.H.; Lee, S.H.; Park, J.S.; Kim, M.J.; Yoo, J.H.; Cho, B.; et al. Safety and tolerability of Korean Red Ginseng in healthy adults: A multicenter, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. J. Ginseng. Res. 2018, 42, 571–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.K.; Kim, S.W.; Seo, H.W.; Hyun, S.H.; Kyung, J.S.; Youn, S.H.; So, S.H.; In, G.; Park, C.K.; Yi, E.C.; et al. Long-term evaluation of safety and biological effects of Korean Red Ginseng (Panax Ginseng): A long-term in vivo study. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2022, 22, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Yang, J.; Lv, Y.; Chen, J.; Yin, F.; Huang, J.; Zheng, Q. A Review of Ginseng Clinical Trials Registered in the WHO International Clinical Trials Registry Platform. Biomed. Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 1843142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseri, K.; Saadati, S.; Sadeghi, A.; Asbaghi, O.; Ghaemi, F.; Zafarani, F.; Li, H.B.; Gan, R.Y. The Efficacy of Ginseng (Panax) on Human Prediabetes and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, G.; Gong, J.; Lu, F.; Diao, Q.; Sun, J.; Zhang, K.; Tian, J.; Liu, J. Ginseng for Alzheimer’s Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2016, 16, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komishon, A.M.; Shishtar, E.; Ha, V.; Sievenpiper, J.L.; de Souza, R.J.; Jovanovski, E.; Ho, H.V.; Duvnjak, L.S.; Vuksan, V. The effect of ginseng (genus Panax) on blood pressure: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled clinical trials. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2016, 30, 619–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G.; Group, P. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooijmans, C.R.; Rovers, M.M.; de Vries, R.B.; Leenaars, M.; Ritskes-Hoitinga, M.; Langendam, M.W. SYRCLE’s risk of bias tool for animal studies. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2014, 14, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.; Yoon, J.W.; Choi, S.H.; Cho, B.J.; Kim, J.T.; Chang, H.S.; Park, H.S.; Park, K.S.; Lee, H.K.; Kim, Y.B.; et al. Effect of ginsam, a vinegar extract from Panax ginseng, on body weight and glucose homeostasis in an obese insulin-resistant rat model. Metabolism 2009, 58, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, Y.S.; Kyung, J.S.; Kim, J.S.; Cho, J.Y.; Rhee, M.H. Anti-hyperlipidemic effects of red ginseng acidic polysaccharide from Korean red ginseng. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2010, 33, 468–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Zhang, J.; Liu, W.; Kimura, Y.; Zheng, Y. Anti-Obesity effects of protopanaxdiol types of Ginsenosides isolated from the leaves of American ginseng (Panax quinquefolius L.) in mice fed with a high-fat diet. Fitoterapia 2010, 81, 1079–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, H.Y.; Yuan, H.D.; Jung, M.S.; Ko, S.K.; Park, Y.G.; Chung, S.H. Ginsenoside Re lowers blood glucose and lipid levels via activation of AMP-activated protein kinase in HepG2 cells and high-fat diet fed mice. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2012, 29, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.H.; Suk, K.T.; Choi, S.H.; Lee, J.W.; Sung, H.T.; Kim, C.H.; Kim, E.J.; Kim, M.J.; Han, S.H.; Kim, M.Y.; et al. Anti-oxidant and natural killer cell activity of Korean red ginseng (Panax ginseng) and urushiol (Rhus vernicifera Stokes) on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease of rat. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 55, 586–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Kim, M.; Shin, S.S.; Yoon, M. Ginseng treatment reverses obesity and related disorders by inhibiting angiogenesis in female db/db mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 155, 1342–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Luo, J.; Anandh Babu, P.V.; Zhang, W.; Gilbert, E.; Cline, M.; McMillan, R.; Hulver, M.; Alkhalidy, H.; Zhen, W.; et al. Dietary supplementation of chinese ginseng prevents obesity and metabolic syndrome in high-fat diet-fed mice. J. Med. Food. 2014, 17, 1287–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.B.; Cho, H.I.; Jin, Y.W.; Lee, E.K.; Ahn, J.Y.; Lee, S.M. Wild ginseng cambial meristematic cells ameliorate hepatic steatosis and mitochondrial dysfunction in high-fat diet-fed mice. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2016, 68, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kho, M.C.; Lee, Y.J.; Park, J.H.; Cha, J.D.; Choi, K.M.; Kang, D.G.; Lee, H.S. Combination with Red ginseng and Polygoni Multiflori ameliorates highfructose diet induced metabolic syndrome. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 16, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.J.; Liu, W.J.; Wen, M.L.; Liang, H.; Wu, S.M.; Zhu, Y.Z.; Zhao, J.Y.; Dong, X.Q.; Li, M.G.; Bian, L.; et al. Ameliorative effects of Compound K and ginsenoside Rh1 on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in rats. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Wang, T.; Yang, L.; Wang, H.Y. Ginsenoside Rb2 Alleviates Hepatic Lipid Accumulation by Restoring Autophagy via Induction of Sirt1 and Activation of AMPK. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, W.; Chen, L.; Zhang, L.; Wang, B.; Li, X.B.; Fan, K.R.; Ai, C.H.; Xia, X.; Li, S.D.; Li, Y. Effects of ginsenoside Rg1 on glucose metabolism and liver injury in streptozotocin-induced type 2 diabetic rats. Genet. Mol. Res. 2017, 16, gmr16019463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H.; Kim, J.W.; Yang, M.S.; Park, C.; Kim, J.H.; Lim, C.W.; Kim, B. Beneficial Effects of Korean Red Ginseng in the Progression of Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis via FABP4 Modulation. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2018, 46, 1581–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.W.; Jo, H.K.; Chung, S.H. Ginseng seed oil ameliorates hepatic lipid accumulation in vitro and in vivo. J. Ginseng. Res. 2018, 42, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Kim, H.J.; Park, M.S.; Ji, G.E. Effects of fermented ginseng root and ginseng berry on obesity and lipid metabolism in mice fed a high-fat diet. J. Ginseng. Res. 2018, 42, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.S.; Yoon, M. Korean red ginseng (Panax ginseng) inhibits obesity and improves lipid metabolism in high fat diet-fed castrated mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 210, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Yang, C.; Zhang, S.; Li, J.; Xiao, Q.; Huang, W. Ginsenoside Rg1 Protects against Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease by Ameliorating Lipid Peroxidation, Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress, and Inflammasome Activation. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2018, 41, 1638–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, N.; Kim, J.W.; Jeong, H.; Shin, D.G.; Seo, J.H.; Kim, J.H.; Lim, C.W.; Han, K.M.; Kim, B. Fermented ginseng, GBCK25, ameliorates steatosis and inflammation in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis model. J. Ginseng. Res. 2019, 43, 196–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.Y.; Park, J.S.; Shon, C.H.; Lee, C.Y.; Ryu, J.M.; Son, D.J.; Hwang, B.Y.; Yoo, H.S.; Cho, Y.C.; Lee, J.; et al. Fermented Korean Red Ginseng Extract Enriched in Rd and Rg3 Protects against Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease through Regulation of mTORC1. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Zhang, C.; Niu, S.; Fan, B.; Gu, D.; Jiang, K.; Li, R.; Li, S. Ginsenoside Rg1 attenuates hepatic insulin resistance induced by high-fat and high-sugar by inhibiting inflammation. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 854, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.C.; Jeon, J.Y.; Yang, W.S.; Kim, C.H.; Eom, D.W. Combined Amelioration of Ginsenoside (Rg1, Rb1, and Rg3)-enriched Korean Red Ginseng and Probiotic Lactobacillus on Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2019, 20, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, B.; Gao, W.; Wu, X.; Zheng, M.; Yu, Y.; Song, C.; Miao, W.; Yang, Z.; He, Y.; Liu, C.; et al. Ginsenoside Rg2 Ameliorates High-Fat Diet-Induced Metabolic Disease through SIRT1. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 4215–4226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Gu, D.; Peng, J.; Jiang, K.; Li, Z.; Shi, J.; Yang, S.; Li, S.; Fan, X. Ginsenoside Rg1 Regulates Liver Lipid Factor Metabolism in NAFLD Model Rats. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 10878–10890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, Y.J.; Hwang, M.J.; Hong, C.O.; Yoo, D.S.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, D.Y.; Lee, K.W. Anti-hyperglycemic and hypolipidemic effects of black ginseng extract containing increased Rh4, Rg5, and Rk1 content in muscle and liver of type 2 diabetic db/db mice. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2020, 29, 1101–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Oh, J.Y.; Kim, S.H.; Oh, I.J.; Lee, Y.H.; Lee, K.W.; Lee, W.H.; Kim, J.H. Pharmaceutical Efficacy of Gypenoside LXXV on Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH). Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.; Yoo, J.H.; Lee, Y.S.; Park, E.J.; Lee, H.J. Ameliorative effects of black ginseng on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in free fatty acid-induced HepG2 cells and high-fat/high-fructose diet-fed mice. J. Ginseng. Res. 2020, 44, 350–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, R.; Jiang, R.; Xiao, H.; Wang, Z.; He, S.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y. Ginsenoside Rg1 protects against d-galactose induced fatty liver disease in a mouse model via FOXO1 transcriptional factor. Life Sci. 2020, 254, 117776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, B.; Sun, Y.; Chu, Y.; Wang, J.; Zheng, H.; Liu, L.; Cai, W.; Zhang, H. Ginsenoside Rb1 Alleviated High-Fat-Diet-Induced Hepatocytic Apoptosis via Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor gamma. Biomed. Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 2315230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y. Ginsenosides reduce body weight and ameliorate hepatic steatosis in high fat diet-induced obese mice via endoplasmic reticulum stress and p-STAT3/STAT3 signaling. Mol. Med. Rep. 2020, 21, 1059–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, D.; Yi, H.; Jiang, K.; Fakhar, S.H.; Shi, J.; He, Y.; Liu, B.; Guo, Y.; Fan, X.; Li, S. Transcriptome analysis reveals the efficacy of ginsenoside-Rg1 in the treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Life Sci. 2021, 267, 118986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.; Ramachandraiah, K.; Murtaza, M.A.; Wang, L.; Li, S.; Ameer, K. Synergistic effects of black ginseng and aged garlic extracts for the amelioration of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) in mice. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 9, 3091–3099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Sui, D.; Li, M.; Xu, H.; Yu, X.; Liu, J.; Yu, Q. Ginsenoside Re Improves Inflammation and Fibrosis in Hepatic Tissue by Upregulating PPARgamma Expression and Inhibiting Oxidative Stress in db/db Mice. