Exclusive Fish Oil Lipid Emulsion Rescue Strategy Improves Cholestasis in Neonates on Partially Fish Oil-Based Lipid Emulsion: A Pilot Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Clinical Outcomes
2.2. Statistical Analysis
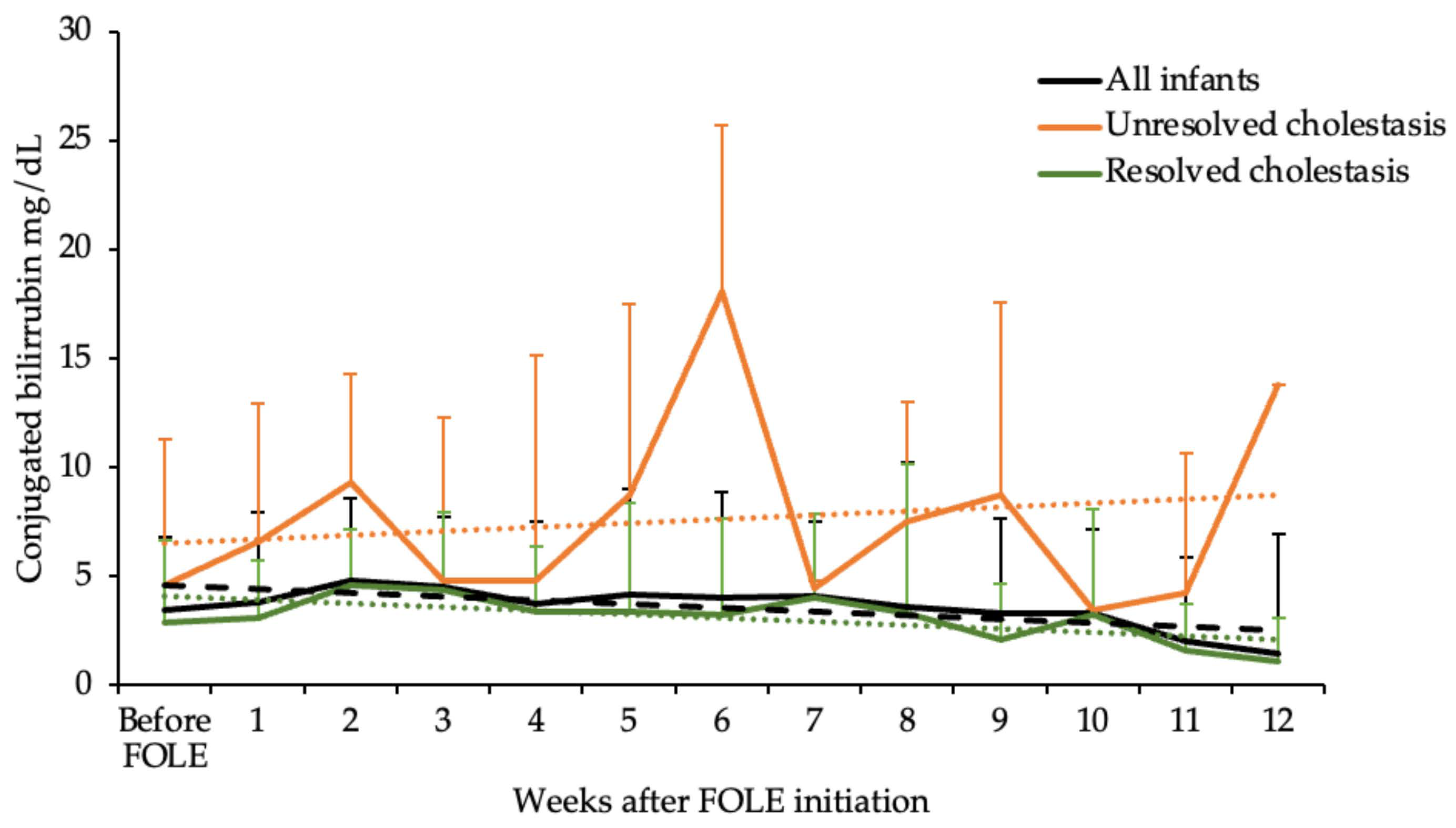
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Buchman, A. Total Parenteral Nutrition-Associated Liver Disease. JPEN J. Parenter. Enteral. Nutr. 2002, 26, S43–S48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Żalikowska-Gardocka, M.; Przybyłkowski, A. Review of Parenteral Nutrition-Associated Liver Disease. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2020, 6, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nehra, D.; Fallon, E.M.; Puder, M. The Prevention and Treatment of Intestinal Failure-Associated Liver Disease in Neonates and Children. Surg. Clin. North Am. 2011, 91, 543–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Secor, J.D.; Yu, L.; Tsikis, S.; Fligor, S.; Puder, M.; Gura, K.M. Current Strategies for Managing Intestinal Failure-Associated Liver Disease. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 2021, 20, 307–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rochling, F.A. Intravenous Lipid Emulsions in the Prevention and Treatment of Liver Disease in Intestinal Failure. Nutrients 2021, 13, 895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guthrie, G.; Burrin, D. Impact of Parenteral Lipid Emulsion Components on Cholestatic Liver Disease in Neonates. Nutrients 2021, 13, 508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Premkumar, M.H.; Carter, B.A.; Hawthorne, K.M.; King, K.; Abrams, S.A. Fish Oil-Based Lipid Emulsions in the Treatment of Parenteral Nutrition-Associated Liver Disease: An Ongoing Positive Experience. Adv. Nutr. 2014, 5, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jobe, A.H.; Bancalari, E. Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2001, 163, 1723–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fenton, T.R.; Kim, J.H. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis to Revise the Fenton Growth Chart for Preterm Infants. BMC Pediatr. 2013, 13, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gila-Diaz, A.; Carrillo, G.H.; Singh, P.; Ramiro-Cortijo, D. Specialized Pro-Resolving Lipid Mediators in Neonatal Cardiovascular Physiology and Diseases. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapoor, V.; Malviya, M.N.; Soll, R. Lipid Emulsions for Parenterally Fed Term and Late Preterm Infants. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019, 6, CD013171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gura, K.; Premkumar, M.H.; Calkins, K.L.; Puder, M. Intravenous Fish Oil Monotherapy as a Source of Calories and Fatty Acids Promotes Age-Appropriate Growth in Pediatric Patients with Intestinal Failure-Associated Liver Disease. J. Pediatr. 2020, 219, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savini, S.; D’Ascenzo, R.; Biagetti, C.; Serpentini, G.; Pompilio, A.; Bartoli, A.; Cogo, P.E.; Carnielli, V.P. The Effect of 5 Intravenous Lipid Emulsions on Plasma Phytosterols in Preterm Infants Receiving Parenteral Nutrition: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 98, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calkins, K.L.; Robinson, D.T. Intravenous Lipid Emulsions in the NICU. Neoreviews 2020, 21, e109–e119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thanhaeuser, M.; Steyrl, D.; Fuiko, R.; Brandstaetter, S.; Binder, C.; Thajer, A.; Huber-Dangl, M.; Haiden, N.; Berger, A.; Repa, A. Neurodevelopmental Outcome of Extremely Low Birth Weight Infants with Cholestasis at 12 and 24 Months. Neonatology 2022, 119, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Total (n = 38) | Cholestasis Resolution | Infants with Gut Disease Cholestasis Resolution | Infants without Gut Disease Cholestasis Resolution | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No (n = 10) | Yes (n = 28) | p | No (n = 5) | Yes (n = 22) | p | No (n = 5) | Yes (n = 6) | p | ||
| Gestational age (weeks) | 31.1 [27.0; 34.3] | 27.7 [25.1; 34.2] | 31.6 [27.0; 34.1] | 0.57 | 27.3 [24.4; 27.6] | 31.1 [27.0; 33.7] | 0.08 | 34.4 [33.6; 36.6] | 34.4 [30.7; 35.7] | 0.86 |
| Prematurity | 92.1% (35) | 90.0% (9) | 92.9% (26) | 0.99 | 100% (5) | 95.5% (21) | >0.99 | 80% (4) | 83.3% (5) | >0.99 |
| Sex (male) | 44.7% (17) | 40.0% (4) | 46.4% (13) | 0.99 | 20% (1) | 50% (11) | 0.34 | 60% (3) | 33.3% (2) | 0.57 |
| BW (g) | 1390 [743; 2298] | 980.0 [707.0; 2268] | 1695 [866.0; 2308] | 0.45 | 736 [645; 830] | 965 [799; 2138] | 0.06 | 2290 [2200; 2300] | 2365 [1888; 3068] | 0.47 |
| Fenton’s BW (percentile) | 49.5 [22.5; 78.2] | 49.5 [22.5; 65.5] | 48.5 [23.2; 79.5] | 0.58 | 51.0 [27.0; 66.0] | 43.0 [10.5; 74.5] | 0.85 | 48.0 [21.0; 64.0] | 74.0 [42.8; 89.5] | 0.20 |
| ELBW | 47.4% (18) | 50.0% (5) | 46.4% (13) | 0.99 | 80% (4) | 54.5% (12) | 0.62 | 20% (1) | 16.7% (1) | >0.99 |