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2021, 2021, 9003603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Qu, Q.; Yang, F.; Li, Z.; Yang, P.; Han, L.; Shi, X. Monascus ruber fermented Panax ginseng ameliorates lipid metabolism disorders and modulate gut microbiota in rats fed a high-fat diet. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 278, 114300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Zhang, J.; Li, J.; Guan, Y.; Shen, T.; Li, F.; Li, X.; Yang, X.; Hu, W. Ginsenoside F2 Suppresses Adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 Cells and Obesity in Mice via the AMPK Pathway. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 9299–9312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhu, Z.; Zhou, R.; Xu, P.; Zhou, L.; Kan, Y.; Li, J.; Zhao, J.; Fang, P.; et al. Upregulation of adiponectin by Ginsenoside Rb1 contributes to amelioration of hepatic steatosis induced by high fat diet. J. Ginseng. Res. 2022, 46, 561–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Liu, L.; Liu, X.; Tao, Y.; Zhao, X.; Gong, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, S. Exploring the Therapeutic Effects of Black Ginseng on Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease by Using Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking. Chem. Biodivers. 2022, 19, e202200719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Liu, L.; Liu, X.; Tao, Y.; Gong, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, S. Black ginseng protects against Western diet-induced nonalcoholic steatohepatitis by modulating the TLR4/NF-kappaB signaling pathway in mice. J. Food. Biochem. 2022, 46, e14432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ma, X.; Fan, D. Ginsenoside CK ameliorates hepatic lipid accumulation via activating the LKB1/AMPK pathway in vitro and in vivo. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 1153–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Zhang, M.; Zhu, X.; Zhu, L.; Chen, S.; Luo, M.; Xie, Q.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, K.; Bu, Q.; et al. Ginsenoside Rb1 Improves Metabolic Disorder in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Mice Associated With Modulation of Gut Microbiota. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 826487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, T.; Liu, F.; Wang, D.; Li, B.; Jiang, P.; Li, J.; Li, H.; Chen, C.; Wu, W.; Jiao, L. Rhamnogalacturonan-I enriched pectin from steamed ginseng ameliorates lipid metabolism in type 2 diabetic rats via gut microbiota and AMPK pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023, 301, 115862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Herck, M.A.; Vonghia, L.; Francque, S.M. Animal Models of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease-A Starter’s Guide. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.T.; Lee, M.J.; Yoon, S.J.; Shin, S.P.; Bang, C.S.; Baik, G.H.; Kim, D.J.; Youn, G.S.; Shin, M.J.; Ham, Y.L.; et al. Effect of Korea red ginseng on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: An association of gut microbiota with liver function. J. Ginseng. Res. 2021, 45, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| PubMed |
| “ginsengs” (All Fields) OR “panax” (MeSH Terms) OR “panax” (All Fields) OR “ginseng” (All Fields) OR “ginsengs” (All Fields)) AND (“fatty liver” (MeSH Terms) OR (“fatty” (All Fields) AND “liver” (All Fields)) OR “fatty liver” (All Fields) |
| Web of Science |
|
| Cochrane Library |
|
| Study | Country | Animal (Sex) | NAFLD Model | Component | Dose | Route and Times |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2009 Lim [19] | Republic of Korea | OLETF rat (male) | 32 weeks | Ginsam (a vinegar extract from Panax ginseng) | 300 mg kg−1 | p.o., daily (last 8 weeks) |
| 2010 Kwak [20] | Republic of Korea | Sprague-Dawley rat (male) | Triton WR1339 (i.v., 150 mg kg−1) | Korean red ginseng | 100, 500, or 1000 mg kg−1 | p.o., daily (for 3 days before Triton) |
| 2010 Liu [21] | China | Kunming mouse (female) | HFD (8 weeks) | Protopanaxdiol | 0.02% or 0.05% in the diet | p.o., daily |
| 2012 Quan [22] | Republic of Korea | C57BL/6J mouse (undefined) | HFD (6 weeks) | Ginsenoside Re | 5, 10, or 20 mg kg−1 | p.o., daily (last 3 weeks) |
| 2013 Hong [23] | Republic of Korea | OLETF rat (male) | 12 months | Korean red ginseng | 200 mg kg−1 in the diet | p.o., daily (last 8 weeks) |
| 2014 Lee [24] | Republic of Korea | db/db mouse (female) | 13 weeks | Total ginsenosides | 5% of the diet | p.o., daily |
| 2014 Li [25] | United States | C57BL/6J mouse (male) | HFD (15 weeks) | Chinese ginseng | 500 mg kg−1 | p.o., daily |
| 2015 Lee [26] | Republic of Korea | C57BL/6 mouse (male) | HFD (10 weeks) | Ginseng cambial meristematic cells | 75, 150, or 300 mg kg−1 | p.o., daily |
| 2016 Kho [27] | Republic of Korea | Sprague-Dawley rat (male) | High-fructose diet (8 weeks) | Red ginseng and Polygoni Multiflori Radix (1:1 ratio) | 100 or 300 mg kg−1 | p.o., daily (last 6 weeks) |
| 2017 Chen [28] | China | Sprague-Dawley rat (male) | HFD (11 weeks) | Chinese ginseng saponins | 50 mg kg−1 | i.p., daily (last 10 weeks) |
| Ginsenoside Compound K | 3 mg kg−1 | |||||
| Ginsenoside Rh1 | 3 mg kg−1 | |||||
| Compound K + Rh1 | 3 mg kg−1 | |||||
| 2017 Huang [29] | China | db/db mouse (male) | 10 weeks | Ginsenoside Rb2 | 10 mg kg−1 | i.p., daily (last 4 weeks) |
| 2017 Tian [30] | China | Sprague-Dawley rat (male) | HFD (12 weeks) | Ginsenoside Rg1 | 25 or 50 mg kg−1 | p.o., daily (last 4 weeks) |
| HFD (16 weeks) | 25 or 50 mg kg−1 | p.o., daily (last 8 weeks) | ||||
| 2018 Jeong [31] | Republic of Korea | C57BL/6 mouse (male) | MCD diet (13 weeks) | Korean red ginseng | 100, 200, or 400 mg kg−1 | p.o., daily |
| 2018 Kim [32] | Republic of Korea | C57BL/6J mouse (undefined) | HFD (12 weeks) | Ginseng seed oil | 250 or 500 mg kg−1 | p.o., daily |
| 2018 Li [33] | Republic of Korea | C57BL/6 mouse (male) | HFD (16 weeks) | Fermented ginseng root | Not indicated, supplemented with a diet | p.o., daily |
| Fermented ginseng berry | ||||||
| 2018 Shin [34] | Republic of Korea | C57BL/6 mouse (male) | HFD (8 weeks) | Ginseng extract | 5% in the diet | p.o., daily |
| 2018 Xu [35] | China | C57BL/6 mouse (female) | HFD (20 weeks) | Ginsenoside Rg1 | 20 or 40 mg kg−1 | p.o., daily (last 4 weeks) |
| 2019 Choi (1) [36] | Republic of Korea | C57BL/6 mouse (male) | Western diet (12 weeks) | GBCK25 | 10, 20, 100, 200, or 400 mg kg−1 | p.o., daily |
| 2019 Choi (2) [37] | Republic of Korea | C57BL/6N mouse (male) | Fast-food diet (14 weeks) | Fermented Korean red ginseng | 100 or 300 mg kg−1 | p.o., daily (last 8 weeks) |
| 2019 Fan [38] | China | Sprague Dawley rats (undefined) | HFHS diet (16 weeks) | Ginsenoside Rg1 | 10, 25, or 50 mg kg−1 | p.o., daily (last 4 weeks) |
| 2019 Kim [39] | Republic of Korea | C57BL/6 mouse (male) | HFD (6 weeks) | Korean red ginseng | 0.4 mg kg−1 | p.o., daily |
| Korean red ginseng and probiotics | 0.4 mg kg−1 + 0.03 mg kg−1 | |||||
| 2020 Cheng [40] | China | C57BL/6J mouse (undefined) | HFD (16 weeks) | Ginsenoside Rg2 | 10 mg kg−1 | i.p., daily (last 4 weeks) |
| 2020 Hou [41] | China | Sprague Dawley rats (undefined) | HFHS diet (14 weeks) | Ginsenoside Rg1 | 30 or 60 mg kg−1 | p.o., daily (last 4 weeks) |
| p.o., daily (last 8 weeks) | ||||||