| NEC | 36.8% (14) | 40.0% (4) | 35.7% (10) | 0.99 | 100% (5) | 45.5% (10) | 0.047 | 0% (0) | 16.7% (1) | >0.99 |
| IVH | 23.7% (9) | 40.0% (4) | 17.9% (5) | 0.21 | 60% (3) | 18.2% (4) | 0.09 | 20% (1) | 16.7% (1) | >0.99 |
| BPD | 50.0% (19) | 70.0% (7) | 42.9% (12) | 0.27 | 80% (4) | 40.9% (9) | 0.17 | 60% (3) | 33.3% (2) | 0.57 |
| Coagulopathy | 15.8% (6) | 30.0% (3) | 10.7% (3) | 0.31 | 20% (1) | 9.1% (2) | 0.47 | 40% (2) | 16.7% (1) | 0.55 |
| Cholestasis diagnoses (DOL) | 15.0 [10.0; 24.8] | 23.5 [11.2; 26.5] | 14.5 [9.8; 19.0] | 0.42 | 25 [23.0; 27.0] | 14.5 [10.5; 25.0] | 0.15 | 10 [9.0; 24] | 13 [8.0; 16.5] | 0.78 |
| Initial conjugated bilirubin (mg/dL) | 3.8 [2.6; 6.0] | 5.1 [3.1; 11.3] | 3.3 [2.6; 5.7] | 0.11 | 4.0 [2.8; 4.1] | 3.1 [2.6; 4.0] | 0.51 | 11.7 [6.0; 17.1] | 4.7 [3.3; 5.9] | 0.17 |
| HA before OVTM | 81.6% (31) | 100% (10) | 75.0% (21) | 0.16 | 100% (5) | 81.8% (18) | 0.56 | 100% (5) | 50% (3) | 0.18 |
| Sepsis before OVTM | 76.3% (29) | 70.0% (7) | 78.6% (22) | 0.67 | 100% (5) | 81.8% (18) | 0.56 | 40% (2) | 66.7% (4) | 0.57 |
| Death | 23.7% (9) | 80.0% (8) | 3.6% (1) | <0.001 | 80% (4) | 5% (1) | 0.002 | 80% (4) | 0% (0) | 0.015 |
| Total (n = 38) | Cholestasis Resolution | Infants with Gut Disease Cholestasis Resolution | Infants without Gut Disease Cholestasis Resolution | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No (n = 10) | Yes (n = 28) | p | No (n = 5) | Yes (n = 22) | p | No (n = 5) | Yes (n = 6) | p | ||
| PN initiation (DOL) | 0 [0; 2] | 0 [0; 0] | 1 [0; 5] | 0.013 | 1 [1; 1] | 1 [1; 1] | 0.15 | 1 [1; 1] | 8 [1; 13] | 0.13 |
| Days with PN | 74 [48; 106] | 70 [44; 112] | 76 [51; 97] | 0.79 | 64 [59; 113] | 89 [70; 106] | 0.71 | 75 [39; 108] | 32 [22; 48] | 0.10 |
| Days on OVTM treatment | 39 [11; 52] | 19 [8.0; 50] | 40 [20; 55] | 0.41 | 22 [9; 41] | 46 [28; 74] | 0.17 | 15 [14; 93] | 16 [6; 23] | 0.36 |
| Sepsis with OVTM | 81.6% (31) | 60.0% (6) | 89.3% (25) | 0.06 | 100% (5) | 90.9% (20) | >0.99 | 20% (1) | 83.3% (5) | 0.08 |
| EN before OVTM (mL/kg/day) | 20.0 [15.0; 50.0] | 16.0 [8.0; 33.0] | 20.0 [15.5; 56.8] | 0.40 | 0.0 [0.0; 16] | 0.0 [0.0; 11.8] | 0.84 | 0.0 [0.0; 0.0] | 7.5 [0.0; 39.0] | 0.08 |
| EN after OVTM (mL/kg/day) | 90.0 [30.0; 110] | 0.0 [0.0; 0.0] | 92.5 [60.0; 110] | 0.10 | 0.0 [0.0; 0.0] | 77.5 [20.8; 100] | 0.002 | 0.0 [0.0; 0.0] | 105 [77.5; 110] | 0.004 |
| 1 EN >100 mL/kg/day | 61.1% (22) | 40.0% (4) | 69.2% (18) | 0.14 | 50% (2) | 65% (13) | 0.62 | 40% (2) | 83.3% (5) | 0.24 |
| DOL when EN >100 mL/kg/day was reached | 47 [30; 61] | 43 [28; 57] | 47 [30; 85] | 0.73 | 27 [25; 28] | 50 [40; 92] | 0.09 | 57 [56.5; 57.5] | 30 [19; 30] | 0.05 |
| Finish OVTM (DOL) | 64 [44; 100] | 60 [46; 101] | 67 [46; 96.0] | 0.80 | 63 [57; 93] | 71 [61; 107] | 0.55 | 56 [43; 133] | 35 [22; 46] | 0.10 |
| Final conjugated bilirubin (mg/dL) | 1.3 [0.7; 1.98] | 4.5 [4.1; 11.1] | 1.1 [0.58; 1.6] | <0.001 | 4.2 [3.67; 7.92] | 0.97 [0.52; 1.30] | 0.002 | 10.4 [4.5; 11.1] | 1.58 [1.29; 1.67] | 0.006 |
| BWG (g/day) | 16.0 [11.2; 21.0] | 14.8 [12.2; 21.0] | 16.0 [10.3; 21.0] | 0.80 | 14.5 [12.0; 15.0] | 16.0 [11.8; 21] | 0.20 | 22.0 [13.0; 28.0] | 16.4 [9.6; 16.9] | 0.41 |
| WG with OVTM (g) | 70.2 [20.5; 154] | 31.0 [10.8; 133] | 79.2 [27.2; 155] | 0.34 | 22.0 [8.8; 66.3] | 105 [35.2; 165] | 0.11 | 40.0 [17.1; 173] | 42.2 [9.8; 79.2] | 0.47 |
| WG with SMOFlipidTM (g) | 67.0 [30.2; 139] | 56.9 [34.5; 102] | 71.5 [28.2; 156] | 0.95 | 68.0 [41.8; 114] | 79.5 [44.5; 177] | 0.90 | 47.8 [32.0; 66.0] | 28.5 [9.3; 94.5] | 0.47 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ramiro-Cortijo, D.; Del Pozo Arribas, S.; Inisterra Viu, L.; Vázquez, N.G.; Saenz de Pipaon, M. Exclusive Fish Oil Lipid Emulsion Rescue Strategy Improves Cholestasis in Neonates on Partially Fish Oil-Based Lipid Emulsion: A Pilot Study. Nutrients 2023, 15, 509. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15030509
Ramiro-Cortijo D, Del Pozo Arribas S, Inisterra Viu L, Vázquez NG, Saenz de Pipaon M. Exclusive Fish Oil Lipid Emulsion Rescue Strategy Improves Cholestasis in Neonates on Partially Fish Oil-Based Lipid Emulsion: A Pilot Study. Nutrients. 2023; 15(3):509. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15030509
Chicago/Turabian StyleRamiro-Cortijo, David, Sonia Del Pozo Arribas, Lidia Inisterra Viu, Natalia García Vázquez, and Miguel Saenz de Pipaon. 2023. "Exclusive Fish Oil Lipid Emulsion Rescue Strategy Improves Cholestasis in Neonates on Partially Fish Oil-Based Lipid Emulsion: A Pilot Study" Nutrients 15, no. 3: 509. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15030509
APA StyleRamiro-Cortijo, D., Del Pozo Arribas, S., Inisterra Viu, L., Vázquez, N. G., & Saenz de Pipaon, M. (2023). Exclusive Fish Oil Lipid Emulsion Rescue Strategy Improves Cholestasis in Neonates on Partially Fish Oil-Based Lipid Emulsion: A Pilot Study. Nutrients, 15(3), 509. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15030509