| 2020 Jeong [42] | Republic of Korea | db/db mouse (male) | 10 weeks | Black ginseng | 100 or 900 mg kg−1 | p.o., daily (last 5 weeks) |
| 2020 Lee [43] | Republic of Korea | C57BL/6J mouse (male) | MCD diet (6 weeks) | Ginsenoside Rg3 | 15 or 30 mg kg−1 | p.o., daily (last 3 weeks) |
| 2020 Park [44] | Republic of Korea | ICR mouse (male) | High-fat high-fructose diet (17 weeks) | Black ginseng | 0.5%, 1%, or 2% in the diet | p.o., daily (last 8 weeks) |
| 2020 Qi [45] | China | C57BL/6J mouse (male) | Intraperitoneal D-galactose (120 mg kg−1 day−1) injection (6 weeks) | Ginsenoside Rg1 | 40 mg kg−1 | i.p., daily (last 4 weeks) |
| 2020 Song [46] | China | C57BL/6J mouse (male) | HFD (24 weeks) | Ginsenoside Rb1 | 10 mg kg−1 | p.o., daily (last 8 weeks) |
| 2020 Yao [47] | China | C57BL/6J mouse (male) | HFD (12 weeks) | Panax ginseng root extract | 120 mg kg−1 | p.o., daily (last 4 weeks) |
| 2021 Gu [48] | China | Sprague Dawley rats (male) | HFHS diet (26 weeks) | Ginsenoside Rg1 | 100 mg kg−1 | p.o., daily (last 8 weeks) |
| 2021 Jiang (1) [49] | Pakistan | C57BL/6 mouse (male) | HFD (6 weeks) | Black ginseng extract | 100 mg kg−1 | p.o., daily |
| 2021 Jiang (2) [50] | China | db/db mouse (male) | 8 weeks | Ginsenoside Re | 30 mg kg−1 | p.o., daily |
| 2021 Liang [7] | China | C57BL/6J mouse (male) | HFD (12 weeks) | Panax ginseng | 100 or 200 mg kg−1 | p.o., daily |
| 2021 Zhao [51] | China | Sprague Dawley rats (male) | HFD (8 weeks) | Fermented Panax ginseng | 200 or 400 mg kg−1 | p.o., daily |
| 2021 Zhou [52] | China | C57BL/6J mouse (male) | HFD (8 weeks) | Ginsenoside F2 | 50 or 100 mg kg−1 | p.o., daily (last 4 weeks) |
| 2022 Li [53] | China | C57BL/6J mouse (male) | HFD (14 weeks) | Ginsenoside Rb1 | 10 mg kg−1 | i.p., daily (last 2 weeks) |
| 2022 Wei (1) [54] | China | C57BL/6J mouse (male) | MCD diet (6 weeks) | Black ginseng extracts | 300, 600, or 900 mg kg−1 | p.o., daily (last 3 weeks) |
| 2022 Wei (2) [55] | China | C57BL/6 mouse (male) | Western diet and sugar water and carbon tetrachloride (2 mL kg−1, once a week) (12 weeks) | Black ginseng extracts | 300, 600, or 900 mg kg−1 | p.o., daily (last 4 weeks) |
| 2022 Zhang [56] | China | C57BL/6 mouse (male) | 30% fructose in water (4 weeks) | Ginsenoside Compound K | 30 or 60 mg kg−1 | p.o., daily |
| 2022 Zou [57] | China | C57BL/6J mouse (male) | HFD (12 weeks) | Ginsenoside Rb1 | 120 mg kg−1 | p.o., daily (last 4 weeks) |
| 2023 Ren [58] | China | Sprague Dawley rats (male) | High-glucose high-fat diet (8 weeks) and streptozotocin (35 mg kg−1) | Rg1-enriched polysaccharide | 100 or 300 mg kg−1 | p.o., daily |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, K.; Kim, H.-H.; Shim, Y.-R.; Song, M.J. The Efficacy of Panax ginseng for the Treatment of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Preclinical Studies. Nutrients 2023, 15, 721. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15030721
Yang K, Kim H-H, Shim Y-R, Song MJ. The Efficacy of Panax ginseng for the Treatment of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Preclinical Studies. Nutrients. 2023; 15(3):721. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15030721
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Keungmo, Hee-Hoon Kim, Young-Ri Shim, and Myeong Jun Song. 2023. "The Efficacy of Panax ginseng for the Treatment of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Preclinical Studies" Nutrients 15, no. 3: 721. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15030721
APA StyleYang, K., Kim, H.-H., Shim, Y.-R., & Song, M. J. (2023). The Efficacy of Panax ginseng for the Treatment of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Preclinical Studies. Nutrients, 15(3), 721. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15030721






